Abstract
In October 2023, a disease outbreak in pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus) farms in Zhongshan City, Guangdong, China, caused high mortality. Diseased fish (mean length: 15 ± 1 cm) exhibited swimming disorders, fin rot, hemorrhage, and an enlarged spleen. Histopathological observations generally revealed inflammation, necrosis, and congestion in the spleen, kidneys, and brain tissues. The most severe pathological changes included interstitial edema and tubular atrophy in the kidneys, hemosiderin deposition in the spleen, massive red blood cell infiltration, and a decrease in lymphocytes. A single strain of bacteria (Tol-1) was isolated from the diseased pufferfish and identified as a Gram-positive streptococcus strain, exhibiting α-hemolysis on sheep blood agar plates. Through biochemical characterization, 16S rDNA sequencing, morphological analysis, and specific primer-based identification, the Tol-1 strain was identified as Lactococcus garvieae, serotype I. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing indicated that Tol-1 was sensitive to Chloramphenicol, Ampicillin, Cephalexin, and Doxycycline, but resistant to Kanamycin, Gentamicin and Ciprofloxacin. In addition, 15 common virulence factors were detected in the Tol-1 strain, including adhPav, adhPsaA, adhC I–II, adh, and hly 1–3. Pufferfish (mean length: 17 ± 1 cm) subjected to artificial infection via intraperitoneal injection (IP) with the Tol-1 strain exhibited clinical symptoms and histopathological damage similar to those observed in naturally infected fish. An infection dose of 1 × 105 CFU/fish resulted in 80% mortality. The study fulfilled Koch’s postulates, indicating that the disease outbreak in pufferfish was caused by L. garvieae, which exhibited a high mortality rate in pufferfish despite the subtle clinical symptoms. These results serve as a warning for pufferfish farming areas and provide a scientific basis for future prevention and control efforts.
Key Contribution:
Lactococcus garvieae was identified as the pathogen causing massive mortality in Takifugu obscurus and it has strong pathogenicity to T. obscurus.
1. Introduction
Takifugu obscurus, also known as the pufferfish or bubble fish, belongs to the order Tetraodontiformes and family Tetraodontidae, Takifugu [1]. It is a freshwater migratory fish that is mainly found in the coastal areas of China, Japan and South Korea [2]. China’s annual allowable pufferfish catch exceeds 100,000 tons, accounting for approximately 70% of the world’s total output, with 70% to 80% of this catch being exported. Consequently, China plays a dominant role in the pufferfish production worldwide [3]. The increase in market demand and the maturity of artificial breeding technology have led to the rapid development of the country’s pufferfish aquaculture [4,5]. According to the China Fisheries Statistical Yearbook 2021, the total aquaculture capacity of the pufferfish farming industry in the country reached 20,000 tons in 2020. However, the expansion of farming scale and high-density farming practices have led to increasingly diverse and frequent fish diseases [6,7]. Many industry-constraining diseases have been reported in pufferfish farming. These diseases include those caused by Vibrio harveyi [8], Cryptocaryon irritans [9], Nocardia [10], Aeromonas hydrophila, and Vibrio Parahaemolyticus [11], among others. In recent years, studies on the immune response mechanisms of pufferfish have increased [12,13,14], but the discovery of pathogens and targeted prevention and control measures remains limited.
Lactococcus garvieae is a Gram-positive bacterium that was initially classified as Streptococcus due to its phenotypic similarities. It was later referred to as Enterococcus seriolicida based on physiological and biochemical studies [15], but was eventually reclassified as Lactococcus based on genotyping developments [16]. As a pathogenic bacterium, L. garvieae can infect not only mammals, such as humans, cows, and pigs [17,18,19], but also fish, having been identified as a pathogen in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchlineus mykiss) in 1958 [20]. Researchers performed a virulence gene analysis on various strains of L. garvieae derived from fish and identified several well-known virulence factors, including hemolysin 1–3, NADH oxidase, superoxide dismutase, phosphoglucomutase, adhesin pav, adhesin psaA, enolase, LPxTG 1–4, adhesin cluster 1–2, and adhesin. These virulence factors are associated with adhesins, surface proteins, anti-inflammatory agents, and hemolysins, each of which plays a pivotal role in L. garvieae virulence [21]. Over time, China, Japan, Kuwait, Brazil, Italy, and many other countries have reported incidents of L. garvieae infections in fish, affecting a wide range of hosts including Oreochromis niloticus L., Pseudoplathystoma corruscans, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, Anguilla japonica, Dicentrarchus labrax, and Tursiops truncates [15,22,23,24,25]. The pathogen has spread to many parts of the world, causing significant economic losses in the aquaculture industry [26].
In October 2023, an outbreak of sudden mortality occurred among pufferfish in Tanzhou Town, Zhongshan City, Guangdong Province, China. Our team visited the area and observed that the pond’s water temperature was approximately 28 °C. The daily mortality rate of pufferfish in the pond reached 100–200 individuals (approximately 1.25–2.5%). The disease lasted about a week, and it tended to recur after ten days of drug treatment, resulting in substantial economic losses for farmers. Based on field observations, no parasites were detected in the infected pufferfish, and the clinical symptoms were consistent. Subsequently, our team successfully isolated L. garvieae from ten infected pufferfish and characterized its bacteriological and molecular characteristics. Since there were no reports of L. garvieae infection in pufferfish worldwide, this study identified the bacterium as the pathogen causing the outbreak through artificial infection experiments, providing a basis for subsequent disease prevention and control in pufferfish culture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolating Bacterium from Diseased T. obscurus
Ten diseased and moribund fish were brought to our laboratory, and their clinical symptoms were recorded. The surface of the fish skin was cleaned with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol. The liver, spleen, kidney, and brain were exposed with dissection tools in a sterile environment and incised using a scalpel. A sterile inoculation ring was inserted into the organ and sampled, then inoculated onto Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) agar plates. The isolated bacteria were cultured on BHI agar plates at 28 °C for 24 h. After incubation, dominant strains were selected from the BHI plate and transferred to a new BHI agar plate for further cultivation. Subsequently, we transferred the Tol-1 isolate (obtained from the brain) to BHI liquid medium for further expansion. The bacterial culture was mixed 1:1 with 50% (v/v) sterile glycerol and stored at −80 °C for future use.
