Characterization of SNX5 in Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides) during In Vitro Viral Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish, Cell Line and Virus
2.2. Cloning of EcSNX5 and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Plasmids Construction
2.4. Tissue Distribution of EcSNX5
2.5. Temporal Expression of EcSNX5 after RGNNV Infection
2.6. Effects of EcSNX5 on RGNNV Infection
2.7. Subcellular Localization of EcSNX5
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
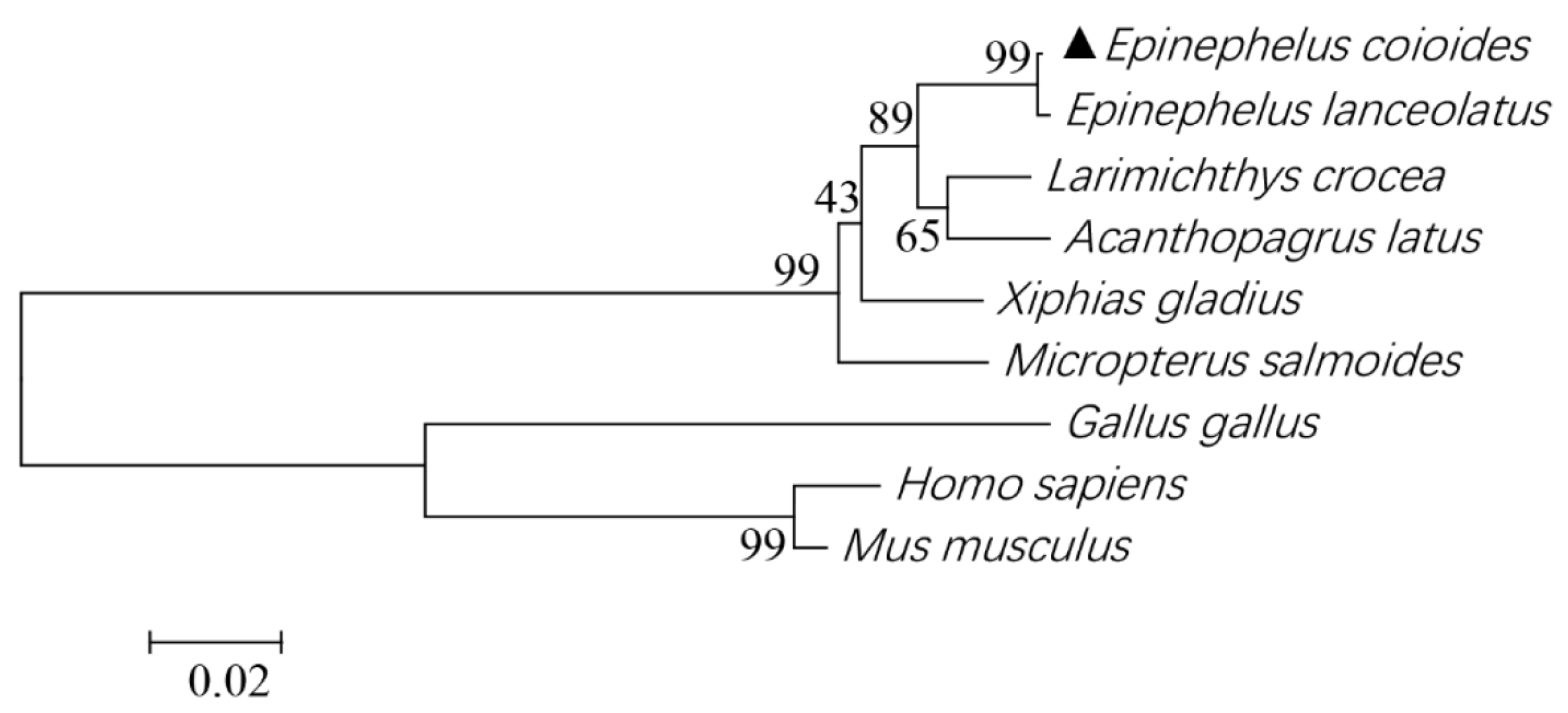
3.1. Sequence Analysis of EcSNX5
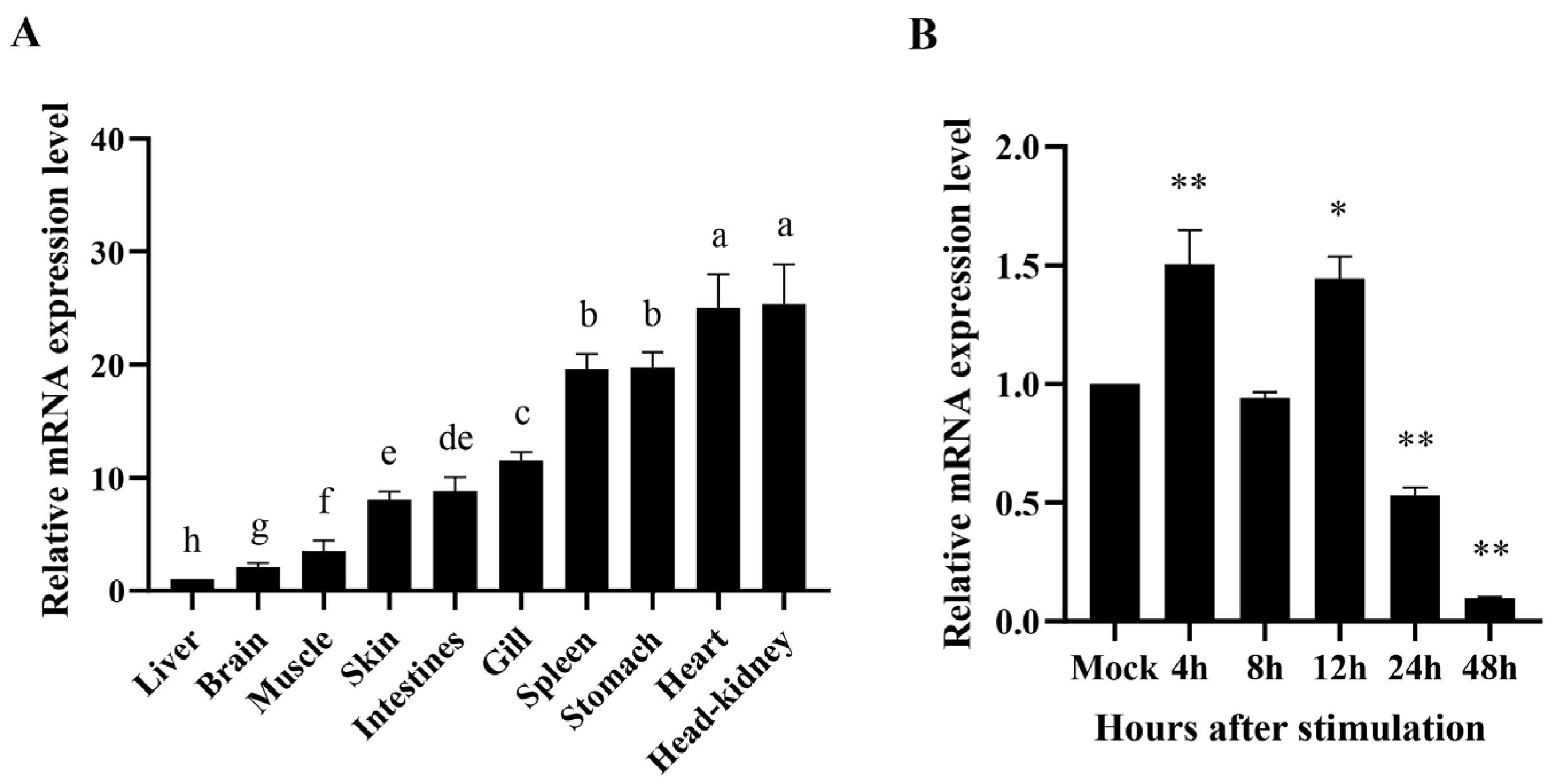
3.2. Tissue Distribution of EcSNX5 Gene
3.3. Expression Pattern of EcSNX5 after RGNNV Stimulation In Vitro
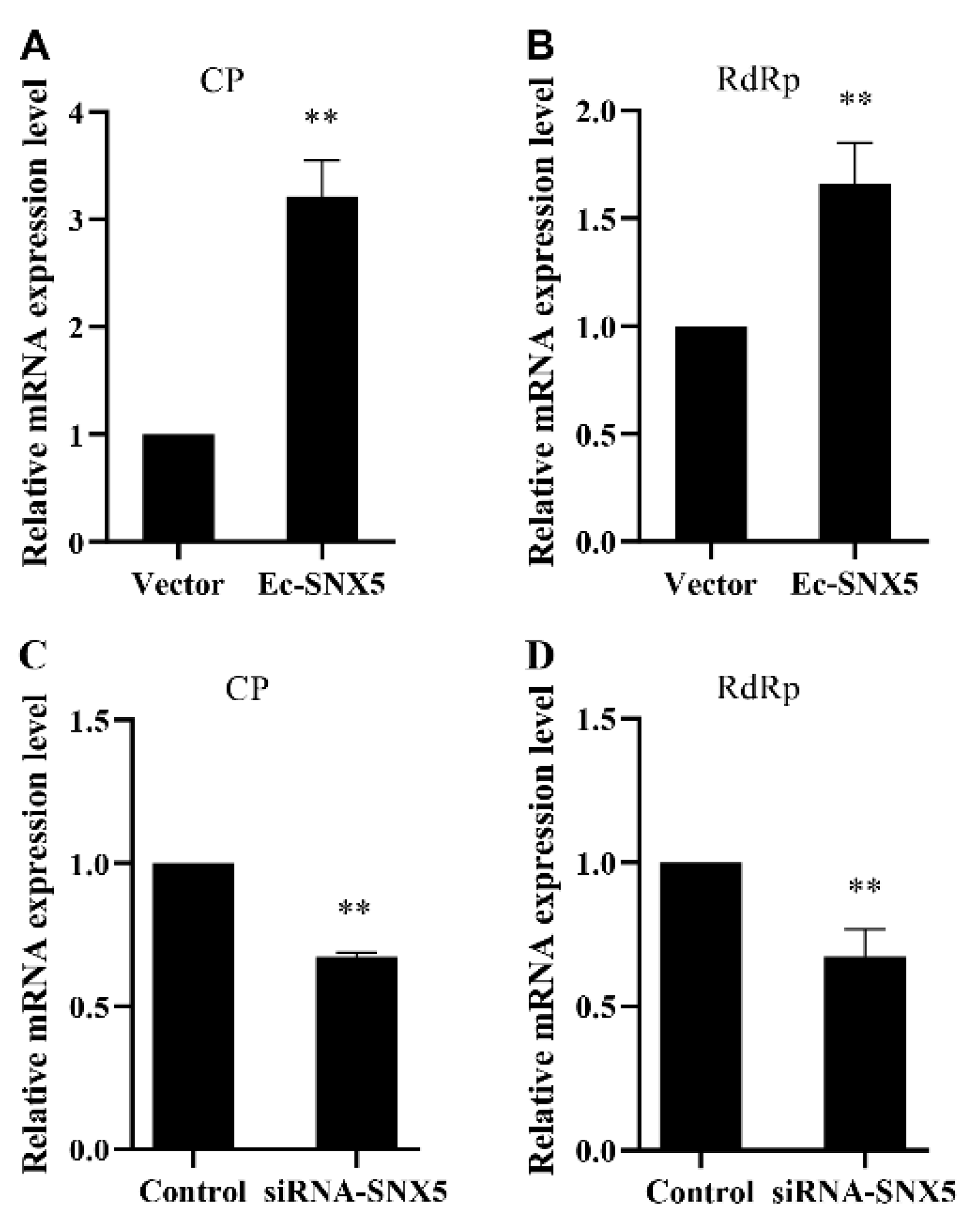
3.4. EcSNX5 Promoted RGNNV Replication
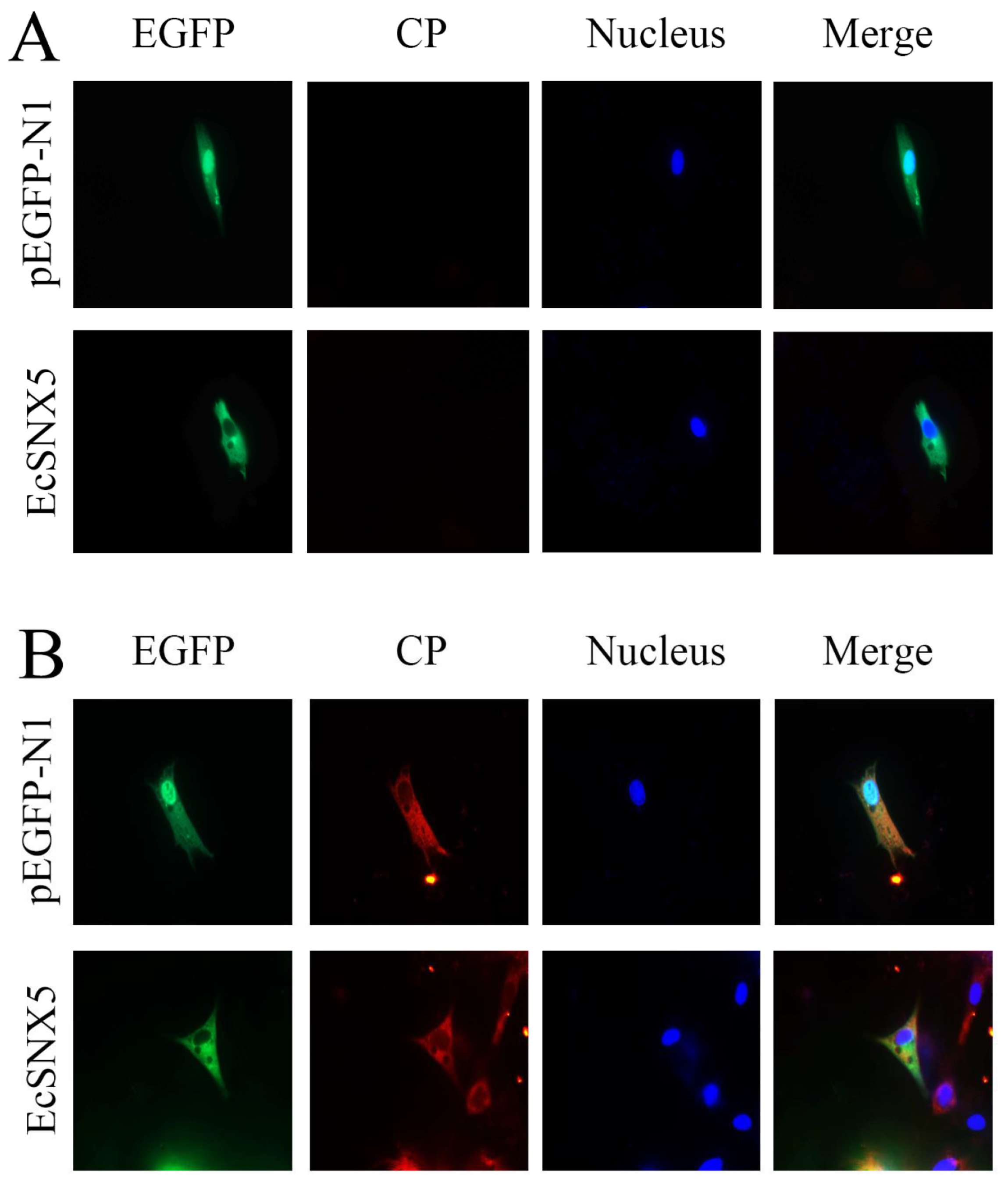
3.5. Co-Localization of EcSNX5 and RGNNV CP
3.6. EcSNX5 Affects Interferon Pathway and Inflammatory Pathway
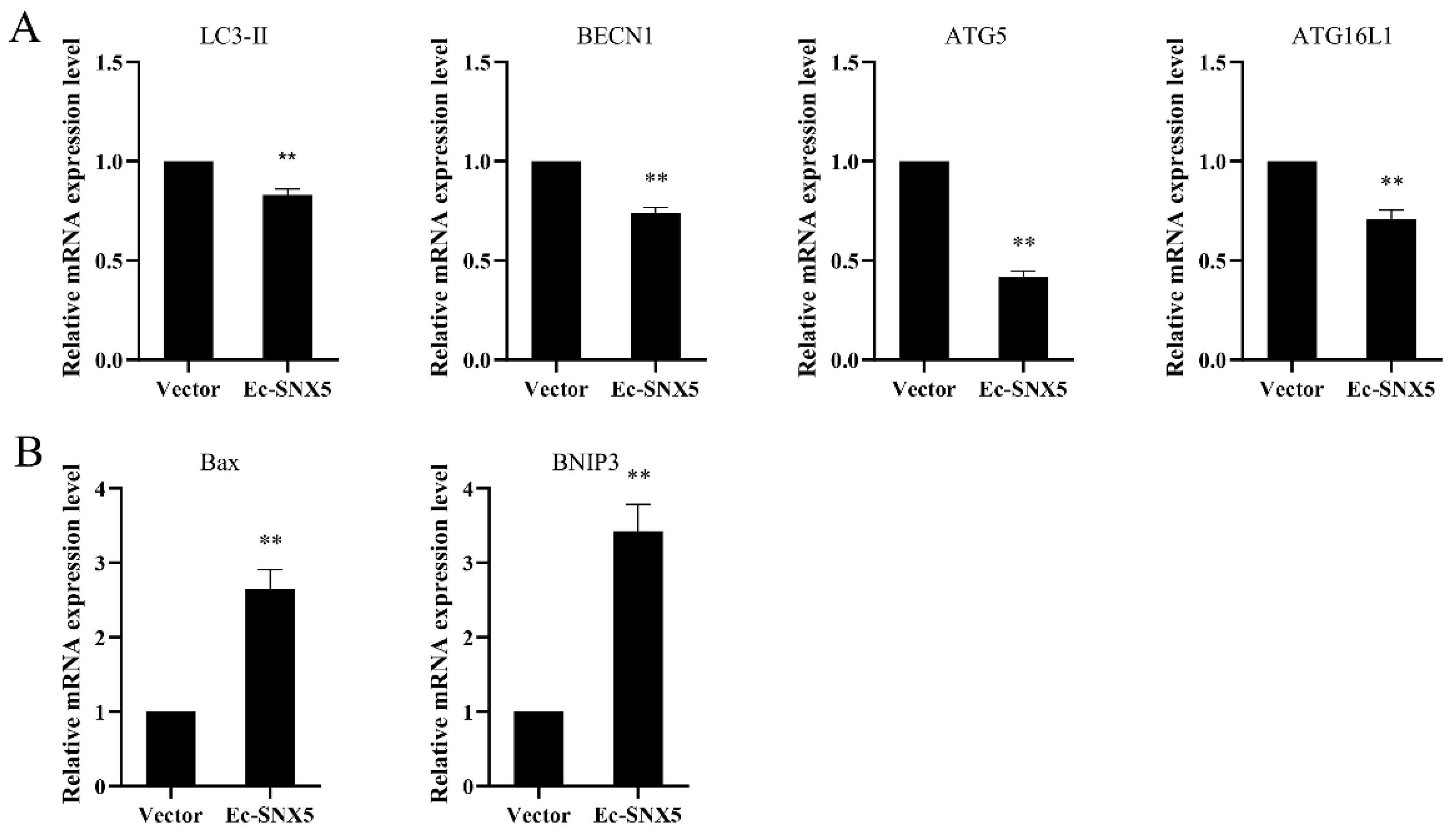
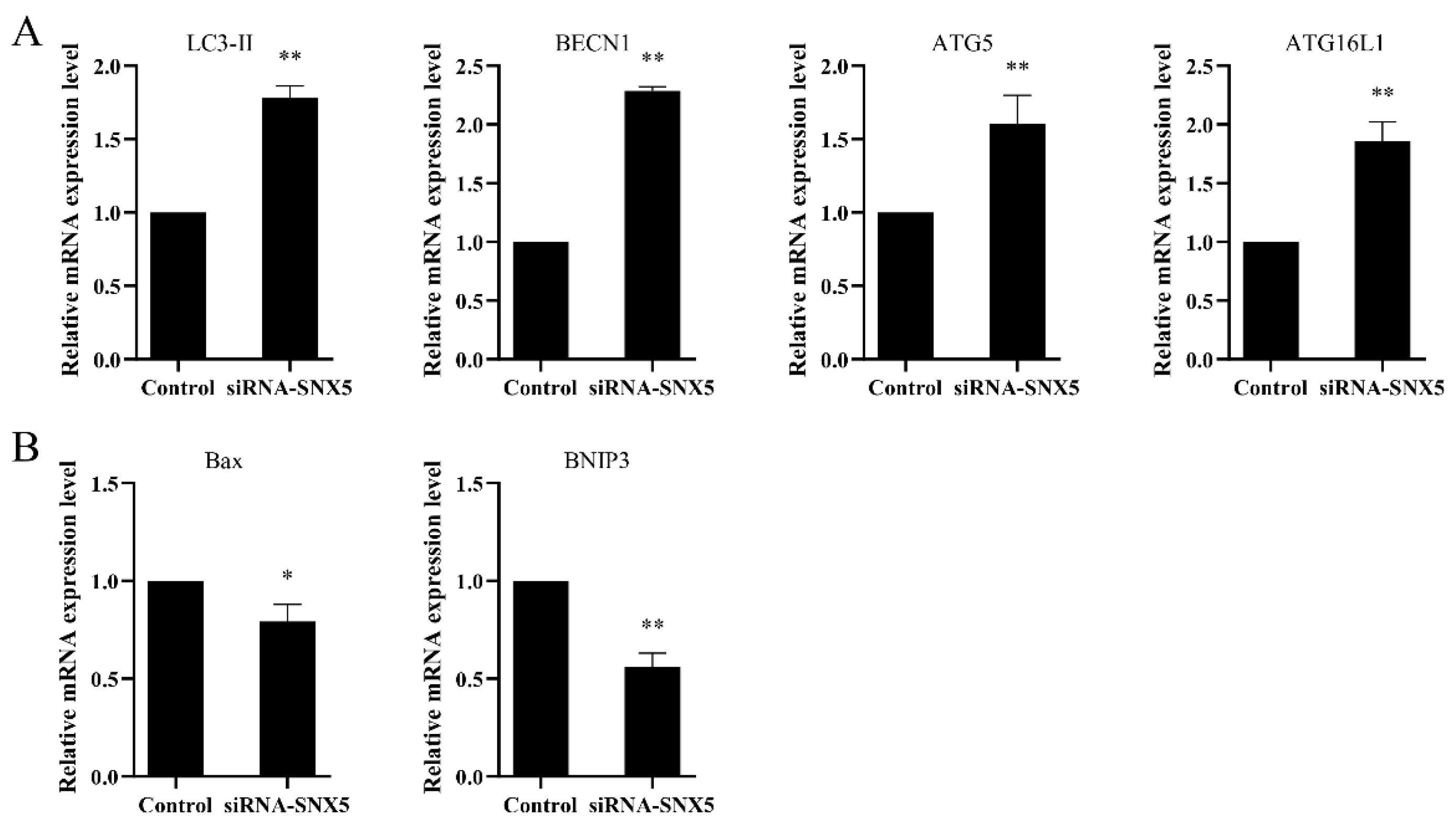
3.7. EcSNX5 Affects the Expression of Autophagy-Related Factors and Apoptosis Factor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cullen, P.J.; Korswagen, H.C. Sorting nexins provide diversity for retromer-dependent trafficking events. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, R.D.; Collins, B.M. Insights into the PX (phox-homology) domain and SNX (sorting nexin) protein families: Structures, functions and roles in disease. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L. The emerging roles of retromer and sorting nexins in the life cycle of viruses. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, V.A.M.; Armando, I.; Sanada, H.; Frazer, L.C.; Russo, C.M.; Notario, P.M.; Lee, H.; Comisky, L.; Russell, H.A.; Yang, Y.; et al. Novel role of sorting nexin 5 in renal D-1 dopamine receptor trafficking and function: Implications for hypertension. