Abstract
Multimetric indices play a pivotal role in assessing river ecological quality, aligning with the European Water Framework Directive (EU WFD) requirements. However, indices developed specifically for large rivers are uncommon. Our objective was to develop a fish-based tool specifically tailored to assess the ecological quality in Portuguese large rivers. Data were collected from seven sites in each of three Portuguese large rivers (Minho, Guadiana, and Tagus). Each site was classified using an environmental disturbance score, combining different pressure types, such as water chemistry, land use, and hydromorphological alterations. The Fish-based Multimetric Index for Portuguese Large Rivers (F-MMIP-LR) comprises four metrics: % native lithophilic individuals; % alien individuals; % migrant individuals; and % freshwater native individuals, representing compositional, reproductive, and migratory guilds. The index showed good performance in separating least- and most-disturbed sites. Least-disturbed sites were rated ‘high’ or ‘good’ by F-MMIP-LR, contrasting with no such classification for most-disturbed sites, highlighting index robustness. The three rivers presented a wide range of F-MMIP-LR values across the gradient of ‘bad’ to ‘high’, indicating that, on a large spatial extent, the biological condition was substantially altered. The F-MMIP-LR provides vital information for managers and decision-makers, guiding restoration efforts and strengthening conservation initiatives in line with the WFD.
Keywords:
ecological quality; large rivers; water framework directive; MMI; fishes; freshwater ecosystems Key Contribution:
Our study is significant in developing a new fish-based tool specifically tailored for assessing the ecological quality of Portuguese large rivers. This tool offers valuable insights to enhance river management and conservation efforts, in alignment with the EU WFD.
1. Introduction
Large rivers and their riparian zones are vital features of the Earth’s hydrological systems, providing many ecosystem services and being globally recognized as hot spots of biodiversity []. However, most European large rivers have been severely degraded by human interventions that include channelization, dam construction, wastewater discharges, and introduction of non-native species, among others [,]. Likewise, Portuguese large rivers (Minho, Tagus, and Guadiana; catchment areas ≥ 10,000 km2) have been altered by humans for centuries [], causing the degradation of the riverbed and the riparian areas, river connectivity, flow regimes, and water quality. The number of non-native species in these systems has also increased exponentially as a result of introductions seeking to improve fisheries []. The ecological condition of Portuguese large rivers has been markedly affected by these historical intensive uses, thus jeopardizing the structure of the aquatic biotic communities. Because they are connected to the sea, these rivers also support several endangered freshwater and diadromous fishes, making them important and valuable resources for conservation and fisheries [].
The Water Framework Directive (WFD) was implemented in 2000 and set the goal of “good ecological status” for all European inland waters []. With this aim, EU member states must assess the ecological status of rivers, lakes, and transitional and coastal water bodies in their territory, and establish programmes of measures to reduce substantial anthropogenic pressures. Ecological status is assessed based on biological quality elements, such as fish assemblages, and their supporting physico-chemical and hydromorphological quality elements, which indicate the condition of an aquatic ecosystem in response to a variety of human-caused stressors. Given the increasing seriousness of the environmental degradation of European waters in general, and large rivers in particular [], the need for effective ecological and biodiversity monitoring programs has never been higher [,].
Multimetric indices (MMIs) are common methods for assessing the biological quality of rivers and evaluating the rehabilitation of aquatic communities [,]. These tools are based on the premise that biological communities respond to human-caused pressures in expectable and measurable ways, facilitating the estimation of the relationship between the biological community and the amount of environmental degradation []. MMIs are composed of a set of metrics related to the species composition and functional attributes of biological assemblages, such as taxa richness, trophic and habitat niche, and abundance. This method has been adapted to a wide range of lotic aquatic ecosystems in European waters to assess ecological status in accordance with the EU WFD [,,,,,,]. However, most methods were not specifically developed for large rivers, which demonstrates the need for the development of new studies and tools focused on bioassessment of these systems [,]. In fact, large rivers are complex and very diverse ecosystems [], presenting unique challenges to their biological assessment, such as the selection of efficient sampling techniques, seasonal changes of fish assemblage composition, and the low number of minimally disturbed sites needed to set reference conditions [,].
The WFD requires EU member states to develop typologies for surface waters based on a set of environmental variables that represent the fixed abiotic conditions, e.g., altitude, size, and basin geology, to explain the natural variability of the ecosystems []. These typologies categorize water bodies into distinct groups (river types) characterized by similar geo-morphological, hydrological, physico-chemical, and biological attributes. This paper aimed to assess the spatial variations of the biological quality of one of those Portuguese river types—large rivers—based on an MMI specifically developed for them. Thus, we expected to detect changes in fish assemblages according to the environmental conditions of the river segments. Such an MMI can serve as a valuable resource for managers and decision-makers to assess the biological quality of Portuguese large rivers, helping to direct rehabilitation efforts towards the most severely disturbed sites, and to strengthen the conservation of the least-disturbed ones. It can aid in identifying areas with the greatest impairments, potentially establishing the underlying causes of these impairments, and recommending mitigation strategies. Furthermore, an MMI can enable the tracking of improvements in fish assemblages over time, thereby evaluating the success or failure of rehabilitation projects and facilitating the implementation of adaptive management strategies, where interventions can be adjusted based on observed outcomes. In fact, the ability of these tools to track fish assemblages over time represents a significant contribution for the effective management and conservation planning of river ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
According to Borgwardt et al. [], Portuguese large rivers are classified into a unique large river type (LRT), the Mediterranean rivers. These rivers are characterized by having catchment areas ≥ 10,000 km2 and where most of the river’s course has not been impounded by large dams to any significant extent. By this definition, Portugal has three large rivers: Minho, Tagus, and Guadiana, corresponding to deep and wide fluvial channels with gentle slopes, and generally with wide floodplains, although they may also cross areas of narrow, rocky valleys. Although the Douro River is one of the Portuguese “big rivers”, its sequence of dams excluded it from this work. The Minho River is in northwestern Iberia and extends ~300 km through Spain to Portugal with the last 75 km of river defining the border between both countries. This international section is classified as an LRT and begins immediately downstream of the Spanish Frieira Dam (Figure 1). The Tagus River is in middle Iberia, between the Douro and Guadiana basins, and it extends ~1100 km through Spain and Portugal, sustaining a series of dams during its course. In Portugal, only the lower 170 km are free flowing waters, a fluvial segment classified as an LRT that extends from the river mouth to the first hydroelectric structure, Belver Dam. Lastly, the Guadiana River is also an Iberian watercourse that flows 820 km into the Atlantic Ocean at the southern border between the two countries. In Portugal, the Guadiana River is classified as an LRT upstream and downstream of the Alqueva/Pedrogão system, which is an important multiple-use water supply system that is located ~150 km from the estuary.
