Abstract
This study investigated the effects of environmental changes on zebrafish larval behavior, using single-factor and orthogonal experiments to assess locomotion during temperature and pH changes. In single-factor experiments, zebrafish larvae were exposed to variations in temperature (22 to 30 °C) and pH levels (6.0, 7.0, 9.0). The simultaneous temperature and pH changes were investigated by orthogonal tests. In both experiments, each zebrafish larva was recorded in three 5 min videos at different stages (before exposure, during short-term exposure (10 min), and after long-term exposure (60 min)). You Look Only Once (YOLOv5) and Deep Simple Online Real Time Tracking (DeepSORT) models were adopted to develop a zebrafish larva tracking system, and YOLOv5 was improved in two aspects of anchor clustering and network structure. The tracking accuracy of the tracking system for small targets effectively improved, reaching more than 98% MOTA (Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy). Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was employed to extract three behavioral features from 13 motion parameters, namely motion activity, edge behavior, and motion direction preference. Our findings reveal that lower temperatures and acidic conditions both led to a decrease in motion behavioral activity, and the former also increased edge behavior. Conversely, elevated temperatures and alkaline conditions had a muted impact on these behaviors. Interestingly, concurrent changes in temperature and pH significantly altered directional preference. Additionally, we observed that lower temperatures elicited distinct temporal behavioral patterns at a constant pH level. In summary, we recommend the precise control and explicit reporting of ambient temperature and pH in both breeding devices and experimental wells to minimize the environmental impact on zebrafish behavior and enhance experiment repeatability and reliability.
Keywords:
zebrafish larvae; locomotor behavior; learning-based tracking; orthogonal experiments; principal component analysis; drug development Key Contribution:
This study introduces an advanced tracking system for zebrafish larvae behavior analysis, significantly enhancing the accuracy of locomotor behavior tracking through the optimization of YOLOv5 and DeepSORT models. Our findings underscore the critical impact of environmental factors, specifically temperature and pH, on zebrafish larval behavior, emphasizing the necessity for precise environmental control in behavioral assays.
1. Introduction
Zebrafish, a classical vertebrate model, shares approximately 70% of its genome with humans, and has homology with around 82% of human disease-related genes [,]. Leveraging this genetic proximity, zebrafish are widely used in biological experiments, drug screening, genetic screening, and neurotoxicity analysis [,]. Zebrafish larvae are characterized by their small size, high transparency, prolific reproduction, rapid growth and development, and low-cost maintenance. These attributes make zebrafish larvae invaluable in drug discovery, significantly enhancing research and development efforts [,].
The quantitative analysis of zebrafish behavioral phenotypes can serve as a valuable tool for studying drug effects and mechanisms of action [,,,,,]. Additionally, it can provide insights into the psychological state of zebrafish []. In one study, anxiety-like symptoms induced by Isoliquiritigenin in zebrafish larvae were demonstrated through the quantification and analysis of behavioral parameters, including measures such as distance traveled and average speed [,]. In toxicology, the behavioral analysis of zebrafish can be employed to evaluate the impact of toxicants on animal and neurological function [,]. A study on the environmental concentration of eight drugs, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-convulsant drugs, was conducted to assess the behavior of zebrafish larvae []. The analysis of locomotor parameters, such as mean velocity, angular velocity, etc., confirmed the sensitivity of zebrafish during their early developmental stages to toxic substances [,]. This sensitivity allowed them to respond to the adverse effects of these substances on the aquatic system [].
It has been established that handing methods and environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, environmental enrichment, etc., affect multiple locomotion endpoints in animals [,,,]. The locomotor behavior of zebrafish larvae and adults is primarily influenced by temperature [,,]. Several studies have confirmed that the optimal water temperature for adult zebrafish swimming falls between 16 °C and 30 °C, with significantly decreased swimming speeds at high and low temperatures []. Heat treatment at 34 °C was observed to reduce anxiety, increase boldness, and decrease group behavior in zebrafish []. Similarly, zebrafish larvae exhibit a significant overall decrease in activity levels at high and low temperatures []. This considerable temperature difference can exert an influence on the swimming behavior of zebrafish larvae. However, the disparities in environmental conditions between the experimental chamber and the incubator are frequently overlooked. While ambient and incubator water temperatures are typically explicitly documented, details regarding the observed temperature of the chamber and the utilization of temperature control devices are seldom mentioned. Previous works compared six behavioral phenotypes in zebrafish larvae exposed to 24 °C, 28 °C, and 30 °C. They observed that temperature changes before and after the experiments led to significant differences in zebrafish speed, resting time, and absolute turning angle []. However, the above studies did not consider the behavioral phenotypic differences within smaller temperature intervals across a broader temperature spectrum. In the experiments, we found that even though the laboratory temperatures were consistently set at 26 °C, the water temperature inside the Petri dish dropped to a minimum of 22 °C. The water temperature in the experiment chamber reached a maximum of 30 °C, influenced by factors such as the temperature control device, air flow conditions, and electronic lighting equipment. Without a temperature control device, the temperature difference before and after the experiment was at minimum 2 °C. Additionally, in drug or behavioral experiments, it is often necessary to analyze the behavior of larvae for at least one hour or more after exposure [,,] because the behavior observed within the first 10 min or even 30 min after exposure may primarily represent short-term stress responses and may not accurately reflect the natural effect of exposure factors on the larvae.
PH is a critical factor influencing zebrafish larvae’s physiological response. As acidity or alkalinity levels increase, there is a significant decrease in the behavioral activity of zebrafish. The toxicity of certain drugs to aquatic organisms is also affected by pH, including drugs like fluoxetine, nicotine, and triclosan [,]. In the current study on zebrafish larvae, only 34.4% of the papers reported pH values ranging from 5.8 to 9.0 []. One study confirmed that the difference between pH 7.0 and 8.0 does not significantly affect the total distance travelled by zebrafish larvae []. However, it is currently unclear whether zebrafish larvae will display specific locomotor patterns when the difference in pH between experimental chambers ranges from 6.0 to 9.0. Meanwhile, the motion parameters referenced in this study [] are not comprehensive enough. In addition to the total distance traveled, various movement parameters are typically employed for the behavioral phenotypic analysis of multiple endpoints. These parameters include the absolute turning angle, frequency of immobility, and percentage of time spent moving at the edge of the well [,]. Multi-endpoint locomotor quantification is crucial in unveiling intricate behavioral patterns and psychological states, including fear and anxiety.
In this study, a series of experiments were conducted to investigate the impact of temperature and pH on the locomotor behavior of zebrafish larvae. One-factor experiments were performed on zebrafish larvae at 7 days post-fertilization, subjecting them to various temperature conditions (22 °C, 24 °C, 26 °C, 28 °C, 30 °C) and pH levels (6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0). Their locomotor behavior was recorded at multiple time points after exposure, including 0 min, 10 min, and 60 min. Furthermore, an orthogonal experiment was conducted to examine the combined effects of temperature and pH on zebrafish larval behavior, addressing the existing research gap in this area.
To comprehensively analyze the behavior of zebrafish larvae, a set of 13 locomotion parameters was defined and quantified to describe their locomotor states. Unlike previous studies, this research validated the Principal Component Analysis’s effectiveness in extracting zebrafish’s meaningful locomotor behavior features. These features were found to have significant statistical relevance in behavioral analysis, providing a novel approach to analyzing zebrafish larval locomotor behavior.
In this study, we present a sophisticated tracking system tailored for zebrafish larvae, leveraging the YOLOv5 [] pedestrian tracking model and the DeepSORT [] algorithm. It is worth noting that in this paper, YOLOv5m-ss, a detection model for zebrafish larvae, is proposed. The model is obtained by improving the anchor clustering method and network structure on the basis of the YOLOv5 model. Complementing these improvements, we introduced a dedicated zebrafish larva body dataset designed to train detection and tracking models. The proposed tracking system exhibits reduced dependency on image resolution, a notable departure from conventional methods. By addressing challenges posed by image noise, such as variations in light, shadows, and impurities, our system achieves heightened tracking accuracy.
The primary aim of this study is to investigate the influence of temperature and pH variations among experimental wells. This study uses the improved zebrafish larvae tracking system based on YOLOv5 and DeepSROT to study locomotor behaviors. In addition, 13 defined motor parameters were used to quantify the motor performance of zebrafish juveniles. Finally, the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [] method was introduced to extract the behavioral features, and the statistical analysis was carried out based on the features. It was confirmed that the temperature and PH value exerted either promoting or inhibitory effects on distinct locomotor behavior traits, with interactive effects observed when both variables changed simultaneously. Moreover, the enhanced tracking system improved accuracy, greatly facilitating behavioral analysis experiments. Furthermore, the results of this study provided evidence for the effectiveness and feasibility of employing PCA in locomotor behavior analysis. This approach effectively reduced data dimensions while enhancing interpretability, thus facilitating the intuitive analysis of specific behavioral patterns.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Breeding and Housing
All the zebrafish larvae utilized in the experiment were offspring from 30 adult zebrafish males and 30 adult zebrafish females raised and maintained in the laboratory. Adult zebrafish were housed at a density of 0.05 fish/L in tanks of size 38 × 26 × 38 (length × width × height) designed by the SUNSUN company, and the water depth in the tank was approximately 33 ± 2 cm. Each tank is equipped with a water circulation system, filtration system, and oxygen pump. The water temperature was maintained at 27.5 ± 0.5 °C by the AH-300 heating rod designed by SUNSUN, the pH was maintained in the range of 7.5 to 8.0 by regular water changes, and the cycle of light and dark time was set to 14 h:10 h by the tank. The night before embryo collection, six adult zebrafish were housed in spawning boxes separated by transparent partitions, with a 1:1 ratio of zebrafish females to males. According to zebrafish feeding recommendations, these partitions were removed after three hours, and the adult zebrafish were returned to the tank 4 h after the next day’s dawn []. Embryos were gathered from the spawning box and placed in a beaker with a blue methylene solution. These embryos were transferred to a controlled environment within a tank, maintaining a temperature of 28 °C. At three days post fertilization (dpf), the embryos hatched, developing into larvae, and at 4 dpf, they began exhibiting spontaneous locomotor behavior. Given the analytical requirements in biomedical experiments, zebrafish larvae at 7 dpf larvae are typically considered to be at a moderate stage of development []. They show motor coordination, possess high body transparency, and are highly maneuverable. In this study, 7 dpf zebrafish larvae were employed to develop a trajectory tracking system.
2.2. Tracking System for Zebrafish Larvae
Accurately tracking the trajectories and positional information of zebrafish larvae during their movements is a fundamental prerequisite for conducting behavioral analyses. Advances in machine learning have provided ways to analyze animal behavior from large amounts of data [,,,,,]. Animal tracking algorithms and methods are commonly used in the analysis of larvae locomotor behavior (Table 1). However, these methods have certain limitations when tracking zebrafish larvae. They typically require high video resolutions and specific experimental setups. Moreover, they are sensitive to factors like variations in lighting, the presence of bubbles, and shadows. Importantly, they can experience target loss or trajectory connection errors when larvae are occluded or undergo shape deformations.