2.2. Histopathology Analysis
The liver, spleen, kidney, and brain tissues of naturally diseased fish were collected and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. The organs were dehydrated, made transparent, wax-infiltrated, embedded, and sectioned (4 μm) via conventional operations. Finally, the tissues were stained with hematoxylin eosin (HE) and observed under an optical microscope (SOPTOP EX20), SUNNY OPYICAL TECHNOLOGY(GROUP)CO., LTD, Ningbo, China.
2.3. Morphology and Hemolytic Activity
The purified bacteria Tol-1 were selected and streaked onto both BHI plates and sheep blood plates (Huankai Microbial, Guangzhou, China). They were then incubated at 28 °C for 18–24 h to observe colony morphology and hemolysis, respectively. Additionally, a single colony smear was prepared for Gram staining, and the bacterial morphology was observed under an oil-immersion optical microscope (SOPTOP EX20).
2.4. Biochemical Characterizations
We biochemically characterized the isolated strain Tol-1 using the Streptococcus Biochemical Identification Kit (https://hzbinhe.cn/list_17/28.html, accessed on 10 December 2023, A203, Hangzhou Binhe, Hangzhou, China). Standard operations were carried out according to the manual provided by Hangzhou Binhe. Tol-1 colonies were selected using an inoculating loop and inoculated into various physiological and biochemical identification tubes. The identification tubes were then incubated at 28 °C for 24 h. The Streptococcus Identification Manual (https://hzbinhe.cn/list_15/844.html, accessed on 10 December 2023, D026) was used to interpret the results of the physiological and biochemical experiments. The bacterial species corresponding to the physiological and biochemical results of the Tol-1 strain were identified with reference to the manual for preliminary identification.
2.5. Molecular Identification
DNA was extracted from the isolated Tol-1 strain using a Gram-positive bacterial DNA extraction kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China). PCR amplification was performed using universal bacterial 16S rDNA primers (27F and 1492R) [27] and 16S-23S rDNA primers (G1 and L1) [28] (Table 1). The PCR mixture comprised 10 μL of 2× M5 HIPer plus Taq HIFi PCR mix (vazyme), 320 nM of each primer, 280 ng of the sample DNA, and ddH2O to make up a final volume of 20 μL. The PCR products were subjected to 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and 16S rDNA products were sent to Liuhe Huada Genes Technology Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). for sequencing using the Sanger method and the ABI3730XL instrument. The 16S rDNA sequences were analyzed using NCBI BLAST blastn, and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA 6.0 software, with Bootstrap testing repeated 1000 times.

Table 1.
PCR primers and conditions for bacterium identification.
2.6. Molecular Serotype
The Tol-1 strain was tested for a serotype using the method and primers described by Ohbayashi et al. [29]. The PCR mixture comprised 10 μL of 2 × M5 HIPer plus Taq HIFi PCR mix (vazyme), 320 nM of each primer, 280 ng of the sample DNA, and ddH2O to make up a final volume of 20 μL. The amplification program was carried out according to the specified conditions outlined in Table 2 [28,29]. The PCR product was electrophoresed on a 1% agarose gel, and the Tol-1 serotype was determined based on the size of the PCR product.

Table 2.
Primers and condition for virulence factor and serotype identification.
2.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
Erythromycin, chloramphenicol, kanamycin, vancomycin, ampicillin, gentamicin, florfenicol, cephalexin, doxycycline, and ciprofloxacin were used in this antibiotic susceptibility test (Hangzhou Binhe, China). According to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI)’s K-B method standards, Tol-1 was cultured in BHI broth medium and adjusted to a 0.5 McFarland standard. The bacterial solution was applied to Mueller Hinton (MH) agar plates supplemented with 5% sheep blood (Huankai Microbial, China), followed by the addition of ten types of antibiotic sensitivity disks. The plates were incubated at 28 °C for 18 h. The inhibition zone diameters were measured, and the sensitivity (S), medium susceptibility (I), and resistance (R) of Tol-1 to various antibiotics were evaluated.
2.8. PCR Detection of Virulence Factors of Tol-1 Strain
Following the method described by Ture M and Altinok I for detecting the virulence factors of L. garvieae, 16 virulence factors were selected for detection in the Tol-1 strain [21]. These factors include hemolysin 1–3, NADH oxidase, superoxide dismutase, phosphoglucomutase, adhesin pav, adhesin psaA, enolase, LPxTG 1–4, adhesin cluster 1–2, and adhesin. The PCR mixture comprised 10 μL of 2× M5 HIPer plus Taq HIFi PCR mix (vazyme), 80 pmol of each primer, 160 ng of the sample DNA, and ddH2O to make up a final volume of 20 μL. The amplification conditions included an initial cycle of 3 min at 94 °C, followed by 35 PCR cycles consisting of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 52−56 °C (see Table 2) for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 10 min [21,28]. The PCR products were electrophoresed on a 1% agarose gel to determine the Tol-1 virulence factors.
