Abstract
Mugil liza juveniles (6.69 ± 0.06 g) were subjected to dietary citral (0-control, 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mL per kg feed) for 45 days, and its possible effects on zootechnical and metabolic parameters, digestive enzymes, innate immunity, oxidative status and liver damage were evaluated. At the end of the experiment, fish fed 2.0 mL citral per kg feed showed a greater weight gain and protein retention efficiency, as well as enhanced activities of pepsin (stomach) and amylase (intestine) compared with control fish. Citral supplementation decreased liver lipoperoxidation and increased the activities of glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase and superoxide dismutase in the gills, liver and brain. The highest level of citral inclusion augmented non-protein thiol content in the brain and gills. Myeloperoxidase activity was lower in fish offered 1.0 and 2.0 mL citral per kg feed. Dietary citral did not influence the plasma levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase or the hepatic histology. As it improved growth, the activity of digestive enzymes and general health, dietary citral may be recommended for M. liza at 2.0 mL per kg feed.
Keywords:
monoterpenoids; pepsin; intestinal enzymes; oxidative stress; myeloperoxidase; hepatic biomarkers Key Contribution:
The addition of 2.0 mL citral per kg feed improves growth, pepsin and amylase activity and health of Mugil liza.
1. Introduction
Common aquaculture practices (e.g., handling and transportation) as well as alterations in water quality parameters and the occurrence of pathogens may have implications for fish welfare, thus impairing productivity [1]. Such stressful factors can also impact the status of the oxidative and immune systems [2,3,4]. An assortment of products has been included in fish feed in an attempt to alleviate oxidative stress and improve growth, feed efficiency and/or disease resistance [5].
In this regard, natural compounds have shown promising results, and the occurrence of side effects following their use is low. Citral, which is a mixture of the isomers geranial and neral, is the main constituent of several essential oils (EOs) [6]. Dietary inclusion of Cymbopogon flexuosus EO (89.2% citral) boosted growth and minimized the effects of bacterial infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) [7]. Addition of Aloysia triphylla EO (50.2% citral) to the diet of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) reduced plasma cortisol levels and lipoperoxidation (LPO) and enhanced growth and antioxidant capacity [8,9]. Dietary supplementation with Cymbopogon citratus EO (73.5% citral) improved growth, hematological variables, muscle glycogen levels and intestinal alkaline protease activity in tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) [10]; it also lowered myeloperoxidase activity in common snook (Centropomus undecimalis) [11]. As mentioned above, citral-rich EOs have a great potential to be used as additives in fish feed. Nonetheless, the inclusion of citral in the diets of fish may not always be recommended [12].
The mullet (Mugil liza) is an important target for both artisanal and industrial fisheries. This detritivorous fish is resistant to handling and can be found in coastal marine waters and brackish estuaries from Argentina to the state of São Paulo, Brazil [13].
The current study was aimed at investigating the possible effects of dietary citral supplementation on the zootechnical, metabolic and redox parameters, digestive enzymes activity and immunology in mullets. Hepatotoxicity was also analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance and Water Quality
Mullet juveniles (8.56 ± 0.01 cm and 6.69 ± 0.06 g) were raised in the laboratory since the larval stage, were randomly placed into four water reuse systems (32.19 ± 0.18 ppt salinity) and were acclimated for four days. During this period, the fish were fed the control diet (without citral) used throughout this study. Each system consisted of three circular tanks (150 L) (n = 30 fish/tank); a full description of the systems has been provided in Mori et al., 2019 [11]. The residues were removed during daily tank siphoning, and the water was renewed at a rate of about 25%.
Water-dissolved oxygen, temperature and pH were measured daily, while ammonia, nitrite and alkalinity were determined once a week, as described in Zeppenfeld et al. [14]. The temperature was kept at 27.11 ± 0.11 °C, dissolved oxygen at 5.16 ± 0.16 mg L−1 and pH at 7.58 ± 0.13. Levels of total ammonia (0.2 ± 0.05 mg L−1), nitrite (0.2 ± 0.04 mg L−1) and alkalinity (103.65 ± 0.34 mg CaCO3 L−1) were maintained within the range for the species.
