Spatiotemporal Variations in Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities in a Marine Bay Ecosystem Based on Stable Isotope Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
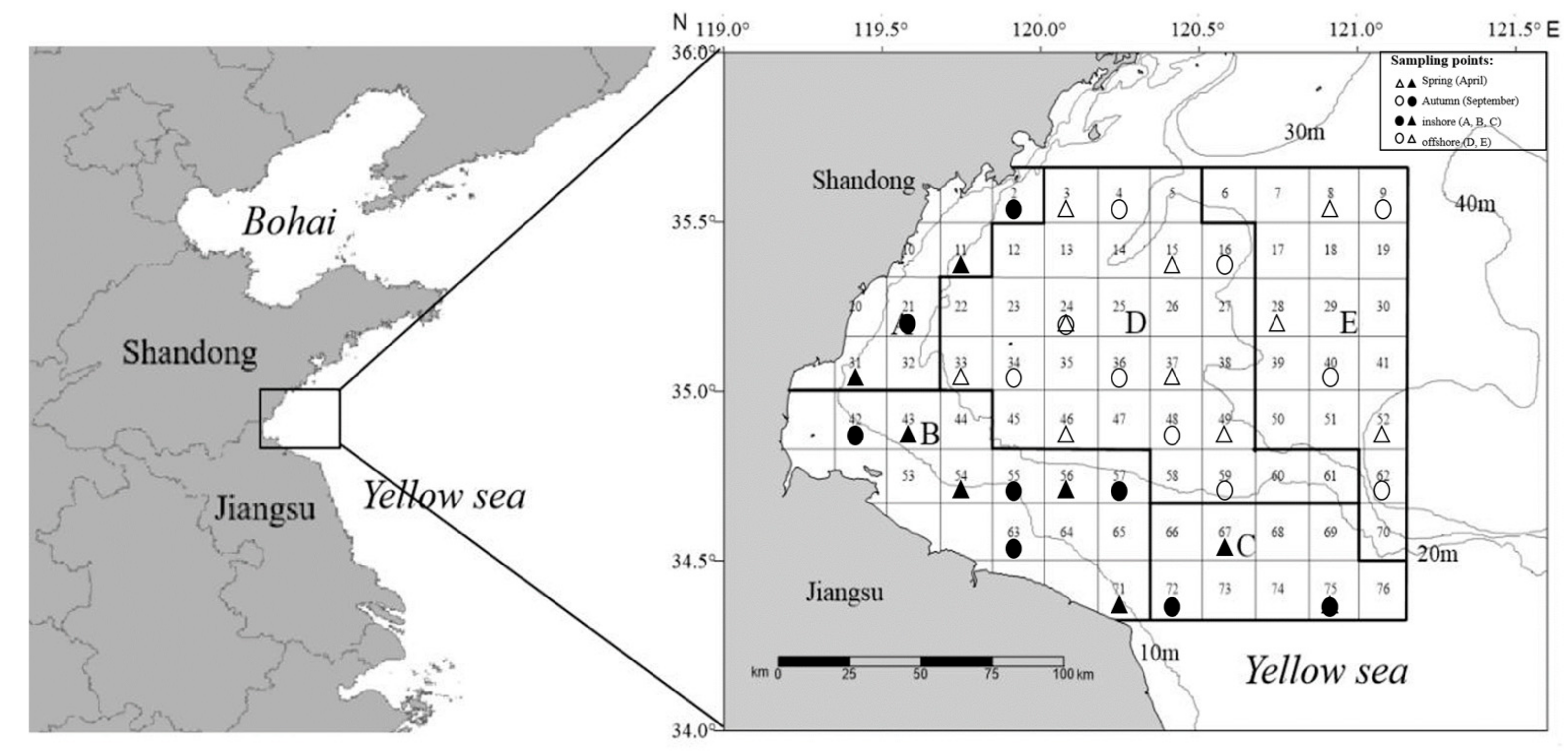
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Treatment
2.3. Stable Isotope Analysis
2.4. Trophic Diversity Indices
3. Results
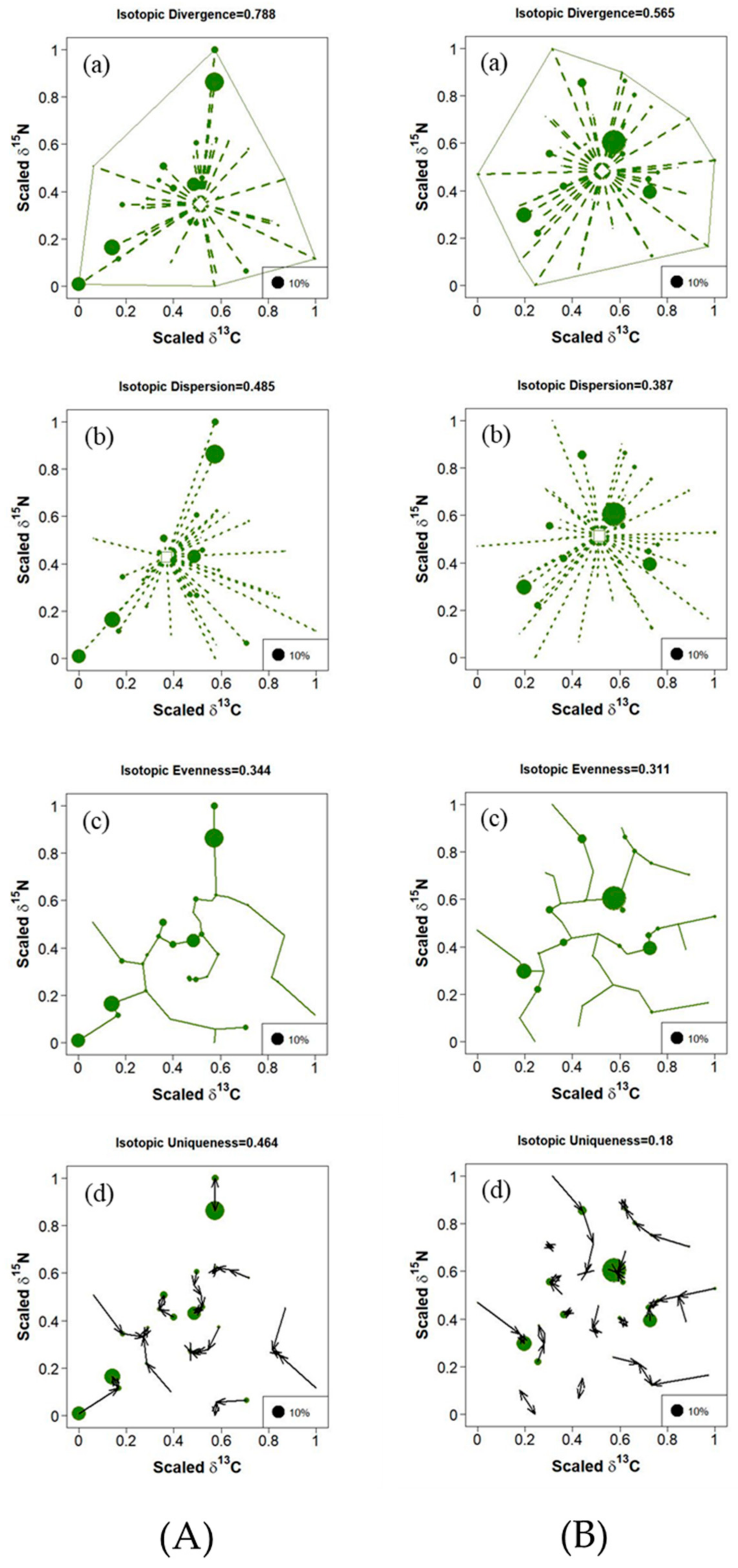
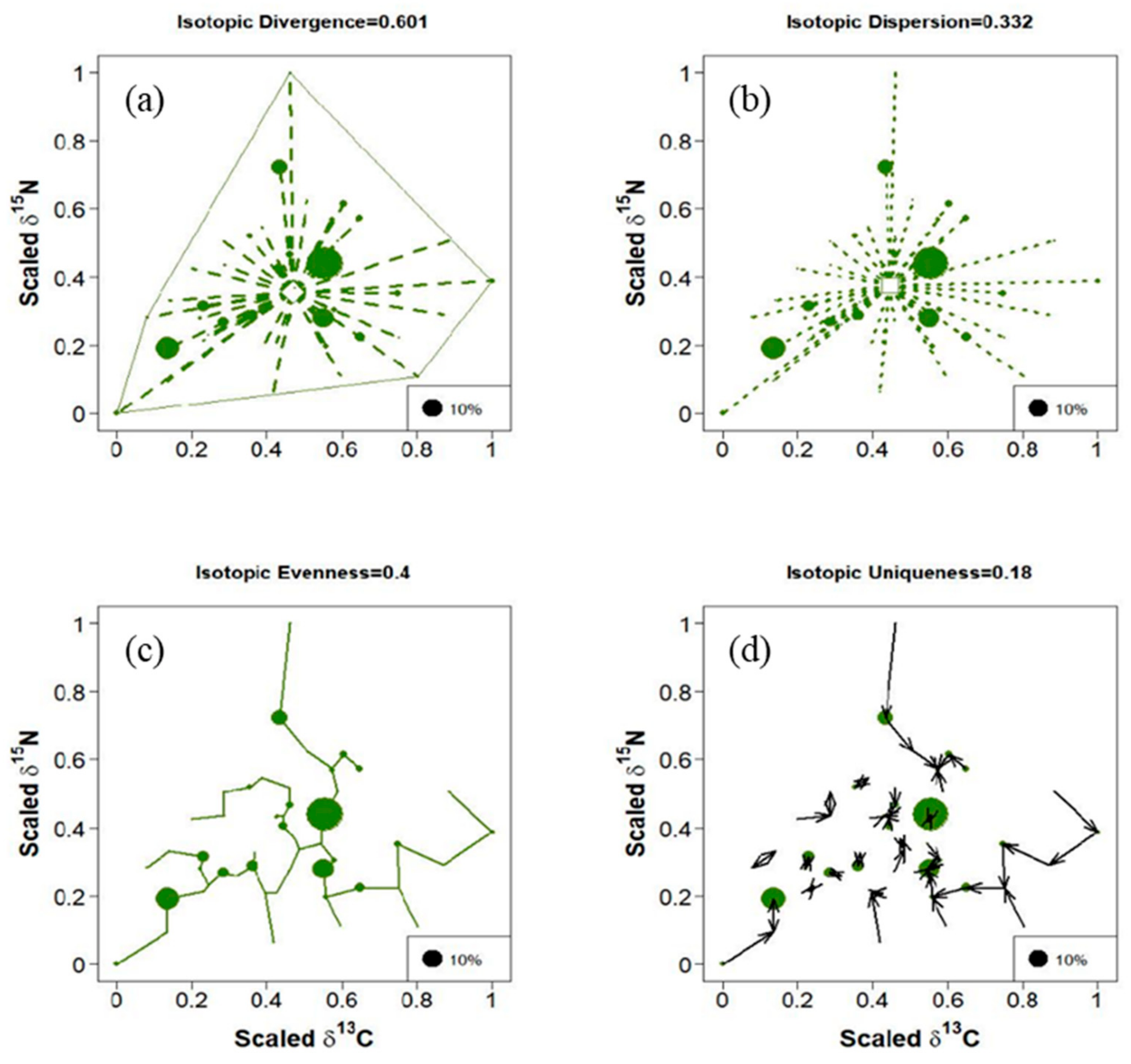
3.1. Temporal Variation in Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities
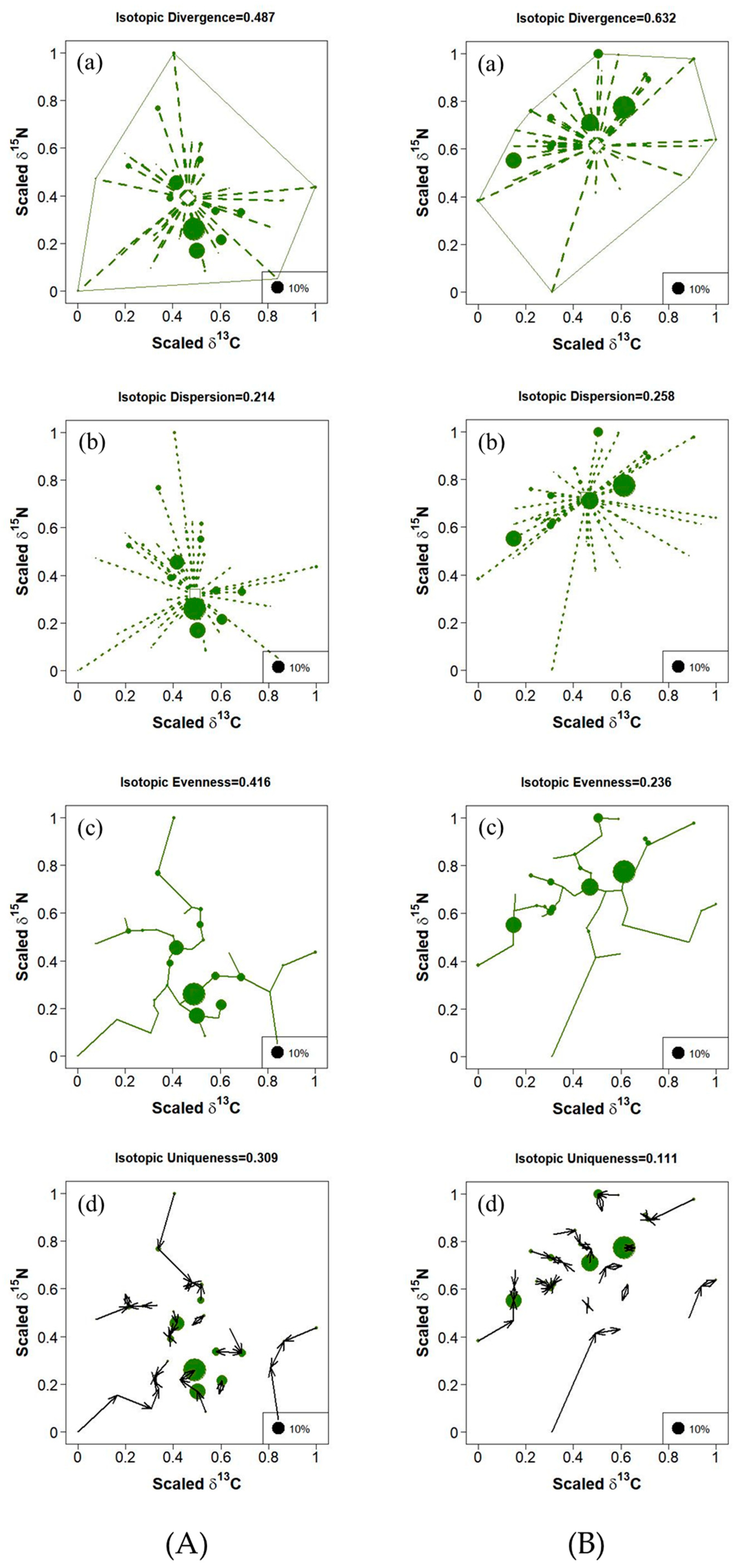
3.2. Spatial Variation in Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities
3.3. Composition and Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leclerc, C.; Reynaud, N.; Danis, P.A.; Moatar, F.; Daufresne, M.; Argillier, C.; Usseglio-Polatera, P.; Verneaux, V.; Dedieu, N.; Frossard, V.; et al. Temperature, productivity and habitat characteristics collectively drive lake food web structure. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 2450–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cury, P.; Shannon, L.; Shin, Y.J. The functioning of marine ecosystems: A fisheries perspective. Responsible Fish. Mar. Ecosyst. 2003, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Wei, H.; Dou, S. Study on food web and trophic structure of fish in the changjiang river estuary. Stud. Mar. Sin. 1997, 38, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Casini, M.; Lövgren, J.; Hjelm, J.; Cardinale, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Kornilovs, G. Multi-level trophic cascades in a heavily exploited open marine ecosystem. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delong, J.; Gilbert, B.; Shurin, J.; Barton, B.; Clements, C.; Dell, A.; Greig, H.; Harley, C.; Kratina, P.; McCann, K.; et al. The body size dependence of trophic cascades. Am. Nat. 2015, 185, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurkowski, D.J.; Hussey, N.E.; Ferguson, S.H.; Fisk, A.T. A temporal shift in trophic diversity among a predator assemblage in a warming Arctic. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villéger, S.; Mason, N.W.H.; Mouillot, D. New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology 2008, 89, 2290–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukes, J.S. Biodiversity and invasibility in grassland microcosms. Oecologia 2001, 126, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Hughes, T.P.; Folke, C.; Nyström, M. Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature 2004, 429, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villasante, S.; Lopes, P.F.M.; Coll, M. The role of marine ecosystem services for human well-being: Disentangling synergies and trade-offs at multiple scales. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucherousset, J.; Villéger, S. Quantifying the multiple facets of isotopic diversity: New metrics for stable isotope ecology. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 56, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, P. Marine Fisheries Ecology by Simon Jennings, Michael J. Kaiser & John D. Reynolds: Book review. Afr. Zool. 2001, 36, 275–276. [Google Scholar]
- Yemane, D.; Field, J.G.; Leslie, R.W. Spatio-temporal patterns in the diversity of demersal fish communities off the south coast of South Africa. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, M.A.; Villéger, S.; Mason, N.W.H.; Mouillot, D. Functional diversity measures: An overview of their redundancy and their ability to discriminate community assembly rules. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Montaña, C.G.; Post, D.M. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 2007, 88, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanden, M.J.V.; Rasmussen, J.B. Variation in δ15N and δ13C Trophic Fractionation: Implications for Aquatic Food Web Studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberté, E.; Legendre, P. A distance-based framework for measuring functional diversity from multiple traits. Ecology 2010, 91, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B. Stable Isotope Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reñones, O.; Polunin, N.V.C.; Goni, R. Size related dietary shifts of Epinephelus marginatus in a western Mediterranean littoral ecosystem: An isotope and stomach content analysis. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 61, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootsma, H.A.; Hecky, R.E.; Hessslein, R.H.; Turner, G.F. Food partitioning among Lake Malawi nearshore fishes as revealed by stable isotope analyses. Ecology 1996, 77, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, C.P.; Tonn, W.M.; Prepas, E.E.; Wassenaar, L.I. Individual specialization and trophic adaptability of northern pike (Esox lucius): An isotope and dietary analysis. Oecologia 1999, 120, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Hu, J.Y.; An, L.H.; An, W.; Yang, M.; Yi-Teng, G.M.; Fu-Bu, D.Y.; Tao, S. Analysis of trophic levels of major species in the food web of Bohai Bay using stable nitrogen and carbon isotopes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Zuo, T.; Dai, F.Q.; Jin, X.S. Trophic level analysis of organisms from Changjiang estuary and adjacent waters of southern Yellow Sea in spring with stable isotope technology. J. Fish. Sci. China 2010, 17, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Xie, P. Variability of stable nitrogen isotopic baselines and its consequence for trophic modeling. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Gregg, J.W. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Araujo, M.S.; Boucek, R.; Hammerschlag-Peyer, C.M.; Harrison, E.; Jud, Z.R.; Matich, P.; Rosenblatt, A.E.; Vaudo, J.J.; Yeager, L.A.; et al. Applying stable isotopes to examine food-web structure: An overview of analytical tools. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecinos, S.; Castro, L.R.; Neira, S. Stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) and trophic position of Patagonian sprat (Sprattus fuegensis) from the Northern Chilean Patagonia. Fish. Res. 2016, 179, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litz, M.N.C.; Miller, J.A.; Copeman, L.A.; Copeman, L.A.; Teel, D.J.; Weitkamp, L.A.; Daly, E.A.; Claiborne, A.M. Ontogenetic shifts in the diets of juvenile Chinook Salmon: New insight from stable isotopes and fatty acid. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2017, 100, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Y.P. Assessing uncertainty of a multispecies size-spectrum model resulting from process and observation errors. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F. Research on Ecological Recovery Suitability Assessment for Haizhou Bay Special Marine Reserves. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.T.; Ding, X.X.; Jiang, X.; Xu, B.D.; Zhang, C.L.; Ren, Y.P.; Xue, Y. Variations in the mean trophic level and large fish index of fish community in Haizhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.P.; Zhang, C.L. Variation in β diversity of fish species in Haizhou Bay. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.D.; Zhang, C.L.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.P.; Chen, Y. Optimization of sampling effort for a fishery-independent survey with multiple goals. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnegar, J.K.; Polunin, N.V.C. Differential Fractionation of δ13C and δ15N among Fish Tissues: Implications for the Study of Trophic Interactions. Funct. Ecol. 1999, 13, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.Z.; Han, D.Y.; Xue, Y.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xu, B.D.; Ren, Y.P. Feeding habits of Hinogobius pflaumi in Jiaozhou Bay, China based on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 3789–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaehler, S.; Pakhomov, E.A.; McQuaid, C.D. Trophic structure of the marine food web at the Prince Edward Islands (Southern Ocean) determined by δ13C and δ15N analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 208, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoffman, J.C.; Sutton, T.T. Lipid correction for carbon stable isotope analysis of deep-sea fishes. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, M.D.; Ebert, D.A.; Cailliet, G.M. Stable-isotope analysis of a deep-sea benthic-fish assemblage: Evidence of an enriched benthic food web. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 1485–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; van der Molen, J. Trophic levels of marine consumers from nitrogen stable isotope analysis: Estimation and uncertainty. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Warr, K.J. Environmental correlates of large-scale spatial variation in the d15N of marine animals. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana, G.; Rasmussen, J.B. Comparison of aquatic food chains using nitrogen isotopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10844–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.X.; Sui, H.Z.; Ren, X.M.; Xu, B.D.; Zhang, C.L.; Ren, Y.P.; Xue, Y. Feeding habits of Saurida elongta in Haizhou Bay, Shandong, China, based on stomach contents and stable isotope. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.; Mazumder, A. Compositional and interlake variability of zooplankton affect baseline stable isotope signatures. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, M.; Wada, E. Stepwise enrichment of along δ15N food chains: Further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, J.R.; Barber, C.B.; Habel, K.; Grasman, R.; Gramacy, R.B.; Mozharovskyi, P.; Sterratt, D.C. Geometry: Mesh Generation and Surface Tessellation. R Package Version 0.4.5. 2019. Available online: http://www.qhull.org (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Geyer, C.J.; Meeden, G.D.; Fukuda, K. R Package rcdd: Computational Geometry, Version 1.4. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/cddlib/cddlib (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matich, P.; Kiszka, J.J.; Gastrich, K.R.; Heithaus, M.R. Trophic redundancy among fishes in an East African nearshore seagrass community inferred from stable-isotope analysis. J. Fish Biol. 2017, 91, 490–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, D.; Thébault, E.; Kehoe, R.; van Veen, F.J.F. Trophic redundancy reduces vulnerability to extinction cascades. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, I.W.; Miller, A.E.; Bowman, W.D.; Suding, K.N. Niche complementarity due to plasticity in resource use: Plant partitioning of chemical N forms. Ecology 2010, 91, 3252–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F. Study on Feeding Ecology and Food Relations of Two High Trophic Level Fishes in Haizhou Bay. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.H.; Xue, Y.; Xu, B.D.; Zhang, C.L.; Ren, Y.P. Composition of food and niche overlap of three Sciaenidae species in Haizhou Bay. J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.D.; Zhang, C.L.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.P. Spatio-temporal variations of functional diversity of fish communities in Haizhou Bay. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, A.; Robert, M.; Cresson, P.; Bris, H.L.; Kopp, D. Food web structure in relation to environmental drivers across a continental shelf ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.F.; Liu, S.D.; Ren, Y.P.; Zhang, C.L.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y. Study on spatial heterogeneity in feeding habitat of Chelidonichthys spinousus in Haizhou Bay during autumn. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 6433–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, D.; Lefebvre, S.; Cachera, M.; Villanueva, M.C.; Ernande, B. Reorganization of a marine trophic network along an inshore-offshore gradient due to stronger pelagic-benthic coupling in coastal areas. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 130, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Chen, W.; Wang, K.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ji, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations in Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities in a Marine Bay Ecosystem Based on Stable Isotope Analysis. Fishes 2024, 9, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070262
Li P, Chen W, Wang K, Xu B, Zhang C, Ji Y, Ren Y, Xue Y. Spatiotemporal Variations in Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities in a Marine Bay Ecosystem Based on Stable Isotope Analysis. Fishes. 2024; 9(7):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070262
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pengcheng, Wan Chen, Kun Wang, Binduo Xu, Chongliang Zhang, Yupeng Ji, Yiping Ren, and Ying Xue. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Variations in Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities in a Marine Bay Ecosystem Based on Stable Isotope Analysis" Fishes 9, no. 7: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070262
APA StyleLi, P., Chen, W., Wang, K., Xu, B., Zhang, C., Ji, Y., Ren, Y., & Xue, Y. (2024). Spatiotemporal Variations in Trophic Diversity of Fish Communities in a Marine Bay Ecosystem Based on Stable Isotope Analysis. Fishes, 9(7), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070262