2.9. Fish Challenge
T. obscurus, with an average length of 17 ± 1 cm, were obtained from a fish farm and acclimated for a minimum of two weeks at 28 °C prior to the infection experiment. The day before the experiment, five fish were randomly selected for anatomical observation. Bacterial isolation was performed on the spleen, kidney, and brain to confirm that no bacterial growth was detected on the BHI plate, thereby ensuring the health and infection-free status of the experimental fish. The bacterial strain Tol-1 was cultured in BHI medium at 28 °C for 18 h to ensure the viability of the bacterial solution. After culturing the Tol-1 strain, it was washed twice with PBS and adjusted to a concentration of 1 × 106 CFU/mL for infection.
Tol-1 was used to challenge two groups of 10 fish each via intraperitoneal injection, with a dose of 0.1 mL per fish administered using a 1 mL syringe. One group was monitored for mortality. The other group was used to observe clinical symptoms of the fish and collected five fish organs for histopathological analysis on the third day post-bacterial injection. Concurrently, 10 healthy fish were injected with 0.1 mL of PBS to serve as the control group.
In this animal experiment, the fish were anesthetized by immersing them in an anesthetic solution (MS-222) prior to artificial infection, and excessive anesthesia was administered before tissue collection. At the conclusion of the experiment, the fish were euthanized.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Symptoms in Naturally Infected T. obscurus
In the pond, diseased fish exhibited symptoms of torpor and poor vitality. Upon clinical observation, the surface of the infected fish appeared to be in good condition, with no obvious symptoms observed. Some seriously diseased fish may have had abdominal skin and stomach hemorrhage (Figure 1A). Additionally, hemorrhage on the dorsal, ventral, and pectoral fins (Figure 1B), as well as the enlargement of the spleen (Figure 1C), accounted for more than 80% of the observed symptoms.
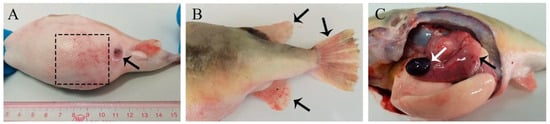
Figure 1.
Clinical symptoms of naturally infected T. obscurus. (A) Abdominal skin hemorrhage (black dashed line box), redness, and abdominal swelling (black arrow); (B) Hemorrhage on dorsal, ventral, and pectoral fins (black arrow); (C) Splenomegaly (white arrow) and gastric congestion (black arrow).
3.2. Histopathological Changes in Naturally Infected T. obscurus
Renal interstitial edema made the renal tissue appear loose, with erythrocyte escape and inflammatory cell infiltration. Renal tubule epithelial cells displayed exfoliation or necrosis. In our experiments, there was renal tubule atrophy and exfoliated cellular debris (Figure 2A). The spleen displayed phagocyte aggregation, increased hemosiderin deposition, fibrinoid degeneration, and mild necrosis (Figure 2B). The meninges showed mild thickening and congestion, the brain tissue became edematous and loose, and some neurons exhibited degeneration and necrosis (Figure 2C).
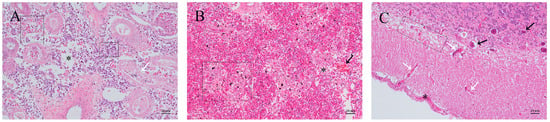
Figure 2.
Histopathological changes in T. obscurus with natural infection. (A) Kidney: scattered erythrocytes and inflammatory cell infiltration appear between the tissues (dashed box), renal interstitial edema (asterisk), renal tubule atrophy, and epithelial cell shedding (white arrow). (B) Spleen: increased erythrocyte count and phagocytic cell aggregation (black arrow) with hemosiderin deposited in several places, accompanied by fibrinoid degeneration (dashed box) and tissue necrosis (asterisk). (C) Brain: slight thickening and congestion of the meninges (asterisks), increased capillaries (white arrows), and neurons exhibited degeneration and necrosis (black arrows); the brain tissue became edematous (dashed box).
3.3. Morphological and Hemolysis Activity of Tol-1 Isolate
After purification, Tol-1 strain colonies on BHI agar plates exhibited a white opaque colony with a round, raised middle, a smooth surface, and a sticky feel (Figure 3A). Gram staining revealed a purple color, and under an oil immersion microscope, the bacteria appeared arranged in variable-length single or paired chains, confirming the strain as Gram-positive streptococci (Figure 3B). On sheep blood agar plates, Tol-1 showed α-hemolysis (Figure 3C).

Figure 3.
Morphology and hemolysis of the Tol-1 isolated strain. (A) Colony morphology observed on BHI agar plates; (B) Gram stain; and (C) hemolysis of strain on sheep blood agar plates.
3.4. Biochemical Characterization
The physiological and biochemical identification results for Tol-1 were evaluated using the Streptococcus Identification Manual (GYZ-12St) from Hangzhou Binhe Microorganism Co., Ltd. (Table 3). According to this manual, the biochemical characteristics of Tol-1 aligned with those of L. garvieae, leading to the preliminary conclusion that the Tol-1 strain was likely L. garvieae.

Table 3.
Physiological and biochemical identification of L. garvieae Tol-1 strain.
3.5. Molecular Identification
According to NCBI blast, the 16S rDNA sequence of the Tol-1 strain (GenBank PQ357226) was 100% identical to that of other L. garvieae. The 16S rDNA sequence of the Tol-1 strain isolated from diseased fish was compared with Lactococcus spp. and Streptococcus spp. for phylogenetic tree construction. The results showed that Streptococcus spp. became an extaxon and formed roots; the Tol-1 strain was classified as belonging to the same clade as Lactococcus spp., with a Bootstrap value of 100% (Figure 4).
