A Multimodal Polygraph Framework with Optimized Machine Learning for Robust Deception Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Release of the first open multimodal polygraph dataset combining BPM, GSR, body temperature and demographics for participants [41].
- Swarm tuned ML that pushes accuracy to 97% ± 0.6% (5-fold CV)—a jump over best prior work.
- 0.06 s inference latency, enabling real-time interviewing on commodity hardware.
- Transparent code, hardware BOM and analysis scripts released for full replication.
Related Work
| Article | Modalities Used |
|---|---|
| A Microcontroller-based Lie Detection System Leveraging Physiological Signals [73] | HRV, GSR |
| Based on physiology parameters to design lie detector [68] | HRV, Body temperature, ECG, PETCO2 |
| Lie Detection using Facial Analysis, Electrodermal activity, pulse, and temperature [68] | GSR, HRV, Body temperature, Facial gestures |
| Using Neural Network Models for BCI Based Lie Detection [18] | GSR, HRV, fNIRS, EEG |
| Truth Identification from EEG Signal by using Convolutional Neural Network: Lie Detection [65] | EEG |
| A Novel Approach for Lie Detection Based on F-Score and Extreme Learning Machine [66] | EEG |
| Bag-of-Lies: A Multimodal Dataset for Deception Detection [62] | EEG, Gaze, Audio, Video |
| Automation of a screening polygraph test increases accuracy [70] | GSR, Blood Pressure |
| Systematic Design of Lie Detector System Utilising EEG Signals Acquisition [67] | EEG |
| Multimodal Deception Detection: Accuracy, Applicability, and Generalizability [63] | Video |
| Using EEG and fNIRS Signals as Polygraphs [18] | fNIRS, EEG |
| Multimodal Machine Learning for deception detection using behavioral and physiological data [42] | EEG, Electrooculography (EOG), Eye gaze, GSR, Audio, Video |
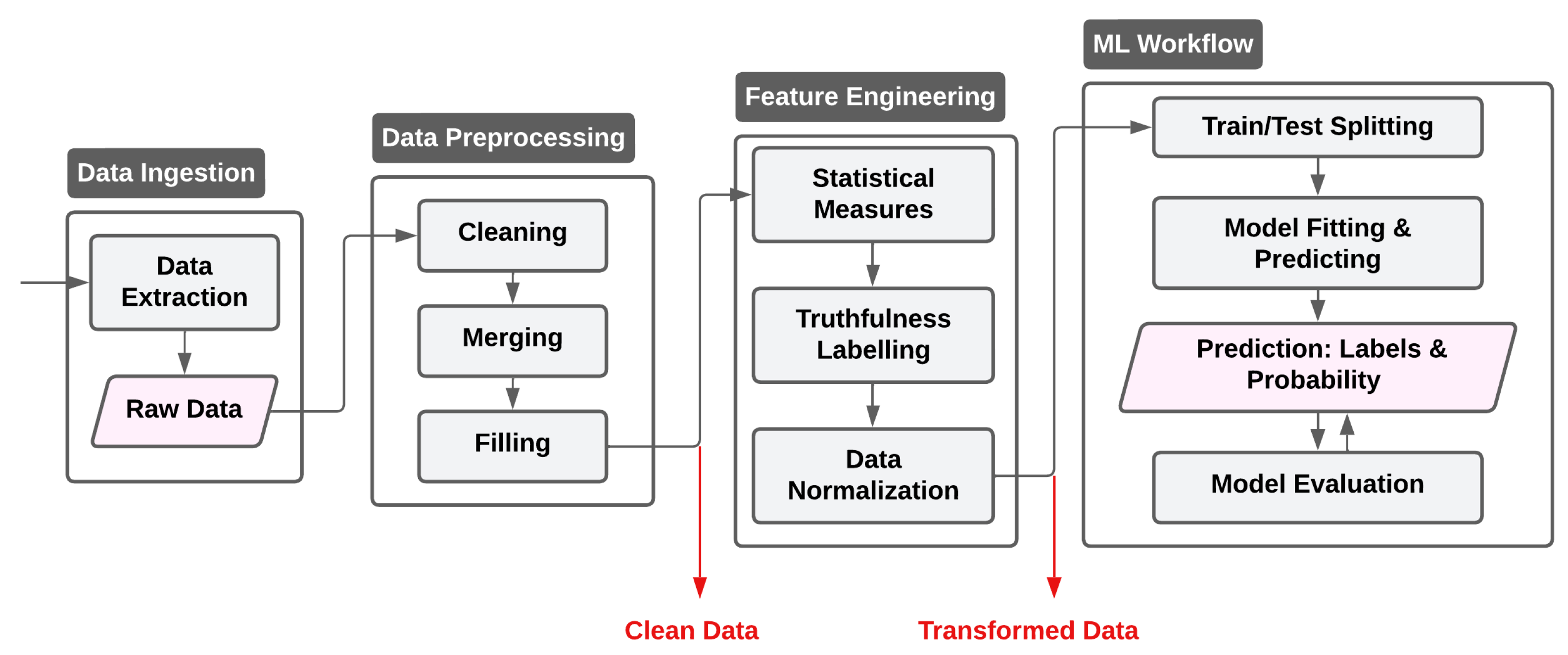
2. Methodology
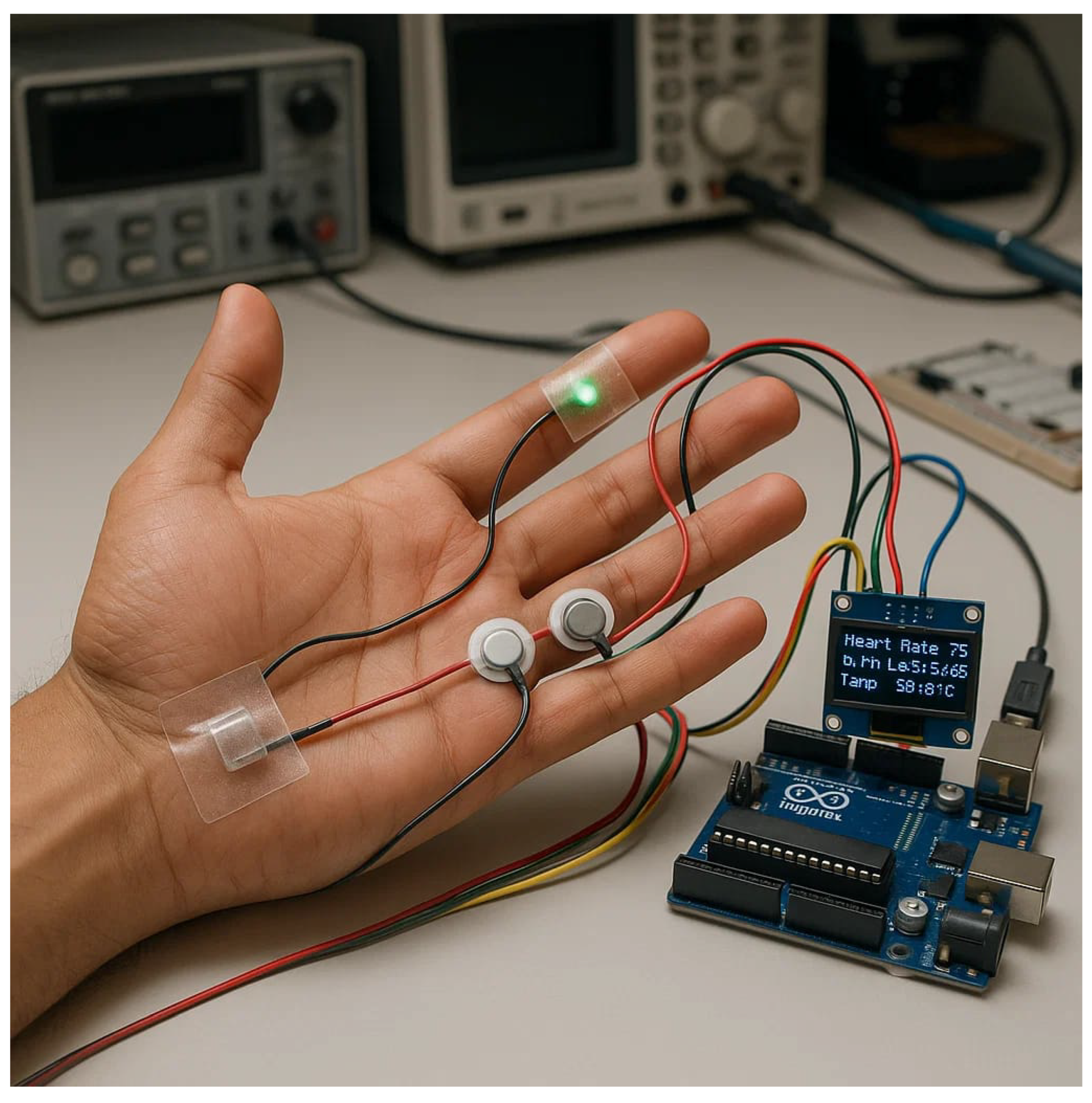
2.1. Sensory System
2.1.1. Environment Setup
- Quiet: so that the subject doesn’t feel interfered with, stressed, or have their train of thought broken during questioning.
