An Investigation of Bacterial Pathogens Associated with Diseased Nile Tilapia in Small-Scale Cage Culture Farms on Lake Kariba, Siavonga, Zambia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
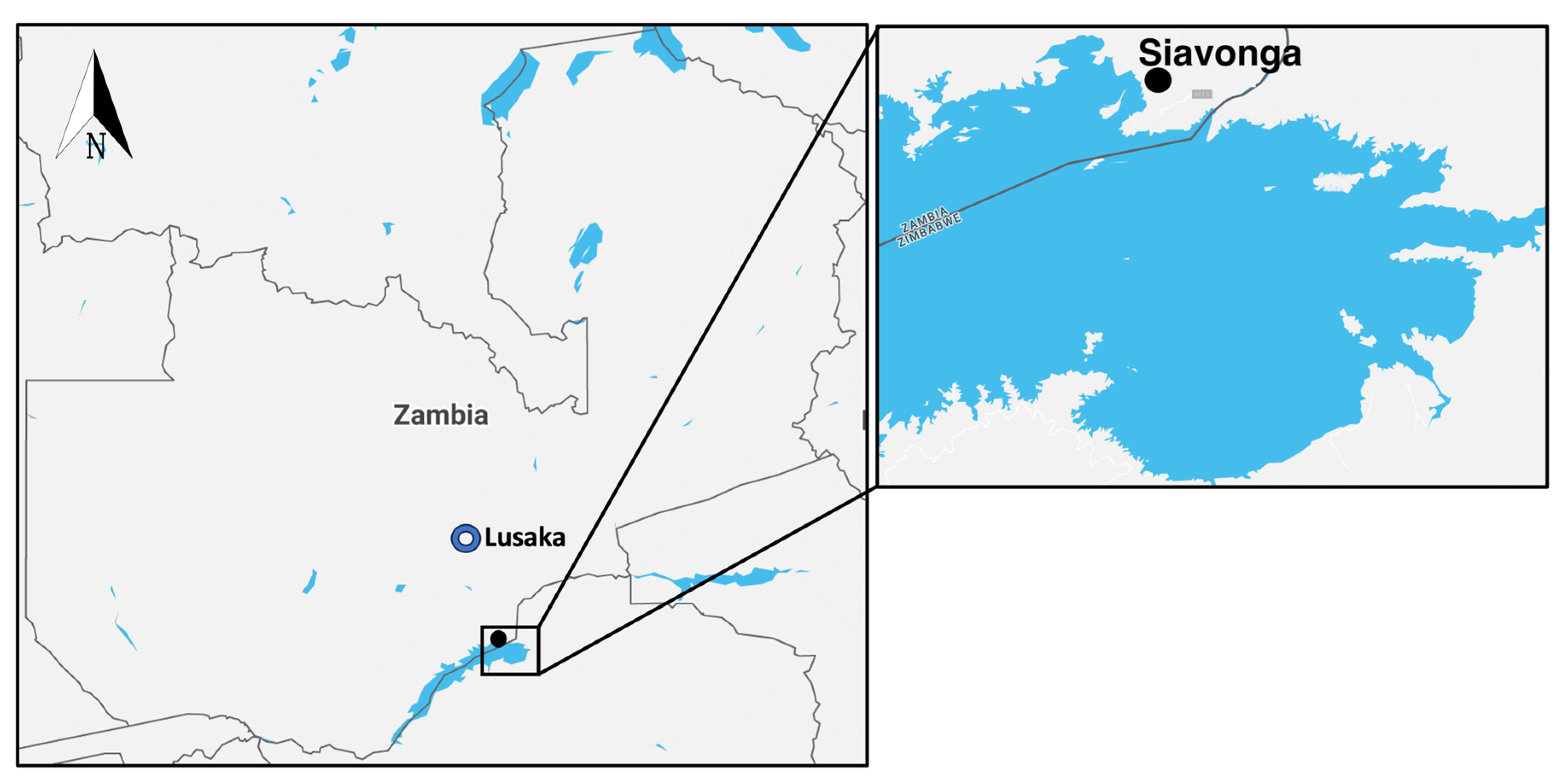
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Design and Sampling
2.3. Assessment of Morphological/Clinical Pathological Symptoms
2.4. Necropsy and Bacterial Inoculation
2.5. Biochemical Characterization
2.6. Determination of the Antibiotic Susceptibility of the Isolates
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
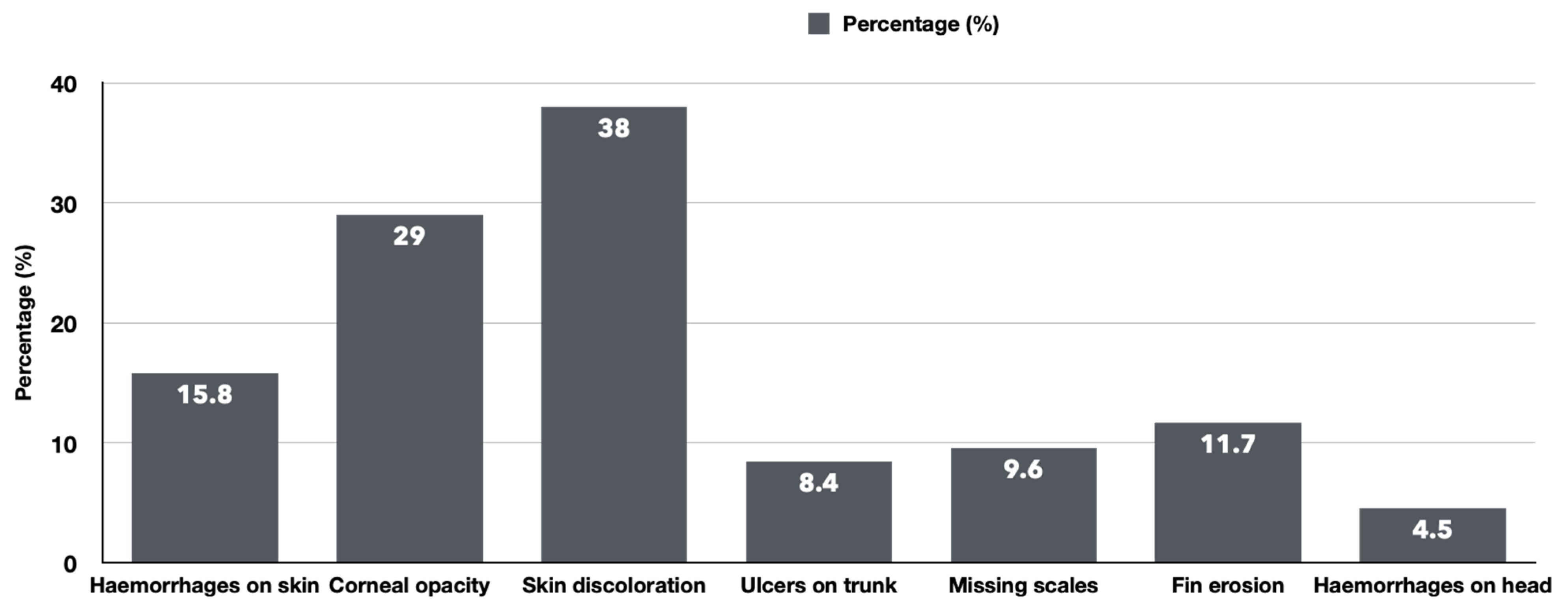
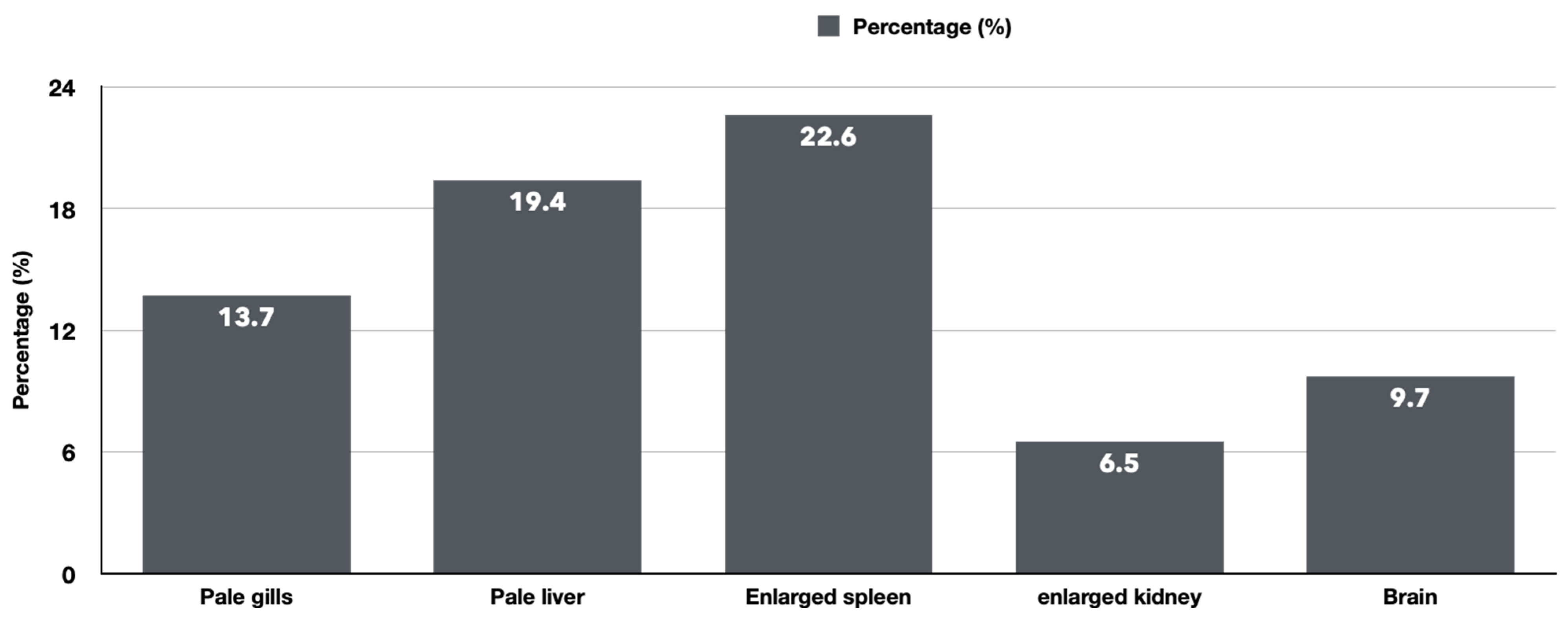
3.1. The Clinical and Necropsy Findings
3.2. Bacterial Identification
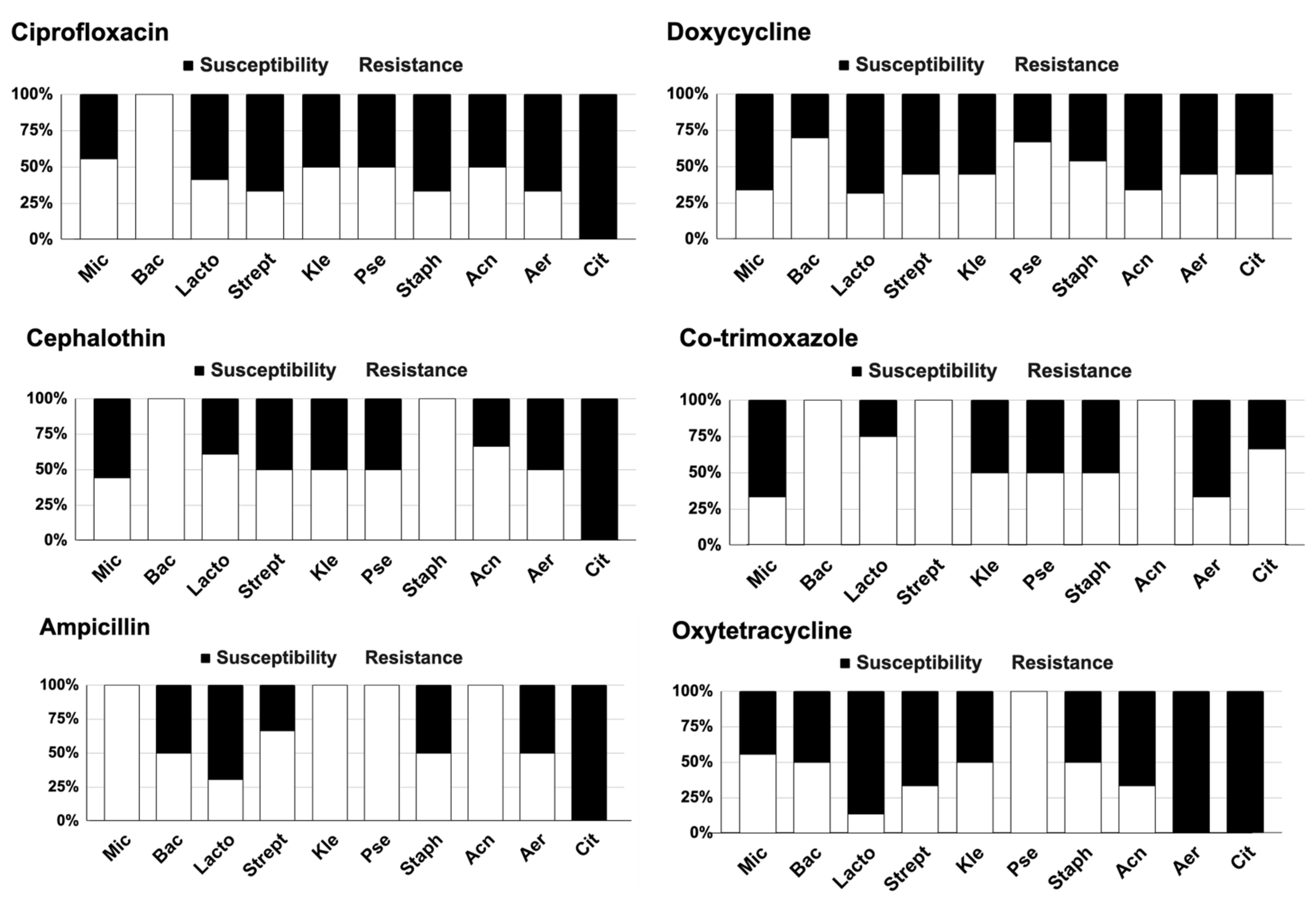
3.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organisation. Aquaculture Production (Metric Tons)—Zambia, Data. 2022. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/ER.FSH.AQUA.MT?locations=ZM (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Kaminski, A.M.; Genschick, S.; Kefi, A.S.; Kruijssen, F. Commercialization and upgrading in the aquaculture value chain in Zambia. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Subasinghe, R.P.; Arthur, J.R.; Ogawa, K.; Chinabut, S.; Adlard, R.; Tan, Z.; Shariff, M. Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture. Veter-Parasitol. 2005, 132, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares-Dias, M.; Martins, M.L. An overall estimation of losses caused by diseases in the Brazilian fish farms. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Major bacterial diseases in aquaculture and their vaccine development. CABI Rev. 2012, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.S.; Southgate, P.C.; Tucker, C.S. Aquaculture: Farming Aquatic Animals and Plants; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, D.; Sunyer, J.O.; Salinas, I. The mucosal immune system of fish: The evolution of tolerating commensals while fighting pathogens. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Techatanakitarnan, C.; Jindakittikul, P.; Thaiprayoon, A.; Taengphu, S.; Charoensapsri, W.