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Experimentation of the Federal University of Santa Catarina (number PP00861/2013).
2.2. Citral
Citral was purchased from Sigma Aldrich® (St. Louis, MI, USA); its composition was analyzed as in Mori et al. [11]. The relative percentage of compounds (geranial or α-citral = 60.15%; neral or β-Citral = 39.85%) was calculated by under peak area integration obtained from chromatogram.
2.3. Diet and Treatments
Citral was added to the diet at four concentrations (three replicates/treatment), 0-control, 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mL per kg feed, which are equivalent to 0, 0.44, 0.88 and 1.76 g per kg feed, respectively. Diet preparation followed the method of Mori et al., 2019 [11] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Ingredients and analyzed proximate average composition of control diet.
Fish were fed four times a day until apparent satiety, for 45 days. Experimentation was conducted at 12 h/12 h light/dark cycling regimen, with lights on at 8 am. Food was withheld for 24 h before sampling and tissue collection.
2.4. Growth Parameters
All fish were anesthetized at days 1 and 45 with 50 mg L−1 benzocaine for biometric analysis. Weight gain, feed conversion rate and specific growth rate were calculated as in Michelotti et al. [15]. Feed intake was measured daily; fish were fed to apparent satiety and the amount of waste feed collected in each tank was registered. Condition factor (K) = (FW/FL3) × 100, where FW is the final weight and FL is the final length. Protein retention efficiency = weight gain (g) × ingested protein−1 (g).
2.5. Sample Collection
At the end of the 45-day feeding trial, 10 mullets/tank were anesthetized with 50 mg L−1 benzocaine and euthanized by spinal cord dislocation. Heparinized syringes were used to collect blood from the caudal vein. Their brains, gills, livers, stomachs, anterior and posterior intestines and muscles were excised and frozen in liquid nitrogen. The samples were then stored at −20 °C pending analysis.
2.6. Digestive Enzymes
Stomach and intestine (both anterior and posterior portions) samples were placed in an ice bath (1:10 tissue: buffer—20 mM Tris/10 mM phosphate, pH 7.0 in 50% (v/v) glycerol) and homogenized with a Turrax type homogenizer (Marconi Equipamentos para Laboratório Ltd., São Paulo, Brazil). The resulting extract was centrifuged, with the supernatant being collected to be used in the assays as an enzyme source.
The activity of pepsin was analyzed according to Hidalgo et al. [16], trypsin and chymotrypsin following Hummel [17] and lipase as in Gawlicka et al. [18]. Amylase activity was assayed as described by Bernfeld [19]. Starch hydrolysis analysis was performed as detailed by Park and Johnson [20]. Protein concentrations were measured in the enzyme extracts as proposed by Lowry et al. [21], with bovine albumin as standard.
2.7. Metabolic Parameters
Liver and muscle were homogenized with 1 mL of trichloroacetic acid 10%; then, the homogenates were spun (4 °C, 5 min, 917 g). Lactate and glucose were assessed in muscle and liver samples following the methods of Harrower and Brown [22] and Dubois et al. [23], respectively.
2.8. Prooxidant and Antioxidant Analyses
Tissues (gills, brain and liver) were homogenized with 30 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) and 120 mM KCl [24]. Protein content was analyzed using the procedure of Lowry et al. [21]. The levels of LPO were determined as indicated by Södergren et al. [24]. The activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) was evaluated as in Misra and Fridovich’s study [25], catalase (CAT) as proposed by Boveris and Chance [26], glutathione peroxidase (GPx) following Flohé and Gunzler [27] and glutathione-S-transferase (GST) as in Habig et al.’s study [28]. Non-protein thiol (NPSH) content, which is an indirect measure of reduced glutathione (GSH), was determined according to Ellman [29].
