First Report of Vibrio vulnificus Outbreak in Farm-Raised Sorubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp.) from Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outbreak Characterization
2.2. Vibrio Vulnificus Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2.1. Isolation and MALDI-TOF/MS Identification
2.2.2. dnaJ and 16S rRNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Experimental Infection Challenge
2.5. Histopathological Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vibrio Vulnificus Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.1.1. Isolation and MALDI-TOF/MS Identification
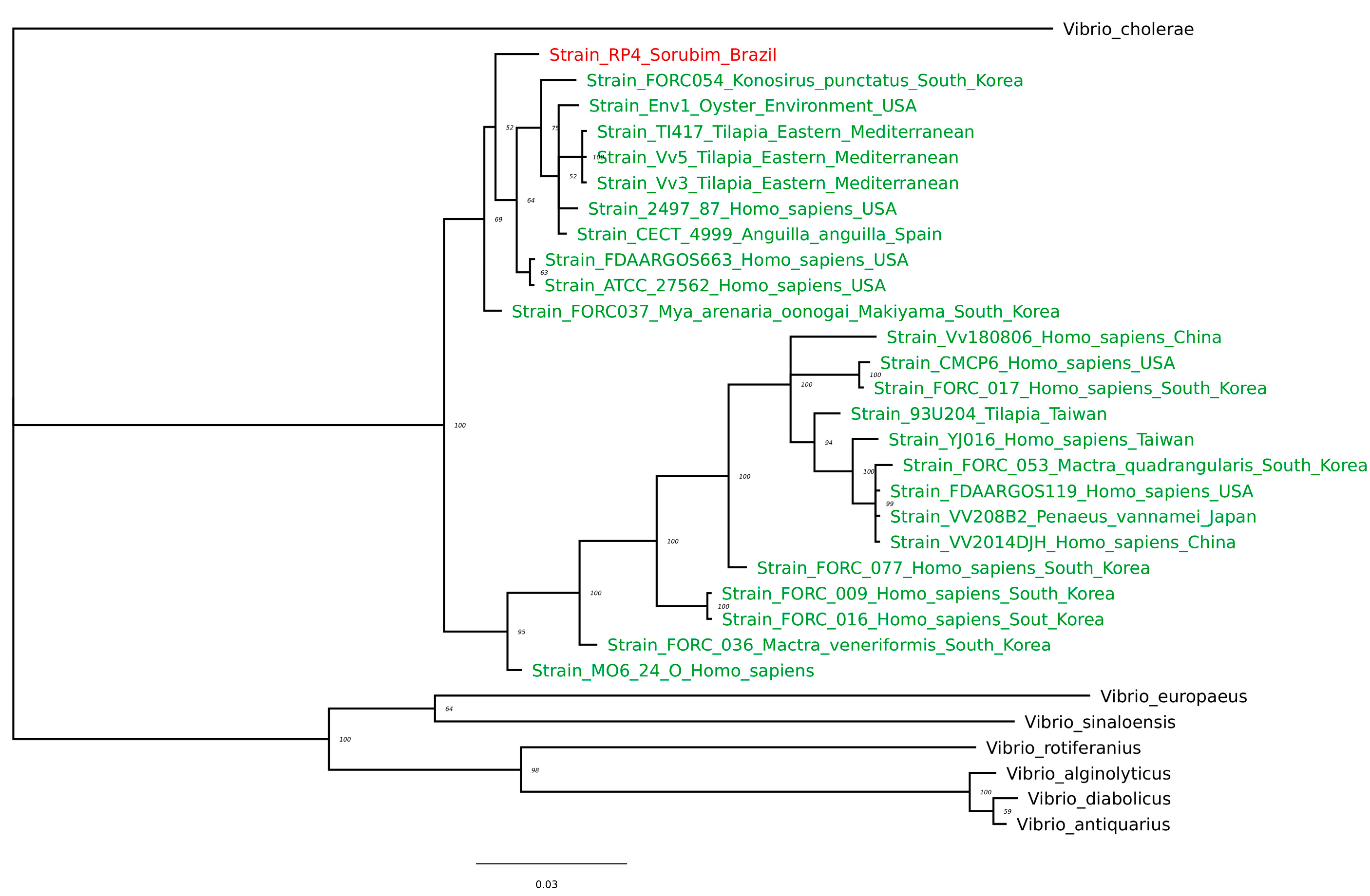
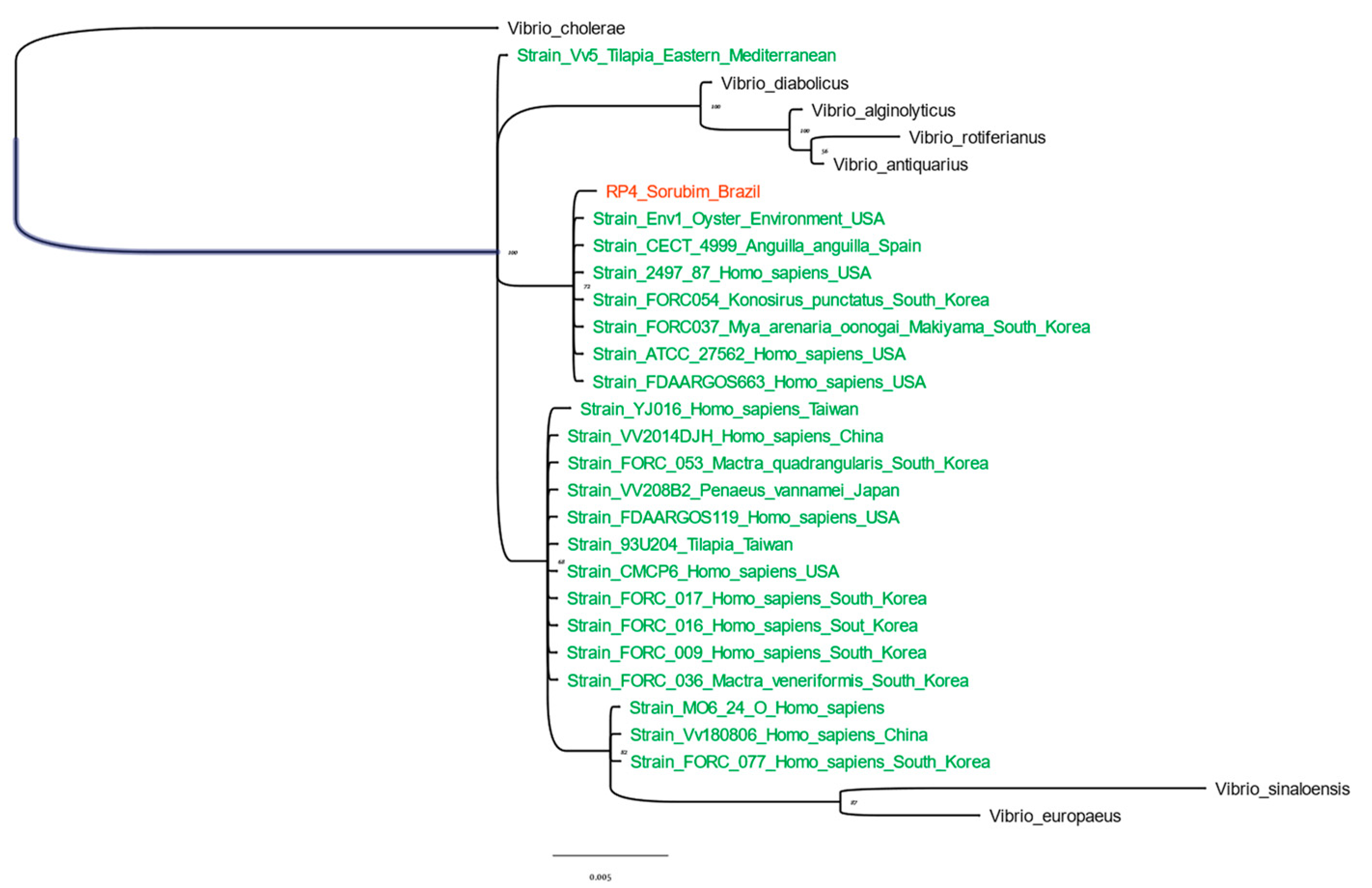
3.1.2. dnaJ and 16S rRNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.3. Experimental Infection Challenge and Histopathological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haftel, A.; Sharman, T. Vibrio vulnificus Infection. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Salido, H.; Fouz, B.; Sanjuán, E.; Carda-Diéguez, M.; Delannoy, C.M.J.; García-González, N.; González-Candelas, F.; Amaro, C. Draft Genome Sequences of Vibrio vulnificus Strains Recovered from Moribund Tilapia. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00094-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumithra, T.G.; Reshma, K.J.; Anusree, V.N.; Sayooj, P.; Sharma, S.R.K.; Suja, G.; Amala, P.V.; Joseph, S.; Sanil, N.K. Pathological Investigations of Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) Cultured at a Floating Cage Farm of India. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, C.; Sanjuán, E.; Fouz, B.; Pajuelo, D.; Lee, C.-T.; Hor, L.-I.; Barrera, R. The Fish Pathogen Vibrio vulnificus Biotype 2: Epidemiology, Phylogeny, and Virulence Factors Involved in Warm-Water Vibriosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Lian, Z.; Hu, X.; Lü, A.; Sun, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Yiksung, Y. First Report of Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus in China. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, D.; Huang, L.; Sun, J.; Gao, D.; Wang, H.; Tan, Y.; Liang, L. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Vibrio vulnificus Isolated from Diseased Trachinotus ovatus in Cage Mariculture. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Cabanyero, C.; Amaro, C. Phylogeny and Life Cycle of the Zoonotic Pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 4133–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelo-Branco, D.D.S.C.M.; Sales, J.A.; Brilhante, R.S.N.; De Melo Guedes, G.M.; De Ponte, Y.B.; De Souza Sampaio, C.M.; Bandeira, T.D.J.P.G.; Moreira, J.L.B.; De Alencar, L.P.; Paiva, M.D.A.N.; et al. Enterobacteria and Vibrio from Macrobrachium amazonicum Prawn Farming in Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubiana, M.; Fernandez, D.; Filho, J.