Abstract
In this study, twelve polymorphic microsatellite loci were screened to evaluate the genetic diversity of five yellow drum (Nibea albiflora) populations in the Zhoushan Sea region of the East China Sea, including one wild population (WP), one artificially propagated population (common population, CP), and three breeding populations (parent population, F4; all-female population, AF; and neo-male population, NeoG). The results of genetic diversity analyses showed that all five yellow drum populations had relatively high genetic diversity, with the highest in WP and the lowest in NeoG. Genetic structure analyses showed that the level of genetic differentiation among populations was low, with that between CP and F4 being the largest, whereas that between CP and WP was the smallest. Mutation–drift equilibrium analysis showed that the five populations likely did not experience a recent bottleneck. Our results suggest the CP population was the most suitable for large-scale release for stock enhancement, and precautionary measures shall be taken for the AF population before it is used for cage culture to avoid potential genetic concerns of the wild population. Nevertheless, further genetic diversity monitoring is needed to evaluate genetic effects and avoid the negative impact of excessive genetic differentiation between breeding and wild populations.
Key Contribution:
Genetic differentiation between the wild and most artificially propagated populations is significant, indicating that only the CP common population of cultured fish is suitable for large-scale release and the that all-female population is suitable for cage culture in the Zhoushan Sea region.
1. Introduction
Genetic diversity is essential for selective breeding and a prerequisite for preservation of germplasm resources [1,2]. In particular, effectively avoiding the loss of genetic diversity in subsequent generations remains challenging [3]. In the process of sustainable development of the aquaculture industry, the neglect of the importance of genetic diversity or improper breeding practices often cause germplasm degradation, ultimately leading to a slower growth rate and larger growth differences between individuals, which limits the sustainable development of aquaculture [4]. Therefore, the detection of population genetic diversity and structure has become an important aspect of germplasm resource protection and improvement of cultured stocks.
DNA-based molecular marker techniques, such as randomly amplified polymorphic DNA, amplified fragment length polymorphisms, single nucleotide polymorphisms, and microsatellites, have proven to be powerful tools for detecting genetic diversity. Microsatellites, also known as simple sequence repeats (SSR), are a PCR-based molecular marker technology. Its advantages, such as a large number of polymorphic loci, large amount of information, and easy detection, make it widely used in studying the genetic diversity of biological populations [5]; it has been applied in the fields of genome mapping, population genetics, ecology, and evolution [6], including population genetic studies of fishery species such as Oplegnathus fasciatus, Scomber japonicus, and Galaxias maculatus [7,8,9].
The yellow drum (Nibea albiflora), which belongs to the Family Sciaenidae of Order Perciformes, is a eurythermic fish naturally distributed in the coastal waters of China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea [10]. It is an important fish species for capture fisheries and aquaculture in East Asia [11]. According to the latest edition of the ‘China Fisheries Statistical Yearbook’, the yearly landing of yellow drum reached 66,000 tons in 2022 [12]. In recent years, owing to overfishing, marine pollution, and climate change, wild yellow drum resources have decreased sharply. Nevertheless, artificial propagation and cage culture of yellow drum have been carried out for many years [13,14], and batches of hatchery-reared fish have been released into the sea for stock enhancement, especially along the Zhoushan Sea region of the East China Sea. Meanwhile, a monosex culture of yellow drum has been confirmed to provide yielded economic advantages to the industry due to the superior growth of females relative to that of males [15,16]. Thus, gynogenesis and exogenous hormone application have been used to breed fast-growing gynogenetic and neomale strains, respectively [17,18]; all-female seedlings have been obtained via hybridization of the F4 and NeoG populations [19]. On one hand, years of artificial propagation and cultivation of this fish may cause an increase in inbreeding and germplasm degradation in cultured populations. On another, releasing hatchery-reared populations may impact the genetic structure of wild populations. Therefore, there is an urgent need to quantify population diversity and provide a basis for subsequent research on yellow drums. In this study, we used fluorescently SSR labelled to study the genetic diversity and population genetic structure of this species, including cultured and wild populations, to monitor the current status of germplasm resources of yellow drums in Zhoushan Sea area. The findings of this research will be valuable for conservation of yellow drum genetic resources and advancement of the aquaculture industry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
