Abstract
This study was conducted to investigate the potential effects of natural polyphenol antioxidant (Cabanin® CSD provided by R2 Agro, Denmark)-supplemented diets on the growth performance and biochemical and antioxidant responses of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). The fish were fed two control diets (low and high levels of vitamin C and vitamin E without added Cabanin® CSD) and two experimental diets with Cabanin® CSD supplementation for 10 weeks. After the trial, the specific growth rate, feed utilization, and survival rate were observed. The blood biochemical parameters, consisting of superoxide dismutase activity, malondialdehyde, cortisol, and glucose, were measured. The presence of malondialdehyde in the flesh meat of the tilapia was also evaluated during refrigerated storage. The fish was then challenged with 60 mg/L ammonia for 168 h. The survival rate and biochemical parameters of the blood (glucose and cortisol) were recorded after exposure to ammonia. The results show that the growth performance of tilapia was significantly improved by Cabanin® CSD supplementation (p < 0.05), while the survival rates were similar between control and Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diet groups. Superoxide dismutase activity and malondialdehyde levels in the blood serum were significantly different between the control and Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diet groups (p < 0.05). The malondialdehyde levels were significantly higher in the control group in comparison with the Cabanin® CSD-supplemented groups at day 1 and day 7 of refrigerated storage (p < 0.05). In the ammonia challenge test, the highest survival rate was observed in the Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diet groups compared to the control group. The fish serum glucose and cortisol levels increased in all the Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diet groups. In general, diets featuring Cabanin® CSD supplementation were found to exert beneficial effects on the growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and biochemical activity of tilapia under ammonia stress.
Key Contribution:
Diets containing Cabanin® CSD supplementation significantly improved the growth performance, biochemical activity, and antioxidant capacity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).
1. Introduction
Tilapia is a common warm-water species cultured worldwide due to its rapid growth, easy adaptation to intensive farming conditions, and the high protein composition of its meat [1]. A stable market price has resulted in the increasing production of tilapia [2]. The intensification of tilapia production consequently exposes fish to stressful conditions that weaken the immune systems of the fish and increase their susceptibility to diseases. Several approaches, such as chemotherapy, antibiotics, and vaccination, have been applied to control these problems in tilapia culture. However, the application of antibiotics and chemotherapeutics in tilapia culture is strictly regulated due to their negative impacts, such as the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, immune suppression in the fish, and antibiotic residues [3]. Hence, the dietary supplementation of alternative, friendly prebiotics, probiotics, and immunostimulants, which help improve the immune responses of the fish and reduce disease susceptibility, is receiving increasing attention in aquaculture [4,5,6,7,8].
Dietary polyphenols from plant foods have received considerable attention as a dietary potential additive to improve the health status and growth performance of aquatic animals [9,10,11]. Many studies have demonstrated that plant immune stimulants can enhance specific and non-specific immune protective mechanisms of fish [12,13].
Cabanin® CSD (European patent No. 1323354; provided by R2 Agro A/S, Denmark) is composed of selected citrus pomace, grape pomace, blackcurrant pomace, and sweet chestnut extract, with a high content of polyphenols (total polyphenol content: a minimum of 8.5%), and can be used to help support the healthy immune function of aquatic animals in the face of expected and unexpected stress events. The objective of the present study was to evaluate the effects of Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets on the growth performance and stress resistance of tilapia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diets
Four diets were formulated to contain various concentrations of vitamin E, vitamin C, and Cabanin® CSD: basal diet plus 50 mg/kg vitamin E (as all-rac-α-tocopheryl acetate) and 50 mg/kg vitamin C (control low); basal diet plus 250 mg/kg vitamin E and 250 mg/kg vitamin C (control high); basal diet plus 150 mg/kg vitamin E, 150 mg/kg vitamin C, and 200 mg/kg Cabanin® CSD (40% Cabanin® CSD replacement); basal diet plus 50 mg/kg vitamin E, 50 mg/kg vitamin C, and 400 mg/kg Cabanin® CSD (80% Cabanin® CSD replacement). Each diet had three replicates. The basal diet had approximately 31% crude protein and 5% crude lipid with different ingredients. All feed ingredients were thoroughly mixed, extruded, and pelleted in a feed mill, then labeled, packed in bags accordingly, and stored at −20 °C until used. The ingredients and proximate analyses of the experimental diets are illustrated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Ingredients and proximate analyses of the experimental diets.