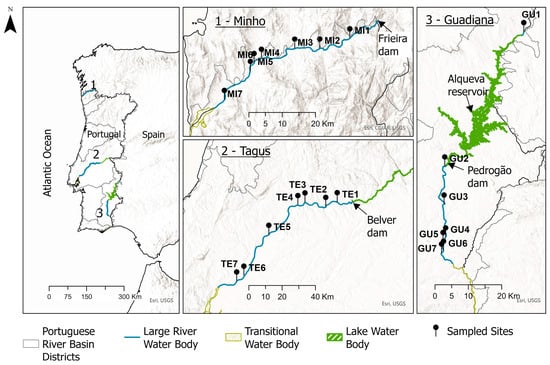
Figure 1.
Study area and location of the sampled sites.
The Convention on Cooperation for the Protection and Sustainable Use of Waters in Portuguese-Spanish River Basins (Albufeira Convention) is the instrument of cooperation between Portugal and Spain, for the protection and sustainable use of water in these basins []. This convention is designed to provide a framework for bilateral cooperation in the context of the WFD, for the protection of water bodies, aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, and for the sustainable use of water resources.
Iberian large rivers have endured a long-history of human interventions and natural disturbances in the fluvial corridors and on the surrounding valleys [], including highly modified river flows []. The fish assemblages in these rivers are dominated by a mixture of larger potamodromous species, several non-native species, and diadromous fish populations with life-cycles spanning marine and freshwater ecosystems [].
We selected 7 sites in each of the international Minho River, the Tagus River downstream from the Belver Dam, and the Guadiana River upstream of the Alqueva Dam and downstream of the Pedrogão Dam (Figure 1). Although the sites were not chosen randomly, we tried to ensure that they encompassed the range of natural conditions and human stressors occurring in the study areas. Except for two sites in the Guadiana River, all samples were taken between 2019 and 2022. Because of the lack of recent samples from least-disturbed reaches in the Guadiana River, we included two sites that were sampled there in 1996 and 1998, prior to the construction of the Alqueva Dam.
2.2. Anthropogenic Disturbance and Site Classification
There are no “near natural” reaches in our large rivers, but only lotic segments that present least-disturbed conditions (i.e., the presently best available condition). This is a common situation in many large rivers of the world, leading to the use of least-disturbed sites, with considerable levels of human influence, as “reference conditions”, which is key for the development of most biotic indices [,,].
To classify each site, we developed an environmental disturbance score (EDS) based on a wide range of pressure types, namely, nutrient enrichment, non-natural land uses, channel morphology modifications, riparian disturbance, and flow regulation (Table 1). Disturbance scores for each variable were based on professional judgement and on adaptations of the classifications proposed by Oliveira et al. and Weigel and Dimick [,], who developed biological indices for large rivers. Variables were scored to the degree from which they deviated from the least-disturbed conditions (from 1 for no deviation, to 4 for highly deviated; Table 1).

Table 1.
Criteria to score variables related to human disturbance. Variables were scored to the degree they deviated from least-disturbed conditions (from 1 for no deviation, to 4 for highly degraded); TP—Total Phosphorus; TN—Total Nitrogen.
For land use data, we used three CORINE Land Cover (CLC) inventories: 2000, 2010, and 2018 (depending on the sampling date) produced within the framework of the Copernicus Land Monitoring Service []. For each inventory, we grouped the categories already defined in CLC in three land use classes: artificial (mostly urban), intensive agriculture, and non-irrigated agriculture. ArcGis Pro data were extracted using a buffer with a 12-km radius, with the buffer centroids being placed exactly 10 km upstream from each sampling site. Agricultural land use was estimated as less than both 10% of agriculture and 3% of intensive farming (1) to more than 70% agriculture or more than 15% intensive farming (4). Artificial land use was estimated as <5% (1) to >25% (4). Chemical data were obtained from SNIRH (National Water Resources Information System) [], and total P (TP) and total N (TN) were calculated as the mean of the available values in the last five years, i.e., considering the sampling year/month and the previous four years. Analyzing a set of data over time offers a more thorough understanding of the chemical composition of water in a site compared to relying only on a single sample []. Based on Weigel and Dimick [], TP and TN ranged from, <0.13 mg/L and 1.0 mg/L (1) to >0.39 mg/L and 3.0 mg/L (4), respectively. Morphological modifications and riparian disturbance were evaluated in the field and from direct observation in Google Earth, on a river reach extending 1 km upstream from each sampling site. Channel morphology and riparian condition were evaluated from no or minor impacts (1) to strongly channelized river (most natural habitat types missing) and/or <50% of the streambank vegetation in natural state (4). Flow regulation was evaluated as a function of the influence of large hydroelectric power plants (LHPPs) upstream from the site (the operation of these structures is similar, imposing an ‘‘on–off’’ pattern of flow that depends on electricity demands). Thus, flow regulation was evaluated as infrequent or no hydropeaking (1) to regular hydropeaking and marked seasonal dewatering of the river (4).
