Abstract
Calorimetric experiments in space of the current and of the next generation measure cosmic rays directly above TeV on satellites in low Earth orbit. A common issue of these detectors is the determination of the absolute energy scale for hadronic showers above TeV. In this work, we propose the use of the Moon–Earth spectrometer technique for the calibration of calorimeters in space. In brief, the presence of the Moon creates a detectable lack of particles in the detected cosmic ray arrival directions. The position of this depletion has an offset with respect to the Moon center due to the deflection effect of the geomagnetic field on the cosmic rays that depends on the energy and the charge of the particle. The developed simulation will explore if, with enough statistics, angular, and energy resolutions, this effect can be exploited for the energy scale calibration of calorimeters on satellites in orbit in Earth’s proximity.
1. Introduction
Cosmic rays (CRs) are energetic particles and nuclei coming from outer space from all directions with an approximately isotropic flux. The Moon, with an average diameter observed from Earth of about 0.52°, causes a directional depletion in the observed CR flux observed from Earth’s vicinity. The shape and magnitude of the deficit observed in CRs provide a measure of the pointing accuracy and angular resolution of the device used to measure it. This methodology was proposed originally by Clark [1] and has been used since in experiments measuring the extensive air showers (EAS) produced by high-energy CRs interacting in the atmosphere: CYGNUS [2], Tibet-AS [3], CASA [4], HEGRA [5], Tibet-III [6], ARGO-YBJ [7], HAWC [8], LHAASO [9], and GRAPES-3 [10,11]. Underground experiments such as MACRO [12], SOUDAN-2 [13], L3+C [14], MINOS [15], IceCube [16], and ANTARES [17] have also employed the Moon’s shadow observed in high-energy muons coming from EAS for determining the detector’s angular resolution.
With enough angular resolution and statistics, the Moon’s shadow displacement in CRs due to the deflection in the geomagnetic field can be measured. Observations of the Moon’s shadow can be used for momentum and charge-based separation of CRs, as originally proposed by Urban, et al. [18], as sketched in Figure 1. By observing the Moon’s shadow as MACRO [19], L3+C [14], Tibet-III [6], ARGO-YBJ [7], and HAWC [8], the authors estimated upper limits on the ratio in CRs. The Moon’s shadow deflection dependence from energy has also been used by EAS experiments to estimate the absolute energy scale, such as in ARGO-YBJ [20] and LHAASO [9].
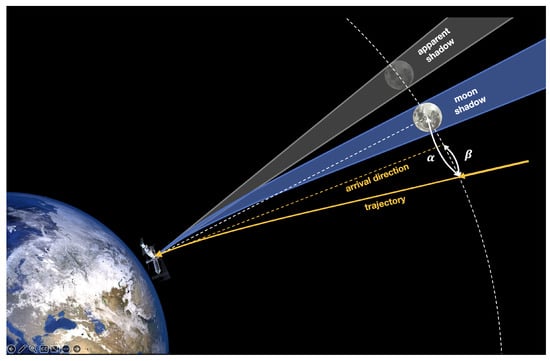
Figure 1.
The Moon causes a depletion on the CR flux observed from Earth’s vicinity. Furthermore, the charged CRs are bent by the geomagnetic field, causing an apparent position displacement of the Moon, as observed in the CR arrival direction at the satellite location. In the figure are defined two angles used in this work: the angle , i.e., the angular separation between the particle and the Moon before entering Earth’s magnetosphere, is derived from the scalar product of the position vector of the Moon and the position vector of the particle as observed at the entrance of the sphere defined by the Moon–Earth distance; and the angle , i.e., the magnetic deflection accumulated by the particle traveling in the geomagnetic field from Moon distance to Earth vicinity, is derived from the scalar product of the particle direction at the satellite location and its position vector observed at the entrance of the sphere defined by the Moon–Earth distance. The angles and do not necessarily lie on the same plane.
Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope (IACT) experiments are able to distinguish EAS induced by -rays and electrons and hadronic showers with good accuracy. This separation has been used by IACTs such as ARTEMIS [21], MAGIC [22], and VERITAS [23] that were able to derive upper limits on the and on the positron fraction in CRs at TeV.