The analyses of the proximate composition of feed ingredients were determined by using standard methods [14]. The crude protein content was determined by using the Kjeldahl method. The crude lipid content was extracted through the use of n-hexane using the Soxhlet method. The ash content was determined via the combustion method. The moisture content was determined via the drying method using an oven at 105 °C.
2.2. Fish and Feeding Trial
Tilapia fingerlings (Oreochromis niloticus) were obtained from a private fish farm in Hochiminh City, Vietnam. The fish were transported to the Experimental Farm of Nong Lam University, Hochiminh City, Vietnam and acclimated in 2000 L tanks. They were cultured for 4 weeks and fed a basal diet twice daily to apparent satiation.
Fish with initial weight of 8 ± 2 g were selected for the trial. The trial was carried out in 12 tanks (500 L per tank) that contained 50 fish per tank. The fish were fed two times a day (7 am and 17 pm) at a total rate of 5% of their mean body weight for a period of 10 weeks. One hour after feeding, the unconsumed feed was collected and dried to calculate the daily consumed feed for each tank. Feed intake was recorded daily to compare the feed intake of the four diets at the end of the experiment. The fish were weighed every two weeks in order to adjust the feeding amount distributed to each tank and to estimate the fish growth.
During the feeding trial, water quality parameters were monitored in order to evaluate the water quality. Water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), and pH were monitored daily using a multi-parameter photome (Hanna, Italy). The total ammonium nitrogen was checked weekly using a TAN meter (Hanna, Italy).
2.3. Ammonia Challenge Test
After 10 weeks of the feeding trial, 10 fish were randomly collected from each tank and distributed into a new tank (100 L) that prepared them for the ammonia challenge. Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl, Merck) was used as a source of total ammonia-nitrogen (TAN). The concentration of TAN was 60 mg L−1. The stress trial ran for a period of 168 h. The TAN levels in each tank were tested every 12 h and adjusted by adding NH4Cl solution. The mortality of the fish was recorded. The blood biochemical parameters of the fish (cortisol and glucose) were measured prior to the challenge test and at the end of the challenge test. Commercial test kits were used in the present study to determine the glucose (GAGO20, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and cortisol (Elisa Kit for Cortisol, Cloud-Clone Corp.,Waltham, MA, USA) levels in the fish serum following the methods of the manufacturer’s instruction.
2.4. Sample Collection and Analysis
At the end of the trial, two fish per tank were randomly sampled and anaesthetized with tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222) with a dosage of 80 mg/L. Approximately 1 mL of blood sample was collected from the caudal vessels of the fish using a 2.5 mL syringe (23-gauze needle), loaded in 1.5 mL tubes, and allowed to clot at room temperature for 2 h. The samples were then centrifuged at 1398× g for 20 min at 4 °C. The separated serum was collected and stored at −80 °C for later analysis.
The SOD (superoxide dismutase) activity and lipid peroxidase in fish serum at the end of trial were measured according to the method described by Fridovich and Thiansilakul [15,16].
2.5. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS) Analysis
At the end of the feeding trial, two fish from each tank were randomly collected. Meat samples (10 g) were taken from each fish, packaged in plastic bags, and stored in refrigeration. At day 1 and day 7 of refrigerated storage, a piece of meat fillet (0.5 g) was homogenized in cold phosphate-buffered saline (0.1 M, pH 7.4). The homogenate was then filtered and centrifuged at 1398× g for 20 min at 4 °C using a high-speed cooling centrifuge. The supernatants were collected and subjected to biochemical determination of TBARS content and expressed as nmol/mg protein [16].
