Effects of Feeding Frequency on Liver Transcriptome: Unveiling Appetite-Regulating Peptides in Mexican Pike Silverside (Chirostoma estor)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Samples
2.2. RNA-seq and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Differential Expression Analysis
2.4. Appetite-Regulating Peptide Expression
3. Results
3.1. Differential Expression
3.2. Appetite Regulating Peptide Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross, L.G.; Martínez-Palacios, C.A.; Aguilar Valdez, M.d.C.; Beveridge, C.M.; Chávez Sánchez, M.C. Determination of feeding mode in fish: The importance of using structural and functional feeding studies in conjunction with gut analysis in a selective zooplanktivore Chirostoma estor Jordan 1880. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 68, 1782–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, N.; Moreira-Konig, I.F.; Ríos-Durán, M.G.; Navarrete-Ramírez, P.; Martínez-Palacios, C.A.; Solis-Murgas, L.D.; Martínez-Chavez, C.C. Feeding frequency has a determinant role in growth performance, skeletal deformities, and body composition in the Mexican pike silverside (Chirostoma estor), an agastric short-intestine fish (Teleostei: Atheriniformes). Aquaculture 2022, 562, 738766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, I.; Yúfera, M.; Ueberschär, B.; Ribeiro, L.; Sæle, Ø.; Boglione, C. Feeding behaviour and digestive physiology in larval fish: Current knowledge, and gaps and bottlenecks in research. Rev. Aquacult. 2013, 5, S59–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H.; Canosa, L.F.; Unniappan, S.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Bernier, N.J.; Kelly, S.P.; Peter, R.E. Neuropeptides and the control of food intake in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rønnestad, I.; Gomes, A.S.; Murashita, K.; Angotzi, R.; Jönsson, E.; Volkoff, H. Appetite-Controlling endocrine systems in teleosts. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H. The neuroendocrine regulation of food intake in fish: A review of current knowledge. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, L.J.; Volkoff, H. The comparative endocrinology of feeding in fish: Insights and challenges. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 176, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H. The effects of environmental changes on the endocrine regulation of feeding in fishes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2024, 379, 20220503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jacinto, V.; Sanchez-Flores, A.; Vega-Alvarado, L. Integrative differential