A Study on the Metabolic Rate Change Pattern in F2 Hybrid Sturgeon, the Bester (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus), during the Early Developmental Stage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Preparation
2.2. Respirometry Tests
2.3. Data Analyses
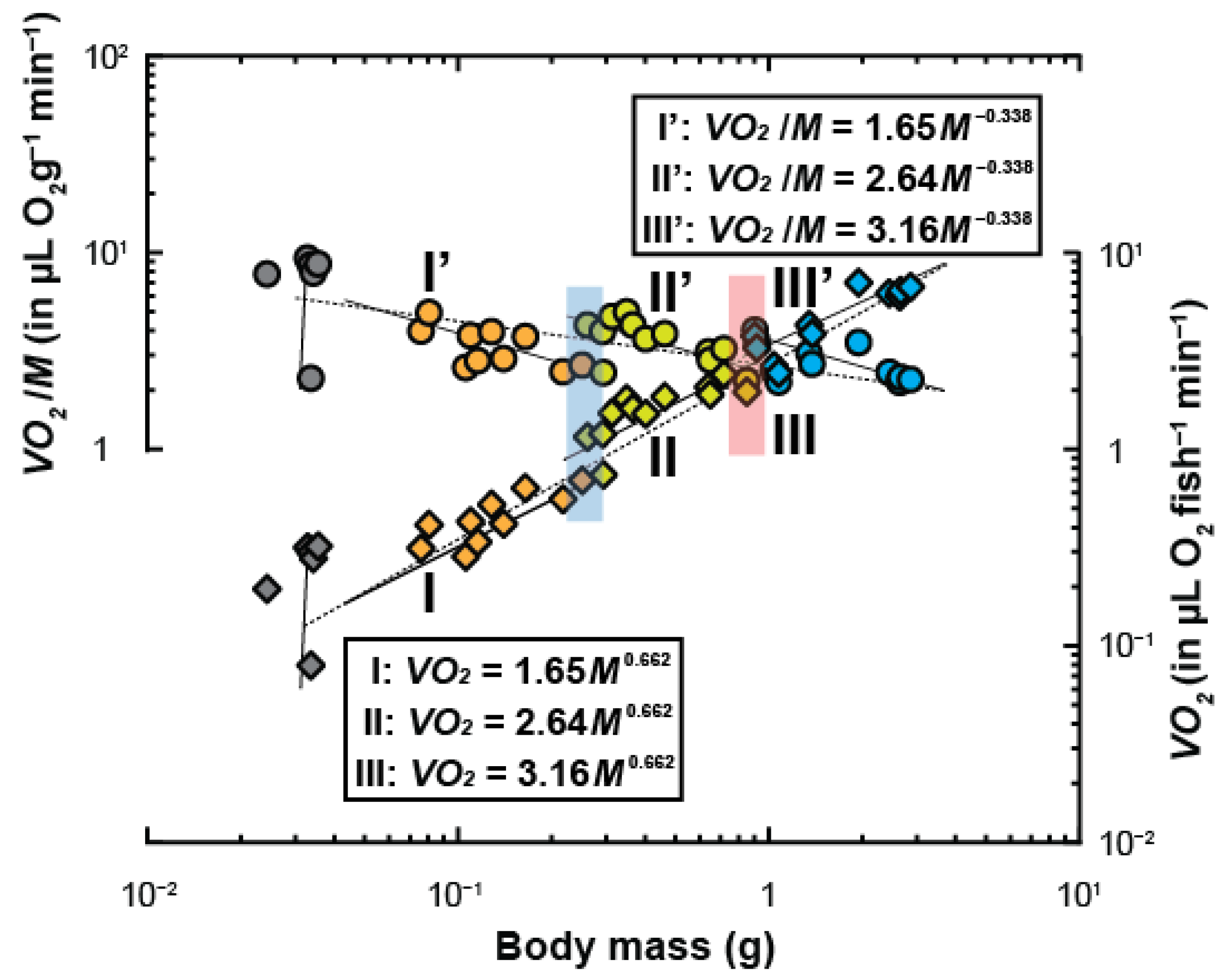
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Importance of Metabolic Scaling Studies in the Aquaculture Industry
4.2. Relationship between Changes in Metabolic Scaling and Development Trajectory
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pillay, T.V.R.; Kutty, M.N. Aquaculture: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 7–41. [Google Scholar]
- Rus, A.S.; Enjuto, C.; Morales, A.E.; Hidalgo, M.C.; García-Gallego, M. Description of a facility for studying energy metabolism in fish: Application to aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 21, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Crețu, M.; Guriencu, R.; Dediu, L.; Stroe, M. Comparison of Metabolic Rates of Young of the Year Beluga (Huso huso), Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) and Bester Hybrid Reared in a Recirculating Aquaculture System. Fishes 2021, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiola, M.; Mendiola, D.; Bostock, J. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) analysis: Main issues on management and future challenges. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 51, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wei, Y.; An, D.; Li, D.; Ta, X.; Wu, Y.; Ren, Q. A review on the research status and development trend of equipment in water treatment processes of recirculating aquaculture systems. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 863–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, L.; Libey, G. Fish Farming in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS); Department of Fisheries and Wildlife, Virginia Tech: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Chebanov, M.; Rosenthal, H.; Gessner, J.; van Anrooy, R.; Doukakis, P.; Pourkazemi, M.; Williot, P. Sturgeon hatchery practices and management for release—Guidelines. FAO Fish. Aquac. 2011, 110, 570. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, J.T.; McNiven, M.A.; Sutterlin, A.M. Metabolic rate of pre-smolt growth-enhanced transgenic Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2000, 188, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A. The Respiratory Exchange of Animals and Man; Longmans: London, UK, 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiber, M. Body Size and metabolism. Hilgardia 1932, 6, 315–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, D.; Steffensen, J.F.; Farrell, A.P. The determination of standard metabolic rate in fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 81–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.R.; Lee, J.A. Metabolic ontogeny of teleost fishes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, N.B.; Van Leeuwen, T.E.; Killen, S.S. Does individual variation in metabolic phenotype predict fish behaviour and performance? J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 298–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, A.A.; Pauly, D. Simulation of the effects of oxygen on food consumption and growth of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquac. Res. 1995, 26, 427–440. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.L.; Landry, C.; Boehm, R.; Manning, S.; Cheek, A.O.; Rees, B.B. Effects of long-term hypoxia on enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in the Gulf killifish, Fundulus grandis. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 3851–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, L.J.; Chapman, C.A.; Brazeau, D.A.; McLaughlin, B.; Jordan, M. Papyrus swamps, hypoxia, and faunal diversification: Variation among populations of Barbus neumayeri. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 54, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buentello, J.A.; Gatlin, D.M., III; Neill, W.H. Effects of water temperature and dissolved oxygen on daily feed consumption, feed utilization and growth of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2000, 182, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, K.; Lee, K.; Guz, L.; Verlhac, V.; Gabaudan, J. Effects of dietary ascorbic acid on oxygen stress (hypoxia or hyperoxia), growth and tissue vitamin concentrations in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2004, 233, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergheim, A.; Gausen, M.; Næss, A.; Hølland, P.M.; Krogedal, P.; Crampton, V. A newly developed oxygen injection system for cage farms. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, A.; Evensen, T.H.; Øiestad, V. Effects of hypoxia and hyperoxia on growth and food conversion efficiency in the spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor (Olafsen). Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosfeld, C.D.; Engevik, A.; Mollan, T.; Lunde, T.M.; Waagbø, R.; Olsen, A.B.; Breck, O.; Stefansson, S.; Fivelstad, S. Long-term separate and combined effects of environmental hypercapnia and hyperoxia in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) smolts. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridell, F.; Gadan, K.; Sundh, H.; Taranger, G.L.; Glette, J.; Olsen, R.E.; Sundell, K.; Evensen, Ø. Effect of hyperoxygenation and low water flow on the primary stress response and susceptibility of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. to experimental challenge with IPN virus. Aquaculture 2007, 270, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Kanda, T.; Takeda, T.; Ishimatsu, A.; Oikawa, S. Ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism: Links to development and anti-predator adaptation. Proc. R. Soc. B 2010, 277, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Oikawa, S. Ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism in a flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I. Ontogeny of the Respiratory Area in Relation to Body Mass with Reference to Resting Metabolism in the Japanese Flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck & Schlegel, 1846). Fishes 2022, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.S.; Butler, E.M.; Lombardi, S.A.; Deptola, T.J.; Reese, A.J.; Satterthwaite, E.V. Ecological effects on metabolic scaling: Amphipod responses to fish predators in freshwater springs. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 599–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, C.E.; Novotny, A.J. Production of Aquatic Animals: Fishes—World Animal Science Series., 1st ed.; Elsevier: Seattle, WA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shimoda, K.; Ura, K.; Adachi, S.; Takagi, Y. Developmental structure of the vertebral column, fins, scutes and scales in bester sturgeon, a hybrid of beluga Huso huso and sterlet Acipenser ruthenus. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 1985–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, A.; Lippold, S.; Debus, L.; Reinartz, R. First evidence of hybridization between endangered sterlets (Acipenser ruthenus) and exotic Siberian sturgeons (Acipenser baerii) in the Danube River. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzi, P.; Rosenthal, H. Present and future sturgeon and caviar production and marketing: A global market overview. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, N.; Maebayashi, M.; Mitsuhashi, E.; Yoshitomi, K.; Adachi, S.; Yamauchi, K. Histological observations of gonadal sex differentiation in the F2 hybrid sturgeon, the bester. Fish Sci. 2001, 67, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birstein, V.J.; Bauer, A.; Kaiser-Pohlmann, A. Sturgeon Stocks and Caviar Trade Workshop; ICUN: Gland, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaramu, S. Hybridization of Sturgeons. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Bohemia, Budejovice, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baradaran, N.S.; Bahmani, M.; Abdolhay, H.; Hosseini, M.R.; Chakmehduz, F.; Hallajian, A.; Darvishi, S.; Farabi, M.V. Bester (Beluga ♀ × Sterlet ♂) Production and Comparing Their Growth with Beluga in Iran; Iranian Fisheries Science Research Institute: Tehran, Iran, 2009; 55p. [Google Scholar]
