Blood Transcriptome Analysis Provides Responsive Changes in Gene Expression between Ex Situ and Captive Yangtze Finless Porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
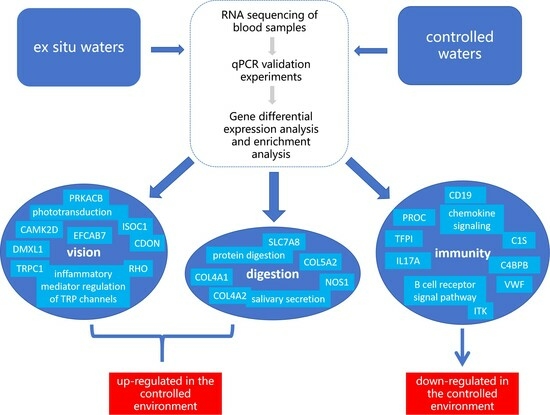
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Samples Collection
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3.2. Sequencing Data Filtering Analysis
- (1)
- Remove the reads with a sequencing adapter;
- (2)
- Remove the reads with an unknown base N content greater than 5%;
- (3)
- Remove the low-quality reads (reads with bases with a mass value below 15, accounting for more than 20% of the total base number of the reads).
2.3.3. Differential Expression Analysis and Enrichment Analysis
2.3.4. Validation of RT-qPCR
- (1)
- Reverse-transcription of the tested RNA at 500 ng was performed at the following reaction temperatures and reaction times: 25 °C for 10 min; 50 °C for 30 min; 85 °C for 5 min, and left at −20 °C for storage after the end of the reaction;
- (2)
- Dilute the cDNA obtained in step 1 by 5-fold, and configure the qPCR reaction (Table S2);
- (3)
- Set the cycling conditions (Table S3).
3. Results
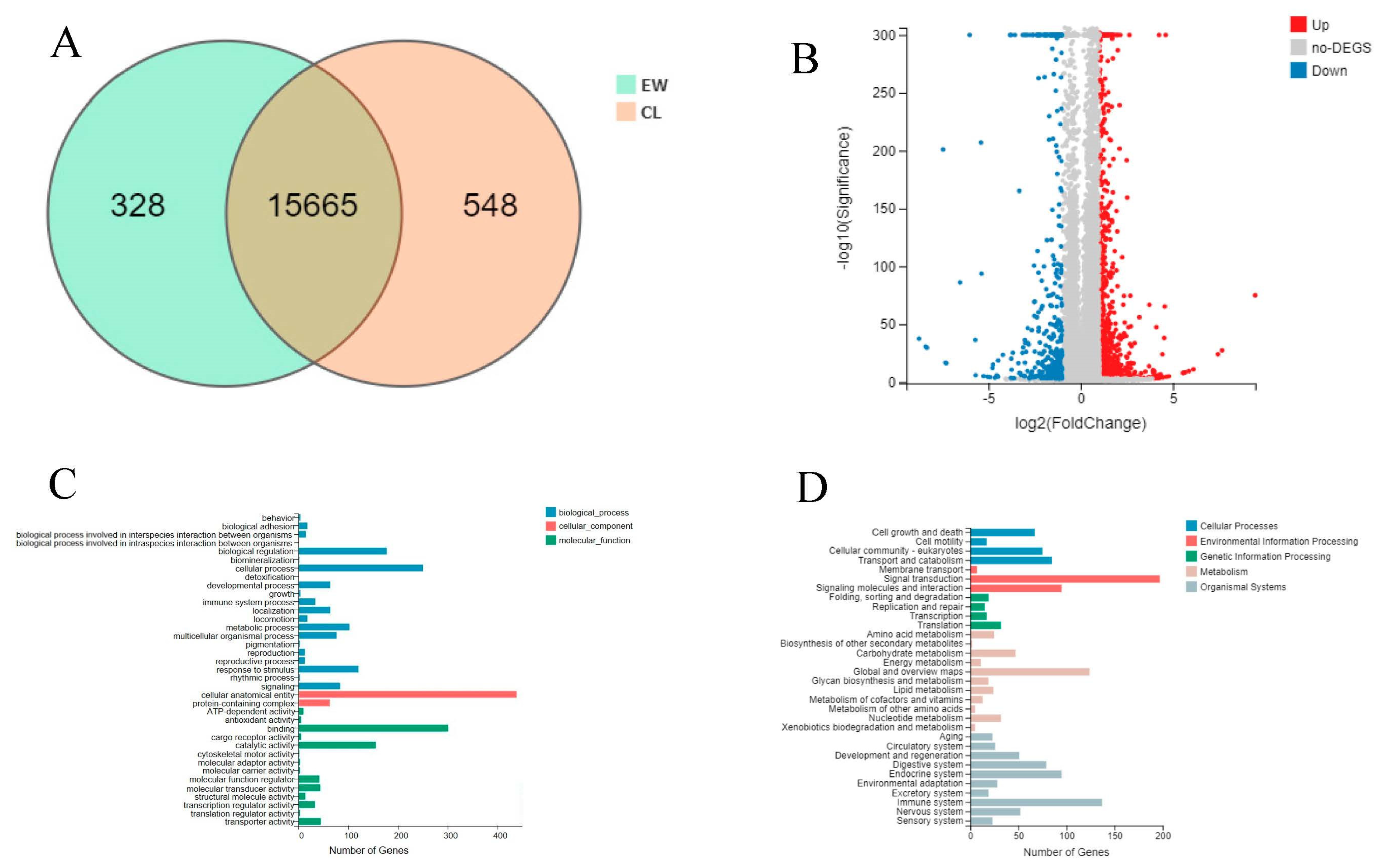
3.1. Analysis of Sequencing Data
3.2. Differential Expression Gene Analysis and Functional Annotation
3.3. Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
3.4. Analysis of Key Genes and Pathways
3.5. Validation of RNA-Seq Results via qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Visual Function Impact of the YFPs
4.2. Analysis of the Impact of YFPs Digestion Function
4.3. Analysis of the Immune Function Impact of the YFPs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X.; Guang, X.; Sun, D.; Xu, S.; Yang, G. Population genomics of finless porpoises reveal an incipient cetacean species adapted to freshwater. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, R.J. The population of finless porpoise in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Acta Theriol. Sin. 1993, 4, 005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Turvey, S.; Zhao, X.; Mei, Z. Neophocaena asiaeorientalis ssp. asiaeorientalis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, Version 3.1; IUCN: Gland, Switzerlandand; Cambridge, UK, 2013.
- Zhao, X.; Barlow, J.; Taylor, B.L.; Pitman, R.L.; Wang, K. Abundance and conservation status of the Yangtze finless porpoise in the Yangtze River, China. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.J.; Aguiar, S.F.H.; Moraes, W.T.; Sanaiotti, M.; Banhos, A.; Moreira, N. Ex situ population of the Harpy Eagle and its potential for integrated conservation. Zookeys 2022, 1083, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G. The Changes of Micro-Ecological of Diseased Yangtze Finless and Research on Its Protection under Ex-Situ; Huazhong Agricultural University: Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Tan, J.; Liu, K. Current status of zooplankton community and assessment of fishery potential in Yangtze finless porpoise ex-situ nature reserve of Xijiang River in Anqing. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, L.; Yu, D.P.; Jiang, W.H.; Zhou, F. Water quality analyzing of rearing Yangtze finless porpoise in semi-nature reserve. J. Anhui Univ. 2003, 4, 93–97+110. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y. Breeding and observation of the Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides). Aquaculture 1993, 3, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Hao, Y.J.; Wang, D. Determinaton of serum amino acid concentration in free-ranging and captive Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2008, 2, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, G.; Li, Y.; McLaughlin, R.W.; Mei, Z.; Wang, K.