The CR Moon’s shadow has usually been employed in experiments measuring CRs above TeV with indirect techniques. Nowadays, direct measurement of CRs from space is reaching TeV energies thanks to large geometric factors, long exposure times, and extended energy ranges. Examples of current and future CR direct measurement experiments in space are AMS-02 [24], CALET [25], DAMPE [26], HERD [27], AMS-100 [28], and ALADInO [29]. In many cases, these experiments are based on a calorimetric approach, in which the energy of the particle is evaluated by absorbing it in thick calorimeters. The measurement of energy within calorimeters, especially for hadronic particles, requires careful calibration of the energy scale [30]. Several techniques have been employed by space-born calorimeters in space. A non-complete list includes:
- Particle Beams: the energy scale can be measured directly by studying the calorimeter response to particle beams of known energy. This calibration is limited by the maximum energy achievable for particle beams, currently set at most at a few hundred GeV [31].
- Geomagnetic Cutoff: in Earth’s magnetosphere, trajectories of particles with rigidity below a given geomagnetic cutoff are forbidden. The geomagnetic cutoff depends on satellite location and particle direction and can be calculated by tracing particles in the geomagnetic field. However, the use of this effect to calibrate the energy scale is limited by the maximum geomagnetic cutoff achievable in space, of the order of tens of GeV [32].
- Cross-calibration: including in the experiment design other devices able to measure particle momentum would allow for energy scale cross-calibration. Some possible solutions may include a magnetic spectrometer or a transition radiation detector [27,28,29]. This solution usually involves a higher degree of design complexity, often not viable for experiments in space.
In this work, we will determine whether a space-born detector with an adequate angular resolution and enough energy resolution would be able to observe the CR Moon’s shadow and use it to evaluate the energy scale for protons in calorimeters in the multi-TeV region.
In Section 2, the simulation of realistic CR particles bent by the geomagnetic field and detected by a realistic device is discussed. In Section 3, the effect of the Moon’s shadow on the observed angular distribution is characterized using a high-statistics simulation. In Section 4, the log-likelihood method used to estimate the energy scale is discussed and applied to a simulated 5-year data-taking period, followed by a discussion in Section 5.
2. Simulation
For the sake of a realistic case, we consider a detector in orbit similar to the high-energy cosmic radiation detection (HERD) facility [27]. HERD is a large-field-of-view, high-energy cosmic ray experiment planned to be installed on the China Space Station (CSS) in 2027. The HERD mission is based on a novel design of a highly segmented, homogeneous LYSO calorimeter of 55 X0 (CALO). The CALO segmentation in 3 cm side LYSO cubes allows for the reconstruction of 3D showers from all incoming directions. The large thickness of the CALO will allow for measuring the energy of CRs up to 1 PeV. The CALO is complemented by a series of detectors for particle identification installed on five sides (top and four sides), enclosing it in a box. Its outermost detector, the Silicon Charge Detector, can identify the absolute charge of the entering cosmic ray, separating precisely all cosmic ray chemical species [33]. Globally, the experiment will have a field of view covering almost an entire hemisphere with a geometric factor approaching 1 m2sr for protons [34].
Let us then assume for the following a test detector located on the CSS orbit, taking data in a at least a 5-year mission, measuring particles arriving from the full hemisphere tangent to the orbit, with an acceptance of 1 m2sr, an energy resolution of about 30%, and an angular resolution of 0.1° [25,26,27].
To study the CR Moon’s shadow observed from this test device, a realistic simulation has been constructed. The orbit of the CSS around Earth has been simulated using the Two-Line Elements of the CSS orbit in the last two years (Predict: https://www.qsl.net/kd2bd/predict.html accessed 30 March 2020, and CelesTrack: https://celestrak.org/ accessed 22 September 2022). The Moon orbit is simulated using analytic calculations [35].
For every second of real elapsed time, protons of different energies were generated at the detector location on the CSS orbit isotropically inside the detector’s full field of view. Each proton has been back-propagated, inverting the sign of its electric charge and arrival direction, effectively simulating a particle moving backward in time in Earth’s magnetic field up to the Earth–Moon distance. Back-traced protons falling into Earth or the Moon are then removed. This procedure effectively simulates a flux of particles incident to our detector isotropically generated at the Moon distance, including the depletion caused by the CR Moon’s shadow.