2.9. Innate Immune System Analyses
Hemolytic activity of the complement system was assessed as indicated in Mori et al. [11]. The percent of hemolysis was calculated by the following equation:
% hemolysis= [(A540 sample − A540 no-hemolysis)/(A540 total hemolysis − A540 no-hemolysis)] × 100.
Lysozyme activity was measured as detailed in Jørgensen et al.’s study [30]. A suspension of Micrococcus lysodeikticus (200 µL) in PBS solution (0.2 g/L, pH 6.2) was mixed with plasma (10 µL). The activity was calculated by the equation [((∆absorbance(4-1 min)/3)/0.001] × 100. Serum content of peroxidase was analyzed as proposed by Quade and Roth [31], with the modifications explained in Mori et al. [11].
2.10. Hepatic Enzymes
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were determined in plasma using commercial kits Gold Analisa® (Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil).
2.11. Liver Histology
Liver samples were fixed in Bouin for 24 h, followed by dehydration, diaphanization and inclusion in historesin (Leica®, Tokyo, Japan). The tissue sections (4 μm thick) were then stained with hematoxylin-eosin. The following histological parameters were evaluated: area of hepatocytes, diameter of sinusoidal capillaries and diameter of lobular central vein.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
Variable distribution was tested using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Comparisons between treatments were made by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s test (GraphPad Prism® 5.0). The significance threshold was set at 0.05. The tanks were considered the experimental unit (n = 3). All determinations were performed in triplicate, and the results are reported as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
3. Results
3.1. Growth Parameters
No fish died throughout the experiment. Fish receiving 2.0 mL citral per kg feed showed a greater weight gain and protein retention efficiency than those in the control group. Specific growth rate, feed intake, feed conversion rate and condition factor were not significantly affected by the treatments (Table 2).

Table 2.
Growth parameters in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days.
3.2. Digestive Enzymes
Fish fed 2.0 mL citral per kg feed showed a higher activity of pepsin in the stomach and amylase in the intestine than those offered the control diet and 1.0 mL citral per kg feed. The addition of dietary citral did not significantly change the activities of trypsin, chymotrypsin or lipase (Figure 1).
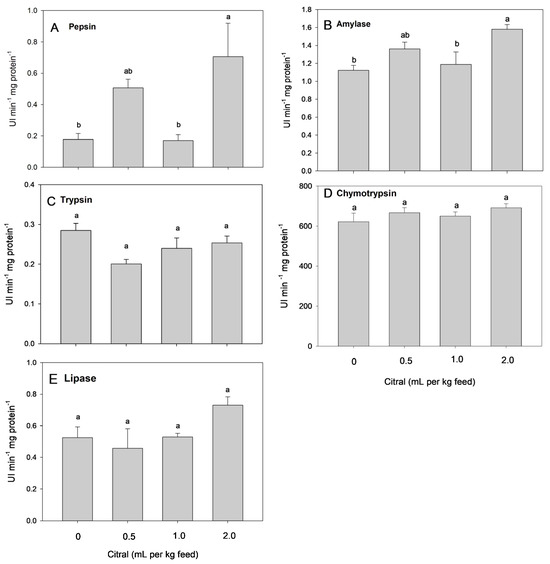
Figure 1.
Pepsin activity in the stomach (A) and intestinal amylase (B), trypsin (C), chymotrypsin, (D) and lipase (E) activities in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days. Different superscript letters indicate significant differences between the treatments using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test (p < 0.05).
3.3. Metabolic Parameters
Lower hepatic glucose levels were observed in fish given 0.5 mL citral per kg feed compared with the fish fed the control diet and 2.0 mL citral per kg feed. Muscle glucose levels remained unaltered across all treatments. Higher hepatic lactate levels were detected in fish fed 2.0 mL citral per kg feed than in the control fish, while muscle lactate measurements were lower in the fish offered the diets containing 0.5 and 1.0 mL citral per kg feed compared with those in the control group (Table 3).

Table 3.