- Dim lighting: The room has to have dimmed light to set the focus on the screen.
- Read the questions: As the attitude of the person asking questions may interfere with the way the subject answers, questions had to be read by the subject from the screen of a computer.
- Question format: the font of the questions had to be clear and moderate size. The font color was set to black on a clear white background.
- Question type: Non-personal questions were created.
- Is Today [this month, today]?
- Is this year [this year]?
- Are you in El-Alamin Campus?
- Are you a Student in the AI College?
- Are you a [Male/Female]?
- The Sun is Bright Today?
2.1.2. Hardware Setup
- 0.1 °C Accuracy (37 °C to 39 °C);
- 16-Bit (0.00390625 °C) Temperature Resolution;
- Temperature range: 0 °C to +50 °C;
- Sampling Frequency: 1 Hz;
- Time Constant: 7 s.
2.1.3. Data Collection
2.1.4. Sanity Check by Signal Quality Verification
- (a)
- Physiological plausibility: Baseline heart rate 62 to 68 , GSR 35 to 38 , and temperature 36.7 °C to 36.9 °C lie within normal resting ranges [44].
- (b)
- Low inter-subject noise: 95% CIs are narrower than ±1 and ± , indicating a stable acquisition chain and minimal packet loss.
- (c)
- Block sensitivity: BPM and GSR rise by ∼1 to 1.5 (or ) after 30 to 40 in the Main block, while temperature remains flat, matching the fast-vs-slow autonomic pattern predicted by deception literature.
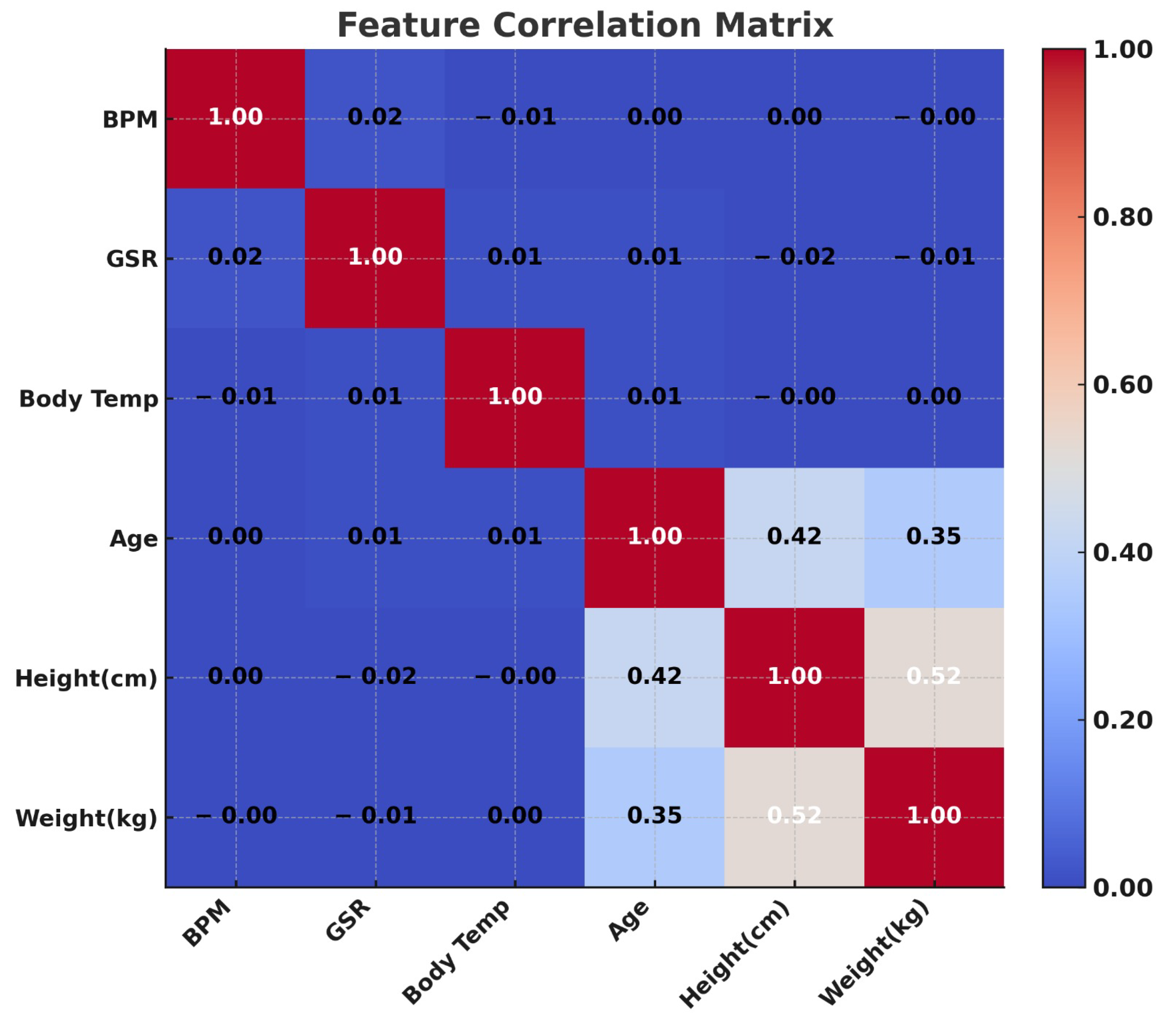
2.2. Applied Methods
| Algorithm 1 Random-Forest Pipeline for Probabilistic Truth Detection |
| Require: Dataset D (physiology, demographics, Q1–Q10 & timestamps) |
| Ensure: Trained model RF and truthfulness probabilities |
| 1. Pre-processing 1: for all feature do 2: if f numeric then 3: impute missing with 4: else 5: impute missing with 6: end if 7: end for 8: if then 9: label-encode 10: end if 2. Feature Engineering 11: for all record do 12: append for BPM, GSR, Temp 13: end for 3. Response-Time Features 14: for to 9 do 15: 16: end for 4. Truth Label Definition 17: , 18: , 5. Train/Test Preparation 19: [BPM, GSR, Temp, Age, Height, Weight] 20: cast X numeric; split ; standardize 6. Training 21: RandomForest(); fit on training data 7. Evaluation 22: 23: 24: report accuracy, precision, recall, F1; attach to return |
2.2.1. Cross-Validation and Hyperparameter Tuning
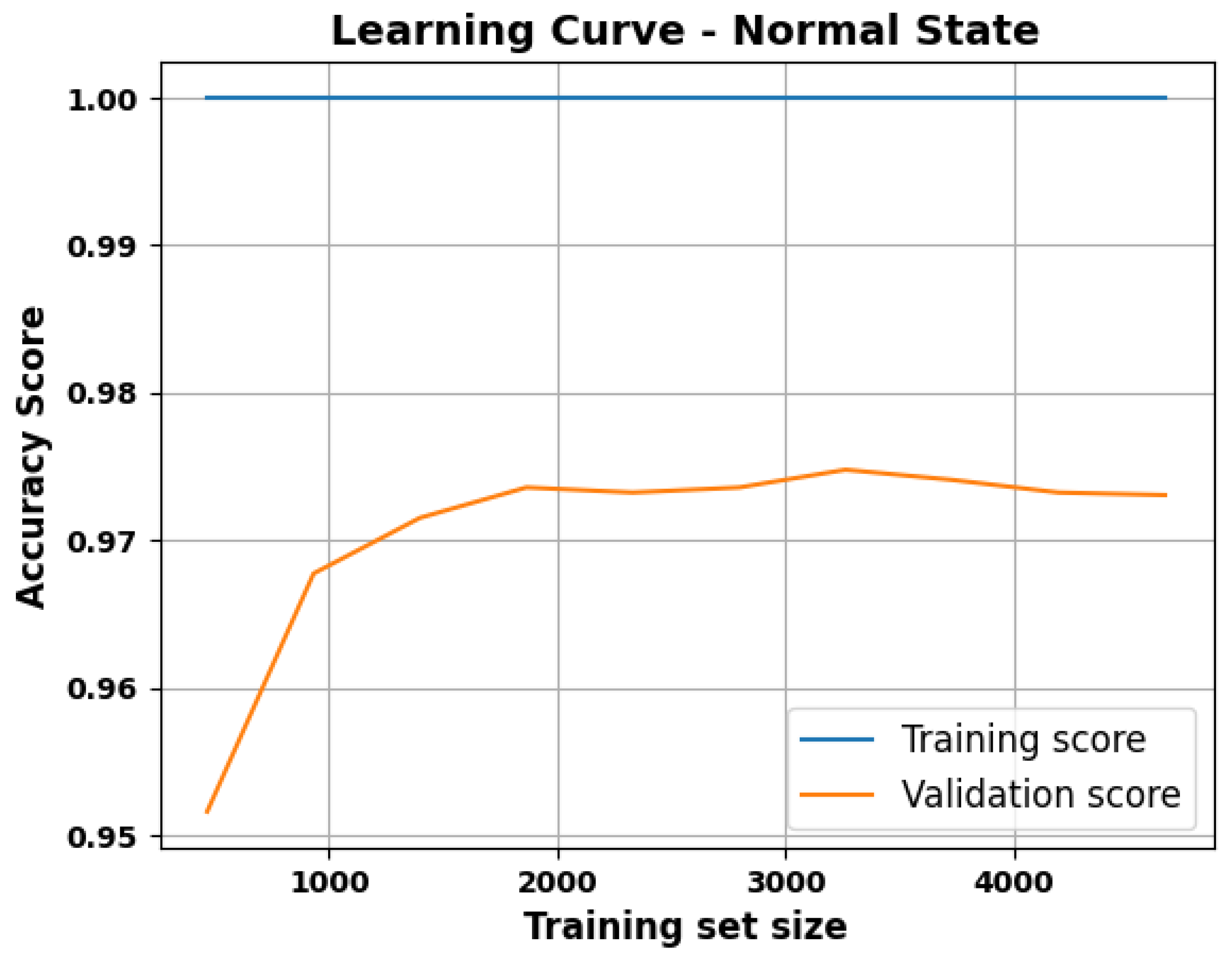
2.2.2. Baseline (Normal State) Model
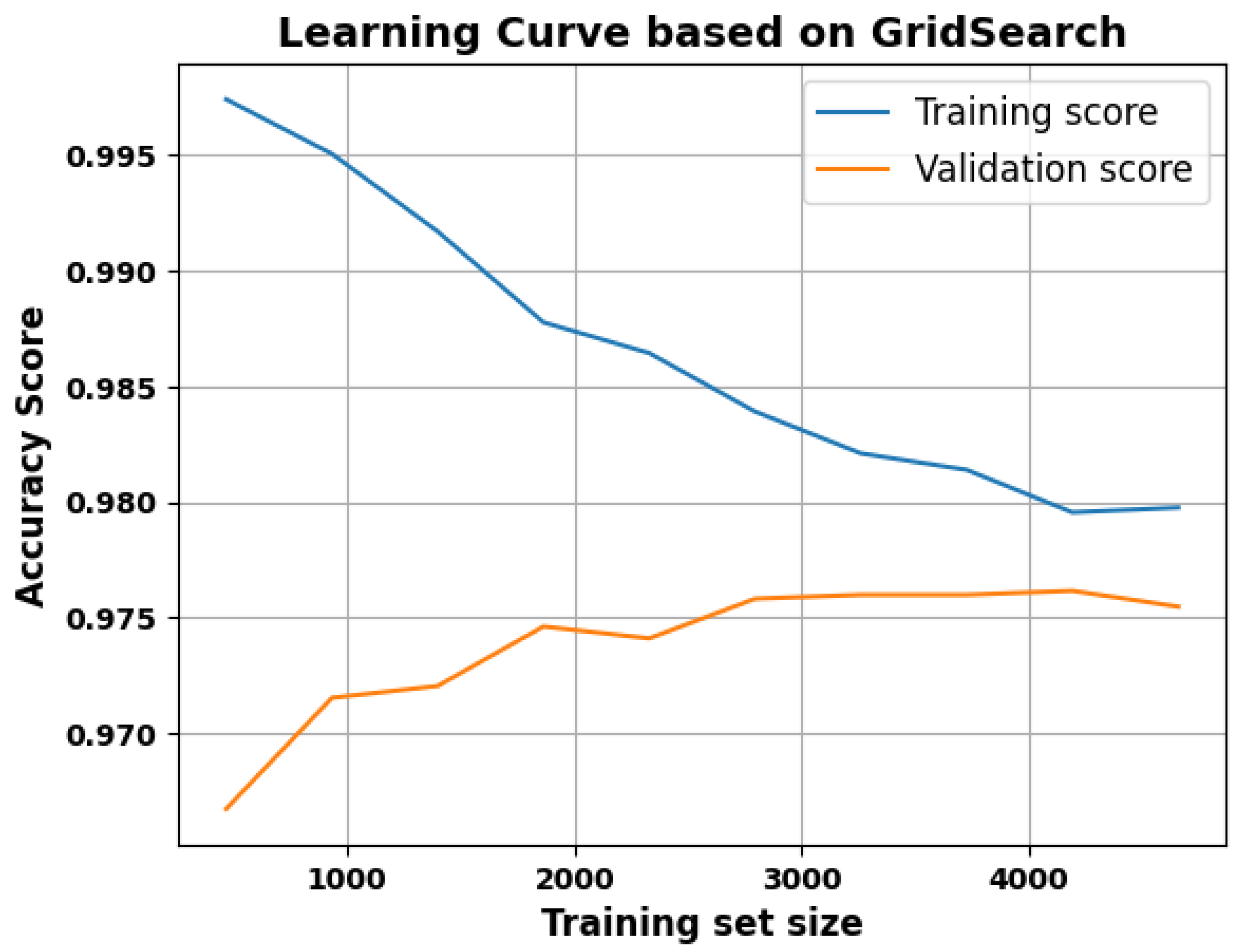
2.2.3. Grid Search for Optimal Parameters
- max_depth = 10
- max_features = 0.5
- min_samples_leaf = 1
- min_samples_split = 2
- n_estimators = 100
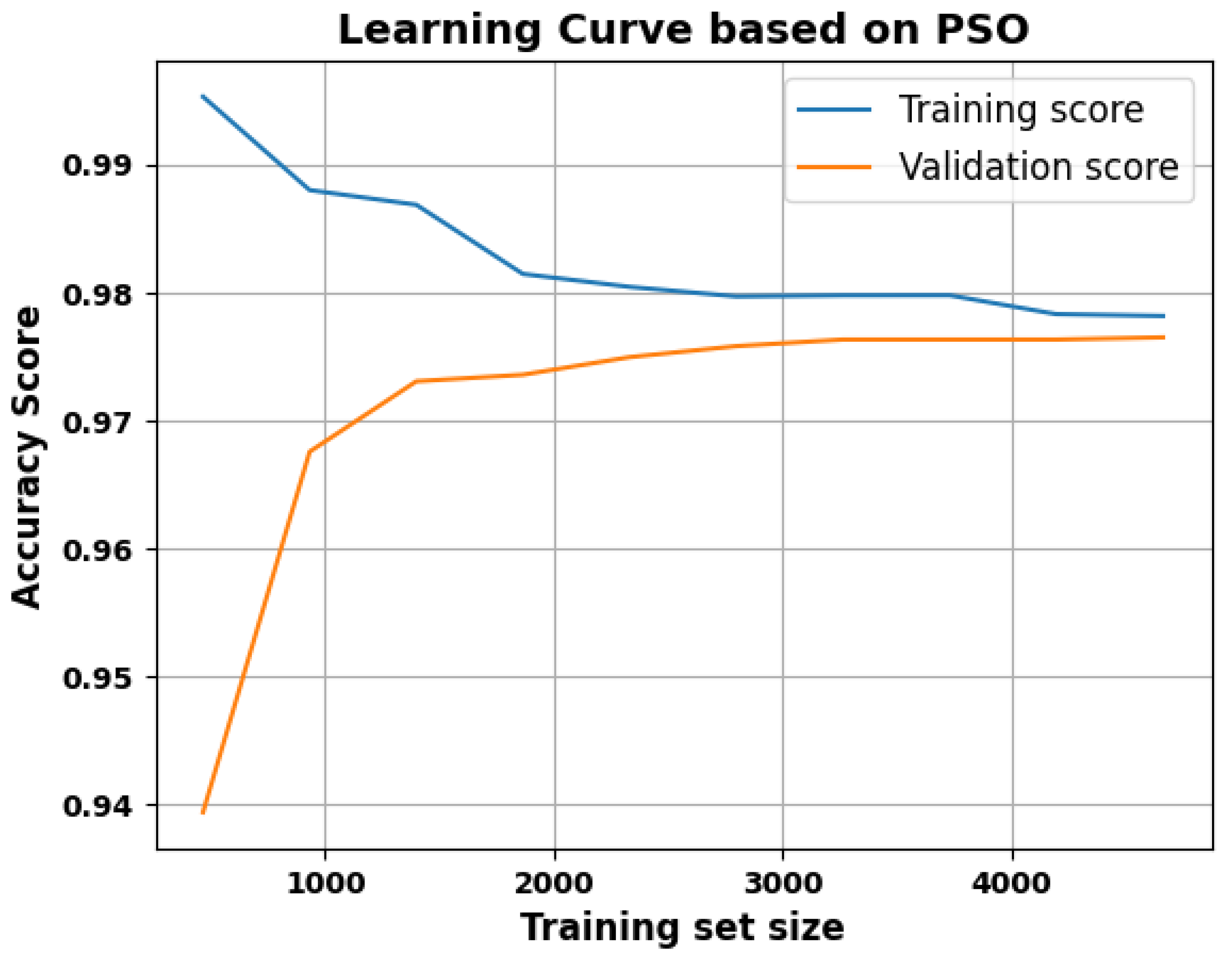
2.2.4. PSO-Based Refinement
2.2.5. Improved Generalization
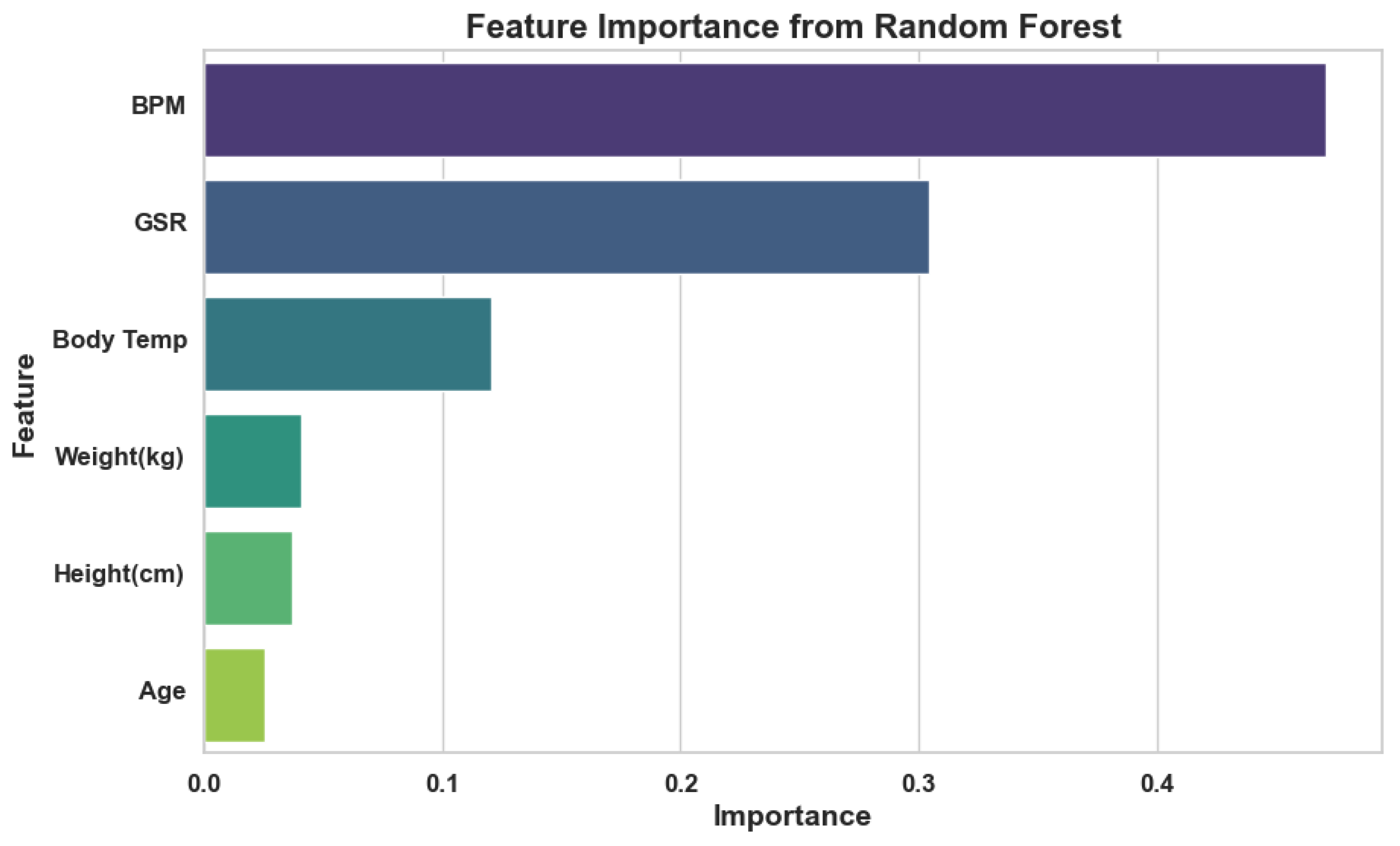
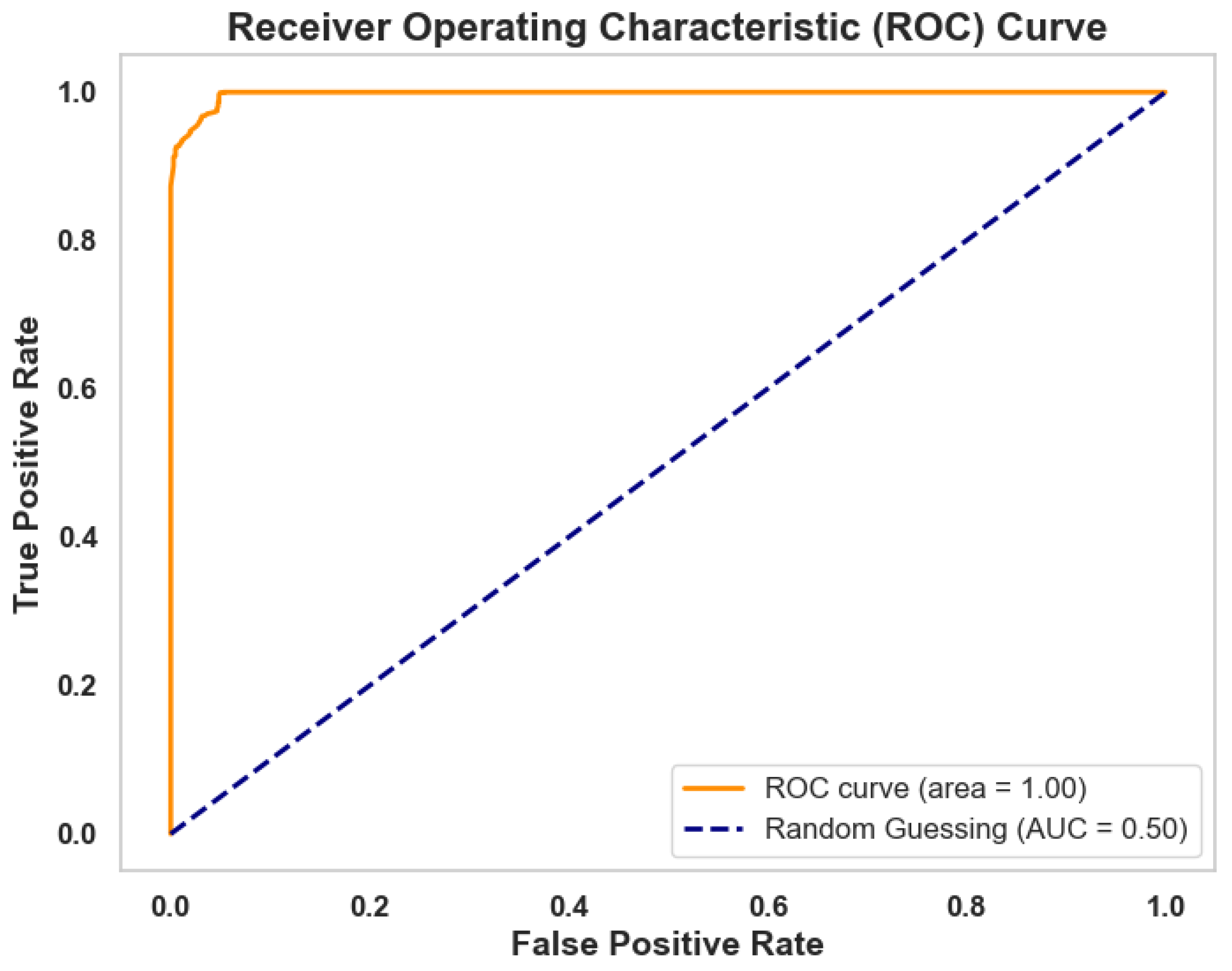
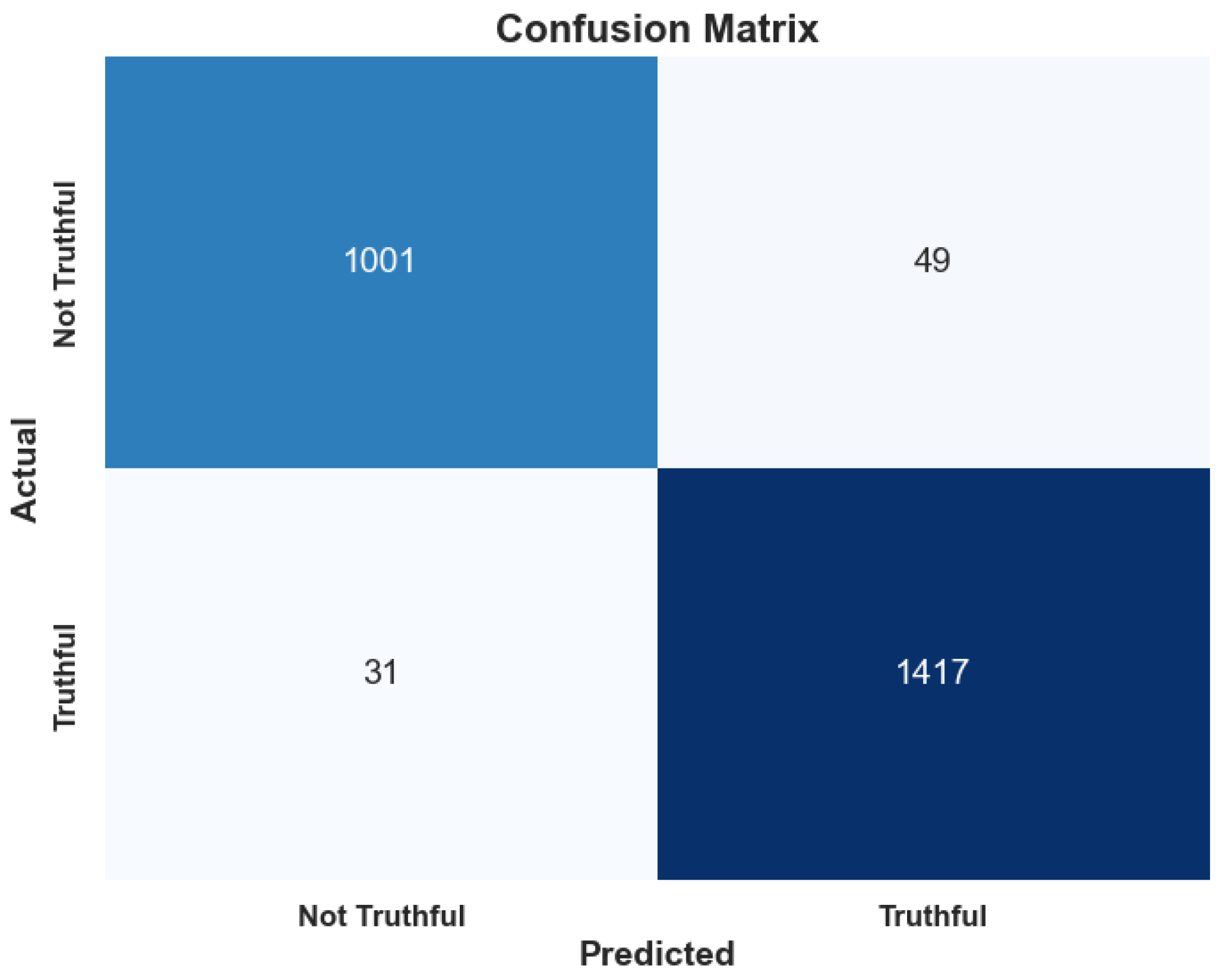
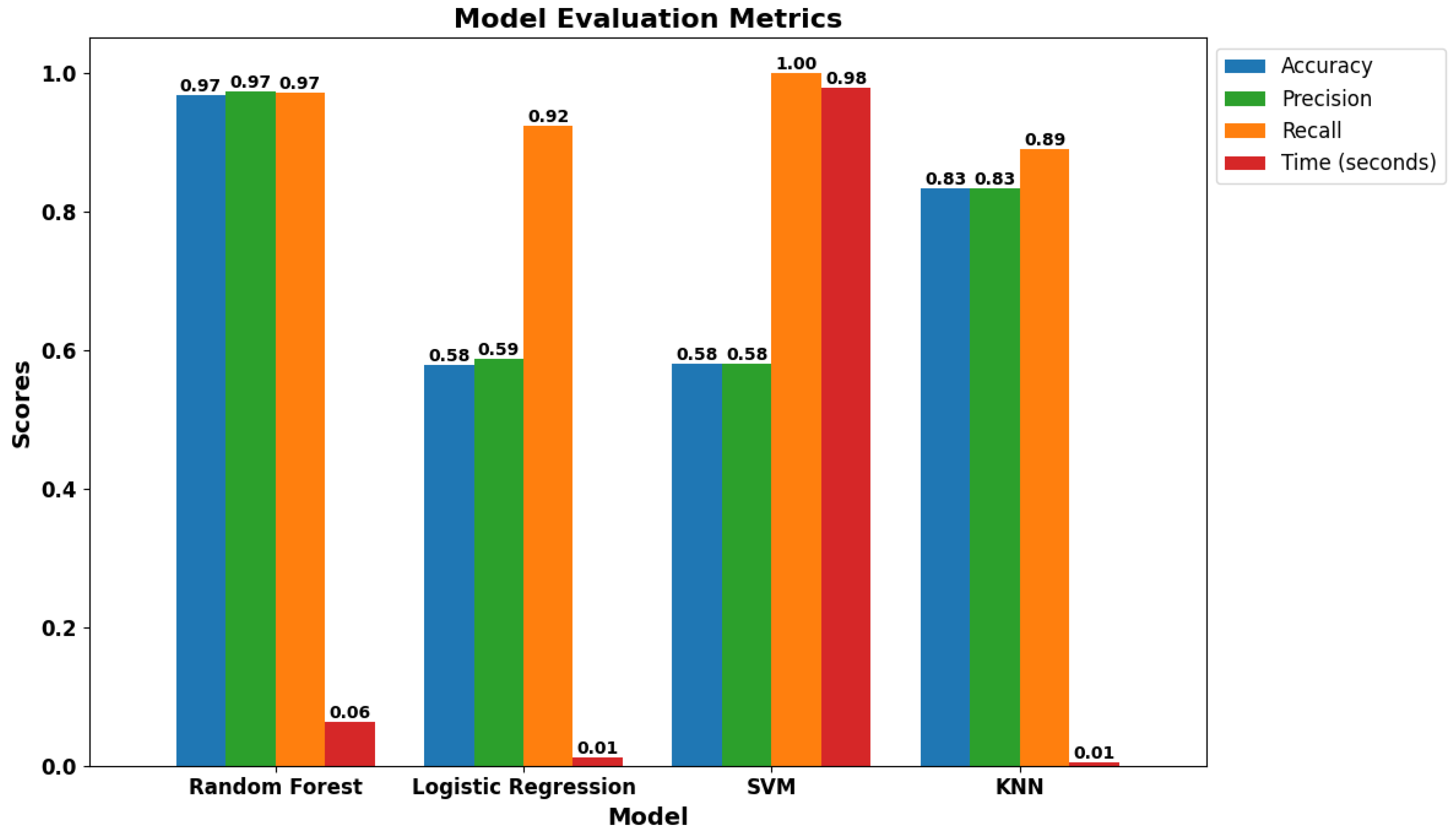
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BPM | Beats Per Minute |
| CV | Cross-Validation |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| fNIRS | Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy |
| GSR | Galvanic Skin Response |
| HRV | Heart Rate Variability |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| RF | Random Forest |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TS | Test Session |
References
