43 Years after H.G. Moser’s Seminal “Morphological and Functional Aspects of Marine Fish Larvae”: The Commonalities of Leptocephali and Larvae of Other Marine Teleosts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
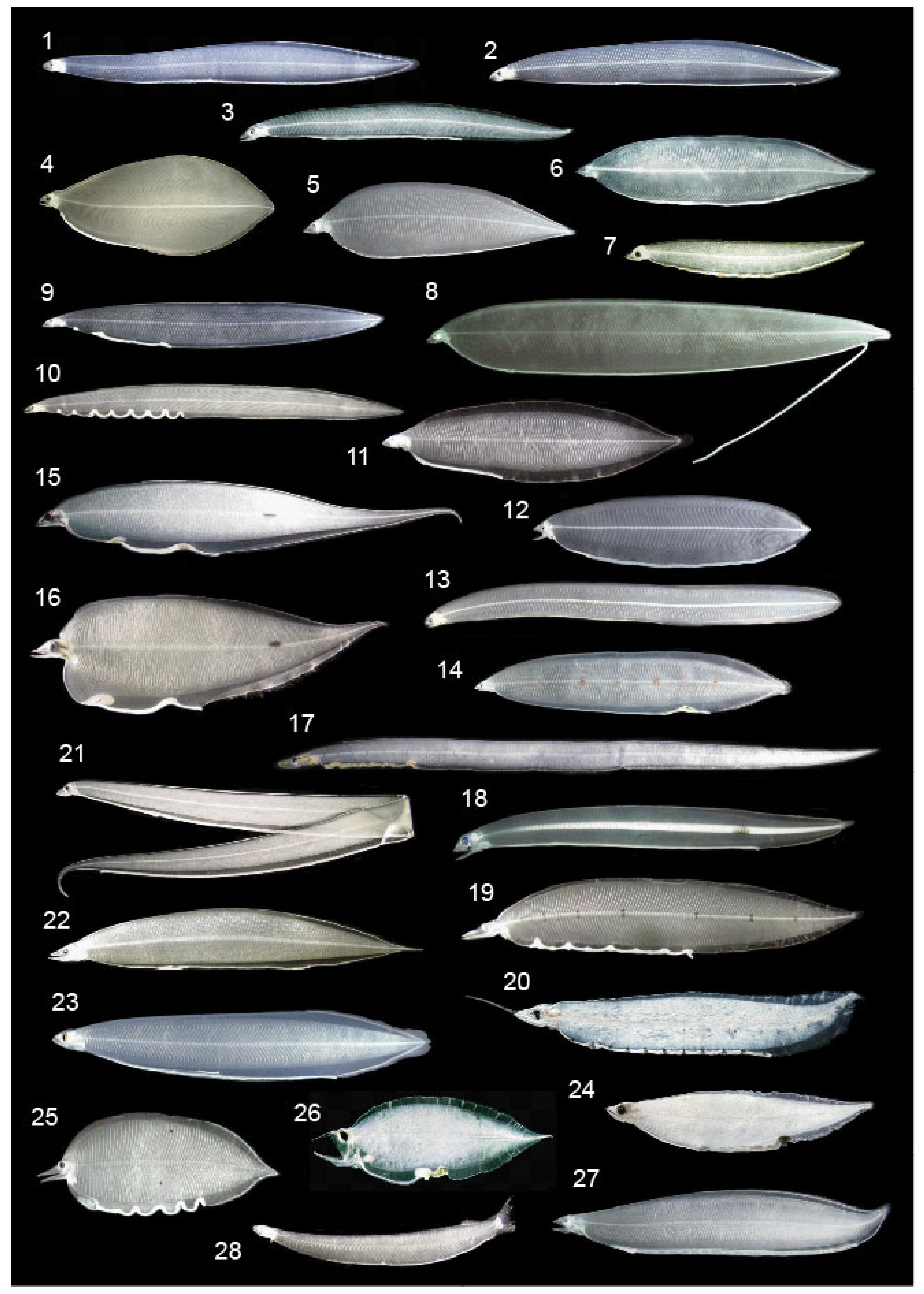


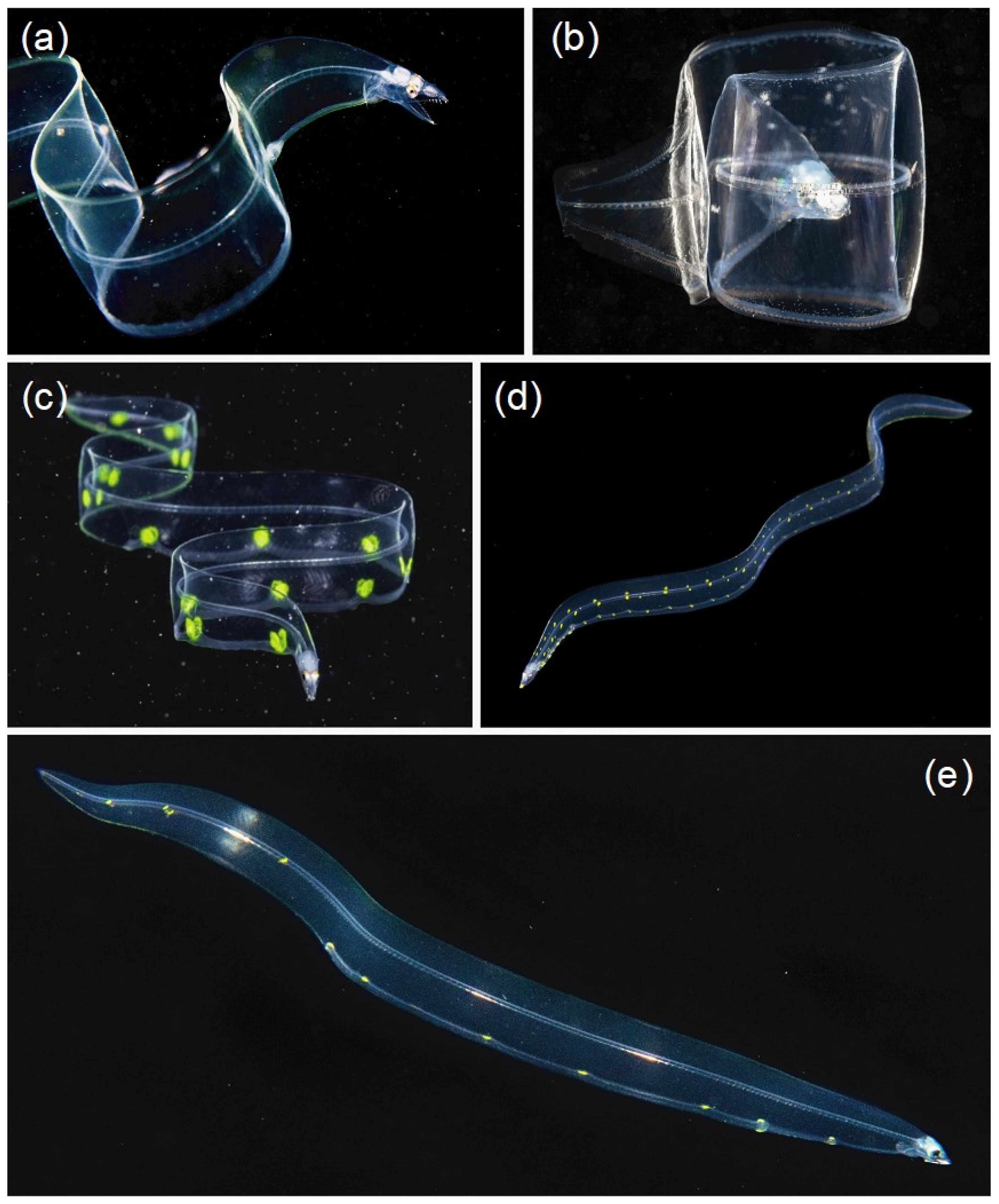
2. Materials and Methods
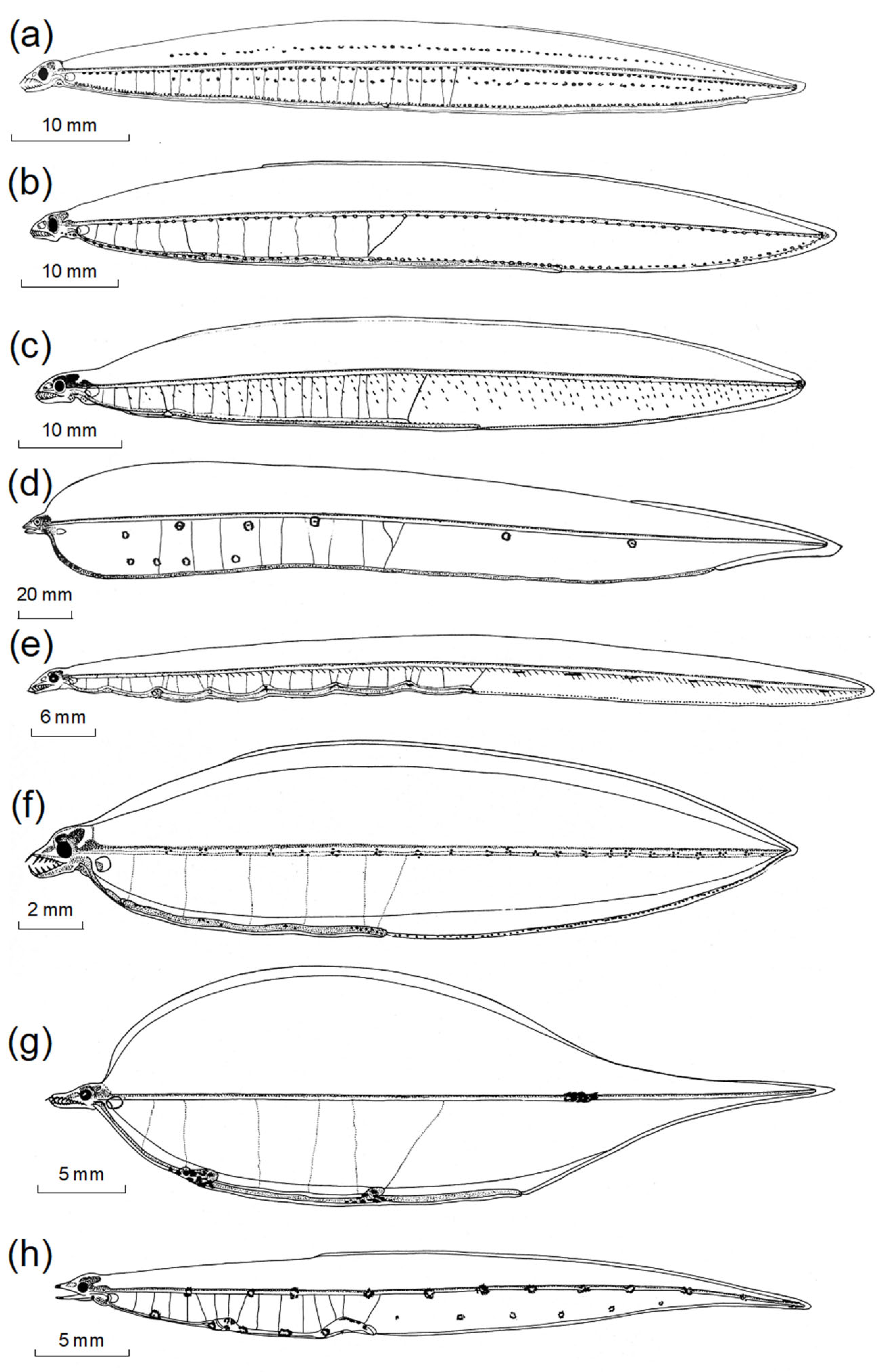
3. Results
3.1. H.G. Moser and Leptocephali
3.2. Commonalities of Eel and Fish Larvae
3.2.1. Body Shape and Morphological Structures
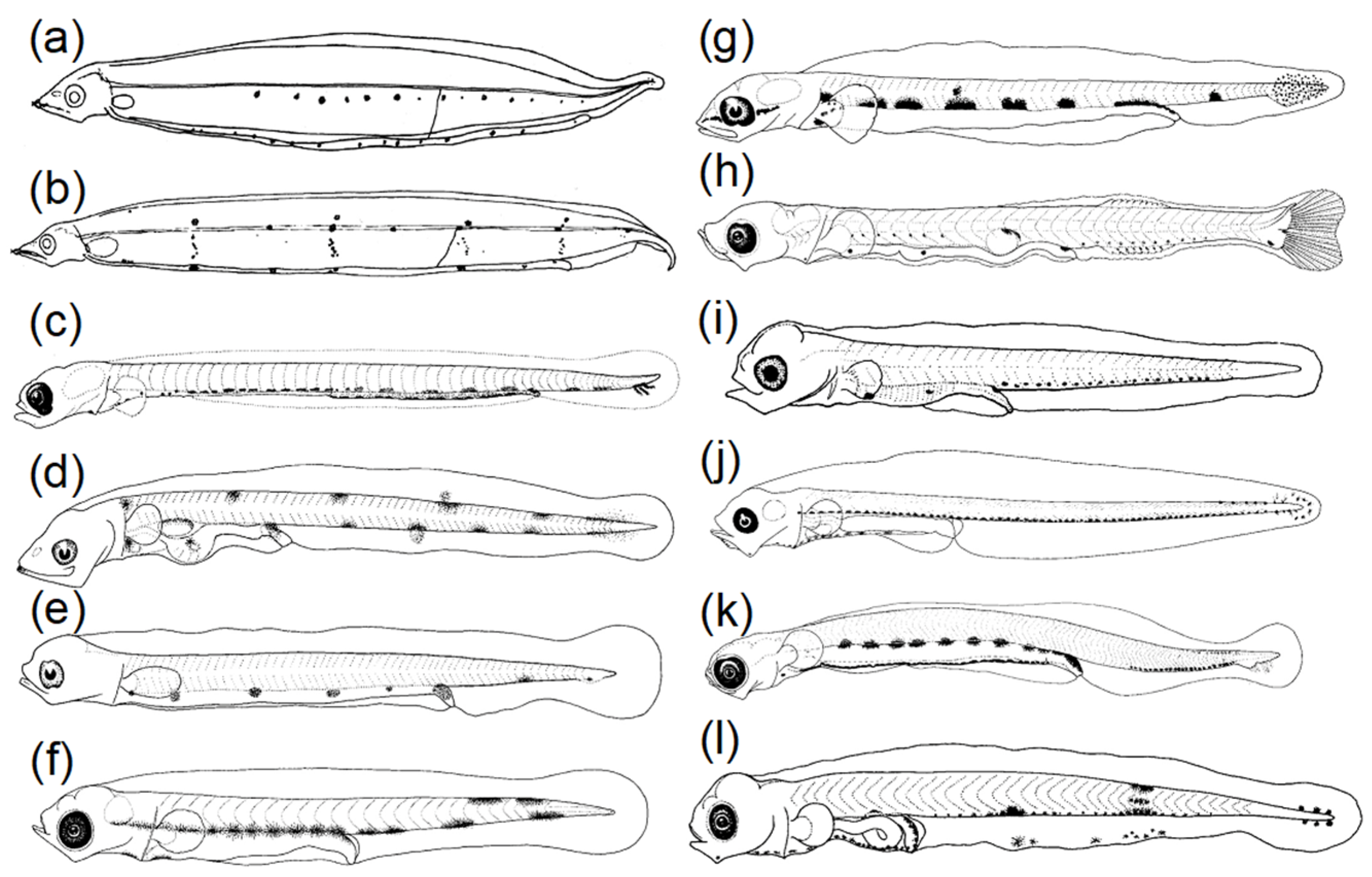
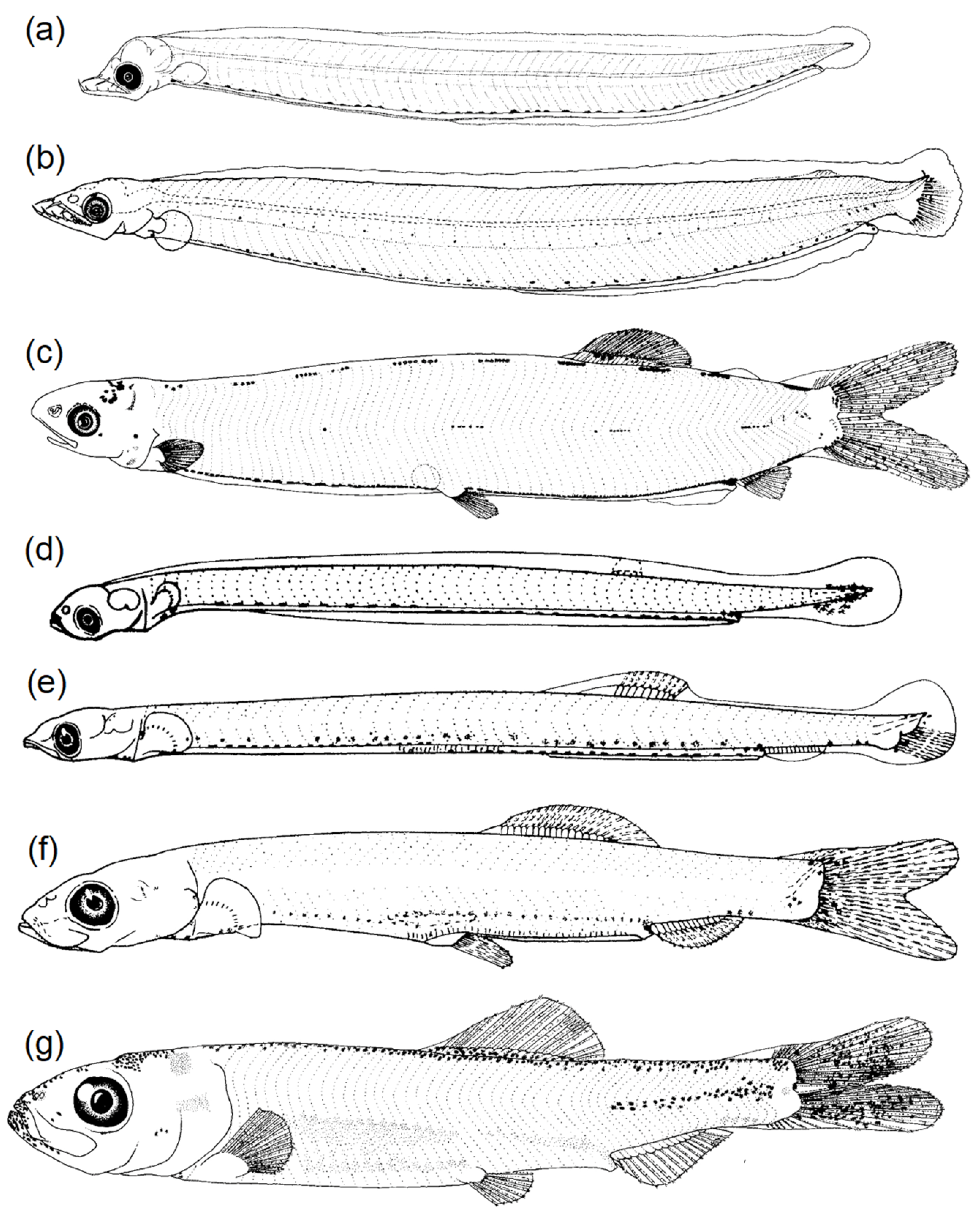
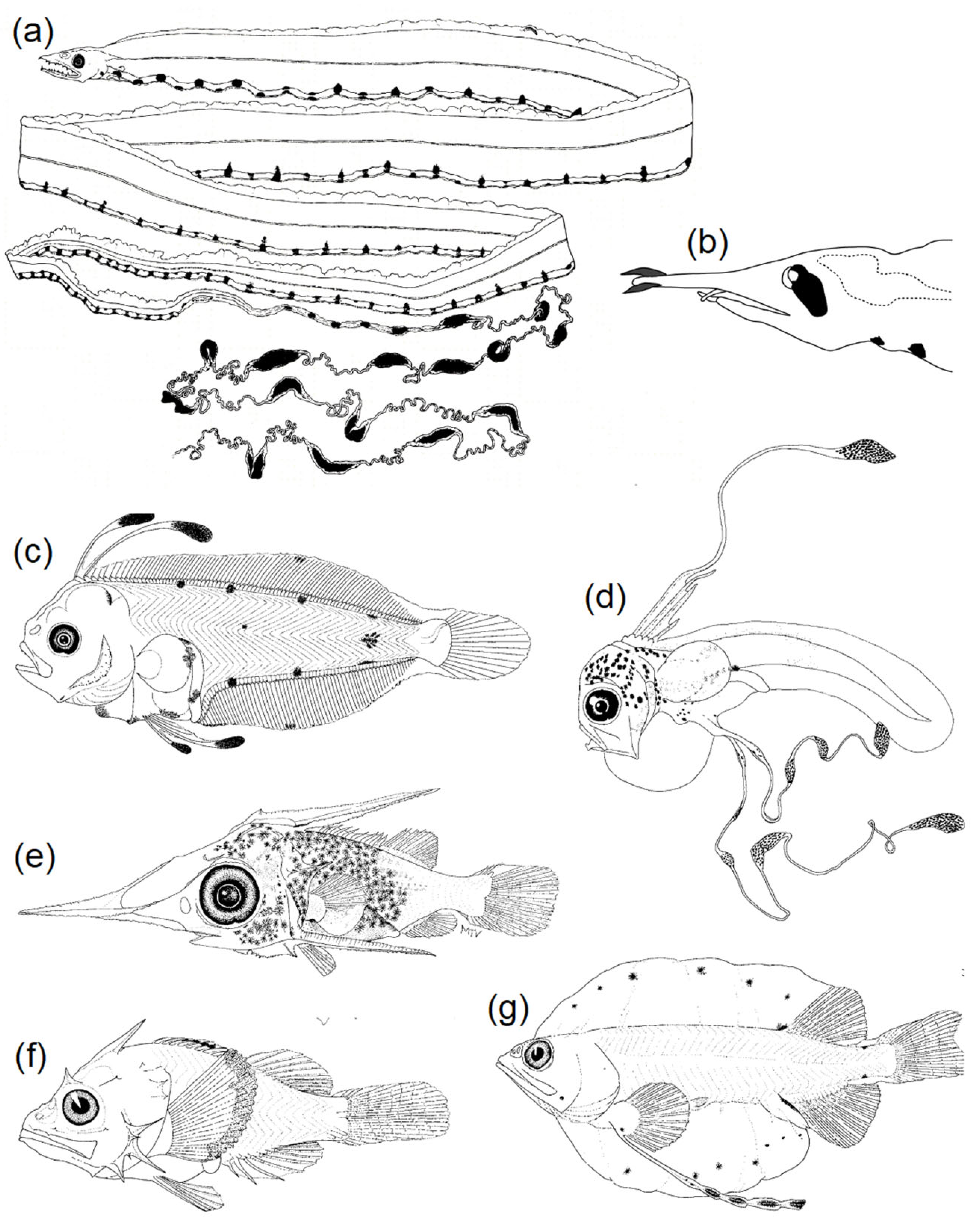
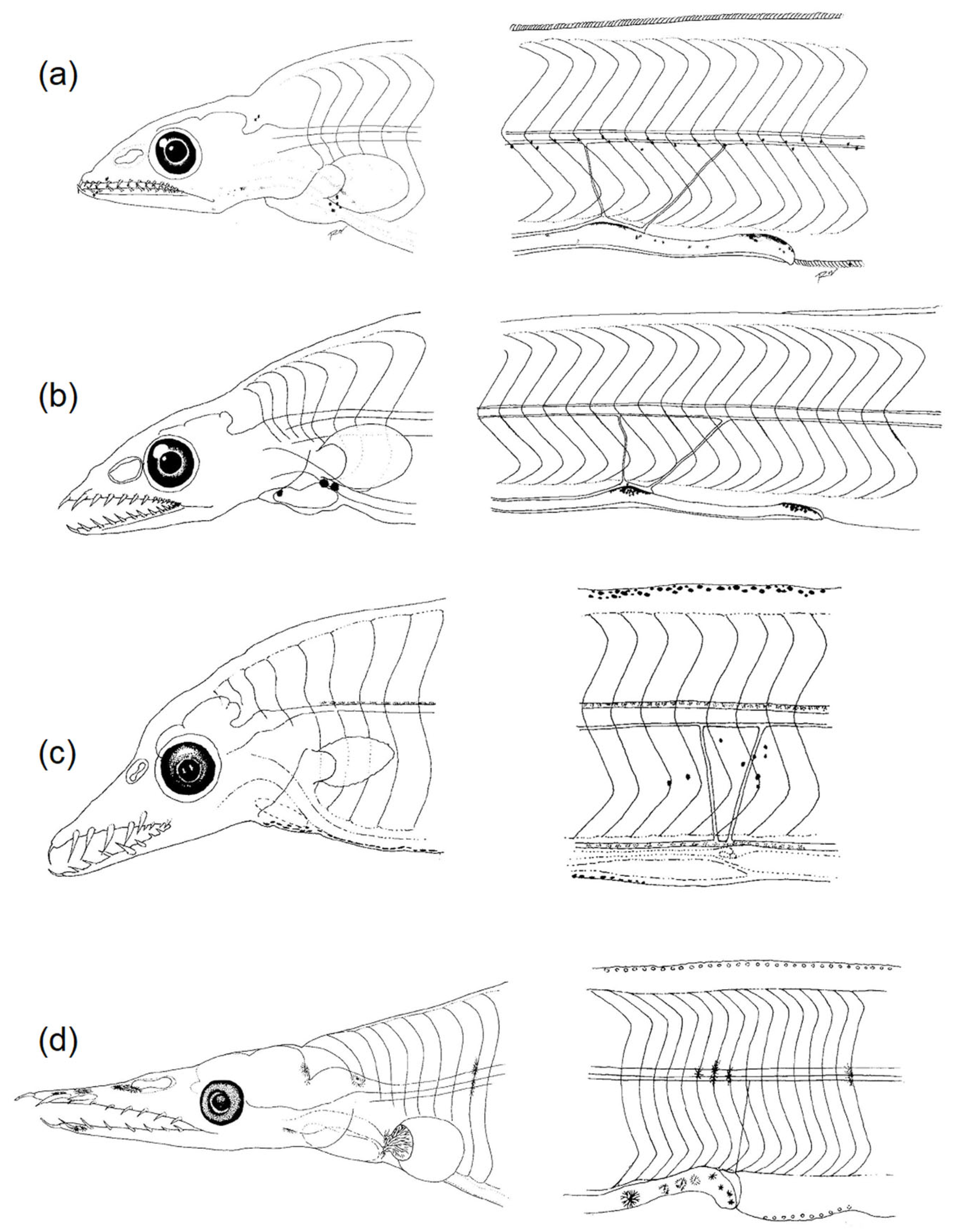
3.2.2. Diversity of Pigmentation
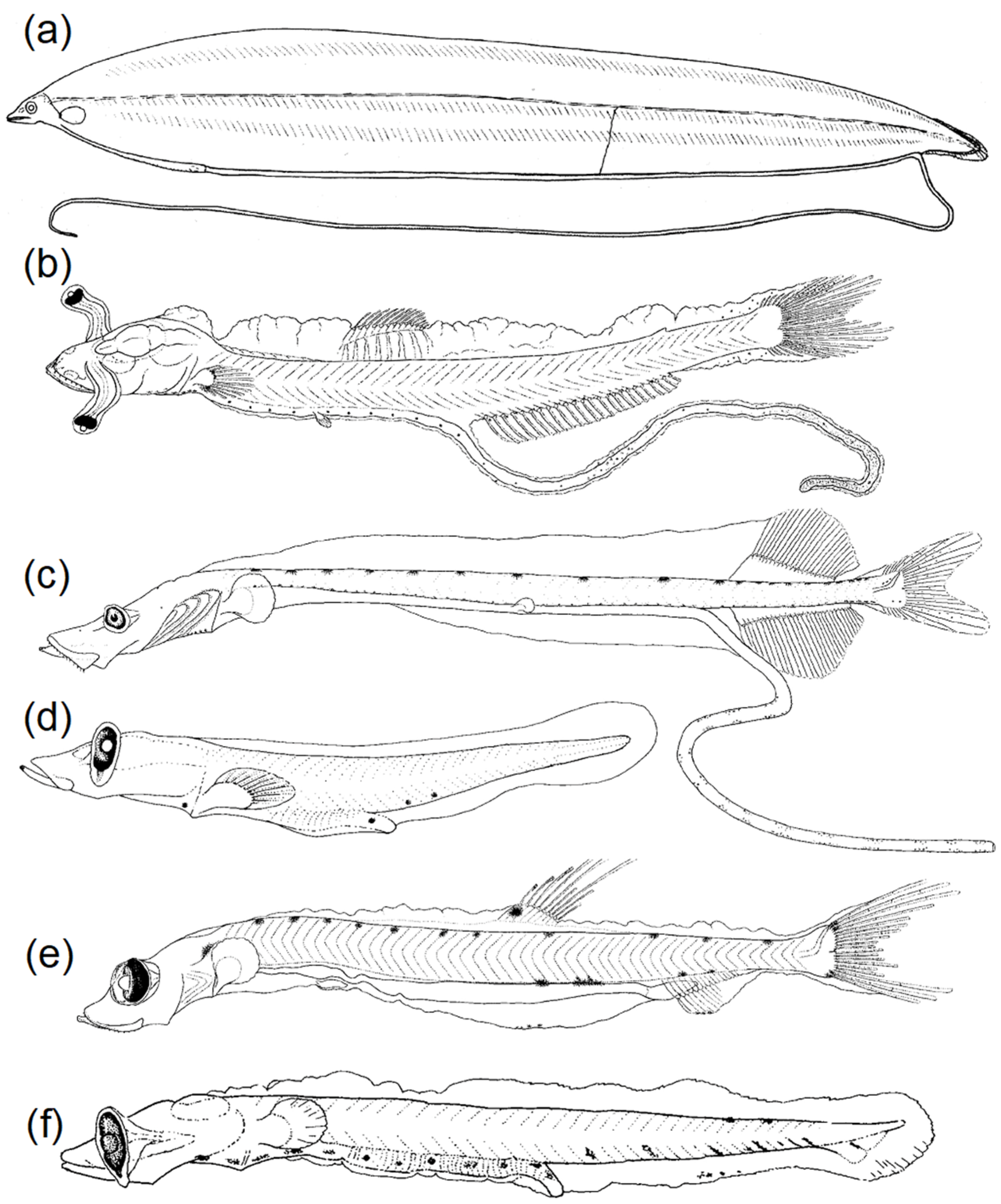
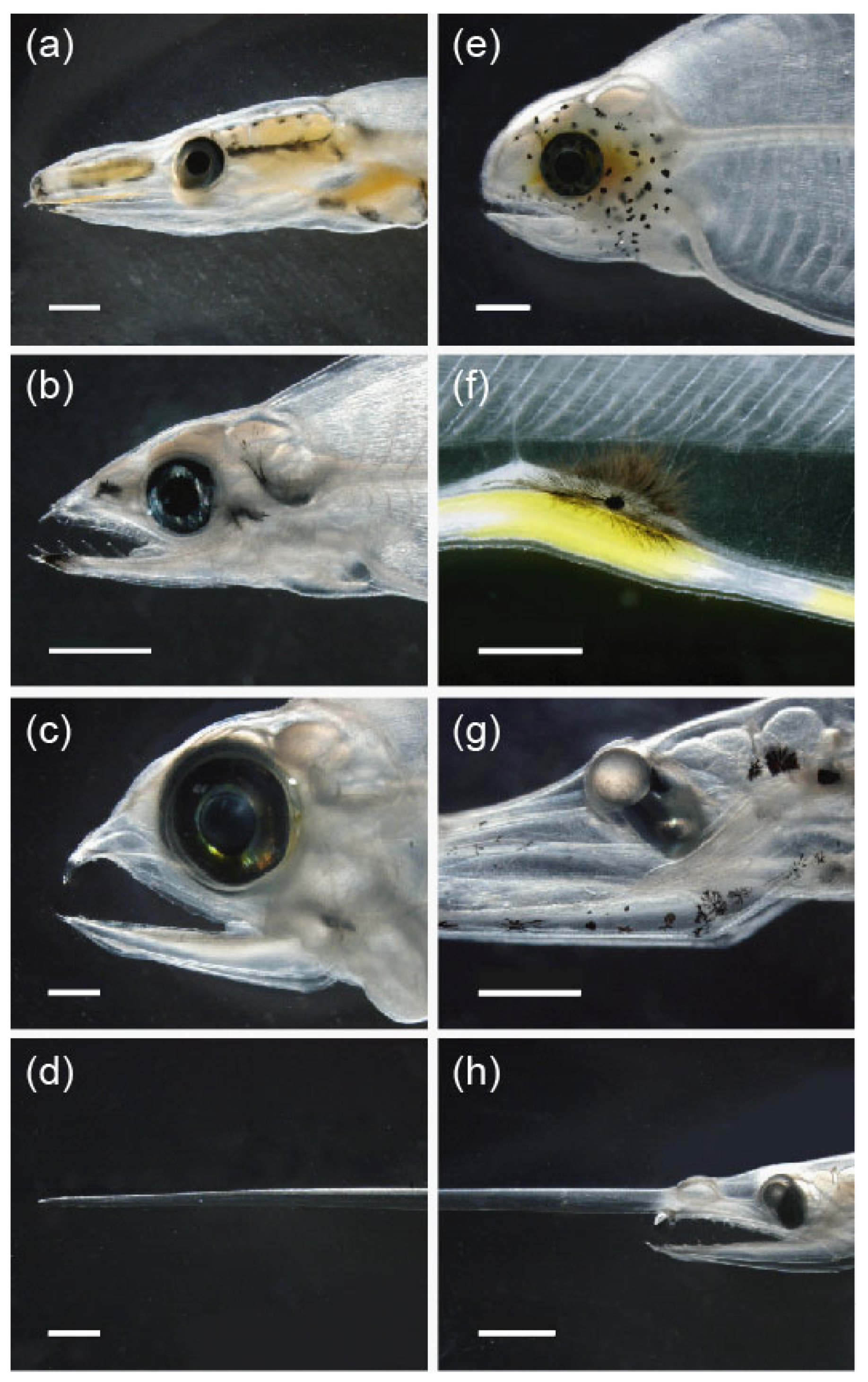
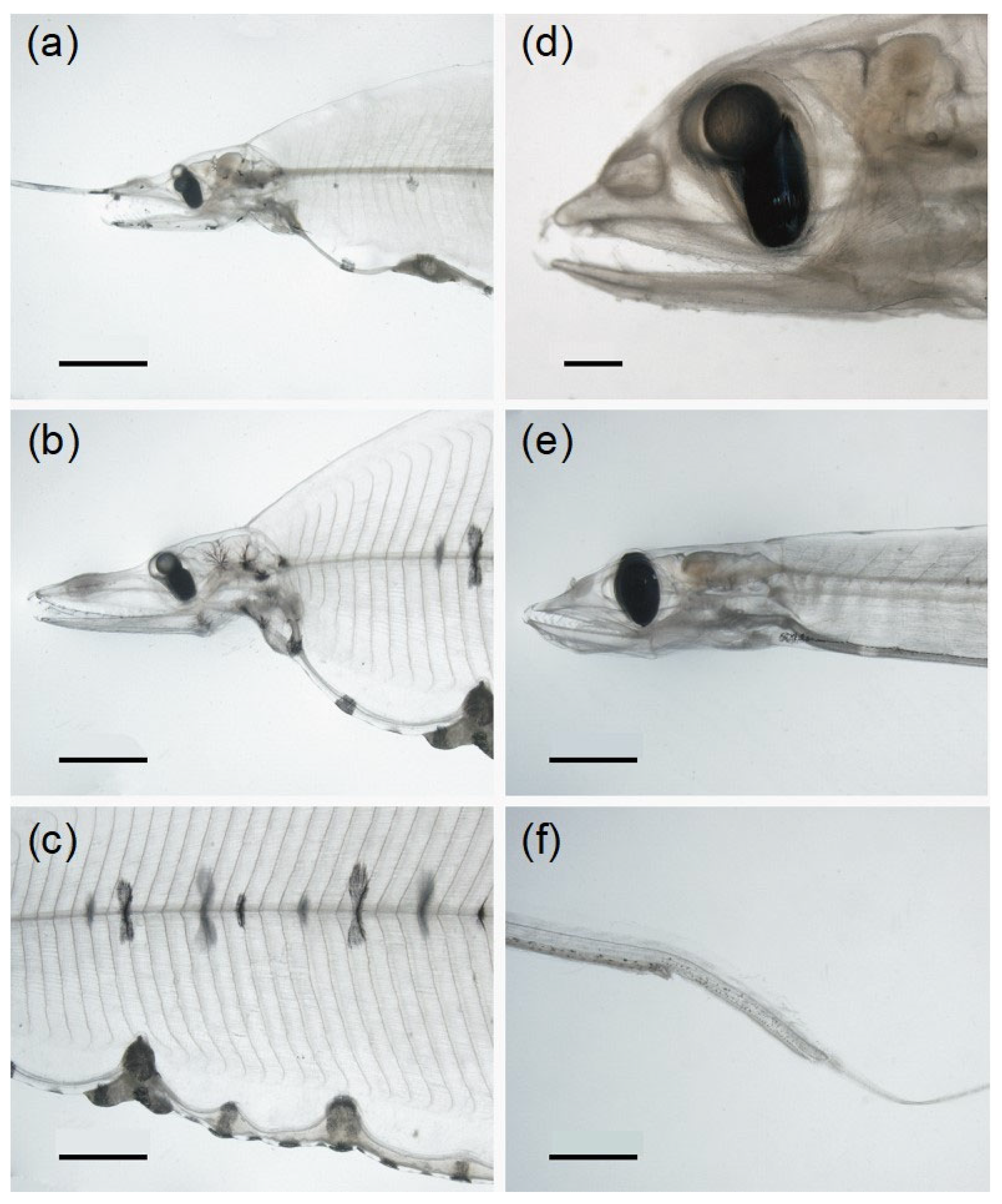
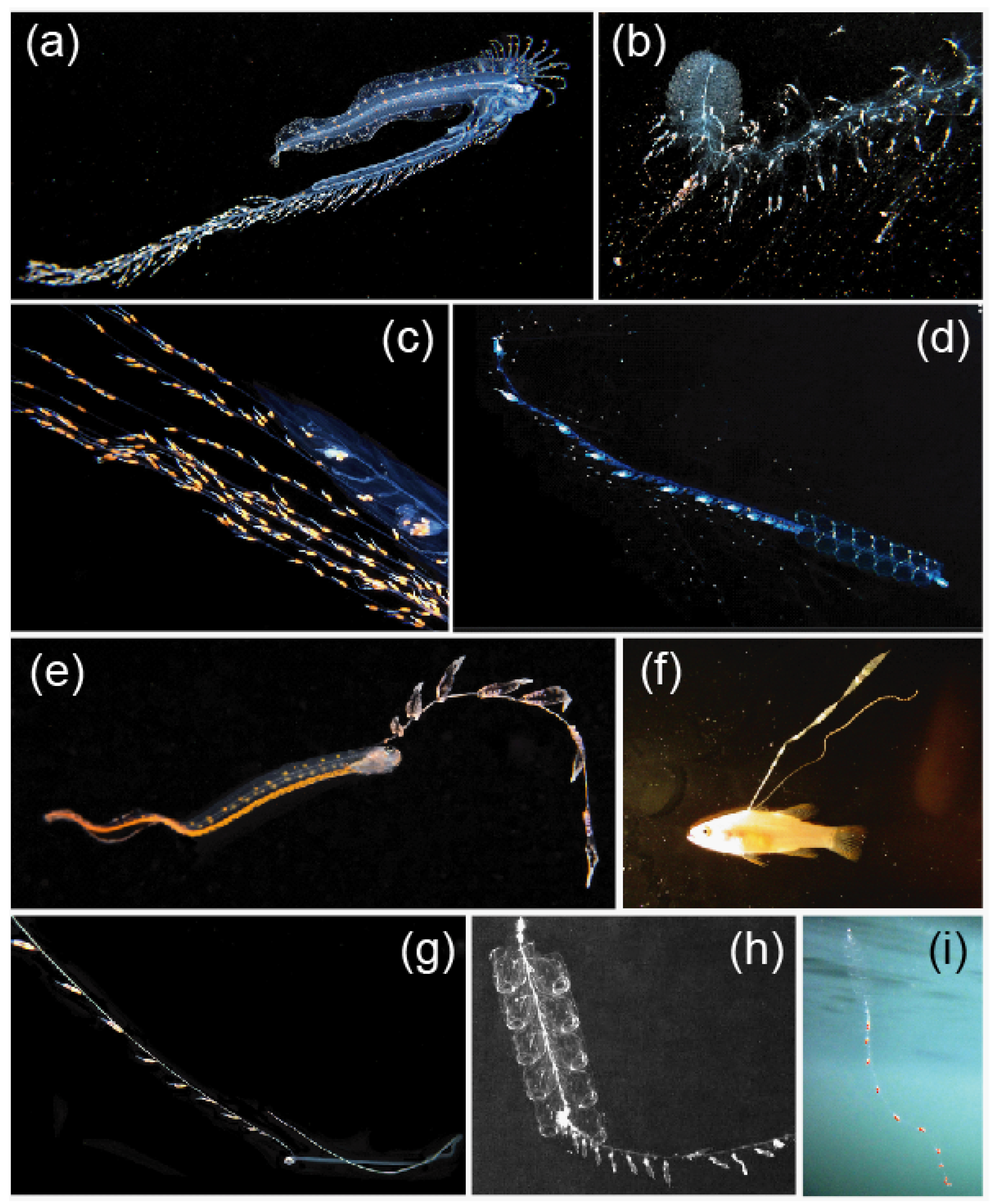
3.3. Mimicry to Reduce Predation

4. Discussion
4.1. Reasons for Similarities and Differences between Fish Larvae and Leptocephali
4.2. Predation on Fish Larvae as a Selective Force
4.3. Future Research on Fish Larvae
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moser, H.G. Morphological and functional aspects of marine fish larvae. In Marine Fish Larvae: Morphology, Ecology, and Relation to Fisheries; Lasker, R., Ed.; Washington Sea Grant Program: Seattle, WA, USA, 1981; pp. 89–131. [Google Scholar]
- Lasker, R. (Ed.) Marine Fish Larvae: Morphology, Ecology, and Relation to Fisheries; Washington Sea Grant Program: Seattle, WA, USA, 1981. Available online: https://swfsc-publications.fisheries.noaa.gov/publications/CR/1981/1981XD.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Sakaue, J. The Wonder World of Juvenile Fish; Aqualife Publishing: Yokohama Japan, 2016. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, A.; Milisen, J.W.; Mundy, B.C.; Johnson, G.D. Blackwater diving: An exciting window into the planktonic arena and its potential to enhance the quality of larval fish collections. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 2021, 109, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, C.C. The phylogenetic significance of colour patterns in marine teleost larvae. