Environmentally Friendly and Efficient Methods for Mitigating the Density of Ascidian Fouling in Mediterranean Mussel Farming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
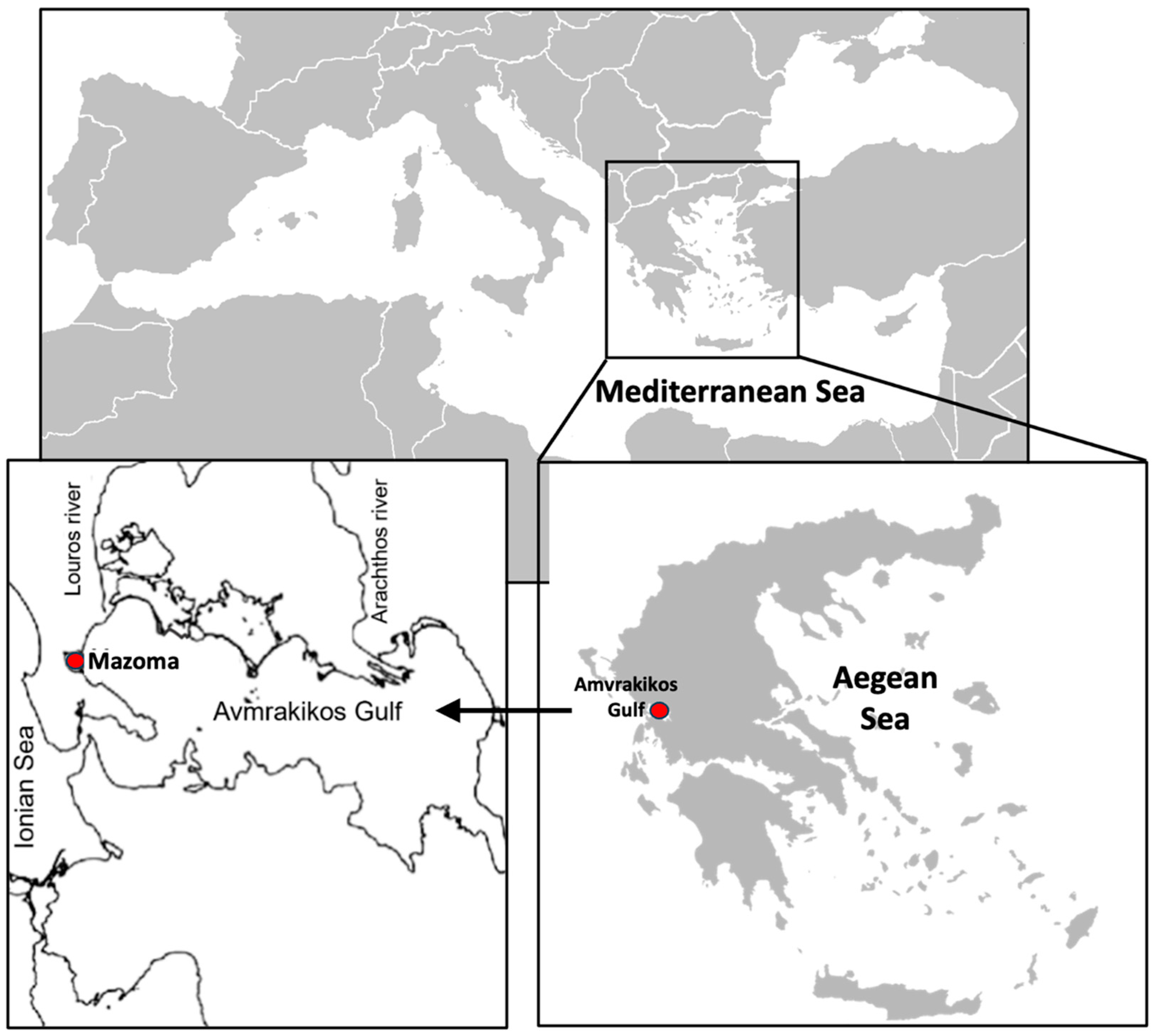
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Preparation of Mussel Socks
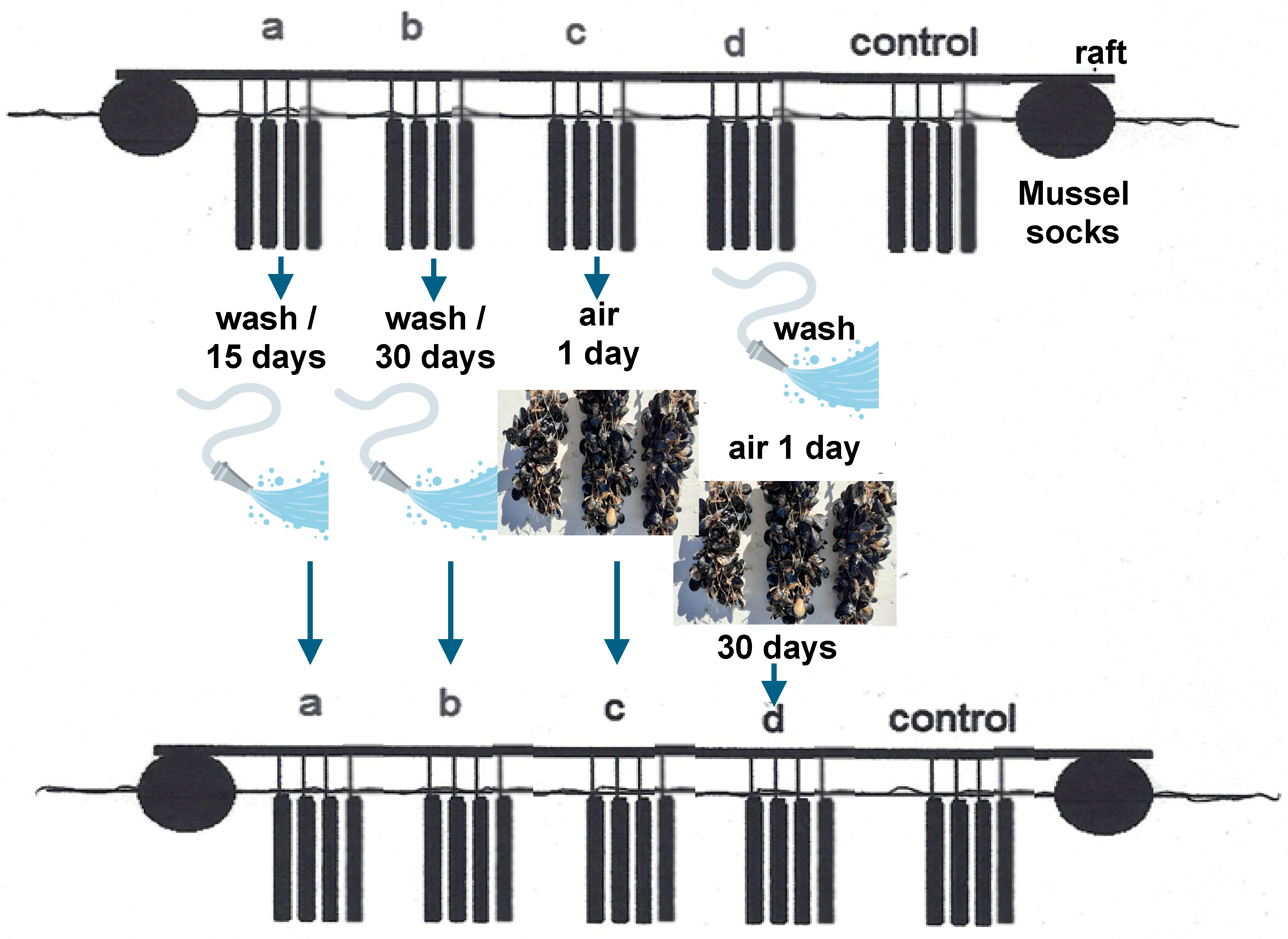
2.3. Field Experiment (Mussel Sock Washing Duration and/or Air Exposure): Designation of Experiment 1
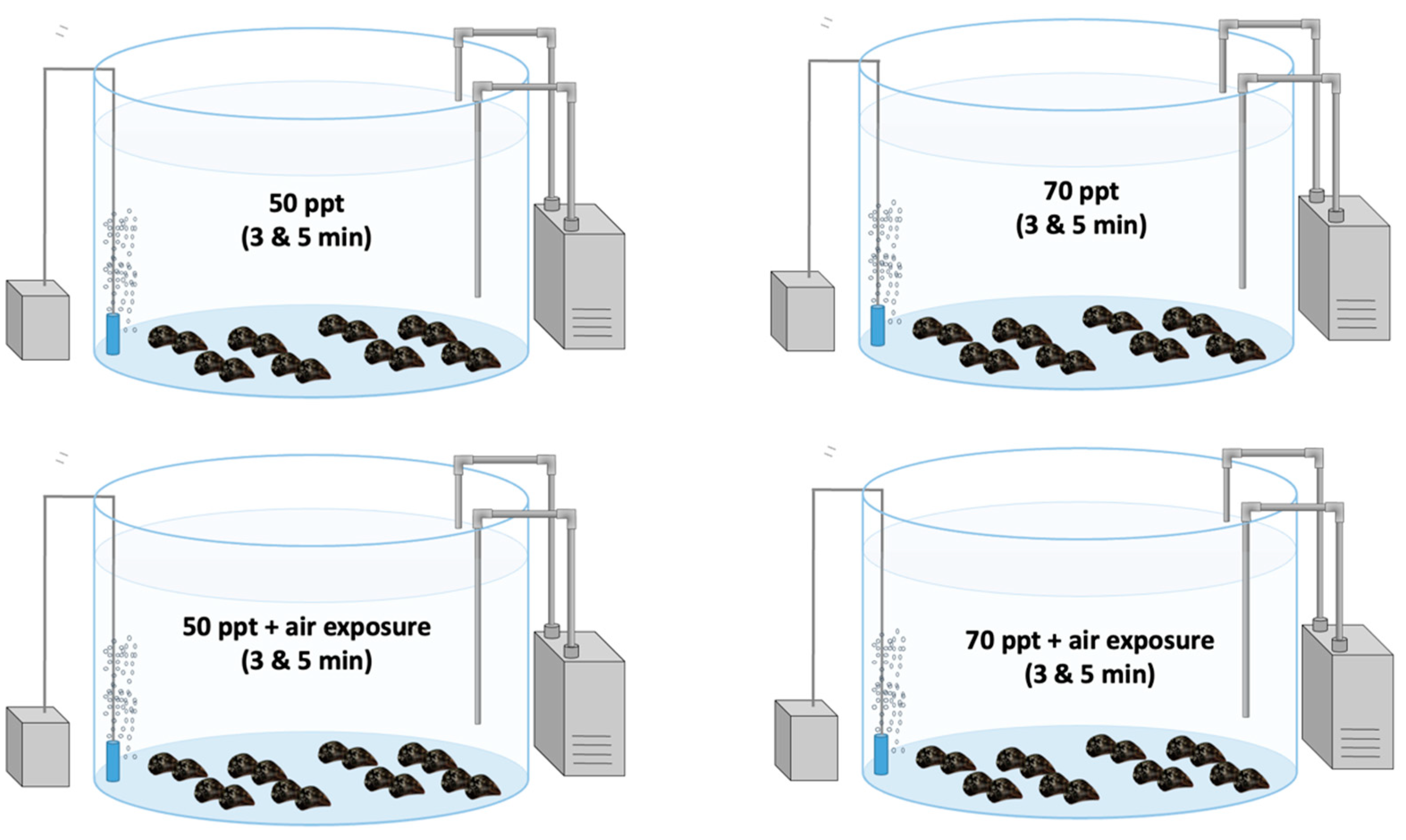
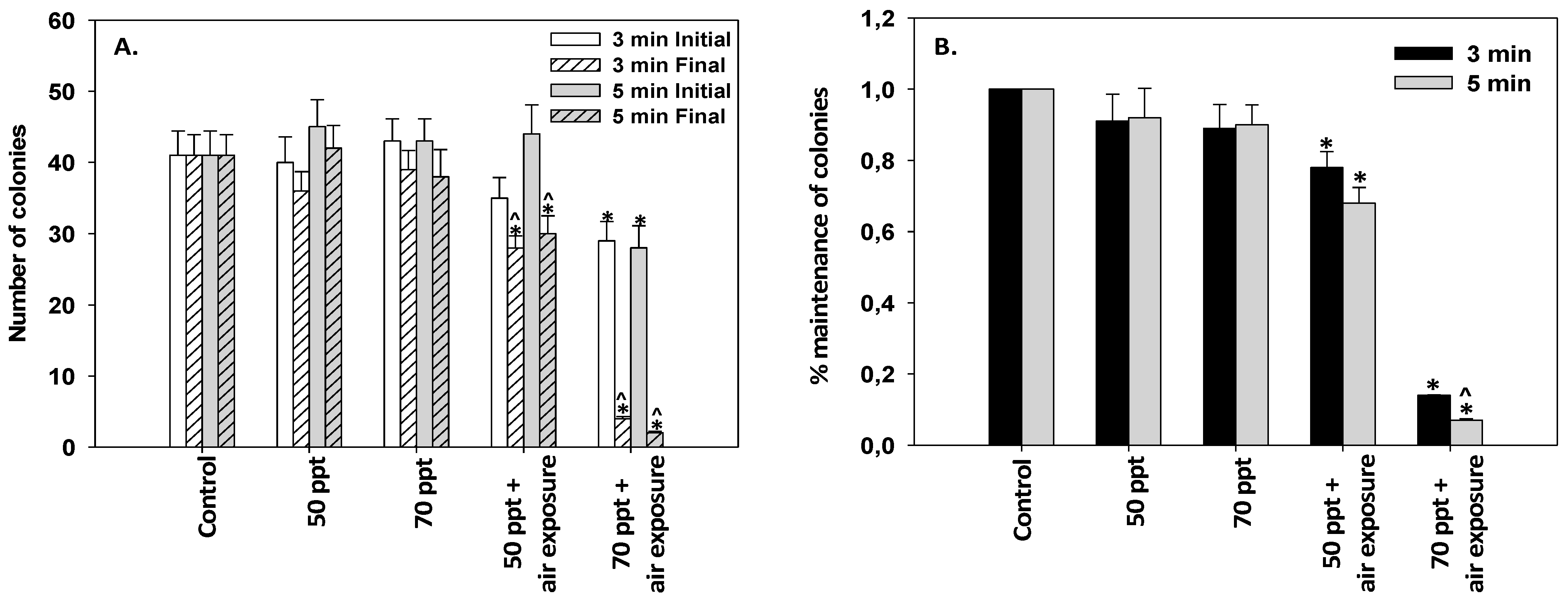
2.4. Laboratory Experiment (Immersion of Mussel Socks in High-Salinity Solutions): Designation of Experiment 2
2.5. Data Treatment and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sea Water Physicochemical Parameters
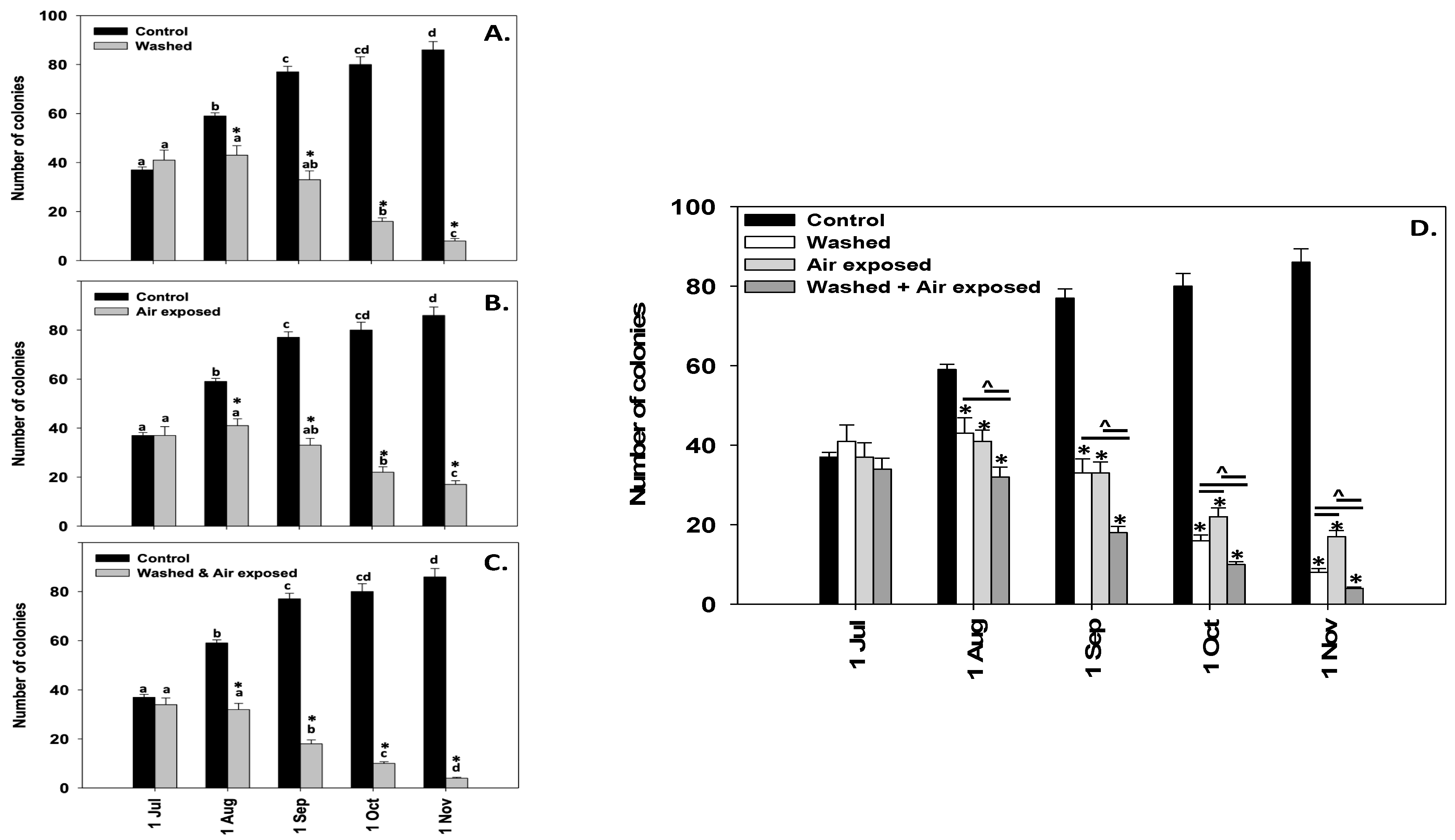
3.2. Mussel Sock Washing and/or Air Exposure
3.3. Immersion of Mussel Socks in High-Salinity Solutions
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Different Treatments
4.2. Strategies to Mitigate Biofouling in Shellfish Aquaculture
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khosravi, M.; Nasrolahi, A.; Shokri, M.R.; Dobretsov, S.; Pansch, C. Impact of warming on biofouling communities in the northern Persian Gulf. J. Therm. Biol. 2019, 85, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.; Willemsen, P.R. Collaborative effort looks into biofouling. Fish Farming Int. 2004, 44, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Enright, C. Control of fouling in bivalve aquaculture. World Aquacult. 1993, 24, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Claereboudt, M.R.; Bureau, D.; Côté, J.; Himmelman, J.H. Fouling development and its effect on the growth of juvenile giant scallops (Placopecten magellanicus) in suspended culture. Aquaculture 1994, 121, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnes, J.V.; Rudi, H.; Loland, G. Chap. 12: Current forces on cage, net deflection. In Engineering for Offshore Fish Farming; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 1990; pp. 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidantsis, K.