Vitamin C Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation Caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diet Formulation
2.2. Proximate Composition of the Diets
2.3. Management of the Experimental Fish
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Challenge Test
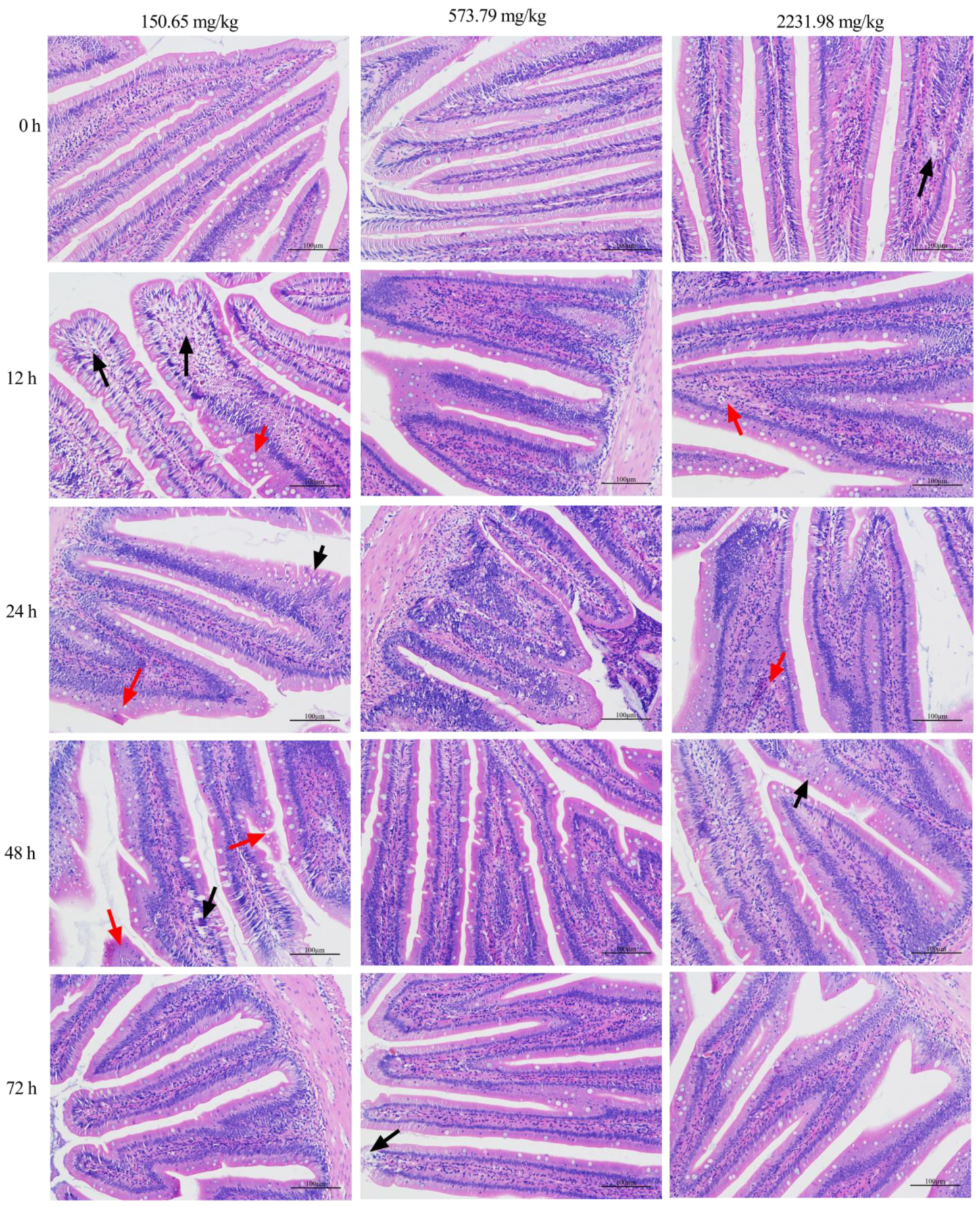
2.6. Intestinal Histology
2.7. Serum and Intestinal Immune-Related Indicator Determination
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, and Survival Rate of Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream
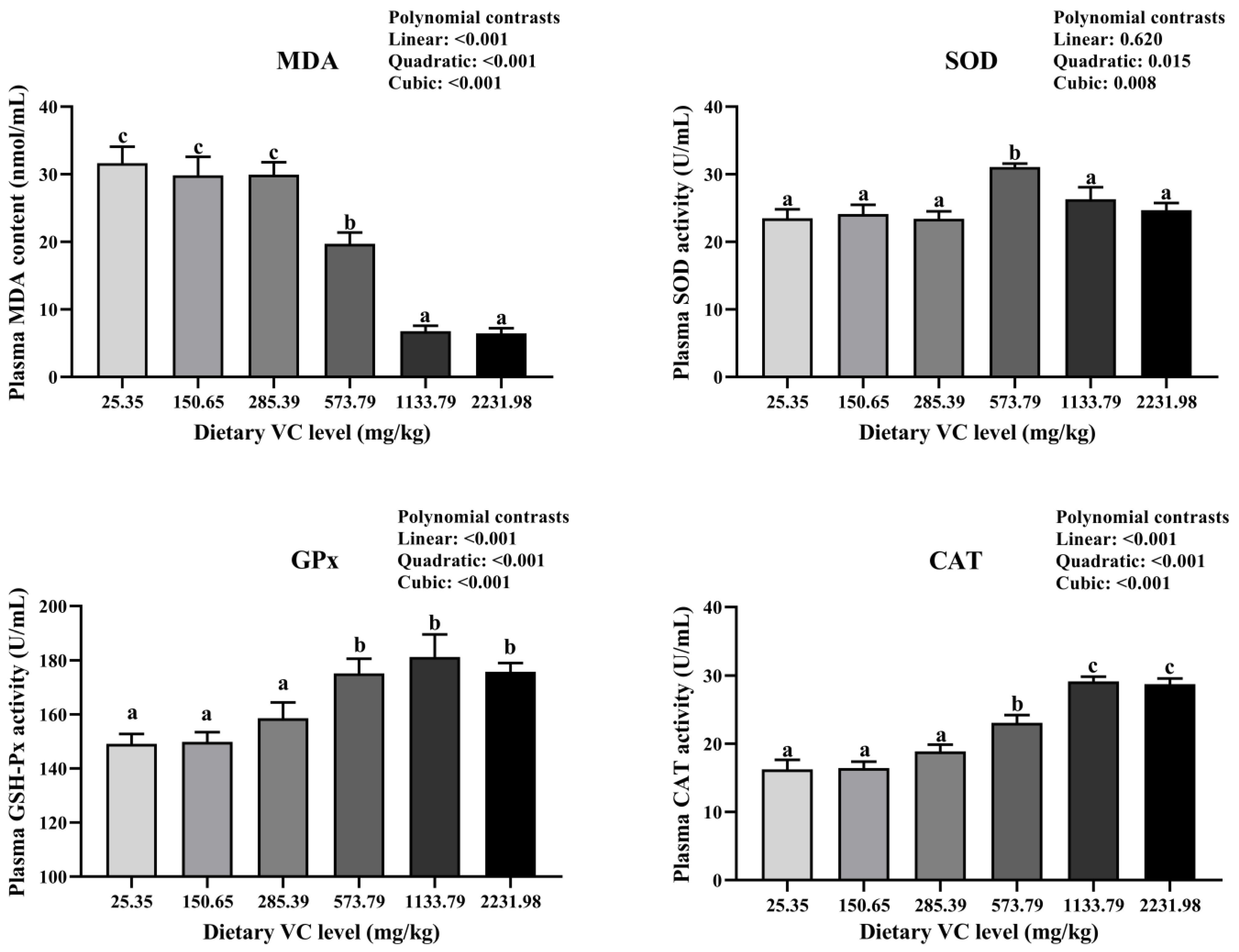
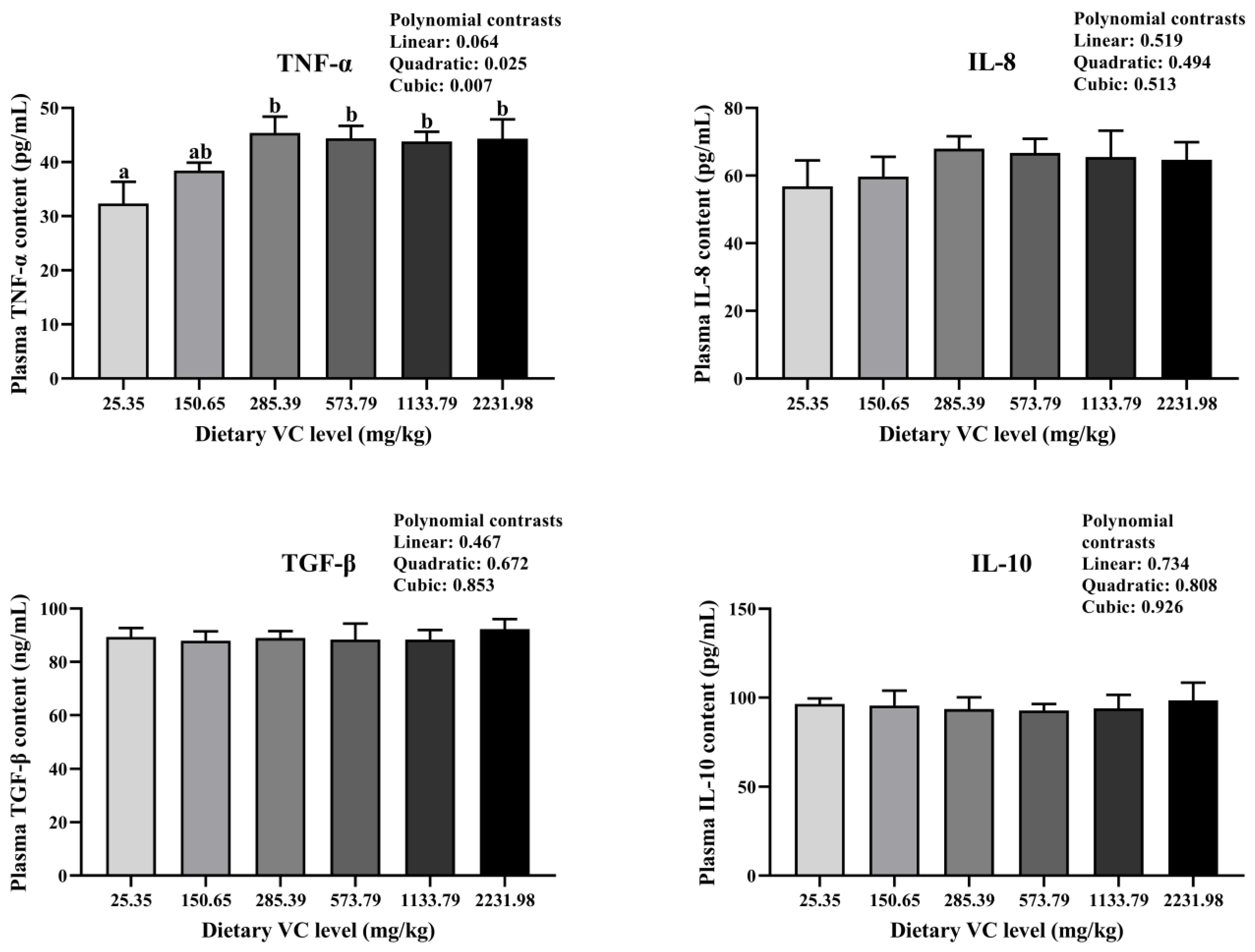
3.2. Serum Immune-Related Indices, Antioxidant Capacity, and Cytokines of Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream in the Feeding Trail
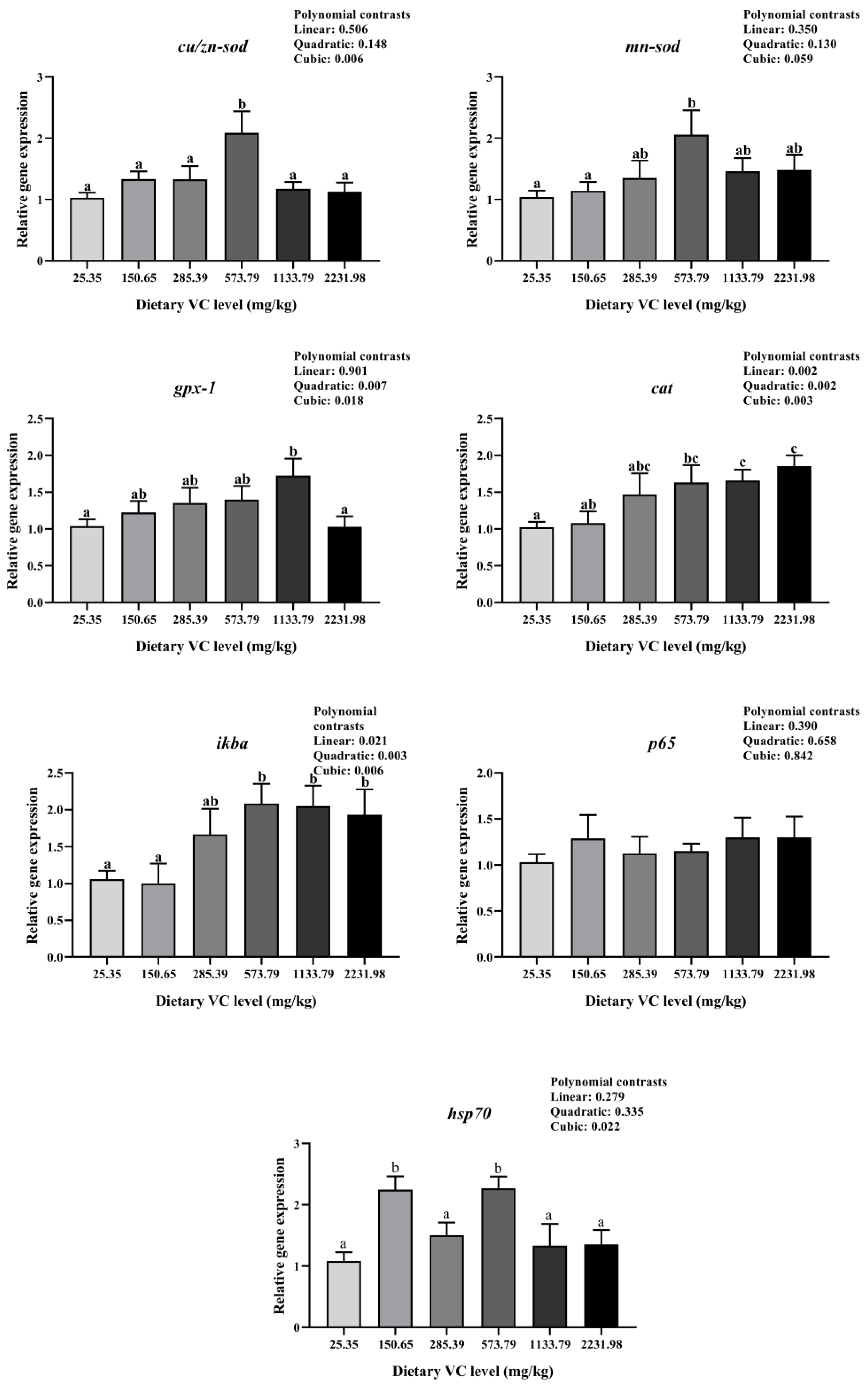
3.3. Immune-Related Gene Expression of Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream in the Feeding Trail
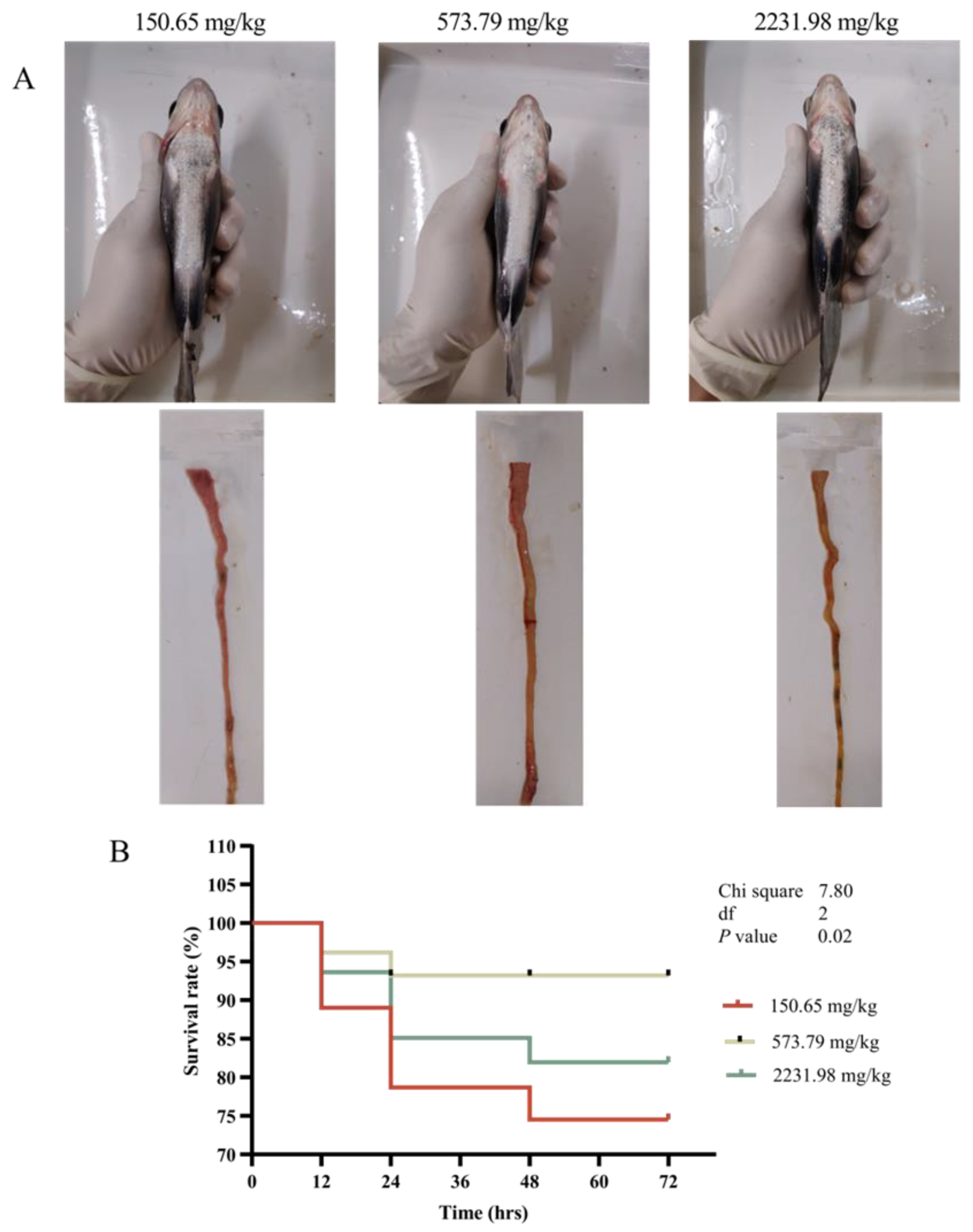
3.4. Survival Curve, Inflammatory Response, and Intestinal Histopathology after A. hydrophila Challenging
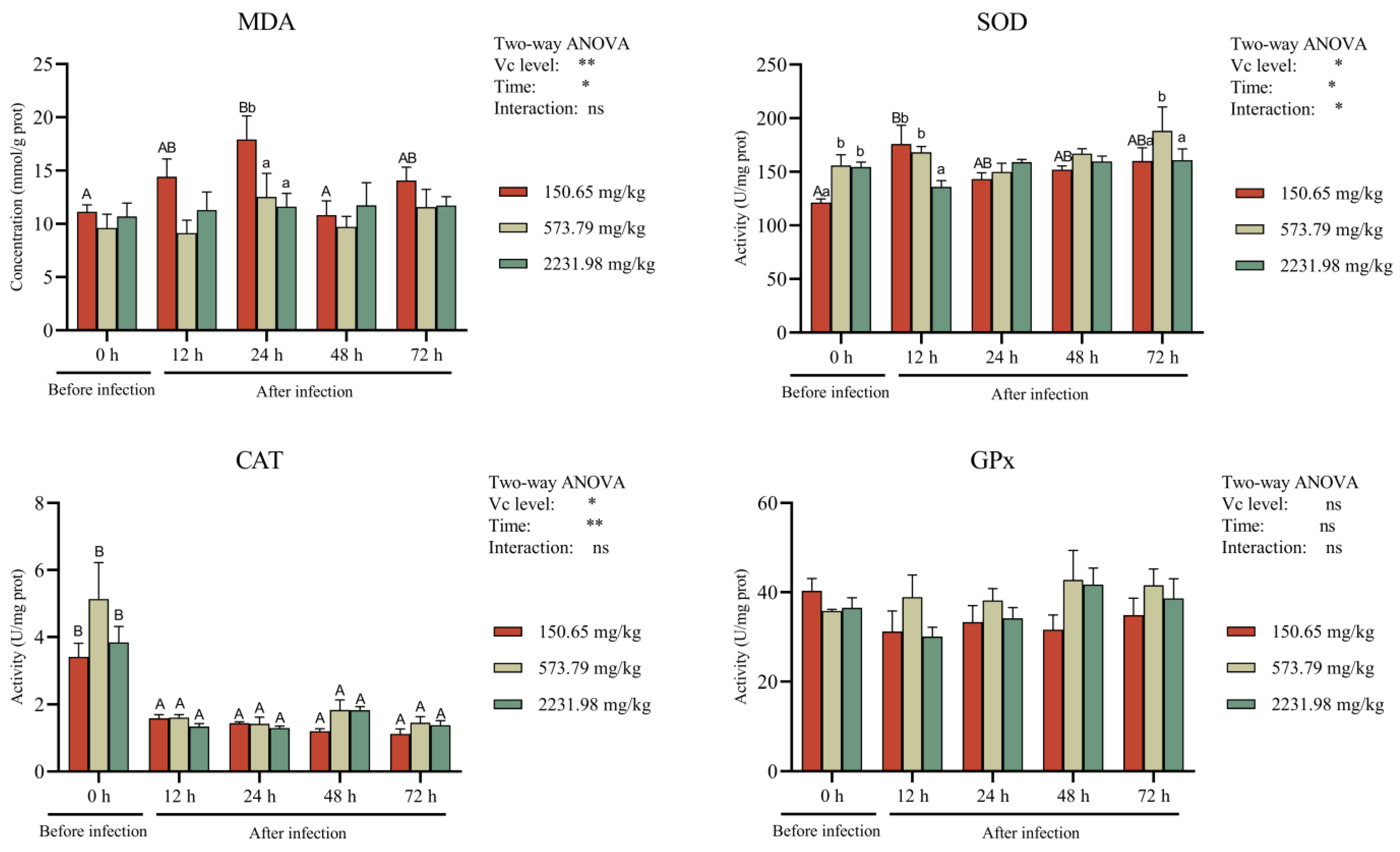
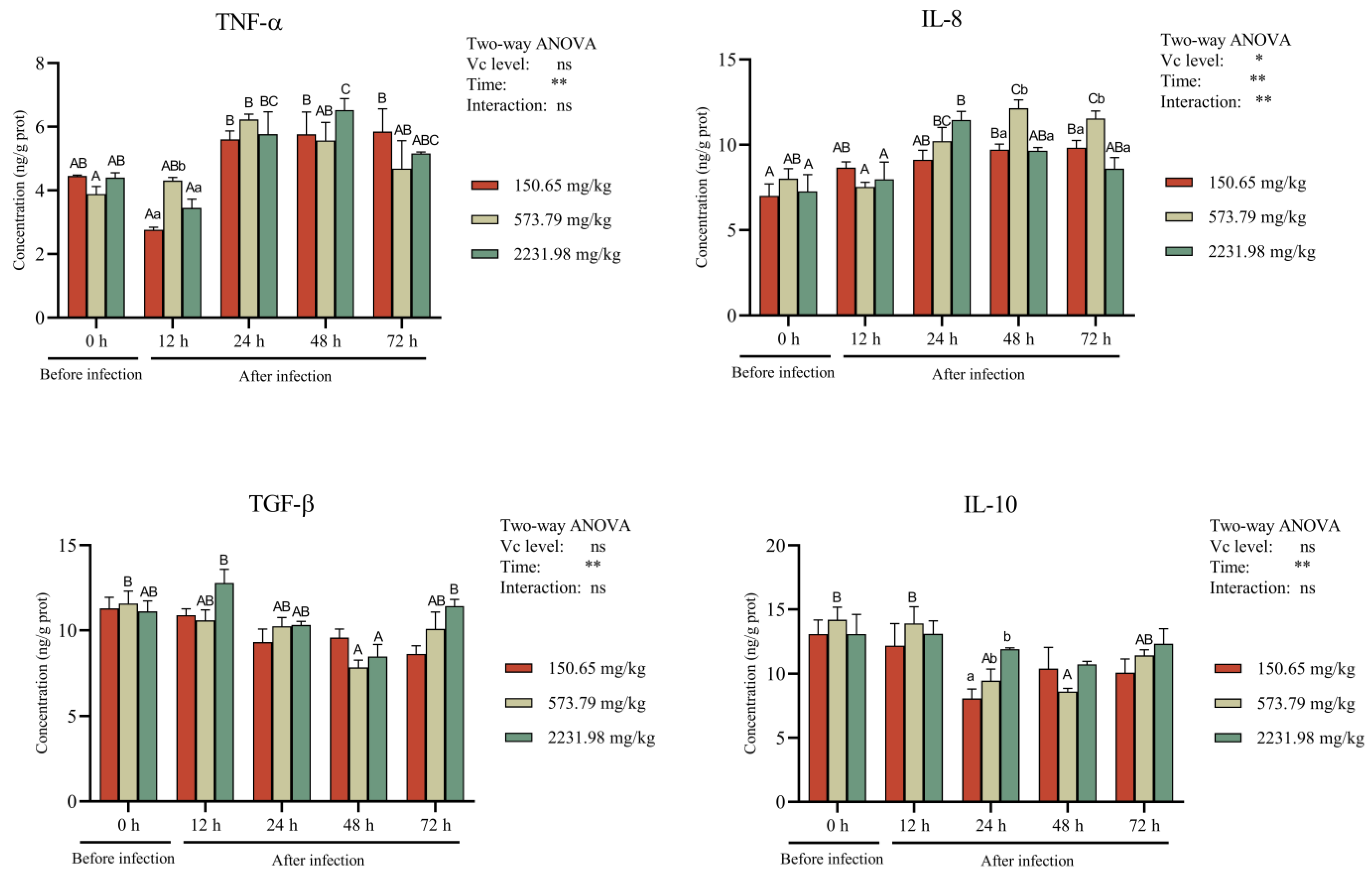
3.5. Intestinal Antioxidant Activity and Cytokines after A. hydrophila Challenge
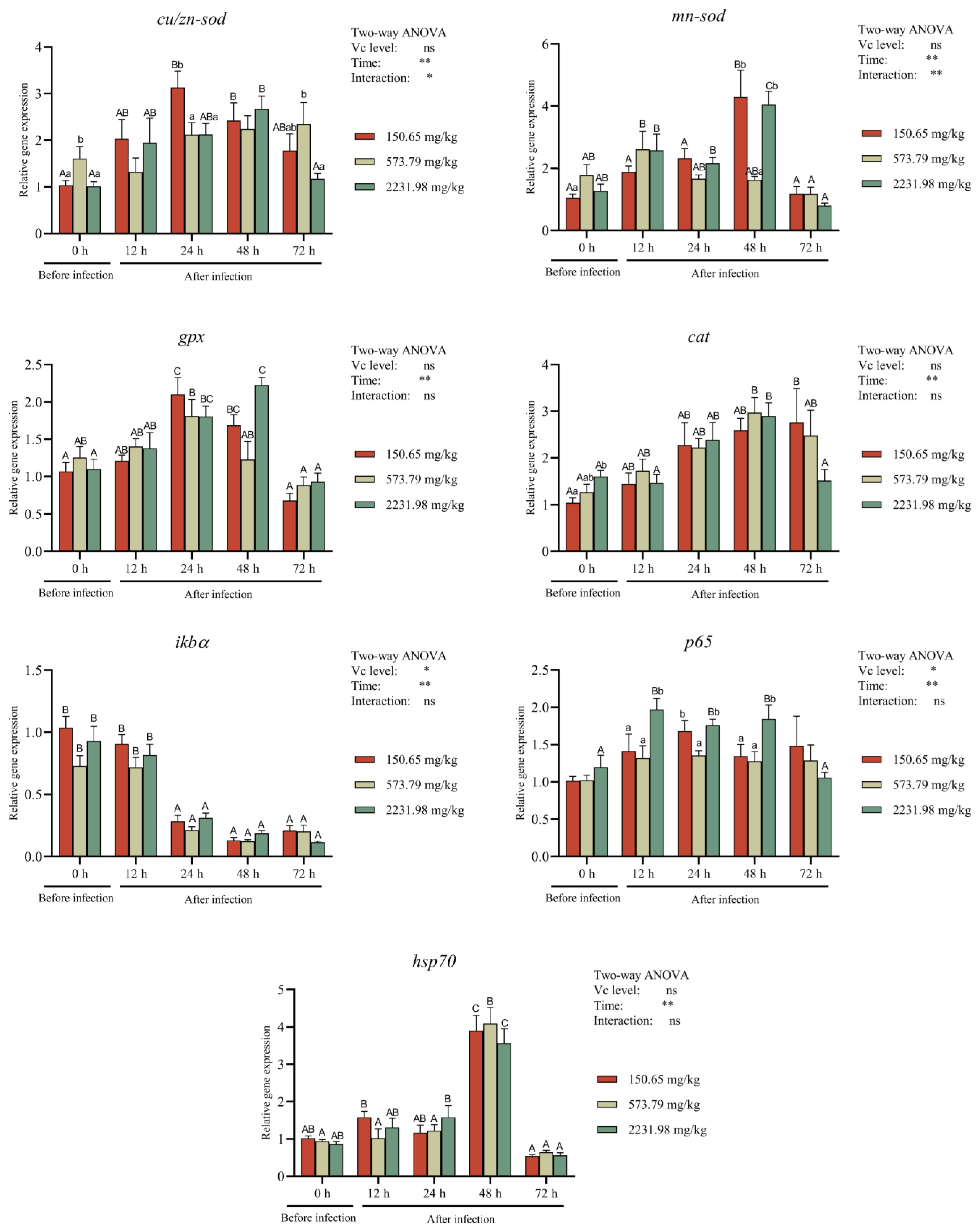
3.6. Immune-Related Gene Expressions after A. hydrophila Challenging
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dewali, S.; Sharma, N.; Melkani, D.; Arya, M.; Kathayat, N.; Panda, A.K.; Bisht, S.S. Aquaculture: Contributions to Global Food Security. In Emerging Solutions in Sustainable Food and Nutrition Security; Ghosh, S., Kumari Panda, A., Jung, C., Singh Bisht, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarex-Pellitero, P. Fish immunity and parasite infections: From innate immunity to immunoprophylactic prospects. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 126, 171198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.J.M.; Peterson, J.M.; Wolf, S.E. Detection of infection and sepsis in burns. Surg. Infect. 