expression analysis for multiple experiments (IDEAMEX): A web server tool for integrated RNA-Seq data analysis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H.; Peter, R.E. Feeding behavior of fish and its control. Zebrafish 2006, 3, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkoff, H.; Hoskins, L.J.; Tuziak, S.M. Influence of intrinsic signals and environmental cues on the endocrine control of feeding in fish: Potential application in aquaculture. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 167, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, M.J.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Soengas, J.L. Hypothalamic integration of metabolic, endocrine, and circadian signals in fish: Involvement in the control of food intake. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, J.I.; Blanco, A.M.; Sundarrajan, L.; Rajeswari, J.J.; Velasco, C.; Unniappan, S. Nutrient regulation of endocrine factors influencing feeding and growth in fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.F.A.; Hassan, H.U.; Yones, A.M.; Abdel-Tawwab, Y.A.; Metwalli, A.T. Assessing the effect of different feeding frequencies combined with stocking density, initial weight, and dietary protein ratio on the growth performance of tilapia, catfish, and carp. Sci. Afr. 2021, 12, e00806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, J.F.; López-Olmeda, J.F.; Martínez, F.J.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. Daily rhythms of lipid metabolic gene expression in zebrafish liver: Response to light/dark and feeding cycles. Chronobiol. Int. 2015, 32, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isorna, E.; de Pedro, N.; Valenciano, A.I.; Alonso-Gómez, Á.L.; Delgado, M.J. Interplay between the endocrine and circadian systems in fishes. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, R141–R159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, Y.; Uni, Z.; Hulata, G.; Harpaz, S. Relationship between intestinal brush border enzymatic activity and growth rate in tilapias fed diets containing 30% or 48% protein. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Casanova, J.C.; Murray, H.M.; Gallant, J.W.; Ross, N.W.; Douglas, S.; Johnson, S.C. Development of the digestive capacity in larvae of haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquaculture 2006, 251, 377–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Ai, Q.; Mai, K.; Xu, W.; Ma, H. The optimal feeding frequency of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea, Richardson) larvae. Aquaculture 2011, 311, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, C.N.; Qian, Y.; Liu, W.B. Optimum