The tracing is realized by solving the relativistic Lorentz equation of motion for a particle with mass m and charge q in a constant magnetic field :
where . Solver is based on a classic Runge–Kutta method [36] with adaptive control of the time step size. During tracing, crossings of Earth or of the Moon are checked with linear interpolation between the steps. The employed magnetic field is the latest International Geomagnetic Reference Field (IGRF-13) [37] that describes the main component of the geomagnetic field caused by sources primarily inside Earth. The IGRF is a set of spherical harmonic coefficients that are used in a mathematical model that represents an accurate description of the geomagnetic field based on current and historical data. A slow secular time variation is present in IGRF, but this variation is completely negligible in the time scale of the particle tracing. The back-tracing code has already been validated by comparison with available online tools such as SPENVIS (https://www.spenvis.oma.be/ accessed 8 March 2022) and has been successfully employed in other applications [38].
The deflection angle , defined in Figure 1 as a function of energy for the developed simulation, is displayed in Figure 2. The average deflection has been fitted as a function of , following the expected behavior at the first order [39]. Long tails of the distribution towards low values of the deflection angle correspond to the polar passages and can be removed by requiring equatorial passages of the CSS within latitudes of .
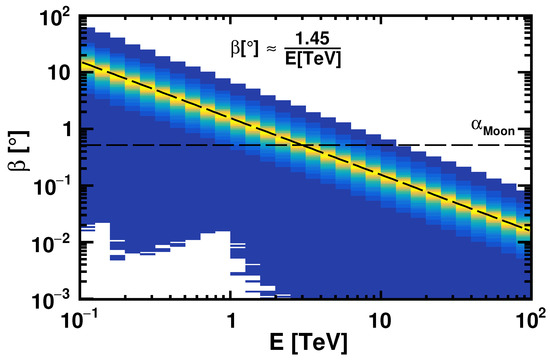
Figure 2.
The deflection angle as a function of the proton energy for the simulated satellite orbit. The average deflection is inversely proportional to the energy. In particular, at about 3 TeV, the deflection is similar to the Moon’s apparent size. The asymmetric tails towards small values of deflection are due to satellite polar passages.
For each proton not shadowed by the Moon, a measured arrival direction and energy are generated to simulate the particle as measured by our test detector. The arrival direction is extracted around the true arrival direction with a Gaussian smearing of 0.1°, while energy is extracted with a Gaussian smearing of . The “measured particle” is back-propagated using the same procedure described above for the “true particle”, and the measured deflection angle and the measured angular distance to the Moon are also determined and used for the analysis. With this approach, the effect of uncertainties in the calorimeter angular and energy resolutions are propagated to the angles of interest of this analysis.
3. Analysis
To study the Moon’s shadow, the angle between the particle to the Moon after deflection subtraction has been used. With a perfect angular and energy resolution, the distribution of z should follow a Heaviside function with a step at the Moon’s angular radius . Instead, the observed distribution of the measured angle is more similar to a sigmoid due to the combined effect of angular and energy resolutions.
To obtain the distribution of as a function of energy, a simulation in 30 energy range bins from 100 GeV to 100 TeV has been carried out, with approximately 8 billion protons generated for each energy bin. All particles have been back-propagated successfully to the Moon–Earth distance. The events have been weighted with a weighing factor dependent on the true energy E to reproduce the CR proton energy spectrum following the parameterization developed in [40] using the latest CR measurements. With this high-statistics sample, it is possible to observe the distribution for each i-th measured energy interval . These distributions have been parametrized following an effective model provided via the convolution of a box distribution, representing the Moon’s shadow, and a Gaussian, representing the effective angular resolution:
the parameter is expected to be roughly independent of energy, with the value of ; however, to allow an effective better fitting, this parameter has been left free. The results of the fitting procedure are exemplified at the top of Figure 3 in three energy bins. A good fit with has been obtained in every energy bin. The model based on Equation (2) with the regularized parameters as a function of energy is shown at the bottom of Figure 3.