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Michaelidis, B.; Giantsis, I.A. Effects of Biofouling by Ascidians on Cultured Mussels: Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Antioxidant Defense. J. Shellfish. Res. 2008, 42, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Michaelidis, B.; Feidantsis, K. The impact of ascidian biofouling on the farmed Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis physiology and welfare, revealed by stress biomarkers. Biofouling 2023, 39, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, A.; Davidson, J.; Landry, T.; Arsenault, G. Process of invasiveness among exotic tunicates in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Biol. Invasions 2008, 10, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, R.M.; Herbinger, C.M. Ecological interactions between the vase tunicate (Ciona intestinalis) and the farmed blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) in Nova Scotia, Canada. Aquat. Invasions 2009, 4, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.M.; Shumway, S.E.; Whitlatch, R.B.; Getchis, T. Biofouling in marine molluscan shellfish aquaculture: A survey assesses the business and economic implications of mitigation. J. World Aquacult Soc. 2011, 42, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckindsey, C.W.; Landry, T.; O’beirn, F.; Davies, I.M. Bivalve aquaculture and exotic species: A review of ecological considerations and management issues. Shellfish Res. 2007, 26, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsotsios, D.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Michaelidis, B.; Theodorou, J.A. Impacts of the establishment of biofoulants on greek aquaculture: Farmers’ Expert knowledge. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitridge, I.; Dempster, T.; Guenther, J.; de Nys, R. The impact and control of biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review. Biofouling 2012, 28, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.; Davidson, J.; Bourque, D.; Stryhn, H. Recruitment patterns and population development of the invasive ascidian Ciona intestinalis in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Aquat. Invasions 2009, 4, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, X. Periods of non-feeding in Polysyncratonlacazei (Ascidiacea: Didemnidae): A rejuvenative process? Mar. Biol. 1992, 112, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Portela, R.; Palacin, C.; Duran, S.; Turon, X. Biological traits of three closely related species of Pycnoclavella (Ascidiacea) in the Western Mediterranean. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, W.R. Environmental factors affecting reproduction and development in ascidians and other prochordates. Can. J. Zool. 2005, 83, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G. Ecology and natural history of the protochordates. Can. J. Zool. 2005, 83, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbody, I. Continuous breeding in three species of tropical ascidians. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1961, 136, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, D.S. Recruitment of a tropical colonial ascidian: Relative importance of pre-settlement vs. post-settlement processes. Ecology 1990, 71, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoste, E.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N. Biofouling impact on production and ecosystem functioning: A review for bivalve aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2015, 7, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, J.; Sievers, M.; Bush, F.; Bloecher, N. Biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review of recent research and developments. Biofouling 2019, 35, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, B.; Kosmeyer, P.; O’Conoe, W.; Dove, M.; Johnstone, K. Oyster Overcatch: Cold Shock Treatment. 2012. Available online: https://www.frdc.com.au/sites/default/files/products/2010-734-DLD.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Paetzold, S.C.; Davidson, J. Aquaculture fouling: Efficacy of potassium monopersulphonate triple saltbased disinfectant (Virkon® Aquatic) against Ciona intestinalis. Biofouling 2011, 27, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.E.; Chisholm, A.; Mallet, A.L. Strategies to mitigate the impact of Ciona intestinalis (L.) biofouling on shellfish production. J. Shellfish Res. 2003, 22, 621–631. [Google Scholar]