Table 1.
Functionality of the zebrafish tracking software and algorithm.
In this paper, the developed zebrafish tracking system is improved based on our preliminary work with YOLOv5 [] and DeepSORT []. YOLOv5 was utilized and improved for detecting the position of zebrafish larvae, while the DeepSORT [] model was used to identify individual differences in larvae and track their motion trajectories. The workflow of the algorithm is shown in Figure 1. The detection and tracking results are shown in Figure 2A and Figure 2B, respectively. Initially, zebrafish larval images were manually annotated and processed to create a dataset for detection and tracking. Each larva in every image is labeled with a bounding box containing category and positional information. During the training process of YOLOv5, the model extracts and learns features of zebrafish larvae from annotated regions. Subsequently, based on the known features, the model predicts the position and category of each zebrafish larva, adjusting network weights according to the accuracy of predictions. The trained model can accurately detect the location of a zebrafish larva labeled in the form of a detection box and outputs relevant information, including the detected frame number (frame), the upper-left corner coordinates of the detection box, the width and height (x, y, w, h), and the confidence in it being detected as that category. DeepSORT is a tracking algorithm that combines neural networks. The re-identification (re-id) network identifies the identities of zebrafish larvae by matching their appearance features, while the motion model identifies their identities based on matching individual motion states. By combining appearance and motion states, zebrafish larvae can be accurately tracked, even if temporarily occluded or if their motion states change rapidly. Cascade-matching techniques connect the motion trajectories of these targets, ensuring precise continuous tracking even in complex scenarios with occlusions or intermittent appearances. Finally, the system outputs the trajectory information file of each larva, which records the identity sequence number (ID) of the larva in a time series (frames), the upper-left corner coordinates, and the width and height (x, y, w, h) of the detection box corresponding to each ID. In this work, the detection model is improved in three key aspects: (1) the refinement of dataset annotation methods, (2) the optimization of anchor-clustering techniques, and (3) modifications to the network structure and feature fusion scales. The resulting YOLOv5m-ss significantly improves the detection performance, tailored explicitly for zebrafish larvae. These changes will be detailed in Section 2.2.1, Section 2.2.2 and Section 2.2.3
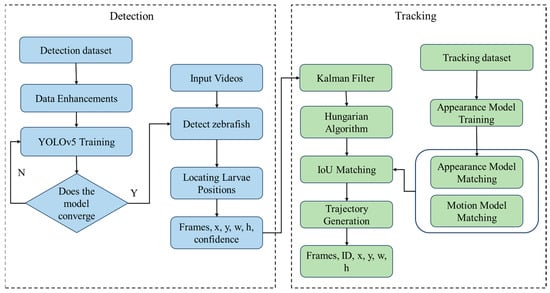
Figure 1.
Flowchart of zebrafish larvae tracking system.
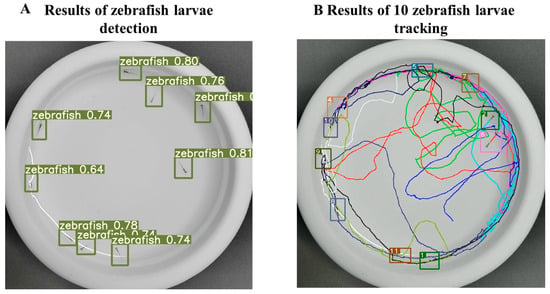
Figure 2.
Detection and tracking results of the zebrafish tracking system. (A) Results of multi-object detection: 10 larvae have been detected and are marked with a green detection box. The top of the detection box is the detected target category and the confidence of the detection category. (B) Trajectories of the zebrafish tracking system. Each tracking box represents a detected larva, and the upper left corner of the tracking box is the ID of the larva. Each line represents the trajectory of a larva, which is connected according to the ID of the larvae.
2.2.1. Preparation of the Dataset
In this work, a dataset with the body as the object of feature extraction was created for detection and tracking model training. As shown in Figure 3A,B, in previous studies [,], detection and tracking are usually achieved based on the local features of zebrafish. In previous studies, most algorithms use fisheyes as the feature to realize the detection of zebrafish larvae []. Figure 3A shows the feature annotation diagram of the fisheye dataset, where the enlarged example of the fisheye part is marked with a blue border on the left. In addition to the fisheyes, the fisheye and yolk of juvenile fish can also be used as detection features [], as shown in Figure 3B in a schematic diagram of the feature markers of the eye and yolk. However, local features such as the egg yolk and fisheyes have some limitations in practical applications. Due to the small size and dimension of local features, it is easy to miss detection due to occlusion or to learn local optimal features, resulting in higher false optimistic prediction. In this study, we employed DarkLabel software (version 2.4) to label the entire fish body, as depicted in Figure 3C. The detection dataset was then reconstructed for YOLOv5 network training, comprising 2097 images with dimensions of 720 × 720 and 544 × 544 pixels, respectively.
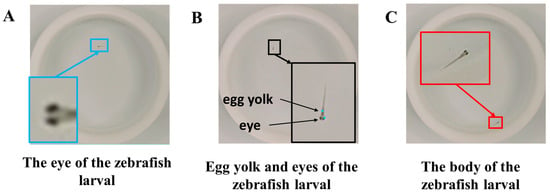
Figure 3.
Comparison of characteristics in the zebrafish larval dataset and the detection performance of the enhanced model (The colored boxes are zoomed-in images for clarity). (A) Annotation of the dataset using zebrafish larvae eyes as reference points. (B) Annotation of the dataset with crucial points at the egg yolk and eyes. (C) Annotation of the dataset based on zebrafish larvae body features.
In the tracking algorithm section, we performed individual cropping and sorting of the detection dataset based on the unique identity of each larva, resulting in Re-identification (Re-id) datasets comprising three distinct zebrafish larva identities. Each identity consists of 300 images, which were employed to train the Re-id network of the tracking model. Figure 4A–C show pictures of three juvenile fish with different identities, respectively, and each juvenile fish is assigned a unique identity identifier. The re-identification network assigns the identity number of the juvenile fish according to its appearance characteristics.
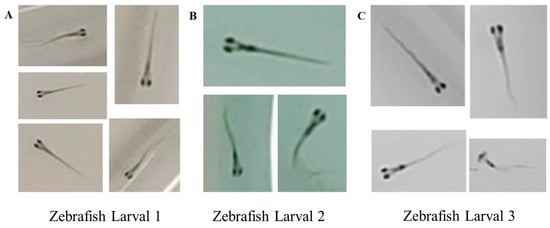
Figure 4.
Samples of different zebrafish larvae identities from the Re-id dataset. (A) Example of the re-identification data plot for zebrafish juvenile 1. (B) Example of the re-identification data plot for zebrafish juvenile 2. (C) Example of the re-identification data plot for zebrafish juvenile 3.
Figure 5 shows the feature map comparison of the two networks detecting the same image. This feature map is presented as a heatmap, where lighter colors represent a higher activation of the feature. (A) is the detected image, and (B) and (C) are the feature maps output by the YOLOv5 model trained on the fisheye dataset and the body dataset after detecting Figure (A), respectively. Panel (B) focuses on the local features associated with the eyes, while in panel (C), more features are extracted, including body contour, length, shape, and eyes. Despite the significance of the fisheye, training with the whole body proved advantageous, allowing the model to fuse multi-scale features and significantly improve the prediction accuracy.
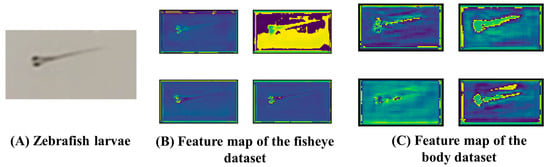
Figure 5.
Comparison of feature maps of an image between the fisheye dataset and body dataset detection. (A) Image of the detected zebrafish. (B) Feature map visualization of YOLOv5 model trained on the fisheye dataset during detection panel (A). (C) Feature map visualization of YOLOv5 model trained on the body dataset during detection panel (A).
2.2.2. Improvement of Anchor Clustering
Before the detection model training, YOLOv5 predefined some anchor boxes. The anchor box predefined the object size at multiple scales to provide prior knowledge when generating candidate bounding boxes, thus improving detection speed and accuracy. Given the limited sample size of the dataset used in the experiment, in this work, the K-means++ algorithm was used to generate the adaptive anchor box for label clustering in the dataset, aiming to avoid the issue of selecting the local optimal anchor boxes. The clustering process is shown in Figure 6. First, a data point is randomly chosen as the cluster center. Then, the distance between the other points and the centroid is calculated, and the data point with the furthest distance is taken as the next center point. The previous step is repeated until all anchors have been selected. This initialization strategy helps reduce the probability of convergence to local minima and improves the clustering accuracy.
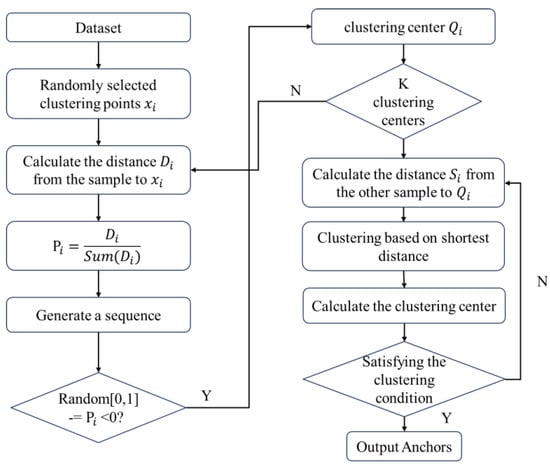
Figure 6.
Flowchart of anchor clustering using K-means ++.
2.2.3. Structural Changes in the Neural Network
YOLOv5m used three detection layers (20 × 20 , 40 × 40 , and 80 × 80 ) for large, medium, and small three-dimension target detection. In this study, anchor-clustering results showed that the length and width of the bounding box of zebrafish larvae were roughly between 30 and 60 pixels. This means that zebrafish larvae are relatively small objects (less than 0.12% of the image pixels). The larger detection layers used, 40 × 40 and 20 × 20, were considered unable to capture small-scale zebrafish larvae effectively. Their inclusion tends to shift the model’s attention to irrelevant features, such as dust, highlights, and shadows in the background, leading to false recognition.
In this work, YOLOv5m-ss is proposed to improve the prediction accuracy for zebrafish larvae. The network structure removes the large and medium detection layers, changes the feature fusion path of the small detection layer, and adds a small detection layer. Figure 7 shows the structure of the network and the change process of the feature map scale (width × height × channel).
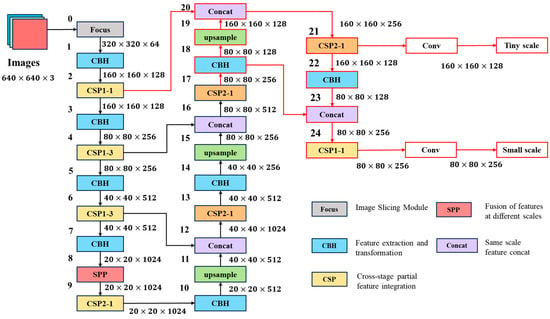
Figure 7.