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, D. Immune Responses of the Critically Endangered Yangtze Finless Porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis ssp. asiaeorientalis) to Escalating Anthropogenic Stressors in the Wild and Seminatural Environments. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yin, D.H.; Lin, D.Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Ying, C.P.; Zhang, J.L.; Xu, P.; Liu, K. Blood Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Gene Expression Differences between Yangtze Finless Porpoises from Two Habitats: Natural and Ex Situ Protected Waters. Fishes 2022, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.B.; Li, C.W.; He, M.; Wu, H.L.; Hang, Y.; Fan, Z.X.; Yue, B.S.; Zhang, X.Y. Transcriptome analysis of the blood of bald male giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). In Proceedings of the 8th Western China Zoological Symposium, Sichuan, China, 17 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. Immune System and High-Altitude Adaptation Study in Wolf (Canis lupus) Based on Blood Transcriptome Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.J.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Wu, H.P.; Chen, D.Q.; Gong, C.; Li, L.; Wang, D. Physiological responses to capture and handling of free-ranging male Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis). Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2009, 42, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, A.F. hypeR: An R package for geneset enrichment workflows. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1307–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Liu, Q.; Shen, F.; Fan, Z.; Hou, R.; Yue, B.; Zhang, X. Transcriptome analysis reveals immune-related gene expression changes with age in giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) blood. Aging 2019, 11, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkun, L.; Slae, M.; Mor-Shaked, H.; Koplewitz, B.; Eventov-Friedman, S.; Harel, T. Homozygous variants in MAPRE2 and CDON in individual with skin folds, growth delay, retinal coloboma, and pyloric stenosis. Am. J. Med. Genetics. Part A 2019, 179, 2454–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anney, P.; Thériault, M.; Proulx, S. Hydrodynamic forces influence the gene transcription of mechanosensitive intercellular junction associated genes in corneal endothelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 206, 108532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, W.; Haas, K.; Ruthazer, E.S.; Cline, H.T. Dendrite growth increased by visual activity requires NMDA receptor and Rho GTPases. Nature 2002, 419, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thébault, S. Minireview: Insights into the role of TRP channels in the retinal circulation and function. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 765, 136285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavenga, D.G.; Grip, W. Progress in phototransduction. Biophys. Struct. Mech. 1983, 9, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, B.; Corman, T.; Lovelace, K.; Hong, M.; Krauss, R.; Epstein, D.J. Prenatal ethanol exposure in mice phenocopies Cdon mutation by impeding Shh function in the etiology of optic nerve hypoplasia. Dis. Models Mech. 2017, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, C.R.; Nagels, J.; Lydiard, E. Stormflow-dominated loads of faecal pollution from an intensively dairy-farmed catchment. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herald, E.S.; Brownell, R.L.; Frye, F.L.; Morris, E.J.; Evans, W.E.; Scott, A.B. Blind River Dolphin: First Side-Swimming Cetacean. Science 1969, 166, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilleri, G. The blind Indus dolphin, Platanista indi. Endeavour 1979, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z. Generation of Nonhuman Primate Retinitis Pigmentosa Model by Knockout of RHO In Vivo; University of Science and Technology of China: Hefei, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.T.; Bi, H.S. Advance on transient receptor potential channels in ophthalmology. Recent Adv. Ophthalmol. 2009, 29, 395–397. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, H.B. Effects of TROC1, 3, and 6 on High Glucose-Induced Human Retinal Vascular Endothelial Cells and Its Mechanism; Guangxi Medical University: Nanning, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y. Expression of TRPC Channels in Rat Retina and the Effects of TRPC6 on Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis in Rat Chronic Ocular Hypertension Model; Fudan University: Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wimmers, S.; Strauss, O. Basal Calcium Entry in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.J.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Cardiovascular and Hemostatic Disorders: SOCE and Ca2+ Handling in Platelet Dysfunction. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 993, 453–472. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Mei, Y. The progress of Rhodopsin in light induced retina degeneration. Sichuan J. Anat. 2011, 19, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Scheuring, U.; Franco, M.; Fievet, B.; Guizouarn, H.; Mirshahi, M.; Faure, J.P.; Motais, R. Arrestin from nucleated red blood cells binds to bovine rhodopsin in a light-dependent manner. FEBS Lett. 1990, 276, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.R.B.; Olsen, D.A.; Christensen, H.; Hansen, S.B.; Christensen, C.; Brandslund, I. Rhodopsin in plasma from patients with diabetic retinopathy—Development and validation of digital ELISA by Single Molecule Array (Simoa) technology. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 446, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshandel, D.; Rafati, M.; Khorami, S.; Novin, B.N.; Jalali, S.; Tabatabaie, R.; Rezai, S.; Ahmadieh, H.; Ghaffari, S.R. Rhodopsin gene mutation analysis in Iranian patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Sheu, S.J.; Gabrielian, K.; Ryan, S.J.; Hinton, D.R. Intercellular gap formation induced by thrombin in confluent cultured bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.X.; He, S.Z. Advances in the study of retinal intercellular gap junctions. J. Chin. PLA Postgrad. Med. Sch. 2006, 2, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.F. Evolution of Cetacean fat Metabolism-Related Genes and Their Relationship to Aquatic Adaptation; Nanjing Normal University: Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.T. Genetic Basis of Cetacean Dietary Shifts; Nanjing Normal University: Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, M.J.; Jiménez, M.D.; Motilva, V. New issues about nitric oxide and its effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 881–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautz, A.; Li, H.; Kleinert, H. Regulation of NOS expression in vascular diseases. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.Q.; Zhu, D.; Tang, Y.D. The history, current status, and direction of cardiovascular metabolic medicine. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 30, 2389–2393. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Liang, N.F.; Chan, K.; Pu, X.Y.; Poston, R.N.; Ren, M.X.; An, W.W.; Zhang, R.X.; Wu, J.C.; Yan, S.Y.; et al. Coronary-Heart-Disease-Associated Genetic Variant at the COL4A1/COL4A2 Locus Affects COL4A1/COL4A2 Expression, Vascular Cell Survival, Atherosclerotic Plaque Stability and Risk of Myocardial Infarction. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, G.; Sidney, T.; Idowu, M.; Eichie, F.; Karnezos, T.P.; Ogunade, I.M. Dietary fenugreek seed extract improves dry matter intake, apparent total tract nutrient digestibility, and alters whole blood transcriptome of Holstein dairy heifers. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2022, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, A.; Pirozzi, I. The interaction of feeding regime and dietary specification on growth and nutrient utilisation in Yellowtail Kingfish Seriola lalandi. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737094. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Cao, H.; Wang, J.; He, F.P.; Jiang, G.S. Gut microbiota and fecal metabolites in captive and wild North China leopard (Panthera pardus japonensis) by comparsion using 16 s rRNA gene sequencing and LC/MS-based metabolomics. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, P.; Sebald, K.; Fischer, K.; Behrens, M.; Schnieke, A.; Somoza, V. Bitter Peptides YFYPEL, VAPFPEVF, and YQEPVLGPVRGPFPIIV, Released during Gastric Digestion of Casein, Stimulate Mechanisms of Gastric Acid Secretion via Bitter Taste Receptors TAS2R16 and TAS2R38. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11591–11602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertiprakhov, G.V.; Grozina, A.A. Pancreatic Exocrine Function in Chickens. Russ. Agric. Sci. 2019, 45, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zou, S.Z.; Liao, S.T. Characteristics of Intestinal Micro-ecological Environment of Wild and Captive Giant Pandas and their differences. J. China West Norm. Univ. 2020, 41, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.J.; Deng, L.; Zhang, B. Advance and studies on ecophysiological effects of starvation on fish. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1998, 22, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.H.; Zhang, X.N.; Ru, S.G. Advance in visual impairment caused by environmental pollutants in fish. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 16, 104–119. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, N.; Guo, H.R.; Wang, Z.C.; Yang, Y.X. Establishment of inflammatory model of lamb peripheral blood mononuclear cells induced by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide in Vitro. Acta Ecol. Anim. Domastici 2022, 43, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.G.; Chen, X.F. Progress of chemokine superfamily. Chin. Bull. Life Sci. 1996, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F. Progress in the study of complement. Prog. Physiol. Sci. 1979, 3, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Rahul, N.; Parham, R.; Maximilian, M.; Cihangir, D.; Leandro, C.; Huimin, G.; Sinisa, D.; Hassan, J.; Hilda, Y.B.; Ari, M.; et al. Pre-B cell receptor-mediated activation of BCL6 induces pre-B cell quiescence through transcriptional repression of MYC. Blood 2011, 118, 15. [Google Scholar]



| Gene Name | Gene ID | Full Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 112391848 | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | AGGTCGGAGTGAACGGATTT | TTCTCAGCCTTGACTGTGCC |
