Metabarcoding by Combining Environmental DNA with Environmental RNA to Monitor Fish Species in the Han River, Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
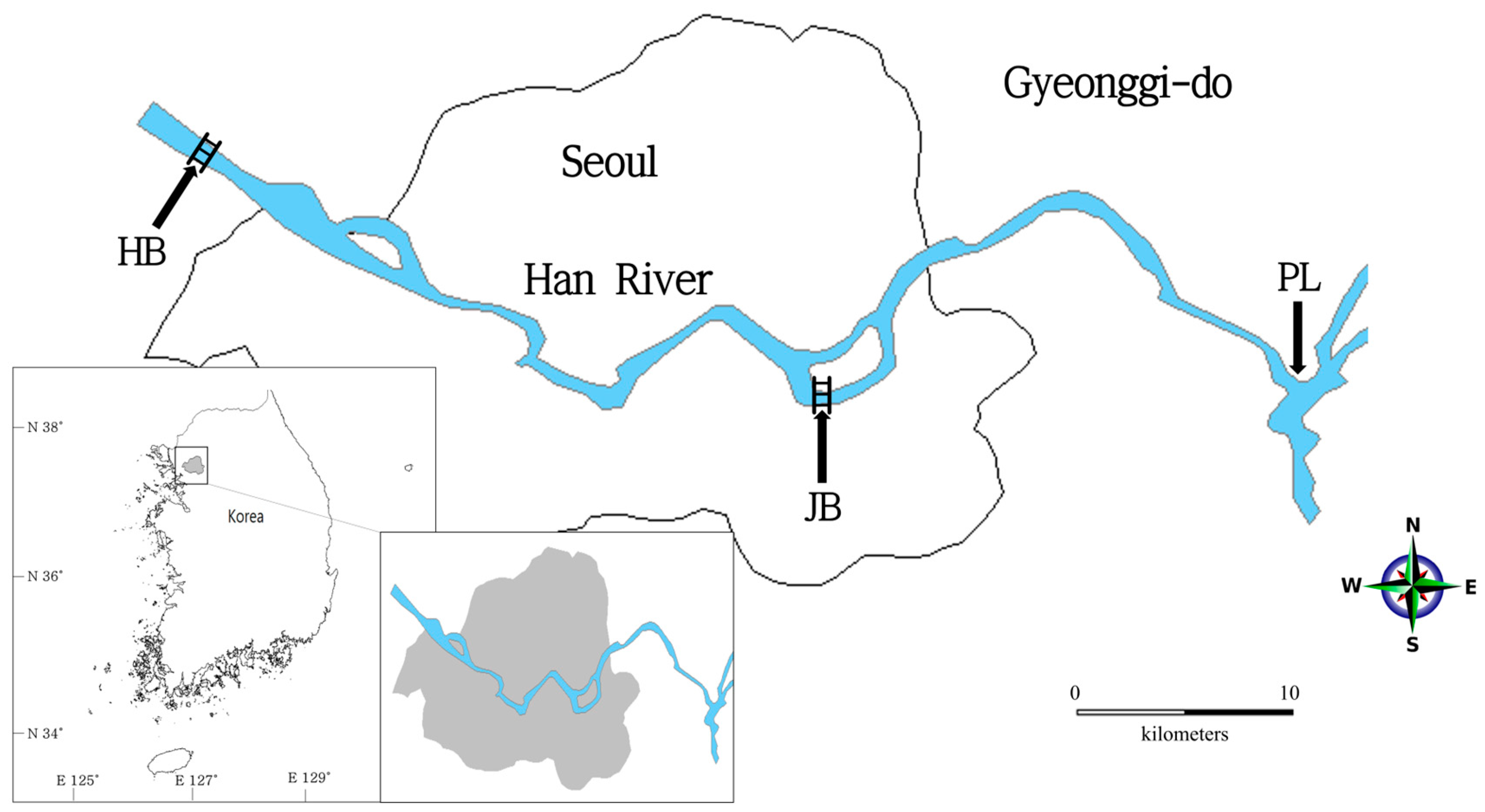
2.1. Sample Processing
2.2. PCR Amplification and Next Generation Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Comparison of eDNA and eRNA Metabarcoding Data with Previous Specimen Capture Survey Data
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Results
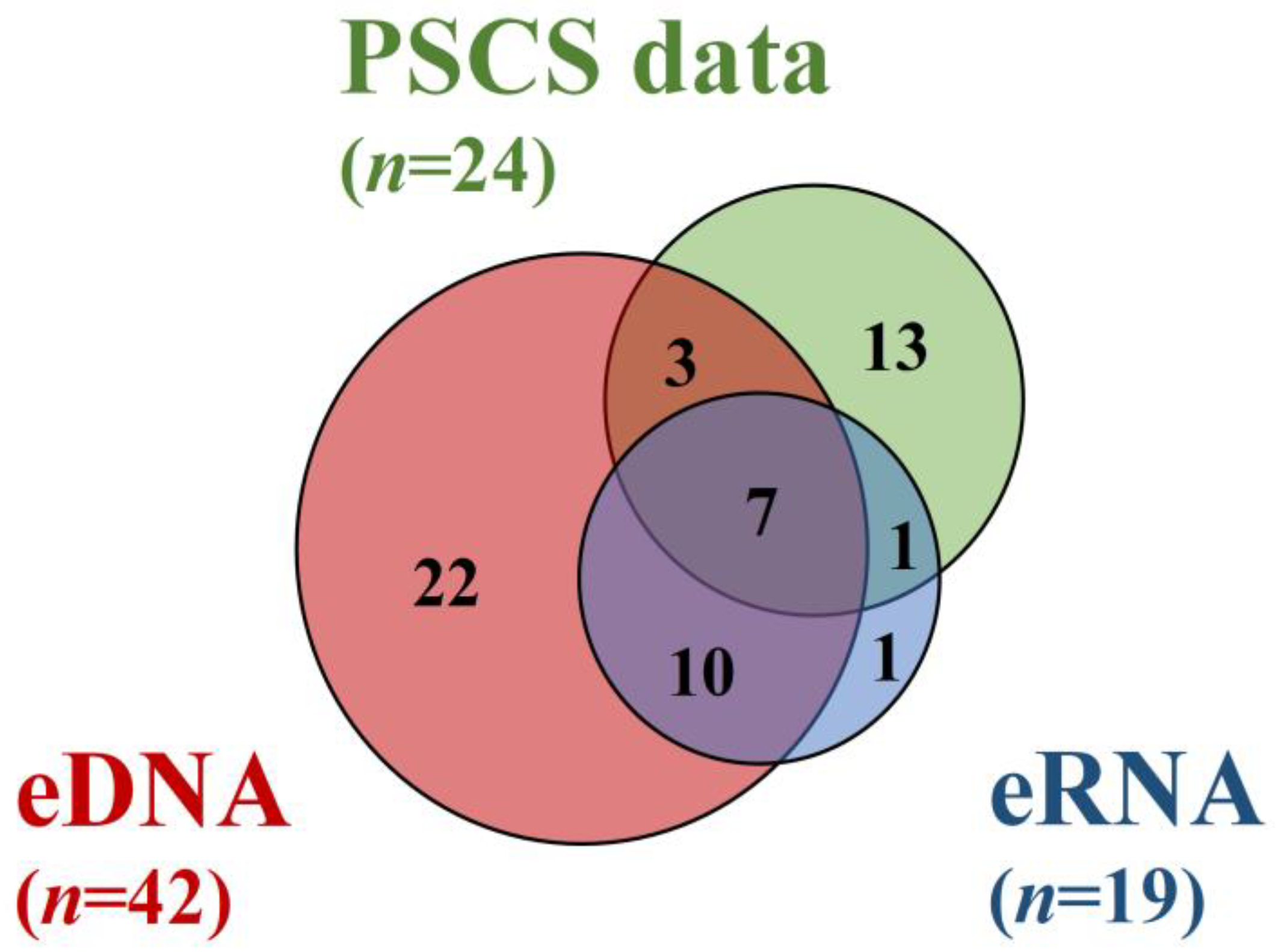
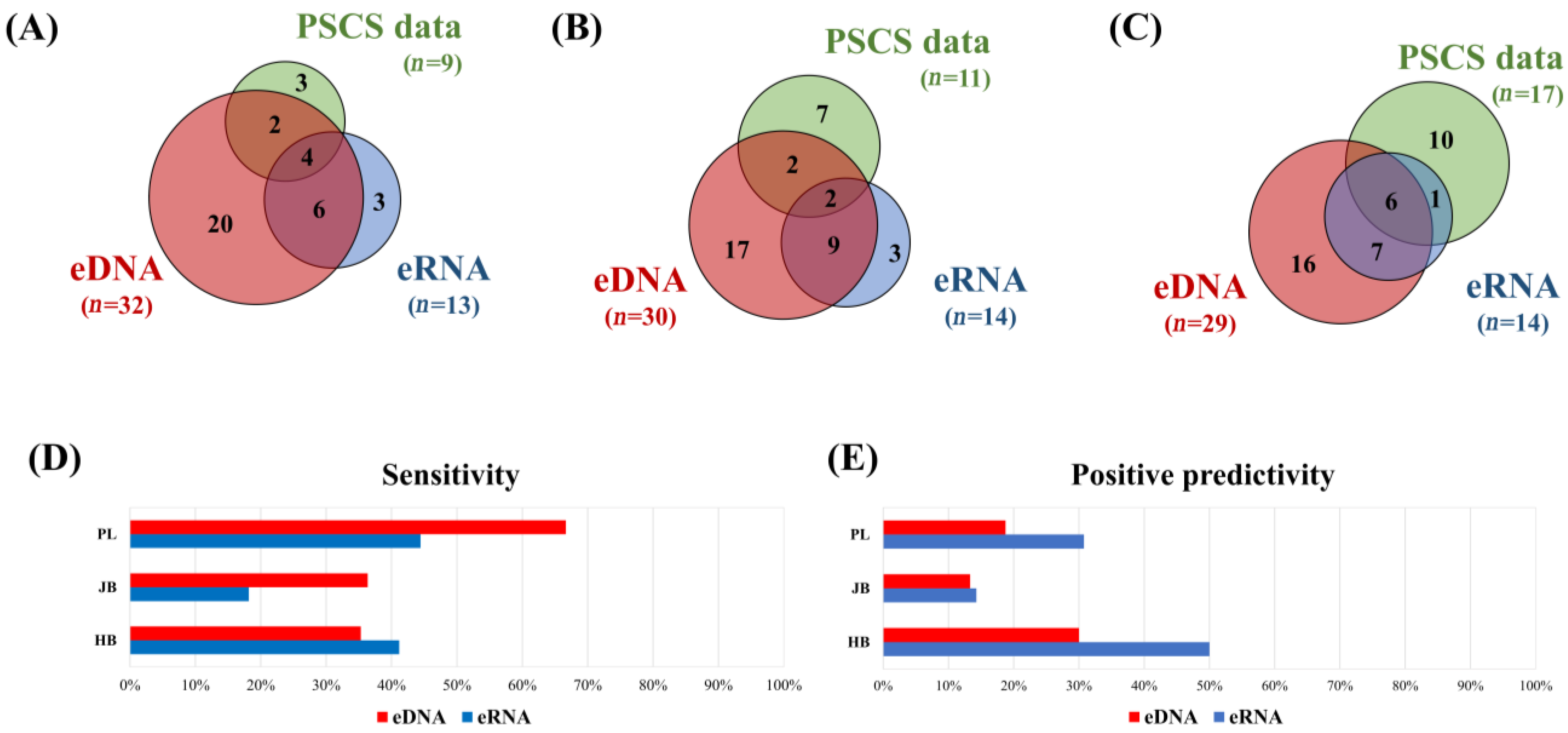
3.2. Comparison of the eDNA and eRNA Metabarcoding Positives, as well as of the Previous Specimen Capture Survey Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karr, J.R. Assessing Biological Integrity in Running Waters: A Method and Its Rationale; Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication No. 05; Illinois Natural History Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.H. The use of fish in ecological assessments. Aust. J. Ecol. 1995, 20, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D. Prospects for sustaining freshwater biodiversity in the 21st century: Linking ecosystem structure and function. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2010, 2, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stat, M.; John, J.; DiBattista, J.D.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M.; Harvey, E.S. Combined use of eDNA metabarcoding and video surveillance for the assessment of fish biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, S.A.; Contreras-Balderas, S.; Iles, A.C. An introduction to standardized sampling. In Standard Methods for Sampling North American Freshwater Fishes; Bonar, S., Hubert, W.A., Willis, D.W., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, K.L.; Lochmann, S.E.; Young, M.K. Methods for assessing fish populations. In Inland Fisheries Management in North America, 3rd ed.; Hubert, W.A., Quist, M.C., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 325–351. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, S.; Minami, K.; Fukaya, K.; Takahashi, K.; Sawada, H.; Murakami, H.; Tsuji, S.; Hashizume, H.; Kubonaga, S.; Horiuchi, T. Environmental DNA as a ‘snapshot’of fish distribution: A case study of Japanese jack mackerel in Maizuru Bay, Sea of Japan. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149786. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, N.T.; Lamberti, G.A. Freshwater fisheries assessment using environmental DNA: A primer on the method, its potential, and shortcomings as a conservation tool. Fish. Res. 2018, 197, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Yoon, S.; Kasai, A.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakata, M.K.; Horiuchi, T.; Sawada, H.; Kondoh, M.; Yamashita, Y. Dispersion and degradation of environmental DNA from caged fish in a marine environment. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, K.M.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, M.S. Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, J.; Clare, E.L.; Jones, J.I.; Day, J.J. Biodiversity assessment across a dynamic riverine system: A comparison of eDNA metabarcoding versus traditional fish surveying methods. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 1247–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautier, M.; Chardon, C.; Goulon, C.; Guillard, J.; Domaizon, I. A quantitative eDNA-based approach to monitor fish spawning in lakes: Application to European perch and whitefish. Fish. Res. 2023, 264, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, G.; Zhao, L.; Du, X.; Gao, T. Assessment of fishery resources using environmental DNA: The large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in the East China Sea. Fish. Res. 2021, 235, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroux, M.S.; Reichman, J.R.; Langknecht, T.; Burgess, R.M.; Ho, K.T. Environmental RNA as a tool for marine community biodiversity assessments. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Su, C.; Liu, Q.; Kong, Y.; Hua, S.; Hu, Z. Comparison of fish communities using environmental DNA metabarcoding and capture methods in a freshwater lake: A new set of universal PCR primers. Fish. Res. 2022, 253, 