Cyclotron Production of Unconventional Radionuclides for PET Imaging: the Example of Titanium-45 and Its Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction: Unconventional Radionuclides for PET Imaging
2. Cyclotrons and the Production of Unconventional Radionuclides
3. Titanium-45 and Its Applications
4. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acharya, R.; Wasserman, R.; Stevens, J.; Hinojosa, C. Biomedical imaging modalities: A tutorial. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 1995, 19, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, S.R. Multimodality in vivo imaging systems: Twice the power or double the trouble? Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Technical Report Series No 492; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1972; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nuclear Medicine and Radiopharmaceuticals Market 2012–2017. Available online: https://healthmanagement.org/c/imaging/news/nuclear-medicine-and-radiopharmaceuticals-market-2012-2017 (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Saha, G.B. Diagnostic Uses of Radiopharmaceuticals in Nuclear Medicine. In Fundamentals of Nuclear Pharmacy; Saha, G.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, G.B. Cyclotron and Production of PET Radionuclides. In Basics of PET Imaging: Physics, Chemistry and Regulations; Saha, G.B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 257–339. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, M.; Eriksson, L. Physics of pure and non-pure positron emitters for PET: A review and a discussion. EJNMMI Phys. 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilian, A.R. The Application of Unconventional PET Tracers in Nuclear Medicine. Iran. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, M.J.; Laforest, R.; Lewis, J.S. Production of Non-Standard PET Radionuclides and Application of Radiopharmaceuticals Labeled with these Nuclides. In PET Chemistry: The Driving Force in Molecular Imaging Series; Schubiger, P.A., Lehmann, L., Friebe, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Arasaratnam, P.; Sadreddini1, M.; Yam, Y.; Kansal, V.; Dorbala, S.; di Carli, M.F.; Beanlands, R.S.; Merhige, M.E.; Williams, B.A.; Veledar, E.; et al. Prognostic value of vasodilator response using rubidium-82 positron emission tomography myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Toschi, L.; Castello, A.; Grizzi, F.; Mansi, L.; Lopci, E. Clinical characteristics of patient selection and imaging predictors of outcome in solid tumors treated with checkpoint-inhibitors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 2310–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, C.G.; Jiang, D.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Rekoske, B.T.; Ellison, P.A.; Hernandez, R.; Barnhart, T.E.; McNeel, D.G.; Huang, P.; Cai, W. 89Zr-labeled nivolumab for imaging of T-cell infiltration in a humanized murine model of lung cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.Y.F.; Ekström, L.P.; Firestone, R.B. WWW Table of Radioactive Isotopes, database version 1999-02-28. Available online: http://nucleardata.nuclear.lu.se/nucleardata/toi/ (accessed on 23 April 2018).