| PDLIM1 | 112409851 | PDZ and LIM domain 1 | GGCATTGTCGGCGTGTTT | GCCCTTCTGTTTCAGGTTCG |
| RHO | 112407247 | rhodopsin | TCGCCAGAGGTCAACAATG | AGCAGATCAGGAAAGCAACG |
| SLC51B | 112393149 | SLC51 subunit beta | GAAACTCACAGCCCTTCTTAGC | CAAAGTTACAGGAGTGGCGAA |
| TRPC1 | 112415902 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily C member 1 | AAAAGGACAGCCTCCGACAT | CACCTCCACAAGGCTTAGTTCT |
| CAMK2D | 112400110 | calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II delta | ACCCTGCCAAGCGTATCAC | TTTCTTCAAGCAGTCAACAGTCTC |
| NOS1 | 112408771 | nitric oxide synthase 1 | CTCGTTTCCTCAAGGTCAAGA | GCTTTGGAGCCGAATCTTT |
| EFCAB7 | 112412952 | EF-hand calcium binding domain 7 | GAAGAAATCCATCCCAAAAGAC | GTGTGTAAAATAGAGCCATCATCAT |
| PRKACB | 112415075 | protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit beta | TCTCAGCAAGGGCTACAATAAG | TCCAAACCGCTTCGTCAG |
| ISOC1 | 112407775 | isochorismatase domain containing 1 | AGGTTCAGACCAGCCATCAA | CCAAATAACACAACACTCCTGACT |
| Sample | Total Raw Reads (M) | Total Clean Reads (M) | Total Clean Bases (Gb) | Clean Reads Q20 (%) | Clean Reads Q30 (%) | Clean Reads Ratio (%) | Total Mapping (%) | Uniquely Mapping (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EW1 | 63.1 | 61.74 | 9.26 | 98.67 | 94.89 | 97.84 | 84.16 | 77.52 |
| EW2 | 58.01 | 56.54 | 8.48 | 98.77 | 95.27 | 97.47 | 81.55 | 73.02 |
| EW4 | 103.11 | 101.93 | 15.29 | 98.62 | 94.66 | 98.85 | 92.49 | 89.18 |
| EW4 | 87.03 | 85.01 | 12.75 | 98.6 | 94.59 | 97.68 | 87.72 | 83.1 |
| CL1 | 96.89 | 95.72 | 14.36 | 98.69 | 94.91 | 98.79 | 92.41 | 89.09 |
| CL2 | 103.11 | 101.9 | 15.28 | 98.62 | 94.67 | 98.82 | 92.1 | 88.81 |
| CL3 | 85.81 | 84.7 | 12.71 | 98.64 | 94.73 | 98.71 | 89.23 | 84.98 |
| CL4 | 93.86 | 92.53 | 13.88 | 98.66 | 94.79 | 98.58 | 89.61 | 85.72 |
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Visual-system-related pathway | ||
| ko04750 | inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | 2.32 × 10−4 |
| ko04745 | phototransduction—fly | 1.71 × 10−2 |
| ko04744 | phototransduction | 4.24 × 10−2 |
| Digestive-system-related pathway | ||
| ko04970 | salivary secretion | 6.23 × 10−9 |
| ko04974 | protein digestion and absorption | 1.87 × 10−7 |
| ko04976 | bile secretion | 1.61 × 10−4 |
| ko04972 | pancreatic secretion | 1.91 × 10−3 |
| ko04971 | gastric acid secretion | 6.23 × 10−3 |
| Immune-system-related pathways | ||
| ko04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 3.66 × 10−9 |
| ko04062 | chemokine signaling pathway | 2.12 × 10−8 |
| ko04610 | complement and coagulation cascades | 5.15 × 10−8 |
| ko04640 | hematopoietic cell lineage | 5.74 × 10−8 |
| ko04672 | intestinal immune network for IgA production | 5.27 × 10−4 |
| ko04611 | platelet activation | 1.79 × 10−3 |
| ko04662 | B cell receptor signaling pathway | 2.88 × 10−3 |
| Category | Gene Name | Gene ID | Full Name | log2 (CL/EW) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual-related genes | RHO | 112407247 | rhodopsin | 1.44 | 5.63 × 10−4 |
| EFCAB7 | 112412952 | EF-hand calcium binding domain 7 | 1.54 | 9.42 × 10−6 | |
| DMXL1 | 112398650 | Dmx like 1 | 1.20 | 8.32 × 10−39 | |
| CAMK2D | 112400110 | calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II delta | 1.03 | 2.52 × 10−33 | |
| F2RL1 | 112391430 | F2R like trypsin receptor 1 | 1.83 | 9.39 × 10−5 | |
| ISOC1 | 112407775 | isochorismatase domain containing 1 | 1.10 | 5.63 × 10−18 | |
| PRKACB | 112415075 | protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit beta | 1.00 | 2.92 × 10−95 | |
