Effects of Phosphate-Enriched Nutrient in the Polyculture of Nile Tilapia and Freshwater Prawn in an Aquaponic System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
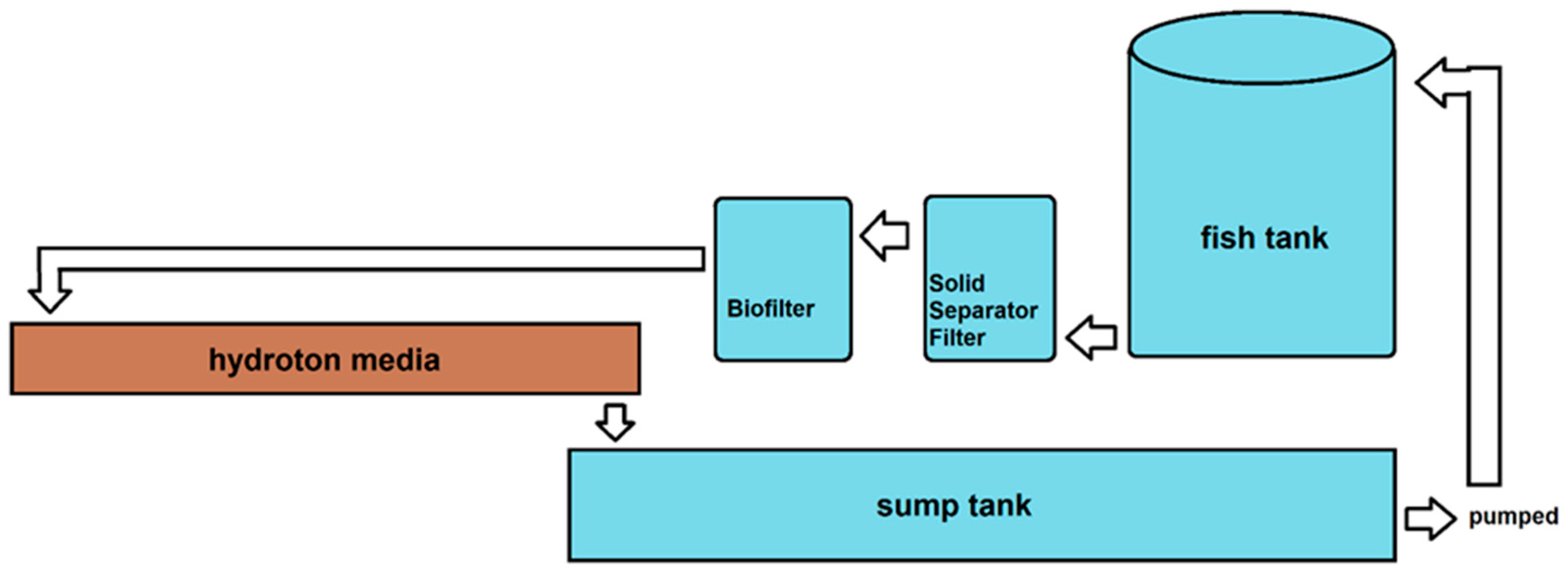
2.1. Aquaponics Design
2.2. Phosphorus Solution Preparation
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Water Quality Monitoring
2.5. Microbiology
2.6. Tilapia, Giant Freshwater Prawn, and Lettuce Growth Performance
2.7. Chlorophyll-a Content of Lettuce
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
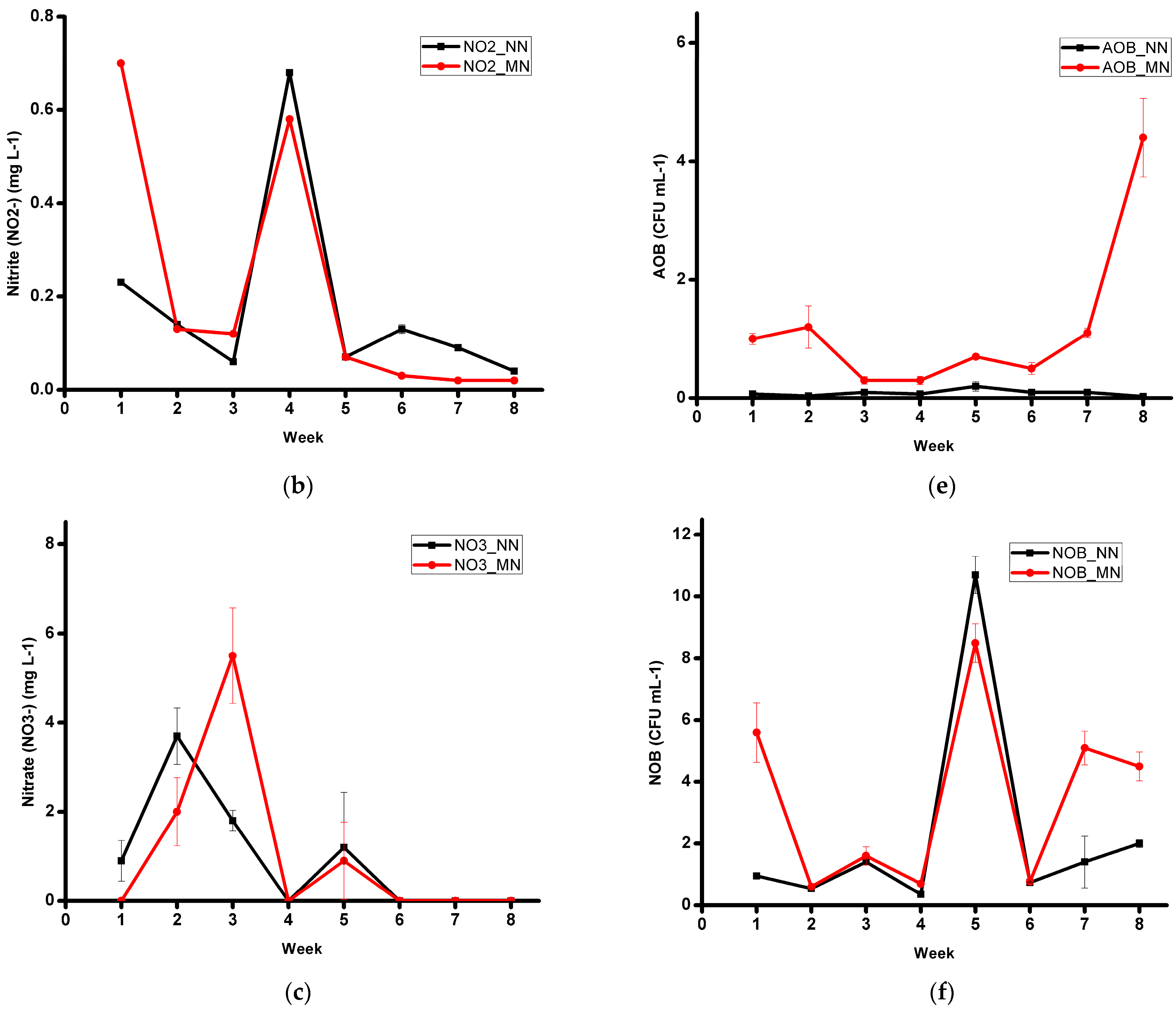
3.1. Water Quality and Microbiology
3.2. Tilapia, Giant Freshwater Prawn, and Lettuce Growth Performance
3.3. Chlorophyll Compounds in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
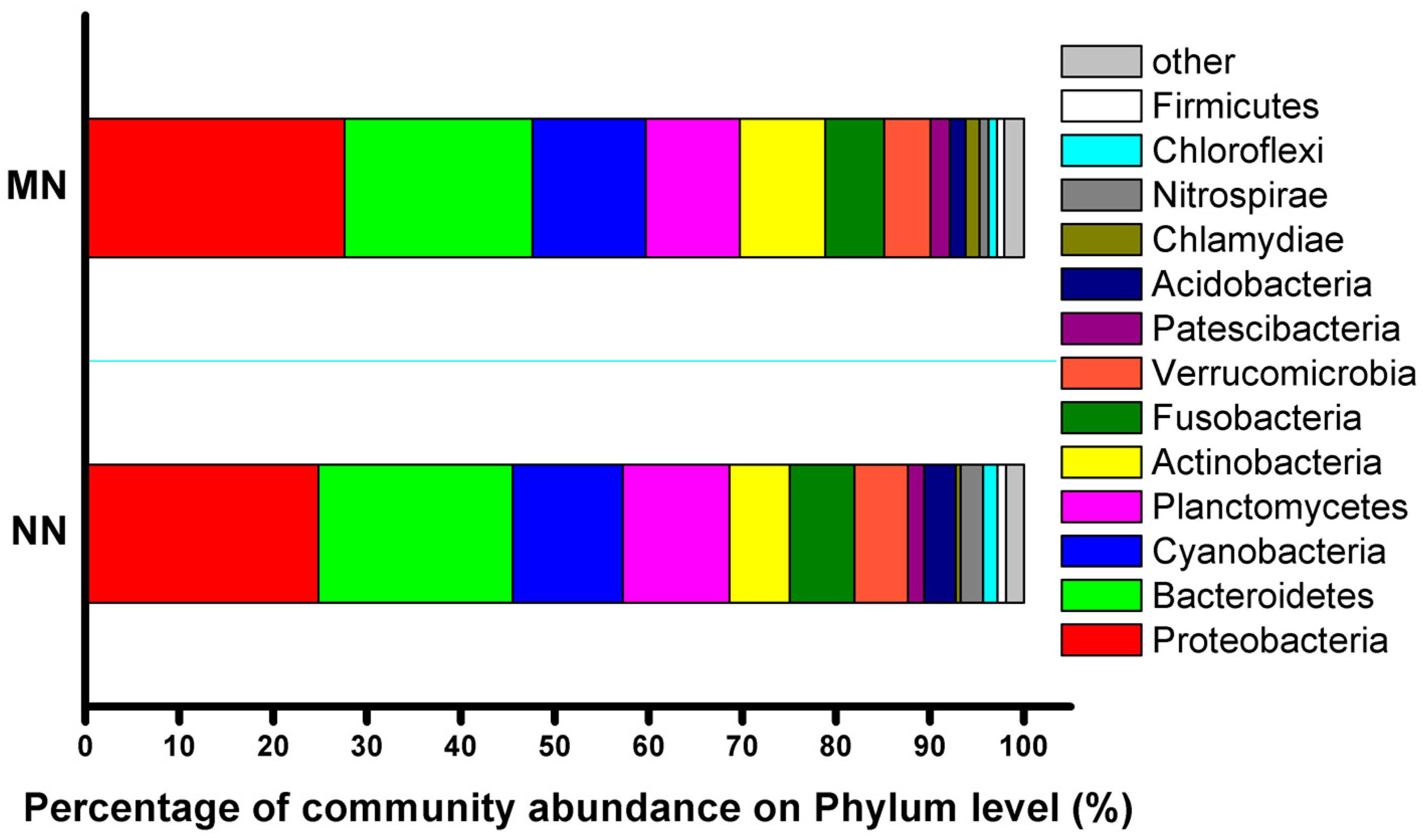
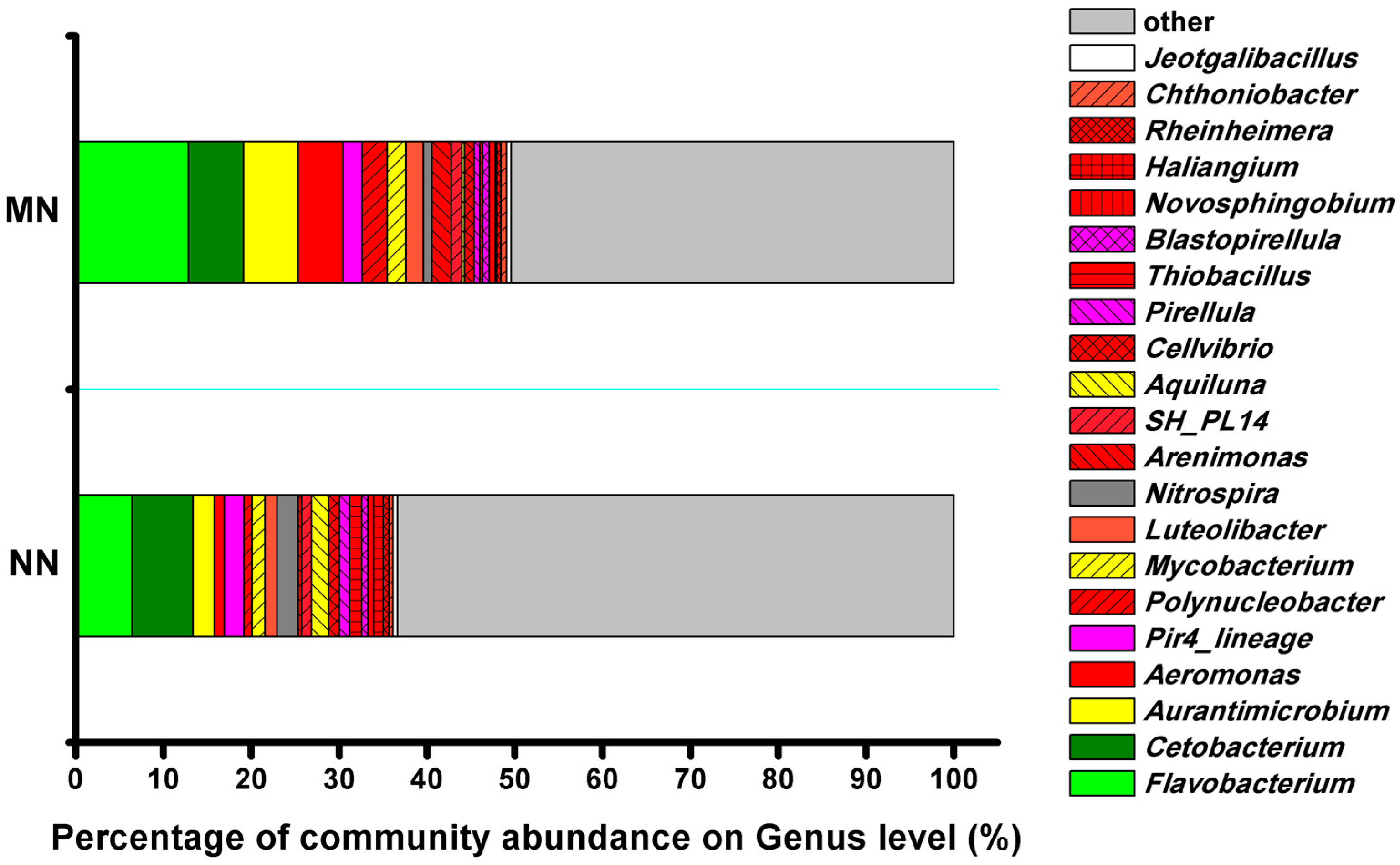
3.4. Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Somerville, C.; Cohen, M.; Pantanella, E.; Stankus, A.; Lovatelli, A. Small-Scale Aquaponic Food Production. Integrated Fish and Plant Farming; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No.589; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; 262p. [Google Scholar]