feeding frequency of juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala. Aquaculture 2015, 437, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.A.; Villarroel, M. Effect of feed type and feeding frequency on macrophage functions in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2009, 27, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Tian, H.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Jiang, G.Z.; Liu, W.B. Feeding frequency affects stress, innate immunity and disease resistance of juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 38, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, F.; Zhou, J.; Ye, J. Effect of feeding frequency on growth, body composition, antioxidant status and mRNA expression of immunodependent genes before or after ammonia-N stress in juvenile oriental river prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 68, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edholm, E.S.; Pasquier, L.D. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) in fish. In Principles of Fish Immunology: From Cells and Molecules to Host Protection; Buchmann, K., Secombes, C.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 355–386. [Google Scholar]
- Augustine, V.; Lee, S.; Oka, Y. Neural control and modulation of thirst, sodium appetite, and hunger. Cell 2020, 180, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assan, D.; Huang, Y.; Mustapha, U.F.; Addah, M.N.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Fish feed intake, feeding behavior, and the physiological response of apelin to fasting and refeeding. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 798903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Larhammar, D. Neuropeptide Y family of peptides: Structure, anatomical expression, function, and molecular evolution. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2000, 78, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Patiño, M.A.; Guijarro, A.I.; Isorna, E.; Delgado, M.J.; Alonso-Bedate, M.; de Pedro, N. Neuropeptide Y has a stimulatory action on feeding behavior in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 377, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, X.F.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, L.; Li, B.; Shen, D. Neuropeptide Y stimulates food intake and regulates metabolism in grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Aquaculture 2013, 380–383, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assan, D.; Mustapha, U.F.