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1808–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ci, B.; Zhong, L.; Bhave, M.; Wang, L.; Kuo, Y.C.; Zang, X.; et al. Sorting nexin 5 mediates virus-induced autophagy and immunity. Nature 2021, 589, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Trigo, A.; Kerr, M.C.; Houghton, F.; Lindberg, A.; Mitchell, C.; Teasdale, R.D.; Gleeson, P.A. Sorting nexin 5 is localized to a subdomain of the early endosomes and is recruited to the plasma imembrane following EGF stimulation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 6413–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, X.; Hu, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Burstein, E.; Jia, D. Expression and purification of the SNX1/SNX6 complex. Protein Expr. Purif. 2018, 151, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Z.; Du, W.; Que, H.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Jian, F.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, R.; et al. Recycling of autophagosomal components from autolysosomes by the recycler complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yong, X.; Sun, X.; Yang, F.; Dai, Z.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Niu, D.; Dai, L.; et al. Structural and functional insights into sorting nexin 5/6 interaction with bacterial effector IncE. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, X.; Zhao, L.; Deng, W.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Mao, L.; Hu, W.; Shen, X.; Sun, Q.; Billadeau, D.D.; et al. Mechanism of cargo recognition by retromer-linked SNX-BAR proteins. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wei, S.; Yu, D.; Song, R.