- Campanhola, C.; and Pandev, S. Sustainable Food and Agriculture: An Integrated Approach; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; 585p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J.E. Aquaponics–integrating fish and plant culture. In Aquaculture Production Systems, 1st ed.; Tidwell, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 343–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.B. Nitrification in marine systems. In Nitrogen in the Marine Environment, 2nd ed.; Capone, D.G., Bronk, D.A., Mulholland, M.R., Carpenter, E.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 199–261. [Google Scholar]
- Arp, D.J.; Stein, L.Y. Metabolism of Inorganic N Compounds by Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 38, 471–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergas, S.J.; Aponte-Morales, V. Biological Nitrogen Removal. In Comprehensive Water Quality and Purification; Ahuja, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 124–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsami-Jones, E. Phosphates. In Encyclopedia of Geology, 2nd ed.; Alderton, D., Elias, S.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Phosphorus cycle. In Encyclopedia of Ecology, 2nd ed.; Fath, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2019; Volume 4, pp. 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barben, S.A.; Hopkins, B.G.; Jolley, V.D.; Webb, B.L.; Nichols, B.A. Optimizing phosphorus and zinc concentrations in hydroponic chelator-buffered nutrient solution for Russet Burbank potato. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endut, A.; Jusoh, A.; Ali, N.; Wan Nik, W.B.; Hassan, A. A study on the optimal hydraulic loading rate and plant ratios in recirculation aquaponic system. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Kim, H. Comparisons of nitrogen and phosphorus mass balance for tomato-, basil-, and lettuce-based aquaponic and hydroponic systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J.E.; Masser, M.P.; Losordo, T.M. Recirculating aquaculture tank production systems: Aquaponics–integrating fish and plant culture. SRAC Publ. 2006, 454, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Seawright, D.E.; Stickney, R.R.; Walker, R.B. Nutrient dynamics in integrated aquaculture hydroponics systems. Aquaculture 1998, 160, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerozi, B.D.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. The effect of pH on phosphorus availability and speciation in an aquaponics nutrient solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerozi, B.D.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. Effect of dietary phytase on phosphorus use efficiency and dynamics in aquaponics. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.-C. The Deployment and Application of Liquid Fertilizer Formula in Facility Vegetable Cultivation. Seminar on R&D and Application of Facility Vegetables and Soilless Culture. The Agricultural Improvement Field of Taichung District, Agricultural Committee of the Executive Yuan, Taichung, Taiwan. Available online: https://www.tdais.gov.tw/upload/tdais/files/web_structure/11962/TC02-133-12.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2017).