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, G. The roles of neuropeptide Y (Npy) and peptide YY (Pyy) in teleost food intake: A mini review. Life 2021, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, R.E.; Chee, M.J.S.; Colmers, W.F. The role of NPY in hypothalamic mediated food intake. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 32, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, E.T.; Fredriksson, R.; Johansson, S.R.T.; Larhammar, D. Cloning, pharmacology, and distribution of the neuropeptide Y-receptor Yb in rainbow trout. Peptides 2003, 24, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaneck, E.; Fredriksson, R.; Larson, E.T.; Conlon, J.M.; Larhammar, D. A neuropeptide Y receptor Y1-subfamily gene from an agnathan, the European river lamprey. A potential ancestral gene. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 6146–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkoff, H.; Wyatt, J. Apelin in goldfish (Carassius auratus): Cloning, distribution and role in appetite regulation. Peptides 2009, 30, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.; Volkoff, H. Characterization of the endocrine, digestive and morphological adjustments of the intestine in response to food deprivation and torpor in cunner, Tautogolabrus adspersus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2014, 170, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H. Cloning and tissue distribution of appetite-regulating peptides in pirapitinga (Piaractus brachypomus). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Qin, C.; Deng, D.; Yang, G.; Feng, J.; Lu, R.; Yang, L.; Meng, X.; Cao, X.; Nie, G.; et al. Apelin and apj in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.): Molecular characterization, tissue expression and responses to periprandial changes and fasting–refeeding. Aquac. Res. 2019, 51, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agulleiro, M.J.; Cortés, R.; Leal, E.; Ríos, D.; Sánchez, E.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M. Characterization, tissue distribution and regulation by fasting of the agouti family of peptides in the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 205, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, T.; Murashita, K.; Uji, S. Characterization and tissue distribution of multiple agouti-family genes in pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes. Peptides 2006, 27, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashita, K.; Kurokawa, T.; Ebbesson, L.O.E.; Stefansson, S.O.; Rønnestad, I. Characterization, tissue distribution, and regulation of agouti-related protein (AgRP), cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 162, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.B.; Yuan, D.Y.; Wang, T.; Zhou, C.W.; Lin, F.J.