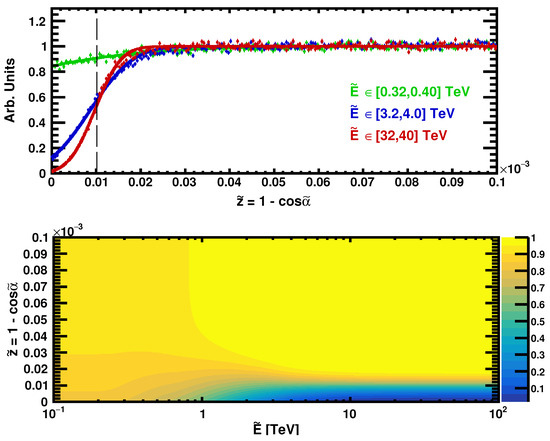
Figure 3.
On the top, the distribution of for three energy bins: 0.32–0.40 TeV in green, 3.2–4.0 TeV in blue, 32–40 TeV in red, as obtained from the simulation. Three fits, with the effective model of Equation (2), are superimposed. The fits have of 1.07, 1.31, and 1.58, respectively. On the bottom is displayed the overall model that was obtained from the regularization of the parameters of the bin-by-bin fit as a function of energy.
The behavior of the distributions in Figure 3 can be understood by noticing that the resolution is the sum of the angular resolution plus the effect of the energy resolution that smears the deflection angle determination. In particular, above 10 TeV, the Moon’s shadow becomes more defined and energy-independent since, in this range, the deflection is negligible with respect to the angular resolution. At low energies, the deflection becomes large up to tens of degrees, and the uncertainty regarding the energy causes a large angular uncertainty for the evaluation of the deflection; this causes a flattening of the distribution. In these two extreme cases, the dependency on energy is weak, but, around TeV, the distribution changes rapidly as a function of the energy. In this region, we should globally have some sensitivity to the energy scale from the observed .
To understand how behaves as a function of a possible energy bias k, the parametrization procedure has been repeated, introducing in the simulation different biases on the energy scale in a range between 0.7 and 1.3. The estimated distributions of for each bias k are then studied employing the functional form provided in Equation (2), and the obtained fits are qualitatively similar to the ones of Figure 3. For each energy bin i, the and obtained for each different scale factor k are regularized as a function of k, obtaining the functions and . Eventually, the distribution of as a function of k in each measured energy bin, , is obtained.
4. Results
To understand the detection of the Moon’s shadow with our test device, a realistic simulation of 5-year data acquisition has been developed following the recipe described in Section 2. Globally, 400 million protons have been generated between 100 GeV and 100 TeV following the energy spectrum described in Ref. [40]. For each i-th reconstructed energy bin and j-th bin, the observed number of events is . The expected number of events that can be constructed from the Moon’s shadow parameterization described in Section 3 is provided in
The top picture of Figure 4 shows an example of the observed number of events and the expected ones for different values of the energy scale parameter k in a single energy bin between 1.00 and 1.26 TeV.
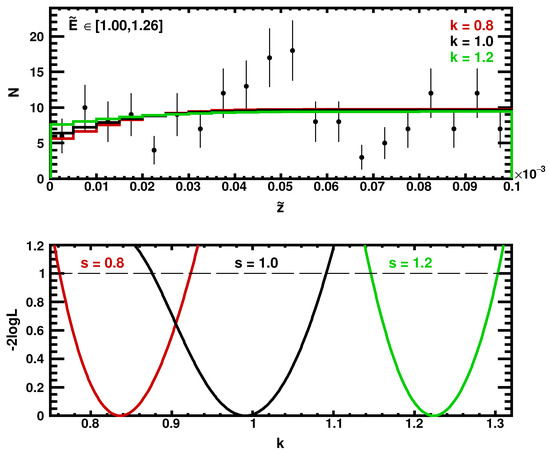
Figure 4.
In the figure on the top is displayed the number of observed counts in the energy bin between 1 and 1.26 TeV compared with the expected number of counts derived for 3 values of energy scale bias, 0.8 (red), 1 (black), and 1.2 (green). On the bottom is presented the likelihood as a function of the energy scale k. In black is presented the dependency from k when no energy scale offset has been applied to the observed measurements, while in green and red are presented the likelihood dependencies in the case of two applied shifts of 0.8 and 1.2.
It is possible to create a global likelihood to measure the discrepancy between the observed number of events and the expected ones at all energies:
this negative log-likelihood can be minimized to derive the best energy scale factor .
At the bottom of Figure 4 is presented the dependence of the log-likelihood as a function of the energy scale k. The distribution leads to the result . The use of a 5-year dataset allows us to measure the energy scale with the Moon’s shadow with 10% accuracy, which is also the minimum detectable scale mis-calibration.