- Kopp, J.F. Method for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes, 3rd ed.; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Columbus, OH, USA, 1978; 920p.
- MacDonald, R.M.; Spokes, J.R. A selective and diagnostic medium for ammonia oxidising bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1980, 8, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, K.; El-Shahawy, R.M.; Atalla, K.M. A new simple method for the enumeration of nitrifying bacteria in different environments. Plant Soil Environ. 2012, 58, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, J.G.; Yao, W.; Ma, Z. Optimization of the Method for Chlorophyll Extraction in Aquatic Plants. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2010, 25, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, C.; Liu, Z. Absorption spectrum estimating rice chlorophyll concentration: Preliminary investigations. J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2009, 1, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; 944p. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, R.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Nishide, H.; Uchiyama, I.; Baba, T.; Toyoda, A.; Fujiyama, A.; Naganuma, T.; Niki, H. Complete Genome Sequence of Aurantimicrobium minutum Type Strain KNCT, a Planktonic Ultramicrobacterium Isolated from River Water. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00616-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakshani, M.; Lukow, T.; Liesack, W. Novel bacterial lineages at the (sub) division level as detected by signature nucleotide-targeted recovery of 16S rRNA genes from bulk soil and rice roots of flooded rice microcosms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daims, H.; Lebedeva, E.V.; Pjevac, P.; Han, P.; Herbold, C.; Albertsen, M.; Jehmlich, N.; Palatinszky, M.; Vierheilig, J.; Bulaev, A.; et al. Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 2015, 528, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.C.; Kampfer, P.; Ho, M.J.; Busse, H.J.; Huber, B.E.; Arun, A.B.; Shen, F.T.; Lai, W.A.; Rekha, P.D. Arenimonas malthae sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from an oil-contaminated site. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2790–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukwambe, B.; Nicholaus, R.; Zhao, L.; Yang, W.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Z. Microbial community and interspecies interaction during grazing of ark shell bivalve (Scapharca subcrenata) in a full-scale bioremediation system of mariculture effluents. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 158, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.R.; He, J. Characterization of a xylanase-producing Cellvibrio mixtus strain J3-8 and its genome analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glockner, F.O.; Kube, M.; Bauer, M.; Teeling, H.; Lombardot, T.; Ludwig, W.; Gade, D.; Beck, A.; Borzym, K.; Heitmann, K.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the marine planctomycete Pirellula sp. strain 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8298–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Zeyad, M.T.; Choudhary, P.; Paul, S.; Chakdar, H.; Rajawat, M.V.S. Thiobacillus. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Amaresan, N., Kumar, M.S., Annapurna, K., Kumar, K., Sankaranarayanan, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallscheuer, N.; Wiegand, S.; Heuer, A.; Rensink, S.; Boersma, A.S.; Jogler, M.; Boedeker, C.; Peeters, S.H.; Rast, P.; Jetten, M.S.M.; et al. Blastopirellula retiformator sp. nov. isolated from the shallow-sea hydrothermal vent system close to Panarea Island. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Bai, P.; Li, Q.; Shen, M.; Li, R.; Li, T.; Zhao, J. Comparative Genomics of Degradative Novosphingobium Strains with Special Reference to Microcystin-Degrading Novosphingobium sp. THN1. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fudou, R.; Jojima, Y.; Iizuka, T.; Yamanaka, S. Haliangium ochraceum gen. nov., Haliangium ochraceum sp. nov. and Haliangium tepidum sp. nov.: Novel moderately halophilic myxobacteria isolated from coastal saline environments. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwan, P.; Chen, X.; Hugenholtz, P.; Janssen, P.H. Chthoniobacter flavus gen. nov., sp. nov., the First Pure-Culture Representative of Subdivision Two, Spartobacteria classis nov., of the Phylum Verrucomicrobia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5875–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakyi, M.E.; Cai, J.; Tang, J.; Abarike, E.D.; Xia, L.; Li, P.; Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Zou, Z.; Liang, Z.; Jian, J. Effects of starvation and subsequent re-feeding on intestinal microbiota, and metabolic responses in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Hao, Q.; Olsen, R.E.; Ringø, E.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, C.; Zhou, Z. Growth performance, hepatic enzymes, and gut health status of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) in response to dietary Cetobacterium somerae fermentation product. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisser, D.; Bock, C.; Hahn, M.W.; Vos, M.; Sures, B.; Rahmann, S.; Boenigk, J. Interaction-specific changes in the transcriptome of Polynucleobacter asymbioticus caused by varying protistan communities. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshiro, T.; Harada, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miki, Y.; Kawamoto, H. Microbial Fucoidan Degradation by Luteolibacter algae H18 with Deacetylation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Rasoul-Amini, S.; Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Zarrini, G.; Kazemi, A.; Mousavi-Khorshidi, S.; Ghoshoon, M.B.; Raee, M.J. Halotolerant Amylase Production by a Novel Bacterial Strain, Rheinheimera aquimaris. Res. J. Microbiol. 2010, 5, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanenko, L.A.; Tanaka, N.; Svetashev, V.I.; Kalinovskaya, N.I.; Mikhailov, V.V. Rheinheimera japonicasp. nov., a novel bacterium with antimicrobial activity from seashore sediments of the Sea of Japan. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Fang, D.; Wang, E.T.; Shao, S.; Du, Z.; Liu, W.; Xie, Z. Jeotgalibacillus proteolyticus sp. nov., a protease-producing bacterium isolated from ocean sediments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3790–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponpukdee, N.; Wangman, P.; Rodkhum, C.; Pengsuk, C.; Chaivisuthangkura, P.; Sithigorngul, P.; Longyant, S. Detection and identification of a fish pathogen Flavobacterium columnare using specific monoclonal antibodies. Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saticioglu, I.B.; Ay, H.; Altun, S.; Sahin, N.; Duman, M. Flavobacterium bernardetii sp. nov., a possible emerging pathogen of farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in cold water. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mallik, S.K.; Kala, K.; Shahi, N.; Pathak, R.; Giri, A.K.; Chandra, S.; Pant, K.; Patiyal, R.S. Characterization of Flavobacterium columnare from farmed infected rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792) of Central Indian Himalayan region, India. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Pathogenicity, and Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, J.A.; Nakagawa, L.K.; Shimojo, R.J. Infection of a cultured freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii de Man (Crustacea: Decapoda), by Mycobacterium spp., Runyon Group II. J. Fish Dis. 1986, 9, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payeur, J.B. Mycobacterium. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard, W.; Goddek, S. Aquaponics: The Basics. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems, 1st ed.; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer Cham: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.M.; David, L.H.; Garcia, F.; Keesman, K.J.; Portella, M.C.; Goddek, S. South American fish species suitable for aquaponics: A review. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 1427–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, H.Y.; Robaina, L.; Pirhonen, J.; Mente, E.; Dominguez, D.; Parisi, G. Fish welfare in aquaponic systems: Its relation to water quality with an emphasis on feed and faeces: A review. Water 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusci, J.C.; Hager, J.; Coyle, S.; Tidwell, J. Evaluation of freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, for biological solids control in raft aquaponic systems and the protective effectiveness of root guards. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 53, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Aquaponic trends and challenges—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S. Pond Aquaculture Water Quality Management, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; 712p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, O.; Sereti, V.; Eding, E.H.; Verreth, J.A.J. Analysis of nutrient flows in integrated intensive aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 32, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becquer, A.; Trap, J.; Irshad, U.; Ali, M.A.; Claude, P. From soil to plant, the journey of P through trophic relationships and ectomycorrhizal association. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebielec, S.; Urbaniak, M.; Siebielec, G.; Kidd, P.; Smreczak, B.; Grzęda, E. Bacterial inoculation effect on bioavailability of trace elements and organic contaminants in bottom sediment contaminated soils. In Proceedings of the XII Symposium Trace elements in the environment, Puławy, Poland, 17–19 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cerozi, B.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. Phosphorus dynamics modeling and mass balance in an aquaponics system. Agric. Syst. 2017, 153, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, A.; Junge, R. Aquaponic systems: Nutrient recycling from fish wastewater by vegetable production. Desalination 2009, 246, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus Dynamics: From Soil to Plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.Z.; Yang, L.Z.; Yan, M.C. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling in Prawn Ponds and the Measures for Sustainable Management. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragh, T.; Søndergaard, M.; Tranvik, L. Effect of exposure to sunlight and phosphorus-limitation on bacterial degradation of coloured dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in freshwater. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 64, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, M.D.; Reed, H.E.; Weihe, C.; Crain, C.M.; Martiny, J.B. Nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment alter the composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in salt marsh sediments. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 4, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, T.; Fujioka, Y.; Srithong, C.; Aryuthaka, C. Phosphorus budget in prawn aquaculture pond with mangrove enclosure and aquaculture performance. Fish Sci. 2005, 71, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douterelo, I.; Dutilh, B.E.; Calero, C.; Rosales, E.; Martin, K.; Husband, S. Impact of phosphate dosing on the microbial ecology of drinking water distribution systems: Fieldwork studies in chlorinated networks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, M.; Fuerst, J.A.; Kramer, E.H.; Logemann, S.; Muyzer, G.; van de Pas-Schoonen, K.T.; Webb, R.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S. Missing lithotroph identified as new planctomycete. Nature 1999, 400, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, C.; Song, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Shan, F. Patterns of Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity Following the Embryonic Development Stages of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh, S.; Sahoo, P.K. Major diseases and the defence mechanism in giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man). Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B 2008, 78, 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yathavamoorthi, R.; Alagarsamy, S.; Farvin, S. Enteric Bacteria and Water Quality of Freshwater Prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man) in Culture Environment from Kerala, India. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2010, 5, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, D.; Bonami, J.R. A review on the diseases of freshwater prawns with special focus on white tail disease of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licamele, J.D. Biomass Production and Nutrient Dynamics in an Aquaponics System. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 16 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Da Rocha, A.F.; Filho, M.B.; Stech, M.R.; da Silva, R.P. Lettuce Production in Aquaponic and Biofloc Systems with Silver Catfish Rhamdia quelen. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2017, 44, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | NN | MN | p-Value (t-Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia (NH3) (mg L−1) | 0.30 ± 0.21 | 0.42 ± 0.23 | 0.074 |
| Nitrite (NO2−) (mg L−1) | 0.18 ± 0.21 | 0.21 ± 0.27 | 0.654 |
| Nitrate (NO3−) (mg L−1) | 0.96 ± 1.46 | 1.05 ± 2.00 | 0.857 |
| Phosphate (PO4−) (mg L−1) | 0.72 ± 0.58 | 1.60 ± 1.93 | 0.040 * |
| Total bacteria | |||
| AOB (CFU mL−1) | 0.09 × 102 ± 0.06 | 1.19 × 102 ± 1.30 | 0.000 * |
| NOB (CFU mL−1) | 2.26 × 104 ± 3.31 | 3.42 × 104 ± 2.83 | 0.198 |
| Parameter | NN | MN | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prawn | |||
| Mean final weight (g) | 19.20 ± 0.75 | 19.00 ± 0.58 | 0.733 |
| Survival (%) | 30.00 ± 0.90 | 17.00 ± 0.63 | 0.000 * |
| Final biomass (Kg) | 0.580 ± 0.040 | 0.323 ± 0.025 | 0.001* |
| Tilapia | |||
| Mean final weight (g) | 170.32 ± 0.17 | 172.10 ± 1.55 | 0.120 |
| Survival (%) | 100 | 100 | 1 |
| Final biomass (Kg) | 17.033 ± 0.015 | 17.213 ± 0.155 | 0.116 |
| Lettuce | |||
| Final Mass (kg) | 1.90 ± 0.37 | 1.65 ± 0.42 | 0.482 |
| Total | |||
| Final biomass (Kg) | 19.51 ± 0.35 | 19.18 ± 0.26 | 0.256 |
| Compound | NN | MN | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a | 23.29 ± 1.88 | 25.98 ± 5.06 | 0.436 |
| Chlorophyll b | 10.495 ± 0.135 | 10.510 ± 2.140 | 0.991 |
| Total | 33.785 ± 2.015 | 36.495 ± 7.205 | 0.564 |
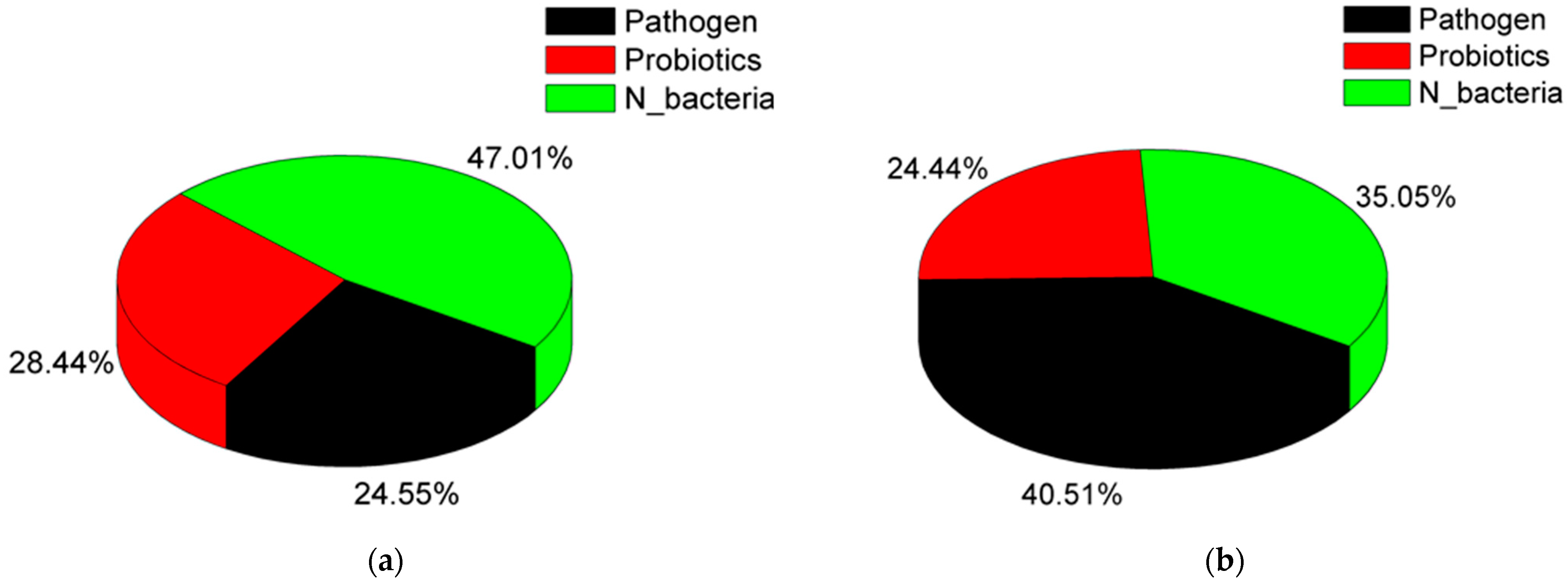
| Bacteria | NN (%) | MN (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen cycle-related bacteria | ||
| Aurantimicrobium [23] | 2.45 | 6.22 |
| Pir4_lineage [24] | 2.25 | 2.20 |
| Nitrospira [25] | 2.40 | 0.96 |
| Arenimonas [26] | 0.43 | 2.19 |
| SH_PL14 [4] | 1.10 | 1.22 |
| Aquiluna [27] | 1.95 | 0.33 |
| Cellvibrio [28] | 1.18 | 1.07 |
| Pirellula [29] | 1.20 | 0.67 |
| Thiobacillus [30] | 1.35 | 0.30 |
| Blastopirellula [31] | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| Novosphingobium [32] | 0.71 | 0.65 |
| Haliangium [33] | 1.07 | 0.20 |
| Chthoniobacter [34] | 0.44 | 0.63 |
| Probiotics | ||
| Cetobacterium [35,36] | 6.89 | 6.26 |
| Polynucleobacter [37] | 0.94 | 2.83 |
| Luteolibacter [38] | 1.39 | 2.02 |
| Rheinheimera [39,40] | 0.67 | 0.49 |
| Jeotgalibacillus [41] | 0.53 | 0.51 |
| Pathogen | ||
| Flavobacterium [42,43,44] | 6.45 | 12.87 |
| Aeromonas [45] | 1.12 | 5.09 |
| Mycobacterium [46,47] | 1.44 | 2.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuswantoro, S.; Sung, T.-Y.; Kurniawan, M.; Wu, T.-M.; Chen, B.; Hong, M.-C. Effects of Phosphate-Enriched Nutrient in the Polyculture of Nile Tilapia and Freshwater Prawn in an Aquaponic System. Fishes 2023, 8, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020081
Nuswantoro S, Sung T-Y, Kurniawan M, Wu T-M, Chen B, Hong M-C. Effects of Phosphate-Enriched Nutrient in the Polyculture of Nile Tilapia and Freshwater Prawn in an Aquaponic System. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020081
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuswantoro, Soko, Tzu-Yuan Sung, Meki Kurniawan, Tsung-Meng Wu, Bonien Chen, and Ming-Chang Hong. 2023. "Effects of Phosphate-Enriched Nutrient in the Polyculture of Nile Tilapia and Freshwater Prawn in an Aquaponic System" Fishes 8, no. 2: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020081
APA StyleNuswantoro, S., Sung, T.-Y., Kurniawan, M., Wu, T.-M., Chen, B., & Hong, M.-C. (2023). Effects of Phosphate-Enriched Nutrient in the Polyculture of Nile Tilapia and Freshwater Prawn in an Aquaponic System. Fishes, 8(2), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020081