- Elsayed, H.; Tawfik, N.S.; Shalash, O.; Ismail, O. Enhancing human emotion classification in human-robot interaction. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Machine Intelligence and Smart Innovation (ICMISI), Alexandria, Egypt, 12–14 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abd, S.; A. Hashim, I.; Jalal, A. Hardware implementation of deception detection system classifier. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN) 2021, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, O.; Sakr, A.; Salem, Y.; Abdelhadi, A.; Elsayed, H.; El-Shaer, A. Position and Orientation Analysis of Jupiter Robot Arm for Navigation Stability. IAES Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2025, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pik, E. Airport security: The impact of AI on safety, efficiency, and the passenger experience. J. Transp. Secur. 2024, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousedikova, L.; Malatinsky, A.; Drofova, I.; Adamek, M. The Role of Lie Detection Based System in Controlling Borders. In Proceedings of the 32nd DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, Vienna, Austria, 28–29 October 2021; pp. 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, Y.; Shalash, O.; Khatab, E.; Hamad, M.; Imam, S. AI-Driven Digital Twin for Optimizing Solar Submersible Pumping Systems. Inventions 2025, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métwalli, A.; Shalash, O.; Elhefny, A.; Rezk, N.; El Gohary, F.; El Hennawy, O.; Akrab, F.; Shawky, A.; Mohamed, Z.; Hassan, N.; et al. Enhancing Hydroponic Farming with Machine Learning: Growth Prediction and Anomaly Detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 157, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oravec, J.A. The emergence of “truth machines”?: Artificial intelligence approaches to lie detection. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2022, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelfarag, A.; Elshenawy, M.A.; Khattab, E.A. Accelerating Sobel Edge Detection Using Compressor Cells Over FPGAs. In Computer Vision: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1133–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Khatab, E.; Onsy, A.; Abouelfarag, A. Evaluation of 3D vulnerable objects’ detection using a multi-sensors system for autonomous vehicles. Sensors 2022, 22, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, M.; Shalash, O.; Hamad, M.S.; Saraya, M.S. Empowering the grid: A comprehensive review of artificial intelligence techniques in smart grids. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Telecommunications Conference (ITC-Egypt), Cairo, Egypt, 22–25 July 2024; pp. 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Sallam, M.; Salah, Y.; Osman, Y.; Hegazy, A.; Khatab, E.; Shalash, O. Intelligent Dental Handpiece: Real-Time Motion Analysis for Skill Development. Sensors 2025, 25, 6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, I.M.; Shalash, O.; Hamad, M.S. Optimized inter-turn short circuit fault diagnosis for induction motors using neural networks with leleru. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Conference on Power Electronics and Renewable Energy (CPERE), Luxor, Egypt, 19–21 February 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mottaleb, S.A.A.; Elhefny, A.; Métwalli, A.; Fayed, H.A.; Aly, M.H. Harnessing the power of ML for robust SISO and MIMO FSO communication systems in fog weather. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métwalli, A.; Abd El-Mottaleb, S.A.; Chehri, A.; Singh, M. Robust Free Space Optical Communication: Leveraging Hermite–Gaussian Modes and Derivative-Based Features. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–12 June 2025; pp. 