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Qin, Q.; Jian, J. BNIP3, a cell pro-apoptotic protein, involved in response to viral infection in orange spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyano, K.; Amagai, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Mushirobira, Y.; Xu, W.-G.; Pham, N.T.; Murata, R. Endocrine Regulation of Maturation and Sex Change in Groupers. Cells 2022, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariff, N.; Abdullah, A.; Azmai, M.N.A.; Musa, N.; Zainathan, S.C. Risk factors associated with viral nervous necrosis in hybrid groupers in Malaysia and the high similarity of its causative agent nervous necrosis virus to reassortant red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus/striped jack nervous necrosis virus strains. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Qin, Q.; Huang, X. Metabolic profiles of fish nodavirus infection in vitro: RGNNV induced and exploited cellular fatty acid synthesis for virus infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.D.; Shi, C.Y.; Huang, J.; Shen, G.M.; Li, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Fan, C. Establishment and application of cross-priming isothermal amplification coupled with lateral flow dipstick (CPA-LFD) for rapid and specific detection of red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Qin, Q.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals different host cell responses to Singapore grouper iridovirus and red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 128, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Chen, W.; Fu, X.; Lin, Q.; Chang, O.; Zhao, L.; Lan, J.; Li, N.; Lin, L. Susceptibility of Chinese Perch Brain (CPB) Cell and Mandarin Fish to Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-P.; Wu, J.-L.; Su, Y.-C.; Hong, J.