Schematic of the improved YOLOv5 network structure.
In this work, the two 40 × 40 and 20 × 20 detection layers and their corresponding feature fusion paths are removed from YOLOv5m. Instead, it employs the continuous neck convolution activated by the hardswish function (CBH) structure to continue feature extraction from the output of the 17 layers, reducing channel dimensions to 256 through a 1 × 1 convolution kernel. Subsequently, normalization and activation layers standardize and learn non-linear relationships within the model.
The 80 × 80 × 256 feature maps from CBH were upsampled to 160 × 160 × 128 and concatenated with the second layer’s output to yield 160 × 160 × 256 for the tiny detection layer. A CBH module doubled the feature map size to 80 × 80 × 128, and the 18th layer’s output was spliced to achieve the 80 × 80 × 256 feature map. Employing a Cross-stage Local Structure (CSP) enhances the model’s feature extraction capabilities, culminating in a new small detection layer (80 × 80 × 256). This layer amalgamates finer shallow features with deeper semantic features, augmenting the sensitivity to small objects.
In this study, three network models were trained on both the fisheye dataset and the body dataset. The training results of the models are shown in Table 2, where the detection accuracy of the proposed model, YOLOv5m-ss, is significantly improved, with a mean Average Precision at 0.5 Intersection over the Union threshold (mAP@0.5) reaching 99.9% at a 0.5 Intersection over Union threshold. Additionally, five videos were captured to evaluate the overall tracking performance of the algorithm. In these videos, each larva was initially assigned a unique identity label, typically represented by a number. Subsequently, the actual motion positions of the larvae were annotated according to their identity labels, which served as the ground truth (GT). The evaluation results of the tracking algorithm are presented in Table 3, where “GT” denotes the ground truth dataset, followed by the corresponding video numbers, each having varying numbers of larvae, total frames, and resolutions. In this study, the algorithm’s tracking performance was primarily assessed using five metrics.

Table 2.
Performance of object detection model evaluation, where mAP@0.5 represents the average of the average precision of the algorithm to detect different classes of objects when the IoU is 0.5.

Table 3.
Performance of tracking model evaluation. This table shows the tracking evaluation results of the proposed zebrafish juvenile tracking system on five homemade ground truth datasets. GT denotes the ground truth dataset, and the following number is the video number, represents the number of undetected real targets, represents the number of falsely detected false targets, represents the number of identity switches of the trajectory, MOTA is the multi-target tracking accuracy, and MOTP is the multi-target tracking precision.
The study additionally captured 5 videos for evaluating the overall tracking performance of the algorithm. In the videos, it is first necessary to assign a unique identity label to each larva, which is usually represented by numbers, and then to annotate the actual motion positions of the larva based on the identity label, i.e., ground truth. The evaluation results of the tracking algorithm are shown in Table 3, where GT represents the ground truth dataset, followed by the video number, and the number of larvae, total frames, and resolutions are different in each video. In this study, the tracking performance of the algorithm is mainly evaluated through five indicators. Among them, represents the number of missed detections of the target; represents the number of false detections of the target; represents the number of identity label switches of the target in the entire video sequence (for example, the 6 larvae in GT1 underwent a total of 7 identity label switches in 1781 frames); MOTA is used to measure the accuracy of the entire multi-target tracking task; and MOTP is used to measure the precision of multi-target tracking. Table 3 shows that the tracking system proposed reaches the Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy (MOTA) at 98.1%.
Figure 8 compares feature maps produced by detection models with different network structures when detecting the same image. Based on the results shown in Figure 8B, YOLOv5m shows promising larvae position detection. However, the network of YOLOv5m tends to focus excessively on the noise around the center of the culture dish and shadows in the upper left corner. In contrast, the red box in Figure 8B shows a more distinct contrast with the culture dish, indicating that YOLOv5m-s provides a more precise detection of the larvae’s position. However, it also demonstrates reduced robustness against interference from the center of the culture dish and the background. Figure 8D shows the feature map of the YOLOv5m-ss model proposed in this paper, which is more accurate for the positioning of larvae and effectively suppresses the expression of interference noise, such as shadows and impurities in the background. The ability of the model to learn fine-grained features has been effectively enhanced so that more and more accurate target-related information can be extracted.
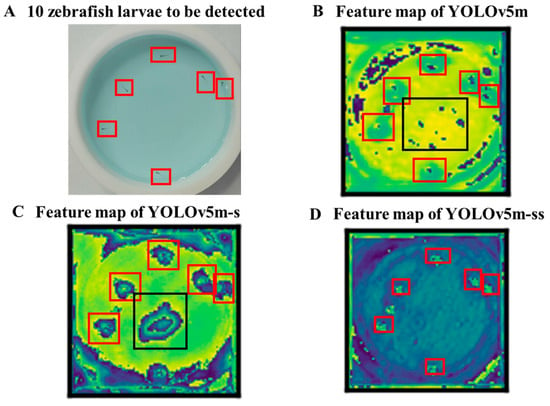
Figure 8.
Feature map comparison of CSP output. (A) The image under examination; (B–D) correspond to the feature maps output by YOLOv5m, YOLOv5-s (model retaining only the small detection layer), and YOLOv5-ss (improved model with an additional tiny detection layer), respectively. Red bounding boxes delineate the positions of zebrafish larvae. The black boxes indicate the impurity noise in the background.
2.3. Experimental Design
In this experiment, two environmental variables, temperature and pH, were manipulated. To investigate the influence of each factor on the swimming behavior of zebrafish larvae, we conducted a preliminary single-factor behavioral experiment. To minimize the impact on larval growth and development, we established five temperature levels, 22 °C, 24 °C, 26 °C, 28 °C, and 30 °C, while maintaining a pH of 8.0 based on the environmental adaptability of zebrafish and typical experimental conditions. In addition, we introduced four pH levels, pH 6.0, pH 7.0, pH 8.0, and pH 9.0, while keeping the temperature constant at 28 °C. The pH value was determined using pH buffer solution and deionized water, and measured with a Shanghai Yueping PHS-3CB digital display table pH meter. The locomotor behavior experiment was divided into single-factor experiments and orthogonal experiments. The specific experimental grouping and operation are shown in Figure 9. Before the experiment, larvae were kept in a 28 °C water tank with only methylene blue solution. At the beginning of the experiment, larvae were sucked through disposable straws and transferred to Petri dishes containing the same methylene blue solution as the rearing environment. The purpose of this step is to obtain the baseline state of the juvenile in the growth environment, which is used as the control group of the experiment. Therefore, in this process, the water temperature of the Petri dish is always maintained at 28 °C by the temperature control platform. After the start of the experiment, the juveniles were transferred by straw to another Petri dish containing the experimental solution, which was maintained at the appropriate temperature in advance by an independent temperature control device. This step was taken to obtain the movement state of the young fish after acute exposure to the new environment, so the video was taken 10 min after exposure. Next, the larvae were allowed to swim freely in this Petri dish until 60 min after exposure, and a video was taken again for behavioral analysis after long-term exposure. Finally, the larvae were transferred back to another rearing box for normal feeding. The larvae were not reused throughout the experiment. At each behavioral observation time point, a five-minute video was recorded to analyze zebrafish larvae swimming behavior. The videos were captured at a frame rate of 30 frames per second (FPS).
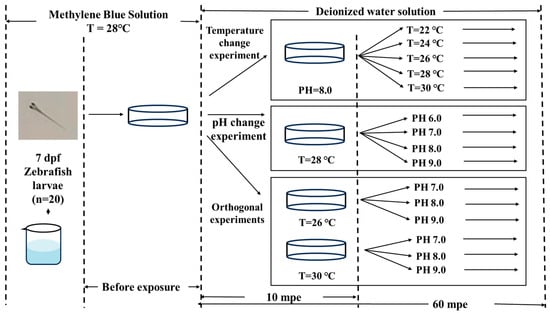
Figure 9.
Schematic of the experimental operation process: “x mpe” means x minutes post exposure.
Figure 10 illustrates the composition of the experimental setup: (1) the adjustable light source, (2) a fixed bracket for camera equipment, (3) the Teflon Petri dish, and (4) the digital heating and thermostat control platform. During the experiment, the adjustable light source above serves two primary purposes: it maintains a consistent light intensity throughout the experiment, ensures clear video footage, and leverages larval phototropism to effectively enhance the behavioral activity of the larvae. The mechanical arm of the fixed device does not cause shadows on the shot due to the projection of the light source above, and does not affect the routine activities of the zebrafish larvae. The recording apparatus was securely positioned approximately 30 cm above the Petri dish to capture video footage. When larvae move in transparent Petri dishes in multiple wells, they are subjected to various visual stimuli, which can lead to fluctuations in motor behavior, such as the specular reflection of images [], or the influence of neighboring larvae []. In this work, Teflon Petri dishes were used to observe the locomotion of larvae, which provided visual isolation for the larvae. Before each experiment, the water temperature of the Petri dish controlled by the digital heating and thermostat control platform (BY 2020) was measured by a thermometer. If the temperature displayed by the platform was different from that measured by the thermometer, the constant temperature platform was corrected until the error range was controlled at ±0.2 °C. During the experiment, the temperature of each platform was corrected in advance and adjusted to the corresponding experimental temperature, which was always maintained.
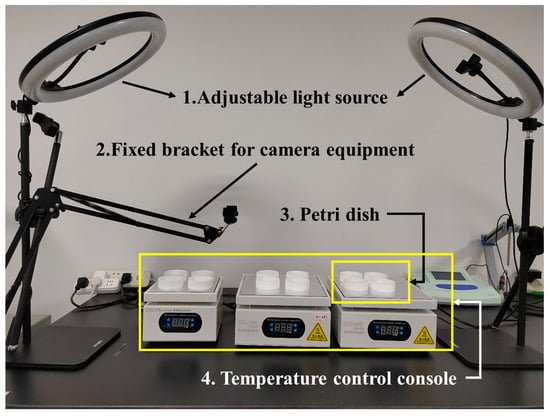

Figure 10.
Experiment setup.
2.4. Quantifying the Parameters of Larval Locomotor Behavior
2.4.1. Basic Motion Parameters
In this study, 13 parameters were used to describe the swimming behavior of zebrafish larvae. These parameters comprehensively quantify locomotion behavior from multiple aspects, such as overall movement ability, movement turning performance, movement position preference, and edge exploration behavior. The definition and description of the motion parameters are shown in Table 4, which is also annotated with the physical meaning of the parameters. Among them, the calculation formula of each motion parameter is as follows.

Table 4.
Definition and description of motion parameters.
- The total distance traveled (D), defined by Equation (1), is the most commonly employed kinematic parameter for behavioral analysis, offering an intuitive measure of locomotor capacity in zebrafish larvae.
