Addressing Development Challenges of the Emerging REEFS Wave Energy Converter
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Inventiveness for Untapping Wave Energy Potential
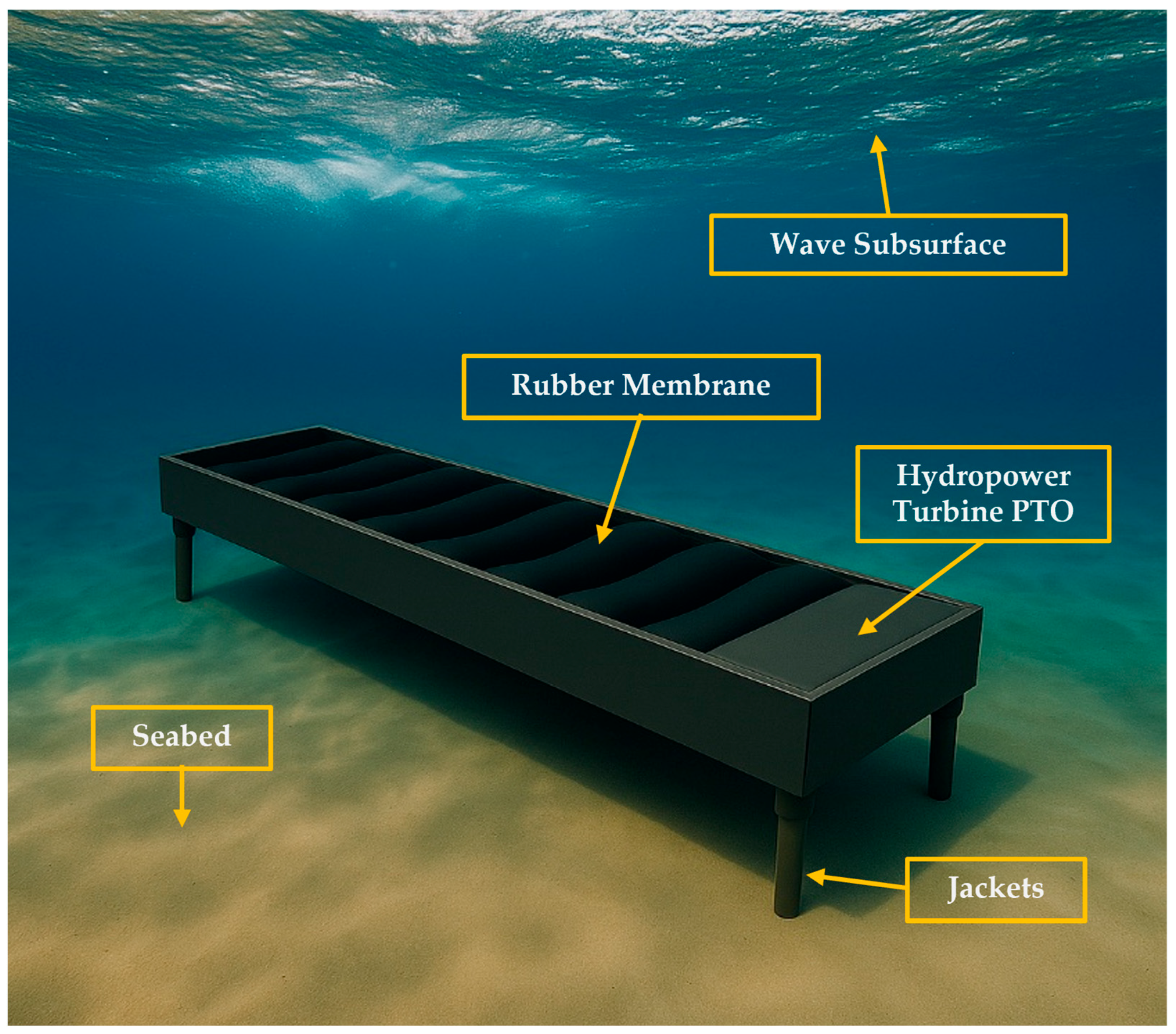
1.2. The Submerged Pressure Differential Principle
1.3. Scope of the Article
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Development Trajectory
3.1.1. Concept Presentation and First Proof-of-Concept
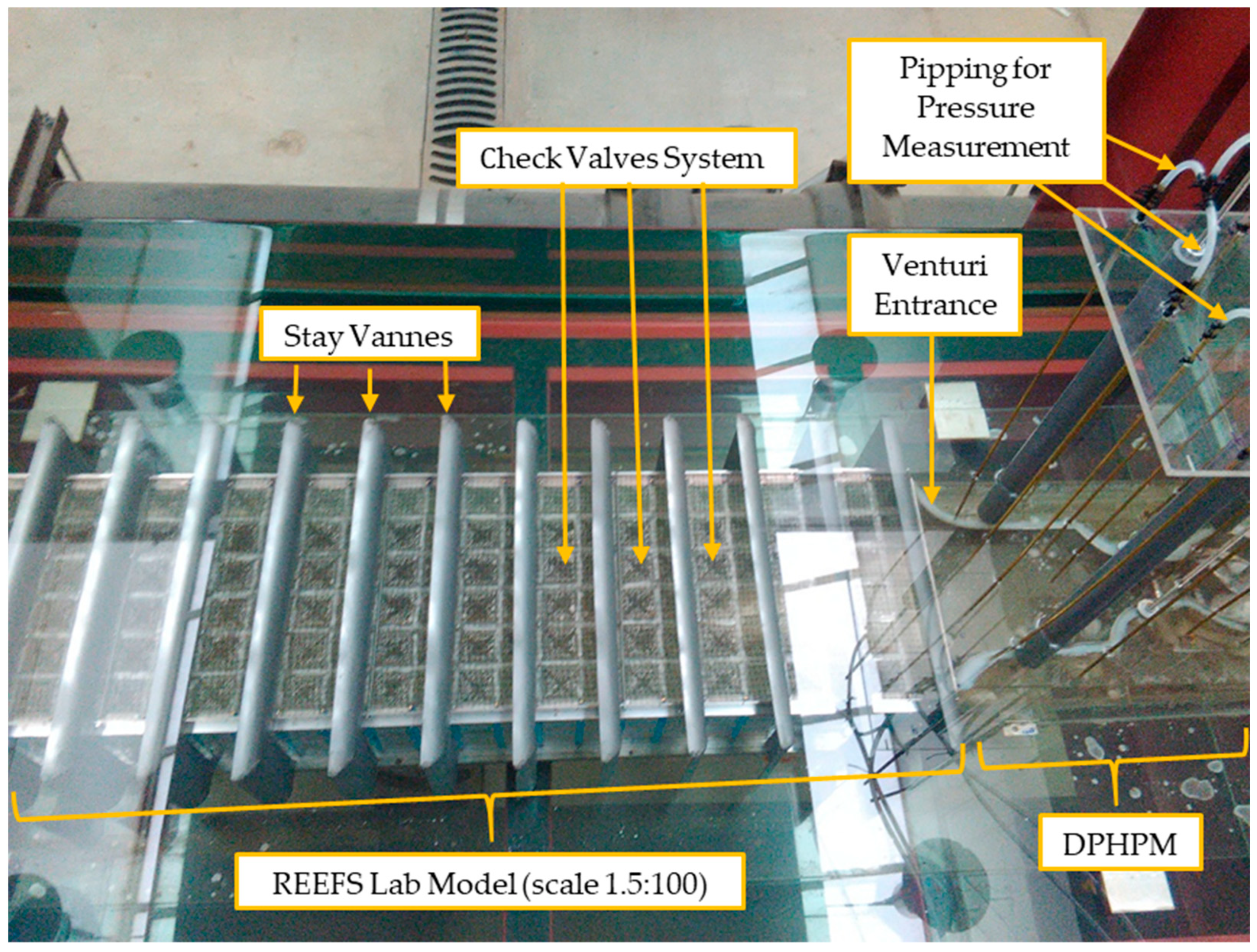
3.1.2. Preliminary Laboratorial Determination of the REEFS WEC Power Output
3.1.3. Simplified Model for Expedient Computational Assessment of the Novel REEFS WEC Power Output
3.1.4. Demonstrating the Shore Protection Environmental Externality
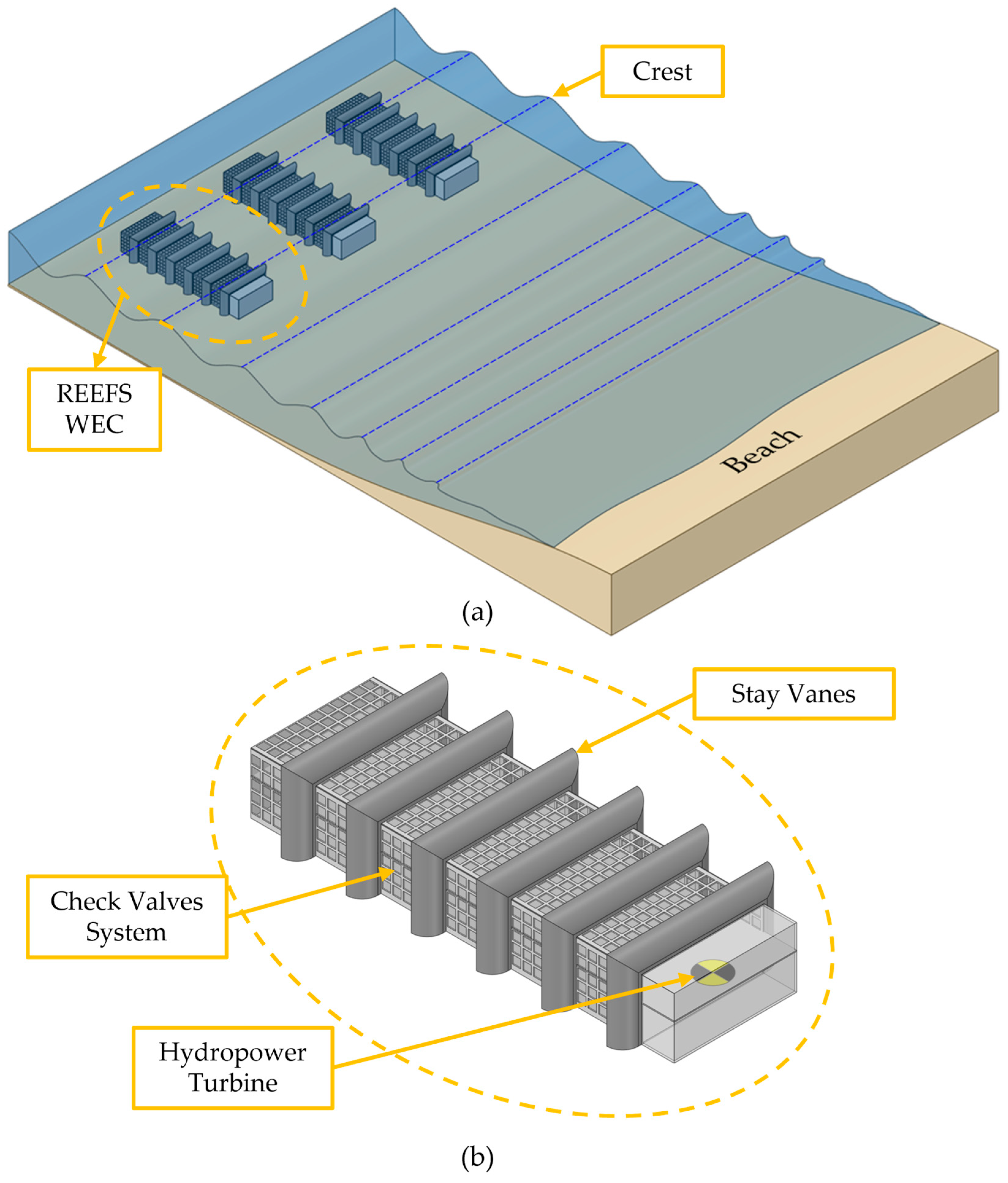
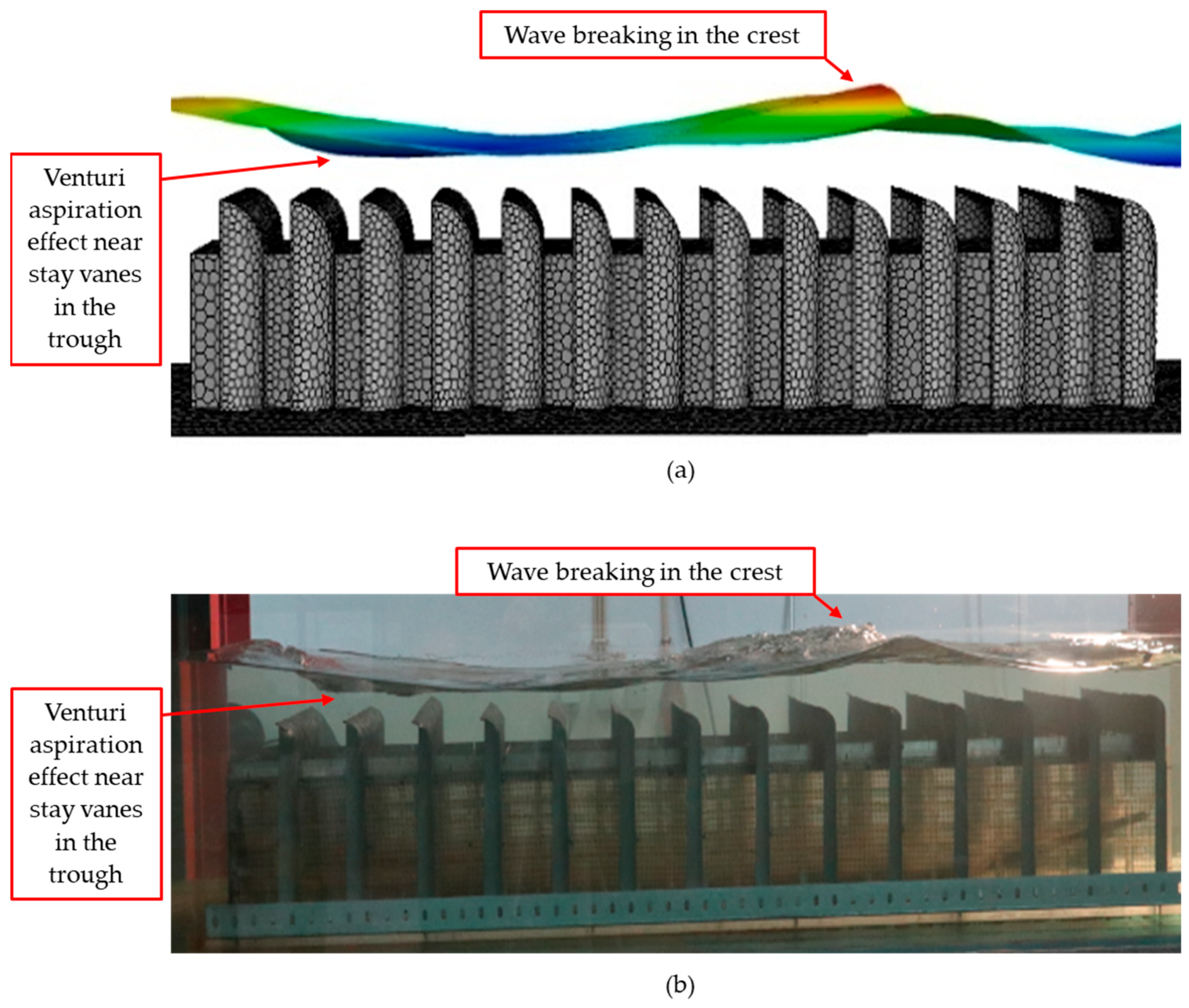
3.1.5. CFD-Based Numerical Wave Tank of the REEFS WEC—Wave Flow Modeling
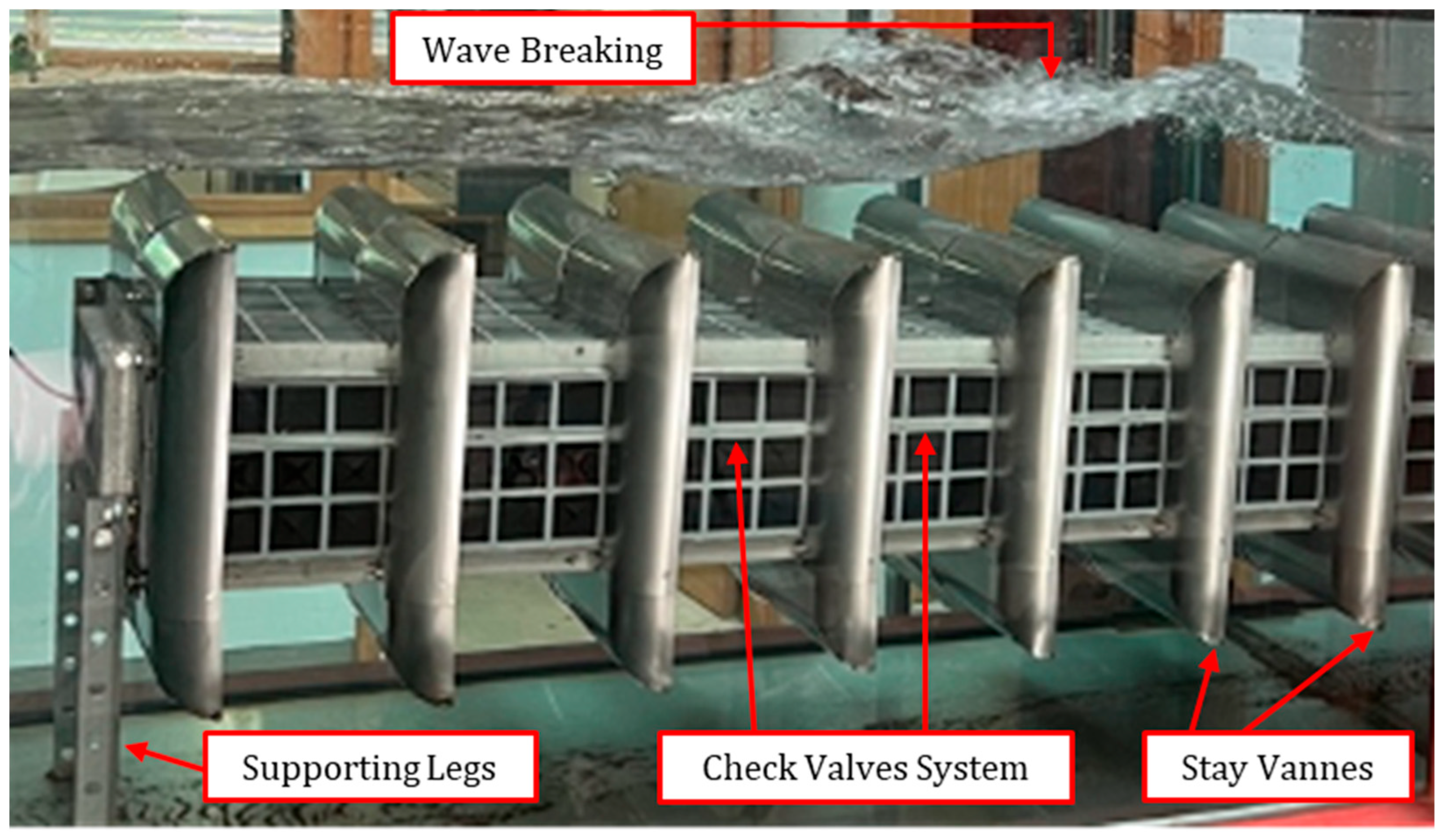
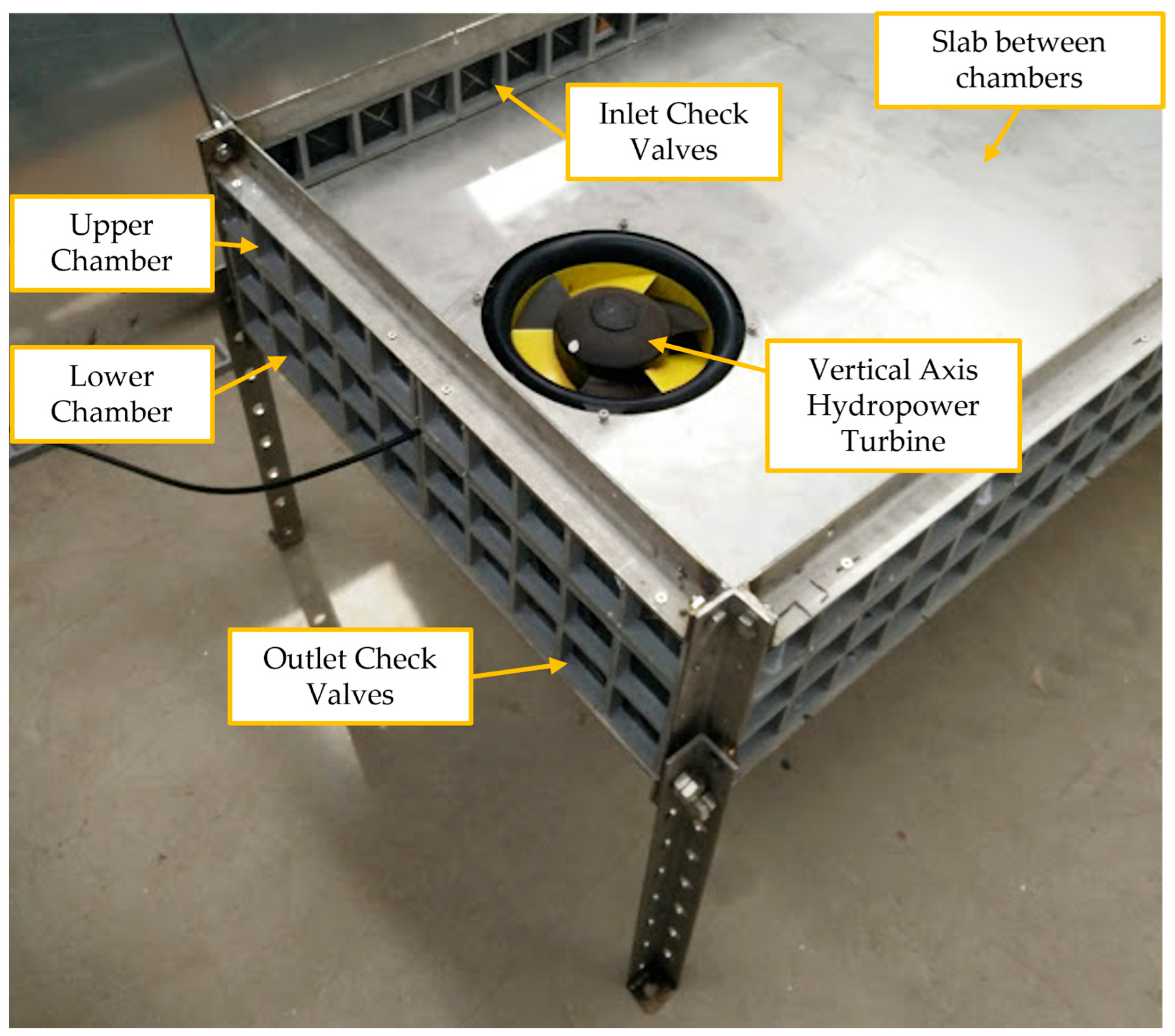
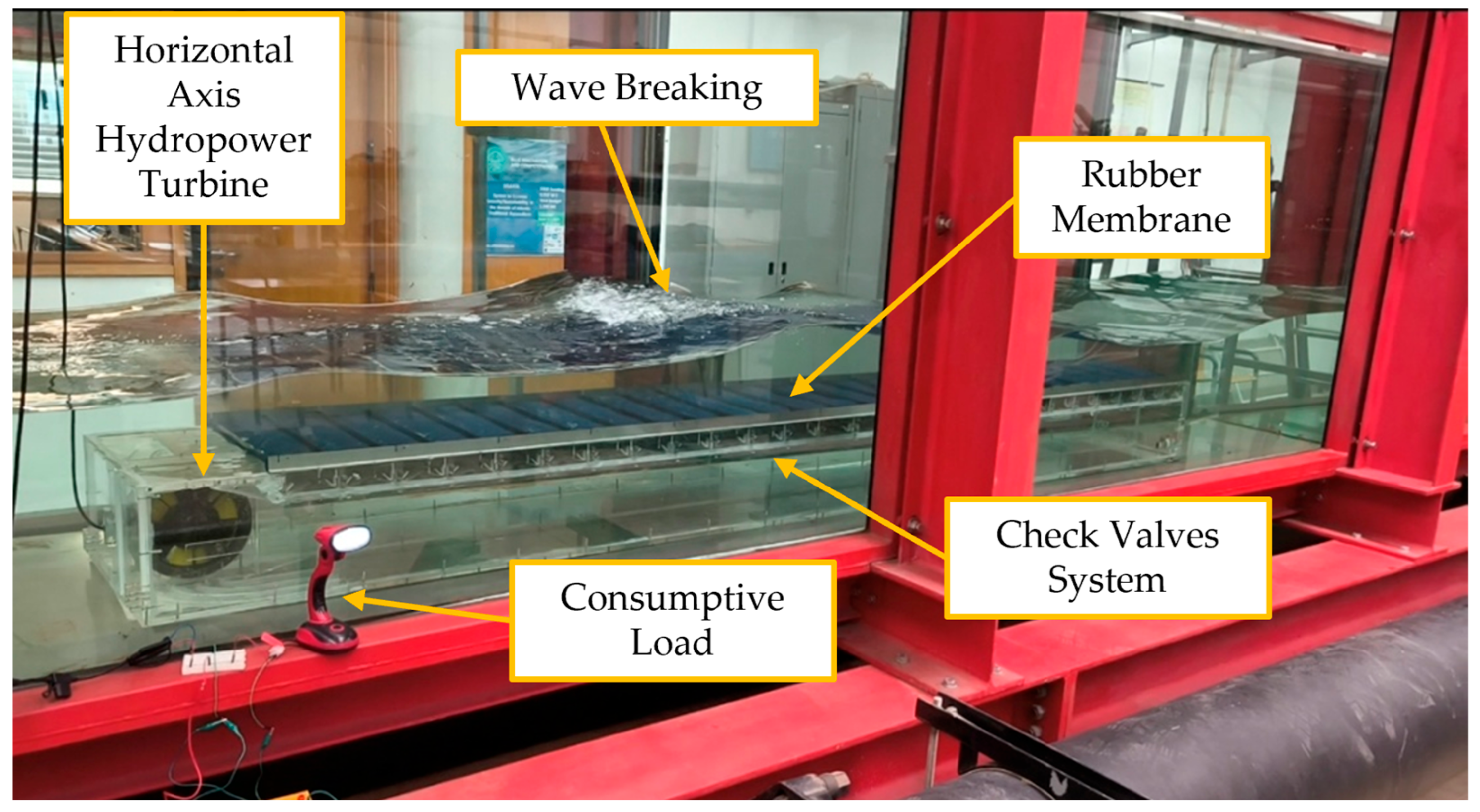
3.1.6. First Wave-to-Wire Proof-of-Concept of the First Version of the REEFS Patent at (3:100) Scale—Turbine in Contact with Seawater
3.1.7. First Wave-to-Wire Proof-of-Concept of the Second Version of the REEFS Patent at (3:100) Scale—Turbine Without Contact with Seawater
3.2. Current Research Status
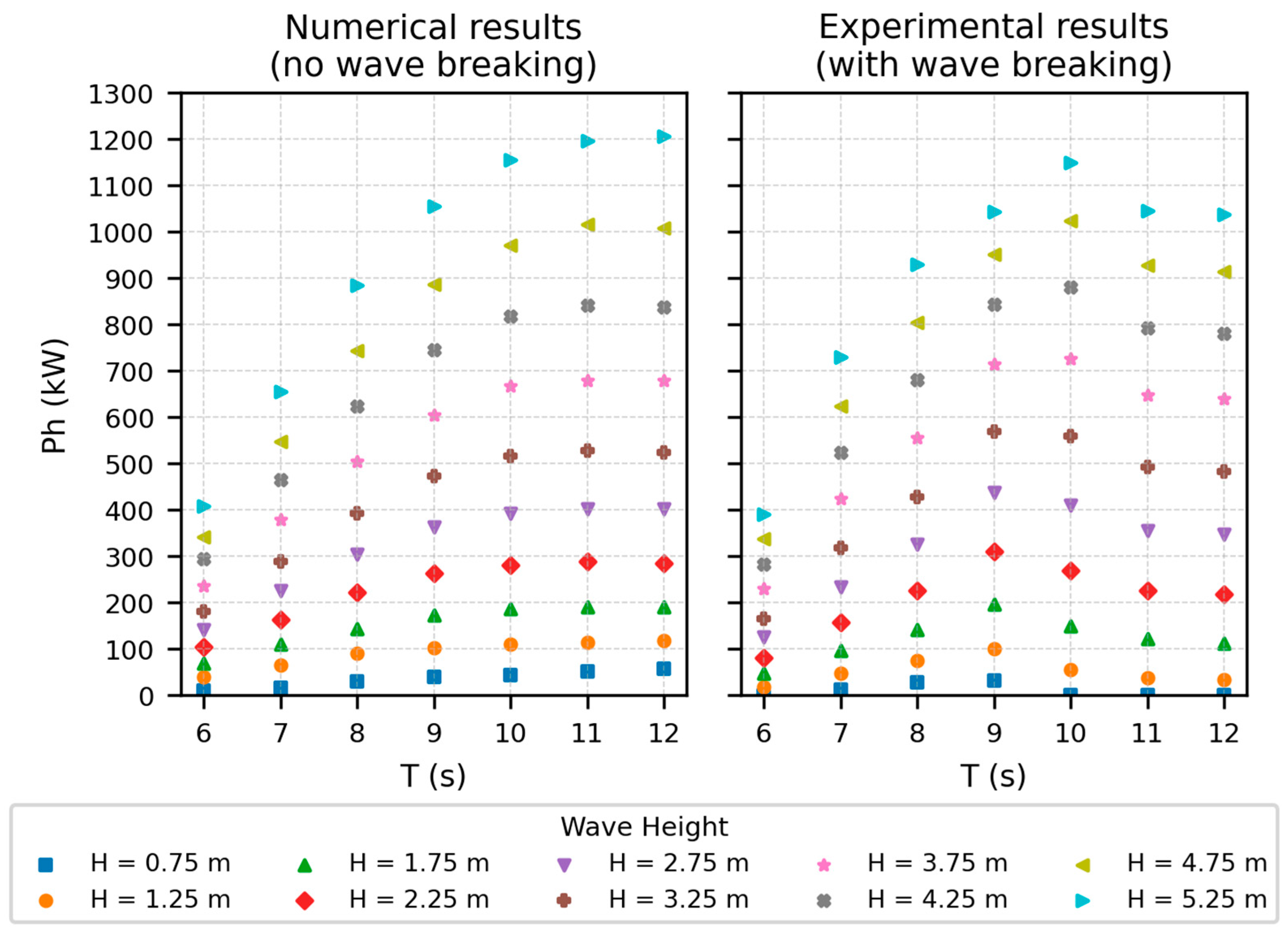
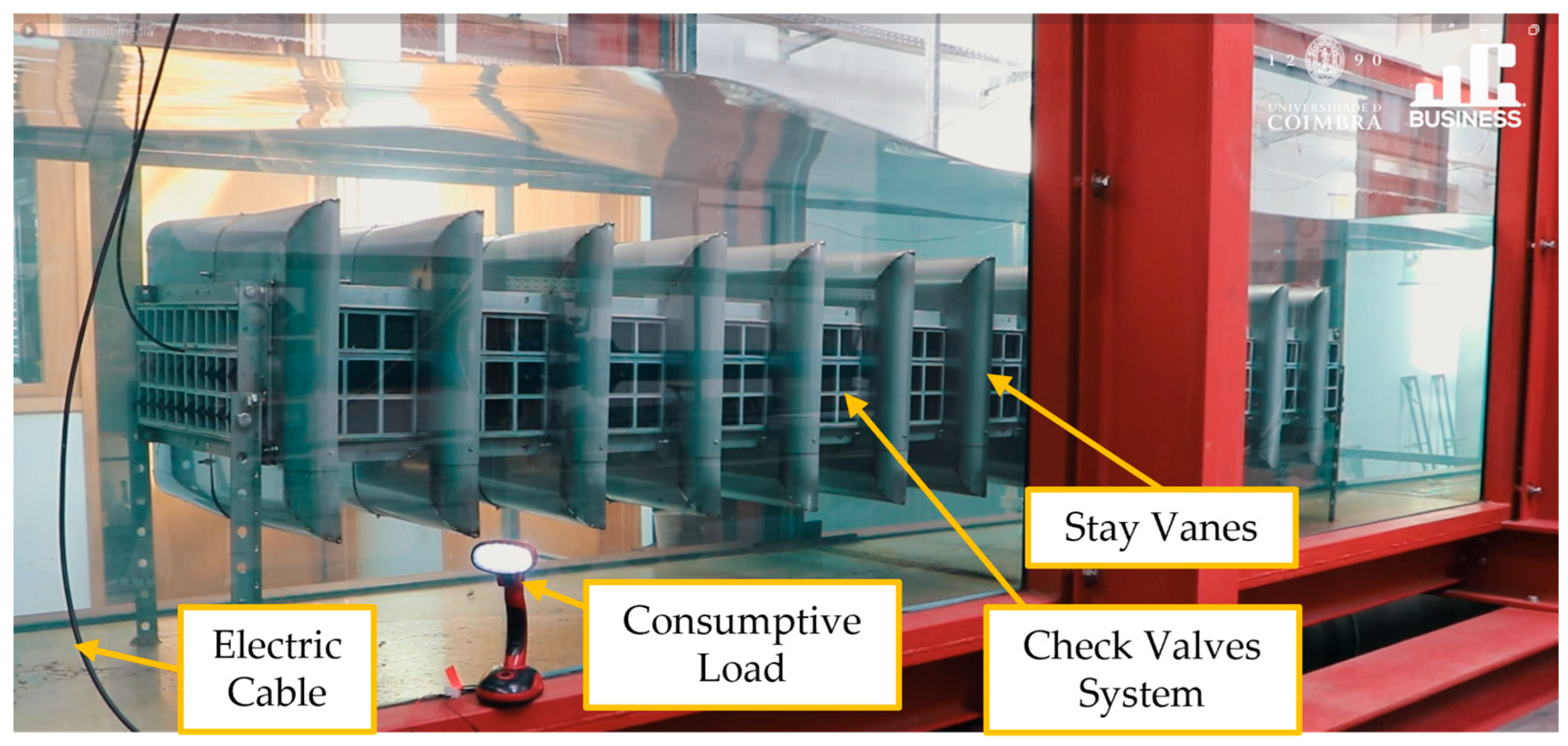
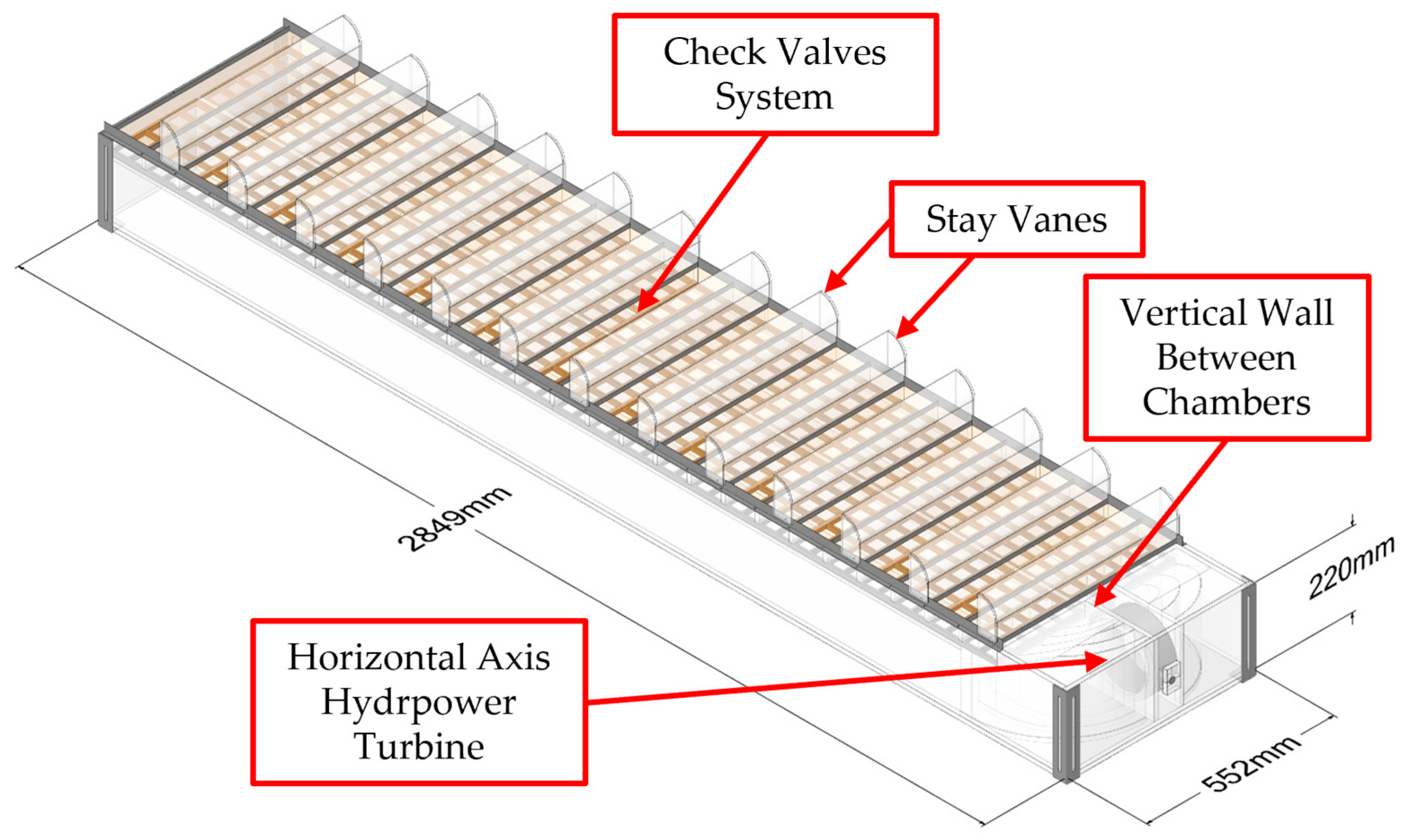
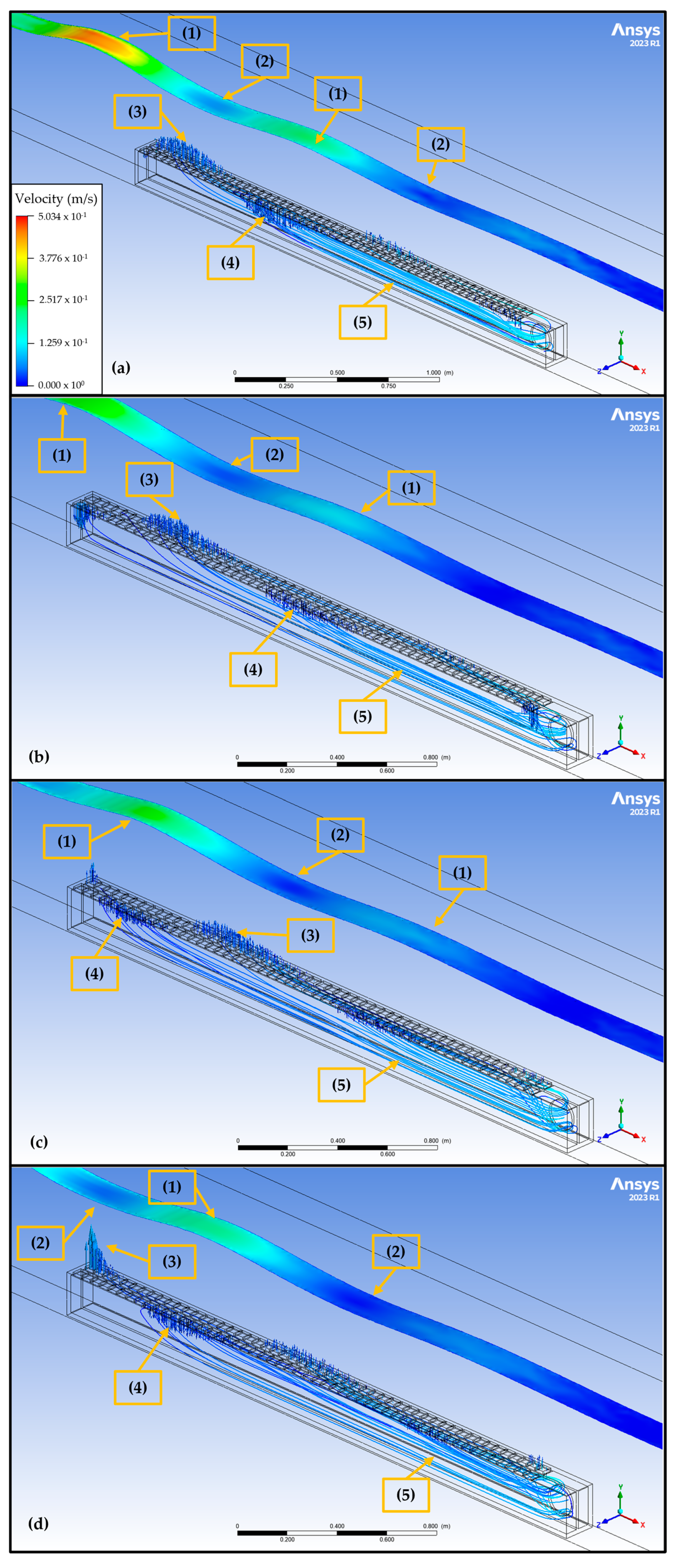
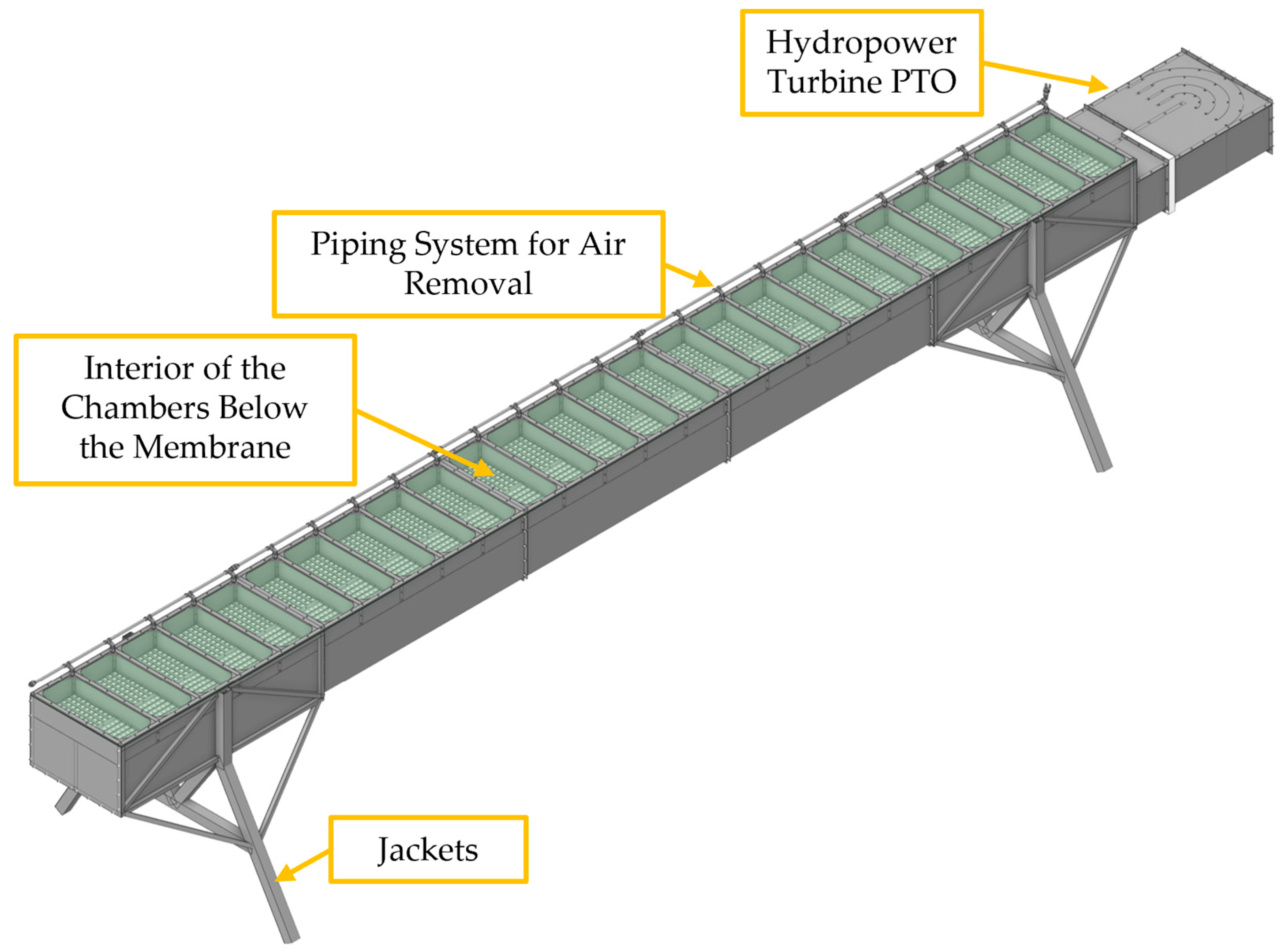
3.2.1. CFD-Based Numerical Wave Tank of the REEFS WEC—Fully Functional Wave-to-Water Modeling
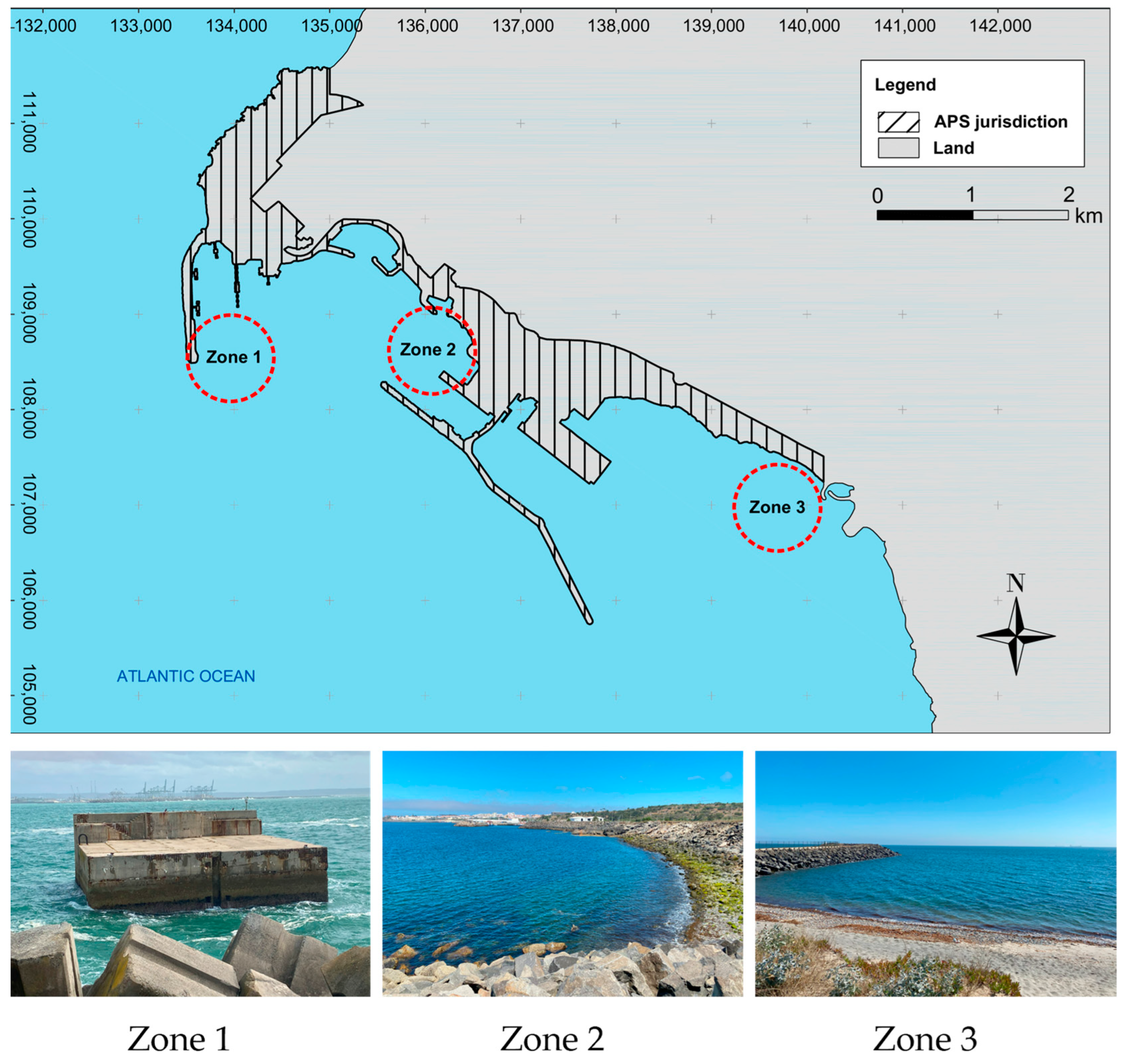
3.2.2. Sea Test of the REEFS Model in Port of Sines, Portugal
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Etymology Dictionary. Available online: https://www.etymonline.com/word/invention (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- European Patent Office—Is It Patentable? Available online: https://www.epo.org/en/new-to-patents/is-it-patentable (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Strange, D.L.P.; Tung, T.; Baker, G.C.; Hagerman, G.; Lewis, L.F.; Clark, R.H. Renewable Energy Resources: Opportunities and Constraints 1990–2020; Chapter 6; World Energy Council: London, UK, 1993; pp. 321–358. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, K.; Stock-Williams, C. Quantifying the global wave power resource. Renew. Energy 2012, 44, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, A.; Salauddin Rasel, M. Advances and challenges in ocean wave energy harvesting. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 61, 103599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.; Andreu, S.; Ceballos, I.; Martínez de Alegría, I.; Kortabarria, I. Review of wave energy technologies and the necessary power equipment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W. Wave energy conversion and hydrodynamics modelling technologies: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 109, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, A.; McCullen, P.; Falcão, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Gardner, F.; Hammarlund, K.; Lemonis, G.; Lewis, T.; Nielsen, K.; Petroncini, S.; et al. Wave energy in europe: Current status and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapting to a Changing Climate in the Management of Coastal Zones—Policy Perspectives. OECD Environment Policy Paper No. 24. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/content/dam/oecd/en/publications/reports/2021/04/adapting-to-a-changing-climate-in-the-management-of-coastal-zones_0f30d847/b21083c5-en.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Yu, P.; Ou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Deng, X.; Xu, N. Nature-based solutions in coastal urbanization: Addressing environmental and socio-economic challenges. Earth Crit. Zone 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, A.F.d.O. Wave energy utilization: A review of the technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falnes, J. A review of wave-energy extraction. Mar. Struct. 2007, 20, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, B.; Plummer, A.R.; Sahinkaya, M.N. A review of wave energy converter technology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2016, 223, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMEC—The European Marine Energy Centre LTD—Wave Developers. Available online: https://www.emec.org.uk/marine-energy/wave-developers/ (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Li, Y.; Yu, Y.H. A synthesis of numerical methods for modeling wave energy converter-point absorbers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4352–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Karimpour, F.; Goudey, C.A.; Jacobson, P.T.; Alam, M.R. Ocean wave energy in the United States: Current status and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.; Yi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Aslam, T.; Mugheri, S.A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Ali, A.; Qi, L. Wave energy evolution: Knowledge structure, advancements, challenges and future opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 205, 114880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, B.; Bauer, P. Wave Energy Converter Concepts: Design Challenges and Classification. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2012, 6, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, M.J.; van Diemen, R.; Skea, J. Examining the Effectiveness of Support for UK Wave Energy Innovation Since 2000: Lost at Sea or a New Wave of Innovation? University of Strathclyde, International Public Policy Institute: Glasgow, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, B.; Nielsen, K. Guidelines for the Development & Testing of Wave Energy Systems. OES-IA Annex II Task 2.1, Report T02.1. 2010. Available online: https://www.ocean-energy-systems.org/publications/oes-reports/guidelines/document/guidelines-for-the-development-testing-of-wave-energy-systems-2010-/ (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Lopes de Almeida, J. Reefs: An artificial reef for wave energy harnessing and shore protection—A new concept towards multipurpose sustainable solutions. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MWaveTM—Technical Overview. Available online: https://bomborawave.com/mwave/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- King, A.J.C. Numerical Modelling of the ‘Bombora’ Wave Energy Conversion Device. In Proceedings of the 19th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 8 November 2014; Available online: https://torroja.dmt.upm.es/congresos/AFMC_Melb2014/Final%20Papers/501.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Ryan, S.; Algie, C.; MacFarlane, G.J.; Fleming, A.N.; Pensis, I.; King, A. The Bombora wave energy converter: A novel multi-purpose device for electricity, coastal protection and surf breaks. In Proceedings of the 2015 Coasts and Ports Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 15–18 September 2015; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/102.100.100/524289 (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Algie, C.; Fleming, A.; Ryan, S. Experimental and numerical modelling of the Bombora wave energy converter. In Proceedings of the 3rd Asian Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, Singapore, 24–28 October 2016; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/102.100.100/523819 (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Algie, C.; Ryan, S.; Fleming, A. Predicted power performance of a submerged membrane pressure-differential wave energy converter. Int. J. Mar. Energy 2017, 20, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thethys—Bombora mWave Demonstration Project. Available online: https://tethys.pnnl.gov/project-sites/bombora-mwave-demonstration-project (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Energy Industry Review—Bombora mWave Solution: World’s Most Powerfull Wave Energy Converter. Available online: https://energyindustryreview.com/renewables/bombora-mwave-solution-worlds-most-powerful-wave-energy-converter/ (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Carrelhas, A.A.D.; Gato, L.M.C.; Falcão, A.F.O.; Henriques, J.C.C. Control law design for the air-turbine-generator set of a fully submerged 1.5 MW mWave prototype. Part 1: Numerical modelling. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 1402–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Global—Bombora Completes Tank Testing of Floating Hybrid Energy Platform. Available online: https://www.energyglobal.com/other-renewables/28042025/bombora-completes-tank-testing-of-floating-hybrid-energy-platform/ (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- TAFLab—Wave Carpet: An Efficient and Multidirectional Ocean Wave Energy Converter. Available online: https://taflab.berkeley.edu/uc-berkeley-ocean-wave-energy-converter (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- University of California News—Seafloor Carpet Catches Waves to Generate Energy. Available online: https://www.universityofcalifornia.edu/news/seafloor-carpet-catches-waves-generate-energy (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Alam, M.R. A Flexible Seafloor Carpet for High-Performance Wave Energy Extraction. In Proceedings of the ASME 31st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Artic Engineering OMAE 2012, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–6 July 2012; Available online: https://taflab.berkeley.