The Effect of Turbidity on the Behavior of Bleak (Alburnus alburnus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Video Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krause, J.; Croft, D.P.; James, R. Social network theory in the behavioural sciences: Potential applications. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2007, 62, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, J.; Ruxton, G.D. Living in Groups; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.; Laland, K.; Krause, J. Fish Cognition and Behaviour; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, J.R.; Davis, N.B. Behavioural Ecology. An Evolutionary Approach; Blackwell Scientific Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Morrel, L.J.; James, R. Mechanisms for aggregation in animals: Rule success depends on ecological variables. Behav. Ecol. 2008, 19, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, W.A.; Treherne, J.E. Evidence for the dilution effect in the selfish herd from fish predation on a marine insect. Nature 1981, 293, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenward, R.E. Hawks and doves: Factors affecting success and selection in goshawk attacks on wood-pigeons. J. Anim. Ecol. 1978, 47, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, T.J.; Parrish, J.K. Functions of shoaling behaviour in teleosts. In Behaviour of Teleost Fishes; Pitcher, T.J., Ed.; Chapmann & Hall: London, UK, 1993; pp. 363–439. [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher, T.J.; Magurran, A.E.; Allan, J.R. Shifts of behaviour with shoal size in Cyprinids. In Proceedings of the 3rd British Freshwater Fish Conference, Liverpool, UK, 28–30 April 1983; pp. 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Magurran, A.E. The adaptive significance of schooling as an antipredator defence in fish. Ann. Zool. Fen. 1990, 27, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Weihs, D. Hydromechanics of fish schooling. Nature 1973, 241, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, P.; Sear, D.; Collins, A.; Naden, P.; Jones, I. The impacts of fine sediment on riverine fish. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1800–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuliskova, P.; Horky, P.; Slavik, O.; Jones, J.I. Factors influencing movement behaviour and home range size in ide Leuciscus idus. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ficke, A.D.; Myrick, C.A.; Hansen, L.J. Potential impacts of global climate change on freshwater fisheries. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2007, 17, 581–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantyka-Pringle, C.S.; Martin, T.G.; Moffatt, D.B.; Linke, S.; Rhodes, J.R. Understanding and predicting the combined effects of climate change and land-use change on freshwater macroinvertebrates and fish. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime: A paradigm for river conservation and restoration. BioScience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammens, E.H.R.R.; Frank-Landman, A.; McGillavry, P.J.; Vlink, B. The role of predation and competition in determining the distribution of common bream, roach and white bream in Dutch eutrophic lakes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1992, 33, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, H.; Orellana, C.P. Functional responses of five cyprinid species to planktonic prey. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1992, 33, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Colley, R.J.; Smith, D.G. Turbidity, suspended sediment, and water clarity: A review. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1085–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horka, P.; Horky, P.; Randak, T.; Turek, J.; Rylkova, K.; Slavik, O. Radio-telemetry shows differences in the behaviour of wild and hatchery-reared European grayling Thymallus thymallus in response to environmental variables. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 86, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, A.; O’Riain, M.J. Movement in a selfish seal herd: Do seals follow simple or complex movement rules? Behav. Ecol. 2012, 24, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberlehner, E. Comparative analysis of feeding and schooling behaviour of the cyprinidae Alburnus alburnus (L.; 1758), Rutilus rutilus (L.; 1758), and Scardinius erythrophthalmus (L.; 1758) in a Backwater of the Danube near Vienna. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. 1988, 73, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Publications Kottelat, Cornol and Freyhof: Berlin, Germany, 2007; 646p. [Google Scholar]
- Chappaz, R.; Doucende, D.; Barthelemy, R. Patterns of change in zooplankton community structures and the selective feeding of Bleak, Alburnus alburnus (L.) in the Serre Poncon dam between 1980 and 1996. Hydrobiologia 1998, 391, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavik, O.; Bartos, L. Spatial distribution and temporal variance of fish communities in the channelized and regulated Vltava River (Central Europe). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2001, 61, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasek, M.; Kubecka, J.; Peterka, J.; Cech, M.; Drastík, V.; Hladík, M.; Prchalova, M.; Frouzova, J. Longitudinal and vertical spatial gradients in the distribution of fish within a canyon-shaped reservoir. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2004, 89, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinni, M.; Horppila, J.; Olin, M.; Ruunijarvi, J.; Nyberg, K. The food, growth and abundance of five co-existing cyprinids in lake basins of different morphometry and water quality. Aquat. Ecol. 2000, 34, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politou, C.Y.; Economidis, P.S.; Sinis, A.I. Feeding biology of bleak, Alburnus alburnus, in Lake Koronia, northern Greece. J. Fish Biol. 1995, 43, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasek, M.; Kubecka, J. In situ diel patterns of zooplankton consumption by subadult/adult roach Rutilus rutilus, bream Abramis brama, and bleak Alburnus alburnus. Folia Zool. 2004, 53, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Krpo-Cetkovic, J.; Hegediš, A.; Lenhardt, M. Diet and growth of asp, Aspius aspius (Linnaeus, 1758), in the Danube River near the confluence with the Sava River (Serbia). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2010, 26, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breder, J.M., Jr. Studies on social groupings in fishes. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1959, 117, 397–481. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J.; Godin, J.-G.J. Predator preferences for attacking particular prey group sizes: Consequences for predator hunting success and prey predation risk. Anim. Behav. 1995, 50, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramoff, M.D.; Magalhaes, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image Processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Lopez, U.; Gautrais, J.; Couzin, I.D.; Theraulaz, G. From behavioural analyses to models of collective motion in fish schools. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utne-Palm, A.C. Visual feeding of fish in a turbid environment: Physical and behavioural aspects. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2002, 35, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, C.L.; Gray, S.M. Visual performance impaired by elevated sedimentary and algal turbidity in walleye Sander vitreus and emerald shiner Notropis atherinoides. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 95, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, M.V.; Kattenfeld, M.G. The role of turbidity as a constraint on predator-prey interactions in aquatic environments. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1997, 40, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, I.M.; Poulin, R. Parasitism and group size in social animals: A meta-analysis. Behav. Ecol. 1995, 6, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranåker, L.; Jönsson, M.; Nilsson, P.A.; Brönmark, C. Effects of brown and turbid water on piscivore–prey fish interactions along a visibility gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E. Schooling fishes: The school, a truly egalitarian form of organization in which all members of the group are alike in influence, offers substantial benefits to its participants. Am. Sci. 1978, 66, 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Overholtzer, K.L.; Motta, P.J. Effects of mixed-species foraging groups on the feeding and aggression of juvenile parrotfishes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2000, 58, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, G.V.N. Experimental analysis of the social value of flocking by starlings (Sturnus vulgaris) in relation to predation and foraging. Anim. Behav. 1974, 22, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treherne, J.E.; Foster, W.A. Group transmission of predator avoidance behaviour in a marine insect: The Trafalgar effect. Anim. Behav. 1981, 29, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, H.; Rita, H.; Ruuhijaervi, J. Diet and prey selection of pikeperch (Stizostedion lucioperca) (L.) in Lake Vesijaervi analyzed with a logit model. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1996, 33, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Antognazza, C.M.; Costantini, T.; Campagnolo, M.; Zaccara, S. One year monitoring of ecological interaction of Silurus glanis in a novel invaded oligotrophic deep lake (Lake Maggiore). Water 2022, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, L.; Berg, S.; Baktoft, H.; Nilsson, P.A.; Skov, C. The effect of turbidity and prey fish density on consumption rates of piscivorous Eurasian perch Perca fluviatilis. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E. Evolutionary Ecology: The Trinidadian Guppy. Oxford Series in Ecology and Evolution; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; 224p. [Google Scholar]
- Botham, M.S.; Hayward, R.K.; Morrell, L.J.; Croft, D.P.; Ward, J.R.; Ramnarine, I.; Krause, J. Risk-sensitive antipredator behavior in the Trinidadian Guppy, Poecilia reticulata. Ecology 2008, 89, 3174–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, N.W.F.; Faria, J.J.; Franks, D.W.; Krause, J.; Wood, A.J. How perceived threat increases synchronization in collectively moving animal groups. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcombe, C.P.; Jensen, J.O.T. Channel suspended sediment and fisheries: A synthesis for quantitative assessment of risk and impact. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1996, 16, 693–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.M.; Bieber, F.M.E.; McDonnell, L.H.; Chapman, L.J.; Mandrak, N.E. Experimental evidence for species-specific response to turbidity in imperiled fishes. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. 2014, 24, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horka, P. Factors Influencing Movement and Behaviour of Animals in the Riverine Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, S.C.J.; Patman, J.; Lutnesky, M.M.F. Water clarity affects collective behavior in two cyprinid fishes. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2021, 75, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, B.; Jonsson, N.; Hansen, L.P. Does juvenile experience affect migration and spawning of adult Atlantic salmon? Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1990, 26, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, B.G.W.; Nienhuis, P.H. Fish zonation and guilds as the basis for assessment of ecological integrity of large rivers. Hydrobiologia 2003, 500, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.C.; Pringle, C.M.; Greathouse, E.A.; Freeman, B.J. Ecosystem-level consequences of migratory faunal depletion caused by dams. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 2003, 35, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Musil, J.; Horký, P.; Slavík, O.; Zbořil, A.; Horká, P. The response of the young of the year fish to river obstacles: Functional and numerical linkages between dams, weirs, fish habitat guilds and biotic integrity across large spatial scale. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Han, X. Three-Gorges Dam: Risk to ancient fish. Science 2003, 302, 1149–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D. River rehabilitation for conservation of fish biodiversity in monsoonal Asia. Ecol. Soc. 2005, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erős, T.; Kuehne, L.; Dolezsai, A.; Sommerwerk, N.; Wolter, C. A systematic review of assessment and conservation management in large floodplain rivers—Actions postponed. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horka, P.; Musilova, Z.; Holubova, K.; Jandova, K.; Kukla, J.; Rutkayova, J.; Jones, J.I. Anthropogenic nutrient loading affects both individual species and the trophic structure of river fish communities. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 10, 1076451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, I.F.; Strat, D.; Mihailescu, S. Role of riparian zones in reducing pollution of surface and groundwater, increase agricultural production and nutrient acquisition and storage in river catchments. In Tools for Landscape-Scale Geobotany and Conservation (Geobotany Studies); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable Name | Variable Type | Variable Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Inter-individual distance (n = 11,600) | Numeric | Dependent |
| Turbidity (n = 3) | Numeric category | Independent |
| Group ID (n = 8) | Category | Random |
| Temperature | Numeric | Random |
| Fish length (n = 40) | Numeric | Random |
| Number of fish per group (n = 5) |
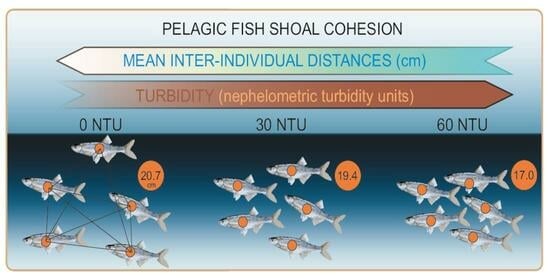
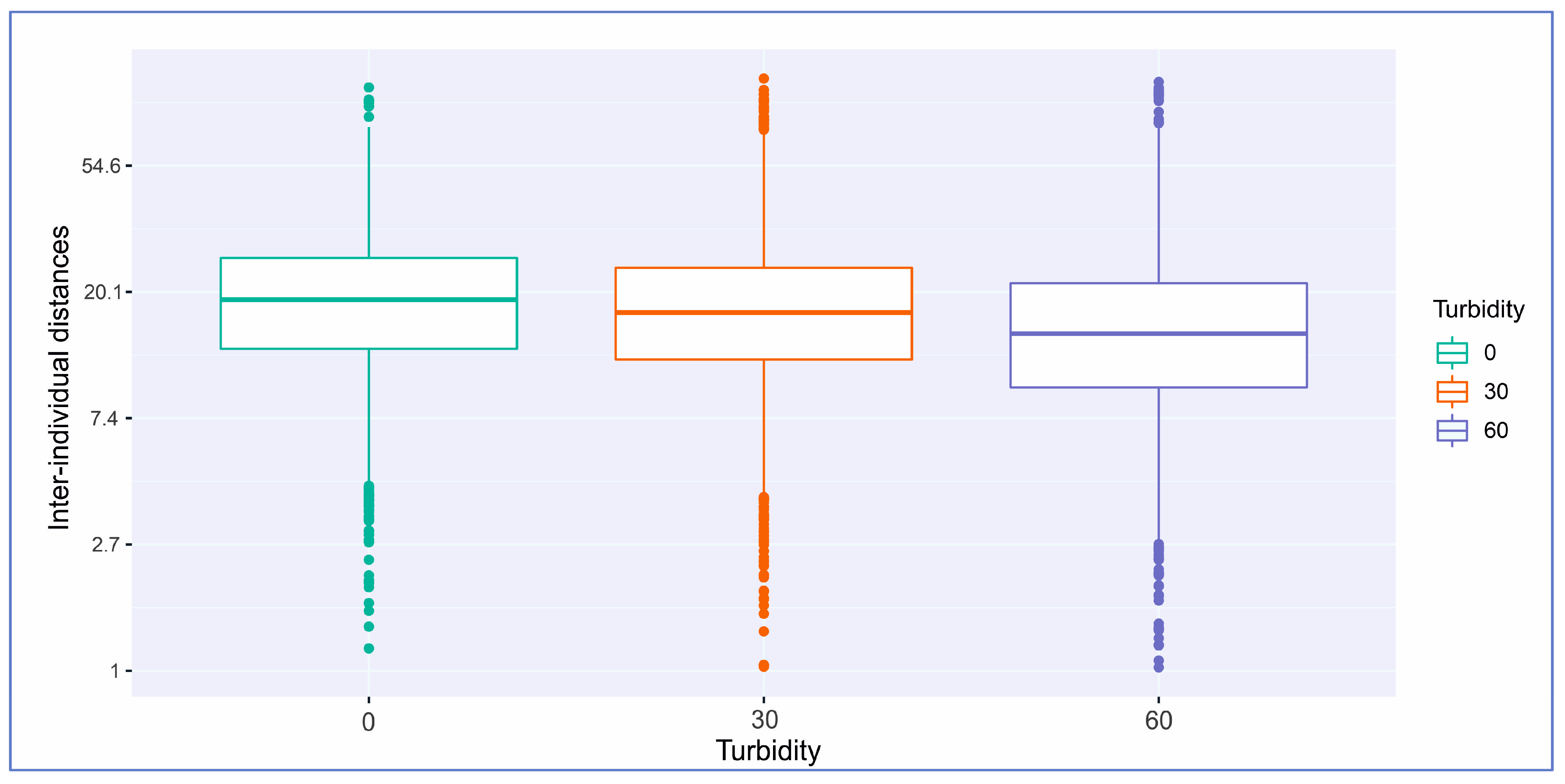
| Turbidity (NTU)/ Distances (cm) | Min. (cm) | 1st Qu (cm) | Median (cm) | Mean (cm) | 3rd Qu. (cm) | Max (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 NTU | 1.2 | 12.8 | 18.9 | 20.7 | 26.3 | 101.4 |
| 30 NTU | 0.6 | 11.8 | 17.1 | 19.4 | 24.3 | 108.8 |
| 60 NTU | 0.2 | 9.4 | 14.4 | 17.0 | 21.5 | 105.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horka, P.; Vlachova, M. The Effect of Turbidity on the Behavior of Bleak (Alburnus alburnus). Fishes 2024, 9, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010003
Horka P, Vlachova M. The Effect of Turbidity on the Behavior of Bleak (Alburnus alburnus). Fishes. 2024; 9(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorka, Petra, and Monika Vlachova. 2024. "The Effect of Turbidity on the Behavior of Bleak (Alburnus alburnus)" Fishes 9, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010003
APA StyleHorka, P., & Vlachova, M. (2024). The Effect of Turbidity on the Behavior of Bleak (Alburnus alburnus). Fishes, 9(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010003