-R. Anti-Bcl-2 family members, zfBcl-x(L) and zfMcl-1a, prevent cytochrome c release from cells undergoing betanodavirus-induced secondary necrotic cell death. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1043–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jia, K.; Jia, P.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, W.; Yi, M. Marine medaka heat shock protein 90ab1 is a receptor for red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus and promotes virus internalization through clathrin-mediated endocytosis. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. RGNNV-induced cell cycle arrest at G1/S phase enhanced viral replication via p53-dependent pathway in GS cells. Virus Res. 2018, 256, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Jiang, S.; Yi, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, L.; Zhao, L.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Tu, J.; Lin, L. Glutamine is required for red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus replication via replenishing the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Virus Res. 2017, 227, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, X.; Qin, Q. Characterization of two grouper Epinephelus akaara cell lines: Application to studies of Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) propagation and virus-host interaction. Aquaculture 2009, 292, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Yu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhou, L.; Wei, S.; Yan, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Qin, Q. MicroRNA-146a promotes red spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) replication by targeting TRAF6 in orange spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Cai, J.; Tang, J.; Xia, L.; Li, P.; Jian, J. Identification of BAG5 from orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) involved in viral infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 116, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Xu, S.F.; Han, C.Z.; Qin, Q.W.; Wei, S.N. High-density lipoproteins negatively regulate innate immunity and facilitate red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus entry via scavenger receptor B type 1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, K.-W.; Kim, E.-H.; Jung, S.-H.; Rhee, M.; Koo, B.-K.; Yoon, K.-J.; Kong, Y.-Y.; Kim, C.-H. Snx5, as a Mind bomb-binding protein, is expressed in hematopoletic and endothelial precursor cells in zebrafish. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 4409–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, T.; Xie, T.; Yang, Y.-X.; He, T.-S.; Xu, L.-G. SNX5 inhibits RLR-mediated antiviral signaling by targeting RIG-I-VISA signalosome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchman, R.; Kilianski, A.; Piper, A.; Vancini, R.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Sprague, T.R.; Nasar, F.; Boyd, G.; Hernandez, R.; Glaros, T. Comparative Characterization of the Sindbis Virus Proteome from Mammalian and Invertebrate Hosts Identifies nsP2 as a Component of the Virion and Sorting Nexin 5 as a Significant Host Factor for Alphavirus Replication. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00694-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-C.; Wu, J.-L.; Hong, J.-R. Betanodavirus up-regulates chaperone GRP78 via ER stress: Roles of GRP78 in viral replication and host mitochondria-mediated cell death. Apoptosis 2010, 16, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-L.; Liu, Y.-T.; Chen, M.-C.; Wu, J.-L.; Hong, J.