Resource Partitioning of Sympatric Lutjanids in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Using Stable Isotope Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spies, R.B.; Senner, S.; Robbins, C.S. An overview of the northern Gulf of Mexico ecosystem. Gulf Mex. Sci. 2016, 1, 98–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnauskas, M.; Walter, J.F., III; Campbell, M.D.; Pollack, A.G.; Drymon, J.M.; Powers, S. Red snapper distribution on natural habitats and artificial structures in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2017, 9, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelcheck, A.J.; Cowan, J.H., Jr.; Shah, A. Influence of reef location on artificial-reef fish assemblages in the northcentral Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2005, 77, 425–440. [Google Scholar]
- Dance, M.A.; Patterson, W.F., III; Addis, D.T. Fish community and trophic structure at artificial reef sites in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2011, 87, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajemian, M.J.; Wetz, J.J.; Shipley-Lozano, B.; Shively, J.D.; Stunz, G.W. An analysis of artificial reef fish community structure along the northwestern Gulf of Mexico shelf: Potential impacts of “rigs-to-reefs” programs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, S.B.; Boswell, K.M.; Lewis, J.P.; Tarnecki, J.H.; Patterson, W.F., III. Effect of reef morphology and depth on fish community and trophic structure in the northcentral Gulf of Mexico. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 230, 106423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnecki, J.H.; Patterson, W.F., III. Changes in red snapper diet and trophic ecology following the deepwater horizon oil spill. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2015, 7, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dance, K.M.; Rooker, J.R.; Shipley, J.B.; Dance, M.A.; Wells, R.J.D. Feeding ecology of fishes associated with artificial reefs in the northwest Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, K.S.; Fleming, C.R.; Slife, C.; Leaf, R.T. Stable isotopic niche variability and overlap across four fish guilds in the north-central Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2021, 13, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, T.W. Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science 1974, 185, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, T.K.; Lindberg, W.J. Refuge spacing similarly affects reef-associated species from three phyla. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 388–400. [Google Scholar]