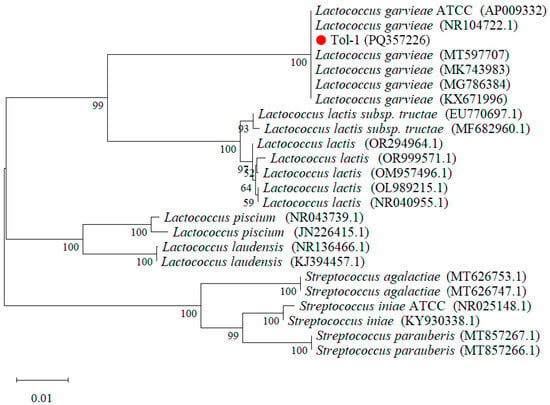
Figure 4.
Construction of neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the existing Lactococcus spp. from GenBank, with Streptococcus spp. as an outgroup.
The Tol-1 strain was verified using 16S-23S rDNA primers (G1 and L1). Gel electrophoresis showed that this strain could amplify the target fragment of 430 bp (Figure 5A). According to Ohbayashi et al.’s method, the target fragment at this location was indicative of L. garvieae [29].
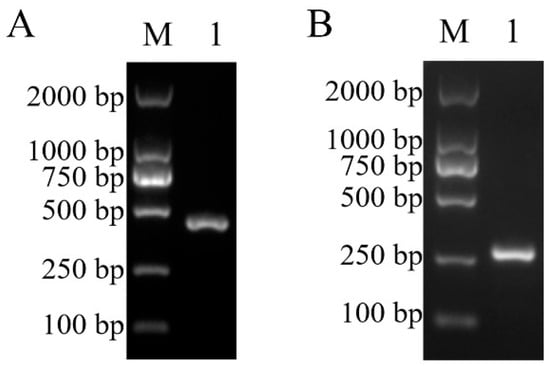
Figure 5.
The Tol-1 isolated strain was amplified using 16S-23S rDNA primers (A) and molecular serotype specific primers for L. garvieae (B). M: DL2000 DNA Marker; 1: isolated strain of T. obscurus.
3.6. Molecular Serotype
The Tol-1 strain isolated from infected fish was identified using molecular serotype specific primers for L. garvieae. The electrophoretic results showed a bright band at 285 bp, confirming that the strain was serotype I (Figure 5B).
3.7. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Test
According to the CLSI’s antimicrobial susceptibility test criteria, the Tol-1 strain exhibited sensitivity to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, cephalexin, and doxycycline, as well as medium susceptibility to erythromycin, vancomycin, and florfenicol (Table 4). It also demonstrated resistance to three other kinds of antibiotics.

Table 4.
Antimicrobial sensitivity testing of L. garvieae Tol-1 strain.
3.8. PCR Detection of Virulence Factors of Tol-1 Strain
In the detection of L. garvieae virulence factors (Figure 6), the Tol-1 strain amplified fragments for 15 virulence factors, including hemolysin 1–3, NADH oxidase, superoxide dismutase, phosphoglucomutase, adhesin pav, adhesin psaA, enolase, LPxTG 1, LPxTG 3–4, adhesin cluster 1–2, and adhesin. However, the Tol-1 strain also produced non-specific amplified fragments during the amplification of adhesin fragments. Additionally, using the specific primer for the virulence factor LPxTG 2, Tol-1 amplified approximately 1900 bp fragments, which were not the target fragments of the virulence factor.
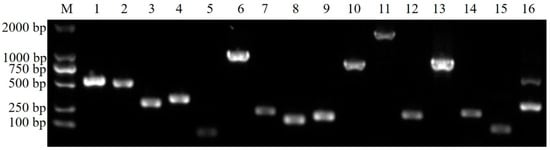
Figure 6.
An amplification of the virulence genes of the Tol-1 isolated strain. M: DL2000 DNA Marker; 1–3: hemolysin 1–3; 4: NADH oxidase; 5: superoxide dismutase; 6: phosphoglucomutase; 7: adhesin pav; 8: Adhesin psaA; 9: enolase; 10–13: LPxTG 1–4; 14–15: adhesin cluster 1–2; 16: adhesin.
3.9. Clinical Signs of In Vivo Infection T. obscurus
In the artificial infection experiment, T. obscurus in the infection group exhibited slower, lessened activity compared to the control group. The main symptoms observed in the diseased fish were spleen enlargement (Figure 7D) and caudal fin hemorrhage and ulceration (Figure 7C). In moribund fish with fewer disease symptoms, a higher abundance of L. garvieae was isolated from the liver, spleen, kidney, and brain.
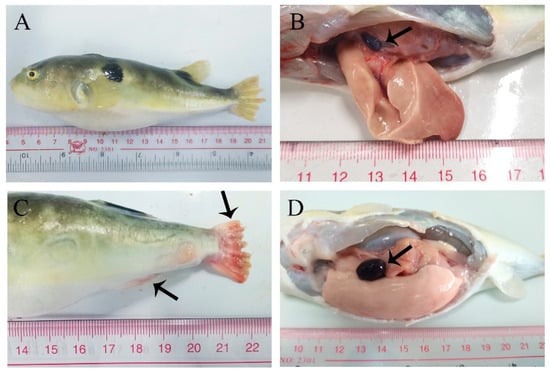
Figure 7.
In vivo infection T. obscurus with L. garvieae Tol-1 strain. (A,B) Control group; (C,D) infection group; (B) healthy spleen (arrow); (C) the caudal fin was severely congested and ulcerated; the anal fin is congested (arrow); and (D) spleen enlargement (arrow).