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 168, 496–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, H.G.; Richards, W.J.; Cohen, D.M.; Fahay, M.P.; Kendall, A.W.; Richardson, S.L. (Eds.) Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Special Publication No. 1; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; Available online: https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/23343#page/13/mode/1up (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Mundy, B.C.; Hilton, E.J. H Geoffrey Moser. Larval fishes: Taxonomy, distribution, and fisheries biology. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 2022, 110, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, W.J. Elopiformes: Development. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Eds.; Spec. Publ. No. 1.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Castle, P.H.J. Notacanthiformes and Anguilliformes: Development. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Eds.; Spec. Publ. No. 1.; Amer. Soc. Ichthyology and Herpetology; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 62–93. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.G. Elopiformes, Notacanthiformes and Anguilliformes: Relationships. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Eds.; Spec. Publ. No. 1.; Amer. Soc. Ichthyology and Herpetology; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 94–108. [Google Scholar]
- Blache, J. Leptocephales des poissons Anguilliformes dans la zone sud du Golfe de Guinée. Faune Trop. 1977, 10, 1–381. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.G. Guide to the Leptocephali (Elopiformes, Anguilliformes, and Notacanthiformes); NOAA Technical Report NMFS Circular 424; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Böhlke, E.B. (Ed.) Leptocephali. In Fishes of the Western North Atlantic; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 657–1055, Part 9, Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Fahay, M.P. Early Stages of Fishes in the