2.6. Data Calculation
At the beginning and at the end of the trial, the initial body weight (IBW) and final body weight (FBW) of fish in each tank were measured. Their consumption of the diet was recorded. The weight gain (WG), specific growth rate (SGR), feed conversion ratio (FCR), feed intake (FI), and survival rate (SR) of the fish were calculated as follows: IBW (g/fish) = initial body weight of fish (g)/initial number of fish; FBW (g/fish) = final body weight of fish (g)/final number of fish; WG (g/fish) = final wet weight (g)—initial wet weight (g); SGR (%.day1) = [(Ln(final weight) − Ln(initial weight))/(Cultured days)] × 100; FCR = feed intake (g)/weight gain (g); FI (g/fish/day) = (Consumed feed in tank/number fish of tank)/cultured days; SR (%) = (Number of survival fish/Number of initial fish) × 100.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The results are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). All data were firstly examined for homogeneity of variance using SPSS statistic 20.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). A one-way ANOVA was used to test the main effect of different diets on fish growth. The Duncan test was used to determined the significant differences among treatment groups. The probability values of p < 0.05 were applied to confirm the statistical difference.
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality
During the trial, water quality parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO) and ammonia (NH3) were sampled and the results are illustrated in Table 2.

Table 2.
Water quality parameters of the trial.
The results show that water temperature in the morning and afternoon varied between 28 and 30 °C. The water temperature in the morning was lower, but not constituting a significant difference compared to the one in the afternoon (p > 0.05). Such variation in the water temperature is optimal for tilapia growth and feeding. According to Azaza [17], the water temperature suitable for growth and feed utilization of tilapia should range between 26 and 30 °C.
Other water quality factors like pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), and NH3 were also in the suitable range to support the normal growth and survival of tilapia. The average pH value of the treatments was relatively stable (6.5–7.5) and was within the appropriate limits for tilapia growth and development [18]. In general, tilapia can survive in the pH levels ranging from 5 to 10 but do best in a pH range of 6 to 9. The dissolved oxygen in water plays a vital role in fish culture. During the trial, the dissolved oxygen (DO) was always above 5 mg/L and suitable for the growth of tilapia [19]. The mean NH3 during the trial was 0.02 mg/L and in the suitable range for tilapia development [20].
3.2. Growth Performance
The growth performance of tilapia expressed as the final body weight (FBW), specific growth rate (SGR), and weight gain (WG) is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Effect of Cabanin® supplementation on the growth performance of tilapia.
The results show that Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets did improve the growth performance of tilapia. After 10 weeks of feeding trial, the best values in terms of specific growth rate (SGR) and weight gain (WG) were recorded in the treatment with 40% Cabanin® replacement compared with the control low or the control high. Significant differences were reported in the tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets in comparison with the control diets (p < 0.05). However, no significant difference was recorded between the tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets.
The feed utilization of the fish is expressed as feeding intake (FI) and feed conversion ratio (FCR). The results of the trial demonstrate that there were significantly differences in the FCR between Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets in comparison with the control diets. The lowest FCR was observed in the treatment with Cabanin® replacement. The feeding intakes of the four treatments were not significantly different. The survival rate of the tilapia was highest in the treatment with 40% Cabanin® replacement (94%) and lowest in the control treatment (87%). In summary, the supplementation of Cabanin® in diets significantly improved the feed conversion ratio and the survival rate of tilapia cultured in the feeding trial.
Combining growth performances and feed utilization (Table 3 and Table 4), we can conclude that Cabanin® supplementation in tilapia diet did improve not only tilapia growth and feed utilization, but also survival.

Table 4.
Effect of Cabanin® supplement on feed utilization and survival rate of tilapia.