- Cachera, M.; Ernande, B.; Villanueva, M.C.; Lefebvre, S. Individual diet variation in a marine fish assemblage: Optimal foraging theory, niche variation hypothesis and functional identity. J. Sea Res. 2017, 120, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, F.; Halpern, B.S. Low functional redundancy in coastal marine assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaber, S.J.M. Feeding selectivity of a guild of piscivorous fish in mangrove areas of north-west Australia. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1986, 37, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixon, M.A.; Jones, G.P. Competition, predation, and density-dependent mortality in demersal marine fishes. Ecology 2005, 86, 2847–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, R.J.; Holbrook, S.J. Gape-limitation, foraging tactics and prey size selectivity of two microcarnivorous species of fish. Oecologia 1984, 63, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, K.J.; Brandt, S.B. Comparative energetics and the development of bioenergetics models for sympatric estuarine piscivores. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 1647–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldonski, N.; Lagrue, C.; Motreuil, S.; Rigaud, T.; Bollache, L. Habitat segregation mediates predation by the benthic fish Cottus gobio on the exotic amphipod species Gammarus roeseli. Naturwissenschaften 2008, 95, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, G. The competitive exclusion principle. Science 1960, 131, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, P.F. Maintenance of high diversity in coral reef fish communities. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, A.C.; Hanson, K.M.; Holbrook, S.J.; Schmitt, R.J.; Brooks, A.J. Predation and landscape characteristics independently affect reef fish community organization. Ecology 2014, 95, 1294–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, J.E. The effects of differential digestion rates of zooplankton by alewife, Alosa pseudoharengus, on determinations of selective feeding. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1976, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.; Duffy, D.C.; Jenkins, J.F.G. Gastric digestion in marine vertebrate predators: In vitro standards. Funct. Ecol. 1987, 1, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnio, K.; Bonsdorff, E. Passing the gut of juvenile flounder, Platichthys flesus: Differential survival of zoobenthic prey species. Mar. Biol. 1997, 129, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, E.J.; Murie, D.J. Differential digestion and evacuation rates of prey in a warm-temperate grouper, gag Mycteroperca microlepis (Goode & Bean). J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 1406–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, K.A.; Patterson, W.F., III. Habitat-specific density and diet of rapidly expanding invasive red lionfish, Pterois volitans, populations in the northern Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.P.; Tarnecki, J.H.; Garner, S.B.; Chagaris, D.D.; Patterson, W.F., III. Changes in reef fish community structure following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Fry, B. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderklift, M.A.; Ponsard, S. Sources of variation in consumer-diet δ15N enrichment: A meta-analysis. Oecologia 2003, 136, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Zanden, M.J.; Rasmussen, J.B. Variation in δ15N and δ13C trophic fractionation: Implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.; Sherr, E.B. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 1984, 27, 13–47. [Google Scholar]
- Daigle, S.T.; Fleeger, J.W.; Cowan, J.H., Jr.; Pascal, P. What is the relative importance of phytoplankton and attached macroalgae and epiphytes to food webs on offshore oil platforms? Mar. Coast. Fish. 2013, 5, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.E. Food habits of reef fishes of the West Indies. Stud. Trop. Oceanogr. 1967, 5, 665–847. [Google Scholar]
- Marancik, K.E.; Hare, J.A. An annotated bibliography of diet studies of fish of the southeast United States and Gray’s Reef National Marine Sanctuary. In Marine Sanctuaries Conservation Series; NOAA/National Ocean Service/Marine Sanctuaries Division: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2005; p. MSD-05. [Google Scholar]
- Rastorgueff, P.-A.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; Richard, P.; Chevaldonné, P. Feeding strategies and resource partitioning mitigate the effects of oligotrophy for marine cave mysids. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 440, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, C.B. Diet and feeding ecology of the vermilion snapper, Rhomboplites aurorubens (Cuvier) from North Carolina and South Carolina waters. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1979, 29, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Sedberry, G.R.; Cuellar, N. Planktonic and benthic feeding by the reef-associated vermilion snapper, Rhomboplites aurorubens (Telostei, Lutjanidae). Fish. B-NOAA 1993, 91, 699–709. [Google Scholar]