Hepatic and muscle glucose and lactate levels in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days.
3.4. Prooxidant and Antioxidant Analyses
After 45 days, the amount of lipid hydroperoxides (LOOHs) significantly decreased in the livers of fish receiving diets supplemented with 0.5 and 2.0 mL citral per kg feed as well as in the gills of fish fed 1.0 mL citral per kg feed. All fish given citral-supplemented diets showed lower brain LOOH levels compared with those in the control group (Table 4).

Table 4.
Biomarkers of oxidative status in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days.
When compared with the control fish, SOD activity was greater in the livers, gills and brains of fish fed 0.5 and 1.0 mL, 1.0 and 2.0 mL, and 0.5 mL citral per kg feed, respectively (Table 4). Nevertheless, dietary citral supplementation did not influence CAT activity in the assessed tissues. The activity of GPx in the brains and livers of fish receiving diets supplemented with citral was significantly higher than in the control group. Moreover, the group offered 2.0 mL citral per kg feed showed the highest GPx activity in gills. Fish fed 1.0 and 2.0 mL citral per kg feed presented the greatest GST activity in the gills and livers; these fish also showed significantly higher GST activity in their brains compared with the control group. Fish given 2.0 mL citral per kg feed had the highest NPSH content in their brains and gills; no effect of citral supplementation on this parameter was detected in their livers (Table 4).
3.5. Innate Immune System Analyses
The addition of dietary citral did not alter lysozyme or complement activity. The lowest myeloperoxidase activity was registered in the fish offered 1.0 mL citral per kg feed, followed by those fed 2.0 mL citral per kg feed (Figure 2).
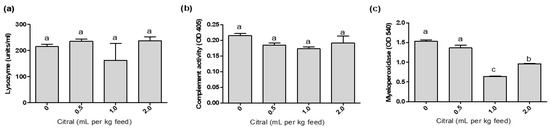
Figure 2.
Plasma lysozyme activity, (a) hemolytic activity of complement system (b) and myeloperoxidase activity (c) in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). Different superscript letters indicate significant difference between treatments using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test (p < 0.05).
3.6. Plasma Levels of Alanine Aminotransferase and Aspartate Aminotransferase
There was no dietary inclusion effect of citral on plasma levels of AST or ALT (Table 5).

Table 5.
Plasma levels of hepatic enzymes in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days.
3.7. Hepatic Histology
Morphology of the hepatocytes, sinusoidal capillaries and lobular central vein were not influenced by the dietary treatments (Table 6). The hepatocytes showed vacuoles in the cytoplasm and a basophilic spheroidal nucleus in the centrobasal portion (Figure 3).

Table 6.
Liver histological parameters in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days.

Figure 3.
Hepatic morphology in mullets fed different dietary citral levels for 45 days (mL per kg feed). A—lobular central vein; B—sinusoidal capillaries; C—hepatocytes; D—hepatic vacuoles.
4. Discussion
The increased weight gain and protein retention efficiency in mullets receiving 2.0 mL per kg feed were as expected. This is because previous works have found comparable results when using the citral-rich EOs of C. flexuosus [7] and A. triphylla [8] at the same level in the feed of omnivorous Nile tilapia and silver catfish, respectively. Dietary supplementation with lower levels (0.25 and 0.5 mL per kg feed) of C. citratus EO, which is also rich in citral, boosted similarly growth in omnivorous tambaqui [10]. However, carnivorous common snook administered 0.5 mL citral per kg feed presented lower growth, and greater citral levels did not influence this parameter [12].
The feeding habit and/or the diet can modulate the activity of digestive enzymes in some fish species; it may be enhanced when feeds have low digestibility in order to improve the absorption of nutrients, i.e., the enzymes may behave in a compensatory manner. Mullets can change their diets depending on the habitat in which they live in [32]; therefore, their digestive enzymes must present high plasticity.