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/OMAE2012-84034.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Alam, M.R. Nonlinear analysis of an actuated seafloor-mounted carpet for a high-performance wave energy extraction. Proc. R. Soc. A 2012, 468, 3165–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Elandt, R.; Pham, H.; Ghorbani, R.; Shakeri, M.; Alam, M.-R. An Artificial Seabed Carpet for Multidirectional and Broadband Wave Energy Extraction: Theory and Experiment. In Proceedings of the 10th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (EWTEC 2013), Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2013; Available online: https://taflab.berkeley.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/742-Marcus-Lehmann.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Lehmann, M.; Elandt, R.; Shakeri, M.; Alam, M.-R. The Wave Carpet: Development of a Submerged Pressure Differential Wave Energy Converter. In Proceedings of the 30th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, Hobart, TAS, Australia, 2–7 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Börner, T.; Alam, M.-R. Real time hybrid modeling for ocean wave energy converters. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madassery, N.J. Design and Layout of Power Conversion Chain for a Wave Energy Converter. Master’s Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Petcovic, D.; Zhang, S. TEAMER: CalWave xWave New Technology Qualification and Path to Certification—Final Report. Marine and Hydrokinetic Data Repository 2022. CalWave Power Technologies Inc. Available online: https://mhkdr.openei.org/submissions/470 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Boerner, T.; Kojimoto, N.; Petcovic, D.; Lehmann, M. CalWave WEC Open Water Demonstration—Public Final Test Report. Marine and Hydrokinetic Data Repository 2022. CalWave Power Technologies Inc. Available online: https://mhkdr.openei.org/submissions/500 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Wiley, W.; Tran, T.T.; Boerner, T.; Weston, C.; Wang, L. An efficient three-dimensional CFD-based numerical wave tank for a wave energy converter in extreme irregular waves. In Proceedings of the ASME 42nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering (OMAE 2023), Melbourne, Australia, 11–16 June 2023; NREL Preprint NREL/CP-5700-85391. June 2023. Available online: https://docs.nrel.gov/docs/fy23osti/85391.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- CalWave Successfully Concludes Historic Wave Energy Pilot in California. PR Newswire US 2022. Available online: https://research.ebsco.com/linkprocessor/plink?id=323aeb17-bf2d-3a34-959e-1b1934fa4cfc (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Raghukumar, K. Acoustic characterization around the CalWave wave energy converter. In Proceedings of the European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, Bilbao, Spain, 3–7 September 2023; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Davidson, R. CalWave—xWave Device, Non-Commercially Sensitive Project Report. Marine and Hydrokinetic Data Repository 2024. CalWave Power Technologies Inc. Available online: https://mhkdr.openei.org/submissions/548 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Boerner, T.; Kojimoto, N.; Lehmann, M. CalWave’s xWave Design for PacWave (Final Technical Report). U.S. Department of Energy. June 2024. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/2496672 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- xWaveTM Series. Available online: https://calwave.energy/solutions/xwave/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- News and Views from College of the North Atlantic, Fall 2004, Volume 5, p. 1. College of the North Atlantic, Fall 2004. Available online: https://www.cna.nl.ca/news/newsletters/Fall%202004.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- News and Views from College of the North Atlantic, Fall 2006, Volume 7, p. 1. College of the North Atlantic, Fall 2006. Available online: https://www.cna.nl.ca/news/newsletters/Fall%202006.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- CNA Burin Campus Making Waves in Applied Research. College of the North Atlantic. 25 November 2011. Available online: https://www.cna.nl.ca/news/News-Article?messageid=789 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Boileau, R.; Raman-Nair, W.; Graham, M. Numerical modelling complements physical testing in staged design of ocean wave-driven pump. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2014 Conference, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 14–19 September 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, R. Wave Resource Assessment for Lord’s Cove, Newfoundland: 2012 Survey; National Research Council Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012; 32p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.; Boileau, R. Wave and meteorological site characterization for the Wave Energy Research Centre in Lord’s Cove. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ocean Energy (ICOE 2014), Halifax, NS, Canada, 4–6 November 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiander, L.; Graham, M.; Murray, H.; Boileau, R. Land based multi-trophic aquaculture research at the Wave Energy Research Centre. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2014 Conference, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 14–19 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counter, R. How College of the North Atlantic Converts Waves into Power to Grow Fish on Land. Maclean’s. 22 September 2016. Available online: https://macleans.ca/education/college-of-the-north-atlantic-is-converting-waves-into-power/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Can Wave Energy Power Land-Based Multi-Trophic Aquaculture? Aquaculture North America. 23 December 2016. Available online: https://www.aquaculturenorthamerica.com/can-wave-energy-power-land-based-multi-trophic-aquaculture-1346/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Wijnberg, S.A.; Berkovitz, A. Pumping pre-filtered seawater at any pressure up to 150 bars using zero electricity for use in desalination, aquaculture and coastal industry. In Proceedings of the Ocean Visions 2021 Summit, Online, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 May 2021; p. 86941. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021ocvi.conf86941W (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- WEROP: Impact Free Water—Wave-Powered Pump for RO Pre-filtration. WADER (Water Technologies Demonstration Programme. Available online: https://wader.org.za/werop/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- WRC Knowledge Tree Report: Science for Development (Digital), 2012|2013. Water Research Commission. 2013. Available online: https://www.wrc.org.za/wp-content/uploads/mdocs/WRC_13244%20Report_Knowledge%20Tree%20Digital%20AP1.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- van Tilburg, L. SA Tech Co. Harnessing Cape Waves for Energy—Impact-Free Water. Good Hope (BizNews). 7 October 2023. Available online: https://www.biznews.com/good-hope-project/sa-tech-co-harnessing-cape-waves-energy-impact-free-water (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- WRC Knowledge Review 2012/13. Water Research Commission, 2012/13. Available online: https://www.wrc.org.za/wp-content/uploads/mdocs/WRC%20Knowledge%20Review%202012_13.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Corporate Plan 2018/19–2022/23. Water Research Commission. 2018. Available online: https://www.wrc.org.za/wp-content/uploads/WRC_Corporate-Plan_final.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Wijnberg, S. Development Status 2015. Presentation PDF, Innovation Summit Lab, Water Research Commission. Available online: https://www.wrc.org.za/wp-content/uploads/mdocs/11h45%204%20Wijnberg%20Plenary%20Fri.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- McNatt, J.C.; Özkan-Haller, H.T.; Morrow, M.; Delos-Reyes, M. Preliminary modeling and analysis of a horizontal pressure differential wave energy converter. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2013, 136, 011901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M3 Wave LLC. Available online: https://www.m3wave.com/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Benham, S. ‘Touchdown!’ Oregon Company Deploys 1-of-a-Kind Wave-Energy Device. KCBY (KATU.com). 15 September 2014. Available online: https://kcby.com/news/local/touchdown-oregon-company-deploys-1-of-a-kind-wave-energy-device-11-13-2015 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Morrow, M.; Delos-Reyes, M.; Gillespie, A.; Coe, R.; Chartrand, C.; Wendt, F.; Özkan-Haller, T.; Lomonaco, P.; Yu, Y.-H.; Roberts, J.; et al. M3 Wave DMP/APEX WEC Final Technical Report. Marine and Hydrokinetic Data Repository, 2018. M3 Wave. Available online: https://mhkdr.openei.org/submissions/298 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Lomonaco, P.; Bosma, B.; Reyes, M.; Gillespie, A.; Maddux, T.; Morrow, M.; Özkan-Haller, T. Physical model testing of the scour induced by APEX, a submerged pressure differential wave energy converter. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Renewable Energies Offshore (RENEW 2018), Lisbon, Portugal, 8–10 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Babarit, A.; Wendt, F.; Yu, Y.