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, N.M.E.; El-Ghiet, E.N.A.; Shaheen, A.A.; Abbass, A. Characterization of Pseudomonas Species Isolated from Tilapia “Oreochromis niloticus” in Qaroun and Wadi-El-Rayan Lakes, Egypt. Glob. Vet. 2010, 5, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gil, B.; Fajer-Avila, E.; García-Vargas, F. Vibrios of the spotted rose snapper Lutjanus guttatus Steindachner, 1869 from northwestern Mexico. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.M.; Abd-Elsalam, R.M.; Younis, N.A. Streptococcosis, Lactococcosis and Enterococcosis are potential threats facing cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochomis niloticus) production. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4183–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barony, G.; Tavares, G.; Assis, G.; Luz, R.; Figueiredo, H.; Leal, C. New hosts and genetic diversity of Flavobacterium columnare isolated from Brazilian native species and Nile tilapia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, G.; Lauteri, C.; Vergara, A. Antibiotic Resistance in the Finfish Aquaculture Industry: A Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndashe, K.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Changula, K.; Yabe, J.; Samutela, M.T.; Songe, M.M.; Kefi, A.S.; Chilufya, L.N.; Sukkel, M. An Assessment of the Risk Factors Associated with Disease Outbreaks across Tilapia Farms in Central and Southern Zambia. Fishes 2023, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwalya, P.; Simukoko, C.; Hang’Ombe, B.M.; Støre, S.C.; Støre, P.; Gamil, A.A.; Evensen, Ø.; Mutoloki, S. Characterization of streptococcus-like bacteria from diseased Oreochromis niloticus farmed on Lake Kariba in Zambia. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakala, T. Identification and Antibiogram Profiles of Bacteria Associated with Diseased Oreochromis niloticus in Lake Kariba, Zambia, Sokoine University of Agriculture. 2017. Available online: http://www.suaire.sua.ac.tz/handle/123456789/2021 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Donbæk, C.; Mørk, A.; Ravlo, I. Early mortality in tilapia fingerlings on Lake Kariba in Zambia. Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Oslo, Norway, 2019. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Early-mortality-in-tilapia-fingerlings-on-Lake-in-Donb%C3%A6k-M%C3%B8rk/f1457ea88742710d01b3dc1e124c054f6359593e (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- M100Ed33. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed. Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Korni, F.M.M.; EL-Nahass, E.-S.; Ahmed, W.M.S. An outbreak of Motile Aeromonas Septicemia in cultured Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus with reference to hematological, biochemical and histopathological alterations. J. Fish Pathol. 2017, 30, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surachetpong, W.; Janetanakit, T.; Nonthabenjawan, N.; Tattiyapong, P.; Sirikanchana, K.; Amonsin, A. Outbreaks of Tilapia Lake Virus Infection, Thailand, 2015–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.M.S.; Cruz, C.F.; Pereira, D.P.; Alves, L.M.C.; de Moraes, F.R. Microbiological water quality and gill histopathology of fish from fish farming in Itapecuru-Mirim County, Maranhão State. Acta Scientiarum. Biol. Sci. 2012, 34, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ellis, T.; Berrill, I.; Lines, J.; Turnbull, J.F.; Knowles, T.G. Mortality and fish welfare. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzani, A.S.; Quintiliano, M.H.; Bolfe, F.; Sans, E.C.D.O.; Molento, C.F.M. Tilapia On-Farm Welfare Assessment Protocol for Semi-intensive Production Systems. Front. Veter-Sci. 2020, 7, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.Á. An Overview of the Immunological Defenses in Fish Skin. ISRN Immunol. 2012, 2012, 853470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.Á.; Cerezuela, R. Fish mucosal immunity: Skin. In Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Amal, M.; Koh, C.; Nurliyana, M.; Suhaiba, M.; Nor-Amalina, Z.; Santha, S.; Diyana-Nadhirah, K.; Yusof, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.; Zamri-Saad, M. A case of natural co-infection of Tilapia Lake Virus and Aeromonas veronii in a Malaysian red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus) farm experiencing high mortality. Aquaculture 2018, 485, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, G.B.N.; Tavares, G.C.; Pereira, F.L.