- Arens, C.; Paetzold, C.; Ramsay, A.; Davidson, J. Pressurized seawater as an antifouling treatment against the colonial tunicates Botrylloides violaceus and Botryllus schlosseri in mussel aquaculture. Aquat. Invasions 2011, 6, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paetzold, S.C.; Hill, J.; Davidson, J. Efficacy of high-pressure seawater spray against colonial tunicate fouling in mussel aquaculture: Inter-annual variation. Aquat. Invasions 2012, 7, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, L.J.F.; Pearce, C.M.; Hodes, V.; Nelson, J.C.; Wasser, C.; Savery, J.; Therriault, T.W. Mitigating non-indigenous species movements: Effects of pressure-washing intensity and duration on the removal of biofouling and mobile invertebrates from cultured Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg, 1793)). Manag. Biol. Invasions 2021, 12, 618–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M.; Fitridge, I.; Bui, S.; Dempster, T. To treat or not to treat: A quantitative review of the effect of biofouling and control methods in shellfish aquaculture to evaluate the necessity of removal. Biofouling 2017, 33, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, L.P.; Atalah, J.; Cunningham, S.; Day, A.; Fletcher, L.; South, P.; Forrest, B.; Hopkins, G. Acetic acid immersion—A reactive pest treatment for bivalve aquaculture. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katselis, G.N.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Dimitriou, E.N.; Koutsikopoulos, C. Long-term changes of fisheries landings in enclosed gulf lagoons (Amvrakikos gulf, W Greece): Influences of fishing and other human impacts. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 131, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountoura, K.; Zacharias, I. Temporal and spatial distribution of hypoxic/seasonal anoxic zone in Amvrakikos Gulf, Western Greece. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountoura, K.; Zacharias, I. Trophic state and oceanographic conditions of Amvrakikos Gulf: Evaluation and monitoring. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaidou, A.; Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, M.; Ignatiades, L. A survey of estuarine benthic, zooplanktonic and phytoplanktonic communities of Amvrakikos Gulf, Ionian Sea. Mar. Ecol.