Sensory Modality in Students Enrolled in a Specialized Training Program for Security Forces and Its Impact on Karate Performance Indicators
Abstract
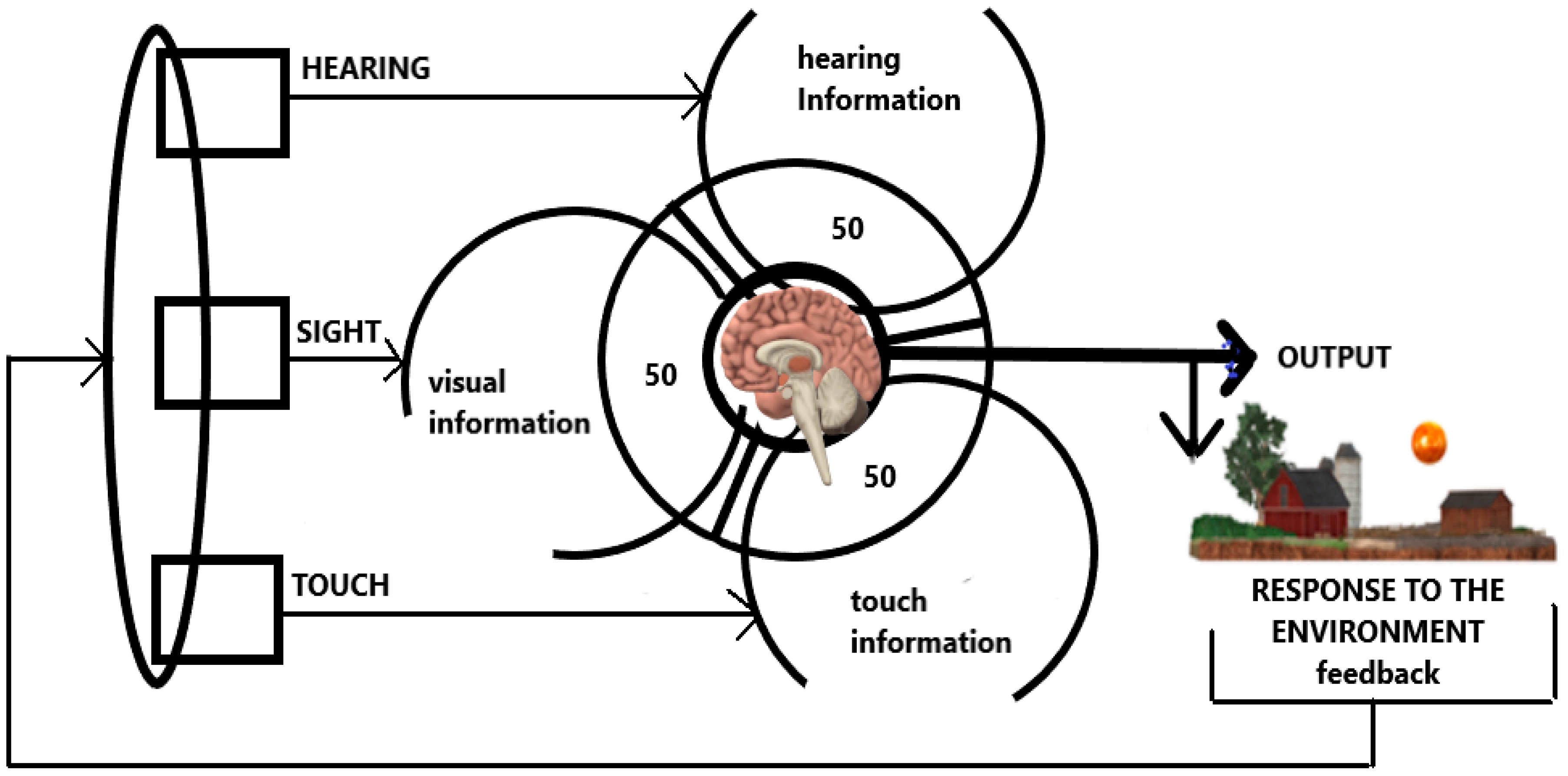
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. The Modified Version of the VARK Questionnaire
2.3. Outcome Variables
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dwyer, C.P.; Campbell, D.; Seery, N. An Evaluation of the Relationship Between Critical Thinking and Creative Thinking: Complementary Metacognitive Processes or Strange Bedfellows. J. Intell. 2025, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lembo, L.; Mariani, A.M. Maltisensory Training: Motor Learning and Sports Perfrormance in Young Athletes. J. Incl. Methodol. Technol. Learn. Teach. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, D.H. Learn Theories an Educational Perspective; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Démuth, A. Teórie Percepcie; Filozofická Fakulta Trnavskej Univerzity: Trnava, Slovakia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Uher, I.; Pivovarník, J.; Majherová, M.; Chovanová, E. Benefits of Interoceptive Awareness: A Correlational Study of the Distinct Sport Education Program among Slovak University Students. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivovarník, J. Dual Concentration in Karate and Its Possible Use in Sport Diagnostics; LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.; Bleibaum, R.N.; Thomas, H.A. Sensory Evaluation Practices; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Kueh, Y.C.; Kuan, G. The influence of the five-factor model of personality on performance in competitive sports: A review. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1284378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosher, B.A.; Lu, Z.L. Perceptual learning: Learning, memory, and models. In The Oxford Handbook of Human Memory: Foundations and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, V.; Manenti, G.L.; Plewe, S.S.; Kagan, I.; Schwiedrzik, C.M. Decision-making processes in perceptual learning depend on effectors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Z.L.; Dosher, B. Transfer of visual perceptual learning over a task-irrelevant feature through feature-invariant representations: Behavioral experiments and model simulations. J. Vis. 2024, 24, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcombe, S.J.; Kennard, C.; Bridge, H. Time course influences transfer of visual perceptual learning across spatial location. Vis. Res. 2017, 135, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.S.; Kattner, F.; Siegel, M.H.; Kersten, D.; Schrater, P.R. Differences in perceptual learning transfer as a function of training task. J. Vision 2015, 15, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Leysen, S.L. Brain Plasticity and the Impact of the Electronic Environment in Law and Learning. Leg. Ref. Serv. Q. 2011, 30, 255–288. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.; Ishida, T. Exploring Cultural Differences in Pictogram Interpretations. In Cognitive Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, J.; Edler, D.; Dickmann, F.; Kuchinke, L. Meaningfulness of landmark pictograms reduces visual salience and recognition performance. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 75, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.F.; Rajan, R.; Baeta, M.; Belbut, B.; Marques, T.; Petreanu, L. Visual experience reduces the spatial redundancy between cortical feedback inputs and primary visual cortex neurons. Neurons 2024, 112, 3329–3342.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lueptow, L.M. Novel object recognition test for the investigation of learning and memory in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 126, 55718. [Google Scholar]
- Minafra, A. Exploring Kinaesthetic and Body Self-Awareness in Professional Musicians. Ph.D. Thesis, The University College London (UCL), London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Finck, C.; Aliv, A.; Jimenez, L.W. A multisensory mindfulness experience: Exploring the promotion of sensory awareness as a mindfulness practice. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1230832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vago, D.R.; Zeidan, F. The brain on silent: Mind wandering, mindful awareness, and states of mental tranquility. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1373, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao, Y.; Summerfield, C.; Park, H.; Giordano, B.L.; Kayser, C. Causal Inference in the Multisensory Brain. Neuron 2019, 102, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarello, N.; Tarantino, V.; Chirico, A.; Menghini, D.; Costanzo, F.; Sorrentino, P.; Fucà, E.; Gigliotta, O.; Alivernini, F.; Oliveri, M.; et al. Sensory processing disorders in children and adolescents: Taking stock of assessment and novel therapeutic tools. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, V.M.; Folha, D.R.S.; Pinheiro, R.C.; Della Barba, P.C. Sensory processing and engagement: A systematic review. Cad. Bras. Ter. Ocup. 2023, 31, e3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisson, E.J. Energy Flows in Low-Entropy Complex Systems. Entropy 2015, 17, 8007–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomič, D. Exploring the VARK model: A review of the validity and reliability of the questionnaire and its relationship to learning outcomes. In Proceedings of the 12th International Scientific Symposium Region, Entrepreneurship, Development, Osijek, Croatia, 15–16 June 2023; Available online: https://www.croris.hr/crosbi/publikacija/prilog-skup/737925 (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Williams, A.M.; Jackson, R. Anticipation and Decision Making in Sport; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; p. 428. [Google Scholar]
- Helms, T.S.; Sainburg, R.L. Multisensory integration for motor control and adaptation. J. Mot. Behav. 2012, 44, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fardilha, F.d.S.; Allen, J.B. Defining, assessing, and developing creativity in sport: A systematic narrative review. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2019, 13, 104–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, A.; Lane, S.J.; Murray, E.A. Sensory Integration: Theory and Practice; F.A Davis: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert, D.M.; Ghahramani, Z. Computational principles of movement neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, L.; Seitz, A.R. Benefits of multisensory learning. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2008, 12, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, A.J. Sensory Integration and the Child: Understanding Hidden Sensory Challenges; Western Psychological Services: Melbourne, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, O.; Soylu, Y.; Erkmen, N.; Kaplan, T.; Batalik, L. Effects of proprioceptive training on sports performance: A systematic review. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. New Metric Invariant of Transitive Dynamical Systems and Endomorphisms of Lebesgue Spaces. Dokl. Russ. Acad. Sci. 1958, 119, 861–864. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Entropy per unit time as a metric invariant of automorphism. Doc. Russ. Acad. Sci. 1959, 124, 754–755. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, J.; Ciorciari, J. A Review on the Role of the Neuroscience of flow States in the Modern World. Behav. Sci. 2020, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow; Harper & Row: Manhattan, NY, USA, 1990; p. 281. [Google Scholar]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. Creativity; HarperCollines: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 443. [Google Scholar]
- Schutte, N.S.; Malouff, J.M. Connections between curiosity, flow and creativity. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2020, 152, 109555. [Google Scholar]
- Anson, E.; Jeka, J. Sensory Reweighting: A Rehabilitative Mechanism? Springer eBooks: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishmael, D. The use of auditory, tactual, olfactory and kinaesthetic senses in developing orientation and mobility (O & M) skills to learners with congenital blindness (CB). J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2015, 20, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liulingzi, X.; Pattananon, N.; Khunthongchan, P. The multi-sensory teaching practice for primary music classroom in China. J. Mod. Learn. Dev. 2023, 8, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Speicher, T.; Khan, M.A.; Wu, Q.; Nanda, V.; Das, S.; Ghosh, B.; Terzi, E. Understanding Memorisation in LLMs: Dynamics, Influencing Factors, and Implications. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2407.19262. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, A.; Schwarz, N. Sensory marketing, embodiment, and grounded cognition: A review and introduction. J. Consum. Psychol. 2014, 24, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Agapito, D.; Pinto, P.; Mendes, J. Tourists’ memories, sensory impressions and loyalty: In loco and post-visit study in Southwest Portugal. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Brečka, P.; Valentová, M.; Lančarič, D. The implementation of critical thinking development strategies into technology education: The evidence from Slovakia. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2022, 109, 103555. [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer, J.; Gollhofer, A.; Ringhof, S.; Assländer, L.; Granacher, U.; Gehring, D. Effects of balance training with visual input manipulations on balance performance and sensory integration in healthy young adults: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28589. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Wurff, I.; Meijs, C.; Hurks, P.; Resch, C.H.; De Groot, R. The influence of sensory processing tools on attention and arithmetic performance in Dutch primary school children. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2021, 209, 105143. [Google Scholar]