2021, 22, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, X.; Gao, J. Effects of dietary vitamin E supplementation on growth performance, fatty acid composition, lipid peroxidation and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) expressions in juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Feng, H.; Zou, J. The biological functions and intestinal inflammation regulation of IL-21 in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) during infection with Aeromonas hydrophila. Cells 2023, 12, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Kumar, A.; Kuma, N. A review on pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and their mitigation through medicinal herbs in aquaculture. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.M.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, L.F.; Wang, W.; Robinson, N.A.; Gao, Z.X. Estimation of genetic parameters for resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Aquaculture 2017, 479, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.; Maggini, S. Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, G.; Godin, J.R.; Pagé, B. The genetics of vitamin C loss in vertebrates. Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habte-Tsion, H.M.; Ge, X.; Liu, B.; Xie, J.; Ren, M.; Zhou, Q.; Miao, L.; Pan, L.; Chen, R. A deficiency or an excess of dietary threonine level affects weight gain, enzyme activity, immune response and immune-related gene expression in juvenile blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.J.; Liu, B.; Ge, X.; Xie, J.; Cui, S.; Zhou, M. Effect of dietary vitamin C on growth performance, hematology and muscle physicochemical indexes of juvenile Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2013, 22, 112–119, (written in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, B.; Xie, J.; Cui, S.; Zhou, M.; Xia, S.; Chen, R. Effect of dietary vitamin C on non-specific immunity and mRNA expression of three heat shock proteins (HSPs) in juvenile Megalobrama amblycephala under pH stress. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, J.; Sahoo, P.K.; Swain, T.; Sahoo, S.K.; Sahu, A.K.; Mohanty, B.R. Seasonal variation in the innate immune parameters of the Asian catfish Clarias batrachus. Aquaculture 2006, 252, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Shiau, S. Dietary l-ascorbic acid affects growth, nonspecific immune responses and disease resistance in juvenile grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus. Aquaculture 2005, 244, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.L.; Su, Y.; He, Y.; Pan, L.; Ge, X.; Xu, P. Effects of anthraquinones extract from rhubarb R. officinale Bail on the crowding stress response and growth of common carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). J. Aquac. 