—Pubbl. Stn. Zool. Napoli 1983, 4, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotidis, P.; Pancucci, M.A.; Balopoulos, E.; Gotsis-Skretas, O. Plankton distribution patterns in a Mediterranean dilution basin: Amvrakikos Gulf (Ionian Sea, Greece). Mar. Ecol.—Pubbl. Stn. Zool. Napoli 1994, 15, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friligos, N.; Balopoulos, E.T.; Psillidou-Giouranovits, R. Eutrophication and hydrography in the Amvrakikos Gulf, Ionian Sea. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 1997, 6, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ferentinos, G.; Papatheodorou, G.; Geraga, M.; Iatrou, M.; Fakiris, E.; Christodoulou, D.; Dimitriou, E.; Koutsikopoulos, C. Fjord water circulation patterns and dysoxic/anoxic conditions in a Mediterranean semi-enclosed embayment in the Amvrakikos Gulf, Greece. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehagias, G.; Aposporis, M. Zooplankton variation in relation to hydrology in an enclosed hypoxic bay (Amvrakikos Gulf, Greece). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, V.; Pascual, M.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Turon, X. When invasion biology meets taxonomy: Clavelina oblonga (Ascidiacea) is an old invader in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillock, K.A.; Costello, M.J. Tolerance of the invasive tunicate Styela clava to air exposure. Biofouling 2013, 29, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, G.A.; Prince, M.; Cahill, P.L.; Fletcher, L.M.; Atalah, J. Desiccation as a mitigation tool to manage biofouling risks: Trials on temperate taxa to elucidate factors influencing mortality rates. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.M.; Venâncio, E.; Dionísio, M.A.; Heumüller, J.; Chainho, P.; Pombo, A. Comparison of the Efficiency of Different Eradication Treatments to Minimize the Impacts Caused by the Invasive Tunicate Styela plicata in Mussel Aquaculture. Animals 2023, 13, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbyson, E.; Locke, A.; Hanson, J.M.; Willison, J.M. Marine boating habits and the potential for spread of invasive species in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Aquat. Invasions 2009, 4, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, L.L. Osmoregulatory capabilities of three macrosympatrics to lidobranch ascidians, Styela clava Herdman, S. plicata (Lesueur), and S. montereyensis (Dall). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1984, 82, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, M.R.; Morris, J.A.; Karney, R.C.; Grunden, D.W. An initial assessment of native and invasive tunicates in shellfish aquaculture of the North American east coast. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2010, 26, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, M.R.; Lindell, S.; Green-Beach, E.; Starczak, V.R. Treatments to eradicate invasive tunicate fouling from blue mussel seed and aquaculture socks. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2016, 7, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M.; Dempster, T.; Fitridge, I.; Keough, M.J. Monitoring biofouling communities could reduce impacts to mussel aquaculture by allowing synchronization of husbandry techniques with peaks in settlement. Biofouling 2014, 30, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, C.M.C.; Floerl, O.; Hayden, B.J. Biofouling on Greenshell (TM) mussel (Perna canaliculus) farms: A preliminary assessment and potential implications for sustainable aquaculture practices. Aquac. Int. 2012, 20, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsson, K.M.; Jonsson, P.R. Temporal and spatial patterns in recruitment and succession of a temperate marine fouling assemblage: A comparison of static panels and boat hulls during the boating season. Biofouling 2003, 19, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, J.; Fitridge, I.; Misimi, E. Potential antifouling strategies for marine finfish aquaculture: The effects of physical and chemical treatments on the settlement and survival of the hydroid Ectopleura larynx. Biofouling 2011, 27, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paetzold, S.C.; Davidson, J. Viability of golden star tunicate fragments after high-pressure water treatment. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, P.; Heasman, K.; Jeffs, A.; Kuhajek, J.; Mountfort, D. Preventing ascidian fouling in aquaculture: Screening selected allelochemicals for anti-metamorphic properties in ascidian larvae. Biofouling 2012, 28, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, B.M.; Hopkins, G.A.; Dodgshun, T.J.; Gardner, J.P.A. Efficacy of acetic acid treatments in the management of marine biofouling. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, N.; Davidson, J.; Tremblay, R.; McNiven, M.; Landry, T. The effect of antifouling treatments for the clubbed tunicate on the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis. Aquaculture 2007, 264, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, C.M. Development of a method to reduce the spread of the ascidian Didemnum vexillum with aquaculture transfers. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M.; Dempster, T.; Keough, M.J.; Fitridge, I. Methods to prevent and treat biofouling in shellfish aquaculture. Aquaculture 2019, 505, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nys, P.C.; Steinberg, P.D.; Charlton, T.S.; Christov, V. Antifouling of Shellfish and Aquaculture Apparatus. U.S. Patent US6692557B1, 17 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Giantsis, I.A.; Mucci, N.; Randi, E.; Abatzopoulos, T.J.; Apostolidis, A.P. Microsatellite variation of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) in central and eastern Mediterranean: Genetic panmixia in the Aegean and the Ionian Seas. JMBA 2014, 94, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.K.; Rhee, J.S. Effects of antifouling biocides on molecular and biochemical defense system in the gill of the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Dougherty, R.H.; Rasco, B.; Kang, D.H. Combined effect of mild heat and acetic acid treatment for inactivating Escherichia coli O157: H7, Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium in an asparagus puree. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piló, D.; Pereira, F.; Carvalho, A.N.; Vasconcelos, P.; Cunha, A.M.; Gaspar, M.B. Are non-indigenous species hitchhiking offshore farmed mussels? A biogeographic and functional approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group | Method | Period | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group a | Sea water washing | Every 15 days | 1 July–31 October |
| Group b | Sea water washing | Every 30 days | 1 July–31 October |
| Group c | Air exposure | Every 30 days | 1 July–31 October |
