Protective Effects of Long Double-Stranded RNA with Different CpG Motifs against Miamiensis avidus and Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV) Infections in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vector Construction
2.2. dsRNA Transcription and Isolation
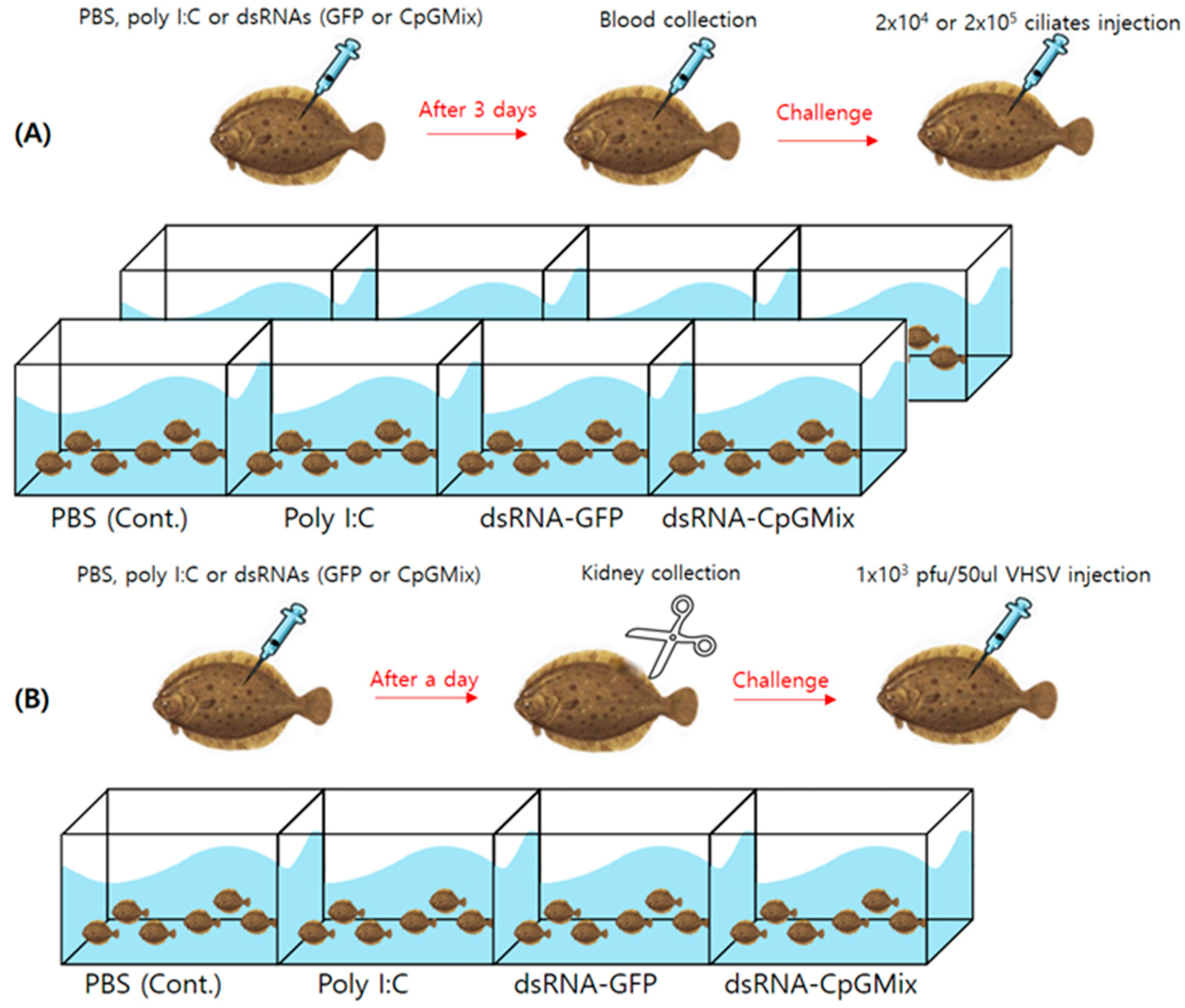
2.3. Immunostimulation and Challenge
2.4. Serum Scuticocidal Activity
2.5. Semi-Quantitative Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
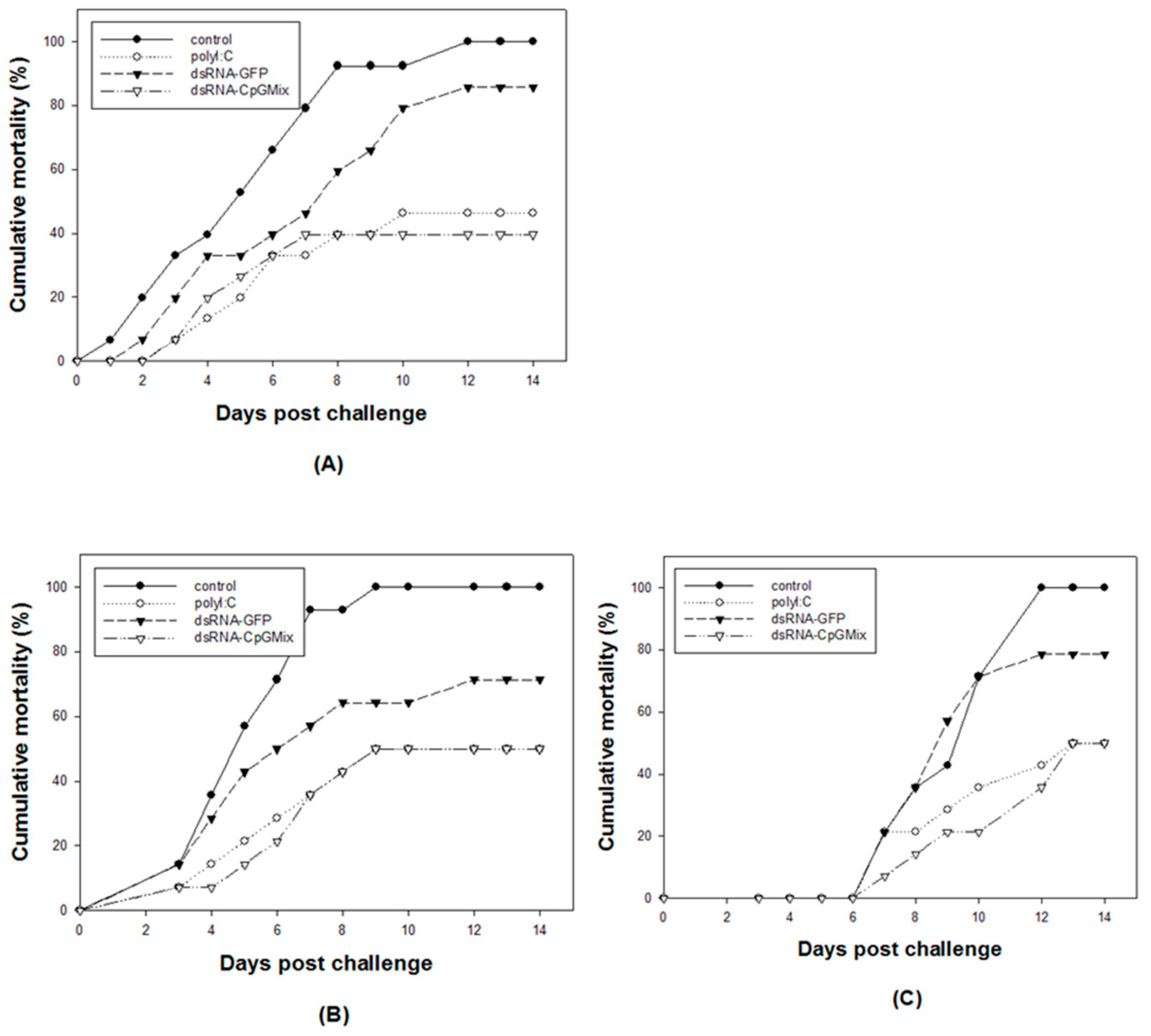
3.1. Effects of Long Double-Stranded RNA Containing the ODN Mix6 Motif against VHSV Infection in Olive Flounders
3.2. Effects of Long Double-Stranded RNA Containing CpG Motifs against M. avidus Infection in Olive Flounders
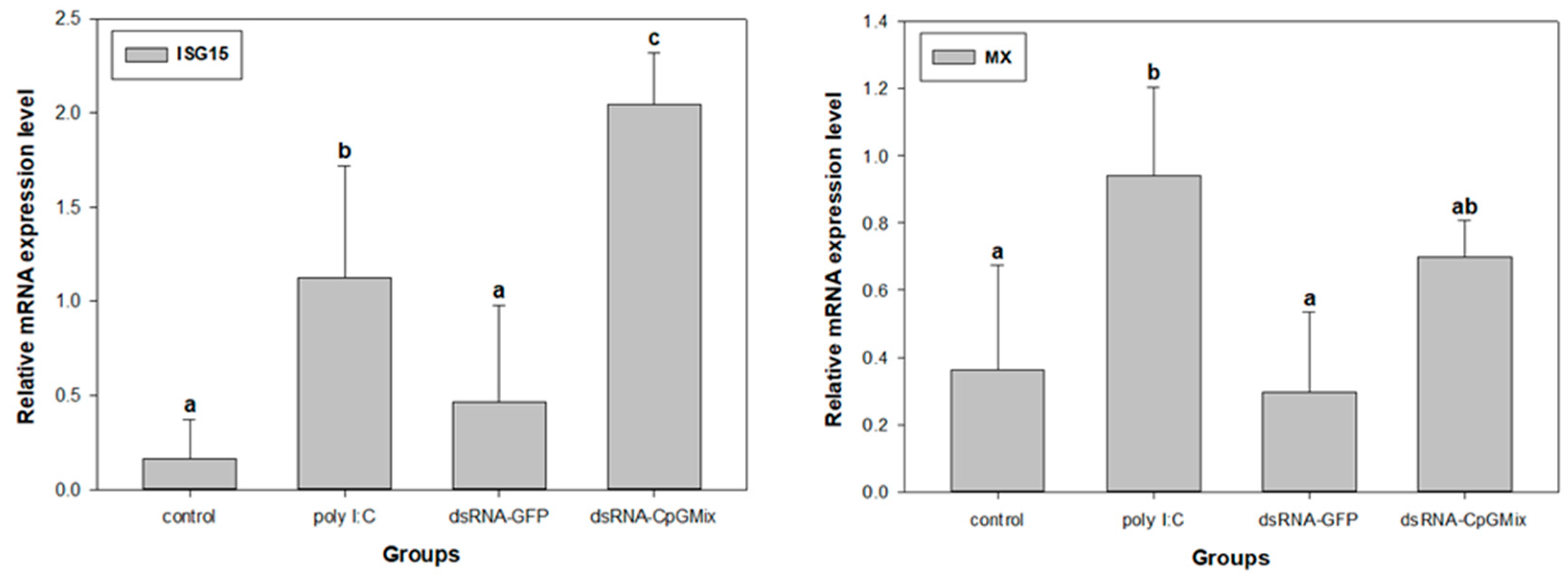
3.3. Gene Expression in Olive Flounders
3.4. Scuticocidal Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, C. A Study on Disaster Risk Management of the Aquaculture Industry. 2017. Available online: https://www.kmi.re.kr/web/contents/contentsView.do?rbsIdx=221 (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Sohn, K.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, J.D.; Han, I.K. The role of immunostimulants in monogastric animal and fish. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 13, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, A.M.; Yi, A.K.; Matson, S.; Waldschmidt, T.J.; Bishop, G.A.; Teasdale, R.; Koretzky, G.A.; Klinman, D.M. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation. Nature 1995, 374, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinman, D.M.; Yi, A.K.; Beaucage, S.L.; Conover, J.; Krieg, A.M. CpG motifs present in bacteria DNA rapidly induce lymphocytes to secrete interleukin 6, interleukin 12, and interferon gamma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2879–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, A.M.; Hartmann, G.; Yi, A.K. Mechanism of action of CpG DNA. In Immunobiology Bacterial CpG-DNA; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, A.P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, A.P. CpG islands as gene markers in the vertebrate nucleus. Trends Genet. 1987, 3, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kataoka, T.; Kuramoto, E.; Yano, O.; Tokunaga, T. Unique palindromic sequences in synthetic oligonucleotides are required to induce IFN [correction of INF] and augment IFN-mediated [correction of INF] natural killer activity. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 4072–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballas, Z.K.; Rasmussen, W.L.; Krieg, A.M. Induction of NK activity in murine and human cells by CpG motifs in oligodeoxynucleotides and bacterial DNA. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1840–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, A.M. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA and their immune effects. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 709–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinman, D.M. Immunotherapeutic uses of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Kaisho, T.; Sato, S.; Sanjo, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Hoshino, K.; Wagner, H.; Takeda, K.; et al. A toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 2000, 408, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.B.; Johansen, A.; Stenersen, B.; Sommer, A.I. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides and plasmid DNA stimulate Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) leucocytes to produce supernatants with antiviral activity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, A.M. CpG motifs: The active ingredient in bacterial extracts? Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.H. Effect of CpG-ODNs belonging to different classes on resistance of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) and Miamiensis avidus (Ciliata; Scuticociliatia) infections. Aquaculture 2012, 324–325, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.H. Therapeutic potential of CpG-ODN 1668 against scuticociliatosis in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2014, 430, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumouna, M.; Jaso-Friedmann, L.; Evans, D.L. Activation of nonspecific cytotoxic cells (NCC) with synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides and bacterial genomic DNA: Binding, specificity and identification of unique immunostimulatory motifs. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2002, 26, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassakka, A.C.M.A.R.; Sakai, M. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides enhance the non-specific immune responses on carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 2002, 209, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Shao, J.; Xiang, L. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides activate grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) macrophages. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellos, T.S.; Sylvester, I.D.; Butler, V.L.; Ambali, A.G.; Partidos, C.D.; Hamblin, A.S.; Russell, P.H. Mammalian granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor and some CpG motifs have an effect on the immunogenicity of DNA and subunit vaccines in fish. Immunology 1999, 96, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, J.B.; Zou, J.; Johansen, A.; Secombes, C.J. Immunostimulatory CpG oligodeoxynucleotides stimulate expression of IL-1β and interferon-like cytokines in rainbow trout macrophages via a chloroquine-sensitive mechanism. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.C.; Kang, Y.J. Effects of a subunit vaccine (FlaA) and immunostimulant (CpG-ODN 1668) against Vibrio anguillarum in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2016, 454, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.H.; Jung, S.J. CpG ODN 1668 induce innate and adaptive immune responses in rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) against rock bream iridovirus (RBIV) infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 69, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.F.; Deng, Y.Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.J.; Han, J.F.; Cao, R.Y.; Qin, E.-D.; Qin, C.F. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides protect against the 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza virus infection in a murine model. Antivir. Res. 2011, 89, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamstrup, S.; Frimann, T.H.; Barfoed, A.M. Protection of Balb/c mice against infection with FMDV by immunostimulation with CpG oligonucleotides. Antivir. Res. 2006, 72, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, E.B.; Clements, J.D.; Voss, T.G.; Cárdenas-Freytag, L. Prophylactic administration of bacterially derived immunomodulators improves the outcome of influenza virus infection in a murine model. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2983–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, E.; Audigé, A.; von Beust, B.; Manolova, V.; Weber, M.; Joller, H.; Bachmann, M.F.; Kundig, T.M.; Speck, R.F. CpG oligodeoxynucleotides block human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in human lymphoid tissue infected ex vivo. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12344–12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wong, J.P.; Christopher, M.E.; Viswanathan, S.; Karpoff, N.; Dai, X.; Das, D.; Sun, L.Q.; Wang, M.; Salazar, A.M. Activation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway for protection against influenza virus infection. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3481–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.P.; Nagata, L.P.; Christopher, M.E.; Salazar, A.M.; Dale, R.M. Prophylaxis of acute respiratory virus infections using nucleic acid-based drugs. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2266–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Lee, C.R.; Kwon, J.Y.; Kang, Y.J. Protective effects of CpG-ODN 2007 administration against Edwardsiella tarda infection in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Sun, L. Identification and analysis of a CpG motif that protects turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) against bacterial challenge and enhances vaccine-induced specific immunity. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4153–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulou, L.; Holt, A.C.