Development of an Accurate Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assay for Genetic Sex Identification in Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) Based on Male-Specific Anti-Mullerian Hormone (amh) Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Primer Design
2.4. Determination of Sex Specificity of Markers
2.5. DNA Sequencing
2.6. Estimation of the Male-Specific Region Coverage
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
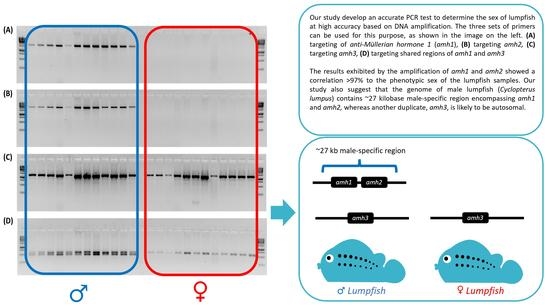
3. Results
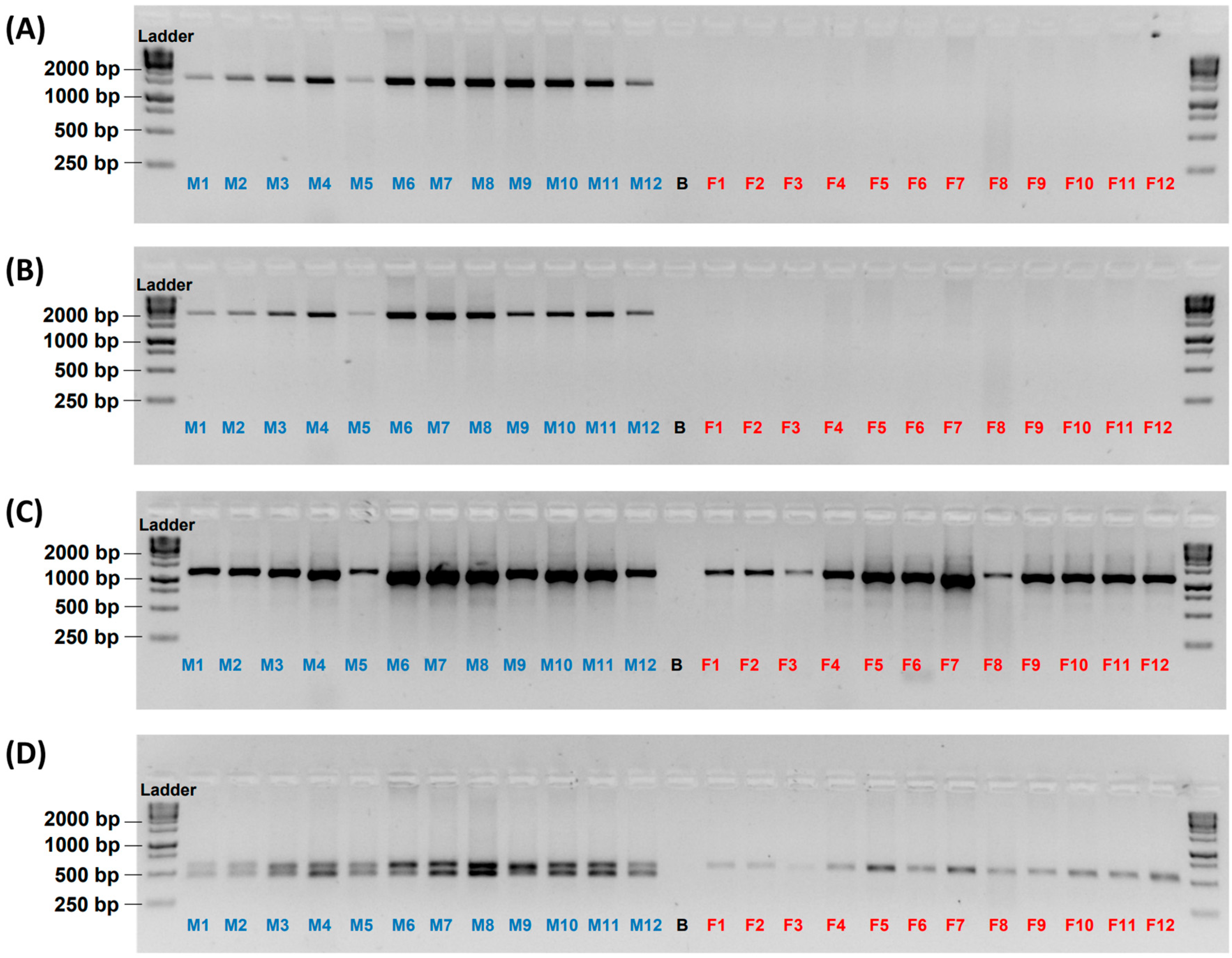
3.1. Male-Specificity of the Markers
3.2. Accuracy of the Male-Specific Markers
3.3. Determination of the Male-Specific Region Length
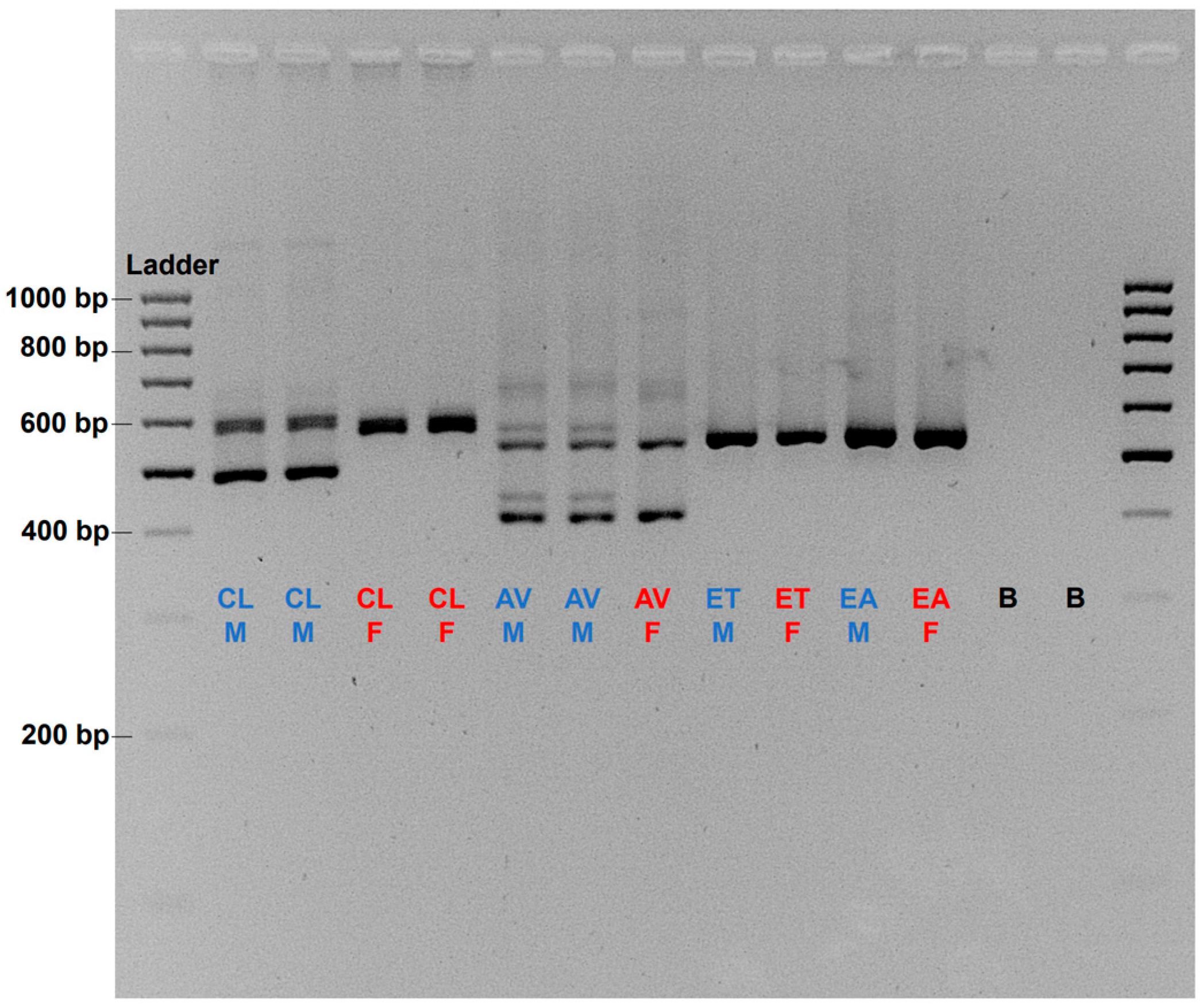
3.4. Sequence Homogeneity and Evolutionary Relationship of the amh Gene in Cyclopterida
4. Discussion
4.1. Application in Aquaculture
4.2. Implication in the Sex-Determination System of Lumpfish
4.3. Implication in the Sex Chromosome Evolution of Lumpfish
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooker, A.J.; Skern-Mauritzen, R.; Bron, J.E. Production, mortality, and infectivity of planktonic larval sea lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer, 1837): Current knowledge and implications for epidemiological modelling. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 1214–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton-Warberg, M. An overview of cleaner fish use in Ireland. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østevik, L.; Stormoen, M.; Evensen, Ø.; Xu, C.; Lie, K.; Nødtvedt, A.; Rodger, H.; Skagøy, A.; Manji, F.; Alarcón, M. Effects of thermal and mechanical delousing on gill health of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2022, 552, 738019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, K.; Dempster, T.; Oppedal, F.; Kristiansen, T.S.; Gismervik, K.; Stien, L.H. Salmon lice treatments and salmon mortality in Norwegian aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 1398–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisic, J.; Cannon, S.; Quinn, B. Cumulative impact of anti-sea lice treatment (azamethiphos) on health status of Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum 1792) in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, A.E.; Escobar-Lux, R.; Sævik, P.N.; Samuelsen, O.B.; Agnalt, A. The impact of anti-sea lice pesticides, azamethiphos and deltamethrin, on European lobster (Homarus gammarus) larvae in the Norwegian marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesson, J. Lumpfish Caviar: From Vessel to Consumer; Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/a0685e/a0685e.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Brooker, A.J.; Papadopoulou, A.; Gutierrez, C.; Rey, S.; Davie, A.; Migaud, H. Sustainable production and use of cleaner fish for the biological control of sea lice: Recent advances and current challenges. Vet. Rec. 2018, 183, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.; Treasurer, J.W.; Pooley, C.L.; Keay, A.J.; Lloyd, R.; Imsland, A.K.; Garcia de Leaniz, C. Use of lumpfish for sea-lice control in salmon farming: Challenges and opportunities. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, J.; Bradshaw, C. Observations on skin colour changes in juvenile lumpsuckers. J. Fish Biol. 1995, 47, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, Y.Y.; Lokman, P.M.; Kilimnik, A.; Symonds, J.E. Sex identification in captive hapuku (Polyprion oxygeneios) using ultrasound imagery and plasma levels of vitellogenin and sex steroids. Aquaculture 2013, 384–387, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoré, Y.; Bestin, A.; Haffray, P.; Morvezen, R.; Alix, M.; Schaerlinger, B.; Fontaine, P.; Chardard, D. Sex identification in immature Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis) using ultrasonography. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 6046–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu-Koo, F.; Dugué, R.; Alván Aguilar, M.; Casanova Daza, A.; Alcántara Bocanegra, F.; Chávez Veintemilla, C.; Duponchelle, F.; Renno, J.-; Tello, S.; Nuñez, J. Gender determination in the Paiche or Pirarucu (Arapaima gigas) using plasma vitellogenin, 17β-estradiol, and 11-ketotestosterone levels. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Reynolds, P.; Hangstad, T.A.; Kapari, L.; Maduna, S.N.; Hagen, S.B.; Jónsdóttir, Ó.D.B.; Spetland, F.; Lindberg, K.S. Quantification of grazing efficacy, growth and health score of different lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) families: Possible size and gender effects. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurvitz, A.; Jackson, K.; Degani, G.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Use of endoscopy for gender and ovarian stage determinations in Russian sturgeon (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii) grown in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2007, 270, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, H.; Guiguen, Y.; Christin, H.; Kreuz, E.; Du, K.; Klopp, C.; Céline, L.; Elena, S.Y.; Ciorpac, M.; Jörn, G.; et al. A 180 My-old female-specific genome region in sturgeon reveals the oldest known vertebrate sex determining system with undifferentiated sex chromosomes. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribner, K.T.; Kanefsky, J. Molecular sexing of lake sturgeon. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, A.; Nicol, B.; Jouanno, E.; Quillet, E.; Fostier, A.; Guyomard, R.; Guiguen, Y. The sexually dimorphic on the Y-chromosome gene (sdY) is a conserved male-specific Y-chromosome sequence in many salmonids. Evol. Appl. 2013, 6, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, B.A.; Consuegra, S.; Garcia de Leaniz, C. Genetic and phenotypic differentiation of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) across the North Atlantic: Implications for conservation and aquaculture. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holborn, M.K.; Einfeldt, A.L.; Kess, T.; Duffy, S.J.; Messmer, A.M.; Langille, B.L.; Brachmann, M.K.; Gauthier, J.; Bentzen, P.; Knutsen, T.M.; et al. Reference genome of lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus Linnaeus provides evidence of male heterogametic sex determination through the AMH pathway. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.G.; Hinze, S.J. Simplex PCR assay for positive identification of genetic sex in the Japanese medaka, Oryzias latipes. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, P.G.; Sarah-Louise, C.S.; John, B.T.; Kokkinias, P.; Thomas, C.; Eduardo, J.F.; Migaud, H.; Lein, I.; Davie, A.; Bekaert, M. Development of genomic markers associated to production traits in lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus). bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, E.B.; Laurie, C.V.; Johnson, S.C.; Koop, B.F. A PCR assay detects a male-specific duplicated copy of Anti-Müllerian hormone (amh) in the lingcod (Ophiodon elongatus). BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, R.S.; Murai, Y.; Oura, M.; Masuda, S.; Majhi, S.K.; Sakamoto, T.; Fernandino, J.I.; Somoza, G.M.; Yokota, M.; Strüssmann, C.A. A Y-linked anti-Müllerian hormone duplication takes over a critical role in sex determination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2955–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Feron, R.; Yano, A.; Guyomard, R.; Jouanno, E.; Vigouroux, E.; Wen, M.; Busnel, J.; Bobe, J.; Concordet, J.; et al. Identification of the master sex determining gene in Northern pike (Esox lucius) reveals restricted sex chromosome differentiation. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquer, A. Phylogéographie Intraspécifique d’un Poisson Marin, le Flet Platichthys flesus L. (Heterosomata): Polymorphisme des Marqueurs Nucléaires et Mitochondriaux. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, F.; Allen, J.E.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Bennett, R.; et al. Ensembl 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D988–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2022; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G+C-content biases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree, version 1.4.4; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2018. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Davenport, J. Synopsis of Biological Data on the Lumpsucker, Cyclopterus lumpus (Linnaeus, 1758); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ap950e/ap950e.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Martínez, P.; Viñas, A.M.; Sánchez, L.; Díaz, N.; Ribas, L.; Piferrer, F. Genetic architecture of sex determination in fish: Applications to sex ratio control in aquaculture. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taslima, K.; Wehner, S.; Taggart, J.B.; de Verdal, H.; Benzie, J.A.H.; Bekaert, M.; McAndrew, B.J.; Penman, D.J. Sex determination in the GIFT strain of tilapia is controlled by a locus in linkage group 23. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shi, H.; Zeng, S.; Ye, K.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, L.; Sun, L.; Tao, W.; et al. A tandem duplicate of anti-Müllerian hormone with a missense SNP on the Y Chromosome is essential for male sex determination in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshel, O.; Shirak, A.; Dor, L.; Band, M.; Zak, T.; Markovich-Gordon, M.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Feldmesser, E.; Weller, J.I.; Seroussi, E.; et al. Identification of male-specific amh duplication, sexually differentially expressed genes and microRNAs at early embryonic development of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Xiao, S.; Xu, S.; Ye, K.; Lin, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z. Identification of a male-specific DNA marker in the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 2017, 480, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Xie, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, X.; Fitzpatrick, C.K.; Vaux, F.; O’Malley, K.G.