Western North Atlantic Ocean (Davis Strait, Southern Greenland and Flemish Cap to Cape Hatteras); Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization (NAFO): Dartmouth, NS, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J. Remarks on the metamorphosis and distribution of the larvae of the eel (Anguilla vulgaris, Turt.). Med. Komm. Hamunders. Ser. Fisk. 1909, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J. On the early larval stages of the fresh-water eels (Anguilla) and some other North Atlantic muraenoids. Medd. Komm. Havunders. Ser. Fisk. 1916, 4, pls-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J. The breeding places of the eel. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. 1922, 211, 179–208. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.G. Introduction to leptocephali. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic; Böhlke, E.B., Ed.; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 657–668, Part 9, Leptocephali, Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner, R.C.; McCleave, J.D. The northern limit of spawning by Atlantic eels (Anguilla spp.) in the Sargasso Sea in relation to thermal fronts and surface water masses. J. Mar. Res. 1988, 46, 647–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Bonhommeau, S.; Munk, P.; Castonguay, M.; Hanel, R.; McCleave, J.D. A century of research on the larval distributions of the Atlantic eels: A re-examination of the data. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 1035–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; McCleave, J.D. Species assemblages of leptocephali in the Subtropical Convergence Zone of the Sargasso Sea. J. Mar. Res. 1994, 52, 743–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; McCleave, J.D. Species assemblages of leptocephali in the southwestern Sargasso Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 344, 197–212. [Google Scholar]