-E.M.; Garnier, J.; De Castro, R.R.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Colwell, R.R.; Monfort, P. Occurence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio cholerae in the Urbanized Guaraja Bay, Amazonia, Brasil. In Proceedings of the 8th Biennial International Conference on the Biology of Vibrios, McGill University, Montréal, Canada, 18–20 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tiba-Casas, M.R.; Lemes-Marques, E.G.; Almeida, E.A.; Soares, F.B.; Camargo, C.H. Draft Genome Sequence of a Pathogenic Vibrio vulnificus Strain Isolated in Brazil. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e01274-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raszl, S.M.; Froelich, B.A.; Vieira, C.R.W.; Blackwood, A.D.; Noble, R.T. Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in South America: Water, Seafood and Human Infections. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, D.R.; Da Rosa, J.V.; Kaefer, K.; Bach, L.G.; Barbosa, A.D.O.; Timm, C.D. Ability of Vibrio vulnificus Isolated from Fish of the Lagoa Dos Patos Estuary in South Brazil to Form Biofilms after Sublethal Stress and Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics and Sanitizers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 303, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.S.; Amorim, S.D.; Santos, A.F.M.; Siciliano, S.; Moreno, I.M.B.; Ott, P.H.; Rodrigues, D.P. Vibrio spp. isolados de mamíferos marinhos capturados na região litorânea do Sudeste ao Sul do Brasil. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2007, 27, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.D.; Lemos, L.S.; Roges, E.M.; De Moura, J.F.; Tavares, D.C.; Matias, C.a.R.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Siciliano, S. A Comprehensive Survey of Aeromonas sp. and Vibrio sp. in Seabirds from Southeastern Brazil: Outcomes for Public Health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhung, P.H.; Shah, M.M.; Ohkusu, K.; Noda, M.; Hata, H.; Sun, X.S.; Iihara, H.; Goto, K.; Masaki, T.; Miyasaka, J.; et al. The dnaJ Gene as a Novel Phylogenetic Marker for Identification of Vibrio Species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 30, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, W.L.; Siboni, N.; Kahlke, T.; Green, T.J.; Labbate, M.; Seymour, J.R. A New High Throughput Sequencing Assay for Characterizing the Diversity of Natural Vibrio Communities and Its Application to a Pacific Oyster Mortality Event. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, L.; Toledo, M.J.; Ibarra, D.A. First Fossil Record of Pseudoplatystoma corruscans (Siluriformes, Pimelodidae) from the Late Pleistocene, Santa Fe, Argentina. J. South. Am. Earth Sci. 2021, 105, 102987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE. Pesquisa da Pecuária Municipal. BRASIL. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/pesquisa/18/16459 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Barony, G.; Tavares, G.; Assis, G.; Luz, R.; Figueiredo, H.; Leal, C. New Hosts and Genetic Diversity of Flavobacterium columnare Isolated from Brazilian Native Species and Nile Tilapia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A.R.; De Abreu, D.C.; Torres Chideroli, R.; Santo, K.; Dib Gonçalves, D.; Di Santis, G.W.; De Pádua Pereira, U. Interspecies Transmission of Edwardsiella ictaluri in Brazilian Catfish (Pseudoplatystoma corruscans) from Exotic Invasive Fish Species. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2021, 145, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.C.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Vieira, F.N.; Jatobá, A.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Martins, M.L. Haemorrhagic Septicaemia in the Hybrid Surubim (Pseudoplatystoma corruscans×Pseudoplatystoma fasciatum) Caused by Aeromonas hydrophila: Haemorrhagic Septicaemia in the Hybrid Surubim. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.C.; De Queiroz, G.A.; Assis, G.B.N.; Leibowitz, M.P.; Teixeira, J.P.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Leal, C.A.G. Disease Outbreaks in Farmed Amazon Catfish (Leiarius marmoratus × Pseudoplatystoma corruscans) Caused by Streptococcus agalactiae, S. iniae, and S. Dysgalactiae. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.J.; Klesius, P.H.; Shoemaker, C.A. First Isolation and Characterization of Lactococcus garvieae from Brazilian Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), and Pintado, Pseudoplathystoma corruscans (Spix & Agassiz). J. Fish. Dis. 2009, 32, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.C.S.; Leal, C.a.G.; Cavalcante, R.B.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Arijo, S.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Ishikawa, M.; Borra, R.C.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Lactococcus garvieae Outbreaks in Brazilian Farms Lactococcosis in Pseudoplatystoma Sp.—Development of an Autogenous Vaccine as a Control Strategy. J. Fish. Dis. 2017, 40, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, G.B.N.; Pereira, F.L.; Zegarra, A.U.; Tavares, G.C.; Leal, C.A.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Use of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry for the Fast Identification of Gram-Positive Fish Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Yan, L.L.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Paster, B.J.; Shames, B.; Murphy, J.C.; Hayward, A.; Belcher, J.C.; Mendes, E.N. Helicobacter bilis sp. Nov., a Novel Helicobacter Species Isolated from Bile, Livers, and Intestines of Aged, Inbred Mice. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/(S(351jmbntvnsjt1aadkposzje))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1383440 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Larsson, A. AliView: A Fast and Lightweight Alignment Viewer and Editor for Large Datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, F.F.; Reis, M.D.; Yang, Z. A Biologist’s Guide to Bayesian Phylogenetic Analysis. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.3.1. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh. 2010. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- CLSI. VET03|Methods for Antimicrobial Broth Dilution and Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated from Aquatic Animals, 2nd Edition. Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/veterinary-medicine/documents/vet03/ (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Luna, L.G. Manual of Histologic Staining Methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968; Available online: https://www.scirp.org/(S(351jmbntvnsjt1aadkposzje))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=854813 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Cheng, W.-C.; Jan, I.-S.; Chen, J.-M.; Teng, S.-H.; Teng, L.-J.; Sheng, W.-H.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Evaluation of the Bruker Biotyper Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry System for Identification of Blood Isolates of Vibrio Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1741–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Kang, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wang, J.; et al. PVBase: A MALDI-TOF MS Database for Fast Identification and Characterization of Potentially Pathogenic Vibrio Species from Multiple Regions of China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 872825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Updating the 97% Identity Threshold for 16S Ribosomal RNA OTUs. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Salido, H.; Fouz, B.; Sanjuán, E.; Carda, M.; Delannoy, C.M.J.; García-González, N.; González-Candelas, F.; Amaro, C. The Widespread Presence of a Family of Fish Virulence Plasmids in Vibrio vulnificus Stresses Its Relevance as a Zoonotic Pathogen Linked to Fish Farms. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Tanaka, M.; Nishikawa, S.; Mino, S.; Romalde, J.L.; Thompson, F.L.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Sawabe, T. Vibrio Clade 3.0: New Vibrionaceae Evolutionary Units Using Genome-Based Approach. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST: Clinical Breakpoints and Dosing of Antibiotics. Version 12.0. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- CLSI M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 27th ed. Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2017.
- CLSI M45; Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria. 3rd ed. Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2015.