Originally, 284 wild yellow drums (weighing > 300 g) were captured from coastal waters along the Zhoushan Sea region of the East China Sea and subsequently domesticated at the experimental field station of the Zhejiang Institute of Marine Fisheries, from which 210 individuals were selected as an original bloodstock. In this study, the genetic diversity of five different yellow drum populations was analyzed, including the F4 population (F4) which was the fourth filial generation of selectively bred stock developed by the Zhejiang Marine and Fisheries Research Institute; the neo-male population (NeoG) was obtained via sex reversal of the meiotic gynogenetic offspring of F3 stock [17], the wild population (WP) collected from the coastal waters along the Zhoushan Sea region of the East China Sea (the same region where the original bloodstock was captured), the all-female population bred by NeoG and F4 (AF) [18], and the common population (CP) cultured by a local breeding company in Xiangshan City, Zhejiang Province, which was artificially propagated by that company with original bloodstock captured from Zhoushan Sea region, serving as a control against the WP population. For each population, the caudal fins of 30 individuals were collected and stored in ethanol, and the samples were then stored at −20 °C until further processing. Genomic DNA was extracted from each sample using the phenol–chloroform method. DNA integrity was verified using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and the quality and concentration were measured using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.2. Microsatellite Analysis
The twelve pairs of SSR primers that were used were previously developed by Xing et al. and Xu et al. [20,21]. The primers were synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and the 5′ end of the forward primer was labeled with FAM or HEX fluorophore. The amplification volume was 20 μL, including 10 μL of 2× Taq Master Mix (L/N 7E691R2, Vazyme, Nanjing, China), 1 μL of each upstream and downstream primer (10 μmol/L), 1 μL of genomic DNA (50 ng/μL), and 7 μL of sterile water to adjust the final volume. Initial denaturation was at 94 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles at 94 °C for 30 s, 55 °C–60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 1 min. The PCR-amplified products were visualized using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and subsequently forwarded to Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. for capillary electrophoretic detection. The fluorescently labelled PCR products of the 12 microsatellites were analyzed on an ABI3730xL DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) using GeneMapper 3.5 software, and the size of the PCR products was determined according to the LIZ-500 size standard.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Microsatellite typing results were statistically analyzed using GeneMarker v.3.0.0 software (SoftGenetics, State College, PA, USA) [22]. The number of alleles (Na), expected heterozygosity (He), observed heterozygosity (Ho), Shannon–Wiener index (I), Nei’s genetic distance, and principal component analysis (PCoA) were conducted using GenAlEx v.6.503 software [23]. The polymorphism information content (PIC) of each SSR locus was calculated using Cervus v.3.0.7 software [24]. The phylogenetic tree of the above genetic distance was reconstructed via the Neighbor-Joining method using MEGA v.5.0 software [25]. Arlequin v.3.5 software [26] was used to calculate the genetic differentiation coefficient (Fst) between paired populations, and the partition of variation was quantified using an analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA).
The Structure v2.3.4 software [27] was used to perform genetic clustering analysis on the five populations to determine the optimal K value. The optimal number of clusters was estimated using the delta K (ΔK) statistical method [28] and calculated using the Structure Harvest online tool [29]. Using the genotype frequency of each locus, the Sign test and Wilcoxon sign-rank test implemented Bottleneck v1.2.02 software [30] to test whether the mutation–drift equilibrium deviated from the mutation–drift equilibrium under the assumptions of three mutation models (IAM, TPM, and SMM).
3. Results
3.1. Polymorphism of Different SSR Loci
All 12 loci showed high levels of polymorphisms. The main parameters for each SSR locus are shown in Table 1. Each locus showed different degrees of polymorphism. A total of 106 alleles were observed in the 12 SSR loci. Na ranged from 5 (Nibea10) to 13 (Nibea08), with an average of 8.850. Ne ranged from 2.726 to 7.627, with an average of 4.999. Ho and He values of these loci ranged from 0.460 to 0.907 (average 0.663) and 0.560 to 0.781 (average 0.706), respectively. I ranged from 1.136 to 1.953, with an average of 1.597, of which Nibea08 had the highest, and Nibea10 had the lowest value. Fst ranged from 0.128 to 0.266, with an average of 0.182, of which Niall28 had the highest and Nibea07 the lowest. The PIC of 12 microsatellite loci ranged from 0.509 to 0.758, with an average of 0.664, which were highly polymorphic loci (PIC ≥ 0.50), of which Niall28 was the highest and Nibea03 was the lowest.