2008, 281, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Huang, X.; Chena, N.; Aprakua, A.; Wanga, W.; Cornela, A.; Rahman, M.R. Impact of dietary vitamin C on plasma metabolites, antioxidant capacity and innate immunocompetence in juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Zhu, Y.F.; Cai, L.S.; Wu, T.X. Effects of fasting on the meat quality and antioxidant defenses of market-size farmed large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Aquaculture 2008, 280, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; He, Y.F.; Lin, S.; Dong, X.H.; Yang, Q.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.Y.; Tan, B.P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae extracts improved the effects of a low fishmeal, complex plant protein diet in the orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liang, H.; Mokrani, A.; Ji, K.; Yu, H.; Ge, X.; Ren, M.; Xie, J.; Pan, L.; Sun, A. Dietary histidine affects intestinal antioxidant enzyme activities, antioxidant gene expressions and inflammatory factors in juvenile blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 25, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Liang, H.; Ren, M.; Ge, X.; Mi, H.; Pan, L.; Yu, H. The immunoreaction and antioxidant capacity of juvenile blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) involves the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and NF-κB signal pathways in response to dietary methionine levels. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 105, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.J.; Jiang, G.Z.; Yuan, X.Y.; Liu, W.B. High-fat-diet-induced inflammation depresses the appetite of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) through the transcriptional regulation of leptin/mammalian target of rapamycin. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.L.; Xia, D.; Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Ge, X.; Sun, C.; Miao, L.; Lin, Y.; Liu, B. Molecular cloning and expression mechanism of Mnp65 in Megalobrama amblycephala response to Aeromonas hydrophilia challenge. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2021, 261, 111046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.H.; Liang, H.Y.; Guo, Z.X.; Wang, A.L.; Ye, C.X. Effect of dietary vitamin C on growth performance, antioxidant status and innate immunity of juvenile Puffer fish (Takifugu obscurus). Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh IJA 2017, 69, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Limbu, S.M.; Rong, H.; Yu, C.; Lin, F.; Wen, X. Effect of dietary vitamin C on growth performance, body composition and biochemical parameters of juvenile Chu’s croaker (Nibea coibor). Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 26, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hao, R.; Zhang, J.; Tian, C.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, G. Improved growth performance, digestive ability, antioxidant capacity, immunity and Vibrio harveyi resistance in coral trout (Plectropomus leopardus) with dietary vitamin. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, N.; Muralidhar, A.P.; Srivastava, P.P.; Jain, K.K.; Pani Prasad, K.; Manish, J.; Sivaramakrishnan, T. Dietary ascorbic acid requirement for growth of striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878) juveniles. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.J.; Jiang, W.D.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.N.; Zhang, Y.A.; et al. Dietary vitamin C deficiency depresses the growth, head kidney and spleen immunity and structural integrity by regulating NF-kappaB, TOR, Nrf2, apoptosis and MLCK signaling in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 52, 111–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowski, K. Primitive actimoterigian fishes can synthesize ascorbic acid. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1994, 50, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, J.; Bo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, K.; Gong, C. Aeromonas hydrophila induces intestinal inflammation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): An experimental model. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turutoglu, H.; Ercelik, S.; Corlu, M. Aeromonas hydrophila-associated skin lesions and septicaemia in a Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus). J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2005, 76, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qiao, N.; Shao, S. Isolation and characterization of a novel biosurfactant produced by hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Alcanivorax dieselolei B5. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, J.M. The main Aeromonas pathogenic factors. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 256261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samayanpaulraj, V.; Velu, V.; Uthandakalaipandiyan, R. Determination of lethal dose of Aeromonas hydrophila Ah17 strain in snake head fish Channa striata. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.K.; Jauncey, K.; Roberts, R.J. Stability of L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and its forms in fish feeds during processing, storage and leaching. Aquaculture 1987, 60, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tian, L.; Liao, J.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W.; Zhou, Y. Antioxidant capacity, non-specific immunity, histopathological analysis and immune-related genes expressions in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus infected with Aeromonas schubertii. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.E.; Ahmed, S.A.A.; Amer, S.A.; Al-Gabri, N.A.; Ahmed, A.I.; Abdel-Warith, A.W.A.; Younis, E.S.M.I.; Metwally, A.E. Influence of vitamin C feed supplementation on the growth, antioxidant activity, immune status, tissue histomorphology, and disease resistance in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, W.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, X. Dietary vitamin C deficiency depressed the gill physical barriers and immune barriers referring to Nrf2, apoptosis, MLCK, NF-κB and TOR signaling in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) under infection of Flavobacterium columnare. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 58, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Chen, C.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Xie, D.Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.H.; You, C.H.; Li, Y.Y. Effects of dietary vitamin C on growth, flesh quality and antioxidant capacity of juvenile golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2856–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.Y.; Han, D.; Yang, Y.X.; Jin, J.Y.; Liu, H.K.; Zhu, X.M.; Xie, S.Q. Effects of dietary vitamin C on growth, gonad development and antioxidant ability of on-growing gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio var. CAS III). Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.S.; Rudinsky, A.J.; Guillaumin, J.; Parker, V.J.; Creighton, K.J. Vitamin C in health and disease: A companion animal focus. Top Companion Anim. Med. 2020, 39, 100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.; Koshio, S. Vitamin C supplementation to optimize growth, health and stress resistance in aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Zommara, M.; Eweedah, N.M.; Helal, A.I.; Aboel-Darag, M.A. The potential role of nano-selenium and vitamin C on the performances of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9843–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclaren, J.E.; Michael, D.R.; Ashlin, T.G.; Ramji, D.P. Cytokines, macrophage lipid metabolism and foam cells: Implications for cardiovascular disease therapy. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Bae, S.; Yu, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.R.; Hwang, Y.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, J.L. The analysis of vitamin C concentration in organs of gulo-/-mice upon vitamin C withdrawal. Immune Netw. 2012, 12, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.I.; Zuchner, S.; Wang, G. Regulation of the epigenome by vitamin C. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, P.; Jenne, C. Immune Responses in the Liver. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Miao, T.Z.; Zhu, H.X.; Symonds, A.L.J.; Li, L.; Schurich, A.; Miani, M.K.; Zhang, J.M.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; Li, S.L.; et al. IL-2-Engineered nano-APC effectively activates viral antigen-mediated T cell responses from chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients. J. Innumon. 2012, 188, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mageid, A.D.; Zaki, A.G.; El Senosi, Y.A.; Fahmy, H.A.; El Asely, A.M.; Abo-Al-Ela, H.G.; El-Kassas, S. Modulatory effect of lipopolysaccharide on immune-related gene expression and serum protein fractionation in grey mullet, Mugil cephalus. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; El-Sabagh, M. Changes in the growth, humoral and mucosal immune responses following β-glucan and vitamin C administration in red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2017, 470, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, the first quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 226, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.; Liu, R.