- Podrihalo, O.; Jagiello, W.; Guo, X.; Podrigalo, L.; Yermakova, T.; Cieslicka, M. Sensory integration research: Priority scientific directions based on the analysis of Web of Science Core Collection resources. Phys. Educ. Stud. 2023, 27, 358–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
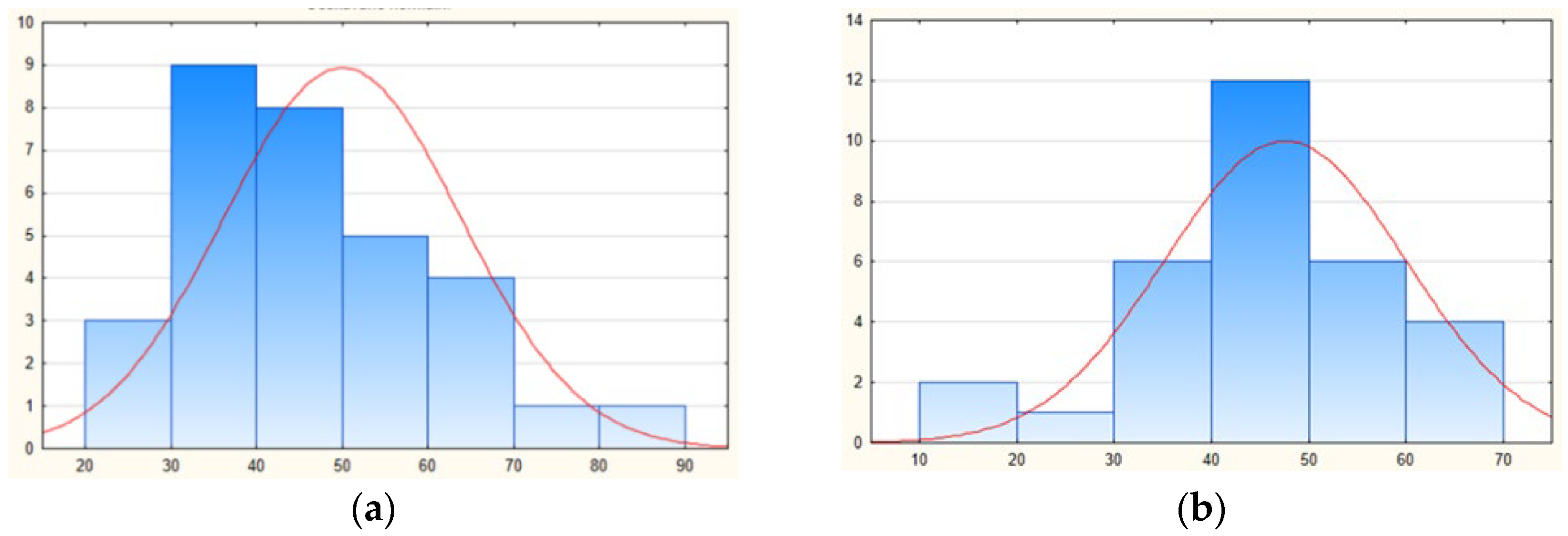
| N | min | max | Average | Median | Variance | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S (2021) | 31 | 20 | 24 | 20.29 | 20 | 0.66 | 0.81 |
| S (2024) | 31 | 22 | 26 | 22.29 | 22 | 0.66 |
| Variable 1Y and 3Y | t-Test for Dependent Samples, Significance at p < 0.05 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | n | Difference | STD | Cohen’s d | t | df | p | |
| Visual Mod 1Y | 45.81 | 18.08 | 31 | −4.68 | 13.96 | 0.258 | −1.87 | 30 | 0.072 |
| Visual Mod 3Y | 50.48 | 17.29 | |||||||
| Aural Mod 1Y | 53.87 | 16.72 | 31 | 1.94 | 15.26 | 0.115 | 0.71 | 30 | 0.485 |
| Aural Mod 3Y | 51.94 | 16.52 | |||||||
| Kinesthetic Mod 1Y | 50.00 | 13.84 | 31 | 2.42 | 15.27 | 0.157 | 0.88 | 30 | 0.385 |
| Kinesthetic Mod 3Y | 47.58 | 12.37 | |||||||
| Students TLP | n | Visual Mo 3Y Mean | Visual Mo 3Y SD | Aural Mo 3Y Mean | Aural Mo 3Y SD | Kinesth. Mo 3Y Mean | Kinesth. Mo 3Y SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kyu | 31 | 51.54 | 17.72 | 47.69 | 16.66 | 50.77 | 14.84 |
| 4. kyu | 31 | 50.00 | 17.97 | 53.93 | 17.12 | 46.07 | 10.22 |
| 5. kyu | 31 | 48.75 | 17.97 | 58.75 | 13.77 | 42.50 | 10.41 |
| TOG | 31 | 50.48 | 17.29 | 51.94 | 16.52 | 47.58 | 12.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uher, I.; Pivovarník, J.; Majherová, M. Sensory Modality in Students Enrolled in a Specialized Training Program for Security Forces and Its Impact on Karate Performance Indicators. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020114
Uher I, Pivovarník J, Majherová M. Sensory Modality in Students Enrolled in a Specialized Training Program for Security Forces and Its Impact on Karate Performance Indicators. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(2):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020114
Chicago/Turabian StyleUher, Ivan, Ján Pivovarník, and Mária Majherová. 2025. "Sensory Modality in Students Enrolled in a Specialized Training Program for Security Forces and Its Impact on Karate Performance Indicators" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 2: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020114
APA StyleUher, I., Pivovarník, J., & Majherová, M. (2025). Sensory Modality in Students Enrolled in a Specialized Training Program for Security Forces and Its Impact on Karate Performance Indicators. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(2), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020114