One of the proposed mechanisms of action by which EOs improve digestion is by increasing the secretion of digestive enzymes [33]. The greater weight gain verified in mullets receiving the highest dietary citral level could be related with the higher pepsin and amylase activities in these fish compared with their control counterparts. Nevertheless, reduced growth as well as increased pepsin, lipase and amylase activities were registered in common snook fed 0.5 mL citral per kg feed [12]. Apparently, mullet, silver catfish, Nile tilapia and tambaqui have more flexible digestive processes than the carnivorous common snook, which may help explain the distinct effects of citral/citral-rich EOs on their growth.
The highest level of citral in the diet may have stimulated mullets’ microintestinal flora, which could account for their increased levels of hepatic and muscle lactate. The dietary addition of 0.25 mL citral-loaded nanoemulsion per kg feed reduced the intestinal bacterial population in silver catfish [34]. Lactate is the major product of lactic acid bacteria metabolism (fermentation) found in the gastrointestinal flora. These bacteria may impact the dominance status within the intestinal microbiota and improve the function of the immune system, survival rate and disease resistance [35].
Oxidative stress is usually linked to diverse stressful stimuli (biotic or environmental) and the occurrence of numerous pathologies; consequently, it is commonly used to assess fish metabolism and their general health [2]. Mullets fed citral-supplemented diets showed lower LPO levels in their gills, livers and brains. Such findings are directly in line with a previous study wherein LPO levels were reduced in the muscle and liver tissues of silver catfish transported with 27 and 36 mg L−1 A. triphylla EO [14]. Similarly, hepatic LPO levels were lower in silver catfish given 2.0 mL A. triphylla EO per kg feed [9]. Citral seems to be the primary factor responsible for the beneficial effects of this EO in silver catfish.
Organisms have developed antioxidant enzymes to avoid, reduce and/or repair the damage provoked by reactive oxygen species [2]. Superoxide dismutase transforms anion superoxide into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and water via dismutation [36]. Mullets receiving diets supplemented with 0.5 and 2.0 mL citral showed greater SOD activity in their brains and gills, respectively. Thus, citral may increase superoxide neutralization and then protect fish against the deleterious effects of oxidative stress. The enzymes CAT and GPx neutralize H2O2 that originates from SOD activity or originates independently, producing water and molecular oxygen [37]. Dietary citral supplementation did not alter CAT activity in the analyzed tissues, most likely because they showed a low activity of this enzyme. Low or absent CAT activity has been frequently reported in marine teleosts [38]. Another hypothesis is that H2O2 levels in mullet tissues were not high enough to activate CAT [39]. The inclusion of citral in the diet of mullets led to increases in GPx activity in their gills (2.0 mL per kg feed), livers and brains. This enzyme has a much greater affinity for H2O2 than CAT [40]. Moreover, the inactivation of H2O2 was improved in mullets fed citral-added diets.
Reduced glutathione is the major non-enzymatic antioxidant and reacts enzymatically with GST and GPx, being involved in their functions [41]. The content of NPSH was raised in the gills and brains of mullets fed the highest concentration of citral tested. Adding C. citratus EO (59.5% citral) increased GSH levels in Nile tilapia [42]. As stated in a previous work, greater GSH levels in fish tissues are associated with an improved antioxidant capacity, non-specific immunity, survival and growth [43]. Glutathione-S-transferases catalyze toxic compounds and protect fish against oxidative damage [44]. The highest level of citral that was included enhanced GST activity in all tissues analyzed in this research. An in vitro assessment using a cultured rat liver epithelial cell line demonstrated that geranial, the E-isomer of citral, is the main activator of GST; furthermore, the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group with a trans-double bond was said to play an important role in this effect [45].
Overall, dietary citral supplementation improved the oxidative status of mullets, which ties well with the earlier studies that tested citral-rich EOs as additives in fish feed. Nonetheless, this does not always occur, as a similar addition of dietary citral triggered oxidative stress in common snook [11].