To check for possible systematic effects, several tests have been performed:
- Parameterization: possible biases due to parametrization of have been checked by applying the minimization procedure on the same samples used to create the parametrization. Given the large statistics employed, the likelihood is conveniently approximated by . For any employed sample, the estimated from the minimization is in agreement with k within a percent.
- Energy Scale: the log-likelihood procedure has been tested with the 5-year synthetic data introducing different energy shifts s from 0.8 to 1.2, and applying to those samples the same minimization procedure described above. The result is exemplified in Figure 4, where the likelihood profile enables estimating for two samples with and . The corresponding estimated values are, respectively, and , in agreement with the imposed energy scale offsets.
- Spectral Shape: to check for a possible systematic effect due to the cosmic ray proton spectrum knowledge, data used to create the Moon’s shadow parametrization have been weighted using a simple power law with index −2.7. The resulting likelihood function has been used to test the synthetic 5-year sample used before and generated following Lipari’s double-break spectral shape. The scale factor has been measured being , with no sizeable impact coming from the different weighting.
5. Discussion
The CR Moon’s shadow position and shape depend on the cosmic ray charge, energy, and arrival direction and on the position of the measuring device, as well as on its angular and energetic resolution. In the case of our test device, the energy dependence of the Moon shadow can be used to measure the energy scale at the TeV scale. At higher energies, the effect is washed out since deflection becomes negligible with respect to angular resolution and the statistics become small. At low energy, the Moon’s shadow becomes too shallow because of the energy resolution effect. In our simulation, the effect has been demonstrated to be sizeable and provided a positive result.
As stated in the introduction, while there is ample literature about the CR Moon’s shadow use for pointing accuracy estimation and for matter-to-anti-matter distinction in indirect CR measurements [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,13,14,15,16,17,19,21,22,23], there is very little literature about the use of it for the energy scale determination or about the observation of the CR Moon’s shadow with CR direct measurement experiments. This is because EAS experiments often study energies so high that there is no significant deflection to be exploited for our purposes, and, conversely, the direct CR measurement experiments study energies that are so low that the uncertainties in the Moon’s position reconstruction dominate. Therefore, in this regard, this publication is exploring new possibilities that have been unveiled with the proposal of a new generation of CR direct measuring devices [27,28,29], with very ambitious goals in terms of energy reach and statistics collected.
We must remark that the results obtained are under the hypothesis of perfect knowledge of angular and energy resolution. In a more realistic case, those quantities may not be known. Deviations in the understanding of resolutions may cause biases in the energy scale evaluation. Various possibilities to understand the energy scale dependency from the resolution can be explored in future work: (a) studying the angular resolution using high-energy samples; (b) introducing the dependencies from variable angular and energy resolutions in the parameterization of the likelihood.
Another possible extension of the work may result from a better description of Earth’s magnetic field. As discussed in Section 2, the employed IGRF-13 model describes what is known as the internal magnetic field of Earth. A weaker component, known as the external field, is produced by electrical currents in the ionosphere and can be dependent on solar activity that can have rapid variations in time. The external component is not included in our calculation since it significantly increases the computation time needed to perform the simulation. We expect a minor impact from this additional field on the deflection angle; however, in the case of application to real data, the external field should be included.
We remark that this work can be extended significantly by also employing the CR Sun’s shadow. The Sun has roughly the same radial diameter of the Moon as observed from Earth’s vicinity. The use of the Sun should approximately double the statistics available for the energy scale determination. However, a model of the interplanetary magnetic field between Earth and the Sun should be included and the computation investigated in more detail.
Eventually including other cosmic ray species in the study of the Moon’s shadow is also of interest. Helium nuclei are quite abundant and exhibit much larger deflection than protons. The use of electrons instead could enable the study of the electromagnetic energy scale.
Other interesting extensions of this work may include the study of the energy scale time variation or its dependency on energy using restricted samples in time and energy. However, statistics is a main concern for those analyses, and only large energy scale variations with respect to the average can be detected.