Table 1.
Genetic diversity indices for 12 microsatellite loci of yellow drum.
3.2. Genetic Diversity of the Yellow Drum Populations
The variation ranges of average genetic diversity parameters for the five yellow drum populations are shown in Table 2. Na and Ne were 4.250–14.083 (average 8.850) and 2.402–8.235 (average 4.999), respectively, with the highest in the WP population and the lowest in the NeoG population. Ho and He were 0.569–0.750 (average 0.663) and 0.518–0.838 (average 0.706), respectively, with the highest in the WP population and lowest in the NeoG population. The PIC results also showed that the WP population (0.7404) was the highest and the NeoG population (0.3826) was the lowest. According to the genetic diversity parameters, every yellow drum population showed relatively high genetic diversity, and the order of genetic diversity within each population was as follows: WP > F4 > CP > AF > NeoG.

Table 2.
Statistics for genetic diversity in five yellow drum populations.
3.3. Analysis of Genetic Structure and Differentiation among Populations
The results of AMOVA showed that the level of genetic differences among populations was low (Fst = 0.0194, p < 0.01); 32.20% of the variation came from within population differences, 1.39% from among population differences, and 66.40% within individual differences (Table 3). The results of the genetic distance analysis showed that the genetic distance between populations ranged from 0.0060 to 0.1790; the distance between the CP and F4 populations was the largest (0.1790), while the distance between the CP and WP populations was the smallest (0.0060). Fst analysis showed that the genetic differentiation index between populations was moderate to high (0.058–0.182). Among them, the CP and F4 populations had the largest genetic differentiation (0.182) and the CP and WP populations had the smallest (0.058), which was consistent with the results of the genetic distance analysis (Table 4).

Table 3.
AMOVA results of five yellow drum populations.

Table 4.
Genetic differentiation index (Fst, above diagonal) and genetic distance (below diagonal) among the yellow drum populations.
A Neighbor-Joining (NJ) tree was constructed based on the genetic distance among populations. The five populations were clustered into two branches, of which CP and WP were one branch; in the other branch, AF and NeoG were first clustered into one branch, and F4 was clustered into one branch (Figure 1). The Structure analysis tested K from 1 to 6. The optimal K value was determined to be 4 according to the maximum ΔK value (Figure 2a). According to the optimal K value, the five yellow drum populations could be divided into four clusters: cluster I contained the F4 population, cluster II contained the NeoG and AF populations, cluster III contained the CP population, and cluster IV contained the WP population (Figure 2b). The results of PCoA also reached a similar conclusion, in which three principal components explained 83.14% of the total molecular variation (Figure 3). The results of PCoA also showed that the WP and CP populations were clustered together and genetically distinct from the other three populations (F4, NeoG, AF).
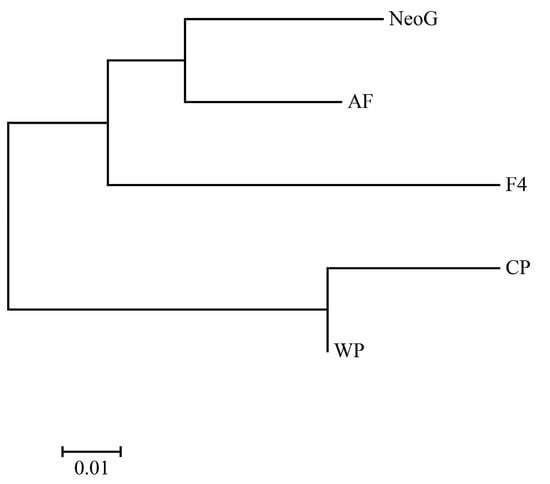
Figure 1.