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, F.S.; Reid, J.E. The reliability of polygraph examiner diagnosis of truth and deception. J. Crim. Law Criminol. Police Sci. 1971, 62, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, F.S.; Reid, J.E. Polygraph Silent Answer Test. J. Crim. Law Criminol. Police Sci. 1972, 63, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khalil, M.A.; George, K. Using Neural Network Models for BCI Based Lie Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 26–29 October 2022; pp. 505–509. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Fienberg, S.E.; Blascovich, J.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Davidson, R.; Ekman, P.; Faigman, D.; Stern, P. The Polygraph and Lie Detection; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Palmatier, J.J.; Rovner, L. Credibility assessment: Preliminary Process Theory, the polygraph process, and construct validity. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 95, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, E.H. Polygraph in Interrogation: What to Know and (Not) to Do. In Legal and Forensic Psychology: What Is It and What It Is Not; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Said, H.; Mohamed, S.; Shalash, O.; Khatab, E.; Aman, O.; Shaaban, R.; Hesham, M. Forearm Intravenous Detection and Localization for Autonomous Vein Injection Using Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiblanco Jimenez, I.A.; Marcolin, F.; Ulrich, L.; Moos, S.; Vezzetti, E.; Tornincasa, S. Interpreting emotions with EEG: An experimental study with chromatic variation in VR. In Advances on Mechanics, Design Engineering and Manufacturing IV, Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Mechanics, Design Engineering & Advanced Manufacturing, Ischia, Italy, 1–3 June 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 318–329. [Google Scholar]
- Khattab, Y.; Pott, P.P. Active/robotic capsule endoscopy—A review. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 127, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.; Werner, P.; Saxen, F.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Gruss, S.; Walter, S. Classification networks for continuous automatic pain intensity monitoring in video using facial expression on the X-ITE Pain Database. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 91, 103743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, S.; Li, H.; Antwi-Afari, M.F.; Umer, W.; Wong, A.Y.L. Evaluation of physiological metrics as real-time measurement of physical fatigue in construction workers: State-of-the-art review. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 03121001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, O. Design and Development of Autonomous Robotic Machine for Knee Arthroplasty. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Prome, S.A.; Ragavan, N.A.; Islam, M.R.; Asirvatham, D.; Jegathesan, A.J. Deception detection using machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques: A systematic review. Nat. Lang. Process. J. 2024, 6, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, Y.; Shalash, O.; Khatab, E. A lightweight speaker verification approach for autonomous vehicles. Robot. Integr. Manuf. Control 2024, 1, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, M. Technologies in the twilight zone: Early lie detectors, machine learning and reformist legal realism. Int. Rev. Law Comput. Technol. 2020, 34, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatab, E.; Onsy, A.; Varley, M.; Abouelfarag, A. A lightweight network for real-time rain streaks and rain accumulation removal from single images captured by AVs. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, A.; Shalash, O.; Ismaeil, O. Multiple Objects Detection and Localization using Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Computer Engineering (ICARCE), Wuhan, China, 14–16 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulridha, F.; Albaker, B.M. Non-invasive real-time multimodal deception detection using machine learning and parallel computing techniques. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2024, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mottaleb, S.A.; Métwalli, A.; Singh, M.; Hassib, M.; Aly, M.H. Machine learning FSO-SAC-OCDMA code recognition under different weather conditions. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, Y.; Zidane, I.F.; El-Habrouk, M.; Rezeka, S. Solving kinematics of a parallel manipulator using artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 31st International Conference on Computer Theory and Applications (ICCTA), Alexandria, Egypt, 11–13 December 2021; pp. 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Fawzy, H.; Elbrawy, A.; Amr, M.; Eltanekhy, O.; Khatab, E.; Shalash, O. A systematic review: Computer vision algorithms in drone surveillance. J. Robot. Integr. 2025, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelfarag, A.; El-Shenawy, M.; Khatab, E. High speed edge detection implementation using compressor cells over rsda. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Interfaces and Human Computer Interaction 2016, Game and Entertainment Technologies 2016 and Computer Graphics, Visualization, Computer Vision and Image Processing 2016-Part of the Multi Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems 2016, Madeira, Portugal, 2–4 July 2016; IADIS Press: Lisbon, Portugal, 2016; pp. 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Mottaleb, S.A.; Métwalli, A.; Chehri, A.; Ahmed, H.Y.; Zeghid, M.; Khan, A.N. A QoS Classifier Based on Machine Learning for Next-Generation Optical Communication. Electronics 2022, 11, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Métwalli, A.; Ahmed, H.Y.; Zeghid, M.; Nisar, K.S.; Abd El-Mottaleb, S.A. K-nearest neighbor model for classification between four different Hermite Gaussian beams in MDM/FSO systems under rainy weather. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2023, 55, 5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.; Métwalli, A.; Aly, M.H.; Badawi, W.K. 5G and Beyond: Channel Classification Enhancement Using VIF-Driven Preprocessing and Machine Learning. Electronics 2023, 12, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwalli, A.; Sallam, M.; Khatab, E.; Shalash, O. Polygraph-Based Truth Detection System Dataset. Mendeley Data 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Tasgaonkar, V.; Deshpande, A.; Desai, A.; Shah, B.; Kushawaha, A.; Sukumar, A.; Kotecha, K.; Kunder, S.; Waykole, Y.; et al. Multimodal machine learning for deception detection using behavioral and physiological data. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.; Cheng, T. Artificial intelligence in lie detection: Why do cognitive theories matter? New Ideas Psychol. 2025, 76, 101128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrij, A.; Fisher, R.P. Lie Detection and Nonverbal Behaviour: Present and Future. In Body Language Communication; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 377–398. [Google Scholar]