6. Conclusions
The CR Moon’s shadow has been employed to study the pointing accuracy, angular resolution, and derive antiproton-to-proton limits in CRs with ground and underground detectors measuring CRs indirectly. In this work, a simulation of a next-generation CR detector in low Earth orbit, similar to the wide-field-of-view calorimetric mission HERD, has been made to look for the Moon’s shadow in CR directly from space. HERD is a large-field-of-view calorimeter whose purpose is to measure CR directly up to the knee. It has been estimated that, with a 5-year mission, it will be possible to observe the Moon’s shadow in CRs with a HERD-like instrument and establish the energy scale for protons at the TeV scale at a 10% level. In general, this result demonstrates the feasibility of using the CR Moon’s shadow for calibrating the proton absolute energy scale at the TeV scale for calorimetric space missions measuring CRs directly.
Funding
This research was funded under INFN and ASI under ASI-INFN agreements No. 2019-19-HH.0, its amendments, and No. 2021-43-HH.0.
Data Availability Statement
This work is based on the use of the publicly available resources for the calculation of the satellite coordinates (Predict: https://www.qsl.net/kd2bd/predict.html accessed 30 March 2020, and CelesTrack: https://celestrak.org/ accessed 22 September 2022) as for the geomagnetic field calculation (https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/IAGA/vmod/igrf.html accessed 4 August 2021). The overall simulation and analysis have been developed in C++ employing the Boost library (http://www.boost.org, version 1.82, accessed 1 August 2023) and the ROOT package (https://root.cern.ch/, version 6.28, accessed 1 August 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used extensively in this manuscript:
| ASI | Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (Italian Space Agency) |
| CALO | HERD calorimeter |
| CR | Cosmic ray |
| CSS | Chinese Space Station |
| EAS | Extensive air showers |
| HERD | High-energy cosmic radiation detection |
| IACT | Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope |
| IGRF | International Geomagnetic Reference Field |
| INFN | Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (Italian National Institute of Nuclear Physics) |
References
- Clark, G.W. Arrival Directions of Cosmic-Ray Air Showers from the Northern Sky. Phys. Rev. 1957, 108, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandreas, D.E.; Allen, R.C.; Berley, D.; Biller, S.D.; Burman, R.L.; Cady, D.R.; Chang, C.Y.; Dingus, B.L.; Dion, G.M.; Ellsworth, R.W.; et al. Observation of shadowing of ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays by the Moon and the Sun. Phys. Rev. D 1991, 43, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenomori, M.; Cao, Z.; Ding, L.K.; Feng, Z.Y.; Hibino, K.; Hotta, N.; Huang, Q.; Huo, A.X.; Jia, H.Y.; Jiang, G.Z.; et al. Cosmic-ray deficit from the directions of the Moon and the Sun detected with the Tibet air-shower array. Phys. Rev. D 1993, 47, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borione, A.; Catanese, M.; Covault, C.E.; Cronin, J.W.; Fick, B.E.; Gibbs, K.G.; Green, K.D.; Hauptfeld, S.; Kieda, D.; Krimm, H.A.; et al. Observation of the shadows of the Moon and Sun using 100 TeV cosmic rays. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 49, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck, M.; Karle, A.; Martinez, S.; Arqueros, F.; Becker, K.H.; Bott-Bodenhausen, M.; Eckmann, R.; Faleiro, E.; Fernandez, J.; Fernandez, P.; et al. Methods to determine the angular resolution of the HEGRA extended air shower scintillator array. Astrop. Phys. 1996, 5, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenomori, M.; Ayabe, S.; Bi, X.J.; Chen, D.; Cui, S.W.; Ding, L.K.; Ding, X.H.; Feng, C.F.; Feng, Z.; Feng, Z.Y.; et al. Moon shadow by cosmic rays under the influence of geomagnetic field and search for antiprotons at multi-TeV energies. Astrop. Phys. 2007, 28, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, B.; Bernardini, P.; Bi, X.J.; Bleve, C.; Bolognino, I.; Branchini, P.; Budano, A.; Melcarne, A.K.C.; Camarri, P.; Cao, Z.; et al. Measurement of the cosmic ray antiproton/proton flux ratio at TeV energies with the ARGO-YBJ detector. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekara, A.U.; Albert, A.; Alfaro, R.; Alvarez, C.; Álvarez, J.D.; Arceo, R.; Arteaga-Velázquez, J.C.; Rojas, D.A.; Solares, H.A.A.; Belmont-Moreno, E.; et al. Constraining the ratio in TeV cosmic rays with observations of the Moon shadow by HAWC. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; An, Q.; Axikegu; Bai, L.X.; Bai, Y.X.; Bao, Y.W.; Bastieri, D.; Bi, X.J.; Bi, Y.J.; Cai, H.; et al. Calibration of the air shower energy scale of the water and air Cherenkov techniques in the LHAASO experiment. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 104, 062007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, A.; Dugad, S.R.; Goswami, U.D.; Gupta, S.K.; Hayashi, Y.; Ito, N.; Iyer, A.; Jagadeesan, P.; Jain, A.; Kawakami, S.; et al. The angular resolution of the GRAPES-3 array from the shadows of the Moon and the Sun. Astrop. Phys. 2010, 33, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, D.; Ahmad, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Dugad, S.R.; Goswami, U.D.; Gupta, S.K.; Hariharan, B.; Hayashi, Y.; Jagadeesan, P.; Jain, A.; et al. Validating the improved angular resolution of the GRAPES-3 air shower array by observing the Moon shadow in cosmic rays. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 022009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, M.; Antolini, R.; Aramo, C.; Auriemma, G.; Baldini, A.; Barbarino, G.C.; Barish, B.C.; Battistoni, G.; Bellotti, R.; Bemporad, C.; et al. Observation of the shadowing of cosmic rays by the Moon using a deep underground detector. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 59, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, J.H.; Marshak, M.L.; Allison, W.W.M.; Alner, G.J.; Ayres, D.S.; Barrett, W.L.; Bode, C.; Border, P.M.; Brooks, C.B.; Cotton, R.J.; et al. Observation of a shadow of the Moon in the underground muon flux in the Soudan 2 detector. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 61, 092002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achard, P.; Adriani, O.; Aguilar-Benitez, M.; Akker, M.v.; Alcaraz, J.; Alemanni, G.; Allaby, J.; Aloisio, A.; Alviggi, M.G.; Anderhub, H.; et al. Measurement of the shadowing of high-energy cosmic rays by the Moon: A search for TeV-energy antiprotons. Astrop. Phys. 2005, 23, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, P.; Andreopoulos, C.; Ayres, D.S.; Backhouse, C.; Barr, G.; Barrett, W.L.; Bishai, M.; Blake, A.; Bock, B.; Bock, G.J.; et al. Observation in the MINOS far detector of the shadowing of cosmic rays by the sun and moon. Astrop. Phys. 2011, 34, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Abbasi, R.; Abdou, Y.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Altmann, D.; Auffenberg, J.; Bai, X.; et al. Observation of the cosmic-ray shadow of the Moon with IceCube. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.; André, M.; Anghinolfi, M.; Anton, G.; Ardid, M.; Aubert, J.-J.; Aublin, J.; Avgitas, T.; Baret, B.; Barrios-Martít, J.; et al. The cosmic ray shadow of the Moon observed with the ANTARES neutrino telescope. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, M.; Fleury, P.; Lestienne, R.; Plouin, F. Can we detect antimatter from other galaxies by the use of the Earth’s magnetic field and the Moon as an absorber? Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) 1990, 14B, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, M.; Antolini, R.; Baldini, A.; Barbarino, G.C.; Barish, B.C.; Battistoni, G.; Becherini, Y.; Bellotti, R.; Bemporad, C.; Bernardini, P.; et al. Moon and Sun shadowing effect in the MACRO detector. Astrop. Phys. 2003, 20, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, B.; Bernardini, P.; Bi, X.J.; Bleve, C.; Bolognino, I.; Branchini, P.; Budano, A.; Melcarne, A.K.C.; Camarri, P.; Cao, Z.; et al. Observation of the cosmic ray moon shadowing effect with the ARGO-YBJ experiment. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomarède, D.; Boyle, P.J.; Urban, M.; Badran, H.M.; Behr, L.; Brunetti, M.T.; Fegan, D.J.; Weekes, T.C. Search for shadowing of primary cosmic radiation by the moon at TeV energies. Astrop. Phys. 2001, 14, 287–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, P.; Tridon, D.B.; Ortega, A.D.; Doert, M.; Doro, M.; Pochon, J.; Strah, N.; Suric, T.; Teshima, M. Probing the CR positron/electron ratio at few hundreds GeV through Moon shadow observation with the MAGIC telescopes. arXiv Prepr. 2011, arXiv:1110.0183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R. Observing the Cosmic Ray Moon Shadow with VERITAS. arXiv Prepr. 