3.3. Evaluation of SOD and TBARs Activity
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in the blood serum of tilapia at the end of the trial are illustrated in Table 5.

Table 5.
Effect of Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets on oxidative parameters of tilapia.
As shown in Table 5, the activity of SOD in the blood serum of tilapia fed with Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets was significantly higher than that in the control groups (p < 0.05), while the serum thiobarbituric acid reactive substances in tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets had lower levels compared to the other treatments (without Cabanin® supplementation). This means that the diets with Cabanin® supplementation (200–400 mg/kg) can prevent oxidative cell stress damage.
The lipid peroxidation/MDA/TBARs values of tilapia flesh meat were also evaluated during storage at day 1 and day 7, respectively, and are illustrated in Table 6.

Table 6.
Effect of Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets on thiobarbituric acid reactive substances activity levels in flesh meat of tilapia during refrigerated storage.
The results show that the TBARs levels were significantly higher in groups without Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets at day 1 and day 7 of refrigerated storage. The low levels of the TBARs in the treatment groups is due to the antioxidant capacity of the Cabanin® product. As proven, Cabanin® contains parts of citrus, grape, blackcurrant, and chestnut with high polyphenol content (a minimum of 8.5%) and high levels of anti-oxidative activity, which can prevent lipid peroxidation.
3.4. Survival Rate of Tilapia after Ammonia Exposure
A concentration of ammonia of 60 mg/L TAN was used for testing the survival of tilapia after 10 weeks of feeding with Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets. The results show that no obvious differences were observed among all treatments in the first 96 h post-stress (p > 0.05). When the trial was extended to 168 h, tilapia in the treatment groups had higher survival rates in comparison with those in the control groups. Significant differences were recorded in the Cabanin®-supplemented diet groups compared to the control groups (p < 0.05) (Figure 1). It can be concluded that the Cabanin® supplementation improve the survival rate of tilapia after ammonia exposure.
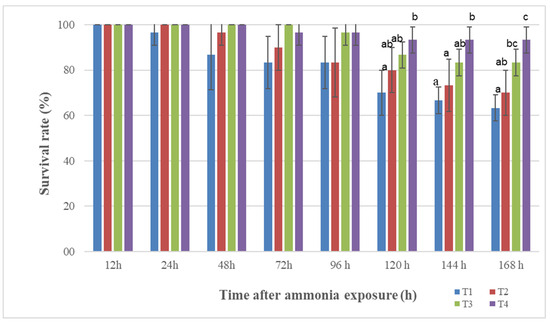
Figure 1.
Survival rate of tilapia fed different levels of Cabanin® after 168 h of ammonia exposure. Results are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). The column with different letters represents significant differences (p < 0.05). T1: control low; T2: control high; T3: 40% Cabanin® replacement; T4: 80% Cabanin® replacement.
The initial and the final biochemical parameters of the blood serum such as the glucose and cortisol levels of tilapia in the ammonia challenge test are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Blood biochemical parameters of tilapia serum before and after ammonia stress.
The results show that the blood glucose and cortisol levels were increased after the ammonia stress (Table 7). The glucose level was in the range of 3.0 to 3.3 mmol/L before the stress test and increased to the range of 3.1 to 4.5 mmol/L after testing. No significant difference in glucose level was recorded before the exposure of the tilapia to ammonia (p > 0.05). However, tilapia fed diets treated with 40% Cabanin® replacement demonstrated more increases and significant differences in their level of glucose than those in the control treatments (p < 0.05) after the ammonia challenge test.
Significant differences in cortisol levels were reported in the tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets in comparison with the control diets before and after the stress test (p < 0.05). In general, the cortisol levels of tilapia increased after the challenge test.