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Leal, C.A.G. Natural coinfection by Streptococcus agalactiae and Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalisin farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Khafaga, A.F. Natural co-infection of cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus with Aeromonas hydrophila and Gyrodactylus cichlidarum experiencing high mortality during summer. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, L.; Nor, R.M.; Salleh, A.; Md Yasin, I.S.; Saad, M.Z.; Abd Rahaman, N.Y.; Barkham, T.; Amal, M.N.A. Co-infections of tilapia lake virus, Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in farmed red hybrid tilapia. Animals 2020, 10, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabana, B.M.; Elkenany, R.M.; Younis, G. Sequencing and multiple antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from Nile tilapia fish in Egypt. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e257144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Thanigaivel, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Acharya, K.; Shinge, D.; Seelan, T.S.J.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Pathogenecity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Oreochromis mossambicus and treatment using lime oil nanoemulsion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwalya, P.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Gamil, A.A.; Munang’Andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø.; Mutoloki, S. A whole-cell Lactococcus garvieae autovaccine protects Nile tilapia against infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hamed, S.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T.; Tachibana, L.; de Carla Dias, D.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Esteban, M.A. Fish pathogen bacteria: Adhesion, parameters influencing virulence and interaction with host cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bacterial Isolates | GM | CM | H | Ox | Cat | Esc | Gal | Raf | Sal | Mal | Xyl | Man | Tre | Inu | Sor | Lac | Urea | Glu | Suc | Lac | G | H2S | Cit | Sul | Mot | Ind | MR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acinetobacter | − | Rod | β | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| Aeromonas spp. | − | Rod | β | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | − |
| Bacillus | + | Rod | β | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | |
| Citrobacter spp. | − | Rod | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | + | |
| Klebsiella spp. | − | Rod | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | |||
| Lactococcus spp. | + | Cocci | α | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | + |
| Micrococcus | + | Cocci | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| Pseudomonas spp. | − | Rod | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | |
| Staphylococcus spp. | + | Cocci | β | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| Streptococcus spp. | + | Cocci | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | + |
| Bacterial Isolates | Number (%) of Isolated Bacterial Species by Source | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm 1 | Farm 2 | Farm 3 | Farm 4 | Farm 5 | Farm 6 | Farm 7 | Farm 8 | Farm 9 | Farm 10 | Farm 11 | Total | |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 4 (1.3) | 3 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.0) | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.0) | 2 (0.7) | 21 (7.0) |
| Aeromonas spp. | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.7) | 6 (2.0) | 3 (1.0) | 7 (2.3) | 1 (0.3) | 9 (3.0) | 3 (1.0) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 4 (1.3) | 39 (13.0) |
| Bacillus spp. | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.0) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 14 (4.7) |
| Citrobacter spp. | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.7) |
| Klebsiella spp. | 4 (1.3) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.7) | 4 (1.3) | 6 (2.0) | 3 (1.0) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | 26 (8.7) |
| Lactococcus spp. | 6 (2.0) | 1 (0.3) | 3 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.7) | 4 (1.3) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | 22 (7.3) |
| Micrococcus spp. | 4 (1.3) | 2 (0.7) | 6 (2.0) | 1 (0.3) | 4 (1.3) | 1 (0.3) | 6 (2.0) | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) | 29 (9.7) |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 4 (1.3) | 1 (0.3) | 5 (1.7) | 2 (0.7) | 9 (3.0) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 3 (1.0) | 31 (10.3) |
| Staphylococcus spp. | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (1.7) |