3.10. Histopathological Changes in of In Vivo Infection T. obscurus
The artificial infection of the L. garvieae Tol-1 strain induced pathological changes in various tissues of T. obscurus (Figure 8). Healthy kidneys had regular and full renal tubules and tightly packed renal tissue (Figure 8A). Infected kidneys exhibited renal interstitial edema, with scattered erythrocytes in the interstitium accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration. The renal tubule epithelial cells underwent degeneration, necrosis, and shedding, resulting in a disordered overall kidney structure. (Figure 8D). Compared to healthy spleens, infected spleens were congested, with significant hemosiderin deposition and a notable decrease in lymphocytes (Figure 8B,E). Compared with healthy brain tissue (Figure 8C), the brain tissue of the infected group showed thickening and congestion in the meninges, the degeneration of some neurons, and capillary congestion (Figure 8F).
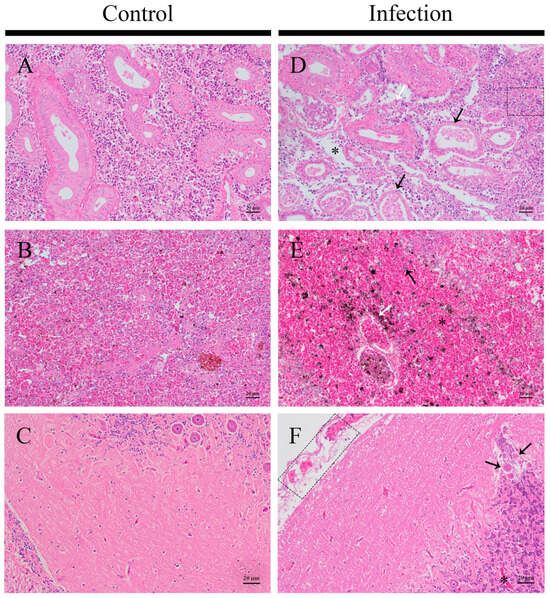
Figure 8.
Histopathological changes in T. obscurus with artificial infection of L. garvieae. (A–C) Control group; (D–F) infection group. (A,D) Kidney: renal tubule atrophy and epithelial cell shed (black arrow), erythrocyte escape (white arrow), renal interstitial edema, loose tissue (asterisk), and inflammatory cell infiltration (dashed box). (B,E) Spleen: a lot of hemosiderosis (white arrow), increases in erythrocyte (asterisk), and a decrease in lymphocytes (black arrow). (C,F) Brain: the meninges are loosened and thickened, with a large number of erythrocytes (dotted box), the degeneration of some neurons (black arrow), and capillary congestion (asterisk).
3.11. Pathogenicity of L. garvieae to T. obscurus
Over the seven days of observation after exposure to Tol-1 strain at a low dose (1 × 105 CFU/fish), the mortality persisted beyond the initial deaths on the second day (Figure 9). The mortality rate notably increased on the fourth and fifth days, after which the remaining T. obscurus did not exhibit further mortality. The mortality rate reached 80% within seven days of exposure to 1 × 105 CFU/fish. There were no deaths in the PBS group during this seven-day period, and the vitality remained high (Figure 9).
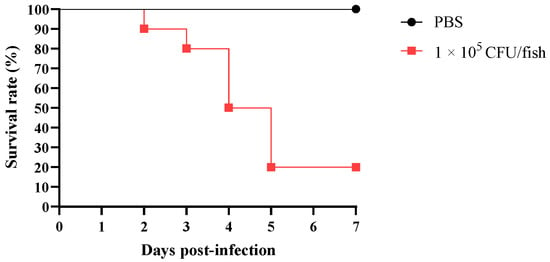
Figure 9.
Survival rate of T. obscurus infected with L. garvieae.
4. Discussion
In recent decades, L. garvieae has been identified as a pathogen affecting fish. Our team isolated bacteria from pufferfish in a farm in Tanzhou Town, Zhongshan City, Guangdong, China, where explosive mortality occurred. The strain was identified as a Gram-positive streptococcus, exhibiting α-hemolysis. Morphological, physiological, biochemical, and molecular identification collectively confirmed that the Tol-1 strain was L. garvieae. Years ago, researchers classified L. garvieae based on its serum characteristics. They considered capsule formation as a decisive feature for serotyping, and this resulted in two serum types: capsule (KG+/agglutination) and non-capsule (KG−/no agglutination) strains [30]. Subsequently, at the genetic level, a comparison between capsule and non-capsule L. garvieae led to molecular typing, categorizing L. garvieae into Type I (KG+) and Type II (KG−) strains [29]. During this period, some researchers experimentally believed that pathogenic L. garviea possess capsules, while non-capsule L. garviea are non-pathogenic [31]; however, the subsequent isolation of non-capsule L. garviea from diseased fish proved this hypothesis to be incorrect [32,33]. The strain of L. garvieae isolated from pufferfish in this study was molecularly identified as Type I serum type, indicating the capsule strain.
Fish infected with lactococcosis species typically exhibit symptoms such as abnormal behavior, cloudy or congested eyes, brain swelling and congestion, fin congestion, and enlarged spleen, as well as symptoms of sepsis such as internal organ surface and external surface bleeding and petechiae [22,34,35,36,37]. In our observations of the clinical symptoms of pufferfish affected by the lactococcosis outbreak, the most common symptoms were fin congestion or ulceration and enlarged spleen. Conversely, only two pufferfish with septicemia exhibited redness of the skin and blood clots in the abdomen. Unlike other fish [34,35], which did not exhibit typical symptoms such as congested eyes, cloudy eyes, and meningitis. The clinical symptoms exhibited in the reinfection experiment primarily included fin congestion and ulceration, as well as spleen enlargement, with no abnormal findings observed on the body’s surface, eyes, or brain under direct observation.