106365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, K.; Inoue, Y.; Amano, Y.; Nishioka, T.; Yamane, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Morita, O.; Honda, H. Fish environmental RNA enables precise ecological surveys with high positive predictivity. Ecol. Ind. 2021, 128, 107796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Yamanaka, H. Meta-Analyses of Environmental DNA Downstream Transport and Deposition in Relation to Hydrogeography in Riverine Environments. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.T.; Vanderploeg, H.A.; Chaganti, S.R. Environmental (e) RNA advances the reliability of eDNA by predicting its age. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, M.E. Can environmental RNA revolutionize biodiversity science? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, O.; Wood, S.A.; Tremblay, L.A.; Lear, G.; Ellis, J.I.; Pochon, X. Metabarcoding monitoring analysis: The pros and cons of using co-extracted environmental DNA and RNA data to assess offshore oil production impacts on benthic communities. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torti, A.; Lever, M.A.; Jørgensen, B.B. Origin, dynamics, and implications of extracellular DNA pools in marine sediments. Mar. Genom. 2015, 24, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahashi, T.; Sugime, S.; Inomata, K.; Nishijima, M.; Kato, S.; Yamamoto, H. Meiofaunal diversity at a seamount in the pacific ocean: A comprehensive study using environmental DNA and RNA. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 160, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, K.; Inoue, Y.; Amano, Y.; Nishioka, T.; Nagaike, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Morita, O.; Yamane, M.; Honda, H. Comparative environmental RNA and DNA metabarcoding analysis of river algae and arthropods for ecological surveys and water quality assessment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.; Malik, A.; An, H.; Kim, J.; Dinh Do, T.; Kim, C. Seasonal Diversity of Microeukaryotes in the Han River, Korea Through 18S rRNA Gene Metabarcoding. Evol. Bioinform. 