The phylogenetic tree of five yellow drum populations reconstructed via the Neighbor-Joining method.
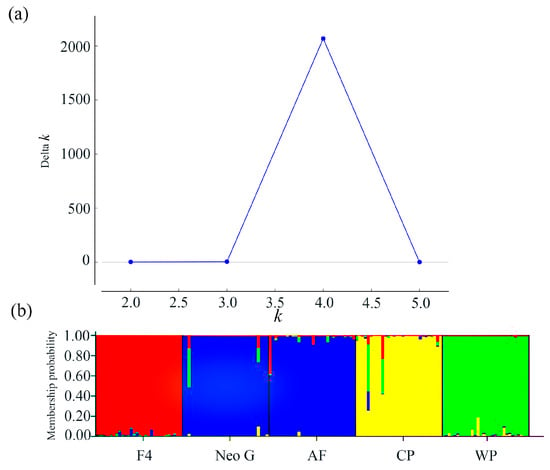
Figure 2.
(a) Graph of the variation in Delta K with the value of K. (b) The genetic structuring of yellow drum populations according to the optimum value of K (K = 4). Different colours indicate different genetic clusters, and each individual is shown as a vertical line divided into segments representing the estimated membership proportion in the four ancestral genetic clusters. F4, parent population; Neo G, neo-male population; AF, all-female population; CP, common population; WP, wild population.
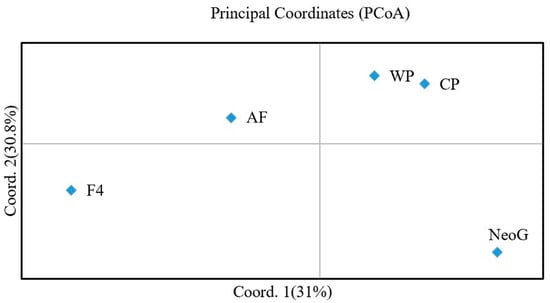
Figure 3.
Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of five yellow drum populations.
3.4. Analysis of Potential Genetic Bottleneck Effects
Mutation–drift equilibrium analysis was performed via a bottleneck effect evaluation for the five yellow drum populations; the results are shown in Table 5. Under the IAM hypothesis, the sign test showed that the CP population deviated from the mutation–drift equilibrium and exhibited significant heterozygous excess. The Wilcoxon sign-rank test showed that all populations deviated from the mutation–drift equilibrium except for the NeoG population. Under the TPM hypothesis, the sign test and Wilcoxon sign-rank test showed that all populations conformed to mutation–drift equilibrium. Under the SMM hypothesis, the sign test showed that the NeoG population conformed to mutation–drift balance, and the Wilcoxon sign-rank test showed that the CP population deviated from the mutation–drift balance.

Table 5.
Mutation–drift equilibrium analysis for five yellow drum populations.
4. Discussion
Detection of genetic diversity plays an important role in germplasm identification. It is now generally recognized that the level of genetic diversity detected is positively correlated with the viability and evolutionary potential of a species or population [30]. It is particularly important to detect genetic diversity during selective breeding. Microsatellites are reliable molecular tools for detecting genetic diversity and have been widely used to assess the level of genetic diversity and population structure, which is of great significance for the conservation of germplasm resources and the development of breeding strategies.
The reliability of microsatellite markers is closely related to PIC, which is often used as an indicator of polymorphism [31,32]. In this study, the microsatellite loci used showed moderate-to-high levels of polymorphism (average PIC value = 0.664). The five populations of yellow drum showed high levels of polymorphism (overall average PIC = 0.6010). The genetic diversity of the WP population was higher than that of the four cultured populations, which was consistent with the results observed in other fish studies [33]. The reason for this phenomenon may be the limited number of parents in the breeding population during artificial reproduction, heightened inbreeding opportunities, and the specific environment [34]. Among the four cultured populations, the genetic diversity of the F4 population (PIC = 0.7292) was the highest and closer to the genetic diversity of the WP population (PIC = 0.7404). This may be due to the high number and diversity of individuals in the breeding population, such that the diversity of F4 was maintained at a high level.