A composite score of the six disturbance measures (i.e., the sum of scores (1–4) across the 6 measures) was calculated for each site (EDS), and the two lowest scoring sites from each of the three rivers were selected as the least-disturbed sites (i.e., a total of six LD sites); an additional condition for a site to be classified as LD was to have a classification of 1 or 2 on at least five pressure variables. The remaining 15 sites were classified as most-disturbed (MD) sites.
The sites spanned a considerable gradient of environmental disturbance as indicated by TN concentrations (0.82–3.67 mg/L), agricultural areas (19–67%), irrigated agriculture (0–44%), channel morphology and riparian condition (1–4), and flow regulation (1–4) (Table S1). These results indicate a clear anthropogenic pressure gradient and environment conditions that are determined independently from the aquatic biota [].
2.3. Fish Sampling
Except for the two sites sampled before 2000 in the Guadiana River (GR sites < 2000), all other fish assemblages were sampled according to the WFD protocol for Portuguese rivers []. Each site was boat-electrofished once during spring–summer base flow. Electrofishing distances were at least 10 times the mean wetted width of the channel and both banks were surveyed. This method was complemented by gill netting in the pelagic zone of the channel, which included the placement of one surface and one deep pelagic multi-mesh net; both nets were 30-m long by 1.5-m deep and were composed of 2.5-m long segments with 12 different mesh sizes (ranging from 5 mm to 55 mm). The nets were fished for 3 h in all segments. The GR sites < 2000 were electrofished in a similar way but no gill nets were used. Fish were identified and measured in the field; native specimens were returned alive to the water, and non-natives were killed, in accordance with Portuguese legislation. For analytical purposes, the total captures resulting from both electrofishing and gill netting were aggregated.
2.4. Index Development
The F-MMIP-LR was developed following Whittier et al., Krause et al., and Gonino et al. [,,]. First, we selected fish metrics from the literature based on species composition or related to the percentage of fish guilds grouped into ecological functions. Although we used a standardized sampling in most of the sites, fish species abundance in large rivers is particularly reliant on sample size or effort, and to account for this, species abundance in each site was quantified in terms of relative abundance (%) rather than absolute numbers. On the other hand, most diadromous species are widely distributed throughout Portuguese larger rivers, but some freshwater species are restricted to one or a few basins (Table 2). For example, two Luciobarbus species occur only in the Guadiana River. Because of this heterogeneity in the number of species between the studied large rivers, our metrics were only based on the relative abundance of individuals. Thus, we considered fourteen metrics grouped into six groups, following Noble et al. and Oliveira et al. [,] (Table 2): (1) compositional metrics (freshwater natives—FNAT, aliens—ALIE, and threatened fishes—THRE (taxa classified as at least vulnerable on the Portuguese Red Book of Freshwater and Diadromous Fishes [])); (2) overall tolerance guilds, based on species ability to endure a wide range of environmental conditions (non-tolerant—NOTO and tolerant—TOLE); (3) trophic guilds, based on the diet of adult individuals (native invertivore—INVE and omnivorous—OMNI); (4) habitat guilds, based on the preferred feeding and living habitats (benthic—BENT and native water column—PELA); (5) reproduction guilds, based on spawning substrate (native lithophilic—LITH and generalist—GENE); (6) migratory behavior guilds (diadromous (species that migrate between marine and freshwater habitats)—DIAD, potamodromous (species that migrate amongst multiple freshwater environments)—POTA, and migrant (the sum of DIAD and POTA)). Biological characteristics of fish species were based on the European EFI+ project [] with a few modifications supported by additional published data [], and best professional judgment (Table 2).

Table 2.
Species distribution by basin (M—Minho; T—Tagus; G—Guadiana), frequency of occurrence (FO) (%), and compositional and functional guilds (FNAT—freshwater native; ALIE—alien; THRE—threatened; NOTO—non-tolerant; TOLE—tolerant; INVE—native invertivore; OMNI—omnivorous; BENT—benthic; PELA—native water column; LITH—native lithophilic; GENE—generalist; DIAD—diadromous; POTA—potamodromous).
Candidate metrics were screened in a four-step process. First, we checked the distribution of metric values across all sites to eliminate those metrics with very small ranges (range test). Second, we performed a Kruskal–Wallis test (p < 0.1) to examine the responsiveness of the metrics that passed the first step in distinguishing the least and most disturbed sites. Third, we used the Spearman correlation coefficient to choose metrics lacking redundant information with other metrics (rs > 0.70). In the last step, we conducted a range test for metric values, based on the examination of box plots representing the metric scores (medians) for the LD and MD sites, to determine if most of the values from the two groups did not overlap. Metrics were scored on a continuous scale from 0 to 1. For metric scoring and calculation of the F-MMIP-LR, floor and ceiling values were defined as the 5th and 95th percentiles of metric values across all sites []. Metric scores between this range of values were interpolated linearly. For negative metrics, we reversed the floor and ceiling values. The scored metrics were then summed, and the summed score was divided by the number of metrics. Thus, the final value of the index was scaled to a range of 0 to 1, where 0 corresponds to the worst and 1 to the best quality of each site.
Following Hering et al. [], we defined five quality classes (high, good, moderate, poor, and bad) with equal ranges to provide five ordinal rating categories for assessment of disturbance in accordance with the demands of the WFD. We performed a Kruskal–Wallis test (p < 0.05) to verify the ability of our index to discriminate least- from most-disturbed sites; and we used a Spearman’s test to check the correlation between the F-MMIP-LR scores and the EDS scores.
3. Results
A total of 9501 individuals comprised of 37 fish species and 20 families were collected (Table 2). Of these, 24 (65%) species were native and 13 were alien (35%). As expected, the most-collected species are widespread throughout the Portuguese large rivers, exploring a great variety of environmental conditions. The alien Lepomis gibbosus was the most frequently occurring species, occurring in 16 sites, followed by the native Anguilla anguilla (13 sites), and the aliens Gambusia holbrooki and Micropterus salmoides (both occurring in 11 sites).