Nutritional strategies may also be applied to strengthen the immune system in captive-bred animals [46]. In the present study, dietary citral did not affect the complement system or lysozyme activity, both of which are important tools that can be used against microorganism infections; however, it reduced myeloperoxidase activity. Likewise, dietary supplementation with citral led to a decrease in myeloperoxidase levels in common snook [11]. In a transport trial, sea bass subjected to 40 mg L−1 lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) EO, whose main compound is citral, presented lower levels of oxidant enzymes (including myeloperoxidase) than the control fish (water only); the authors attributed such outcome to a superior antioxidant capacity in the EO-treated fish [47]. The current findings also evidence an anti-inflammatory potential of citral, which has been previously reported [48] and requires further investigation.
In spite of their therapeutic effects, EOs and their major constituents may display cytotoxic effects. Thus, considering the hepatic metabolism of citral [6], its effects upon liver histology and enzymes (AST and ALT) were investigated in mullets. Results showed no influence of dietary citral on these parameters, thus indicating that the compound did not cause hepatic injury in the tested conditions; this is consistent with an earlier study in common snook [11]. The occurrence of hepatic vacuoles is not surprising since the liver parenchyma of various teleost species is rich in glycogen and lipids [49].
5. Conclusions
As it increased weight gain and protein retention efficiency, improved oxidative status and did not induce liver damage, citral supplementation at 2.0 mL per kg feed may be recommended for mullets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.C.M., B.T.M., B.B. and B.M.H.; methodology, V.R.C., M.A.P., B.B. and B.M.H.; validation, V.R.C., B.B. and B.M.H.; formal analysis, B.B. and B.M.H.; investigation, C.C.F.M., C.A.B., L.B.B., F.J.S., A.P.G.A., S.T.d.C., L.C.K., N.C.M. and B.T.M.; resources, V.R.C., B.B. and B.M.H.; data curation, N.C.M. and B.T.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.C.M., B.T.M. and L.B.B.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, V.R.C., B.B. and B.M.H.; supervision, V.R.C., B.B. and B.M.H.; project administration, V.R.C., B.B. and B.M.H.; funding acquisition, B.B., B.M.H., V.R.C., M.A.P., S.T.d.C. and L.C.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Tecnológico (CNPq, Brazil) in the form of research fellowships granted to B. Baldisserotto (process number 301816/2022-0), and L.C. Kreutz (process number 306642/2022-0). A.P.G. Almeida and B.T. Michelotti were funded by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, Brazil, Finance Code 001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Experimentation of the Federal University of Santa Catarina (number PP00861/2013).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Fernando J. Sutili is employed at ELOAQUA Consulting, Research and Solutions in Aquaculture, Brazil. The author declares this conflict of interest did not influence the results of the study. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of this manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Moreira, M.; Schrama, D.; Farinha, A.P.; Cerqueira, M.; Raposo de Magalhaes, C.; Carrilho, R.; Rodrigues, P. Fish pathology research and diagnosis in aquaculture of farmed fish; a proteomics perspective. Animals 2021, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Saikia, S.K. Oxidative Stress in Fish: A Review. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 12, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Dixon, B. Understanding acute stress-mediated immunity in teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbinati, E.C.; Zanuzzo, F.S.; Biller, J.D. Stress and immune system in fish. In Biology and Physiology of Freshwater Neotropical Fish; Baldisserotto, B., Urbinati, E.C., Cyrino, J.E.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciji, A.; Akhtar, M.S. Stress management in aquaculture: A review of dietary interventions. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2190–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Habib, S.; Sahu, D.; Gupta, J. Chemical properties and therapeutic potential of citral, a monoterpene isolated from lemongrass. Med. Chem. 2021, 17, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, E.M.; Souza, R.C.; Melo, J.F.B.; Costa, M.M.; Souza, S.A.; Souza, A.M.; Copatti, C.E. Cymbopogon flexuosus essential oil as an additive improves growth, biochemical and physiological responses and survival against Aeromonas hydrophila infection in Nile tilapia. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2020, 92, e20190140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppenfeld, C.C.; Hernández, D.R.; Santinón, J.J.