- Böhlke, E.B. (Ed.) Orders Anguilliformes and Saccopharyngiformes. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 1, p. 655, Part 9, Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K. An Introduction to Leptocephali: Biology and Identification; Ocean Research Institute, The University of Tokyo: Tokyo, Japan, 2004; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K. The behavioral ecology and distribution of leptocephali: Marine fish larvae with unforeseen abilities. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M. Ecology of Anguilliform Leptocephali: Remarkable Transparent Fish Larvae of the Ocean Surface Layer. Aqua-BioScience Monogr. 2009, 2, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; D’Avella, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K. Enlarged chromatophores in an actively swimming ophichthid leptocephalus observed over deep-water off Kona, Hawaii. Zool. Stud. 2010, 49, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.J.; Norman, M.D.; Tsukamoto, K.; Finn, J.K. Evidence of mimicry of gelatinous zooplankton by anguilliform leptocephali for predator avoidance. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2013, 45, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Rutgers, R.; Haythorne, B.; Yavuzdogan, T.; Obata, S.; Wu, T.; Rutgers, H.; Powell, J.; Tsukamoto, K. Observations of large muraenid leptocephali in coastal Indonesia: Locations of sightings and behavior of the larvae. Mar. Biodiv. Rec. 2013, 6, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Hanel, R.; Feunteun, E.; Tsukamoto, K. The food source of Sargasso Sea leptocephali. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Miller, M.J. The mysterious feeding ecology of leptocephali: A unique strategy of consuming marine snow materials. Fish. Sci. 2020, 87, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.R. Feeding ecology and predation of marine fish larvae. In Marine Fish Larvae: Morphology, Ecology and Relation to Fisheries; Lasker, R., Ed.; Washington Sea Grant Program: Seattle, DC, USA, 1981; pp. 33–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sumida, B.Y.; Moser, H.G. Food and feeding of bocaccio (Sebastes paucispinis) and comparison with Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) larvae in the