2022, 18, 11769343221074688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, B. Primary productivity in lake Paldang. Korean J. Limn. 1990, 23, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Pochon, X.; Zaiko, A.; Fletcher, L.M.; Laroche, O.; Wood, S.A. Wanted dead or alive? Using metabarcoding of environmental DNA and RNA to distinguish living assemblages for biosecurity applications. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundermark, E.L.; Takahashi, M.K. Improving the yield of environmental DNA from filtered aquatic samples. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2020, 12, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2. High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, L.; Beirinckx, S.; Haegeman, A.; Debode, J.; Vandecasteele, B.; Baeyen, S.; Goormachtig, S.; Clement, L.; De Tender, C. Daring to be differential: Metabarcoding analysis of soil and plant-related microbial communities using amplicon sequence variants and operational taxonomical units. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Thompson, L.R. Mitohelper: A mitochondrial reference sequence analysis tool for fish eDNA studies. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A mitochondrial genome database of fish with an accurate and automatic annotation pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Biessy, L.; Latchford, J.L.; Zaiko, A.; von Ammon, U.; Audrezet, F.; Cristescu, M.E.; Pochon, X. Release and degradation of environmental DNA and RNA in a marine system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.; Lejzerowicz, F.; Reo, E.; Caruso, A.; Maccotta, A.; Coccioni, R.; Pawlowski, J.; Frontalini, F. Environmental RNA outperforms eDNA metabarcoding in assessing impact of marine pollution: A chromium-spiked mesocosm test. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.S. Salinity distribution and ecological environment of Han river estuary. J. Wetl. Res. 2004, 6, 149–166. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, T.; Shan, X.; Wang, W.; Jin, X. Effects of Temperature on the Timeliness of eDNA/eRNA: A Case Study of Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Water 2022, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Takao, K.; Minamoto, T. Linking the state of environmental DNA to its application for biomonitoring and stock assessment: Targeting mitochondrial/nuclear genes, and different DNA fragment lengths and particle sizes. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagzi, K.; Hechler, R.M.; Fussmann, G.F.; Cristescu, M.E. Environmental RNA degrades more rapidly than environmental DNA across a broad range of pH conditions. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsley, M.B.; Goldberg, C.S. Environmental RNA can distinguish life stages in amphibian populations. In Molecular Ecology Resources; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, M.K.; Watanabe, T.; Maki, N.; Ikeda, K.; Kosuge, T.; Okada, H.; Yamanaka, H.; Sado, T.; Miya, M.; Minamoto, T. Determining an effective sampling method for eDNA metabarcoding: A case study for fish biodiversity monitoring in a small, natural river. Limnology 2021, 22, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefair, J.E.; Rennie, M.D.; Cristescu, M.E. Environmental nucleic acids: A field-based comparison for monitoring freshwater habitats using eDNA and eRNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2928–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, H.-E.; Mun, M.-H.; Kim, C.-B. Metabarcoding by Combining Environmental DNA with Environmental RNA to Monitor Fish Species in the Han River, Korea. Fishes 2023, 8, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110550
An H-E, Mun M-H, Kim C-B. Metabarcoding by Combining Environmental DNA with Environmental RNA to Monitor Fish Species in the Han River, Korea. Fishes. 2023; 8(11):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110550
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Hyung-Eun, Min-Ho Mun, and Chang-Bae Kim. 2023. "Metabarcoding by Combining Environmental DNA with Environmental RNA to Monitor Fish Species in the Han River, Korea" Fishes 8, no. 11: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110550
APA StyleAn, H.-E., Mun, M.-H., & Kim, C.-B. (2023). Metabarcoding by Combining Environmental DNA with Environmental RNA to Monitor Fish Species in the Han River, Korea. Fishes, 8(11), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110550