- 2.
- Activity frequency (AF) is a behavioral analysis metric. In this paper, it is defined as the percentage of frames with moving distance () over the total number of frames (), as shown in Equation (2).
- 3.
- The maximum average velocity (Vmax-m) and minimum average velocity (Vmin-m) are employed to evaluate zebrafish larvae’s locomotion threshold and stability, as shown in Equations (3) and (4), where v is the average motion speed calculated independently for each second.
- 4.
- Rotation angle () serves as a vital metric for assessing changes in trajectory direction, as well as a significant indicator for burst movements and evasive responses, as in Figure 11 and Equations (5) and (6). This paper uses the total rotation angle (A) to gauge the overall directional alterations in the movement of zebrafish larvae, as outlined in Equation (7).
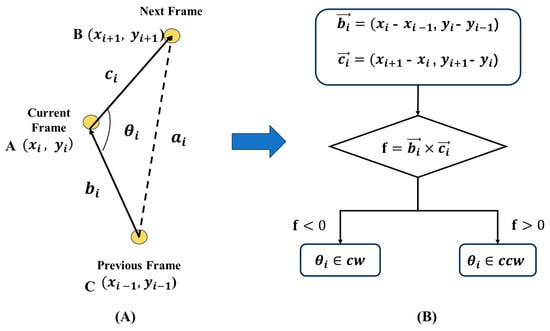 Figure 11. Definition of rotation angle, CCW, and CW. (A) definition of the rotation angle; (B) flow chart of the calculation of the CCW and CW.
Figure 11. Definition of rotation angle, CCW, and CW. (A) definition of the rotation angle; (B) flow chart of the calculation of the CCW and CW.
- 5.
- The sums of clockwise (CW) and counterclockwise (CCW) rotation angles are separately employed to evaluate angular variations along the two directions, with the methodology illustrated in Equations (8) and (9) and Figure 11.
- 6.
- The directional preference index (DPI) is defined to measure the extent of the directional bias. The calculation method is presented in Equation (10).
- 7.
- The summation of distances to the center point (Dc) serves as a measure for the spatial distribution of motion trajectories, as defined in Equation (11).
- 8.
- The total activity square (S), as defined in Equation (12), serves as a metric for quantifying the overall activity range of zebrafish larvae.
- 9.
- The high-frequency active square (S-hf) is used to describe the size of the area in which zebrafish larvae exhibit concentrated activity. In this experiment, the high-frequency active area is defined as the set of trajectory points with a kernel density estimate (KDE) greater than 0.5. Equation (14) represents the density estimation function used to calculate the data distribution density around trajectory points.
These parameters collectively facilitate the characterization of behavioral alterations in zebrafish larvae across various dimensions, encompassing global motor performance, motility, directional bias, and spatial preferences. All these parameters are amenable to automated computation using the location data generated by the algorithm.
2.4.2. Behavioral Characteristic Indicators
In this study, the dimensions of the above 13 basic movement parameters were reduced by Principal Component Analysis, and then the reduced principal components were used as behavioral characteristic indicators to quantify the movement changes of juvenile fish.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was applied to the 13 parameters from 840 samples. The existence of a correlation between the original variables is the first condition for PCA. Therefore, before using PCA to reduce the dimensionality of the data, the correlation between the variables was determined by the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) test and Bartlett’s sphere test []. As shown in Table 5, the test result of the KMO value was 0.795, and Bartlett’s sphere test results showed p < 0.001, which indicates that the 13 motion parameters are suitable for dimensionality reduction by PCA.

Table 5.
The results of KMO and Bartlett’s test.
In the experiment, 840 motion states were collected, and each motion contained 13 variables, which formed the matrix , where n = 840 and m = 13. Firstly, the original data were standardized, as shown in Equation (15):
where is the value of the j-th motion variable of the i-th evaluated object and and are the mean and standard deviation of the j-th motion variable, respectively. is the normalized .
Then, the correlation coefficient matrix R between the variables was established, as presented in Equations (16) and (17):
where , , and equals the correlation coefficient between the i-th motion variable and the j-th motion variable. The eigenvalues of the correlation coefficient matrix R are calculated.
Each λ corresponds to a principal component, and the variance interpretation of the principal component is shown in Table 6. The variance interpretation refers to the proportion of variance of the original data that each principal component can capture. In this work, three components with characteristics greater than 1 were extracted as principal components and used as behavioral characteristic indicators to quantify the movement changes of juveniles. Among them, Principal Component 1 (PC1), Principal Component 2 (PC2), and Principal Component 3 (PC3) accounted for 48.278%, 19.463%, and 7.994% of the total variances, respectively, and the three principal components accounted for 75.735% of the total variance; that is to say, these three principal components could explain most of the variability of the overall data. A two-dimensional scatter plot was created using PC1 on the x-axis and PC2 on the y-axis to represent the positions of each initial motion parameter.

Table 6.
Variance interpretation of components.
To enhance the interpretability of the principal components, orthogonal rotation was applied to the results of the Principal Component Analysis (PCA), ensuring that the rotated components remained statistically independent. The matrix of the rotated principal components is presented in Table 7, where the original variables (basic motion parameters) are arranged in descending order according to their magnitude. The magnitude of the rotation coefficients indicates the degree of contribution of the original variables to the corresponding rotated components. The larger the absolute value of the coefficient, the more significant the influence of the original variable on that component. Specifically, PC1 is predominantly constituted by parameters such as CCW (counterclockwise), A (amplitude), CW (clockwise), AF (angular frequency), D (distance), S (speed), Vmin-m (minimum velocity in meters), Vmax-m (maximum velocity in meters), and S-hf (high-frequency signal), which encompass motion angles, traveled distances, motion speeds, and motion ranges, collectively assessing the behavioral activity of the larvae. PC 2 is mainly composed of parameters P_edge (proximity to the edge), Dc (distance to the center), and C (curvature), all of which are related to the edge behavior of the larvae. The main parameter in PC3 is PI (preference index), which measures the movement direction preference. The names of the behavioral characteristic indicators corresponding to the three principal components and their physical meanings are shown in Table 8. The contribution rate of each basic behavior parameter to the three principal components is shown in Table 9. Figure 12 is a visualization of the PCA results. In Figure 12A, the positioning of data points was determined by the weights of these parameters. The size of each data point was determined by the sum of their weights on the two feature dimensions. Figure 12B–D displays the contribution of each motion parameter to the different principal components.

Table 7.
Rotated component matrix.

Table 8.
Comparison table of principal components and exercise variables.

Table 9.
Contribution of motion parameters to each principal component.
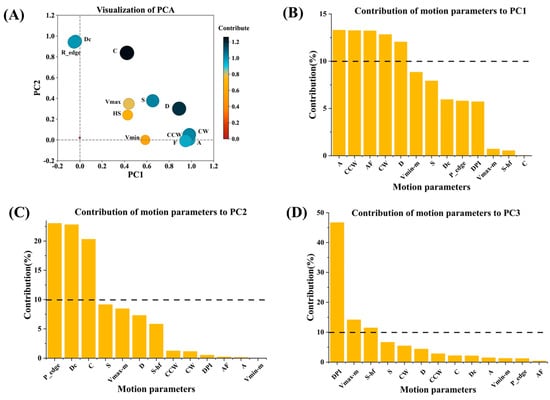
Figure 12.
PCA dimensionality reduction results. Three feature dimensions are identified based on the principle that the eigenvalue is more significant than one (λ > 1). (A) The proportion of each component in 1, 2 dimensions. Principal Component 1 (PC1) is plotted as the x-axis, and Principal Component 2 (PC2) is plotted as the y-axis. The circles represent each initial motion parameter whose position characterizes the parameter’s contribution in the two dimensions; the size indicates the sum of the contribution in the two dimensions. (B) The significance of the 13 motion parameters in Principal Component 1 is displayed. Predominant contributors are the overall activity variables linked to motion angle and magnitude. (C) The role of the 13 motion parameters in Principal Component 2 is presented, with the primary contributor being the motion position preference variable associated with edge behavior. (D) The extent of the contribution of the 13 motion parameters in Principal Component 3 is visualized, with primary contributors comprising variables related to motion direction preference.
The basal motor parameters are directly quantified from the movement position, while the behavioral characteristic index is the weighted sum of the basal motor parameters. Its weight is determined by the component score coefficients, and the matrix of component score coefficients is shown in Table 10. The principal component scores (PCS) are calculated using Equations (18) and (19). The contribution rate of the principal components to the original data is calculated from the eigenvalues in Equation (20).
where is the weight of the j-th motion parameter in the principal component m, and c is the component matrix coefficient.

Table 10.
Component score coefficient matrix.
In the present study, Principal Component 1 (PC1), Principal Component 2 (PC2), and Principal Component 3 (PC3) were utilized as novel behavioral quantification indices corresponding to three distinct behavioral characteristics of juvenile fish: overall activity, thigmotaxis (tendency to stay close to walls or boundaries), and movement direction preference, respectively. These indices were employed for statistical analysis and the interpretation of experimental outcomes. Using the experimental data of a single larva as an example, Figure 13 demonstrates the variation in behavioral quantification data, movement trajectory diagrams, and heatmaps across different observation times. The left side of the figure visualizes the behavioral changes of zebrafish larvae, while the right side provides a quantitative analysis of the overall activity and thigmotaxis of the larvae based on the scores of Principal Component 1 and Principal Component 2. It also lists the changes in several original motion parameters with higher contribution rates to the two principal components. According to the temporal variable, both trajectory and parameter quantifications are presented in three phases from top to bottom: before exposure, 10 min after exposure, and 60 min after exposure.
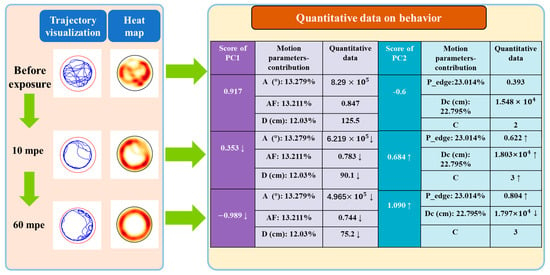
Figure 13.
Comparison of representative trajectory plots with thermograms and locomotor parameters. The left side of the figure shows changes in trajectory and thermograms with increasing exposure time for a zebrafish larva in the pH = 8.0, temperature = 22 °C group. The trajectory heat map is generated by calculating the distribution density of trajectory points. On the right side are the scores for behavioral activity (PC1S) and thigmotaxis behavior (PC2S) at each exposure time, as well as quantitative values for the dominant factors total distance traveled (D), absolute angle of rotation (A), and percentage of active frequency (AF) in PC1S, and the dominant factors total distance to the center (Dc), percentage of active area at the edge (P_edge), and the number of wall-adjacent circular motions (C) in PC2S. The “↑” indicates a significant increase in this parameter compared to the previous exposure phase; conversely, the “↓” means a significant decrease.