California Current. Calif. Coop. Oceanic Fish. Investig. Rep. 1984, 25, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Llopez, J.K.; Cowan, R.K. Variability in the trophic role of coral reef fish larvae in the oceanic plankton. Mar. Ecol Prog. Ser. 2009, 381, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alldredge, A.L.; Silver, M.W. Characteristics, dynamics and significance of marine snow. Progr. Oceanogr. 1988, 20, 41–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigg, A.; Santschi, P.H.; Burd, A.; Chin, W.-C.; Kamalanathan, M.; Xu, C.; Ziervogel, K. From nano-gels to marine snow: A synthesis of gel formation processes and modeling efforts involved with particle flux in the ocean. Gels 2021, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, H.G. (Ed.) The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; CalCOFI Atlas 33; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; Available online: https://calcofi.org/downloads/publications/atlases/CalCOFI_Atlas_33.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Richards, W.J. Early Stages of Atlantic Fishes: An Identification Guide for the Western Central North Atlantic; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Leis, J.M.; Carson-Ewart, B.M. (Eds.) The Larvae of Indo-Pacific Coastal Fishes: An Identification Guide to Marine Fish Larvae; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2000; 850p. [Google Scholar]
- Robison, B.H. Shape change behavior by mesopelagic animals. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 1999, 32, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.; Woodson, C.; Guigand, C.; Cowen, R. Larval fishes utilize Batesian mimicry as a survival strategy in the plankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 551, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapstone, G.M. Global diversity and review of Siphonophorae (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, E.D.; Damian-Serrano, A.; Haddock, S.H.D.; Dunn, C.W.; Choy, C.A. Integrating siphonophores into marine food-web ecology. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2022, 7, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon; Gravili, C.; Pagès, F.; Gili, J.-M.; Boero, F. An Introduction to Hydrozoa; Mémoires du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle: Paris, France, 2006; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, J.E.; Arai, M.N. Interactions of pelagic cnidarians and ctenophores with fish: A review. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.N. Predation on pelagic coelenterates: A review. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 2005, 85, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.P.; Somvanshi, V.S.; Dalvi, R.S. Diet composition, feeding niche partitioning and trophic organisation of large pelagic predatory fishes in the eastern Arabian Sea. Hydrobiologia 2014, 736, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, A.C.; Kendall, A.W., Jr.; Blood, D.M.; Vinter, B.M. Laboratory Guide to Early Life History Stages of Northeast Pacific Fishes; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; NOAA Technical Rep. NMFS 80. [Google Scholar]
- Konishi, Y.; Chayakul, R.; Chamchang, C.; Duangdee, T. Early Stages of Marine Fishes in the Southeast Asian Region; Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center: Samutprakan, Thailand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Okiyama, M. (Ed.) An Atlas of the Early Stage Fishes in Japan; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1988. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Okiyama, M. (Ed.) An Atlas of Early Stage Fishes in Japan, 2nd ed.; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Leis, J.M. Taxonomy and systematics of larval Indo-Pacific fishes: A review of progress since 1981. Ichthyol. Res. 2015, 62, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sköld, H.N.; Aspengren, S.; Cheney, K.L.; Wallin, M. Fish Chromatophores—From molecular motors to animal behavior. Internat. Rev. Cell Molec. Biol. 2016, 321, 171–219. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.J.; Robinet, T. Life history and morphology of eel larvae in the Gulf of Guinea of western Africa: Revisiting Jacques Blache’s research (1960–1977) 40 years later. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2018, 28, 355–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, J.; Watanabe, S.; Miller, M.J.; Mochioka, N.; Otake, T.; Yoshinaga, T.; Tsukamoto, K. Spawning sites of the Japanese eel in relation to oceanographic structure and the West Mariana Ridge. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.J.; Shimizu, M.; Aoyama, J.; Watanabe, S.; Kuroki, M.; Feunteun, E.; Higuchi, T.; Takeuchi, A.; Han, Y.-S.; Sasal, P.; et al. Distribution and abundance of leptocephali in the western South Pacific region during two large-scale sampling surveys. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 206, 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Chow, S.; Otake, T.; Kurogi, H.; Mochioka, N.; Miller, M.J.; Aoyama, J.; Kimura, S.; Watanabe, S.; Yoshinaga, T.; et al. Oceanic spawning ecology of freshwater eels in the western North Pacific. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.J.; Feunteun, E.; Aoyama, J.; Watanabe, S.; Kuroki, M.; Lecomte-Finiger, R.; Minegishi, Y.; Robinet, T.; Réveillac, E.; Gagnaire, P.-A.; et al. Biodiversity and distribution of leptocephali west of the Mascarene Plateau in the southwestern Indian Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 137, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Wouthuyzen, S.; Feunteun, E.; Aoyama, J.; Watanabe, S.; Syahailatua, A.; Kuroki, M.; Robinet, T.; Hagihara, S.; Otake, T.; et al. Contrasting biodiversity of eel larvae across the central Indian Ocean subtropical gyre. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019a, 161, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Wouthuyzen, S.; Sugeha, H.Y.; Kuroki, M.; Tawa, A.; Watanabe, S.; Syahailatua, A.; Suharti, S.; Tantu, F.Y.; Otake, T.; et al. High biodiversity of leptocephali in Tomini Bay Indonesia in the center of the Coral Triangle. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Marohn, L.; Wysujack, K.; Freese, M.; Pohlmann, J.