- Bortone, S.A.; Cody, R.P.; Turpin, R.K.; Bundrick, C.M. The impact of artificial-reef fish assemblages on their potential forage area. Ital. J. Zool. 1998, 65, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeds, K.A.; Smith, J.A.; Suthers, I.M.; Johnston, E.L. An ecological halo surrounding a large offshore artificial reef: Sediments, infauna, and fish foraging. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 141, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, J.S.; VanderKooy, K.E. Feeding habits of juvenile lane snapper Lutjanus synagris from Mississippi coastal waters, with comments on the diet of gray snapper Lutjanus griseus. Gulf Caribb. Res. 2000, 12, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.J.D.; Cowan, J.H., Jr.; Fry, B. Feeding ecology of red snapper Lutjanus campechanus, in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 361, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B. Coupled N, C, and S stable isotope measurements using a dual-column gas chromatography system. Rapid Commun. Mass Sp. 2007, 21, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Parnell, A.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNiro, M.J.; Epstein, S. Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 42, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, L.; Crowder, L.B. Fish-habitat interactions mediated via ontogenetic niche shifts. In The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, B.W.; Wilson, D.S. Optimal foraging, specialization, and a solution to Liem’s paradox. Am. Nat. 1998, 151, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloca, F.; Carpentieri, P.; Balestri, E.; Adizzone, G. Food resource partitioning in a Mediterranean demersal fish assemblage: The effect of body size and niche width. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.O.; García, C.B. Diet of the Lane Snapper, Lutjanus synagris (Lutjanidae), in the Gulf of Salamanca, Colombia. Caribb. J. Sci. 1999, 35, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q.; Wiseman, W.J., Jr.; Sen Gupta, B.K. Nutrient changes in the Mississippi River and system responses on the adjacent continental shelf. Estuaries 1996, 19, 386–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radabaugh, K.R.; Hollander, D.J.; Peebles, E.B. Seasonal δ13C and δ15N isoscapes of fish populations along a continental shelf trophic gradient. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 68, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breed, G.A.; Jackson, G.A.; Richardson, T.L. Sedimentation, carbon export and food web structure in the Mississippi River plume described by inverse analyses. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 278, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, B.; Fry, B. Tracing Mississippi River influences in estuarine food webs of coastal Louisiana. Oecologia 2005, 144, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado, S.; Rooker, J.R.; Wissel, B.; Quigg, A. Isotope baseline shifts in pelagic food webs of the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 464, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, S.; Hobbie, J.E.; Elmgren, R.; Larsson, U.; Fry, B.; Johansson, S. The stable nitrogen isotope ratio as a marker of food-web interactions and fish migration. Ecology 1997, 78, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerot, C.; Lorrain, A.; Grall, J.; Gillikin, D.P.; Munaron, J.-M.; Le Bris, H.; Paulet, Y.-M. Stable isotope variations in benthic filter feeders across a large depth gradient on the continental shelf. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, B.N.; Laws, E.A.; Bidigare, R.R.; Dore, J.E.; Hanson, K.L.; Wakeham, S.G. Effect of phytoplankton cell geometry on carbon isotopic fractionation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Wolf-Gladrow, D.A.; Takahashi, T.; Sutherland, S.C.; Six, K.D.; Maier-Reimer, E. Stable carbon isotope distribution of particulate organic matter in the ocean: A model study. Mar. Chem. 2000, 72, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, M.R.; Bernhardt, P.W.; Heil, C.A.; Bronk, D.A.; O’Neil, J.M. Nitrogen fixation and release of fixed nitrogen by Trichodesmium spp. In the Gulf of Mexico. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1762–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.T.; Drymon, J.M.; Powers, S.P. Spatial and dietary overlap creates potential for competition between red snapper (Lutjanus campechanus) and vermilion snapper (Rhomboplites aurorubens). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, N.A.; Ault, J.S. Grouper and snapper movements and habitat use in Dry Tortugas, Florida. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 433, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, D.T.; Szedlmayer, S.T. Home range and movement patterns of red snapper (Lutjanus campechanus) on artificial reefs. Fish. Res. 2011, 112, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Grove, L.J.; Szedlmayer, S.T. Depth preferences and three-dimensional movements of red snapper, Lutjanus campechanus, on an artificial reef in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Fish. Res. 2017, 190, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohaboy, E.C.; Cass-Calay, S.L.; Patterson, W.F., III. Fine-scale movement of northern Gulf of Mexico red snapper and gray triggerfish estimated with three-dimensional acoustic telemetry. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Zanden, M.J.; Clayton, M.K.; Moody, E.K.; Solomon, C.T.; Weidel, B.C. Stable isotope turnover and half-life in animal tissues: A literature synthesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alldredge, A.L.; King, J.M. Distribution, abundance, and substrate preferences of demersal reef zooplankton at Lizard Island Lagoon, Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 1977, 41, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, C.A.; Greenwood, J.G. Emergent zooplankton in Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia: Seasonal, lunar, and diel patterns in emergence and distribution with respect to substrata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 51, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacheler, N.M.; Shertzer, K.W.; Runde, B.J.; Rudershausen, P.J.; Buckel, J.A. Environmental conditions, diel period, and fish size influence the horizontal and vertical movements of red snapper. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, D.E.; Parma, A.M.; Iribarne, O.O. Influence of predatory reef fishes on the spatial distribution of Munidia gregaria (=M. subrugosa) (Crustacea; Galatheidae) in shallow Patagonian soft bottoms. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 354, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.D.; Rose, K.; Boswell, K.; Cowan, J., Jr. Individual-based modeling of an artificial reef fish community: Effects of habitat quantity and degree of refuge. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3895–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, T.D.; Kidd, K.A.; Fisk, A.T. Applications, considerations, and sources of uncertainty when using stable isotope analysis in ecotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7501–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeil, M.A.; Drouillard, K.G.; Fisk, A.T. Variable uptake and elimination of stable nitrogen isotopes between tissues in fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheister, A.; Latour, R.J. Turnover and fractionation of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes in tissues of a migratory coastal predator, summer flounder (Paralichthys dentatus). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perga, M.E.; Gerdeaux, D. ‘Are fish what they eat’ all year round? Oecologia 2005, 144, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapp Sluis, M.; Boswell, K.M.; Chumchal, M.M.; Wells, R.J.D.; Soulen, B.; Cowan, J.H., Jr. Regional variation in mercury and stable isotopes of red snapper (Lutjanus campechanus) in the northern Gulf of Mexico, USA. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
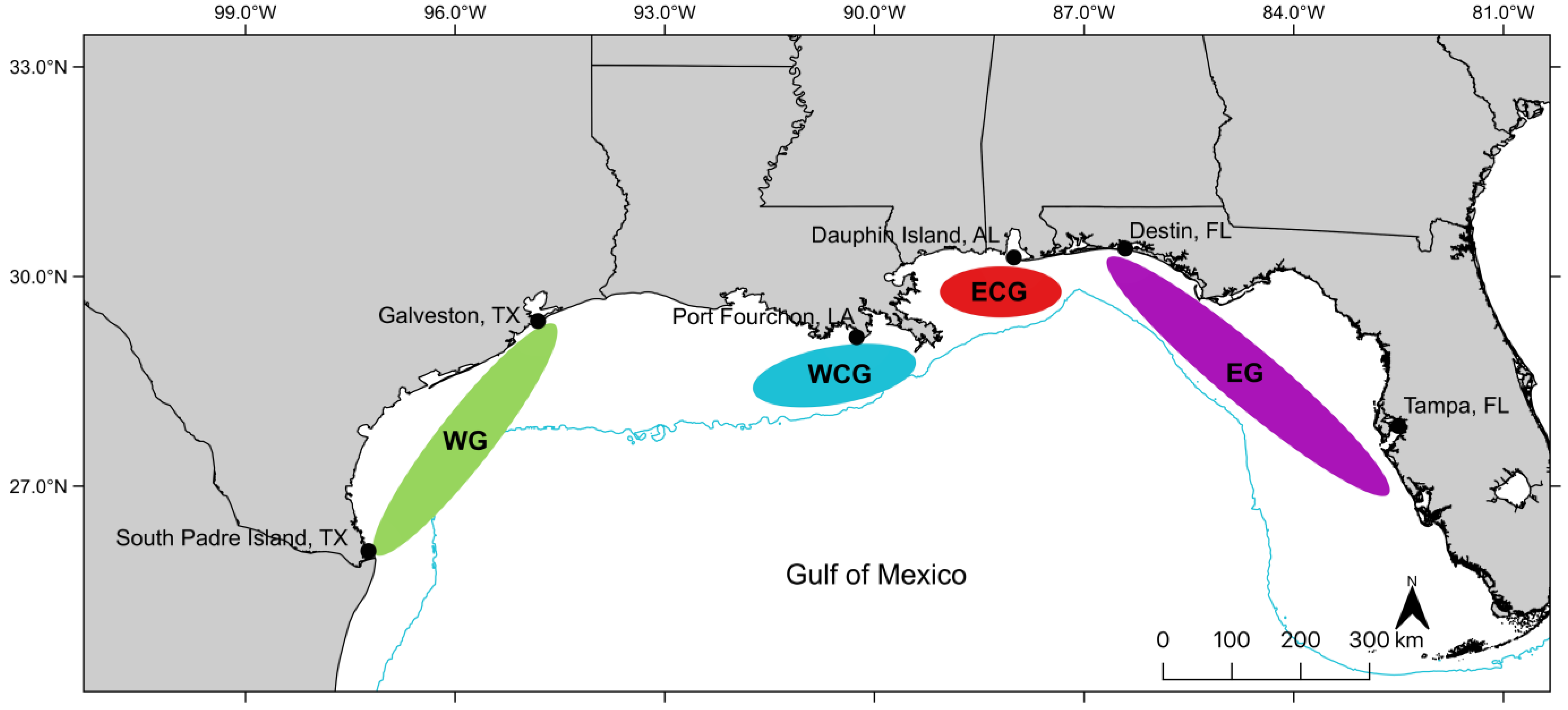
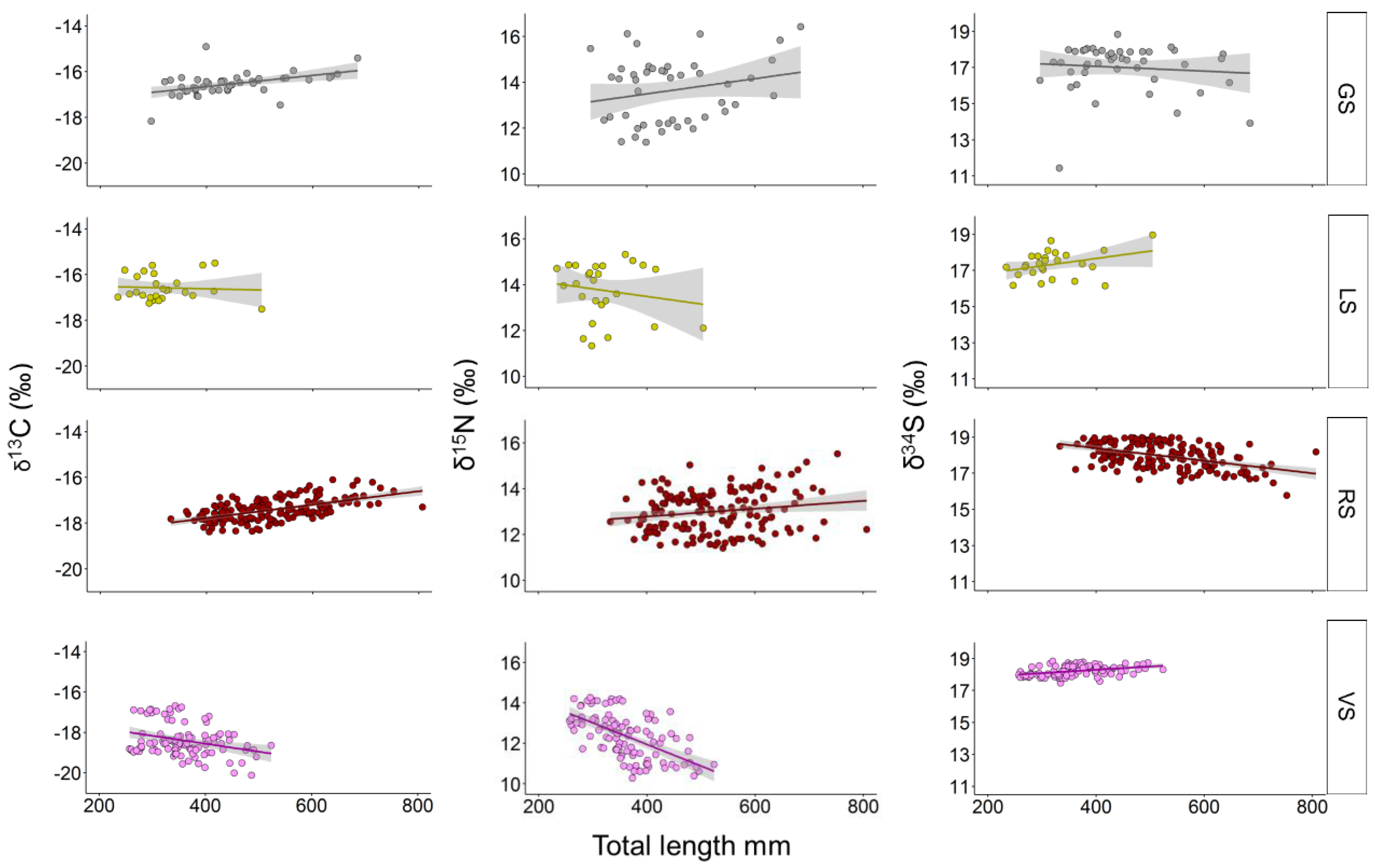
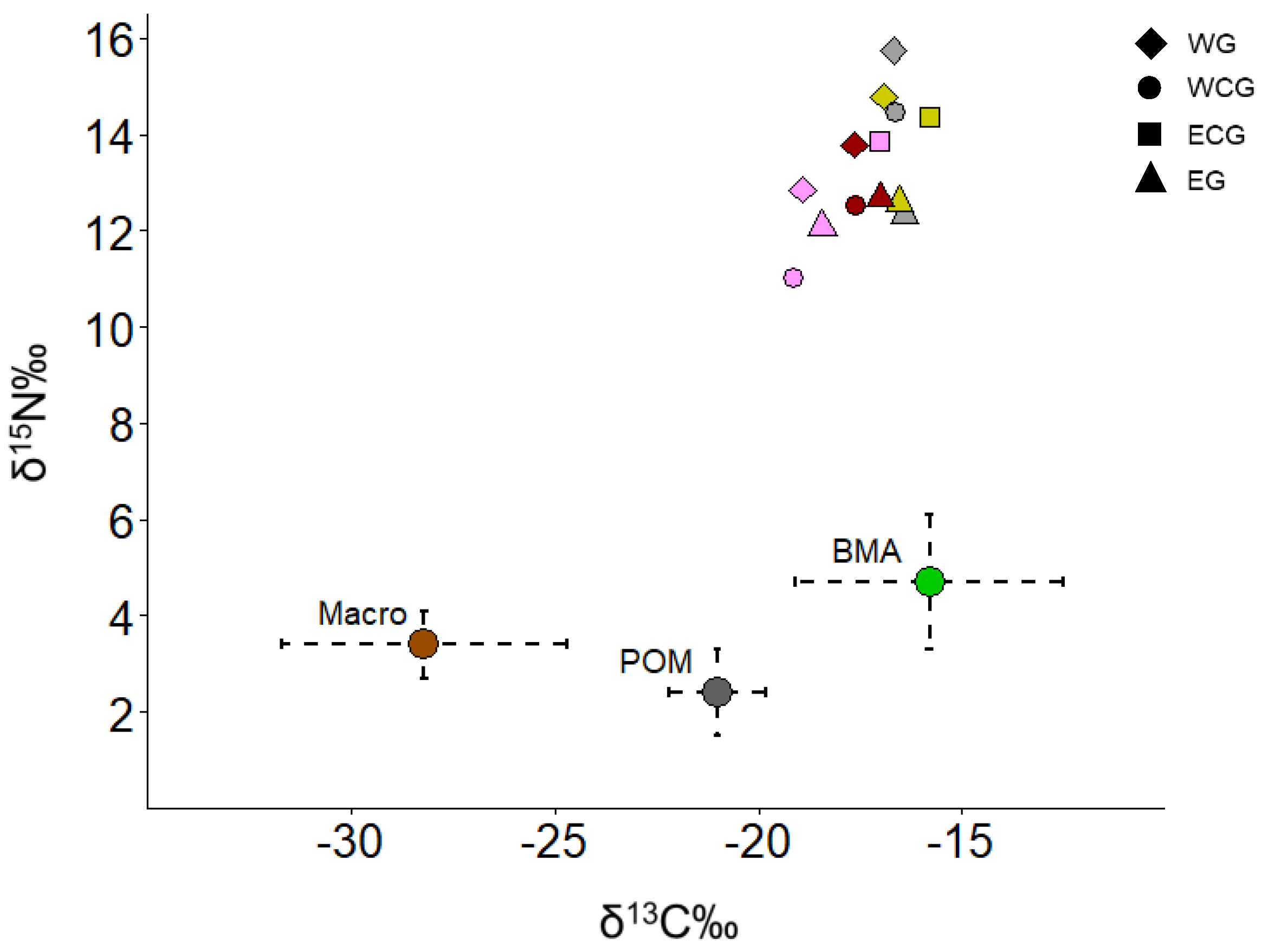
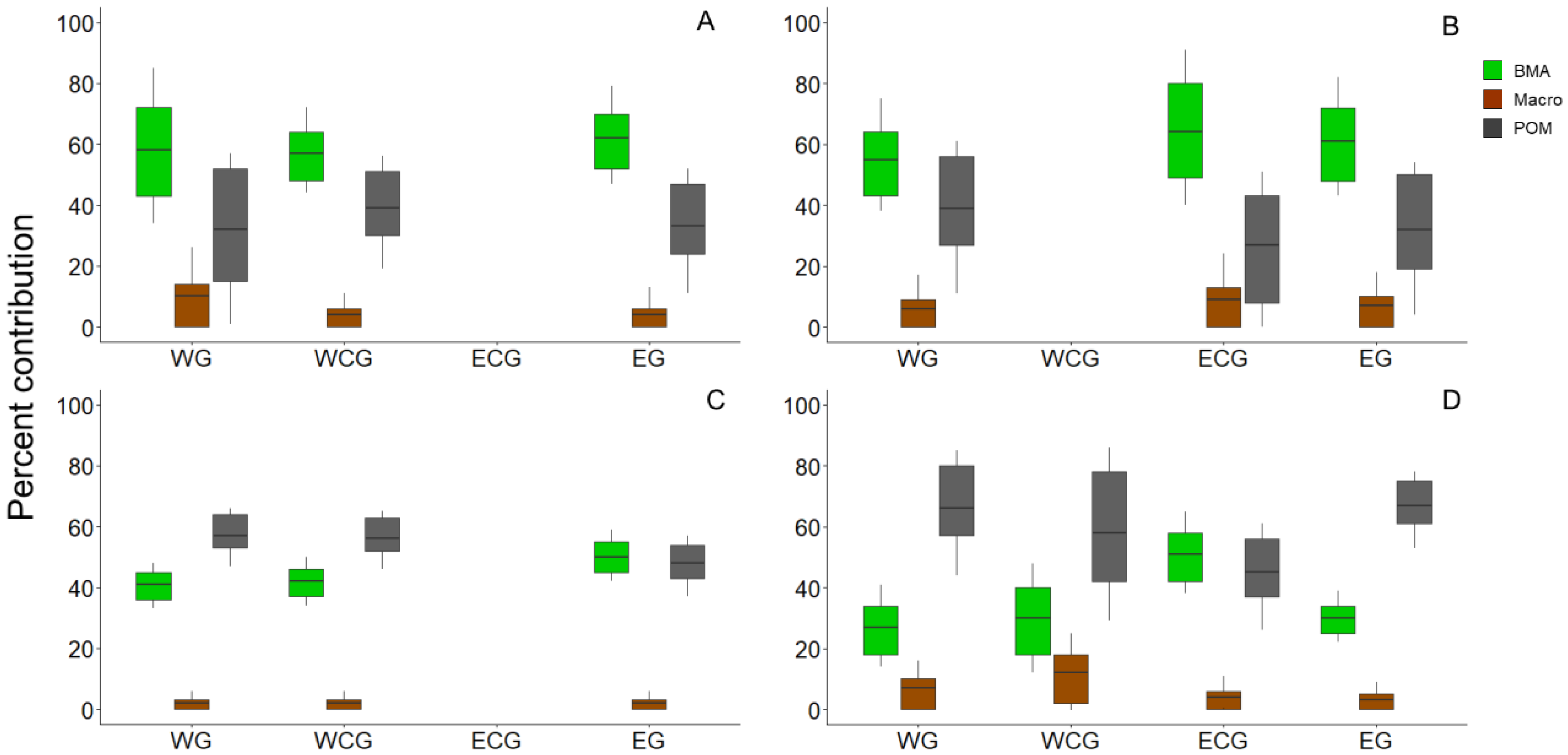

| Species | Region | N | TL | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gray snapper | WG | 5 | 439.4 (69.9) | 296–685 |
| WCG | 20 | 461.3 (20.0) | 335–647 | |
| ECG | 0 | NA | NA | |
| EG | 20 | 434.1 (18.6) | 321–635 | |
| Lane snapper | WG | 10 | 300.9 (13.8) | 233–374 |
| WCG | 2 | 477.5 (26.5) | 451–504 | |
| ECG | 5 | 325.0 (33.8) | 246–416 | |
| EG | 10 | 319.0 (12.3) | 280–414 | |
| Red snapper | WG | 50 | 530.2 (13.4) | 391–753 |
| WCG | 50 | 490.5 (13.6) | 333–807 | |
| ECG | 0 | NA | NA | |
| EG | 50 | 552.1 (11.8) | 415–728 | |
| Vermilion snapper | WG | 20 | 309.4 (10.0) | 257–412 |
| WCG | 21 | 427.6 (10.7) | 357–524 | |
| ECG | 20 | 330.1 (9.1) | 265–407 | |
| EG | 40 | 366.2 (7.9) | 279–479 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garner, S.B.; Zapp Sluis, M.; Wells, R.J.D.; Boswell, K.M.; Cowan, J.H., Jr. Resource Partitioning of Sympatric Lutjanids in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Using Stable Isotope Analysis. Fishes 2023, 8, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050244
Garner SB, Zapp Sluis M, Wells RJD, Boswell KM, Cowan JH Jr. Resource Partitioning of Sympatric Lutjanids in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Using Stable Isotope Analysis. Fishes. 2023; 8(5):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050244
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarner, Steven B., Michelle Zapp Sluis, R. J. David Wells, Kevin M. Boswell, and James H. Cowan, Jr. 2023. "Resource Partitioning of Sympatric Lutjanids in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Using Stable Isotope Analysis" Fishes 8, no. 5: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050244
APA StyleGarner, S. B., Zapp Sluis, M., Wells, R. J. D., Boswell, K. M., & Cowan, J. H., Jr. (2023). Resource Partitioning of Sympatric Lutjanids in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Using Stable Isotope Analysis. Fishes, 8(5), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050244