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Cunha, M.A.; Schmidt, D.; Baldisserotto, B. Essential oil of Aloysia triphylla as feed additive promotes growth of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppenfeld, C.; Saccol, E.; Pes, T.; Salbego, J.; Koakoski, G.; dos Santos, A.; Heinzmann, B.; da Cunha, M.; Barcellos, L.; Pavanato, M.; et al. Aloysia triphylla essential oil as food additive for Rhamdia quelen–Stress and antioxidant parameters. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copatti, C.E.; Felix e Silva, A.; Lorenzo, V.P.; Costa, M.M.; Melo, J.F.B. Addition of essential oil from lemongrass to the tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) diet: Effects on growth, intestinal enzymes, haematological and metabolic variables, and antimicrobial challenge. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5656–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.C.; Michelotti, B.T.; Pês, T.d.S.; Bressan, C.A.; Sutili, F.; Kreutz, L.C.; Garlet, Q.; Baldisserotto, B.; Pavanato, M.A.; Cerqueira, V.R.; et al. Citral as a dietary additive for Centropomus undecimalis juveniles: Redox, immune innate profiles, liver enzymes and histopathology. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelotti, B.T.; Mori, N.C.; Magnotti, C.C.F.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Almeida, A.P.G.; Cerqueira, V.R.; Baldisserotto, B. Citral as food additive for common snook—Zootechnical parameters and digestive enzymes. Cien. Rural 2020, 50, e20190577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, V.M.; Cabral, H.; Pasquaud, S.; Vieira, J.P. Occurrence and abundance of young mullet Mugil liza (Teleostei: Mugilidae) in the surf zone along the southern coast of Brazil. Sci. Mar. 2021, 85, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppenfeld, C.C.; Toni, C.; Becker, A.G.; dos Santos Miron, D.; Parodi, T.V.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Koakoski, G.; Da Rosa, J.G.S.; Loro, V.L. Physiological and biochemical responses of silver catfish, Rhamdia quelen, after transport in water with essential oil of Aloysia triphylla (L‘Herit) Britton. Aquaculture 2014, 418, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelotti, B.T.; Passini, G.; Carvalho, C.; Salbego, J.; Mori, N.C.; Vieira, R.; Baldisserotto, B.; Cerqueira, V.R. Growth and metabolic parameters of common snook juveniles raised in freshwater with different water hardness. Aquaculture 2018, 482, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M.C.; Urea, E.; Sanz, A. Comparative study of digestive enzymes in fish with different nutritional habits. Proteolytic and amylase activities. Aquaculture 1999, 170, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, B.C.W. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawlicka, A.; Parent, B.; Horn, M.H.; Ross, N.; Opstad, I.; Torrissen, O.J. Activity of digestive enzymes in yolk-sac larvae of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus): Indication of readiness for first feeding. Aquaculture 2000, 184, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernfeld, P.; Colowick, S.P. Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 149. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.T.; Johnson, M.J. A submicrodetemination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 181, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farra, L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, J.R.; Brown, C.H. Blood lactic acid–a micromethod adapted to field collection of microliter samples. J. Appl. Physiol. 1972, 32, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergren, E.; Nourooz-Zadeh, J.; Berglund, L.; Vessby, B. Re-evaluation of the ferrous oxidation in xylenol orange assay for the measurement of plasma lipid hydroperoxides. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1998, 37, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, H.P.; Fridovich, I. The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 3170–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boveris, A.; Chance, B. Mitochondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide. General properties and effect of hyperbaric oxygen. Biochem. J. 1973, 134, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flohé, L.; Gunzler, W.A. Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-transferases the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, J. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, J.B.; Sharp, G.J.E.; Secombes, C.J.; Robertsen, B. Effect of a yeast-cell-wall glucan on the bactericidal activity of rainbow trout macrophages. Fish Shellfish Immun. 1993, 3, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quade, M.J.; Roth, J.A. A rapid, direct assay to measure degranulation of bovine neutrophil primary granules. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 58, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.F.S.; Garcia, A.M.; Vollrath, S.R.; Schneck, F.; Silva, C.F.M.; Marchetti, I.J.; Vieira, J.P. Spatial diet overlap and food resource in two congeneric mullet species revealed by stable isotopes and stomach content analyses. Community Ecol. 2018, 19, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, P.; Zitterl-Eglseer, K.; Köhler, B.; Gabler, C.; Losa, R.; Zimpernik, I. The effect of two different blends of essential oil components on the proliferation of Clostridium perfringens in the intestines of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutili, F.J.; Kreutz, L.C.; Flores, F.C.; da Silva, C.D.B.; Kirsten, K.S.; Voloski, A.P.D.S.; Frandoloso, R.; Pinheiro, C.G.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Baldisserotto, B. Effect of dietary supplementation with citral-loaded nanostructured systems on innate immune responses and gut microbiota of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen). J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, K.; Mei, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Guan, Y.; Pang, H.; Wang, Y. The effect of dietary lactic acid bacteria on intestinal microbiota and immune responses of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) under water temperature decrease. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 847167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.N.; Rauf, A.; Fahad, F.I.; Emran, T.B.; Mitra, S.; Olatunde, A.; Shariati, M.A.; Rebezov, M.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Mubarak, M.S. Superoxide dismutase: An updated review on its health benefits and industrial applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7282–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho e Martins, M.D.C.; Martins Oliveira, A.S.S.S.; da Silva, L.A.A.; Primo, M.G.S.; Lira, V.B.D.C. Biological indicators of oxidative stress [malondialdehyde, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase] and their application in nutrition. In Biomarkers in Nutrition; Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications; Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Alavez, M.; De Anda-Montañez, J.A.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Comparative study of enzymatic antioxidants in muscle of elasmobranch and teleost fishes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 187, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surai, P.F.; Surai, A. Antioxidant defence systems in health and diseases. In Silymarin Puzzle; Surai, P.F., Surai, A., Eds.; Wageningen Academic: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Averill-Bates, D.A. The antioxidant glutathione. In Vitamins and Hormones; Litwack, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 109–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sagheer, A.A.; Mahmoud, H.K.; Reda, F.M.; Mahgoub, S.A.; Ayyat, M.S. Supplementation of diets for Oreochromis niloticus with essential oil extracts from lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) and geranium (Pelargonium graveolens) and effects on growth, intestinal microbiota, antioxidant and immune activities. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 24, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.H.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Xu, P.; Xie, J. Effects of dietary reduced glutathione on growth performance, non-specific immunity, antioxidant capacity and expression levels of IGF-I and HSP70 mRNA of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2015, 438, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.S.; Singh, S.P.; Singhal, P.; Horne, D.; Singhal, J.; Awasthi, S. Antioxidant role of glutathione S-transferases: 4-Hydroxynonenal, a key molecule in stress-mediated signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2015, 289, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Murakami, A.; Ohigashi, H.; Osawa, T.; Uchida, K. A phase II detoxification enzyme inducer from lemongrass: Identification of citral and involvement of electrophilic reaction in the enzyme induction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 302, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, J.W.; Warne, R.W. Captivity and animal microbiomes: Potential roles of microbiota for influencing animal conservation. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 820–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. The effects of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) essential oil on the stress response, anti-oxidative ability, and kidney metabolism of sea bass during live transport. Animals 2022, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, T.; Varshney, C.; Khan, A.; Singh, B.; Jainer, S.; Tiwari, A.K.; Nagarjan, K.; Singh, A.P. Pharmacological potential of lemongrass oil: A systematic review and meta analysis. Biochem. Cell. Arch. 2024, 24, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyková, I.; Žák, J.; Blažek, R.; Reichard, M.; Součková, K.; Slabý, O. Histology of major organ systems of Nothobranchius fishes: Short-lived model species. J. Vertebr. Biol. 2022, 71, 21074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).