| TRPC1 | 112415902 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily C member 1 | 1.94 | 6.99 × 10−11 | |
| CDON | 112396881 | cell adhesion molecule-related/down-regulated by oncogenes | 1.89 | 8.13 × 10−6 | |
| Digestive-system-related genes | NOS1 | 112408771 | nitric oxide synthase 1 | −1.83 | 2.66 × 10−136 |
| COL4A2 | 112405545 | collagen type IV alpha 2 chain | 1.00 | 1.56 × 10−20 | |
| COL5A2 | 112392120 | collagen type V alpha 2 chain | 1.03 | 2.09 × 10−10 | |
| COL4A1 | 112405565 | collagen type IV alpha 1 chain | 1.35 | 6.09 × 10−6 | |
| KIRREL3 | 112396840 | kirre like nephrin family adhesion molecule 3 | 1.00 | 2.31 × 10−4 | |
| KIRREL1 | 112403475 | kirre like nephrin family adhesion molecule 1 | 1.05 | 3.26 × 10−3 | |
| SLC7A8 | 112397487 | solute carrier family 7 member 8 | 1.23 | 3.17 × 10−95 | |
| SOWAHB | 112405618 | sosondowah ankyrin repeat domain family member B | 1.51 | 5.02 × 10−39 | |
| FAM110D | 112414353 | family with sequence similarity 110 member D | 1.71 | 7.49 × 10−5 | |
| FAM120C | 112414621 | family with sequence similarity 120C | 1.06 | 2.19 × 10−37 | |
| Immune-system-related genes | C1S | 112391771 | complement C1s | −2.78 | 3.02 × 10−3 |
| CCR10 | 112399840 | C-C motif chemokine receptor 10 | −1.85 | 3.59 × 10−4 | |
| PROC | 112395009 | protein C, inactivator of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa | −1.79 | 9.03 × 10−8 | |
| IL17A | 112414006 | interleukin 17A | −1.76 | 6.98 × 10−12 | |
| C4BPB | 112403521 | complement component 4 binding protein beta | −1.36 | 6.54 × 10−4 | |
| VWF | 112391767 | von Willebrand factor | −1.22 | 4.27 × 10−17 | |
| TFPI | 112400364 | tissue factor pathway inhibitor | −1.14 | 5.13 × 10−4 | |
| CD19 | 112399325 | CD19 molecule | −1.07 | 5.67 × 10−66 | |
| S100A8 | 112401769 | S100 calcium binding protein A8 | −1.17 | 0 | |
| ITK | 112409812 | IL2 inducible T cell kinase | 1.24 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Z.; Yin, D.; Li, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Lin, D.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ying, C.; et al. Blood Transcriptome Analysis Provides Responsive Changes in Gene Expression between Ex Situ and Captive Yangtze Finless Porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis). Fishes 2023, 8, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120593
Cao Z, Yin D, Li Z, Yan Y, Zhang P, Zhang S, Lin D, Hua Z, Zhang J, Ying C, et al. Blood Transcriptome Analysis Provides Responsive Changes in Gene Expression between Ex Situ and Captive Yangtze Finless Porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis). Fishes. 2023; 8(12):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120593
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Zhichen, Denghua Yin, Zhanwei Li, Yan Yan, Peng Zhang, Sigang Zhang, Danqing Lin, Zhong Hua, Jialu Zhang, Congping Ying, and et al. 2023. "Blood Transcriptome Analysis Provides Responsive Changes in Gene Expression between Ex Situ and Captive Yangtze Finless Porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis)" Fishes 8, no. 12: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120593
APA StyleCao, Z., Yin, D., Li, Z., Yan, Y., Zhang, P., Zhang, S., Lin, D., Hua, Z., Zhang, J., Ying, C., Zhang, H., Xu, P., Dong, G., & Liu, K. (2023). Blood Transcriptome Analysis Provides Responsive Changes in Gene Expression between Ex Situ and Captive Yangtze Finless Porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis). Fishes, 8(12), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120593