- Constâncio, A.S.; Tsunoda, D.F.; Silva, H.d.F.N.; Silveira, J.M.d.; Carvalho, D.R. Deception detection with machine learning: A systematic review and statistical analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkholy, M.; Shalash, O.; Hamad, M.S.; Saraya, M. Harnessing Machine Learning for Effective Energy Theft Detection Based on Egyptian Data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy Systems, Cairo, Egypt, 29–30 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsoglou, K.N.; Biedermann, A. Polygraph-based deception detection and machine learning. Combining the worst of both worlds? Forensic Sci. Int. Synerg. 2024, 9, 100479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, N.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Vaxelaire, B.; Sock, R.; Ling, Z. Lie Detection Based on Acoustic Analysis. J. Voice 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, G.; Ursino, M.; Scarpazza, C.; Zangrossi, A.; Sartori, G. Detecting lies in investigative interviews through the analysis of response latencies and error rates to unexpected questions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.A.; Babinec, M.; George, K. LSTM Model for Brain Control Interface Based-Lie Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Medicine, Health and Care (AIMHC), Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 5–7 February 2024; pp. 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Rad, D.; Paraschiv, N.; Kiss, C. Neural Network Applications in Polygraph Scoring—A Scoping Review. Information 2023, 14, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler-Galicki, J.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Synowiec, D.; Dąbrowska, R.; Mądry, E. Polygraph analyses: Technical and practical background. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 91, e590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennen, T.; Magnussen, S. Lie detection: What works? Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2023, 32, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, N.; Aspandi, D.; Sukno, F.M.; Binefa, X. Machine learning-based lie detector applied to a novel annotated game dataset. Future Internet 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.; Baykara, M.; Alakus, T.B. LieWaves: Dataset for lie detection based on EEG signals and wavelets. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 1571–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, J.B.; Benus, S.; Brenier, J.M.; Enos, F.; Friedman, S.; Gilman, S.; Girand, C.; Graciarena, M.; Kathol, A.; Michaelis, L.; et al. Distinguishing deceptive from non-deceptive speech. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2005, Lisbon, Portugal, 4–8 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Turnip, A.; Amri, M.F.; Fakrurroja, H.; Simbolon, A.I.; Suhendra, M.A.; Kusumandari, D.E. Deception detection of EEG-P300 component classified by SVM method. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Software and Computer Applications, Bangkok, Thailand, 26–28 February 2017; pp. 299–303. [Google Scholar]
- Nasri, H.; Ouarda, W.; Alimi, A.M. ReLiDSS: Novel lie detection system from speech signal. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACS 13th International Conference of Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Agadir, Morocco, 29 November–2 December 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, N.; Dilsizian, M.; Metaxas, D.; Burgoon, J.K. Motion profiles for deception detection using visual cues. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2010, Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, September 5–11, 2010, Proceedings, Part VI 11; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 462–475. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rosas, V.; Mihalcea, R. Experiments in open domain deception detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 1120–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, R.; Badr, M.M.; Shalash, O.; Othman, A.A.; Hamdan, E.; Hamad, M.S.