From the trajectory diagram, it is evident that before exposure, the trajectory distribution of the larvae is relatively uniform and the overall activity level is high, with a PC1 score of 0.917, which is also considered high. The trajectory heatmap indicates a denser distribution of trajectory points closer to the right side of the culture dish, but there is no apparent thigmotactic behavior in the overall distribution, corresponding to a PC2 score of −0.6, which is a lower level.
Ten minutes after exposure, the movement trajectories of the larvae are significantly reduced, indicating a marked decrease in overall activity. The corresponding PC1 score is 0.353, which is a noticeable decline from before exposure, and the values of several original motion parameters (A, AF, D) are also significantly reduced. During this phase, the trajectory points are noticeably concentrated in the peripheral area of the culture dish, but there are still traces of activity in the central area, suggesting that the larvae exhibit a certain degree of thigmotaxis. The PC2 score for this phase is 0.684, demonstrating an increase of 1.284 compared to before exposure, consistent with an increase in thigmotactic behavior. Motion parameters associated with thigmotaxis, such as P_edge (proximity to the edge), Dc (distance to the center), and C (curvature), also show an upward trend.
Sixty minutes after exposure, the overall activity level of the larvae, as observed from the trajectory diagram, shows no significant difference compared to the previous stage, but the overall range of activity has narrowed, with a more concentrated distribution in the peripheral area of the culture dish. Although there is no apparent change in the trajectory at this time, the PC1 values continue to decrease, with significant downward trends observed in the total rotation angle (A), activity time proportion (AF), and total distance moved (D). The heatmap, with its red circle close to the inner wall of the culture dish, indicates a more pronounced thigmotactic behavior of the larvae, and almost no activity traces in the central area of the container. At this time, the PC2 score is 1.090, with an increase of 0.406 compared to the previous stage, showing an overall upward trend less than that of the previous stage. Only the values of P_edge and Dc have increased, which is consistent with the trend of change in thigmotaxis.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All data were analyzed using Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) 2.7. The statistical analysis process was expanded based on 13 motion parameters calculated from the Python file on the position information output by the tracking system. The specific flow of statistical analysis is shown in Figure 14; in the preprocessing part, box plots exclude outliers in each data group. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [] reduces the dimensionality of the 13 motion parameters. The principal component scores were then calculated from the dimensionality reduced weights, which were used in place of the 13 motion parameters for subsequent statistical analysis. In the statistical analysis section, the Shapiro–Wilk test [] was used to test the normality of the data distribution for each group. However, due to the non-normal distribution of some data groups, the Kruskal–Wallis test [] was used for single-factor experiments, and the Scherer–Ray–Hare test [] was used for the analysis of orthogonal experiments.
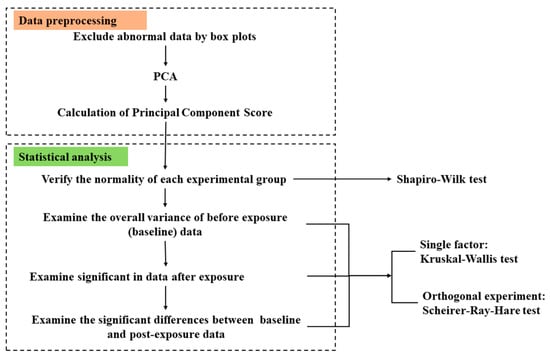
Figure 14.
Flow chart of data preprocessing and statistical analysis.
3. Results
The PCA results classified the movement performance of zebrafish larvae into three categories, where PC1 represents behavioral activity, PC2 represents marginal behavior, and PC3 represents movement direction preference. The results of the following behavioral experiments will also be developed from these three aspects. The overall effects of temperature and PH changes individually and simultaneously on the three locomotor behaviors are shown in Table 11. In the table, “↑” represents the more obvious performance of the behavioral feature, and “↓” represents a decreased performance of the behavioral feature. With the increase in temperature, the overall activity of juveniles decreased, while the thigmotaxis and movement direction preference increased. The opposite was observed for the larvae when the temperature was lowered. With the increase in pH value, the overall activity and thigmotaxis of larvae showed a downward trend, and there was no significant change in the preference of movement direction. Unlike temperature changes, larval locomotor performance did not show an opposite trend when the pH was decreased, although overall activity still showed a decreasing trend and both thimmotaxis and movement direction preference behaviors increased. When both factors were changed simultaneously, there was no significant effect on motion direction preference. However, both temperature increase and pH decrease, and both temperature decrease and pH increase, resulted in decreased overall activity and thigmotaxis performance.

Table 11.
Effects of changing environmental conditions on three motor behaviors. The up and down arrows represent the enhancement and weaken of the behaviors, respectively.
3.1. Single-Factor Experiment
The statistical analysis of the single-factor experiment is divided into two parts: the first part involves testing for differences in behavioral characteristic indicators among larvae from different experimental groups exposed for the same duration; the second part examines differences in these indicators among larvae from the same experimental group exposed for varying durations. Both analyses are conducted using the Kruskal–Wallis test, with multiple comparisons adjusted using Bonferroni correction.
3.1.1. Temperature Change Experiment
As illustrated in Figure 15A–C, variations in temperature resulted in significant differences in behavioral activity (PC1) and edge behavior (PC2), while having no significant impact on movement direction preference (PC3). Figure 16 presents the overall trends of these three behavioral characteristics. In general, from the perspective of overall activity, a decrease in temperature tends to reduce this behavioral expression, whereas high temperatures do not have a pronounced effect on this indicator. Regarding edge behavior, both a decrease and an increase in temperature lead to an enhancement of this behavior. The preference for movement direction does not appear to be sensitive to changes in environmental temperature.
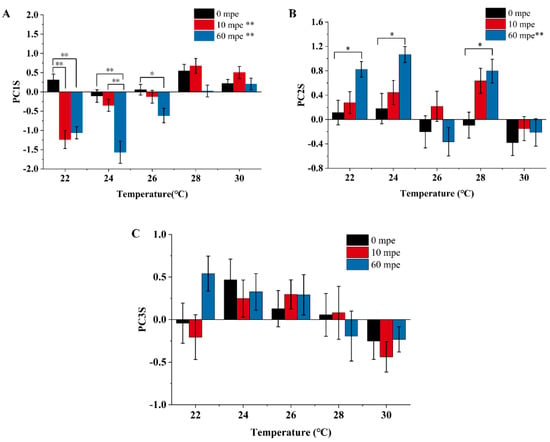
Figure 15.
Analysis and comparison of three principal component scores. (A) Comparison of Principal Component 1 score (PC1S) characterizing the first behavioral feature, behavioral activity performance. (B) Comparison of Principal Component 2 scores (PC2S) characterizing the second behavioral trait, thigmotaxis behavior. (C) Comparison of Principal Component 3 scores (PC3S) characterizing the third behavioral trait, direction of motion preference behaviors. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. and were analyzed by the Kruskal–Wallis test, df = 4, n = 100, with multiple comparisons by Bonferroni correction; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.001.
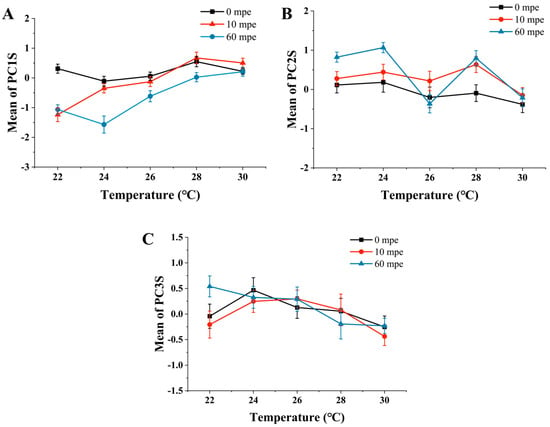
Figure 16.
Changes in the three principal components (motor characteristic scores) exposed to different temperatures. (A) PC1S (behavioral activity) was significantly altered by temperature. (B) PC2S (thigmotaxis behavior) was altered considerably by temperature change. (C) PC3S was not particularly limited by temperature.
Behavioral activity. As illustrated in Figure 15A, when comparing data from the same experimental group for different exposure times, the Kruskal–Wallis test revealed statistically significant differences in the Principal Component 1 scores (PC1S) for the three low-temperature exposures (Kruskal–Wallis test: 22 °C, p < 0.001; 24 °C, p < 0.001; 26 °C, p = 0.041). With Bonferroni correction, using the pre-exposure data (0 mpe, minutes before exposure) as a control, a sudden drop in temperature to 22 °C resulted in a significant decrease in PC1S at 10 min post-exposure (10 mpe) and 60 min post-exposure (60 mpe) (0 mpe–10 mpe: p < 0.001; 0 mpe–60 mpe: p < 0.001; 10 mpe–60 mpe). When the temperature was abruptly changed to 24 °C, with the pre-exposure data (0 mpe) serving as a control, the lower temperature significantly decreased PC1S at 60 min post-exposure; using the data from 10 min pre-exposure (10 mpe) as a control, PC2S still significantly decreased at 60 min post-exposure (Bonferroni correction: 0 mpe–60 mpe: p < 0.001; 10 mpe–60 mpe: p = 0.001). At a sudden change in temperature to 26 °C, using the pre-exposure data (0 mpe) as a control, PC1S significantly decreased at 60 min post-exposure (Bonferroni correction: 0 mpe–60 mpe, p = 0.04).
When comparing data from the same exposure duration across different temperatures, the trends for the three behavioral characteristic indicators were largely consistent with the aforementioned findings. After a 10 min exposure, the Kruskal–Wallis test indicated that Principal Component 1 scores (PC1S) increased significantly with rising temperature (p < 0.001). Bonferroni correction revealed that there were significant differences in activity levels between the groups exposed to 22 °C and 26 °C, and between 22 °C and 28 °C (p = 0.03; p < 0.001, respectively).
After a 60 min exposure, the Kruskal–Wallis test showed that Principal Component 2 scores (PC2S) increased with temperature, demonstrating significant differences (p < 0.001). Bonferroni correction specified the following significant differences: between 22 °C and 28 °C (p < 0.001), 28 °C (p < 0.001), 22 °C and 30 °C (p < 0.001), 24 °C and 28 °C (p < 0.001), 24 °C and 30 °C (p = 0.004), and between 26 °C and 28 °C (p = 0.04). No statistically significant results were observed for the other comparisons not mentioned above.
Edge behavior. As depicted in Figure 15B, when comparing data from the same experimental group across different exposure times, the Kruskal–Wallis test revealed that the scores for Principal Component 2 (PC2), which represents edge behavior, were significantly different under low temperatures (22 °C, p < 0.001; 24 °C, p < 0.001; 26 °C, p < 0.001) and at 28 °C. Bonferroni correction indicated that, using pre-exposure data as a control, only the edge behavior at 60 min post-exposure showed a significant decrease (22 °C, 0 mpe–60 mpe: p < 0.001; 24 °C, 0 mpe–60 mpe: p < 0.001; 28 °C, 0 mpe–60 mpe: p < 0.001).