-R. Zebrafish anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-xL can prevent aquatic birnavirus-induced cell death in fish cells without affecting expression of viral proteins. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 31, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, X.; Pan, H.; Yi, M.; Jia, K. The Capsid Protein of Nervous Necrosis Virus Antagonizes Host Type I IFN Production by a Dual Strategy to Negatively Regulate Retinoic Acid–Inducible Gene-I–like Receptor Pathways. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschkowitz, G.; Gaertner, S.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Fickenscher, H.; Winkler, M. Interaction of Human Cytomegalovirus Tegument Proteins ppUL35 and ppUL35A with Sorting Nexin 5 Regulates Glycoprotein B (gpUL55) Localization. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00013-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jia, D.; Ren, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Guo, S.; Wei, T. VDAC1 balances mitophagy and apoptosis in leafhopper upon arbovirus infection. Autophagy 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z. Overexpression of lncRNA HOXA-AS2 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by mediating SNX5 expression. BMC Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wei, J.; Qin, Q. Red grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) induces autophagy to promote viral replication. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Size |
|---|---|---|
| EcSNX5-ORF-F | ATGACATCCACAATAGACGAAAG | 1236 bp |
| EcSNX5-ORF-R | CTTGGTAATGGCAGGACATGGAT | |
| pcDNA-EcSNX5-F | CCGCTCGAGATGACATCCACAATAGACGAAAG | 1255 bp |
| pcDNA-EcSNX5-R | CCGGAATTCCCTTGGTAATGGCAGGACATGGAT | |
| EcSNX5-RT-F | TCCACAATAGACGAAAGCAAT | 136 bp |
| EcSNX5-RT-R | GGACAGTAAACTTGACTTTATCCC | |
| 18S–RT-F | ATTGACGGAAGGGCACCACCAG | 158 bp |
| 18S-RT-R | TCGCTCCACCAACTAAGAACGG | |