As an important parameter reflecting the genetic diversity of a population, the magnitude of genetic heterozygosity reflects the degree of population genetic diversity, and populations with high heterozygosity are more likely to adapt to environmental changes [35]. In this study, the overall He of the five populations was 0.706, which was higher than the Ho of 0.663, showing loss of heterozygosity. This phenomenon may be caused by random genetic drift, especially when the population size is small, and loss of rare alleles. Our study results showed significant loss of heterozygosity through bottlenecks, which supports the hypothesis that genetic drift affected population genetic structure. Therefore, during artificial reproduction and breeding, as many parents as possible should be used to avoid inbreeding [36]. Compared with the NeoG population, the Na, PIC, Ho, and He in the AF population were higher than those in the NeoG population because the parents of the gynogenetic population were only a few fish, and the neomales were induced by the sex reversal of the gynogenetic population; the female fish in the F4 population with high diversity was introduced as the parent in the production of the all-females, thus improving the diversity of the AF population. Studies have shown that gynogenesis can increase the genetic homozygosity of large yellow croakers, resulting in higher genetic diversity in the AF population than in the NeoG population [37]. Since the AF population was bred for monosex culture due to the superior growth of female yellow drum, its medium level of genetic diversity suggested that precautionary measures such as sterilization of the AF population shall be taken before cage culture in the Zhoushan Sea region because its possible escape from the cage would have an impact on the genetic structure of the wild population in the future.
The genetic differentiation index (Fst) reflects the degree of genetic differentiation between populations. An Fst of 0~0.05 is regarded as a small genetic differentiation among populations, while an Fst of 0.05~0.15 is regarded as moderate and an Fst > 0.15 is regarded as high [38,39]. In this study, the Fst among the yellow drum populations was 0.058–0.182, which was within the range of moderate to high. Significant genetic differentiation was observed between cultured populations and between cultured populations and WPs. However, the results of the AMOVA analysis showed that the genetic variation mainly came from the genetic diversity within individuals (66.40%), whereas the genetic variation among populations was small (1.39%), indicating that the level of genetic variation within yellow drum individuals was high. In the previous study, the genetic variation of Nibea albiflora in four different geographical locations was compared and analyzed; AMOVA results showed that the genetic variation within populations was significantly greater than that between populations, which was consistent with the results of this study. However, the Fst values (0.001~0.056) between the four wild populations in that study were lower than the Fst values of the five different populations in this study [40,41]. This may be because the populations sampled in the previous study were wild populations, and the sources of the five populations in this study were more diverse, including wild, artificially propagated, and breeding populations; with the passage of more generations, more random genetic drift has occurred. This may be because, when the basic population is initially established, the gynogenetic individuals maintained a strain genetic relationship with the parent generation [42,43]. Population differentiation is primarily influenced by selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and their interrelationships. This result suggests that we may have greater genetic differentiation from WPs because of the reduction in genetic diversity in the current fish breeding process.
The genetic distance between the CP and WP populations was the closest (Da = 0.0060), and the genetic distance between the CP and F4 population was the farthest (Da = 0.1790), indicating that the genetic relationship between the CP and WP population was close, and the genetic difference between the CP and F4 population was large. In previous studies, researchers have also observed a similar phenomenon; that is, there are significant differences between wild populations and cultured populations, and the genetic distance between the two is far. The reason for this phenomenon can be attributed to the long-term domestication process of the breeding population. This process led to a moderate genetic differentiation between cultured and wild populations [44,45]. The results of the NJ phylogenetic tree, PcoA, and population genetic structure analysis showed that F4, NeoG, and AF were genetically similar, which was also in line with the theoretical results because the parents of the AF population were the F4 and NeoG populations, and theoretically, there should be a closer genetic relationship. There may be many reasons for this, such as limited and accidental sampling numbers and reproductive pressure caused by artificial propagation.