4. Discussion
Water quality, which directly affects the reproduction, growth, and survival of aquatic organisms, is considered one of the most important factors in aquaculture. The water quality of the aquatic ecosystem maintains a suitable environment for fish culturing. Aquatic organisms are susceptible to suffering stress when the ecological conditions are not adequate. High stress levels generate low feeding rates and low growing rates as well, resulting in the appearance of sickness in the organisms [21]. During the feeding trial, the physicochemical parameters of the water were within the range for culture of tilapia.
In the current study, it was shown that the growth performance of tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets was improved significantly after 10 weeks of feeding trials. As demonstrated in the aquaculture aspect, providing an artificial fish diet with essential elements and/or polyphenols extracted from plants is extremely important for maintaining normal growth performance and the proper physiological status of fish [12,22,23]. Cabanin® contains citrus pomace, grape pomace, blackcurrant pomace, and sweet chestnut extract, with high polyphenol content and a high level of anti-oxidative activity. Citrus has a variety of biological properties such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities [24,25]. Pectin derived from citrus and orange peels is considered to be one of the most promising immunomodulation agents, with antiviral and antibacterial effects [26]. Grape pomace contains phytochemicals and is rich in flavonoids such as catechin, anthocyanins, and epicatechin [27]. Anthocyanins have been known to have antioxidant capacity and prevent cells from oxidative damage [28]. Blackcurrant and chestnut are mainly presented as condensed tannins and anthocyanins. Low-concentration tannin supplementation can improve the growth performance and health status of animals [29]. Our results are similar to the results of Coccia; Jahazi; Laein; and Ahmadi [30,31,32,33]. These authors concluded that dietary polyphenol supplementation significantly increased the weight gain, specific growth rate, and feed conversion ratio of fish such as common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.), rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), and Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer).
SODs are a group of metallo-enzymes that play a crucial antioxidant role and constitute the primary defense mechanism against the toxic effect of oxygen in aerobic organisms [34]. The results of the present study show that the SOD activity levels in tilapia fed 200–400 mg/kg of Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets have significant differences from levels in the other treatments (p < 0.05). This finding proves the antioxidant activity of the Cabanin® product. Our results are in agreement with the results of Mirvaghefi and Almarri [8,35] conducted on rainbow trout and tilapia. These authors mentioned that SOD levels increased significantly in the specimens treated with supplemented products compared to the untreated group.
Lipid peroxidation is considered as a complex process that is self-propagating and causes cellular membrane destruction. MDA formation, one of the final products of lipid peroxidase, is widely used to evaluate the lipid peroxidase. The level of MDA is direct evidence of the toxic process caused by free radicals [36,37]. In the current study, a significantly lower MDA/TBARS concentration in tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets was recorded compared to that in the control groups. The decrease in MDA level could be an indicator of an increase in the enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants of defense mechanisms. Our results are in accordance with other findings [8,38,39]. These authors found that low lipid peroxidation reflects the protective effects of oxidative enzymes.
Ammonia can cause physical stress in fish. According to Portsz [40] and Frances [41], the survival rate of fish reduced with increasing levels of ammonia and exposure time. Dietary polyphenols may help fish against ammonia stress [42,43]. Cabanin®, which contains high levels of polyphenol and possesses high anti-oxidative activity, is able to improve the stress resistance of fish. The present study demonstrates that tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets could improve in resistance against ammonia stress and experienced an increased survival rate compared with that in the control group after ammonia exposure. Similar results were observed in the study of Hossain [44]. These authors mentioned that fish fed nucleotide-supplemented diets significantly improved in terms of stress resistance.
Glucose is also considered as an innate immune parameter that is mediated by stress. When fish are under stress, a high level of blood glucose has been recorded [45,46]. The increase in glucose levels in the present study could be due to a consequence of the glycogenolytic activity of catecholamines and gluconeogenetic effect of glucocorticoids via a stress response under toxic substance exposure [47,48]. During the stress period, catecholamines act directly on the liver to stimulate glycogenolysis, resulting in the mobilization of glucose. Catecholamines then promote the phosphorylation of the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase that results in increased glycogenolysis. It should be noted that tilapia fed Cabanin® CSD-supplemented diets are able to modulate more glucose in the stress condition.