- Carrol, V.; Demoin, D.W.; Hoffman, T.J.; Jurisson, S.S. Inorganic chemistry in nuclear imaging and radiotherapy: Current and future directions. Radiochim. Acta 2012, 100, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, G.B. Production of Radionuclides, 6th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Directory of Cyclotrons used for Radionuclide Production in Member States—2006 Update; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Technical Report Series No465—Cyclotron Produced Radionuclides: Principles and Practice; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Papash, A.I.; Alenitskii, Y.G. Commercial Cyclotrons. Part I: Commercial Cyclotrons in the Energy Range 10–30 MeV for Isotope Production. Phys. Part. Nucl. 2008, 39, 597–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaim, S.M. Nuclear data relevant to the production and application of diagnostic radionuclides. Radiochim. Acta 2001, 89, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M. Particle accelerators for PET radionuclides. Nucl. Med. Rev. 2012, 15, C9–C12. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.; Williamson, M.; Lewis, J. Unconventional Nuclides for Radiopharmaceuticals. Mol. Imaging 2010, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Enferadi, M.; Aref, M.; Jafari, H. Nuclear data for the cyclotron production of 66Ga, 86Y, 76Br, 64Cu and 43Sc. Nucleonika 2010, 55, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Link, J.; Krohn, K.A.; O’Hara, M.J. A simple thick target for production of 89Zr in an 11 MeV cyclotron. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 122, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaim, S. Production of High Purity 94mTc for Positron Emission Tomographic Studies. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2000, 27, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asabella, A.; Cascini, G.; Altini, C.; Paparella, D.; Notaristefano, A.; Rubini, G. The Copper Radioisotopes: A systematic review with special interest to 64Cu. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 786463. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, J. The production of [124I]iodine and [86Y]yttrium. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38 (Suppl. 1), S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.; Metello, L.F.; do Carmo, S.J.C.; Alves, F.; Duarte Naia, M. Titanium-45 as an innovative radionuclide for PET imaging: From cyclotron production to potential biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Congress of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine 2016, Barcelona, Spain, 15–19 October 2016. Oral Presentation 447. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata, K.; Ido, T.; Monma, M.; Murakami, M.; Fukuda, H.; Yamada, K.; Endo, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Sato, T.; Matsuzawa, T. Preparation and Medical Application of 45Ti; CYRIC Annual Report; CYRIC: Tohoku, Japan, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata, K.; Ido, T.; Monma, M.; Murakami, M.; Fukuda, H.; Kameyama, M.; Yamada, K.; Endo, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Sato, T.; et al. Potential radiopharmaceuticals labeled with titanium-45. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1991, 42, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, R.N.; Mattner, F.; Najdovski, L.; Collier, T.L.; Fallon, J. Synthesis and Characterisation of [111In]-Liposome Encapsulated [45Ti]-Budotitane. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Symposium on Radiopharmaceutical Chemistry, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 13–17 August 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Vavere, A.L.; Laforest, R.; Welch, M.J. Production, processing and small animal PET imaging of titanium-45. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2005, 32, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavere, A.L.; Welch, M.J. Preparation, biodistribution, and small animal PET of 45Ti-transferrin. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, R.I.; Sheil, R.W.; Scharli, R.K.; Chan, S.; Gibbons, P.; Jeffery, C.; Morandeau, L. Titanium-45 as a Candidate for PET Imaging: Production, Processing & Applications. In Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on Targetry and Target Chemistry, Prague, Czech Republic, 18–21 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Siikanen, J.; Hong, H.; Valdovinos, H.; Hernandez, R.; Zhang, Y.; Barnhart, T.; Cai, W.; Nickles, R. Production, separation and labeling of 45Ti. In Proceedings of the SNMMI Annual Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tshuva, E.Y.; Ashenhurst, J.A. Cytotoxic Titanium(IV) Complexes: Renaissance. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 2203–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immel, T.A.; Groth, U.; Huhn, T. Cytotoxic Titanium Salan Complexes: Surprising Interaction of Salan and Alkoxy Ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2775–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.; Szigeti, K.; Mathé, D.; Metello, L.F. The role of molecular imaging in modern drug development. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Severin, G.W.; Nielsen, C.H.; Jensen, A.I.; Fonslet, J.; Kjær, A.; Zhuravlev, F. Bringing Radiotracing to Titanium-Based Antineoplastics: Solid Phase Radiosynthesis, PET and ex Vivo Evaluation of Antitumor Agent [45Ti](salan)Ti(dipic). J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7591–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assadi, M.; Afrasiabi, K.; Nabipour, I.; Seyedabadi, M. Nanotechnology and nuclear medicine; research and preclinical applications. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 14, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zarytova, V.F.; Zinov’ev, V.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Levina, A.S.; Repkova, M.N.; Shikina, N.V.; Evdokimov, A.A.; Belanov, E.F.; Balakhnin, S.M.; Serova, O.A.; et al. An Examination of the Ability of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Its Conjugates with Oligonucleotides to Penetrate into Eucariotis Cells. Nanotechnol. Russia 2009, 4, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanou, E.; Evangelou, A.; Falaras, P. Effects of UV-irradiated titania nanoparticles on cell proliferation, cancer metastasis and promotion. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Said, K.S.; Ali, E.M.; Kanehira, K.; Taniguchi, A. Molecular mechanism of DNA damage induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in toll-like receptor 3 or 4 expressing human hepatocarcinoma cell lines. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mund, R.; Panda, N.; Nimesh, S.; Biswas, A. Novel titanium oxide nanoparticles for effective delivery of paclitaxel to human breast cancer cells. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, Z. Anticancer efficacy enhancement and attenuation of side effects of doxorubicin with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gibson, N.; Holzwarth, U.; Abbas, K.; Simonelli, F.; Kozempel, J.; Cydzik, I.; Cotogno, G.; Bulgheroni, A.; Gilliland, D.; Ponti, J.; et al. Radiolabelling of engineered nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo tracing applications using cyclotron accelerators. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 751–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salber, D.; Manuvelpillai, J.; Spahn, I.; Klein, S.; Uhlenbruck, F.; Palm, C.; Matusch, A.; Becker, S.; Langen, K.J.; Coenen, H.H. 45Ti-cations as potential PET-tracers for cerebral neurodegeneration. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Technetium and Other Radiometals in Chemistry and Medicine, Bressanone, Italy, 8–11 September 2010. [Google Scholar]

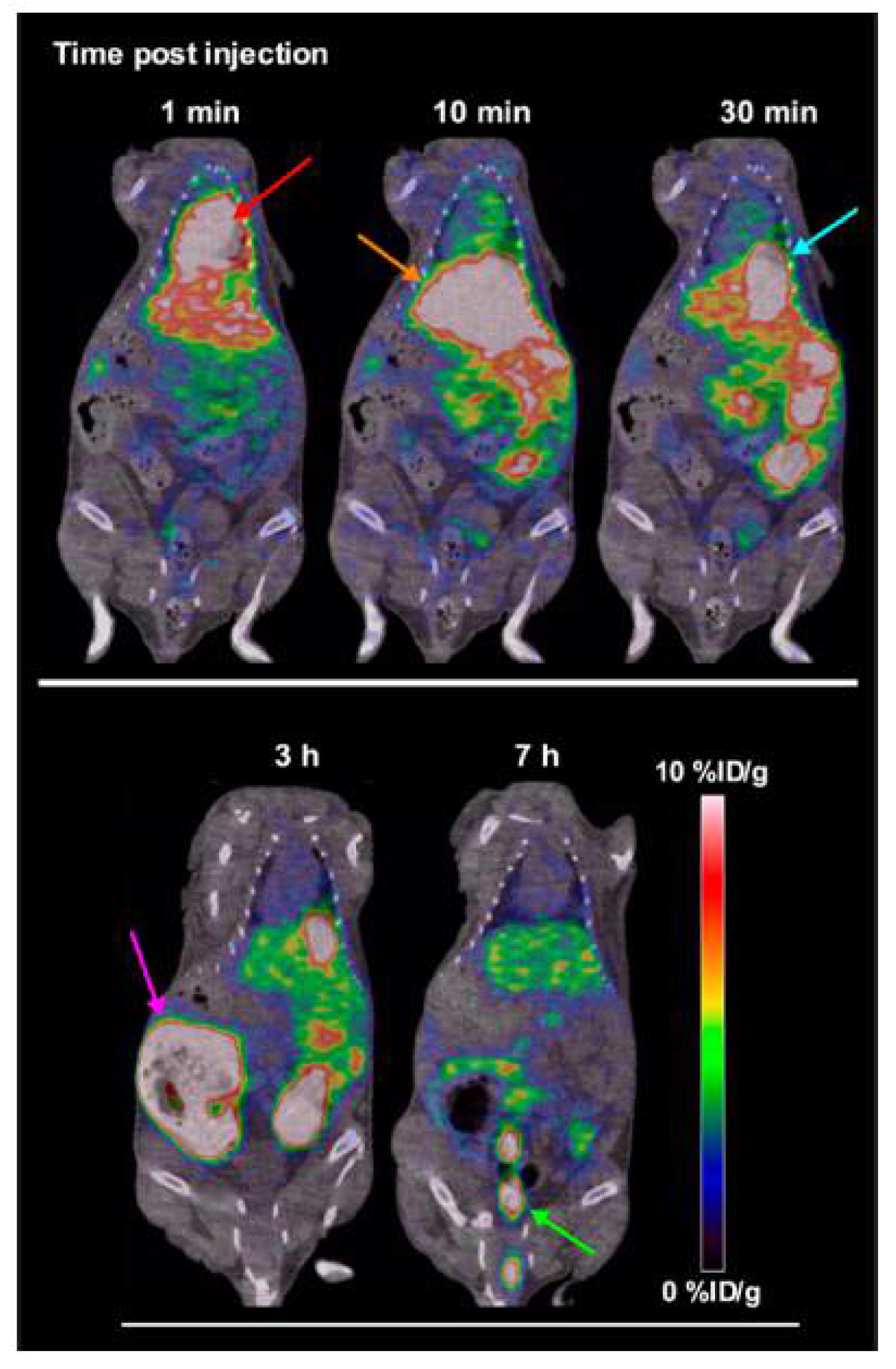
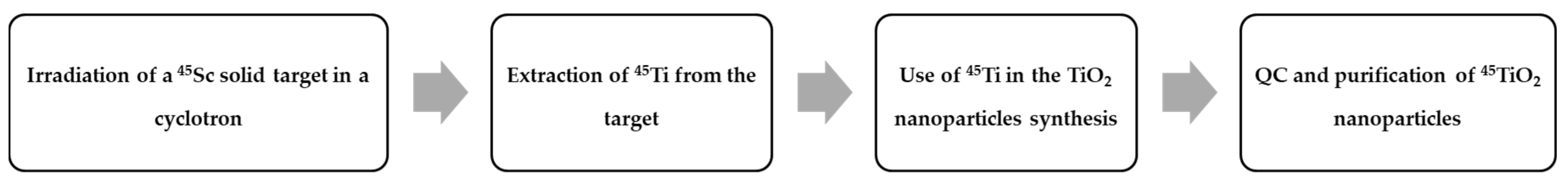
| Radionuclide | Half-Life | β+ Endpoint Energy (MeV) |
|---|---|---|
| 44Sc | 3.927 h | 1.47 |
| 45Ti | 3.1 h | 1.04 |
| 55Co | 17.53 h | 1.50 |
| 60Cu | 23.7 min | 3.77 |
| 61Cu | 3.333 h | 1.21 |
| 64Cu | 12.700 h | 0.653 |
| 76Br | 16.2 h | 3.94 |
| 82Rb | 1.273 min | 3.15 |
| 86Y | 14.7 h | 3.14 |
| 89Zr | 3.3 day | 0.902 |
| 94mTc | 52.0 min | 2.44 |
| 124I | 4.176 day | 2.14 |
| Radionuclide | Most Common Nuclear Reaction |
|---|---|
| 44Sc | 44Ca(p,n)44Sc |
| 45Ti | 45Sc(p,n)45Ti |
| 55Co | 58Ni(p,α)55Co |
| 60Cu | 60Ni(p,n)60Cu |
| 61Cu | 61Ni(p,n)61Cu |
| 64Cu | 64Ni(p,n)64Cu |
| 76Br | 76Se(p,n)76Br |
| 86Y | 86Sr(p,n)86Y |
| 89Zr | 89Y(p,n)89Zr |
| 94mTc | 94Mo(p,n)94mTc |
| 124I | 124Te(p,n)124I |
| Mean Beam Energy (MeV) | Cross-Section (mbarn) | Uncertainty (mbarn) |
|---|---|---|
| 16.1 ± 1.0 | 1.2 × 102 | ±0.4 × 102 |
| 15.3 ± 1.0 | 2.1 × 102 | ±0.7 × 102 |
| 12.4 ± 0.9 | 4.4 × 102 | ±1.4 × 102 |
| 8.9 ± 0.8 | 3.4 × 102 | ±1.0 × 102 |
| 4.9 ± 0.7 | 1.2 × 102 | ±0.4 × 102 |
| 3.4 ± 0.7 | 0.8 × 101 | ±0.3 × 101 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, P.; Metello, L.F.; Alves, F.; Duarte Naia, M. Cyclotron Production of Unconventional Radionuclides for PET Imaging: the Example of Titanium-45 and Its Applications. Instruments 2018, 2, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments2020008
Costa P, Metello LF, Alves F, Duarte Naia M. Cyclotron Production of Unconventional Radionuclides for PET Imaging: the Example of Titanium-45 and Its Applications. Instruments. 2018; 2(2):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments2020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Pedro, Luís F. Metello, Francisco Alves, and M. Duarte Naia. 2018. "Cyclotron Production of Unconventional Radionuclides for PET Imaging: the Example of Titanium-45 and Its Applications" Instruments 2, no. 2: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments2020008
APA StyleCosta, P., Metello, L. F., Alves, F., & Duarte Naia, M. (2018). Cyclotron Production of Unconventional Radionuclides for PET Imaging: the Example of Titanium-45 and Its Applications. Instruments, 2(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments2020008