Of all candidate metrics, only four metrics were approved in all tests to compose the final F-MMIP-LR: % lithophilics, % migrants, % aliens, and % freshwater natives (Figure 2; Table 3). The F-MMIP-LR clearly discriminated least- from most-disturbed sites (Kruskal–Wallis test: H = 10.188; p < 0.001; n = 21) (Figure 3, Table S1), and we found a significant negative Spearman’s correlation between F-MMIP-LR and EDS for all sites (rs = −0.639, p < 0.0021) (Figure 4). All but one of the least-impacted sites were classified as ‘high’ or ‘good’ by the F-MMIP-LR, and none of the most-impacted sites were classified as ‘high’ or ‘good’, (Figure 5; Table S1).
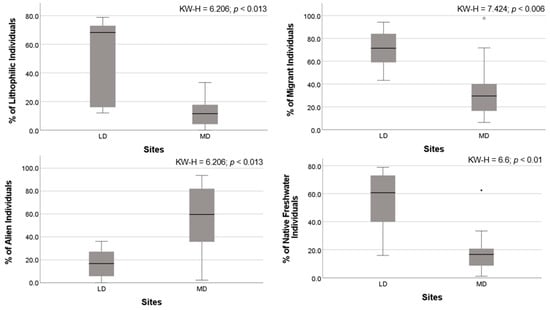
Figure 2.
Distribution of metric values from the final range test for the least disturbed (LD) and most disturbed (MD) sites, and results from the Kruskal–Wallis test (n = 21).

Table 3.
The 5th percentile (P5) and 95th percentile (P95) values for the selected metrics.
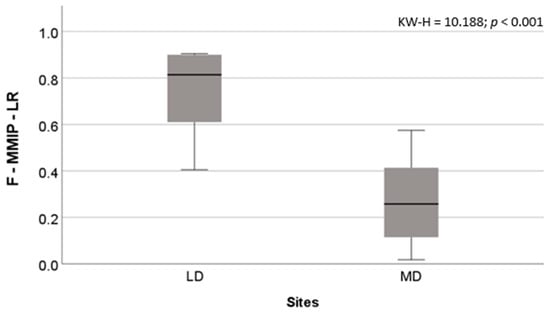
Figure 3.
Distribution of F-MMIP-LR scores across least disturbed (LD) and most disturbed (MD) sites, and results from the Kruskal–Wallis test (n = 21).
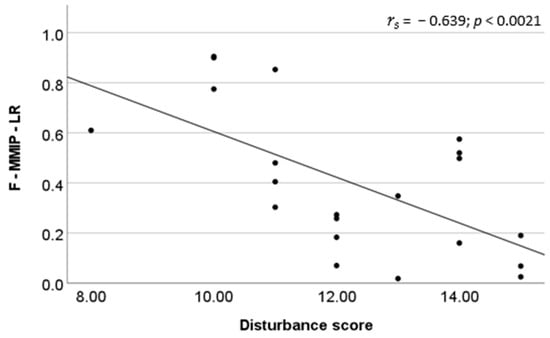
Figure 4.
Relationship between the F-MMIP-LR scores and the environmental disturbance scores (rs = −0.639; n = 21).
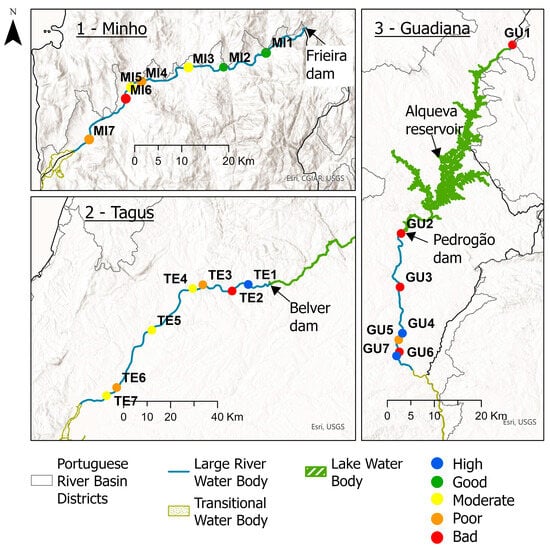
Figure 5.
F-MMIP-LR quality classes (High; Good; Moderate; Poor; Bad) across sampled sites.
The F-MMIP-LR scores ranged from 0.018 to 0.905 (Table S1). Based on the five quality classes with equal ranges, our index classified three sites (2 in Guadiana and 1 in Tagus) (14%) as ‘high’, two sites (both in Minho) (10%) as ‘good’, five sites (2 in Minho and 3 in Tagus) (24%) as ‘moderate’, four sites (2 in Minho, 1 in Tagus, and 1 in Guadiana) (19%) as ‘poor’, and seven sites (1 in Minho, 2 in Tagus, and 4 in Guadiana) (33%) as ‘bad’ (Figure 5). Thus, the three rivers presented a wide range of F-MMIP-LR values across the gradient of ‘bad’ to ‘high’, indicating that 76% of sites were in not-good condition, but still showing some sites with less substantial human impacts.
4. Discussion
The development of fish-based indices in assessing the quality of large rivers is a challenging task [,,]. Large rivers require expensive and time-demanding fishing efforts to adequately characterize fish assemblages [,]. Moreso than in wadeable streams, sampling fish in large rivers requires striking a balance between accuracy, precision, and cost, as all three factors are critical for effective and practical monitoring programs []. The distribution and catchability of fish in large rivers are highly variable because of extensive local movements and seasonal distribution of fish, presence of very deep habitats, variation in water levels, and relatively small sampling units []. Thus, all assessment metrics that are applied in large rivers can be based only on proxies of abundances and taxa richness because of gear and habitat selectivity and insufficient sampling effort [,,,]. We are aware of these limitations, which obviously extend to the tool we developed to assess the quality of large Portuguese rivers. For example, our sampling period most likely underestimated anadromous species that spawn in winter–early spring, i.e., P. marinus and Alosa spp. However, we believe that the use of a standardized protocol that also included two sampling techniques (electrofishing and gillnetting) enhanced the robustness of our fish assemblage assessments [,] and provided a more accurate picture of the biotic condition of our rivers.