- Arefjev, V.A. Cytogenetics of interploid hybridization of sturgeons. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 1999, 15, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, D.; Oprea, L. The effect of density on bester (H. huso× A. ruthenus) larvae reared in a superintensive system. USAMV Iaşi.Lucr. Ştiinţifice Ser. Zooteh. 2009, 52, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa, S.; Itazawa, Y.; Gotoh, M. Ontogenetic change in the relationship between metabolic rate and body mass in a sea bream Pagrus major (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Fish Biol. 1991, 38, 483–496. [Google Scholar]
- Helm, I.; Jalukse, L.; Vilbaste, M.; Leito, I. Micro-Winkler titration method for dissolved oxygen concentration measurement. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2009, 648, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, K.A. Statistical Theory and Methodology in Science and Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, H.A.; McMahon, T.A. The 3/4 mass exponent for energy metabolism is not a statistical artifact. Respir. Physiol. 1983, 52, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summerfelt, S.T.; Vinci, B.J. Better management practices for recirculating aquaculture systems. In Environmental Best Management Practices for Aquaculture; Tucker, C.S., Hargreaves, J.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 297, pp. 389–426. [Google Scholar]
- Seginer, I.; Mozes, N. A note on oxygen supply in RAS: The effect of water temperature. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 50, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, J.A.; Cowen, R.K. Size, growth, development, and survival of the planktonic larvae of Pomatomus saltatrix (Pisces: Pomatomidae). Ecol. 1997, 78, 2415–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Okada, K.; Kamiya, N. Organogenesis and behavioral changes during development of laboratory-reared tiger puffer, Takifugu rubripes. Aquac. Sci. 1995, 43, 461–474. [Google Scholar]
- Harder, W. Anatomy of Fishes; Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung: Stuttgart, Germany, 1975; pp. 1–612. [Google Scholar]
- Yarmohammadi, M.; Shabani, A.; Pourkazemi, M.; Baradaran Noveiri, S. Identification of bester hybrids (female Huso huso Linnaeus, 1758 and male sterlet Acipenser ruthenus Linnaeus, 1758) using AFLP molecular technique. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2012, 11, 415–423. [Google Scholar]
- Tranah, G.J.; Bagley, M.; Agresti, J.J.; May, B. Development of codominant markers for identifying species hybrids. Conserv. Genet. 2003, 4, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Takagi, Y.; Seikai, T.; Tanaka, M.; Tagawa, M. Asymmetrical development of bones and soft tissues during eye migration of metamorphosing Japanese flounder, Paralichthys Olivaceus. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 304, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Hirst, A.G.; Glazier, D.S.; Atkinson, D. Ecological pressures and the contrasting scaling of metabolism and body shape in coexisting taxa: Cephalopods versus teleost fish. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 2019, 374, 20180543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, A.G.; Glazier, D.S.; Atkinson, D. Body shape shifting during growth permits tests that distinguish between competing geometric theories of metabolic scaling. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.S.; Hirst, A.G.; Atkinson, D. Shape shifting predicts ontogenetic changes in metabolic scaling in diverse aquatic invertebrates. Proc. R. Soc. B 2015, 282, 20142302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokeš, M.; Baruš, V.; Mareš, J.; Peňáz, M.; Baránek, V. Growth of sterlet Acipenser ruthenus under experimental and farm conditions of the Czech Republic, with remarks on other sturgeons. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2014, 59, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdali, H.; Eagderi, S. Ontogeny of gill structure in Sterlet, Acipenser ruthenus (Linnaeus, 1758). Iran. J. Ichthyol. 2015, 2, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Rybnikár, J.; Prokeš, M.; Mareš, J.; Cileček, M. Early development and growth of sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) in the Czech Republic. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2014, 59, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykov, V.A.; Ruban, G.I.; Pavlov, D.S. Migrations and resources of sterlet Acipenser ruthenus (Acipenseridae) from the lower reaches of the Volga River. J. Ichthyol. 2010, 50, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, R.; Rafiee, G.; Poorbagher, H.; Agh, N.; Zadeh, H.E. Body shape changes during the early development of the Beluga (Huso huso). Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2013, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gisbert, E.; Asgari, R.; Rafiee, G.; Agh, N.; Eagderi, S.; Eshaghzadeh, H.; Alcaraz, C. Early development and allometric growth patterns of beluga Huso huso (Linnaeus, 1758). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | N | Body Mass (g) | Scaling Constant | Scaling Exponent (x ± SEM) | P | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 a | 10 | 0.0761–0.2511 | 1.50 | 0.616 ± 0.164 | 4.77 × 10−2 | 0.637 |
| 2 a | 12 | 0.2612–0.8507 | 2.54 | 0.613 ± 0.159 | 3.55 × 10−2 | 0.597 |
| 3 a | 12 | 0.9033–2.8647 | 3.06 | 0.727 ± 0.118 | 4.28 × 10−2 | 0.792 |
| 1–3 b | 34 | 0.0761–2.8647 | α = 2.93 | = 0.911 ± 0.014 | 2.38 × 10−7 | 0.993 |
| 1–3 c | 34 | 0.0761–2.8647 | 2.86 | 0.878 ± 0.035 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 0.952 |
| Total d | 40 | 0.0243–2.8647 | 2.80 | 0.800 ± 0.034 | 1.03 × 10−6 | 0.935 |
| Term | SS | DoF | MS | MSR | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| log α | 1.128248 | 1 | 1.128248 | 165 | 9.76 × 10−14 |
| µi | 0.039872 | 1 | 0.039872 | 5.84 | 2.19 × 10−2 |
| 0.055444 | 1 | 0.055444 | 8.12 | 7.83 × 10−3 | |
| xij | 5.993409 | 1 | 5.993409 | 878 | 8.94 × 10−24 |
| εij | 0.204753 | 30 | 0.006825 | ||
| Total (approximate mean) | 6.293478 | 33 | |||
| Total (about zero) | 7.421726 | 34 |
| Shifting Point (Body Mass: g) | Name of Fish | Morphological Changes | Behavioral Changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| – (about 0.2) | Sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus) |
|
|
| Beluga sturgeon (Huso huso) |
| ||
| F1 bester (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus) |
| ||
| – (about 0.8) | Sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus) |
| |
| Beluga sturgeon (Huso huso) |
|
| |
| F1 Bester (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.I. A Study on the Metabolic Rate Change Pattern in F2 Hybrid Sturgeon, the Bester (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus), during the Early Developmental Stage. Fishes 2023, 8, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020113
Kim DI. A Study on the Metabolic Rate Change Pattern in F2 Hybrid Sturgeon, the Bester (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus), during the Early Developmental Stage. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong In. 2023. "A Study on the Metabolic Rate Change Pattern in F2 Hybrid Sturgeon, the Bester (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus), during the Early Developmental Stage" Fishes 8, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020113
APA StyleKim, D. I. (2023). A Study on the Metabolic Rate Change Pattern in F2 Hybrid Sturgeon, the Bester (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus), during the Early Developmental Stage. Fishes, 8(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020113