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Ahmed, S.; Imam, S.M. A data-driven digital twin of electric vehicle Li-ion battery state-of-charge estimation enabled by driving behavior application programming interfaces. Batteries 2023, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Agarwal, M.; Arora, M.; Chakraborty, T.; Singh, R.; Vatsa, M. Bag-of-lies: A multimodal dataset for deception detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Belavadi, V.; Zhou, Y.; Bakdash, J.Z.; Kantarcioglu, M.; Krawczyk, D.C.; Nguyen, L.; Rakic, J.; Thuriasingham, B. MultiModal deception detection: Accuracy, applicability and generalizability. In Proceedings of the 2020 Second IEEE International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Intelligent Systems and Applications (TPS-ISA), Atlanta, GA, USA, 28–31 October 2020; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.A.; Ramirez, M.; George, K. Using EEG and fNIRS signals as polygraphs. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26–29 January 2022; pp. 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Baghel, N.; Singh, D.; Dutta, M.K.; Burget, R.; Myska, V. Truth identification from EEG signal by using convolution neural network: Lie detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 43rd International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Milan, Italy, 7–9 July 2020; pp. 550–553. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tao, C.; Guan, J.; Rao, N. A novel approach for lie detection based on F-score and extreme learning machine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanna, R.K.; Kripa, N.; Vasuki, R. Systematic Design Of Lie Detector System Utilising EEG Signals Acquisition. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 9, 610–612. [Google Scholar]
- Zhiyu, W. Based on physiology parameters to design lie detector. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling (ICCASM 2010), Taiyuan, China, 22–24 October 2010; Volume 8, pp. V8–634. [Google Scholar]
- Aranjo, S.; Kadam, M.A.; Sharma, M.A.; Antappan, M.A. Lie Detection Using Facial Analysis Electrodermal Activity Pulse and Temperature. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2021, 8, d999–d1011. [Google Scholar]
- Honts, C.R.; Amato, S. Automation of a screening polygraph test increases accuracy. Psychol. Crime Law 2007, 13, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, M.U.; Perez-Rosas, V.; Yanikoglu, B.; Abouelenien, M.; Burzo, M.; Mihalcea, R. Multimodal deception detection using real-life trial data. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 13, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, O.; Rowe, P. Computer-assisted robotic system for autonomous unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 70, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlina, T.; Ferdian, R.; Rizal, A.; Aisuwarya, R. A Microcontroller-based Lie Detection System Leveraging Physiological Signals. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and Intelligence Systems (IoTaIS), Bali, Indonesia, 28–30 November 2023; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rosas, V.; Mihalcea, R.; Narvaez, A.; Burzo, M. A Multimodal Dataset for Deception Detection. In Proceedings of the LREC, Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; pp. 3118–3122. [Google Scholar]