The F-MMIP-LR was composed of four metrics (all metrics as percent relative abundance of individuals): native lithophilics, aliens, native migrants, and freshwater natives. We agree with Karr and Chu [] that the selection of appropriate metrics is the key step in robustness of these biological indices. To this concept, we also add the need to produce a versatile set of metrics, that can be quickly and easily calculated to provide user-friendly tools for managers and decision makers. The fish data for the calculation of our metrics are easy to collect (e.g., do not require fish measurements or the identification of DELT—deformities, erosion, lesions, and tumors—specimens), and the metrics themselves are easy to apply, interpret, and communicate to broad audiences.
A decrease in lithophilic fish was associated with degradation of the index score, and typically reflects a degradation of the riverbed because they require clean, coarse substrates for reproductive success [,]. In our study, the most-impacted sites were generally present in larger or more intensive agricultural areas, with more channel and riparian degradation. Agricultural land use is commonly seen as a key variable in assessing the effects of human activity on stream and river ecosystems and a good predictor of both physical habitat quality and in-stream biotic condition [,,]. In fact, agricultural activities are the most widespread cause of stream degradation, increasing nonpoint inputs of sediments, and often being a principal factor affecting riparian areas [,,,]. Riparian areas serve crucial ecological functions for river systems, such as bank stability, nutrient and sediment trapping, and habitat availability for fish in the form of woody debris, overhanging vegetation, and rootwads [,,].
The number of non-native fish species and individuals has been growing exponentially in Portugal (and Iberia) in the last few decades mainly as a result of the growing use of these species for sport fisheries and in the aquarium trade []. This is particularly evident in large rivers, because of the natural spread of individuals from Spanish populations []. Research has largely revealed that non-native fishes can flourish in degraded conditions, thereby causing substantial negative impacts on natural fish assemblages [,,], and thus representing one of the main causes of decline in biotic condition. Our index successfully included freshwater fish natives as a positive metric and non-native individuals as a sign of degradation. We also excluded the latter group from the other metrics. In fact, several authors have emphasized the problem of considering non-natives in MMIs, especially in the Iberian Peninsula, as the use of metrics with both native and non-native fish could restrict the ability of the index to detect the effect of non-native intrusions [,,]. The metrics we developed also suggested a large influence of the proportion of non-natives in the degradation of the biological indices.
Least-disturbed river reaches are likely to support and maintain a wide range of ecological processes and functions, so it is not surprising that they include higher abundances of migrants. In fact, it is reasonable to assume that these river reaches generally present higher water quality, riparian cover, and shelter, together with lower levels of pollutants and sedimentation, creating suitable spawning areas for potamodromous and anadromous species, as well as feeding grounds for catadromous species. Additionally, least-disturbed sites might have better connectivity with other stream reaches, including the tributaries of the main rivers, that are used by different life stages of migratory fish. As emphasized by Jungwirth et al. [], the ecological condition of large rivers is largely associated with the spatial/temporal connectivity of habitat subsystems, which are viewed as a crucial basis for a wide range of exchange processes and migration opportunities. However, McDowall and Taylor [] pointed out the problems in establishing relationships between migratory species and environmental quality, as species become rarer with increasing distance inland/elevation. In that case, differences in abundance may not reflect differences in proximal habitat quality. However, we believe that this is not a relevant factor in our study, because historically these species abundantly occupied the habitat network along these rivers, including segments located many kilometres upstream of our study areas [,].
We found no clear relationship between the flow-regulated sites and fish biotic condition because sites with higher F-MMIP-LR scores in the Minho and Tagus Rivers were farther upstream, closer to large hydroelectric dams (Figure 5). In contrast, in the Guadiana River, the sites closest to the Pedrogão Dam presented the lowest MMI scores, and these results are aligned with Lyons et al. [], who observed similar trends in Wisconsin rivers, where hydroelectric-peaking caused fish-habitat degradation and were associated with low fish MMI scores. The differences observed in the Guadiana River, particularly at site “GU4”, can be attributed to its proximity to the Pedrogão Dam (<1 km), showing the direct influence of hydroelectric flow regimes, as opposed to the more upstream points of the Tagus and Minho Rivers, which are located ~10 km from the dam immediately upstream. The lack of a clear relationship in our study could be influenced by several factors and be context-dependent []. One of these factors may be the better adaptability of native species, mostly cypriniforms, to lotic habitats with frequent high-flow events, compared to some non-native fish which are more successful in stable limnological conditions [,]. Native species possess natural adaptive responses to high flows that are detrimental to some non-native species by disrupting their critical life stages.
We believe that our tool is very useful for interpreting, comparing, and conveying the biotic condition of Portuguese large rivers. The F-MMIP-LR showed a significant ecological consistency in relation to the degree of perturbation of a site, and both the metrics and the overall index were able to discriminate between least- and most-disturbed sites. However, limitations should be considered in interpreting our results. First, we used few sites to construct the index—e.g., Yoder and Rankin [] suggested >30 sites to develop a more robust tool—and second, we did not validate the index with an independent data set to assess its performance []. Finally, these river systems are degraded by altered temperature, salinity gradients, flow rates, and toxic chemicals [], which may not have been fully addressed in our study. Future research should consider the inclusion of these and other factors, which certainly provide additional insights for understanding human impacts on fish assemblages and implications for species management and conservation. Ultimately, we are confident in the usefulness of the F-MMIP-LR for informing managers and decision-makers in evaluating the biological quality of Portuguese large rivers within the framework of the EU WFD.