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lv, C.; Yang, G. Identification and functional characterization of the transcription factor NF-κB subunit p65 in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 95, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Hou, Q.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Mi, Y.; Hu, C. Ctenopharyngodon idella NF-κB subunit p65 modulates the transcription of IκBα in CIK cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Nagaraja, G.M.; Kaur, P.; Asea, E.E.; Asea, A. Chaperokine function of recombinant Hsp72 produced in insect cells using a baculovirus expression system is retained. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, P.; Qi, Z.L.; He, J. Studies on blood biochemical indices and expression of hepatic HSP70 mRNA of different tilapia strains artificially challenged with Streptococcus iniae. J. Fish. China 2010, 36, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.B.; Ren, H.C.; Wu, Y.J.; Yang, S.; Fei, H. Benefits and applications of vitamin C in farmed aquatic animals: An updated review. Aquac. Int. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredient | (%) | Nutrient Composition | Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish meal a | 8.00 | Moisture | 6.38 |
| Soybean meal a | 22.00 | Crude protein | 34.69 |
| Cottonseed meal a | 12.00 | Ether extract | 9.14 |
| Canola meal a | 22.00 | Ash | 7.82 |
| Wheat a | 19.00 | ||
| Rice bran a | 6.80 | ||
| Soybean oil | 3.40 | ||
| Lecithin b | 2.00 | ||
| Chlorine chloride b | 0.10 | ||
| Vitamin premix b,c | 1.00 | ||
| Mineral premix b,c | 1.00 | ||
| Ca(H2PO4)2 b | 1.80 | ||
| Lysine | 0.60 | ||
| Methionine | 0.30 |
| Target Genes | Sequence Information | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | Reference | |
| cu/zn-sod | AGTTGCCATGTGCACTTTTCT | AGGTGCTAGTCGAGTGTTAGG | [20] |
| mn-sod | AGCTGCACCACAGCAAGCAC | TCCTCCACCATTCGGTGACA | [20] |
| cat | CAGTGCTCCTGATACCCAGC | TTCTGACACAGACGCTCTCG | [21] |
| gpx-1 | GAACGCCCACCCTCTGTTTG | CGATGTCATTCCGGTTCACG | [20] |
| ikbα | TCTTGCCATTATTCACGAGG | TGTTACCACAGTCATCCACCA | [22] |
| p65 | TGGACGTGCTGAACTCCATC | AGAAGCGTTTAGGTCGGGTG | [23] |
| hsp70 | CGACGCCAACGGAATCCTAAAT | CTTTGCTCAGTCTGCCCTTGT | [24] |
| β-actin | TCGTCCACCGCAAATGCTTCTA | CCGTCACCTTCACCGTTCCAGT | [21] |
| Dietary Vitamin C Levels (mg/kg) | p Values 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 25.35 (0) | 150.65 (150) | 285.39 (300) | 573.79 (600) | 1133.79 (1200) | 2231.98 (2400) | Linear | Quadratic | Cubic |