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, J.; He, Y. A duplicated amh is the master sex-determining gene for Sebastes rockfish in the Northwest Pacific. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 210063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dai, S.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, M.; Tan, D.; Pu, D.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Roles of anti-Müllerian hormone and its duplicates in sex determination and germ cell proliferation of Nile tilapia. Genetics 2022, 220, iyab237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Robichaud, D.; Peterson, R.H.; Benfey, T.J.; Crim, L.W. Direct feminization of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) using 17β-oestradiol-enriched Artemia as food. Aquaculture 1994, 123, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, R.S.; Somoza, G.M.; Fernandino, J.I.; Colautti, D.C.; Miyoshi, K.; Gong, Z.; Yamamoto, Y.; Strüssmann, C.A. The duplicated Y-specific amhy gene is conserved and linked to maleness in Silversides of the genus Odontesthes. Genes 2019, 10, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sarida, M.; Hattori, R.S.; Strüssmann, C.A. Coexistence of genotypic and temperature-dependent sex determination in pejerrey Odontesthes bonariensis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bej, D.K.; Miyoshi, K.; Hattori, R.S.; Strüssmann, C.A.; Yamamoto, Y. A duplicated, truncated amh gene is involved in male sex determination in an Old World silverside. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2017, 7, 2489–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardell, J.M.; Josephson, M.P.; Dalziel, A.C.; Peichel, C.L.; Kirkpatrick, M. Heterogeneous histories of recombination suppression on stickleback sex chromosomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 4403–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peichel, C.L.; McCann, S.R.; Ross, J.A.; Naftaly, A.F.S.; Urton, J.R.; Cech, J.N.; Grimwood, J.; Schmutz, J.; Myers, R.M.; Kingsley, D.M.; et al. Assembly of the threespine stickleback Y chromosome reveals convergent signatures of sex chromosome evolution. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Kay, T.; Depincé, A.; Adolfi, M.; Schartl, M.; Guiguen, Y.; Herpin, A. Evolution of master sex determiners: TGF-β signalling pathways at regulatory crossroads. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpin, A.; Braasch, I.; Kraeussling, M.; Schmidt, C.; Thoma, E.C.; Nakamura, S.; Tanaka, M.; Schartl, M. Transcriptional rewiring of the sex determining dmrt1 gene duplicate by transposable elements. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, U.; Herpin, A.; Schartl, M. Expression of the male determining gene dmrt1bY and its autosomal coorthologue dmrt1a in medaka. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.F.; Clyburne, S. New cell line from the marine lumpfish, Cyclopterus lumpus. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1977, 34, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, R.; Zahm, M.; Cabau, C.; Klopp, C.; Roques, C.; Bouchez, O.; Eché, C.; Valière, S.; Donnadieu, C.; Haffray, P.; et al. Characterization of a Y-specific duplication/insertion of the anti-Mullerian hormone type II receptor gene based on a chromosome-scale genome assembly of yellow perch, Perca flavescens. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.P. Evolution of sex determination and sex chromosomes: A novel alternative paradigm. BioEssays 2020, 42, 1900212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myosho, T.; Takehana, Y.; Hamaguchi, S.; Sakaizumi, M. Turnover of sex chromosomes in Celebensis group medaka fishes. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woram, R.; Gharbi, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Høyheim, B.; Holm, L.; Naish, K.; Mcgowan, C.; Ferguson, M.; Phillips, R.; Stein, J.; et al. Comparative genome analysis of the primary sex-determining locus in salmonid fishes. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Set | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| AMH1_E3I6 | TTTGACCTCCCACCGTTTAC | TATGCCCTCGTGTTGATTCC |
| AMH2_I6E4 | GAGCCGGATTACTGACAGAC | GAAAAGCACAAGAGGGCAAC |
| AMH3_E3I6 | TCGTGTTGACCTTTGACCTC | GGGATGTGGACTAAAGGAGC |
| AMH1+3_E6I6 | GTCATACGGGAGGAGCAAGT | CTCGTTCCCACCACAGATCT |
| Primer Set | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 4K_Up | ACCGGAAGAGTGAGCTTTGA | GTTAAGGGCCCCAAAACAGG |
| 6K_Up | TTTAAGCGGCGGAAAGATCG | CTGAGTTTGGAAGGCTGCTC |
| 10K_Up | ACCCTGAAGAAGCACCTCTC | CATCTGTATGGTTCGCGCAA |
| 4K_Down | TGCGCCAGAAGTTTTCCAAA | GGGATCTCTGTCTACACATGC |
| 14K_Down | CAACAGGTCGATGCAGATGG | GCAGCAGAAAACGTCAGGAA |
| 16K_Down | AAACAACGACAGGTCAGTGC | CAGCAACACACTCCAAACGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaiyasut, K.; Merviel, P.; Palma, P.; Perschthaler, J.; Jimenez-Fernandez, E.; Davie, A.; Gutierrez, A.P. Development of an Accurate Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assay for Genetic Sex Identification in Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) Based on Male-Specific Anti-Mullerian Hormone (amh) Gene. Fishes 2023, 8, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060327
Chaiyasut K, Merviel P, Palma P, Perschthaler J, Jimenez-Fernandez E, Davie A, Gutierrez AP. Development of an Accurate Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assay for Genetic Sex Identification in Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) Based on Male-Specific Anti-Mullerian Hormone (amh) Gene. Fishes. 2023; 8(6):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060327
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaiyasut, Kasidis, Paul Merviel, Peter Palma, Johanna Perschthaler, Eduardo Jimenez-Fernandez, Andrew Davie, and Alejandro P. Gutierrez. 2023. "Development of an Accurate Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assay for Genetic Sex Identification in Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) Based on Male-Specific Anti-Mullerian Hormone (amh) Gene" Fishes 8, no. 6: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060327
APA StyleChaiyasut, K., Merviel, P., Palma, P., Perschthaler, J., Jimenez-Fernandez, E., Davie, A., & Gutierrez, A. P. (2023). Development of an Accurate Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assay for Genetic Sex Identification in Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) Based on Male-Specific Anti-Mullerian Hormone (amh) Gene. Fishes, 8(6), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060327