For groups exposed to different temperatures for the same duration, the Kruskal–Wallis test demonstrated that PC2 scores exhibited irregular changes after prolonged exposure (p < 0.001). Bonferroni correction showed that there were statistically significant differences in PC2 scores between the following six temperature comparisons: 22–30 °C, 24–30 °C, 26–22 °C, 26–24 °C, 26–28 °C, and 28–30 °C (p = 0.03, p < 0.001, p = 0.01, p = 0.01, p = 0.03).
Directional Preference. The dominant locomotor parameter within Principal Component 3 (PC3) was the locomotor direction preference parameter (PI). These parameters signify whether zebrafish larvae preferred to move in a particular direction, clockwise or counterclockwise, during their locomotion. Neither of the two Kruskal–Wallis tests conducted on PC3S revealed statistically significant differences.
3.1.2. PH Change Experiment
As shown in Figure 17, similar to the results from the temperature group, only the scores for PC1 and PC2 exhibited significant changes, indicating that behavioral activity and edge behavior are more sensitive to variations in temperature and pH. As depicted in Figure 18A, although the horizontal comparison showed no apparent effect of pH changes on the larvae’s activity, the vertical comparison revealed that activity levels altered with exposure time. Figure 18B illustrates that pH values of 6.0, 7.0, and 9.0 did not cause a significant increase or decrease in edge behavior. However, at a pH of 8.0, there was a notable increase in the larvae’s edge behavior.
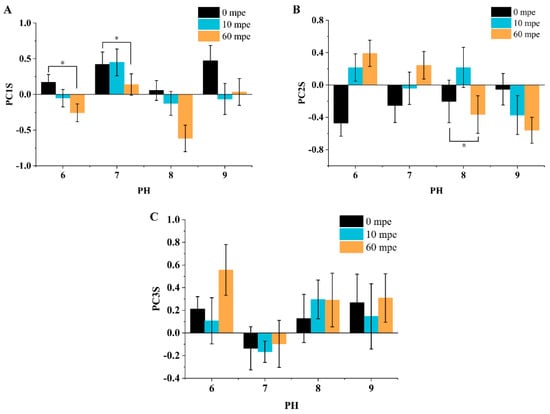
Figure 17.
Calculation and comparison of behavioral characteristics scores. (A) Comparison of PC1S. (B) Comparison of PC2S. (C) Comparison of PC3S. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. and were analyzed by the Kruskal–Wallis test, with multiple comparisons by Bonferroni correction; N = 80, df = 3. * p < 0.05.
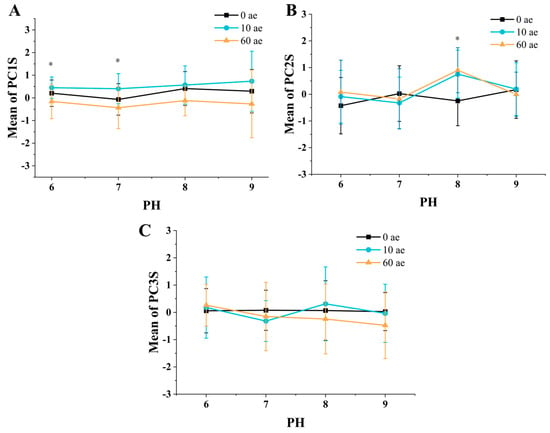
Figure 18.
Changes in the three principal components (motor characteristic scores) exposed to different solutions of different pH values. (A) pH significantly altered PC1S (behavioral activity). (B) PC2S (thigmotaxis behavior) was significantly altered by pH change. (C) pH did not significantly alter PC3S. * p < 0.05.
Behavioral activity. From the statistical analysis results, when comparing different exposure times with the same pH value, the Kruskal–Wallis test showed that compared to the control data at 0 min post-exposure (mpe), there was a significant decrease in the Principal Component 1 (PC1) scores after 60 min of exposure to pH 6.0 and pH 7.0 (pH 6.0, p < 0.001; pH 7.0, p = 0.01), indicating a notable reduction in the behavioral activity of the larvae.
Unlike the results from the temperature group tests, the Kruskal–Wallis test for different pH groups at the same exposure time did not reveal any statistically significant differences. This implies that the overall activity of the experimental larvae is largely unaffected by variations in pH. As illustrated in Figure 18A, the two lines representing 10 min post-exposure (10 mpe) and 60 min post-exposure (60 mpe) show no fluctuations, indicating that there is no significant impact of pH changes on the general activity levels of the larvae.
Edge behavior. As illustrated in Figure 18B, when comparing data at the same pH level across different exposure times, the Kruskal–Wallis test indicated that, in comparison to the control at 0 min post-exposure (mpe), the Principal Component 2 (PC2) scores, which represent edge behavior, significantly decreased only at pH 8.0 (p = 0.13). However, the Bonferroni correction revealed that the reduction in edge behavior became statistically significant only after a longer exposure time (p = 0.02).
Similar to the results observed for Principal Component 1 (PC1) scores, the Kruskal–Wallis test conducted across different pH groups at the same exposure time showed that variations in pH did not result in significant differences in PC2 scores. This suggests that changes in pH do not substantially affect the edge behavior of the larvae when measured at equivalent exposure durations.
Directional preference. Similar to the statistical results observed for Principal Component 3 (PC3) in the temperature variation experiment, the Kruskal–Wallis test within the pH variation groups did not show any significant differences in PC3 scores. This indicates that isolated changes in neither temperature nor pH led to significant alterations in the movement direction preference of zebrafish larvae. The consistency in PC3 scores across different experimental conditions suggests that the preference for movement direction is relatively stable and not greatly influenced by the environmental variables tested.
3.2. Orthogonal Experiments
In single-factor experiments, it has been possible to find that lower temperatures (22 °C, 24 °C) and acidic environments (pH 6.0) had a somewhat more significant effect on the behavior of zebrafish larvae. In contrast, high temperatures and alkaline environments generally did not significantly change the swimming behavior of zebrafish larvae. However, it remains uncertain whether there is a statistically significant effect on larval behavior when both pH and temperature simultaneously fluctuate within the range suitable for the survival of zebrafish larvae. Therefore, changes in larval behavior were recorded over a range of environmental conditions close to ideal for survival (temperature = 26 °C, 28 °C, 30 °C, and pH = 7.0, 80, 9.0), which aimed to determine whether the two variables had a statistically significant effect at the most suitable larval survival threshold. The orthogonal experiments were conducted to investigate whether slight changes in the threshold most suitable for larval survival resulted in an interaction effect that caused a shift in larval behavior. Since the data from the orthogonal experiments did not conform to chi-squared, we utilized the Scheirer–Ray–Hare method for the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test and the Kruskal–Wallis “All pairwise” approach for multiple comparisons [].
3.2.1. Behavioral Activity
The results of the Scheirer–Ray–Hare test indicate that there is an interaction between different pH levels and temperatures on the three behavioral characteristics of zebrafish larvae, as depicted in Figure 19. Initially, the impact of temperature variation on Principal Component 1 (PC1), which represents overall behavioral activity, was pronounced. Exposure to lower temperatures for 10 min led to a significant decrease in PC1 scores, while exposure to higher temperatures for the same duration resulted in a significant increase (p = 0.02).
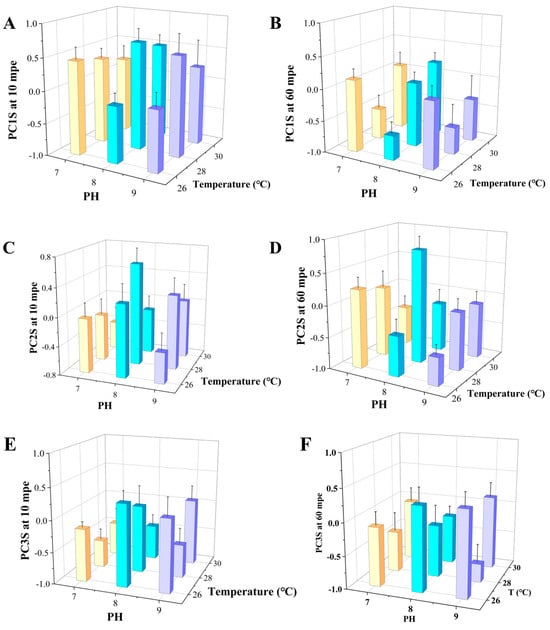
Figure 19.
(A) Comparison of PC2S at 10 mpe. (B) Comparison of PC2S at 60 mpe. (C) Comparison of PC2S at 10 mpe. (D) Comparison of PC2S at 60 mpe. (E) Comparison of PC3S at 10 mpe. (F) Comparison of PC3S at 60 mpe.
Subsequently, as observed in the single-factor experiments, pH did not independently affect any of the behavioral characteristics. However, the interaction between temperature and pH on PC1 became evident as early as 10 min into the exposure (p = 0.04). Furthermore, in the orthogonal experiment, the interactive effect of pH and temperature led to statistically significant differences in the behavioral activity of the larvae after both short-term and long-term exposures (p = 0.04). These findings suggest that the combined effects of temperature and pH, rather than each factor individually, play a significant role in influencing the behavioral patterns of zebrafish larvae.
3.2.2. Edge Behavior
Figure 19C,D illustrate the comparison of PC2 scores when both temperature and pH are simultaneously varied. Consistent with the results from the Scheirer–Ray–Hare test, similar to the single-factor experiments, changes in temperature significantly reduced PC2 scores at both low and high temperatures (p = 0.00). However, this difference only became apparent after a prolonged exposure period.
In comparison to the single-factor experiments, PC2 scores were also influenced by changes in pH. At a pH of 8.0, an increase or decrease of 1.0 unit in pH significantly reduced PC2 scores (p = 0.04), but this difference was only observed after short-term exposure. Additionally, due to the interactive effect between pH value and temperature (p = 0.01), PC2 also showed significant statistical differences in the Scheirer–Ray–Hare test after long-term exposure.
These findings suggest that the interaction between temperature and pH has a complex impact on the edge behavior of zebrafish larvae, with the effects becoming more pronounced under certain conditions and exposure durations.
3.2.3. Directional Preference
In the single-factor experiments, according to the Scheirer–Ray–Hare test, variations in pH and temperature did not result in statistically significant differences in PC3, which represents the preference for movement direction. In the orthogonal experiments, there was no interactive effect between the two factors on movement preference direction, yet both pH and temperature had independent effects. PC3 scores showed statistically significant fluctuations (p = 0.03) when exposed to different pH levels in the short term and to different temperatures over the long term (pH: p < 0.05, temperature: p = 0.03), as depicted in Figure 19E,F.
These findings indicate that while the individual impact of pH and temperature on the movement direction preference of zebrafish larvae may not be substantial, their combined or prolonged effects can lead to notable changes in PC3. The statistical variations observed in PC3 underscore the nuanced influence of environmental factors on the behavioral attributes of the larvae.