| RGNNV-CP-RT-F | CAACTGACAACGATCACACCTTC | 162 bp |
| RGNNV-CP-RT-R | CAATCGAACACTCCAGCGACA | |
| RGNNV-RdRp-RT-F | GTGTCCGGAGAGGTTAAGGATG | 192 bp |
| RGNNV-RdRp-RT-R | CTTGAATTGATCAACGGTGAACA | |
| EcIRF1-RT-F | AGGGAGCCAGTGGAGTGAATC | 457 bp |
| EcIRF1-RT-R | GATGCCTGTGCCCAAAGTTAT | |
| EcIRF3-RT-F | ATGGTTTAGATGTGGGGGTGTCGGG | 148 bp |
| EcIRF3-RT-R | GAGGCAGAAGAACAGGGAGCACGGA | |
| EcIRF7-RT-F | CAACACCGGATACAACCAAG | 153 bp |
| EcIRF7-RT-R | GTTCTCAACTGCTACATAGGGC | |
| EcMxI-RT-F | CGAAAGTACCGTGGACGAGAA | 117 bp |
| EcMxI-RT-R | TGTTTGATCTGCTCCTTGACCAT | |
| EcISG15-RT-F | CCTATGACATCAAAGCTGACGAGAC | 179 bp |
| EcISG15-RT-R | GTGCTGTTGGCAGTGACGTTGTAGT | |
| EcISG56-RT-F | CAGGCATGGTGGAGTGGAAC | 126 bp |
| EcISG56-RT-R | CTCAAGGTAGTGAACAGCGAGGTA | |
| EcMDA5-RT-F | ACCTGGCTCTCAGAATTACGAACA | 142 bp |
| EcMDA5-RT-R | TCTGCTCCTGGTGGTATTCGTTC | |
| EcTRIF-RT-F | AAACCAACCACTGGACCAAACTT | 189 bp |
| EcTRIF-RT-R | GATGGCATCCTCGACACACCTCA | |
| EcIL6-RT-F | ACCTGGCTCTCAGAATTACGAACA | 169 bp |
| EcIL6-RT-R | TCATCTTCAAACTGCTTTTCGTG | |
| EcIL8-RT-F | GCCGTCAGTGAAGGGAGTCTAG | 131 bp |
| EcIL8-RT-R | ATCGCAGTGGGAGTTTGCA | |
| EcIL-1β-RT-F | CTCCACCGACTGATGAGGATATG | 128 bp |
| EcIL-1β-RT-R | GGCTGTTATTGACCCGAACTAAG | |
| EcTNFa-RT-F | ATGAACAAAGAAGTAGATTGGGTCG | 162 bp |
| EcTNFa-RT-R | GTCCGACTTGATTAGTGCTT | |
| EcLC3-II-RT-F | GCACCCCAACAAGATACCAGT | 145 bp |
| EcLC3-II-RT-R | CGTAGACCTCGGAGATGGCA | |
| EcBecline1-RT-F | GAGATACCGTCTGGTCCCGTAT | 265 bp |
| EcBecline1-RT-R | CCTTTTTCCACCTCCTCTTTGA | |
| EcATG5-RT-F | CCACTGAGGAGGGAGGCTT | 88 bp |
| EcATG5-RT-R | CAGATGAAACAGGGCGAAA | |
| EcATG16L1-RT-F | GAACAGCCAACTCCTTCAGCACG | 154 bp |
| EcATG16L1-RT-R | TCCTTTAGGCTCACAGCGACCAG | |
| EcBax-RT-F | GACCCAAATACCAAGAGG | 47 bp |
| EcBax-RT-R | TGTGGGACTGAGTGAAGAG | |
