The Identification of a Cell Cycle Regulation Gene Cyclin E from Hong Kong Oysters (Crassostrea hongkongensis) and Its Protein Expression in Response to Salinity Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Shellfish
2.2. cDNA Cloning
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Multiple Sequence Alignment
2.5. Expression of CCNE mRNA in Different Tissues
2.6. Protein Expression and Purification
2.7. Polyclonal Antibody Generation
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
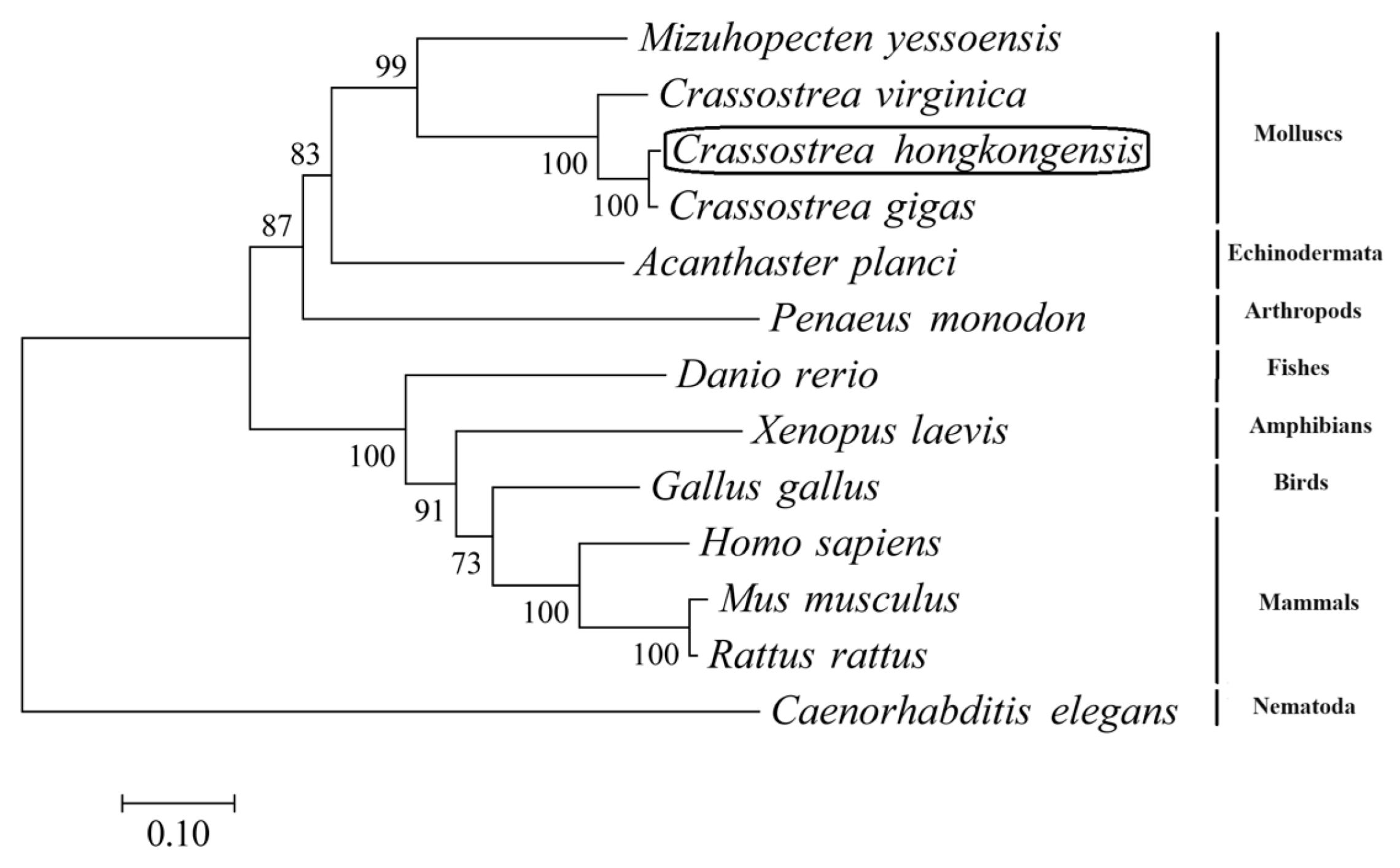
3.1. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses
3.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment
3.3. mRNA Tissue Distribution
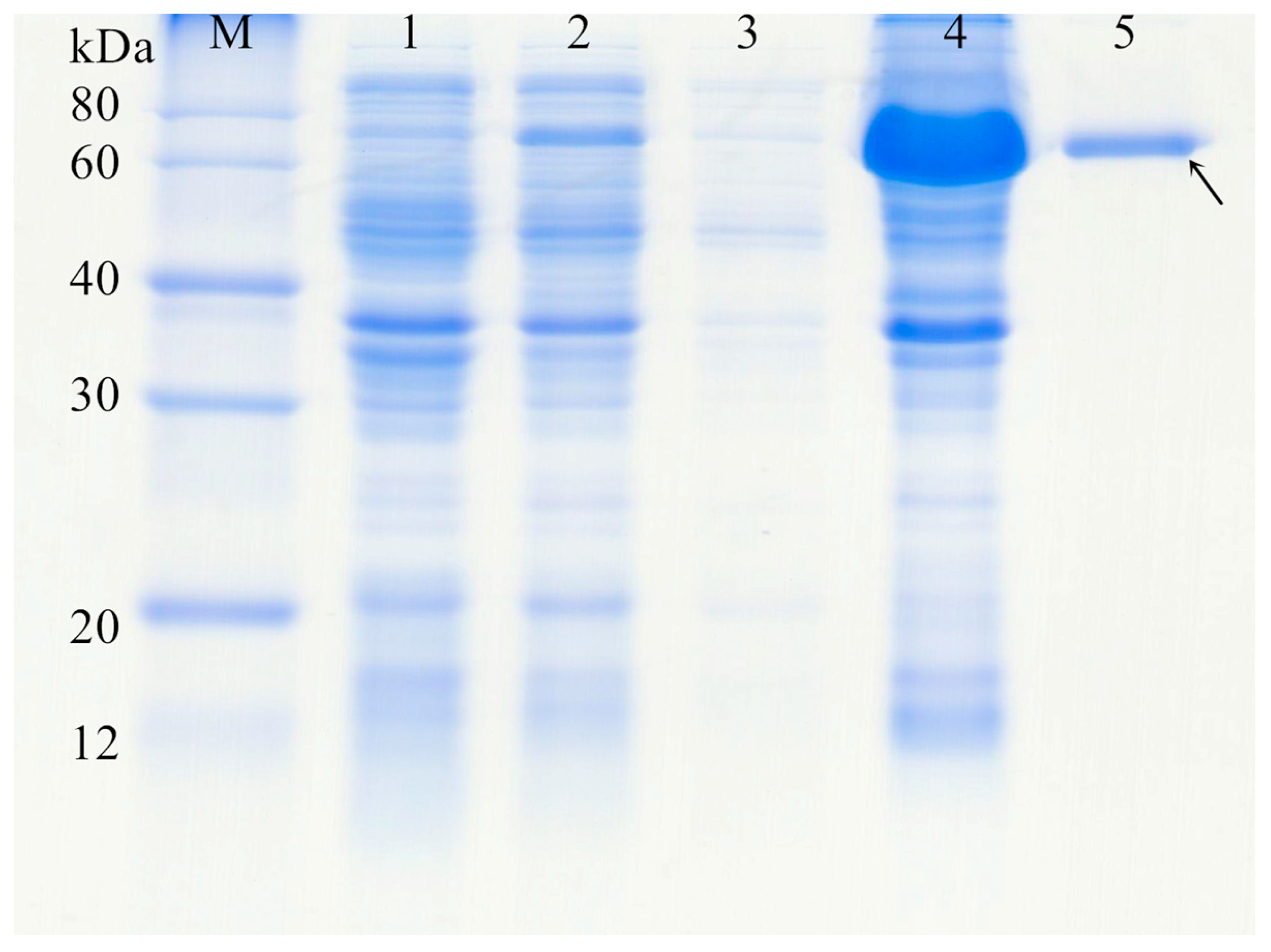
3.4. Protein Expression and Purification
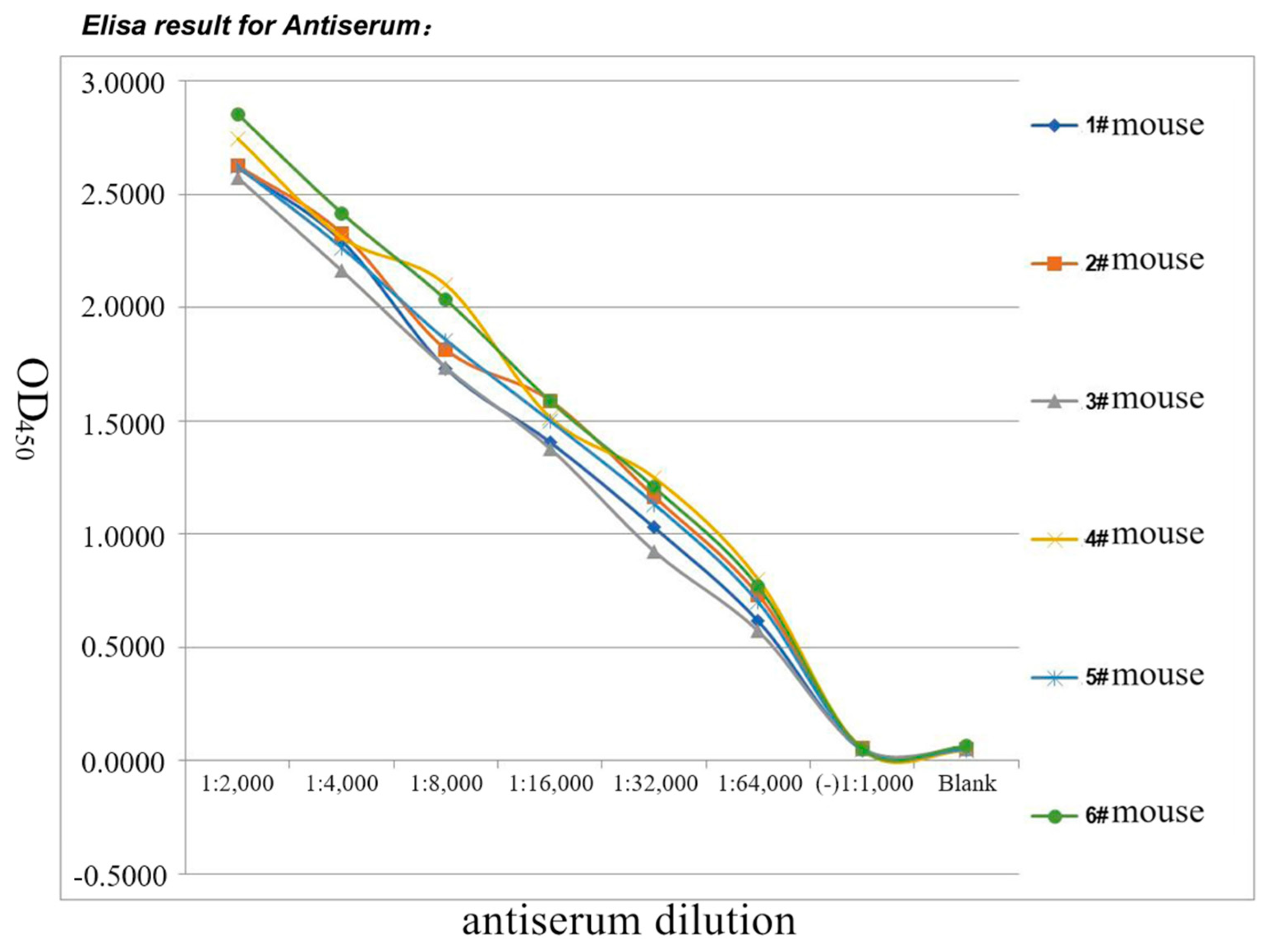
3.5. Polyclonal Antibody Generation
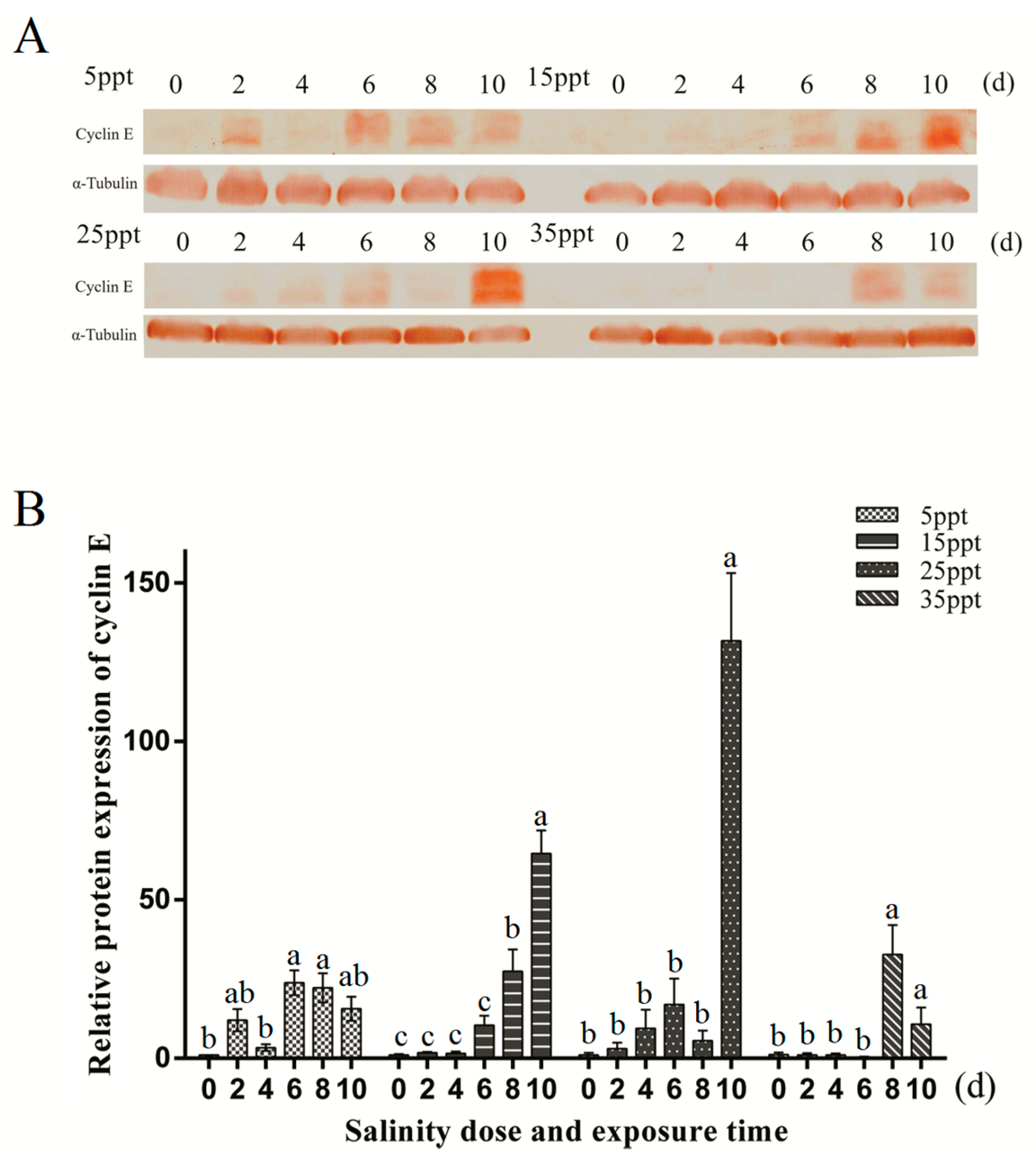
3.6. Protein Expression Level Detection
3.7. Protein Localization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim, S.; Yang, C.; Yue, C.; Song, X.; Deng, Y.; Li, Q.; Lü, W. Whole Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Global Molecular Responses of mRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, circRNAs, and Their ceRNA Networks to Salinity Stress in Hong Kong Oysters Crassostrea hongkongensis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 624–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Pang, D.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, R.; Lin, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhu, Y. The oyster fishery in China: Trend, concerns and solutions. Mar. Policy 2021, 129, 104524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wong, N.K.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Mo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. Analysis of in situ Transcriptomes Reveals Divergent Adaptive Response to Hyper- and Hypo-Salinity in the Hong Kong Oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiong, K.; Tu, Z.; Waiho, K.; Yang, C.