4. Discussion
In this study, based on a multi-object tracking algorithm, we conducted research on the behavior of zebrafish larvae, aiming to explore the impact of temperature and pH changes on the behavioral characteristics of zebrafish larvae. Target tracking is fundamental to the analysis of behavior. In this paper, we propose a multi-object tracking algorithm for zebrafish larvae based on improved YOLOv5 and DeepSORT methods. To study the effects of environmental changes on zebrafish larvae, we designed experiments with pH and temperature as ecological variables, including single-factor and cross-factor experiments. The single-factor experiments expanded the range of observed variables and considered the time effect; the dual-factor experiments confirmed that the combined effects of pH and temperature have a significant impact on the movement behavior of zebrafish larvae. Additionally, in conjunction with the behavioral analysis requirements of the experiment, we introduced three new behavioral quantification indices and analysis methods.
4.1. The Zebrafish Larvae Tracker
This study presents an enhanced tracking algorithm that significantly improves the accuracy of multi-object detection and tracking of zebrafish larvae, addressing challenges such as occlusions and identity switches. Traditionally, researchers have relied on local features like the eye and yolk sac to label datasets for tracking algorithms. However, the high degree of visual similarity among zebrafish larvae, coupled with their lack of distinct textural features, results in a limited number of characteristic points for algorithmic learning. This can lead to missed detections, false positives, and errors in identity matching, ultimately reducing tracking precision.
To overcome these limitations, we constructed a novel dataset of zebrafish larvae that provides the algorithm with fine-grained local features as well as holistic contour characteristics. This dataset enables the algorithm to leverage multidimensional information, thus enhancing both detection and tracking accuracy. Considering the small target size of zebrafish larvae, we also made structural improvements to the detection network YOLOv5 and its anchor clustering method. The refined YOLOv5 demonstrated a marked enhancement in its ability to extract fine-grained features, more effectively integrating superficial appearance features with deep semantic features, which in turn improves detection accuracy.
The zebrafish larvae tracker proposed in this study integrates the improved YOLOv5 with DeepSORT, trained using our novel body dataset. This combination effectively tackles the detection and tracking challenges associated with zebrafish larvae, reducing the likelihood of false detections, missed detections, and identity switches.
Additionally, our algorithm is designed to be robust across various scenarios and video resolutions, ensuring the reliable extraction of larval features for tracking tasks. This flexibility is crucial for the practical application of the algorithm in diverse experimental settings and real-world conditions.
4.2. Effects of Temperature and pH on Behavioral Characteristics
4.2.1. Behavioral Activity
This study revealed the effects of temperature and pH on the behavioral characteristics of zebrafish larvae through single-factor and orthogonal experiments. We found that low temperatures significantly reduced larval mobility and slowed metabolic processes, which is consistent with the study by Wakamatsu et al. [], which found that swimming ability was significantly affected by water temperature. However, it is important to note that the high temperature conditions did not significantly increase the behavioral activity of larvae, which may indicate that there is a suitable temperature range beyond which even high temperatures do not promote increased activity. As a kind of aquatic organism, zebrafish has a certain adaptability to changes in environmental temperature [,,,]. This adaptation may be manifested through behavioral plasticity, which means that within a certain range, zebrafish larvae are able to adapt their behavior to temperature changes. However, when the temperature changes beyond its adaptive range, behavioral plasticity may be limited, leading to changes in behavioral patterns.
The behavioral activities of zebrafish larvae were less sensitive to pH changes. However, the effects of different pH levels on PC1 behaviors of the same experimental larvae always followed the same pattern. Short-term exposure resulted in higher activity, while long-term exposure resulted in decreased activity. This may be related to the adaptability of larvae to environmental changes. Recently, the study of Toni et al. [] also emphasized the impact of environmental temperature change on the cognitive ability of adult zebrafish, further confirming the important role of temperature on fish behavior and cognition. Changes in pH may affect the activity of chemical and neurotransmitters in the water environment, which in turn affects the behavior of zebrafish larvae [,]. For example, changes in pH may alter the release or reuptake of neurotransmitters, thereby affecting the behavioral responses of larvae []. Changes in pH also affect the toxicity of drugs, as the solubility, dissociation, and bioavailability of many drugs are related to pH. For example, certain drugs may be more toxic in acidic environments because they are more easily absorbed or converted into toxic metabolites in the body [].
4.2.2. Edge Behavior
The preference for environmental peripheries in zebrafish larvae is commonly associated with anxiety and exploratory behavior [,,]. This study found that low-temperature conditions significantly increased the edge behavior of zebrafish larvae, which may indicate that under suboptimal temperatures the larvae exhibit higher levels of anxiety or a stronger need to explore the environment due to uncertainty. This finding is consistent with previous research [,], which pointed out that environmental temperature is a key factor influencing the behavior of zebrafish larvae. On the other hand, the impact of pH variation on peripheral behavior was not significant, which may suggest that zebrafish larvae have a stronger adaptability to changes in pH, or that the influence of pH on the behavior of larvae is not as direct as that of temperature changes. However, it should be noted that extreme changes in pH value can affect the chemical properties of water, which may indirectly influence the behavior of the larvae. The study by Cleal et al. [] emphasizes the importance of maintaining an appropriate pH range for assessing the behavior of larvae exposed to drugs, which may also be applicable to the study of natural behavior.
4.2.3. Directional Preference
Directional preference is a descriptive behavior that characterizes the inclination of zebrafish larvae towards specific directions when swimming in an aquatic environment. In this study, variations in temperature and pH did not significantly impact the directional preference of zebrafish larvae, which may suggest that the directional preference behavior of the larvae possesses a certain degree of environmental stability, or that the influence of these environmental factors on directional preference is not as pronounced as their impact on other behavioral parameters, such as activity level and peripheral behavior. However, it is noteworthy that extreme changes in environmental temperature may affect the neurological function of the larvae, thereby indirectly influencing their directional preference in movement.
4.3. Interaction of Temperature and pH on Behavioral Characteristics
The results of the orthogonal experiments further elucidate the interactive effects between temperature and pH value on the behavior of zebrafish larvae. This discovery holds significant implications for understanding how complex environmental factors collectively influence biological behavior. For instance, the combined changes in temperature and pH on the first two principal components (PC1 and PC2) suggest that these environmental factors may alter the behavior of the larvae by affecting their metabolism and nervous system. The identification of these interactions also implies that when assessing the effects of drugs, the comprehensive impact of environmental factors should be taken into account. Moreover, the interactive effect of temperature and pH on peripheral behavior became evident in the orthogonal experiments. Under conditions close to the ideal thresholds for the survival of zebrafish larvae, minor environmental variations can lead to significant changes in the behavior of the larvae. This suggests that even under relatively stable environmental conditions, the behavior of the larvae may be sensitive to subtle environmental changes, which is of great importance for the experimental design and interpretation of results. The standardization of experimental conditions is crucial to reduce the variability brought about by such interactive effects. Especially in drug development and toxicity testing, controlling these environmental variables can enhance the reliability and reproducibility of experimental outcomes. Given that the impact of pH value and temperature changes on the larvae’s activity has a temporal aspect, the experimental design should also consider the effects of different exposure durations to fully understand the impact of pH changes.
4.4. Behavioral Quantification Methods
Through Principal Component Analysis (PCA), we condensed thirteen kinematic parameters into three principal components, using method whose efficacy has been validated in the analysis of behavior. Initially, data generated from high-throughput experiments typically contain a substantial amount of redundant information. PCA can simplify this information into representative principal components, thereby reducing the complexity and storage requirements of the data. Furthermore, PCA is capable of extracting hidden patterns and structures within the data, assisting in the discovery of novel kinematic characteristics or the interrelations between motion indicators. By analyzing the principal components, we were able to identify the behavioral activity level, peripheral behavior, and directional preference traits of the juvenile fish, as well as the correlations between the original motion indicators and these behavioral characteristics. Additionally, the principal components obtained from PCA are linear combinations of the original data, thus possessing high interpretability. By examining the weights and contribution rates of the principal components, a deeper understanding of the biological traits and behavioral patterns represented by each component can be achieved. Importantly, in high-throughput experiments, it is necessary to integrate data from different experimental conditions and time points. The use of PCA allows for the consolidation of these data into a unified analytical framework, providing a better understanding of the overall behavioral characteristics and trends of zebrafish larvae. In summary, the extraction of behavioral characteristic parameters to quantify the behavior of larvae through PCA simplifies the data structure, uncovers new behavioral traits, enhances data interpretability, and integrates data frameworks, offering a novel perspective for the behavioral analysis of larvae.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a novel target-tracking system for zebrafish larvae has been developed based on YOLOv5 and DeepSORT to investigate the impact of environmental variables, specifically temperature and pH, on the behavioral characteristics of zebrafish larvae. Through the development of a dedicated dataset and structural enhancements to the detection network, the study significantly improves the accuracy of behavioral analysis, achieving a remarkable 98% Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy (MOTA). The findings of this research provide valuable insights into the behavioral responses of zebrafish larvae to environmental changes and underscore the importance of precise control and explicit reporting of environmental conditions in experimental settings.
The purpose of this study was to quantify the variability in zebrafish larvae’s locomotor behavior across different experimental conditions, focusing on temperature and pH changes. The research has demonstrated that lower temperatures reduce larval activity, while higher temperatures do not significantly increase it. Changes in pH did not markedly impact activity levels, but there was a notable decrease in short-term activity and an increase in activity after prolonged exposure. The study also found that both high and low temperatures increased edge behavior, which is indicative of anxiety or exploratory tendencies. However, neither temperature nor pH changes significantly affected the directional preference of the larvae.
Furthermore, the experimental results have showcased the feasibility and convenience of using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for the dimensionality reduction of multiple motion parameters and to extract features for analysis. This approach, coupled with our comprehensive experimental design, sheds light on the intricate interplay between environmental factors and zebrafish larval motion behavior.
There are still some limitations in this study. Firstly, the study primarily focuses on temperature and pH as environmental variables, potentially overlooking other factors that may influence zebrafish larvae behavior. Secondly, the study’s findings are based on a controlled laboratory setting, which may not fully represent the complexities of natural environments. Additionally, the study’s conclusions are drawn from specific time points of observation, which may not capture the complete temporal dynamics of the larvae’s behavioral responses.
Future studies can further explore the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of temperature and pH value on the behavioral characteristics of zebrafish larvae. Understanding the mechanisms of these interactions is of significant importance for the development of more effective drug screening models and toxicity testing methods. In terms of tracking algorithms, a temporal series processing approach could be integrated to extract behavioral characteristics along the temporal dimension from continuous video frames. This would enhance the accuracy of identity recognition and tracking.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z., X.C., G.S. and X.Z.; methodology, X.C.; software, X.C.; validation, Z.Z., G.S. and X.Z.; investigation, X.C.; resources, G.S.; data curation, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.C.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z., G.S. and X.Z.; visualization, X.C.; supervision, G.S. and X.Z.; project administration, G.S. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52005407.