In the histopathological observations of natural and in vivo infected pufferfish, the brain did not exhibit severe macrophage infiltration, as seen in infected pompano. They primarily exhibited the thickening and congestion of the meninges, the degeneration of some neurons, and capillary congestion [34]. As an immune organ, the spleen exhibits a strong immune response, continuously accumulating erythrocytes and exhibiting a persistent decrease in lymphocytes. If the condition persists long term, the lymphocyte count may decrease to a certain extent, leading to spleen atrophy. In the histopathological observations of naturally infected and reinfected pufferfish, the kidneys were the most severely damaged, exhibiting interstitial edema leading to loose kidney tissue and the appearance of tubular atrophy. The pathological alterations in the kidneys may impair the fish’s ability to excrete metabolic wastes. From the above, it can be seen that pufferfish infected with L. garvieae may experience kidney collapse first, leading to the inability to excrete metabolites. The toxic effects of waste in the body ultimately result in the death of affected pufferfish.
Although it has been proven that the mass death of pufferfish was caused by L. garvieae, current disease prevention and control measures are insufficient, making antibiotics the most direct method for alleviating Lactococcosis. In this experiment, ten antibiotics were used to conduct antibiotic susceptibility tests on L. garvieae isolated from pufferfish. Among them, L. garvieae showed resistance to three antibiotics, and exhibited medium sensitivity or sensitivity to the remaining seven. Among the antibiotics available in aquaculture, only doxycycline and florfenicol were effective against L. garvieae. Over the years, using antibiotics to control Lactococcosis has been common practice, but the development of resistant strains remains a limiting factor [26,38,39]. During the on-site sampling in this study, we observed that, while antibiotic treatment for Lactococcosis in pufferfish was effective, the condition tended to recur after a certain period of time, requiring the use of antibiotics again to alleviate symptoms. Such control measures not only increase costs for fish farmers but also lead to long-term fish mortality. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find green and healthy disease control technologies to address this issue.
Some studies suggest that the pathogenicity of L. garvieae in fish partially depends on its ability to form capsules [40]. It is well known that bacteria exert pathogenicity on hosts primarily through various virulence factors [41]. To investigate the virulence factors of L. garvieae isolated from pufferfish, this study selected 16 common virulence factors for the Tol-1 strain [21,42]. In the results of this study, 15 virulence factors, including hemolysin 1–3 (hly 1–3), NADH oxidase, superoxide dismutase (sod), phosphoglucomutase, adhesin pav (adhPav), adhesin psaA (adhPsaA), enolase (eno), LPxTG 1, LPxTG 3–4, adhesin cluster 1–2 (adhC I–II), and adhesin (adh) were detected. Adhesion is a critical step in the pathogenic mechanism of bacteria, and four important adhesins were detected in the Tol-1 strain (adhPav, adhPsaA, adhC I-II, adh) [42,43,44]. Additionally, other virulence factors, such as surface proteins (LPxTG 1, LPxTG 3–4) [45], anti-inflammatory factors (sod) [46], and hemolysins (hly 1–3) [42], play roles in adhesion, immune evasion, cell surface binding, toxin production, host–cell destruction, and immune escape into the host brain to damage nerves [47].
Lactococcosis primarily refers to a fish disease caused by infection with L. garvieae, resulting in acute hemorrhagic septicemia [26,48]. According to the current reports of L. garvieae in fish, mortality rates ranged from 20% to 50% in cobia (Rachycentron canadum) after infection [28]; rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) can experience up to 60% mortality when infected at temperatures rising to 15 °C [49], and in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) farming in Brazil, mortality rates due to lactococcosis exceed 15%, with subsequent outbreaks of L. garvieae observed in different regions [35]. Over the past few decades, lactococcosis has rapidly emerged as a significant threat to fish worldwide [47]. In addition to fish, the mortality rate in Penaeus vannamei after infection with L. garvieae exceeds 70% [50]. The pufferfish involved in this lactococcosis outbreak were adult fish with an average size of 18 ± 1cm. During mild outbreaks, the daily loss in the pond was 40–50 fish. During severe outbreaks, the daily mortality reached 100–200 fish, lasting for about a week and causing aquaculture farmers significant losses. Employing a bacterial concentration of 105 CFU/fish resulted in an 80% mortality rate in pufferfish, indicating the high virulence of the prevalent L. garvieae in pufferfish farming ponds.