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Characterization, tissue distribution and regulation of agouti-related protein (AgRP) in a cyprinid fish (Schizothorax prenanti). Gene 2013, 527, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Su, Y.; Pan, F.; Ge, X. Molecular cloning of AGRP and NPY and their expression analysis during fasting and refeeding in juvenile blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, G.; Wei, K.; Xiong, B.; Liang, T.; Ping, H. Molecular characterization of cholecystokinin in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus): Cloning, localization, developmental profile, and effect of fasting and refeeding on expression in the brain and intestine. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Wang, T.; Zhou, C.; Lin, F.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.; Wei, R.; Xin, Z.; Li, Z. Leptin and cholecystokinin in Schizothorax prenanti: Molecular cloning, tissue expression, and mRNA expression responses to periprandial changes and fasting. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 204, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Björnsson, B.T. Leptin signaling in the rainbow trout central nervous system is modulated by a truncated leptin receptor isoform. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zahir, I.; Ogawa, S.; Dominic, N.A.; Soga, T.; Parhar, I.S. Spexin and galanin in metabolic functions and social behaviors with a focus on non-mammalian vertebrates. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 882772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkoff, H. Control of appetite. In The Encyclopedia of Fish Physiology: From Genome to Environment; Farrell, A.P., Cech, J.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Chapter 273. [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum, L.; Wang, G.; Yokogawa, T.; Skariah, G.M.; Smith, S.J.; Mourrain, P.; Mignot, E. Circadian and homeostatic regulation of structural synaptic plasticity in hypocretin neurons. Neuron 2010, 68, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H.; Peter, R.E. Characterization of two forms of cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptide precursors in goldfish: Molecular cloning and distribution, modulation of expression by nutritional status, and interactions with leptin. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 5076–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, A.S.; Volkoff, H. The effects of temperature on feeding and expression of two appetite-related factors, neuropeptide Y and cocaine-and amphetamine-tegulated transcript, in Atlantic cod, Gadus Morhua. J. World. Aquac. Soc. 2008, 39, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Peterson, B.C.; Waldbieser, G.C. Association of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) messenger RNA level, food intake, and growth in channel catfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 151, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, E.; Volkoff, H. Neuropeptide Y (NPY), cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) and cholecystokinin (CCK) in winter skate (Raja ocellata): cDNA cloning, tissue distribution and mRNA expression responses to fasting. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
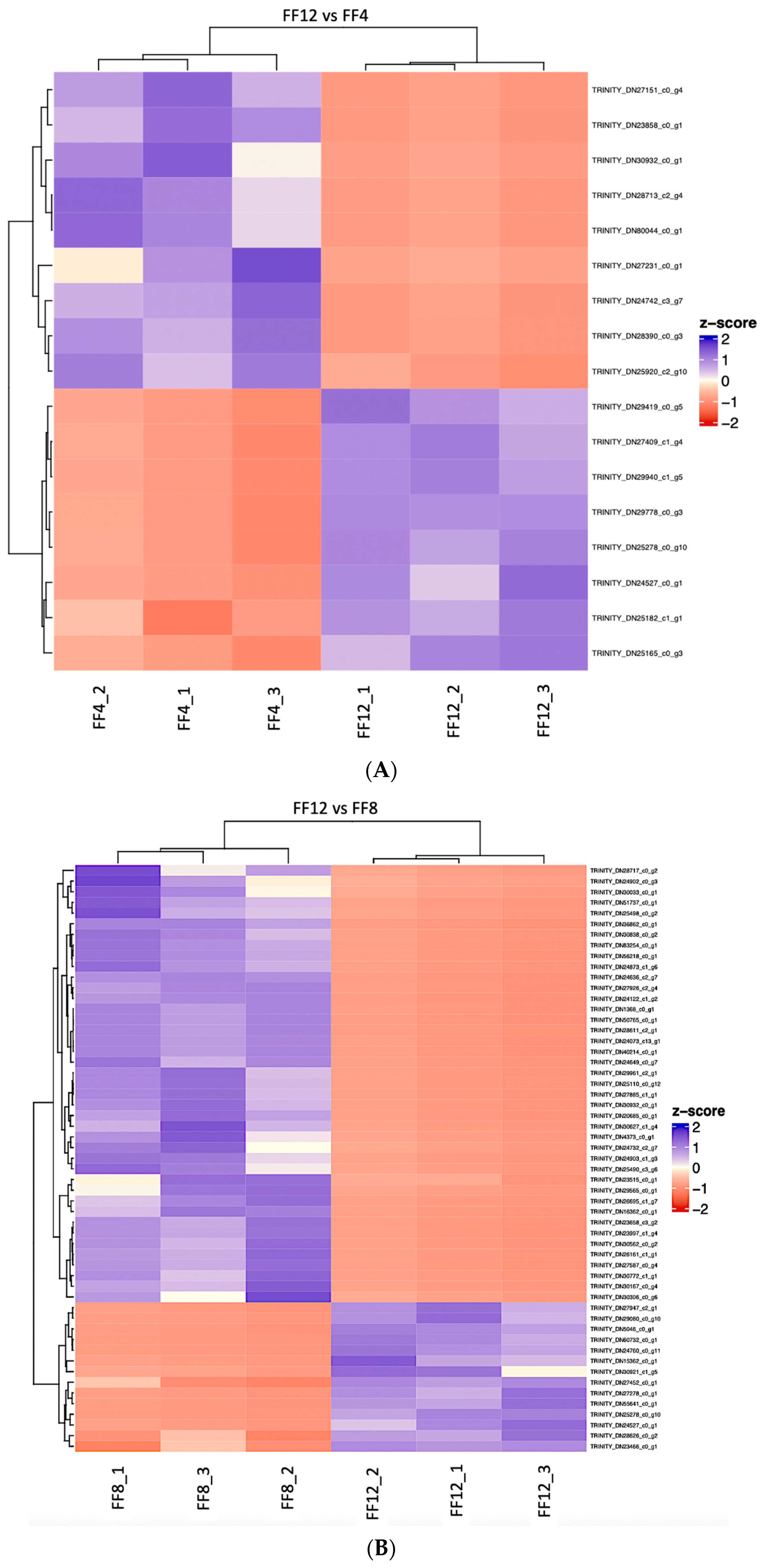
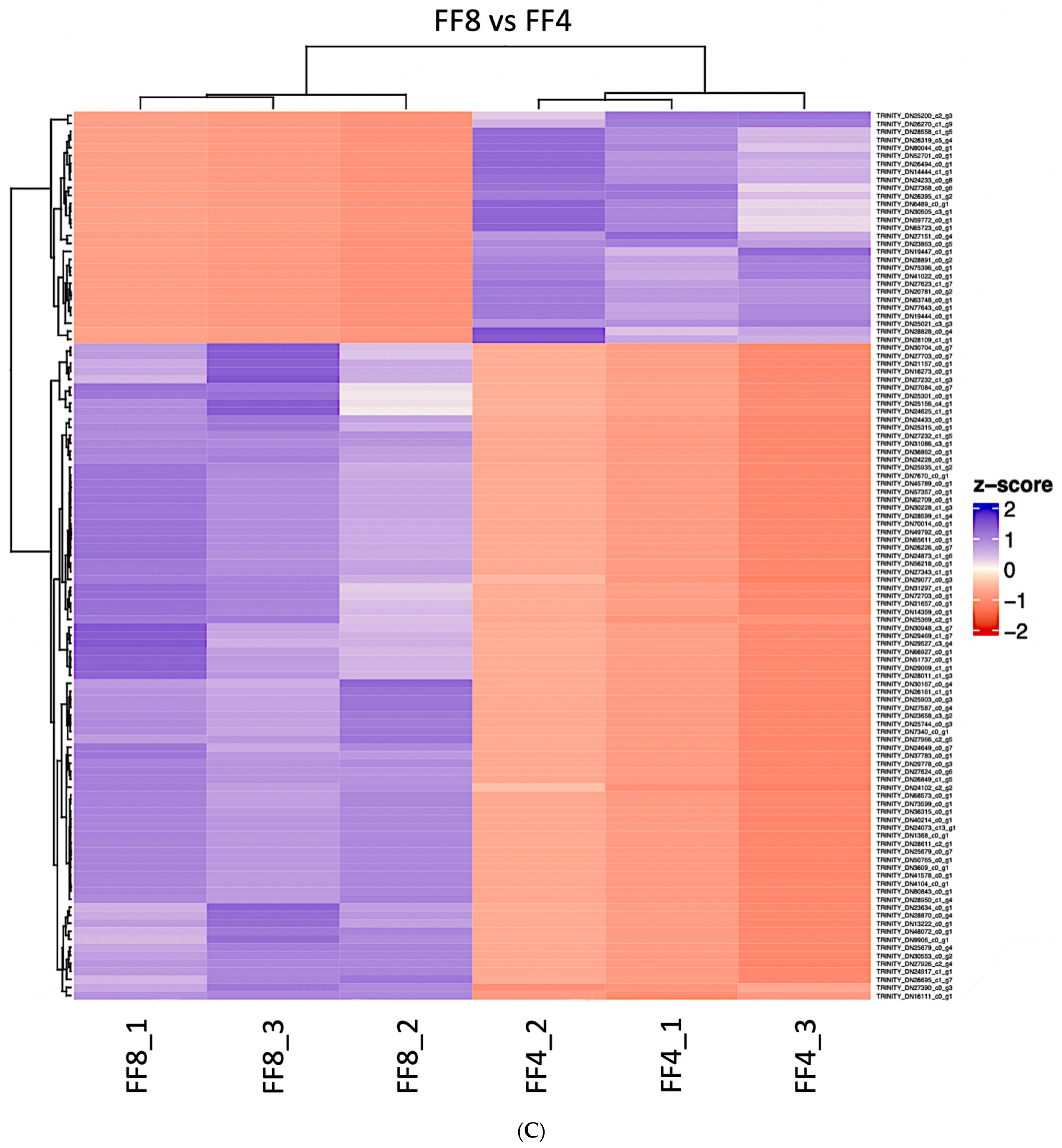
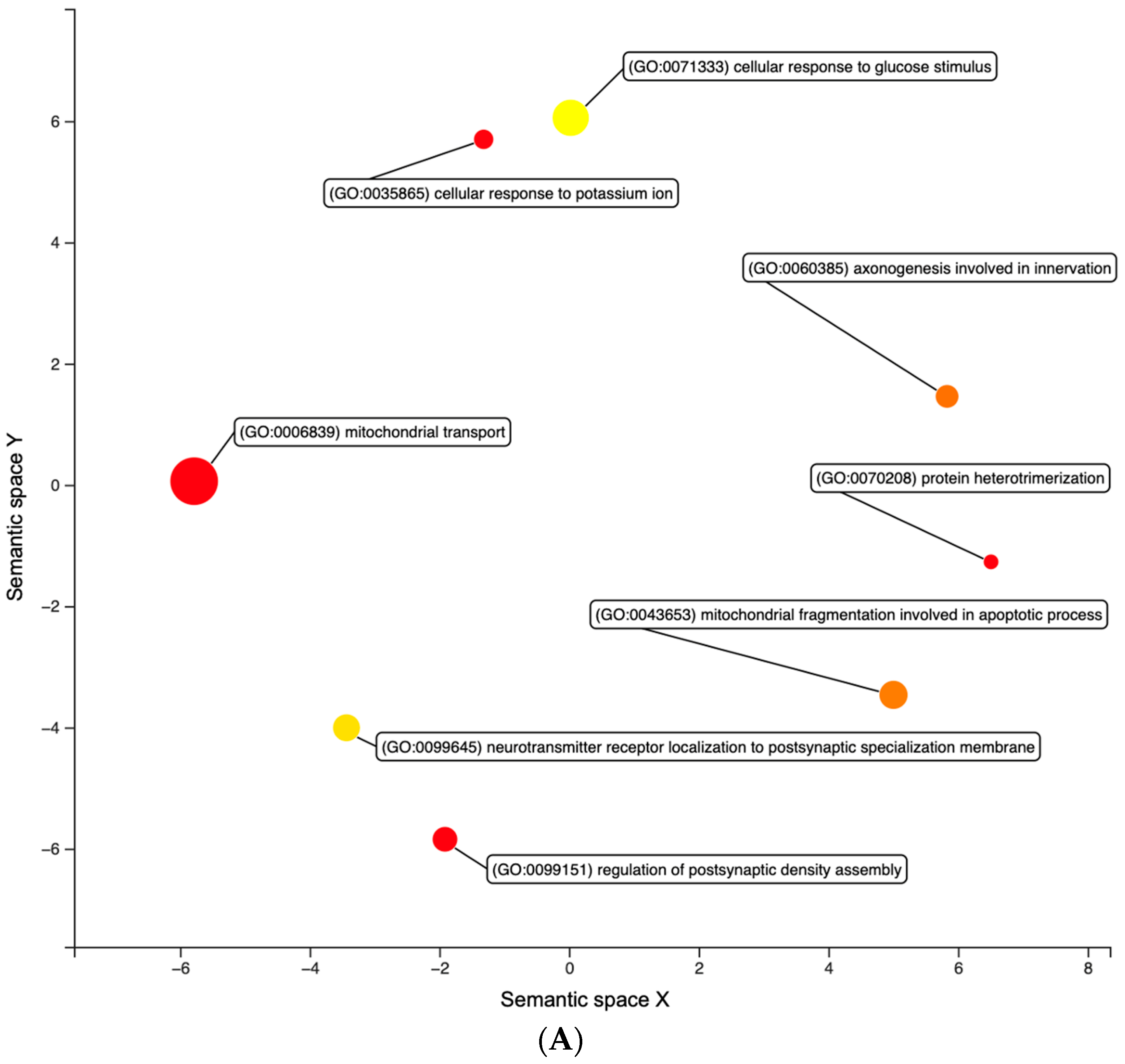
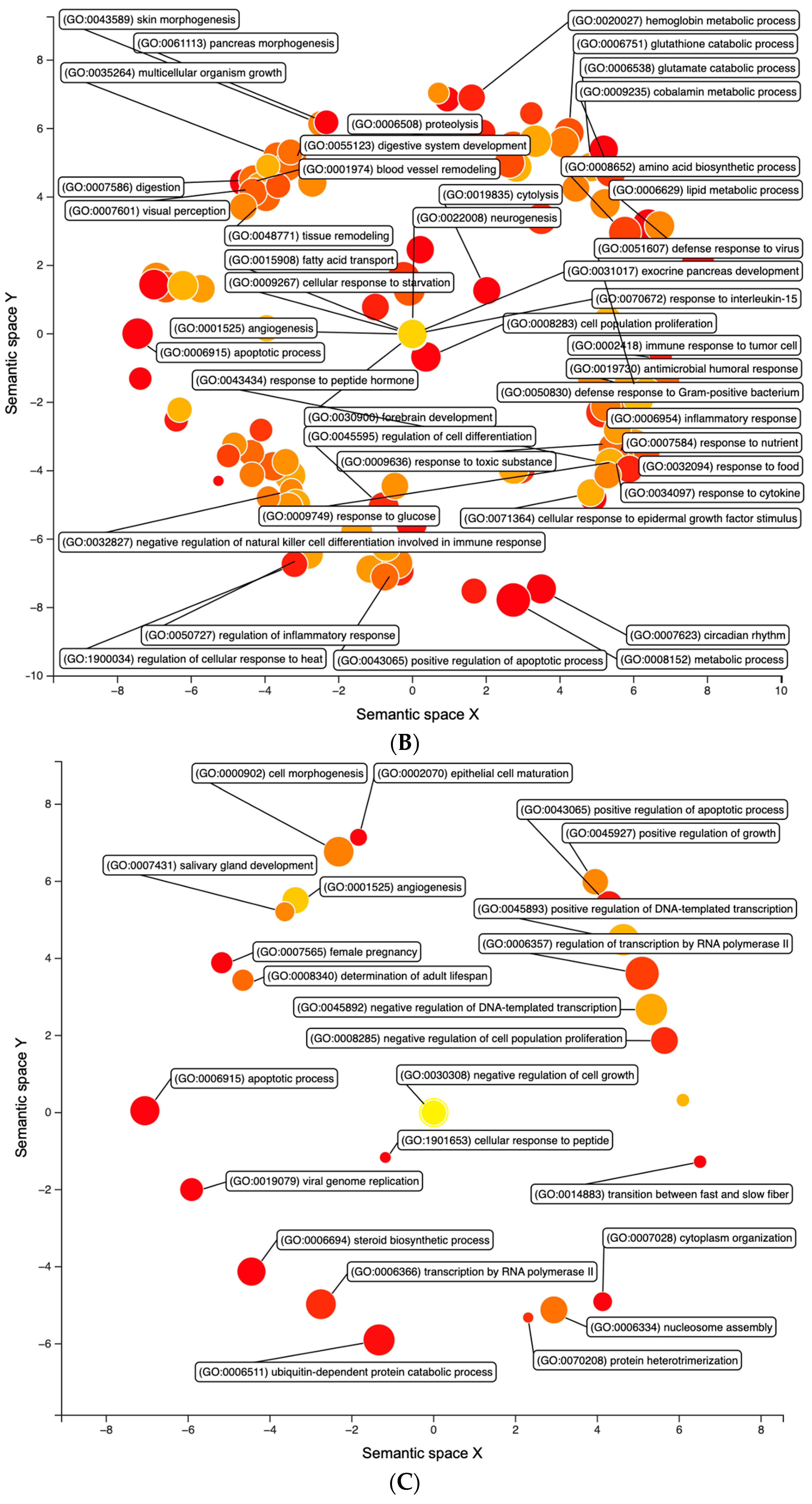
| FF12 vs. FF4 | FF8 vs. FF4 | FF12 vs. FF8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| UP-REGULATED GENES | Complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 6 | Complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 6 | Mitochondrial glycine transporter A |
| Neuronal pentraxin-1 | General transcription factor II-I repeat domain-containing protein 2 | Mitochondrial glycine transporter B | |
| U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein B | Putative histone H2B type 2-C | Glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 | |
| ELL-associated factor 2 * | Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 3B * | ||
| COP9 signalosome complex subunit 3 | Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 * | ||
| Krueppel-like factor 11 | C2 domain-containing protein At1g53590 | ||
| Upstream-binding protein 1 | Perforin-1 | ||
| Transcription factor CP2-like protein 1 * | Chaperone protein HscA | ||
| Whey acidic protein | Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 1 | ||
| WAP four-disulfide core domain protein 2 | Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 2A | ||
| Histone H2B | Chymotrypsin-C | ||
| UPF0415 protein C7orf25 | Chymotrypsinogen B | ||
| Interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglycan 1 | High choriolytic enzyme 2 | ||
| Low choriolytic enzyme Zinc metalloproteinase nas-2 | |||
| Zinc metalloproteinase nas-3 | |||
| [Pyruvate dehydrogenase [acetyl-transferring]]-phosphatase 1 | |||
| Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC1 | |||
| DnaJ homolog subfamily B member 1 | |||
| Probable DNA repair protein RAD50 | |||