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Fang, J.K.H.; Hu, M.; et al. Combined effect of salinity and hypoxia on digestive enzymes and intestinal microbiota in the oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 331, 121921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wen, G.; Su, H.; Hu, X.; Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Yu, Z. Study on purification effect of shellfish and algae coupling on intensive aquaculture tailwater. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; He, P.; Wei, P.; Zhang, X.; Guan, L.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, H.; Li, Q. Investigation and analysis of death of Qinzhou oyster in Spring in Guangxi. J. Aquacult. 2020, 41, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, H.; Kong, L.; Li, Q. Transcriptomic Responses to Salinity Stress in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, M.; Sondermann, M.; Sures, B.; Hering, D. Effects of salinity gradients on benthic invertebrate and diatom communities in a German lowland river. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterkeyn, A.; Grillas, P.; Vanschoenwinkel, B.; Brendonck, L. Invertebrate community patterns in Mediterranean temporary wetlands along hydroperiod and salinity gradients. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 1808–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.Z.; Rott, L.S.; Lowe, A.W.; Omary, M.B. Hyposmotic Stress Induces Cell Growth Arrest via Proteasome Activation and Cyclin/Cyclin-dependent Kinase Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19295–19303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenstein, S.; Casas, S.M.; Tiersch, T.R.; La Peyre, J.F. Energetic budget of diploid and triploid eastern oysters during a summer die-off. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1194296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroney, D.A.; Walker, R.L. The effects of tidal and bottom placement on the growth, survival and fouling of the Eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 1999, 30, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuryń, A.; Opacka, A.; Krajewski, A.; Zielińska, W.; Grzanka, A. The Less Known Cyclins-Uncovered. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.; Rosenthal, E.T.; Youngblom, J.; Distel, D.; Hunt, T. Cyclin: A protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell 1983, 33, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koff, A.; Cross, F.; Fisher, A.; Schumacher, J.; Leguellec, K.; Philippe, M.; Roberts, J.M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell 1991, 66, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, D.J.; Dulić, V.; Reed, S.I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell 1991, 66, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.; Gong, B.; Almasan, A. Cyclin E induction by genotoxic stress leads to apoptosis of hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, T.; Van Tine, B.A.; Wei, Y.; Garrett, M.D.; Nelson, D.; Adams, P.D.; Wang, J.; Qin, J.; Chow, L.T.; Harper, J.W. Cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of p220NPAT by cyclin E/Cdk2 in Cajal bodies promotes histone gene transcription. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2298–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Fu, M.J.; Qiu, L.H. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of cyclin E and CDK2 from Penaeus monodon. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, gmr.15038716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Bai, Z.; Li, W. Screening and expression of cyclins gene in Hyriopsis cumingii. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2021, 33, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Yarden, A.; Geiger, B. Zebrafish cyclin E regulation during early embryogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 1996, 206, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, D.; Akasaka, K.; IVIitsunaga-Nakatsubo, K.; Shimada, H. Cloning of Cyclin E cDNA of the Sea Urchin, Hernicentrotus pulcherrimus. Zool. Sci. 1997, 14, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, H.W.; Lee, T.H.; Han, H.J.; Park, I. Comparative Analysis of Tissue and Cell Cycle on the Far Eastern Catfish, Silurus asotus between Diploid and Triploid. Dev. Reprod. 