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by toll-like receptor 3. Nature 2001, 413, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmeier, M.R.; Scarim, A.L.; Corbett, J.A. Double-stranded RNA-induced inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression and interleukin-1 release by murine macrophages requires NF-κB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15301–15307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auch, C.J.; Saha, R.N.; Sheikh, F.G.; Liu, X.; Jacobs, B.L.; Pahan, K. Role of protein kinase R in double-stranded RNA-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase in human astroglia. FEBS Lett. 2004, 563, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulka, M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Flavell, R.A.; Metcalfe, D.D. Activation of mast cells by double-stranded RNA: Evidence for activation through toll-like receptor 3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, I.; Albuquerque, A.; Sommer, A.I.; Robertsen, B. Effect of poly I:C on the expression of Mx proteins and resistance against infection by infectious salmon anaemia virus in Atlantic salmon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 13, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, I.; Larsen, R.; Robertsen, B. An antiviral state induced in chinook salmon embryo cells (CHSE-214) by transfection with the double-stranded RNA poly I:C. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 13, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, I.; Robertsen, B. Effect of double-stranded RNA and interferon on the antiviral activity of Atlantic salmon cells against infectious salmon anemia virus and infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 13, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint-Jean, S.R.; Pérez-Prieto, S.I. Interferon mediated antiviral activity against salmonid fish viruses in BF-2 and other cell lines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 110, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, K.P.; Harbottle, H.; Thune, R.L. Poly I:C induces an antiviral state against Ictalurid herpesvirus 1 and Mx1 transcription in the channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Trujillo, A.; Ferro, P.; Garcia-Rosado, E.; Infante, C.; Alonso, M.C.; Bejar, J.; Borrego, J.J.; Manchado, M. Poly I:C induces Mx transcription and promotes an antiviral state against sole Aquabirnavirus in the flatfish Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Town, T.; Alexopoulou, L.; Anderson, J.F.; Fikrig, E.; Flavell, R.A. Toll-like receptor 3 mediates West Nile virus entry into the brain causing lethal encephalitis. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, O.; Diebold, S.S.; Chen, M.; Näslund, T.I.; Nolte, M.A.; Alexopoulou, L.; Azuma, Y.T.; Flavell, R.A.; Liljeström, P.; Sousa, C.R.e. Toll-like receptor 3 promotes cross-priming to virus-infected cells. Nature 2005, 433, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Hoshino, K.; Kaisho, T.; Sanjo, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sugiyama, M.; Okabe, M.; Takeda, K.; et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 2003, 301, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoebe, K.; Du, X.; Georgel, P.; Janssen, E.; Tabeta, K.; Kim, S.O.; Goode, J.; Lin, P.; Mann, N.; Mudd, S.; et al. Identification of Lps2 as a key transducer of MyD88-independent TIR signalling. Nature 2003, 424, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; tenOever, B.R.; Grandvaux, N.; Zhou, G.P.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 2003, 300, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meylan, E.; Burns, K.; Hofmann, K.; Blancheteau, V.; Martinon, F.; Kelliher, M.; Tschopp, J. RIP1 is an essential mediator of toll-like receptor 3–induced NF-κB activation. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Veer, M.J.; Holko, M.; Frevel, M.; Walker, E.; Der, S.; Paranjape, J.M.; Silverman, R.H.; Williams, B.R. Functional classification of interferon-stimulated genes identified using microarrays. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, A.; Oshiumi, H.; Tsujita, T.; Mitani, H.; Kasai, H.; Yoshimizu, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. Teleost TLR22 recognizes RNA duplex to induce IFN and protect cells from birnaviruses. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3474–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, T.; Takami, I.; Kokawa, Y.; Yoshimizu, M. Fish immunization using a synthetic double-stranded RNA Poly (I: C), an interferon inducer, offers protection against RGNNV, a fish nodavirus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 83, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinohe, T.; Watanabe, I.; Ito, S.; Fujii, H.; Moriyama, M.; Tamura, S.I.; Takahashi, H.; Sawa, H.; Chiba, J.; Kurata, T.; et al. Synthetic double-stranded RNA poly (I: C) combined with mucosal vaccine protects against influenza virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2910–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilleman, M.R. Double-stranded RNAs (poly I: C) in the prevention of viral infections. Arch. Intern. Med. 1970, 126, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, S.; Mori, K.; Hoshino, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Cutting edge: A novel Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter that preferentially activates the IFN-β promoter in the toll-like receptor signaling. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6668–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tort, L.; Balasch, J.C.; MacKenzie, S. Fish health challenge after stress. Indicators of immunocompetence. Contrib. Sci. 2004, 2, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, A.E. Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Preventive and therapeutic effects of auxotrophic Edwardsiella tarda mutant harboring CpG 1668 motif-enriched plasmids against scuticociliatosis in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 144, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, K.H. Protective potential of CpG 1668 motif-harbouring plasmids against Miamiensis avidus (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida) infection in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.H. Protective potential of a plasmid having different classes of CpG motifs against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus and Miamiensis avidus (Ciliata; Scuticociliatida) infections in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2015, 446, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Gursel, M.; Takeshita, F.; Coban, C.; Conover, J.; Kaisho, T.; Akira, S.; Klinman, D.M.; Ishii, K.J. CpG RNA: Identification of novel single-stranded RNA that stimulates human CD14+CD11c+ monocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.-J.; Choi, D.-Y.; Park, J.-J.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, B.-S.; Hong, S.-C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kang, Y.J. Protective Effects of Long Double-Stranded RNA with Different CpG Motifs against Miamiensis avidus and Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV) Infections in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fishes 2024, 9, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060227
Choi H-J, Choi D-Y, Park J-J, Jung HJ, Kim B-S, Hong S-C, Kim J-H, Kang YJ. Protective Effects of Long Double-Stranded RNA with Different CpG Motifs against Miamiensis avidus and Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV) Infections in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fishes. 2024; 9(6):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060227
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hee-Jae, Da-Yeon Choi, Jung-Jin Park, Hye Jin Jung, Bo-Seong Kim, Sung-Chul Hong, Jun-Hwan Kim, and Yue Jai Kang. 2024. "Protective Effects of Long Double-Stranded RNA with Different CpG Motifs against Miamiensis avidus and Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV) Infections in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)" Fishes 9, no. 6: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060227
APA StyleChoi, H.-J., Choi, D.-Y., Park, J.-J., Jung, H. J., Kim, B.-S., Hong, S.-C., Kim, J.-H., & Kang, Y. J. (2024). Protective Effects of Long Double-Stranded RNA with Different CpG Motifs against Miamiensis avidus and Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV) Infections in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fishes, 9(6), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060227