Institutional Review Board Statement
As our research solely involves observing the behavior of zebrafish larvae in suitable environmental conditions, without any interventions or procedures beyond observation, Ethics Committee or Institutional Review Board approval was not sought.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Choi, T.-Y.; Choi, T.-I.; Lee, Y.-R.; Choe, S.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Zebrafish as an animal model for biomedical research. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teame, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Xie, M.; Gao, C.; Ye, Y.; Duan, M.; et al. The use of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as biomedical models. Anim. Front. 2019, 9, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, J.G.S.; Lima, C.; Lopes-Ferreira, M. Zebrafish larvae behavior models as a tool for drug screenings and pre-clinical trials: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazio, M.; Ablain, J.; Chuan, Y.; Langenau, D.M.; Zon, L.I. Zebrafish patient avatars in cancer biology and precision cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custódio, B.; Carneiro, P.; Marques, J.; Leiro, V.; Valentim, A.M.; Sousa, M.; Santos, S.D.; Bessa, J.; Pêgo, A.P. Biological Response Following the Systemic Injection of PEG–PAMAM–Rhodamine Conjugates in Zebrafish. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Urcera, J.; Romero, A.; Cruz, P.; Vasconcelos, V.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B.; Rodríguez, F. Screening of Microalgae for Bioactivity with Antiviral, Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Assays. Biology 2024, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, E.E.; Zon, L.I.; Langenau, D.M. Zebrafish disease models in drug discovery: From preclinical modelling to clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Echevarria, D.J.; Homechaudhuri, S.; Stewart, A.M.; Collier, A.D.; Kaluyeva, A.A.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, J. Zebrafish neurobehavioral phenomics for aquatic neuropharmacology and toxicology research. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner-Piquer, I.; Faucherre, A.; Byram, J.; Blaquiere, M.; de Bock, F.; Gamet-Payrastre, L.; Ellero-Simatos, S.; Audinat, E.; Jopling, C.; Marchi, N. Differential impact of dose-range glyphosate on locomotor behavior, neuronal activity, glio-cerebrovascular structures, and transcript regulations in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orger, M.B.; de Polavieja, G.G. Zebrafish behavior: Opportunities and challenges. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 40, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintos, S.; Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Vera, L.M.; Bertolucci, C. Daily rhythms in the behavioural stress response of the zebrafish Danio rerio. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 268, 114241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, P.; Roitman, M.F.; Jung, E.E. Caloric state modulates locomotion, heart rate and motor neuron responses to acute administration of d-amphetamine in zebrafish larvae. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 264, 114144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zoubi, R.M.; Abu-Hijleh, H.; Zarour, A.; Zakaria, Z.Z.; Yassin, A.; Al-Ansari, A.A.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Bawadi, H. Zebrafish Model in Illuminating the Complexities of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders: A Unique Research Tool. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basnet, R.M.; Zizioli, D.; Taweedet, S.; Finazzi, D.; Memo, M. Zebrafish Larvae as a Behavioral Model in Neuropharmacology. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Mou, L.; Guan, S.; Wang, C.; Sik, A.; Stoika, R.; Liu, K.; Jin, M. Isoliquiritigenin induces neurodevelopmental-toxicity and anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 266, 109555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-González, A.; Dragomir, E.I.; Haghdousti, G.; Yáñez, J.; Dadswell, C.; González-Méndez, R.; Wilson, S.W.; Tuschl, K.; Folgueira, M. Manganese Overexposure Alters Neurogranin Expression and Causes Behavioral Deficits in Larval Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, Q.; Di Paolo, C.; Shao, Y.; Hollert, H.; Seiler, T.-B. Behavioral profile alterations in zebrafish larvae exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of eight priority pharmaceuticals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Gebhardt, M.; Stewart, A.M.; Cachat, J.M.; Brimmer, M.; Chawla, J.S.; Craddock, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Roth, A.; Landsman, S.; et al. Towards a Comprehensive Catalog of Zebrafish Behavior 1.0 and Beyond. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, E.; Bruzzone, M.; Maschio, M.D.; Dadda, M. Effects of environmental enrichment on recognition memory in zebrafish larvae. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2022, 247, 105552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishis, S.; Tsang, B.; Ren, G.J.; Gerlai, R. Effects of different handling methods on the behavior of adult zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 262, 114106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Prieto, B.; Caycho-Salazar, F.; Manzo, J.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Coria-Avila, A.G.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Rojas-Dúran, F.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E.; Pérez-Estudillo, C.A.; Toledo-Cárdenas, M.R. Effect of Enriched Environment on Cerebellum and Social Behavior of Valproic Zebrafish. NeuroSci 2024, 5, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgersson, L.; Odenlund, S.; Sturve, J. Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Exposure to Human-Relevant Mixtures of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Zebrafish. Animals 2024, 14, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toni, M.; Angiulli, E.; Miccoli, G.; Cioni, C.; Alleva, E.; Frabetti, F.; Pizzetti, F.; Scalvini, F.G.; Nonnis, S.; Negri, A. Environmental temperature variation affects brain protein expression and cognitive abilities in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio): A proteomic and behavioural study. J. Proteom. 2019, 204, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfakianakis, D.G.; Leris, I.; Kentouri, M. Effect of developmental temperature on swimming performance of zebrafish (Danio rerio) juveniles. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 90, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiulli, E.; Pagliara, V.; Cioni, C.; Frabetti, F.; Pizzetti, F.; Alleva, E.; Toni, M. Increase in environmental temperature affects exploratory behaviour, anxiety and social preference in Danio rerio. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, Y.; Ogino, K.; Hirata, H. Swimming capability of zebrafish is governed by water temperature, caudal fin length and genetic background. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Luna, J.; Al-Jubouri, Q.; Al-Nuaimy, W.; Sneddon, L.U. Impact of analgesic drugs on the behavioural responses of larval zebrafish to potentially noxious temperatures. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 188, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozaid, A.; Tsang, B.; Gerlai, R. The effects of small but abrupt change in temperature on the behavior of larval zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 227, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtright, A.; Rosser, M.; Goh, S.; Keown, B.; Wagner, E.; Sharifi, J.; Raible, D.W.; Dhaka, A. Modeling nociception in zebrafish: A way forward for unbiased analgesic discovery. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrikanova, T.; Serruys, A.-S.K.; Buenafe, O.E.M.; Clinckers, R.; Smolders, I.; de Witte, P.A.M.; Crawford, A.D.; Esguerra, C.V. Validation of the zebrafish pentylenetetrazol seizure model: Locomotor versus electrographic responses to antiepileptic drugs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bae, S. The pH-dependent toxicity of triclosan on developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos using metabolomics. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 226, 105560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Gong, Z.; Kelly, B.C. Assessing pH-dependent toxicity of fluoxetine in embryonic zebrafish using mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 650, 2731–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleal, M.; Gibbon, A.; Fontana, B.D.; Parker, M.O. The importance of pH: How aquarium water is affecting behavioural responses to drug exposure in larval zebrafish. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 199, 173066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, S.V.; Kakodkar, R.; Del Rosario Hernández, T.; Edmister, S.T.; Creton, R. Zebrafish Larvae Position Tracker (Z-LaP Tracker): A high-throughput deep-learning behavioral approach for the identification of calcineurin pathway-modulating drugs using zebrafish larvae. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Diaconu, L.; Poznanski, J.; Yu, L.; Rai, P.; Ferriday, R. Zenodo, 2020. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3 (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Azhar, M.I.H.; Zaman, F.H.K.; Tahir, N.M.; Hashim, H. People Tracking System Using DeepSORT. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE), Penang, Malaysia, 21–22 August 2020; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Maćkiewicz, A.; Ratajczak, W. Principal components analysis (PCA). Comput. Geosci. 1993, 19, 303–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C. The husbandry of zebrafish (Danio rerio): A review. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valletta, J.J.; Torney, C.; Kings, M.; Thornton, A.; Madden, J. Applications of machine learning in animal behaviour studies. Anim. Behav. 2017, 124, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-K. AniWellTracker: Image Analysis of Small Animal Locomotion in Multiwell Plates. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graving, J.M.; Chae, D.; Naik, H.; Li, L.; Couzin, I.D. DeepPoseKit, a software toolkit for fast and robust animal pose estimation using deep learning. eLife 2019, 8, e47994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ke, W.; Xiong, Z. Improving 3-D Zebrafish Tracking With Multiview Data Fusion and Global Association. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 17245–17259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; He, Y.; Sheng, H. 3D zebrafish tracking with topology association. IET Image Process. 2023, 17, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Restrepo, J.E.; Forero, D.A.; Vargas, R.A. A review of freely available, open-source software for the automated analysis of the behavior of adult zebrafish. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Escudero, A.; Vicente-Page, J.; Hinz, R.C.; Arganda, S.; De Polavieja, G.G. idTracker: Tracking individuals in a group by automatic identification of unmarked animals. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.; Collins, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Pham, M.; Roth, A.; Gaikwad, S.; Cachat, J.; Stewart, A.M.; Landsman, S.; Grieco, F. Automated high-throughput neurophenotyping of zebrafish social behavior. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 210, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Chaumont, F.; Dallongeville, S.; Chenouard, N.; Hervé, N.; Pop, S.; Provoost, T.; Meas-Yedid, V.; Pankajakshan, P.; Lecomte, T.; Le Montagner, Y. Icy: An open bioimage informatics platform for extended reproducible research. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Marsden, A.N.; Slusarski, D.C. Automated, high-throughput, in vivo analysis of visual function using the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 2016, 245, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Tracking Multiple Zebrafish Larvae Using YOLOv5 and DeepSORT. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA), Prague, Czech Republic, 18–20 February 2022; pp. 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lavery, J.M.; Mason, G.J. Mirror, mirror on the wall… How tank material and the presence of “enrichments” affect competition and agonism in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2023, 266, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.F.; De Leaniz, C.G.; Luchiari, A.C. Fear contagion in zebrafish: A behaviour affected by familiarity. Anim. Behav. 2019, 156, 521187. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, N. Factor analysis as a tool for survey analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2021, 9, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlens, J. A tutorial on principal component analysis. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.1100. [Google Scholar]
- Hanusz, Z.; Tarasinska, J.; Zielinski, W. Shapiro–Wilk test with known mean. REVSTAT-Stat. J. 2016, 14, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- McKight, P.E.; Najab, J. Kruskal-wallis test. In The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- López-Olmeda, J.F.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. Thermal biology of zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Therm. Biol. 2011, 36, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, F. Pharmacokinetics: The absorption, distribution, and fate of drugs. In Pharmacology and Therapeutics for Dentistry, 7th ed.; Mosby Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2017; pp. 15–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, R.W.; Kumai, Y.; Perry, S.F. The physiology of fish at low pH: The zebrafish as a model system. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamprea, M.R.; Cardenas, F.P.; Setem, J.; Morato, S. Thigmotactic responses in an open-field. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2008, 41, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.; Guo, N.; Li, Q. Effects of diphenylhydantoin on locomotion and thigmotaxis of larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2016, 53, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).