5. Conclusions
The discovery of L. garvieae infection in pufferfish represents a novel finding, confirming its lethal pathogenic potential. Moreover, due to the relatively inconspicuous clinical symptoms of pufferfish after L. garvieae infection, as well as the limited effectiveness of antibiotic treatments, controlling the disease becomes particularly crucial in pufferfish farming. Various measures for controlling L. garvieae have been the focus of research in the aquaculture industry, including vaccines [51,52], diagnostic methods [53,54], extracts [55,56,57], probiotics [58], and other approaches. Whether these control methods can be applied in pufferfish farming is a topic worth further investigation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.H., Y.C. and Z.M.; Data curation, Z.H.; Funding acquisition, X.D. and Y.L.; Investigation, Y.C. and Z.M.; Methodology, R.X. and Y.D.; Project administration, X.D. and Y.L.; Validation, Y.D.; Writing—original draft, R.X.; Writing—review and editing, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Nansha-South China Agricultural University Fishery Research Institute, grant number NSYYKY202303.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal experiments in this manuscript were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of South China Agricultural University. The animal ethics approval number is 2024G021.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Special Science Found of Nansha-South China Agricultural University Fishery Research Institute (Grant number NSYYKY202303).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, K. The scientific names of Takifugu and Takifugu obscurus. J. Zool. 2005, 5, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.F. Differences in reproductive strategies between obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus and ocellated puffer Takifugu ocellatus during their spawning migration. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2008, 24, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhike, D.; Qingli, G.; Jianzhou, C. Industry situation and development strategy of Pufferfish in China. Sci. Fish Farming 2006, 3, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, W.F. Effect of temperature on incubation period and hatching success of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus (Abe) eggs. Aquaculture 2005, 246, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.F. Induced ovulation in obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus by injections of LHRH-a. Aquac. Int. 2004, 12, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, L.-R.; Ketola, T.; Laanto, E.; Kinnula, H.; Bamford, J.K.; Penttinen, R.; Mappes, J. Intensive aquaculture selects for increased virulence and interference competition in bacteria. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20153069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.A.; Kurath, G.; Brito, I.L.; Purcell, M.K.; Read, A.F.; Winton, J.R.; Wargo, A.R. Potential drivers of virulence evolution in aquaculture. Evol. Appl. 2016, 9, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeong-Seong, L.I.M.; Dae-Hyun, K.I.M.; Woo, P.S. Vibrio harveyi Infection in River Puffer (Takifugu obscurus) Broodstock Cultured in Sea Water. J. Fish. Mar. Sci. Educ. 2021, 33, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.S. Cryptocaryon irritans infection in River puffer (Takifugu obscurus) cultured in sea water. J. Fish Pathol. 2004, 17, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, K.; She, R.; Qi, K.; Zhu, G.; Bao, C. Adiposis Hepatica Complicating Nocardiosis in Obscure Puffer Fugu obscurus (Abe). Aquat. Sci. 2008, 27, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Cheng, H.; Huang, C. Sensitivity Tests of Pathogenic Bacteria Found in Obscure puffer Fugu obscurus to Several Drugs. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 24, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, R.X.; Xie, M.F.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Z. Calreticulin functions in antimicrobial immunity of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 140, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, R.X.; Jiang, F.H.; Xu, X.T.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Z. A new calnexin modulates antibacterial immune response in obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 127, 104288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.H.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Cui, L.F.; Shi, Y.; Song, X.R.; Zhao, Z. length Identification and characterization of an L-type lectin from obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus in response to bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuda, R.; Kawai, K.; Salati, F.; Banner, C.; Fryer, J. Enterococcus seriolicida sp. nov., a fish pathogen. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1991, 41, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenech, A.; Prieta, J.; Fernandez-Garayzabal, J.; Collins, M.D.; Jones, D.; Dominguez, L. Phenotypic and phylogenetic evidence for a close relationship between Lactococcus garviae and Enterococcus seriolicida. Microbiologia 1993, 9, 63. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8397967/ (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Cabrales, H.J.; García-Posada, M.J.; Porto-Valiente, J.M.; Espinosa, A.; Narváez, Y. Bacteriemia por Lactococcus garvieae: Primer caso en Colombia. Infectio 2020, 24, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakawa, T.F.; da Costa, F.A.A.; Vilela, M.C.; Rigon, M.; Abensur, H.; de Araújo, M.R.E. Lactococcus garvieae Endocarditis: First Case Report in Latin America. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2011, 97, E108–E110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xie, X.M.; Pan, Z.H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.R.; Wu, F.; Dong, J.; Wang, T.C.; Li, L. Prevalence, Virulence, and Antibiotics Gene Profiles in Lactococcus garvieae Isolated from Cows with Clinical Mastitis in China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Sano, T.; Morimoto, Y. A Streptococcus pathogenic to fish. J. Tokyo Univ. Fish. 1958, 44, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ture, M.; Altinok, I. Detection of putative virulence genes of Lactococcus garvieae. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 119, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salogni, C.; Bertasio, C.; Accini, A.; Gibelli, L.R.; Pigoli, C.; Susini, F.; Podavini, E.; Scali, F.; Varisco, G.; Alborali, G.L. The Characterisation of Lactococcus garvieae Isolated in an Outbreak of Septicaemic Disease in Farmed Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, Linnaues 1758) in Italy. Pathogens 2024, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.; Klesius, P.; Shoemaker, C. First isolation and characterization of Lactococcus garvieae from Brazilian Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), and pintado, Pseudoplathystoma corruscans (Spix & Agassiz). J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.J.; Pasnik, D.J.; Klesius, P.H.; Al-Ablani, S. First report of Streptococcus agalactiae and Lactococcus garvieae from a wild bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-C.; Lin, Y.-D.; Liaw, L.-L.; Wang, P.-C. Lactococcus garvieae infection in the giant freshwater prawn Macrobranchium rosenbergii confirmed by polymerase chain reaction and 16S rDNA sequencing. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2001, 45, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyburgh, C.; Bragg, R.; Boucher, C. Lactococcus garvieae: An emerging bacterial pathogen of fish. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 123, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, X.-F.; Yang, S.-J.; Liu, W.-H.; Hu, X.-F. Design and application of specific 16S rDNA-targeted primers for assessing endophytic diversity in Dendrobium officinale using nested PCR-DGGE. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9825–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Pham, T.H.; Poudyal, S.; Cheng, L.W.; Nazareth, S.C.