Cortisol is considered to be the major corticosteroid hormone in teleost fish and plays a major regulatory role in metabolism. Cortisol is recognized as a key mediator of stress-associated responses. It is secreted and released by internal cells of the head kidney during activation of the hypothalamic pituitary internal axis. In the current study, a high cortisol level was recorded in fish fed Cabanin®-supplemented diets in comparison with those fed the control diet before and after ammonia exposure. An increase in cortisol in fish exposed to ammonia was also reported by Metwally and Wafeek [49]. An explanation of the increase in cortisol is that the hypothalamo-pituitary internal axis of fish is stimulated by ammonia as a stressor, causing elevated blood levels of cortisol, which in turn lead to lipolysis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis to provide energy under stress conditions.
5. Conclusions
Cabanin® CSD supplementation at a dosage of 200–400 mg/kg of feed has effectiveness with regard to the growth performance, feed utilization, survival rate, biochemical activity (glucose and cortisol levels), and antioxidant capacity (SOD and TBARs) of tilapia.
Dietary supplementation of Cabanin® CSD at a level of 200 mg/kg is considered to be the most suitable dose for tilapia in aquafeed to improve the aquaculture industry.
Author Contributions
V.V.T. and L.T.H. conceived and designed the experiments. V.V.T. and L.T.H. performed the data analysis and prepared the manuscript, the tables, and the figure. V.T.T.B. and V.V.T. collected the samples. The literary and scientific corrections in paper were carried out by L.T.H., V.V.T. and V.T.T.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The current research work was financially supported by R2 Agro A/S, Ondinsvej 23, DK-8722 Hedensted, Denmark.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was carried out in accordance with national guidelines on the protection of animals and experimental animal welfare in Vietnam, Law of Animal Health, 2015 (Report number: VM5068).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors (corresponding and co-authors) declare no personal conflicts of interest in the present research. The authors declare a financial conflict of interest with the funder who is also a provider of the feed: R2 Agro A/S, Ondinsvej 23, DK-8722 Hedensted, Danmark. The authors declare the financial conflict did not influence the content and results of this study.
References
- Abdel-Aziz, M.F.A.; Hassan, H.U.; Yones, A.M.; Abdel-Tawwab, Y.A.; Metwalli, T. Assessing the effect of different feeding frequencies combined with stocking density, initial weight, and dietary protein ratio on the growth performance of tilapia, catfish and carp. Sci. Afr. 2021, 12, 00806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lu, M. Tilapia polyculture: A global review. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Jang, E.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, B.H.; Kim, S.K. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria isolated from freshwater aquacultures and prediction of the persistence and toxicity of antimicrobials in the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2013, 48, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.K.; Beck, B.R.; Kim, D.; Park, J.; Kim, J. Prebiotics as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamam, M.S.A.; Pantami, H.A.; Azam, A.A.; Shaari, K.; Min, C.C.; Ismail, I.S. The immunostimulant effects of Isochrysis galbana supplemented diet on the spleen of red hydrid tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) evaluated by nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics. Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 1154558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sîrbu, E.; Dima, M.F.; Tenciu, M.; Cretu, M.; Coada, M.T.; Totoiu, A.; Cristea, V.; Patriche, N. Effects of dietary supplementation with probiotics and prebiotics on growth, physiological condition, and resistance to pathogens challenge in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes 2022, 7, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Ringo, E.; Ahmadifar, E.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. Probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotics used to control Vibriosis in fish: A review. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almarri, S.H.; Khalil, A.A.; Mansour, A.T.; El-Houseiny, W. Antioxidant, immunostimulant, and growth-promoting effects of dietary Annona squamosal leaf extract on Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, and its tolerance to thermal stress and Aeromonas sobria infection. Animals 2023, 13, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.T.; Tu, H.C.; Chang, W.N.; Chen, B.H.; Shi, Y.Y.; Chang, T.C.; Fu, T.F. Grape seed extract inhibits the growth and pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus by interfering with dihydrofolate reductase activity and folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 14, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.W.; Lu, J.J.; Chen, X.H. Effects of dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins on growth performance, some serum biochemical parameters and body composition of tilapia (Orechromis niloticus) fingerlings. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 13, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penglase, S.; Ackery, T.; Kitchen, B.; Flavel, M.; Condon, K. The effects of a natural polyphenol extract from sugarcane (Saccharum offcinarum) on the growth, survival, and feed conversion efficiency of juvenile black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, H.V.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Hung, T.Q.; Lumsangkul, C.; Jaturasitha, S.; El-Haroun, E.; Paolucci, M. Diatery inclusion of chesnut (Castanea sativa) polyphenols to Nile tilapia reared in biofloc technology: Impacts on growth, immunity, and disease resistance against Streptococcus agalactiae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 105, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, P.; Kurian, A.; Lakshmi, S.; Faggio, C.; Esteban, M.A.; Ringo, E. Herbal immunomodulators in aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich, I. Superoxide radical and superoxide dismutases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiansilakul, Y.; Benjakul, S.; Richards, M.P. Effect of myoglobin from Eastern little tuna muscle on lipid oxidation of washed Asian seabass mince at different pH conditions. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azaza, M.S.; Dhraief, M.N.; Kraiem, M.M. Effect of water temperature on growth and sex ratio of juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus reared in geothermal waters in southern Tunisia. J. Therm. Biol. 2008, 33, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherif, M.S.; El-Feky, A.M.I. Performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings. I. Effect of pH. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2009, 11, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Dandruff, P.; Dean, L.S. Dissolved oxygen criteria for the protection of fish. Am. Fish. Soc. 1967, 4, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tamil Nadu Agricultural University (TNAU). Water Quality Management; Tamil Nadu Agricultural University (TNAU): Tamil, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chainark, S.; Boyd, C.E. Water and sediment quality, phytoplankton communities and channel catfish production in sodium nitrate-treated ponds. J. Appl. Aquac. 2010, 22, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Krishnani, K.K.; Singh, N.P. Effect of dietary zinc-nanoparticles on growth performance, anti-oxidative and immunological status of fish reared under multiple stressors. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, M.N.; Shaheen, A.A.M.; Hamed, H.S. Potential role of dietary parsley and/or parsley nanoparticles against zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity induced physiological, and histological alterations in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, A.; Nagarani, G.; Siddhuraju, P. Hepatoprotective effect of leaf extracts from Citrus hystrix and C. maxima against paracetamol induced liver injury in rats. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, E.; Acar, U.; Ontas, C.; Kesbiç, O.S.; Yilmaz, S. Evaluation of Citrus limon peels essential oil on growth performance, immune response of Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus challenged with Edwardsiella tarda. Aquaculture 2016, 465, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Elumalai, P.; Tongsiri, S.; Chitmanat, C.; Jaturasitha, S.; Doolgindachbaporn, S. Effects of orange peels derived pectin on innate immune response, disease resistance and growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured under indoor biofloc system. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.K. Anthocyanins Increase Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in ht-29 Adenocarcinoma Cells. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Hu, T.; Wang, Y. Potential and challenges of tannins as an alternative to in-feed antibiotics for farm animal production. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccia, E.; Siano, F.; Volpe, M.G.; Varricchio, E.; Eroldogan, T.; Paolucci, M. Chestnut shell extract modulates immune parameters in the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fishes 2019, 4, 36218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahazi, M.A.