5. Conclusions
Several EU member states rely on locally developed fish indices customized to their specific regions to assess the biological quality of their rivers in the context of the WFD. In line with this approach, the objective of this study was to pioneer the development of the first fish-based index to assess the biological quality of Portuguese large rivers. The Fish-based Multimetric Index for Portuguese Large Rivers (F-MMIP-LR) incorporates four metrics: native lithophilics, aliens, migrants, and freshwater natives. The fish data for the calculation of the metrics are easy to collect, and the metrics themselves are easy to apply, interpret, and communicate to broad audiences. Our findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the index in discerning between least- and most-disturbed sites and its significant ecological consistency in relation to the degree of perturbation of a site. The research underscores the importance of evaluating both native and non-native fish species when assessing river quality, while also acknowledging the impact of human activities, such as agriculture, on aquatic biodiversity. Furthermore, the study emphasizes the critical role of preserving ecological processes and functions within rivers, as these foster healthier fish assemblages. We conclude that our index could be an effective monitoring tool in the context of the EU WFD and can be used to communicate river health to the public and policy makers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes9050149/s1, Table S1: Detailed Environmental Disturbance Score—EDS and F-MMIP-LR classification per site. Coordinate system: World Geodetic System 1984. LAT—Latitude, LNG—Longitude; Total P—Total Phosphorus; Total N—Total Nitrogen.
Author Contributions
A.T.F.: methodology, software, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. M.T.F.: writing—review and editing. J.M.O.: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—review and editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received funding from the project ALBUFEIRA (0489_ALBUFEIRA_6_E) INTERREG V POCTEP) and by the project “Aquisição de serviços para melhorar e complementar os critérios de classificação do estado das massas de água superficiais interiores” for APA—Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente I.P., supported by the POSEUR—“Programa Operacional Sustentabilidade e Eficiência no Uso de Recursos” through the application POSEUR-03-2013-FC-000001—“Melhoria da Avaliação do Estado das Massas de Água”. Forest Research Centre (CEF) is a research unit funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. (FCT), Portugal (UIDB/00239/2020). The publication in Open Access was funded by the Project UIDB/00239/2020 from CEF (Forest Research Centre). The Associate Laboratory TERRA (LA/P/0092/2020) is also funded by FCT. António Faro was supported by a Ph.D. grant from the FLUVIO–River Restoration and Management program funded by FCT, Portugal (2021.06859.BD). J.M.O. was funded by the Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. (FCT) under Project UIDP/00681/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDP/00681/2020). M.T.F. was funded by the Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. (FCT) under Project UIDB/00239/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/00239/2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in line with national and international guidelines of animal welfare.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article. The data of fish assemblages are unavailable to the public due to privacy restrictions associated with the involved projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K.; Schiemer, F. Biodiversity of floodplain river ecosystems: Ecotones and connectivity. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1999, 15, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, J.J.; Buijse, A.D.; Haidvogl, G.; Lapinska, M.; Noble, R.; Repecka, R.; Virbickas, T.; Wiśniewolski, W.; Wolter, C. Challenges in developing fish-based ecological assessment methods for large floodplain rivers. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, K.; Uehlinger, U.; Robinson, C.T. Rivers of Europe; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, M.R.; Aguiar, F.C.; Martins, M.J.; Rivaes, R.; Ferreira, M.T. Long-term human-generated alterations of Tagus river: Effects of hydrological regulation and land-use changes in distinct river zones. CATENA 2020, 188, 104466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastácio, P.M.; Ribeiro, F.; Capinha, C.; Banha, F.; Gama, M.; Filipe, A.F.; Rebelo, R.; Sousa, R. Non-native freshwater fauna in Portugal: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Alves, M.J.; Ribeiro, F.; Domingos, I.; Almeida, P.R.; Costa, L.; Gante, H.; Filipe, A.F.; Aboim, M.A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; et al. Guia dos Peixes de água doce e Migradores de Portugal Continental; Edições Afrontamento: Porto, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission: Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for the Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; Official Journal of the European Union: Strasbourg, France, 2000.
- Solheim, A.-L.; Globevnik, L.; Austnes, K.; Kristensen, P.; Moe, S.J.; Persson, J.; Phillips, G.; Poikane, S.; Van De Bund, W.; Birk, S. A new broad typology for rivers and lakes in Europe: Development and application for large-scale environmental assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radinger, J.; Britton, J.R.; Carlson, S.M.; Magurran, A.E.; Alcaraz-Hernández, J.D.; Almodóvar, A.; Benejam, L.; Fernández-Delgado, C.; Nicola, G.G.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; et al. Effective monitoring of freshwater fish. Fish Fish. 2019, 20, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyjol, Y.; Argillier, C.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Buijse, A.D.; Cardoso, A.C.; Daufresne, M.; Kernan, M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Poikane, S.; et al. Assessing the ecological status in the context of the European Water Framework Directive: Where do we go now? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruaro, R.; Gubiani, É.A.; Hughes, R.M.; Mormul, R.P. Global trends and challenges in multimetric indices of biological condition. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, R.L.; Hughes, R.M.; Bae, Y.J.; Baek, M.J.; Gonzáles, O.C.B.; Callisto, M.; Carvalho, D.R.D.; Chen, K.; Ferreira, M.T.; Fierro, P.; et al. Assemblage-based biomonitoring of freshwater ecosystem health via multimetric indices: A critical review and suggestions for improving their applicability. Water Biol. Secur. 2022, 1, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R.; Fausch, K.; Angermeier, P.L.; Yant, P.R.; Schlosser, I.J. Assessing Biological Integrity in Running Waters. A Method and Its Rationale; Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication: Champaign, IL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kesminas, V.; Virbickas, T. Application of an adapted index of biotic integrity to rivers of Lithuania. Assess. Ecol. Integr. Run. Water 2000, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breine, J.; Simoens, I.; Goethals, P.; Quataert, P.; Ercken, D.; Van Liefferinghe, C.; Belpaire, C. A fish-based index of biotic integrity for upstream brooks in Flanders (Belgium). Hydrobiologia 2004, 522, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, D.; Hugueny, B.; Rogers, C. Development of a fish-based index for the assessment of river health in Europe: The European Fish Index. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, M.F.; Ramalho, C.E.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. Assessing biotic integrity in a Mediterranean watershed: Development and evaluation of a fish-based index. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2008, 15, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, E.; Carmona-Catot, G.; Moyle, P.B.; García-Berthou, E. Development and evaluation of a fish-based index to assess biological integrity of Mediterranean streams. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2011, 21, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Prus, P.; Buras, P.; Wiśniewolski, W.; Ligięza, J.; Szlakowski, J.; Borzęcka, I.; Parasiewicz, P. Development of a new tool for fish-based river ecological status assessment in Poland (EFI+IBI_PL). Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2017, 47, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramos-Merchante, A.; Prenda, J. Macroinvertebrate taxa richness uncertainty and kick sampling in the establishment of Mediterranean rivers ecological status. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegert, G. Considerations regarding development of index of biotic integrity metrics for large rivers. Environ. Sci. Pol. 2000, 3, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, C.O.; Kulik, B.H. The development and application of multimetric indices for the assessment of impacts to fish assemblages in large rivers: A review of current science and applications. Can. Water Resour. J. 2003, 28, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E.; Nestler, J.; Kennedy, R. Advancing science for water resources management. Hydrobiologia 2006, 565, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgwardt, F.; Leitner, P.; Graf, W.; Birk, S. Ex uno plures–Defining different types of very large rivers in Europe to foster solid aquatic bio-assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Convenção de Albufeira (Cooperação Luso-Espanhola). Available online: https://apambiente.pt/agua/convencao-de-albufeira-cooperacao-luso-espanhola (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Feio, M.J.; Ferreira, V. Rios de Portugal: Comunidades, Processos e Alterações; Imprensa da Universidade de Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, T.P.; Evans, N.T. Environmental quality assessment using stream fishes. In Methods in Stream Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 39, pp. 319–334. [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard, J.L.; Larsen, D.P.; Hawkins, C.P.; Johnson, R.K.; Norris, R.H. Setting expectations for the ecological condition of streams: The concept of reference condition. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Morgado, P.; Hughes, R.M.; Teixeira, A.; Cortes, R.M.; Bochechas, J.H. A preliminary fishery quality index for Portuguese streams. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2009, 29, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, B.M.; Dimick, J.J. Development, validation, and application of a macroinvertebrate-based Index of biotic integrity for nonwadeable rivers of Wisconsin. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2011, 30, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environmental Agency: Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. CORINE Land Cover. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/datahub/datahubitem-view/a5144888-ee2a-4e5d-a7b0-2bbf21656348 (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- SNIRH–Sistema Nacional de Informação de Recursos Hídricos: Rede Hidrométrica do Sistema Nacional de Informação de Recursos Hídricos da APA (SNIRH). Localização Geográfica, Classificação e Caracterização. Available online: https://snirh.apambiente.pt/ (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Smith, R.A.; Alexander, R.B.; Wolman, M.G. Water-quality trends in the nation’s rivers. Science 1987, 235, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto da Água I. P. Manual para a Avaliação Biológica da Qualidade da Água em Sistemas Fluviais Segundo a Directiva Quadro da Água: Protocolo de Amostragem e Análise para a Fauna Piscícola; Ministério do Ambiente, do Ordenamento do Território e do Desenvolvimento Regional; Instituto da Água: Alfragide, Portugal, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Whittier, T.R.; Hughes, R.M.; Stoddard, J.L.; Lomnicky, G.A.; Peck, D.V.; Herlihy, A.T. A structured approach for developing indices of biotic integrity: Three examples from streams and rivers in the western USA. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2007, 136, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.R.; Bertrand, K.N.; Kafle, A.; Troelstrup, N.H. A fish index of biotic integrity for South Dakota’s Northern glaciated plains ecoregion. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonino, G.; Benedito, E.; Cionek, V.D.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Oliveira, J.M. A fish-based index of biotic integrity for neotropical rainforest sandy soil streams—Southern Brazil. Water 2020, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.A.A.; Cowx, I.G.; Goffaux, D.; Kestemont, P. Assessing the health of European rivers using functional ecological guilds of fish communities: Standardising species classification and approaches to metric selection. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Segurado, P.; Santos, J.M.; Teixeira, A.; Ferreira, M.T.; Cortes, R.V. Modelling stream-fish functional traits in reference conditions: Regional and local environmental correlates. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, M.F.; Amaral, S.D.; Sousa, M.; Alexandre, C.M.; Almeida, P.R.; Alves, M.J.; Cortes, R.; Farrobo, A.; Filipe, A.F.; Franco, A.; et al. Livro Vermelho dos Peixes Dulciaquícolas e Diádromos de Portugal Continental; FCiências.ID & ICNF, I.P.: Lisboa, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pont, D.; Bady, P.; Logez, M.; Veslot, J. EFI+ Project. Improvement and Spatial Extension of the European Fish Index Deliverable 4.1: Report on the Modelling of Reference Conditions and on the Sensitivity of Candidate Metrics to Anthropogenic Pressures. Deliverable 4.2: Report on the Final Development and Validation of the New European Fish Index and Method, Including a Complete Technical Description of the New Method. 6th Framework Programme Priority FP6-2005-SSP-5-A. N° 0044096. 2009. Available online: https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-02592964/document (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Hering, D.; Feld, C.K.; Moog, O.; Ofenböck, T. Cook book for the development of a multimetric index for biological condition of aquatic ecosystems: Experiences from the European AQEM and STAR projects and related initiatives. Hydrobiologia 2006, 566, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, E.B.; Simon, T.P.; McCormick, F.H.; Angermeier, P.L.; Deshon, J.E.; Yoder, C.O.; Sanders, R.E.; Pearson, W.D.; Hickman, G.D.; Reash, R.J.; et al. Development of a multimetric index for assessing the biological condition of the Ohio river. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, N.W.R.; Corkum, L.D.; Mandrak, N.E. A comparison of methods for sampling fish diversity in shallow offshore waters of large rivers. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2006, 26, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.M.; Peck, D.V. Acquiring data for large aquatic resource surveys: The art of compromise among science, logistics, and reality. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 837–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.M.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Herlihy, A.T.; Intelmann, S.S.; Corbett, S.C.; Arbogast, M.C.; Hjort, R.C. Electrofishing distance needed to estimate fish species richness in raftable Oregon rivers. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2002, 22, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.M.; Herlihy, A.T.; Peck, D.V. Sampling efforts for estimating fish species richness in western USA river sites. Limnologica 2021, 87, 125859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.G.; Paukert, C.P. A flexible survey design for monitoring spatiotemporal fish richness in nonwadeable rivers: Optimizing efficiency by integrating gears. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 77, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffaux, D.G. Electrofishing versus gillnet sampling for the assessment of fish assemblages in large rivers. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 162, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R.; Chu, E.W. Sustaining living rivers. Hydrobiologia 2000, 422–423, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkman, H.E.; Rabeni, C.F. Effect of siltation on stream fish communities. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1987, 18, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, P.; Sear, D.; Collins, A.; Naden, P.; Jones, I. The impacts of fine sediment on riverine fish. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1800–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.M.; Vadas, R.L. Agricultural effects on streams and rivers: A western USA focus. Water 2021, 13, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, P.R.; Hughes, R.M.; Paulsen, S.G.; Peck, D.V.; Seeliger, C.W.; Weber, M.H.; Mitchell, R.M. Physical habitat in conterminous US streams and rivers, Part 1: Geoclimatic controls and anthropogenic alteration. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlihy, A.T.; Sifneos, J.C.; Hughes, R.M.; Peck, D.V.; Mitchell, R.M. The relation of lotic fish and benthic macroinvertebrate condition indices to environmental factors across the conterminous USA. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lyons, J.; Kanehl, P.; Gatti, R. Influences of watershed land use on habitat quality and biotic integrity in Wisconsin streams. Fisheries 1997, 22, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M.; Blanco-Garrido, F.; Prenda, J. Invasive species and habitat degradation in Iberian streams: An analysis of their role in freshwater fish diversity loss. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierro, P.; Bertrán, C.; Tapia, J.; Hauenstein, E.; Peña-Cortés, F.; Vergara, C.; Cerna, C.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Effects of local land-use on riparian vegetation, water quality, and the functional organization of macroinvertebrate assemblages. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, S.V.; Swanson, F.J.; McKee, W.A.; Cummins, K.W. An ecosystem perspective of riparian zones. BioScience 1991, 41, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Decamps, H.; Pollock, M. The role of riparian corridors in maintaining regional biodiversity. Ecol. Appl. 1993, 3, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusey, B.J.; Arthington, A.H. Importance of the riparian zone to the conservation and management of freshwater fish: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelo, J.; Da Costa, L.; Ribeiro, D.; Gago, J.; Magalhães, M.; Gante, H.; Alves, M.; Cheoo, G.; Gkenas, C.; Banha, F.; et al. Evaluating the range expansion of recreational non-native fishes in Portuguese freshwaters using scientific and citizen science data. BioInvasions Rec. 2021, 10, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, M.J.; Arthington, A.H.; Pusey, B.J.; Harch, B.D. Are alien fish a reliable indicator of river health? Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Caiola, N.; Casals, F.; Oliveira, J.M.; De Sostoa, A. Assessing perturbation of river fish communities in the Iberian ecoregion. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Merchante, A.; Prenda, J. The ecological and conservation status of the Guadalquivir river basin (s Spain) through the application of a fish-based multimetric index. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M. Revisiting ecological integrity 30 years later: Non-native species and the misdiagnosis of freshwater ecosystem health. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, E.; Alcaraz, C.; Rocaspana, R.; Pou-Rovira, Q.; García-Berthou, E. Adaptation of the European Fish Index (EFI+) to include the alien fish pressure. Fishes 2023, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungwirth, M.; Muhar, S.; Schmutz, S. Fundamentals of fish ecological integrity and their relation to the extended serial discontinuity concept. Assess. Ecol. Integr. Run. Waters 2000, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowall, R.M.; Taylor, M.J. Environmental indicators of habitat quality in a migratory freshwater fish fauna. Environ. Manag. 2000, 25, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, G.; Moreira, M.; Branco, P.; Da Costa, L.; Ferreira, M.T.; Segurado, P. One millennium of historical freshwater fish occurrence data for Portuguese rivers and streams. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G.; Branco, P.; Haidvogl, G.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pont, D.; Segurado, P. iPODfish–A new method to infer the historical occurrence of diadromous fish species along river networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.; Piette, R.R.; Niermeyer, K.W. Development, validation, and application of a fish-based index of biotic integrity for Wisconsin’s large warmwater rivers. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2001, 130, 1077–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, K.; Turpin, C.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Dams have varying impacts on fish communities across latitudes: A quantitative synthesis. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1501–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, J.M.; Ilhéu, M.; Matono, P.; Costa, A.M. Interannual variation of fish assemblage structure in a Mediterranean river: Implications of streamflow on the dominance of native or exotic species. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propst, D.L.; Gido, K.B. Responses of native and nonnative fishes to natural flow regime mimicry in the San Juan river. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2004, 133, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, C.O.; Rankin, E.T. Biological response signatures and the area of degradation value: New tools for interpreting multimetric data. In Biological Assessment and Criteria: Tools for Water Resources Planning and Decision Making; Davis, W.S., Simon, T.P., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.M.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Herlihy, A.T.; Kincaid, T.M.; Reynolds, L.; Larsen, D.P. A process for developing and evaluating indices of fish assemblage integrity. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, S.; Elosegi, A.; Ludwig, R. Multiple Stressors in River Ecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).