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. First report on genetic characterization, cell-surface properties and pathogenicity of Lactococcus garvieae, emerging pathogen isolated from cage-cultured cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohbayashi, K.; Oinaka, D.; Hoai, T.D.; Yoshida, T.; Nishiki, I. PCR-mediated Identification of the Newly Emerging Pathogen Lactococcus garvieae Serotype II from Seriola quinqueradiata and S. dumerili. Fish Pathol. 2017, 52, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hirono, I. Identification of genes in a KG- phenotype of Lactococcus garvieae, a fish pathogenic bacterium, whose proteins react with anti KG- rabbit serum. Microb Pathog 1999, 27, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A.C.; Ellis, A.E. Role of capsule in serotypic differences and complement fixation by Lactococcus garvieae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyburgh, C.M.; Bragg, R.R.; Boucher, C.E. Detection of virulence factors of South African Lactococcus garvieae isolated from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2018, 85, a1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, N.; Mallik, S.K.; Sahoo, M.; Chandra, S.; Singh, A.K. First report on characterization and pathogenicity study of emerging Lactococcus garvieae infection in farmed rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), from India. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, S.; Rao, S.; Yan, W.X.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. First identification, molecular characterization, and pathogenicity assessment of Lactococcus garvieae isolated from cultured pompano in Taiwan. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, R.C.; Rosa, J.C.C.; Resende, L.F.L.; de Pádua, S.B.; de Oliveira Barbosa, F.; Zerbini, M.T.; Tavares, G.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Emerging fish pathogens Lactococcus petauri and L. garvieae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) farmed in Brazil. Aquaculture 2023, 565, 739093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrell, D.; Balcázar, J.L.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; De Blas, I.; Gironés, O.; Múzquiz, J.L. Lactococcus garvieae in fish: A review. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 29, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldar, A.a.; Ghittino, C. Lactococcus garvieae and Streptococcus iniae infections in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: Similar, but different diseases. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 36, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Truong, T.; Tran, L.T.; Nguyen, D.H.; Pham, T.P.T.; Ng, C. Antibiotic resistance in the aquatic environments: The need for an interdisciplinary approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 3395–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Research progress on distribution, migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortina, M.; Ricci, G.; Foschino, R.; Picozzi, C.; Dolci, P.; Zeppa, G.; Cocolin, L.; Manachini, P. Phenotypic typing, technological properties and safety aspects of Lactococcus garvieae strains from dairy environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, M.S.; Ferretti, J.J. Microbiology. The thin line between gut commensal and pathogen. Science 2003, 299, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyauchi, E.; Toh, H.; Nakano, A.; Tanabe, S.; Morita, H. Comparative genomic analysis of Lactococcus garvieae strains isolated from different sources reveals candidate virulence genes. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 728276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutte, L.; Alonso, S.; Reveneau, N.; Willery, E.; Quatannens, B.; Locht, C.; Jacob-Dubuisson, F. Role of adhesin release for mucosal colonization by a bacterial pathogen. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, P.; Schembri, M.A. Bacterial adhesins: Function and structure. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 290, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariscotti, J.F.; Quereda, J.J.; Pucciarelli, M.G. Contribution of sortase A to the regulation of Listeria monocytogenes LPXTG surface proteins. Int. Microbiol 2012, 15, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí, J.; Gironella, M.; Sans, M.; Granell, S.; Gil, F.; Gimeno, M.; Coronel, P.; Pique, J.M.; Panes, J. Superoxide dismutase ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by reducing oxidative stress, adhesion molecule expression, and leukocyte recruitment into the inflamed intestine. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 76, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Baldisserotto, B.; Shekarabi, S.H.; Shafiei, S.; Bashiri, M. Lactococcosis a Re-Emerging Disease in Aquaculture: Disease Significant and Phytotherapy. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Characteristics of the diseases. In Bacterial Fish Pathogens; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 15–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.M.I.; Saccà, E.; Galeotti, M.; Sciuto, S.; Stoppani, N.; Acutis, P.L.; Öztnrk, R.C.; Bitchava, K.; Blanco, M.D.; Fariano, L.; et al. In field study on immune-genes expression during a lactococcosis outbreak in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2023, 574, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, R.; Lee, J.W.; Liu, C.H. First identification and histopathological analysis of Lactococcus garvieae infection in whiteleg shrimp, Penaeus vannamei cultured in low salinity water. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Yang, L.D.; Li, Y.P.; Yang, S.P.; Cai, S.H.; Jian, J.C.; Huang, Y.C. Efficacy of a formalin-inactivated vaccine against Lactococcus garvieae infection in golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Isr. J. Aquac.-Bamidgeh 2023, 75, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.M.I.; Bulfon, C.; Galeotti, M.; Acutis, P.L.; Altinok, I.; Kotzamanidis, C.; Vela, A.I.; Fariano, L.; Prearo, M.; Colussi, S.; et al. Immune profiling of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to Lactococcus garvieae: Evidence in asymptomatic versus symptomatic or vaccinated fish. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciuto, S.; Volpatti, D.; Esposito, G.; Pastorino, P.; Khalil, S.M.I.; Stoppani, N.; Esposito, G.; Prearo, M.; Gabetti, A.; Maganza, A.; et al. Near infrared spectroscopy as a novel non-invasive tool for the detection of lactococcosis in rainbow trout. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, K.; Mukkatira, K.; Yazdi, Z.; Richey, C.; Kwak, K.; Heckman, T.; Mohammed, H.H.; Ortega, C.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Keleher, B.; et al. Development of a quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of the aetiological agents of piscine lactococcosis. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, O.; Karabulut, H.A.; Er, A. Dandelion root extract in trout feed and its effects on the physiological performance of Oncorhynchus mykiss and resistance to Lactococcus garvieae infection. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabakci, D.; Ürkü, Ç.; Önalan, S. Determination of the antibacterial effect of bee venom against rainbow trout pathogens and antibiotic resistance gene expression. Acta Vet.-Beogr. 2023, 73, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.W.; Li, C.Y.; Chieng, Z.X.; Cheng, W.T. Dietary administration of mangosteen, Garcinia mangostana, peel extract enhances the growth, and physiological and immunoendocrinological regulation of prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 140, 108982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekebayeva, Z.; Zakarya, K.; Abzhalelov, A.B.; Beisenova, R.R.; Tazitdinova, R.M. Efficiency of a probiotic in carp lactococcosis in an in vitro experiment. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 161, 105289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).