| Solute carrier family 41 member 2 | |||
| N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase | |||
| ERBB receptor feedback inhibitor 1 | |||
| Inositol oxigenase | |||
| Biglycan | |||
| Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase with EF-hands 2 | |||
| Glutamine synthetase | |||
| DOWN- REGULATED GENES | Galactose-specific lectin nattectin | Interferon alpha-inducible protein 27 | Ras-related protein Rab-11A |
| Ladderlectin | Class I histocompatibility antigen, F10 alpha chain | Caskin-1 | |
| Chymotrypsin | Major histocompatibility complex class I-related gene protein | Polysialic acid O-acetyltransferase | |
| Kallikrein-13 | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, B-57 alpha chain | Apolipoprotein A-I | |
| Cationic trypsin-3 | H-2 class I histocompatibility antigen, K-K alpha chain | General transcription factor II-I repeat domain-containing protein 2 | |
| Blarinasin-2 | Transmembrane prolyl 4-hydroxylase | Probable polyketide synthase 3 | |
| Ras-related protein Rab-11A | DmX-like protein 1 | Ribosome-binding protein 1 | |
| Phosphatidylinositol phosphatase PTPRQ | Protein SON | ||
| Zinc finger protein SNAI2 | Complement C3 | ||
| Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3C-B | Fibrinogen beta chain | ||
| Mucin-1 | Fibrinogen C domain-containing protein 1-A | ||
| Allograft Inflammatory Factor 1 | Tenascin-N | ||
| Synaptogyrin-3 | Neoverrucotoxin subunit beta | ||
| Gap junction alpha-1 protein * | Stonustoxin subunit alpha | ||
| L-rhamnose-binding lectin SML | |||
| Malignant fibrous histiocytoma-amplified sequence 1 homolog | |||
| G1/S-specific cyclin-D2 |
| Peptide | Transcript Name | Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Apelin | Apelin receptor B Apelin receptor A Apelin | ⇑ FF12–⇓ FF4 ⇓ FF12–⇑ FF4 ⇑ FF12–⇓ FF4 |
| Ghrelin | N/A | - |
| Orexin | N/A | - |
| Galanin | Galanin receptor type 1 Galanin peptides | ⇓ FF12–⇑ FF4 ⇓ FF12–⇑ FF4 |
| Secretoneurin | N/A | - |
| Melanin-concentrating hormone | N/A | - |
| Agouti-related protein | Agouti-related protein | ⇑ FF12–⇓ FF4 |
| Neuropeptide Y | Pro-neuropeptide Y Neuropeptide Y receptor type 1 | ⇓ FF12–⇑ FF4 ⇑ FF12–⇓ FF4 |
| Peptide | Transcript Name | Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Leptin | Leptin receptor | N/E |
| Nesfatin-1/Nucleobindin-2 | Nucleobindin-1 Nucleobindin-2 | N/E N/E |
| Spexin | Spexin | N/E |
| Amylin | N/A | - |
| Cholecystokinin | Cholecystokinin Cholecystokinin receptor type A | ⇓ FA12–⇑ FA4 ⇑ FA12–⇓ FA4 |
| Gonadotropin-releasing hormone | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone II receptor | N/E |