In the present study, the evaluation results of the mutation–drift balance test for the five yellow drum populations under the three mutation models (IAM, TPM, and SMM) were different. Because existing studies suggest that microsatellite data are more consistent with the TPM model, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test is more efficient than the sign test [30]. Under the TPM hypothesis, the results of the sign-rank test showed that the five populations did not deviate from the mutation–drift equilibrium, which was consistent with the conclusion that genetic diversity was high. Therefore, these five groups probably did not experience a bottleneck in the recent past.
5. Conclusions
The genetic diversity of five yellow drum populations (F4, NeoG, AF, CP, and WP) was analyzed using microsatellite markers. The genetic diversity of the five yellow drum populations was relatively high and there was significant genetic differentiation among the populations. The CP and WP populations were similar, which indicated that these particular artificially propagated fish were suitable for large-scale release along the Zhoushan Sea region for stock enhancement. Under the pressure of artificial directional breeding, there was a medium level of genetic differentiation between the AF and WP populations, indicating that the genetic structure of the AF population had changed. However, owing to the short generation intervals and breeding programs, this differentiation is significant and already at a medium level, indicating that, while the AF population is used for cage culture in Zhoushan Sea region due to its superior growth, precautionary measures such as sterilization of the AF population should be taken to avoid potential genetic concerns of the wild population. From the perspective of development and utilization, considering the emphasis on resource conservation, additional genetic analyses will be required to obtain necessary information to comprehend the ongoing genetic issues in aquaculture and fisheries management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Z. and D.X.; methodology, Q.Y. and S.L.; validation, Q.Y., S.L. and Q.Z.; resources, R.C. and W.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Y.; writing—review and editing, Q.Z. and D.X.; supervision, Q.Z. and D.X.; project administration, D.X.; funding acquisition, D.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China for Distinguished Young Scientists under grant number LR21C190001 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant number 31972785.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Ocean University and Zhejiang Marine Fisheries Research Institute (1 January 2019).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gjedrem, T.; Robinson, N.; Rye, M. The importance of selective breeding in aquaculture to meet future demands for animal protein: A review. Aquaculture 2012, 350, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.B.; Christian, S. Microsatellites, Evolution and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Ellegren, H.; Galtier, N. Determinants of genetic diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, J.; Maria Porta, J.; Cañavate, P.; Martínez-Rodríguez, G.; Carmen Alvarez, M. Substantial loss of genetic variation in a single generation of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) culture: Implications in the domestication process. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagshaw, A.T. Functional mechanisms of microsatellite DNA in eukaryotic genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2428–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodel, R.G.; Segovia-Salcedo, M.C.; Landis, J.B.; Crowl, A.A.; Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Douglas, N.A.; Germain-Aubrey, C.C.; Chen, S.; et al. The report of my death was an exaggeration: A review for researchers using microsatellites in the 21st century. Appl. Plant Sci. 2016, 4, 1600025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astorga, M.P.; Valenzuela, A.; Segovia, N.I.; Poulin, E.; Vargas-Chacoff, L.; Gonzalez-Wevar, C.A. Contrasting patterns of genetic diversity and divergence between landlocked and migratory populations of fish Galaxias maculatus, evaluated through mitochondrial DNA sequencing and nuclear DNA microsatellites. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 854362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X. High polymorphism and moderate differentiation of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus (Perciformes: Scombridae), along the coast of China revealed by fifteen novel microsatellite markers. Conserv. Genet. 2014, 15, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, G.; Ma, D.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, S. Pronounced population genetic differentiation in the rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Takita, T.; Saito, H.; Oiwa, A. Orcurrence of two cohorts in young of the year of Nibea albiflora in the Arake Sound Japan and comparison of their growth and changes in body composition. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 2008, 55, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Wu, X.X. 2023 China Fisheries Statistical Yearbook, 1st ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2023; pp. 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Xu, D.; Shi, H.; Lou, B.; Mao, G.; Li, S. Study on development and growth of early life stages of Nibea albiflora (Richardson). Adv. Mar. Sci. 2012, 30, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z. Study on Seed Production Techniques of Nibea albiflora from the Inshore Water of Zhoushan; Zhejiang Ocean University: Zhoushan, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q. A study on holding culture technique for fingerling of Nibea albiflora (Richardson) in net-cage. Mod. Fish. Inf. 2009, 24, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Budd, A.M.; Banh, Q.Q.; Domingos, J.A.; Jerry, D.R. Sex control in fish: Approaches, challenges and opportunities for aquaculture. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 329–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Adams, M.; Wilkinson, R. Sex reversal of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) by 17α-methyltestosterone exposure: A serial experimental approach to determine optimal timing and delivery regimes. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 175, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Lou, B.; Xu, D.; Zhan, W.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, F. Induction of meiotic gynogenesis in yellow drum (Nibea albiflora, Sciaenidae) using heterologous sperm and evidence for female homogametic sex determination. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lou, B.; Xue, B.; Shi, H.; Zhan, W.; Ma, S.; Mao, G. Artificial induction of diploid gynogenesis in Nibea alibiflora and evidence for female homogamety. Oceanol. Limnol. SinIca 2013, 44, 310–317. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Chen, R.; Lou, B.; Zhan, W.; Hayashida, T.; Takeuchi, Y. Production of neo-males from gynogenetic yellow drum through 17α-methyltestosterone immersion and subsequent application for the establishment of all-female populations. Aquaculture 2018, 489, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Shao, C.; Liao, X.; Tian, Y.; Chen, S. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite loci from a dinucleotide-enriched genomic library of spotted maigre (Nibea albiflora). Conserv. Genet. 2009, 10, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lou, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhan, W. Isolation and characterization of novel microsatellite loci in Nibea albiflora. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 6156–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.M.; Parson, W. GeneMarker. J. Forensic Sci. 2011, 56, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornuet, J.M.; Luikart, G. Description and power analysis of two tests for detecting recent population bottlenecks from allele frequency data. Genetics 1996, 144, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Bohra, A.; Yu, J.; Graner, A.; Zhang, Q.; Sorrells, M.E. Designing future crops: Genomics-assisted breeding comes of age. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Di Rienzo, A.; Peterson, A.C.; Garza, J.C.; Valdes, A.M.; Slatkin, M.; Freimer, N.B. Mutational processes of simple-sequence repeat loci in human populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3166–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Song, W.; Jiang, L.; Yan, X. Genome-wide radseq reveals genetic differentiation of wild and cultured populations of large yellow croaker. Genes 2023, 14, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Hsu, H.H.; Chua, C.S.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, T.Y. Development of pedigree classification using microsatellite and mitochondrial markers for giant grouper broodstock (Epinephelus Lanceolatus) management in Taiwan. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 1978, 89, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvin, S.D.; Wetterstrand, K.A.; Hutter, C.M.; Aquadro, C.F. Genetic variation and differentiation at microsatellite loci in Drosophila simulans: Evidence for founder effects in New World populations. Genetics 1998, 150, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Yao, C. Genetic structure and genetic diversity analysis of four consecutive breeding generations of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) using microsatellite markers. J. Fish. China 2010, 34, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirmans, P.G.; Hedrick, P.W. Assessing population structure: Fst and related measures. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balloux, F.; Lugon-Moulin, N. The estimation of population differentiation with microsatellite markers. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lou, B.; Zhou, W.; Chen, R.; Zhan, W.; Liu, F. Genetic diversity and population differentiation in the yellow drum Nibea albiflora along the coast of the China Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Tang, X.N.; Li, M.Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, J. Artificial gynogenesis in Pseudosciaena crocea (Perciformes, Sciaenidae) with heterologous sperm and its verification using microsatellite markers. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Enriquez, R.; Valadez-Rodriguez, J.A.; Max-Aguilar, A.; Dumas, S.; Diaz-Viloria, N. Parental contribution in a cultivated stock for the spotted rose snapper Lutjanus guttatus (Steindachner, 1869) estimated by newly developed microsatellite markers. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 48, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zheng, J.; Gao, T.X.; Song, N. Comparative analysis of genetic variation between cultured and wild populations of Nibea albiflora based on mitochondrial DNA control region. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2021, 51, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Lou, B.; Shi, H.; Geng, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Genetic diversity and population structure of Nibea albiflora in the China Sea revealed by mitochondrial COI sequences. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 45, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).