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Jafari, V.; Hajimoradloo, A.; Doan, H.V.; Paolucci, M. Dietary supplementation of polyphenols positively affects the innate immune response, oxidative status, and growth performance of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laein, S.S.; Salari, A.; Shahsavani, D.; Baghshani, H. Effect of supplementation with lemon (Citrus lemon) pomace powder on the growth performance and antioxidant response in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 15, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, A.; Bagheri, D.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Morshedi, V.; Paolucci, M. Beneficial role of polyphenols as feed additives on growth performances, immune response and antioxidant status of Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790) juveniles. Aquaculture 2022, 552, 737955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Bhavan, P.; Seenivasan, C.; Shanthi, R.; Muralisankar, T. Replacement of fish meal with Spirulina platensis, Chorella vulgaris and Azolla pinnata on nonenzymatic and enzymatic antioxidant activities of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2014, 67, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirvaghefi, A.; Ali, M.; Sadi, F. Effects of vitamin E, selenium and vitamin C on various biomarkers following oxidative stress caused by diazinon exposure in rainbow trout. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2015, 2, 00035. [Google Scholar]
- Doba, T.; Burton, G.W.; Ingold, K.U. Antioxidant and co-antioxidant activity of vitamin C. The effect of vitamin C, either alone or in the presence of vitamin E or a water-soluble vitamin E analogue, upon the peroxidation of aqueous multi lamellar phospholipid liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 835, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, C.W.; Quinhones, E.B.; Jung, E.A.C.; Zeni, G.; Rocha, J.B.T. Anti-inflammatory and antiociceptive activity of biphenyl diselenide. Inflamm. Res. 2003, 52, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Pacheco, M.; Santos, M.A. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants as an adaptation to phagocyte-induced damage in Anguilla anguilla L. following in situ harbor water exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, F.; Cairang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Du, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Role of dietary tea polyphenols on growth performance and gut health benefits in juvenile hybrid sturgeon (Acipenser baerii × A. schrenckii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portz, D.E.; Woodley, C.M.; Cech, J.J. Stress-associated impacts of short-term holding on fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2006, 16, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frances, J.; Nowak, B.F.; Allan, G.L. Effects of ammonia on juvenile silver perch (Bidyanus bidyanus). Aquaculture 2000, 183, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.R.; Saha, R.K.; Saha, H. Muli bamboo (Melocanna baccifera) leaves ethanolic extract a non-toxic phyto-prophylactic against low pH stress and saprolegniasis in Labeo rohita fingerlings. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.P.; Cardoso, I.L.; Ishikawa, M.M.; de Oliveira, A.D.S.S.; Sartoratto, A.; Jonsson, C.M.; de Queiroz, S.C.D.N.; Duarte, M.C.T.; Rantin, F.T.; Sampaio, F.G. Effects of Artemisia annua alcohol extract on physiological and innate immunity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to improve health status. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 105, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Sony, N.M. Dietary effects of adenosine monophosphate to enhance growth, digestibility, innate immune responses and stress resistance of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnaani, C.; Tinman, S.; Ron, Y.; Hulata, G. Comparative study of biochemical parameters in response to stress in Oreochromis aureus, O. mossambicus and two strains of O. niloticus. Aquac. Res. 2004, 35, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, G.K.; Afonso, L.O.B.; Vijayan, M.M. Stress in fishes. In The Physiology of Fishes, 3rd ed.; Evans, D.H., Claiborne, J.B., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 319–342. [Google Scholar]
- Kubokawa, K.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshioka, M.; Iwata, M. Effects of acute stress on plasma cortisol, sex steroid hormone and glucose levels in male and female sockeye salmon during the breeding season. Aquaculture 1999, 172, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobsikova, R.B.; Modra, J.; Skoric, H.; Svobodova, M.Z. The effect of acute exposure to herbicide Gardoprim Plus Gold 500 SC on hematological & biochemical indicators and histopathological changes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). J. Vet. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 80, 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- Metwally, M.A.A.; Wafeek, M. Effect of ammonia toxicity on carbohydrate metabolism in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 252–261. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).