| Melanocyte-stimulating hormone | N/A | - |
| Neuromedin | Neuromedin-B Neurotensin/neuromedin N Neuromedin-U Neuromedin-K receptor | ⇓ FA12–⇑ FA4 N/E N/E N/E |
| Octadecaneuropeptide | N/A | - |
| Arginine-vasotocin | [Arg8]-vasotocin receptor | N/E |
| Corticotropin-releasing factor | Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 2 Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 | N/E N/E |
| Urocortin | Urocortin-3 | N/E |
| Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript | Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript protein | N/E |
| Pro-opiomelanocortin | N/A | - |
| Gastrin-releasing peptide/Bombesin | Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor Gastrin-releasing peptide | N/E N/E |
| Glucagon-like peptide | Glucagon-like peptide 2 receptor Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor | ⇓ FA12–⇑ FA4 ⇑ FA12–⇓ FA4 |
| Tachykinins | Protachykinin | ⇓ FA12–⇑ FA4 |
| Urotensins | N/A | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juárez-Gutiérrez, M.E.; Martínez-Chávez, C.C.; Godoy-Figueroa, C.Y.; Jiménez-Jacinto, V.; Ríos-Durán, M.G.; Martínez-Palacios, C.A.; Navarrete-Ramírez, P. Effects of Feeding Frequency on Liver Transcriptome: Unveiling Appetite-Regulating Peptides in Mexican Pike Silverside (Chirostoma estor). Fishes 2024, 9, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100393
Juárez-Gutiérrez ME, Martínez-Chávez CC, Godoy-Figueroa CY, Jiménez-Jacinto V, Ríos-Durán MG, Martínez-Palacios CA, Navarrete-Ramírez P. Effects of Feeding Frequency on Liver Transcriptome: Unveiling Appetite-Regulating Peptides in Mexican Pike Silverside (Chirostoma estor). Fishes. 2024; 9(10):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100393
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuárez-Gutiérrez, Mitzi Ernestina, Carlos Cristian Martínez-Chávez, Claudia Yaneth Godoy-Figueroa, Verónica Jiménez-Jacinto, María Gisela Ríos-Durán, Carlos Antonio Martínez-Palacios, and Pamela Navarrete-Ramírez. 2024. "Effects of Feeding Frequency on Liver Transcriptome: Unveiling Appetite-Regulating Peptides in Mexican Pike Silverside (Chirostoma estor)" Fishes 9, no. 10: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100393
APA StyleJuárez-Gutiérrez, M. E., Martínez-Chávez, C. C., Godoy-Figueroa, C. Y., Jiménez-Jacinto, V., Ríos-Durán, M. G., Martínez-Palacios, C. A., & Navarrete-Ramírez, P. (2024). Effects of Feeding Frequency on Liver Transcriptome: Unveiling Appetite-Regulating Peptides in Mexican Pike Silverside (Chirostoma estor). Fishes, 9(10), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100393