2017, 21, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzohairy, A.M. BioEdit: An important software for molecular biology. GERF Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenneth, J.; Livak, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.D.; Kornbluth, S.; Hunt, T. Identification of the nuclear localization signal in Xenopus cyclin E and analysis of its role in replication and mitosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4388–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Honda, R.; Lowe, E.D.; Dubinina, E.; Skamnaki, V.; Cook, A.; Brown, N.R.; Johnson, L.N. The structure of cyclin E1/CDK2: Implications for CDK2 activation and CDK2-independent roles. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Liu, J.X.; Ma, Z.Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Suzuki, E.; Liu, Q.X.; Hirose, S. Evolutionarily conserved roles for Apontic in induction and subsequent decline of Cyclin E expression. iScience 2020, 23, 101369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pok, S.; Barn, V.A.; Wong, H.J.; Blackburn, A.C.; Board, P.; Farrell, G.C.; Teoh, N.C. Testosterone regulation of cyclin E kinase: A key factor in determining gender differences in hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pang, Z.; Gao, J.; Dai, Q.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Baloch, W.A.; Noonari, S.; Wang, P.; Gao, H. Functional analysis of the cell cycle protein E gene (ccne) in ovarian development of the white ridgetail prawn, Exopalaemon carinicauda. Aquacult. Rep. 2023, 32, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Yamashita, M. Non-dependence of cyclin E/Cdk2 kinase activity on the initiation of oocyte maturation in goldfish. Dev. Growth Differ. 2001, 42, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilli, L.; Schiavone, R.; Zonno, V.; Rossano, R.; Storelli, C.; Vilella, S. Effect of cryopreservation on sea bass sperm proteins. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, J.; Deng, D.; Deng, K.; Xu, J.; Gao, H. Effects of salinity on growth and related indicators of gonadal development in Exopalaemon carinicauda (Decapoda, Caridea, Palaemonidae). Crustaceana 2023, 96, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ituarte, R.B.; Spivak, E.D.; Camiolo, M.; Anger, K. Effects of Salinity on the Reproductive Cycle of Female Freshwater Shrimp, Palaemonetes Argentinus. J. Crustacean Biol. 2010, 30, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ables, E.T.; Drummond-Barbosa, D. Cyclin E controls Drosophila female