-H.; Weber, J. Investigation on the energy absorption performance of a fixed-bottom pressure-differential wave energy converter. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2017, 65, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, F.; Yu, Y.; Babarit, A.; Delos-Reyes, M. Numerical analysis and validation of a pressure-differential wave energy converter. In Proceedings of the 4th Asian Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (AWTEC), Taipei, Taiwan, 9–13 September 2018; Available online: https://tethys-engineering.pnnl.gov/sites/default/files/publications/AWTEC2018-427.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Parand, S.; Moghim, M.N.; Boroomand, B. The M3 Pressure-Differential Wave Energy Converter in Persian Shores; Numerical Modeling and Design. SSRN. 2022. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4229974 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Milani, L.; Thorniley, S.; Kurniawan, A.; Wolgamot, H. Modelling and testing of a pressure-differential wave energy converter with flexible membranes. Appl. Ocean Res. 2023, 134, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-H. M3 Wave System Modeling: Cooperative Research and Development Final Report (CRADA Number CRD-17-697); National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2019; NREL/TP-5000-75410. Available online: https://docs.nrel.gov/docs/fy20osti/75410.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Gilboa, S. Methods and Apparatus for Energy Production. U.S. Patent US 2009/0165455 A1, 2 July 2009. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20090165455A1/en (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Kloosterman, K. Riding and Holding the Waves. ISRAEL21c. 6 January [Year Inferred: 2010]. Available online: https://israel21c.org/riding-and-holding-the-waves/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Kloosterman, K. Seanergy Rides and Holds Wave Power. Green Prophet. 6 January 2010. Available online: https://www.greenprophet.com/2010/01/seanergy-waves/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Vantoch-Wood, A.R. Quantifying Methods for an Innovation Systems Analysis of the UK Wave Energy Sector. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK, October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Civil Engineering—University of Coimbra. Available online: https://www.uc.pt/fctuc/dec (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- MARE—Marine and Environmental Sciences Centre. Available online: https://www.mare-centre.pt/en (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Regional OP Centro. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/in-your-country/programmes/2014-2020/pt/2014pt16m2op002_en (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Lopes de Almeida, J.; Mujtaba, B.; Oliveira Fernandes, A. Preliminary laboratorial determination of the reefs novel wave energy converter power output. Renew. Energy 2018, 122, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes de Almeida, J.; Abrantes, J.; Bento, J. A simplified model for expedient computational assessment of the novel reefs wave energy converter power output. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, J.L.; Santos Martinho, M. Experimental evaluation of the shore protection potential of the novel reefs wave energy converter. Ocean Eng. 2020, 217, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.; Lopes de Almeida, J.; Santiago, A.; Rigueiro, C. Development of a cfd-based numerical wave tank of a novel multipurpose wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2022, 199, 226–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Lily—River Power. Available online: https://get.waterlilyturbine.com/paddling-charger/ (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- UC Business—REEFS: Renewable Electric Energy from Sea. Available online: https://www.uc.pt/ucbusiness/reefs-renewable-electric-energy-from-sea/ (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- NEXUS—Digital Sustainable Logistics. Available online: https://nexuslab.pt/ (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Dean, R.G.; Dalrymple, R.A. Water Wave Mechanics for Engineers and Scientists; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Miquel, A.M.; Kamath, A.; Alagan Chella, M.; Archetti, R.; Bihs, H. Analysis of Different Methods for Wave Generation and Absorption in a CFD-Based Numerical Wave Tank. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihs, H.; Kamath, A.; Alagan Chella, M.; Aggarwal, A.; Arnstsen, Ø.A. A new level set numerical wave tank with improved density interpolation for complex wave hydrodynamics. Comput. Fluids 2016, 140, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.; Vitola, M.A.; Pinto, W.T.P.; Levi, C.A. Numerical Simulation of monochromatic wave generated in laboratory: Validation of a CFD code. In Proceedings of the 23th Congresso Nacional de Transporte Aquaviário, Construção Naval e Offshore, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 25–29 October 2010; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes de Almeida, J.; Machado, V.G.; Santiago, A.; Silva, J.S.; Araújo, J.P. Can Ports Serve as Testbeds for New Wave Energy Converters? A Methodology Applied to Port of Sines considering REEFS WEC. Ocean Eng. 2025. submitted. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes de Almeida, J.P.P.G.; Machado, V.G. Addressing Development Challenges of the Emerging REEFS Wave Energy Converter. Inventions 2025, 10, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10050085
Lopes de Almeida JPPG, Machado VG. Addressing Development Challenges of the Emerging REEFS Wave Energy Converter. Inventions. 2025; 10(5):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10050085
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes de Almeida, José P. P. G., and Vinícius G. Machado. 2025. "Addressing Development Challenges of the Emerging REEFS Wave Energy Converter" Inventions 10, no. 5: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10050085
APA StyleLopes de Almeida, J. P. P. G., & Machado, V. G. (2025). Addressing Development Challenges of the Emerging REEFS Wave Energy Converter. Inventions, 10(5), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10050085