2015, arXiv:1508.07197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Cavasonza, L.A.; Ambrosi, G.; Arruda, L.; Attig, N.; Barao, F.; Barrin, L.; Bartoloni, A.; Pree, S.B.; Bates, J.; et al. The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) on the international space station: Part II—Results from the first seven years. Phys. Rep. 2021, 894, 1–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, S. Highlights from the CALET observations for 7.5 years on the International Space Station. In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemanno, F.; Altomare, C.; An, Q.; Azzarello, P.; Barbato, F.C.T.; Bernardini, P.; Bi, X.J.; Cagnoli, I.; Cai, M.S.; Casilli, E.; et al. DArk Matter Particle Explorer: 7 years in Space. In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; p. 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, F. The High Energy cosmic-Radiation Detection (HERD) facility on board the Chinese Space Station: Hunting for high-energy cosmic rays. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Berlin, Germany, 15–22 July 2021; p. 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schael, S.; Atanasyan, A.; Berdugo, J.; Bretz, T.; Czupalla, M.; Dachwald, B.; von Doetinchem, P.; Duranti, M.; Gast, H.; Karpinski, W.; et al. AMS-100: The next generation magnetic spectrometer in space—An international science platform for physics and astrophysics at Lagrange point 2. Nucl. Inst. Meth. Phys. Res. A 2019, 944, 162561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriani, O.; Altomare, C.; Ambrosi, G.; Azzarello, P.; Barbato, F.C.T.; Battiston, R.; Baudouy, B.; Bergmann, B.; Berti, E.; Bertucci, B.; et al. Design of an Antimatter Large Acceptance Detector In Orbit (ALADInO). Instruments 2022, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, Y.; Akaike, Y.; Komiya, Y.; Miyata, R.; Torii, S.; Adriani, O.; Asano, K.; Bagliesi, M.G.; Bigongiari, G.; Binns, W.R.; et al. Energy calibration of CALET onboard the International Space Station. Astrop. Phys. 2017, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, P.; Kobayashi, K. Measurement of the energy spectrum of cosmic-ray helium with CALET on the International Space Station. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 130, 171002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Yue, C.; Li, X. Measurement of absolute energy scale of ECAL of DAMPE with geomagnetic rigidity cutoff. In Proceedings of the 35th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Busan, Republic of Korea, 12–20 July 2017; p. 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Altomare, C.; Ambrosi, G.; Barbanera, M.; Bertucci, B.; Cui, Y.X.; Duranti, M.; Formato, V.; Gong, K.; Graziani, M.; et al. The Silicon Charge Detector of the High Energy Cosmic Radiation Detection facility. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Berlin, Germany, 15–22 July 2021; p. 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, L.; Adriani, O.; Bai, Y.L.; Bao, T.W.; Berti, E.; Bottai, S.; Cao, W.W.; Casaus, J.; Cui, X.Z.; D’Alessandro, R.; et al. Design and expected performances of the large acceptance calorimeter for the HERD space mission. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Berlin, Germany, 15–22 July 2021; p. 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeus, J.H. Astronomical Algorithms, 2nd ed.; Willmann-Bell Inc.: Richmond, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fehlberg, E. New High-Order Runge-Kutta Formulas with Step Size Control for Systems of First-and Second-Order Differential Equations. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1964, 44, T17–T19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alken, P.; Thébault, E.; Beggan, C.D.; Amit, H.; Aubert, J.; Baerenzung, J.; Bondar, T.N.; Brown, W.J.; Califf, S.; Chambodut, A.; et al. International Geomagnetic Reference Field: The thirteenth generation. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, M.; Giovacchini, F.; Oliva, A. Observation of Z > 2 trapped nuclei by AMS on ISS. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Berlin, Germany, 15–22 July 2021; p. 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascio, G.D.; Iuppa, R. Simulation of the cosmic ray Moon shadow in the geomagnetic field. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 2011, 630, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipari, P.; Vernetto, S. The shape of the cosmic ray proton spectrum. Astrop. Phys. 2020, 120, 102441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).