- Elkateb, S.; Métwalli, A.; Shendy, A.; Abu-Elanien, A.E. Machine learning and IoT–Based predictive maintenance approach for industrial applications. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 88, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.; Métwalli, A.; Aly, M.H.; Badawi, W.K. Wireless Communication Channel Scenarios: Machine-learning-based identification and performance enhancement. Electronics 2022, 11, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.; Métwalli, A.; Aly, M.H.; Badawi, W.K. Enhanced feature selection method based on regularization and kernel trick for 5G applications and beyond. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 11589–11600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasser, M.; Shalash, O.; Ismail, O. Optimized decentralized swarm communication algorithms for efficient task allocation and power consumption in swarm robotics. Robotics 2024, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métwalli, A.; Fayed, H.A.; Aly, M.H. Intelligent 18-Tupling Optical Links: PSO-Tuned ML for Predicting and Minimizing Signal Penalties. J. Light. Technol. 2025. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Modality | References |
|---|---|
| Video | [62,63] |
| Audio | [62] |
| Electroencephalogram (EEG) | [18,62,64,65,66,67] |
| Heart Rate Variability (HRV) | [18,68,69] |
| Body Temperature | [68,69] |
| Functional Near Infra-red Spectroscopy (fNIRS) | [18,64] |
| Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) | [18,69,70] |
| Blood Pressure | - |
| Facial Gestures | [69] |
| Dataset | Subjects | Modalities (Number) | Total | Collection Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSC [56] | 32 | Audio (1) | - | Hypothetical Scenario |
| ReLiDDB [58] | 40 | Audio (1) | - | Hypothetical Scenario |
| Open Domain [60] | 512 | Text (1) | 7168 | Crowdsourcing |
| EEG-P300 [57] | 11 | EEG (1) | 88 | Hypothetical Scenario |
| Real Life Trials [71] | 56 | Video, Audio, Text (3) | 121 | Realistic Scenario |
| Multi-Modal [74] | 30 | Video, Audio, Thermal, Physiological (4) | 150 | Hypothetical Scenario |
| Bag-of-Lies [62] | 35 | Video, Audio, EEG, Gaze (4) | 325 | Realistic Scenario |
| Article | Year | Modalities | Method | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A microcontroller-based Lie Detection System Leveraging Physiological Signals [73] | 2023 | HRV, GSR | Reid | 80% |
| LSTM Model for Brain Control Interface Based-Lie Detection [50] | 2024 | EEG, fNIRS, HRV | LSTM | 70% |
| Using EEG and fNIRS Signals as Polygraphs [64] | 2022 | EEG, fNIRS, HRV, GSR | Neural Network | 71.9% |
| Proposed technique | 2025 | BPM, GSR, Body Temp, Height, Age, Weight | RF or AdaBoost | 97% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shalash, O.; Métwalli, A.; Sallam, M.; Khatab, E. A Multimodal Polygraph Framework with Optimized Machine Learning for Robust Deception Detection. Inventions 2025, 10, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060096
Shalash O, Métwalli A, Sallam M, Khatab E. A Multimodal Polygraph Framework with Optimized Machine Learning for Robust Deception Detection. Inventions. 2025; 10(6):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060096
Chicago/Turabian StyleShalash, Omar, Ahmed Métwalli, Mohammed Sallam, and Esraa Khatab. 2025. "A Multimodal Polygraph Framework with Optimized Machine Learning for Robust Deception Detection" Inventions 10, no. 6: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060096
APA StyleShalash, O., Métwalli, A., Sallam, M., & Khatab, E. (2025). A Multimodal Polygraph Framework with Optimized Machine Learning for Robust Deception Detection. Inventions, 10(6), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10060096