- Nascimento, S.M.M.D.; Vieira, R.H.S.D.F.; Theophilo, G.N.D.; Rodrigues, D.D.P.; Vieira, G.H.F. Vibrio vulnificus as a Health Hazard for Shrimp Consumers. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2001, 43, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, F.P.; Falcão, J.P. Analysis of the Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Frequency in Whole-Genome Sequenced Vibrio from Latin American Countries. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, L.C.; Sarda Carbasse, J.; Koblitz, J.; Podstawka, A.; Overmann, J. Vibrio vulnificus (Reichelt et al. 1979) Farmer 1980 Emend. West et al. 1986. 2023. Available online: https://bacdive.dsmz.de/pdf-view/17277?site=pdf_view&id=17277&doi=doi%3A10.13145%2Fbacdive17277.20230509.8 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Valiente, E.; Padrós, F.; Lamas, J.; Llorens, A.; Amaro, C. Microbial and Histopathological Study of the Vibriosis Caused by Vibrio vulnificus Serovar E in Eels: The Metalloprotease Vvp Is Not an Essential Lesional Factor. Microb. Pathog. 2008, 45, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaro, C.; Biosca, E.G.; Fouz, B.; Alcaide, E.; Esteve, C. Evidence that Water Transmits Vibrio vulnificus Biotype 2 Infections to Eels. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.-J.; Kim, W.-S.; Kitamura, S.-I.; Lee, H.; Son, B.W.; Jung, T.-S.; Jung, S.-J. Change of Pathogenicity in Olive Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus by Co-Infection of Vibrio harveyi, Edwardsiella tarda and Marine Birnavirus. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; De La Roca, E.; Núñez, S.; De La Herran, R.; Navas, J.; Manchado, M.; Herrera, M.; Toranzo, A. Identification of Vibrio harveyi Isolated from Diseased Cultured Wedge Sole Dicologoglossa cuneata. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 84, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco-Noales, E.; Milán, M.; Fouz, B.; Sanjuán, E.; Amaro, C. Transmission to Eels, Portals of Entry, and Putative Reservoirs of Vibrio vulnificus Serovar E (Biotype 2). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4717–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodur, D.M.; Coulter, P.; Isaacs, J.; Pu, M.; Fernandez, N.; Waters, C.M.; Rowe-Magnus, D.A. Environmental Calcium Initiates a Feed-Forward Signaling Circuit That Regulates Biofilm Formation and Rugosity in Vibrio vulnificus. mBio 2018, 9, e01377-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Pu, M.; Subramanian, S.; Kearns, D.; Rowe-Magnus, D. PlzD Modifies Vibrio vulnificus Foraging Behavior and Virulence in Response to Elevated c-di-GMP. mBio 2023, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antibiotic | Inhibition Diameter of RP4 Isolate (mm) | CLSI * (mm) | EUCAST ** (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S a | I b | R c | S | R | ||
| Neomycin (10 µg) | 14 (S) | – | – | – | >12 1 | <12 1 |
| Erythromycin (15 µg) | 22 (S) | – | – | – | >12 2 | <12 2 |
| Amoxicillin (10 µg) | 23 (S) | >17 2 | 14–16 2 | <13 2 | >14 3 | <14 3 |
| Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (25 µg) | 26 (S) | >16 2 | 11–15 2 | <10 2 | >18 2 | <18 2 |
| Nitrofurantoin (300 µg) | 29 (S) | >17 4 | 15–16 4 | <14 4 | x | x |
| Norfloxacin (10 µg) | 32 (S) | >17 4 | 13–16 4 | <12 4 | >22 3 | <22 3 |
| Oxytetracycline (30 µg) | 35 (S) | >15 5 | 12–14 5 | <11 5 | >20 5 | <20 5 |
| Florfenicol (30 µg) | 34 (S) | >18 6 | 13–17 6 | <12 6 | >17 7 | <17 7 |
| Lincomycin (10 µg) | 8 | – | – | – | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janampa-Sarmiento, P.C.; Reis, F.Y.T.; Egger, R.C.; de Pádua, S.B.; Marcelino, S.A.C.; Cunha, J.L.R.; Pierezan, F.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Tavares, G.C. First Report of Vibrio vulnificus Outbreak in Farm-Raised Sorubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp.) from Brazil. Fishes 2024, 9, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020054
Janampa-Sarmiento PC, Reis FYT, Egger RC, de Pádua SB, Marcelino SAC, Cunha JLR, Pierezan F, Figueiredo HCP, Tavares GC. First Report of Vibrio vulnificus Outbreak in Farm-Raised Sorubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp.) from Brazil. Fishes. 2024; 9(2):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020054
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanampa-Sarmiento, Peter C., Francisco Y. T. Reis, Renata C. Egger, Santiago B. de Pádua, Sóstenes A. C. Marcelino, João L. R. Cunha, Felipe Pierezan, Henrique C. P. Figueiredo, and Guilherme C. Tavares. 2024. "First Report of Vibrio vulnificus Outbreak in Farm-Raised Sorubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp.) from Brazil" Fishes 9, no. 2: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020054
APA StyleJanampa-Sarmiento, P. C., Reis, F. Y. T., Egger, R. C., de Pádua, S. B., Marcelino, S. A. C., Cunha, J. L. R., Pierezan, F., Figueiredo, H. C. P., & Tavares, G. C. (2024). First Report of Vibrio vulnificus Outbreak in Farm-Raised Sorubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp.) from Brazil. Fishes, 9(2), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020054