| Streptococcus spp. | 3 (1.0) | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 4 (1.3) | 4 (1.3) | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 21 (7.0) |
| Unidentified | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.0) | 3 (1.0) | 2 (0.7) | 5 (1.7) | 2 (0.7) | 7 (2.3) | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.7) | 30 (10.0) |
| No Growth | 5 (1.7) | 3 (1.0) | 8 (2.7) | 5 (1.7) | 13 (4.3) | 3 (1.0) | 11 (3.7) | 5 (1.7) | 2 (0.7) | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.0) | 60 (20.0) |
| Total | 30 (10.0) | 20 (6.7) | 40 (13.3) | 20 (6.7) | 45 (15.0) | 20 (6.7) | 60 (20.0) | 25 (8.3) | 15 (5.0) | 10 (3.3) | 15 (5.0) | 300 (100.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siamujompa, M.; Ndashe, K.; Zulu, F.C.; Chitala, C.; Songe, M.M.; Changula, K.; Moonga, L.; Kabwali, E.S.; Reichley, S.; Hang’ombe, B.M. An Investigation of Bacterial Pathogens Associated with Diseased Nile Tilapia in Small-Scale Cage Culture Farms on Lake Kariba, Siavonga, Zambia. Fishes 2023, 8, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090452
Siamujompa M, Ndashe K, Zulu FC, Chitala C, Songe MM, Changula K, Moonga L, Kabwali ES, Reichley S, Hang’ombe BM. An Investigation of Bacterial Pathogens Associated with Diseased Nile Tilapia in Small-Scale Cage Culture Farms on Lake Kariba, Siavonga, Zambia. Fishes. 2023; 8(9):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090452
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiamujompa, Mazuba, Kunda Ndashe, Frederick Chitonga Zulu, Chanda Chitala, Mwansa M. Songe, Katendi Changula, Ladslav Moonga, Emmanuel Shamulai Kabwali, Stephen Reichley, and Bernard Mudenda Hang’ombe. 2023. "An Investigation of Bacterial Pathogens Associated with Diseased Nile Tilapia in Small-Scale Cage Culture Farms on Lake Kariba, Siavonga, Zambia" Fishes 8, no. 9: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090452
APA StyleSiamujompa, M., Ndashe, K., Zulu, F. C., Chitala, C., Songe, M. M., Changula, K., Moonga, L., Kabwali, E. S., Reichley, S., & Hang’ombe, B. M. (2023). An Investigation of Bacterial Pathogens Associated with Diseased Nile Tilapia in Small-Scale Cage Culture Farms on Lake Kariba, Siavonga, Zambia. Fishes, 8(9), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090452