germline stem cell maintenance independently of its role in proliferation by modulating responsiveness to niche signals. Development 2013, 140, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, A.; Bible, J.M.; Pespeni, M.H.; Sanford, E.; Evans, T.G. Transcriptomic responses to extreme low salinity among locally adapted populations of Olympia oyster (Ostrea lurida). Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4225–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lin, T.; Yao, Z.; Lai, Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, K. Effects of water salinity on the antioxidant enzyme activities and growth of clam Cyclina sinensis. Chin. J. Ecol. 2012, 31, 2625–2630. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Guo, X. Regulation of the Cell Cycle, Apoptosis, and Proline Accumulation Plays an Important Role in the Stress Response of the Eastern Oyster Crassostrea virginica. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 921877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xin, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, C.; Mu, C.; Li, R. Physiological, biochemical and molecular responses of Sepia pharaonis juveniles to low salinity. Aquacult. Res. 2021, 52, 4317–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardella, B.A.; Matey, V.; Cooper, J.; Gonzalez, R.J.; Brauner, C.J. Physiological, biochemical and morphological indicators of osmoregulatory stress in ‘California’ Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus × O. urolepis hornorum) exposed to hypersaline water. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xuan, L.; Qiu, X.; Yu, H.; Chu, J.; Guo, J.; Chang, Y. Albicanol modulates oxidative stress and the p53 axis to suppress profenofos induced genotoxicity in grass carp hepatocytes. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 122, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; Bahuguna, A.; Krishnan, M.; Shukla, S.; Lee, H.; Min, S.H.; Choi, D.K.; Cho, Y.; Bajpai, V.K.; Huh, Y.S.; et al. The effect of biogenic manufactured silver nanoparticles on human endothelial cells and zebrafish model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zou, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, C. Cellular