| Group d | Sea water washing and air exposure | Every 30 days | 1 July–31 October |
| Group e | Control |
| Group | Immersion | Duration | Air exposure | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50/3 | 50 ppt salinity solution | 3 min | 8 days | |
| 50/5 | 50 ppt salinity solution | 5 min | 8 days | |
| 70/3 | 70 ppt salinity solution | 3 min | 8 days | |
| 70/5 | 70 ppt salinity solution | 5 min | 8 days | |
| 50/3a | 50 ppt salinity solution | 3 min | 24 h | 8 days |
| 50/5a | 50 ppt salinity solution | 5 min | 24 h | 8 days |
| 70/3a | 70 ppt salinity solution | 3 min | 24 h | 8 days |
| 70/5a | 70 ppt salinity solution | 5 min | 24 h | 8 days |
| control | 8 days |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsotsios, D.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Alvanou, M.V.; Georgoulis, I.; Lattos, A.; Michaelidis, B.; Feidantsis, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A. Environmentally Friendly and Efficient Methods for Mitigating the Density of Ascidian Fouling in Mediterranean Mussel Farming. Fishes 2024, 9, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040135
Tsotsios D, Papadopoulos DK, Alvanou MV, Georgoulis I, Lattos A, Michaelidis B, Feidantsis K, Giantsis IA, Theodorou JA. Environmentally Friendly and Efficient Methods for Mitigating the Density of Ascidian Fouling in Mediterranean Mussel Farming. Fishes. 2024; 9(4):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040135
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsotsios, Dimitrios, Dimitrios K. Papadopoulos, Maria V. Alvanou, Ioannis Georgoulis, Athanasios Lattos, Basile Michaelidis, Konstantinos Feidantsis, Ioannis A. Giantsis, and John A. Theodorou. 2024. "Environmentally Friendly and Efficient Methods for Mitigating the Density of Ascidian Fouling in Mediterranean Mussel Farming" Fishes 9, no. 4: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040135
APA StyleTsotsios, D., Papadopoulos, D. K., Alvanou, M. V., Georgoulis, I., Lattos, A., Michaelidis, B., Feidantsis, K., Giantsis, I. A., & Theodorou, J. A. (2024). Environmentally Friendly and Efficient Methods for Mitigating the Density of Ascidian Fouling in Mediterranean Mussel Farming. Fishes, 9(4), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040135