| IBW (g) 3 | 12.76 ± 0.38 | 12.68 ± 0.41 | 12.72 ± 0.16 | 12.91 ± 0.18 | 13.05 ± 0.14 | 12.95 ± 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.852 | 0.283 |
| IBW CV (%) 4 | 3.02 | 3.30 | 1.28 | 1.40 | 1.08 | 1.97 | |||
| FBW (g) 5 | 43.70 ± 1.66 b | 50.26 ± 1.90 ab | 52.31 ± 0.75 a | 51.72 ± 0.71 a | 50.16 ± 4.48 a | 47.43 ± 6.03 ab | 0.863 | 0.145 | 0.035 |
| FBW CV (%) 6 | 3.08 | 3.78 | 1.45 | 1.39 | 8.94 | 12.71 | |||
| WG (%) 7 | 242.58 ± 15.76 b | 296.28 ± 4.52 a | 311.25 ± 9.70 a | 300.59 ± 9.25 a | 284.22 ± 33.44 ab | 266.73 ± 50.91 ab | 0.611 | 0.254 | 0.052 |
| SGR (% day−1) 8 | 2.05 ± 0.07 b | 2.29 ± 0.02 a | 2.35 ± 0.04 a | 2.31 ± 0.03 a | 2.24 ± 0.14 ab | 2.15 ± 0.23 ab | 0.571 | 0.241 | 0.053 |
| FCR 9 | 1.61 ± 0.02 a | 1.45 ± 0.02 b | 1.33 ± 0.06 c | 1.35 ± 0.07 c | 1.48 ± 0.07 b | 1.53 ± 0.04 ab | 0.488 | 0.102 | 0.001 |
| SR (%) 10 | 98.33 ± 2.88 | 96.97 ± 5.77 | 91.67 ± 7.63 | 91.67 ± 5.77 | 93.33 ± 7.63 | 95.00 ± 8.66 | 0.776 | 0.496 | 0.493 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhammad, A.M.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, B.; Miao, L.; Gao, G.; Zhou, Q. Vitamin C Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation Caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fishes 2024, 9, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040129
Muhammad AM, Yang C, Wang J, Ge X, Liu B, Miao L, Gao G, Zhou Q. Vitamin C Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation Caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fishes. 2024; 9(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhammad, Abdullateef Mukhtar, Chang Yang, Jingyuan Wang, Xianping Ge, Bo Liu, Linghong Miao, Guodong Gao, and Qunlan Zhou. 2024. "Vitamin C Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation Caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala)" Fishes 9, no. 4: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040129
APA StyleMuhammad, A. M., Yang, C., Wang, J., Ge, X., Liu, B., Miao, L., Gao, G., & Zhou, Q. (2024). Vitamin C Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation Caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in Juvenile Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fishes, 9(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040129