senescence in metabolic-associated kidney disease: An update. Cells 2022, 11, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezina, L.; Purmessur, N.; Antonov, A.V.; Ivanova, T.; Karpova, E.; Tentler, D.; Garabadgiu, A.V.; Krishan, K.; Ivan, M.; Aksenova, V.; et al. miR-16 and miR-26a target checkpoint kinases WEE1 and CHK1 in response to p53 activation by genotoxic stress. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Huang, S.; Qiu, H.T.; Li, Z.; Mao, Y.; Hong, W.S.; Chen, S.X. Optimal salinity for rearing Chinese black sleeper (Bostrychus sinensis) fry. Aquaculture 2017, 476, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canosa, L.F.; Bertucci, J.I. The effect of environmental stressors on growth in fish and its endocrine control. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1109461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewing, A.; Rönicke, V.; Bürger, C.; Funk, M.; Müller, R. Alternative splicing of human cyclin E. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minella, A.C.; Loeb, K.R.; Knecht, A.; Welcker, M.; Varnum-Finney, B.J.; Bernstein, I.D.; Roberts, J.M.; Bruce, E.C. Cyclin E phosphorylation regulates cell proliferation in hematopoietic and epithelial lineages in vivo. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, F.; Shi, H.; Xue, C.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, H. Proteomics analysis of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) under acute and longer-term chronic salinity stress treatment as examined by label-free mass spectrometry. Aquaculture 2022, 551, 37868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.X.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Z.; Jiang, Y. Physiological responses to salinity stress in the Managua Cichlid, Cichlasoma managuense. Aquacult. Res. 2020, 51, 4387–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Velasco, R.; Manzano-Sarabia, M.; Hurtado-Oliva, M.A. Effect of hypo-and hypersaline stress conditions on physiological, metabolic, and immune responses in the oyster Crassostrea corteziensis (Bivalvia: Ostreidae). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, B.; Shi, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, S. Synergistic Interaction of Low Salinity Stress with Vibrio Infection Causes Mass Mortalities in the Oyster by Inducing Host Microflora Imbalance and Immune Dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Genes | Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| cyclin E | Outer F | CCACCCGAAAATCGTTGGCGGG | Nested PCR |
| Outer R | TTCATAGAATTGTTCATCAGTATC | Nested PCR | |
| Inner F | CACCTTATTACGCTACGGTCTGC | Nested PCR | |
| Inner R | TTCAACTCCATATTTAAAATGCAC | Nested PCR | |
| PE F | gatccgaattcATGTCGAGAAAAAGTGCACGATTG | Expression vector construction | |
| PE R | gcttgtcgacTTATTTGAACTCTTCATTTTCCTT | Expression vector construction | |
| Rt F | CCTCTCGGTCGACAACTATGTC | RT-qPCR | |
| Rt R | CGAGTCGGGAGACAATGGTTCAC | RT-qPCR | |
| β actin | Rt F | ATATTGCAGCTTTAGTCGTAGAC | RT-qPCR |
| Rt R | GGTGAGGATACCTCTCTTGCTC | RT-qPCR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, H.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Hu, L.; Huang, Y.; Ye, Y. The Identification of a Cell Cycle Regulation Gene Cyclin E from Hong Kong Oysters (Crassostrea hongkongensis) and Its Protein Expression in Response to Salinity Stress. Fishes 2024, 9, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030102
Qiu H, Wang H, Yan X, Hu L, Huang Y, Ye Y. The Identification of a Cell Cycle Regulation Gene Cyclin E from Hong Kong Oysters (Crassostrea hongkongensis) and Its Protein Expression in Response to Salinity Stress. Fishes. 2024; 9(3):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030102
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Hengtong, Huan Wang, Xiaomin Yan, Lin Hu, Yonglin Huang, and Yanni Ye. 2024. "The Identification of a Cell Cycle Regulation Gene Cyclin E from Hong Kong Oysters (Crassostrea hongkongensis) and Its Protein Expression in Response to Salinity Stress" Fishes 9, no. 3: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030102
APA StyleQiu, H., Wang, H., Yan, X., Hu, L., Huang, Y., & Ye, Y. (2024). The Identification of a Cell Cycle Regulation Gene Cyclin E from Hong Kong Oysters (Crassostrea hongkongensis) and Its Protein Expression in Response to Salinity Stress. Fishes, 9(3), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030102