| EcBNIP3-RT-F | ATGAACAAAGAAGTAGATTGGGTCG | 232 bp |
| EcBNIP3-RT-R | GTGAGATGAGTAAGGAAGGGATGA |
| Analysis Content | Website/Software |
|---|---|
| Primer design | Primer 5.0 |
| Nucleic acid and protein sequence analysis | DNAMAN 9.0 |
| Conservative functional domain prediction | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cg (accessed on 4 July 2021) |
| Amino acid sequence alignment analysis | MUSCLE |
| Evolutionary tree construction | MEGA version 6.0 |
| Quantitative analysis of data | SPSS 22.0 |
| Graphic creation | GraphPad Prism 8.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, R.; Li, J.; Liang, Z.; Han, H.; Tang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Jian, J.; Cai, J. Characterization of SNX5 in Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides) during In Vitro Viral Infection. Fishes 2023, 8, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050231
Wu R, Li J, Liang Z, Han H, Tang J, Huang Y, Wang B, Jian J, Cai J. Characterization of SNX5 in Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides) during In Vitro Viral Infection. Fishes. 2023; 8(5):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050231
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Riming, Jinze Li, Zhenyu Liang, Honglin Han, Jufen Tang, Yu Huang, Bei Wang, Jichang Jian, and Jia Cai. 2023. "Characterization of SNX5 in Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides) during In Vitro Viral Infection" Fishes 8, no. 5: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050231
APA StyleWu, R., Li, J., Liang, Z., Han, H., Tang, J., Huang, Y., Wang, B., Jian, J., & Cai, J. (2023). Characterization of SNX5 in Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides) during In Vitro Viral Infection. Fishes, 8(5), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050231