-D.; Westerberg, H.; Tsukamoto, K.; Hanel, R. Morphology and gut contents of anguillid and marine eel larvae in the Sargasso Sea. Zool. Anz. A J. Comp. Zool. 2019, 279, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiler, E. Developmental physiology of elopomorph leptocephali. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1999, 123, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rass, T.S.; Moser, H.G.; Ahlstrom, E.H. Development of Lanternfishes (Family Myctophidae) in the California Current. Pt I. Species with Narrow-Eyed Larvae. Bull. Mus. Nat. Hist. Sci. 1970, 1970, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, H.G.; Ahlstrom, E.H. Myctophidae: Lanternfishes. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; CalCOFI Atlas 33; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 387–475. [Google Scholar]
- Olivar, M.P.; Moser, H.G.; Beckley, L.E. Lanternfish larvae from the Agulhas current (SW Indian Ocean). Sci. Mar. 1999, 63, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, H.G.; Watson, W. Preliminary Guide to the Identification of the Early Life History Stages of Myctophiform Fishes of the Central Western Atlantic; NOAA Technical Memorandum, NOAA-TM-NMFS-SEFSC-453; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sassa, C.; Moser, H.G.; Kawaguchi, K. Horizontal and vertical distribution patterns of larval myctophid fishes in the Kuroshio Current region. Fish. Oceanogr. 2002, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charter, S.R.; Moser, H.G. Elopidae: Tenpounders. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 75–77, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Charter, S.R.; Moser, H.G. Albulidae: Bonefishes. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 79–81, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Charter, S.R.; Moser, H.G. Muraenidae: Morays. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 88–91, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, H.G.; Charter, S.R. Notacanthidae: Spiny eels. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 82–85, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K. The ecology of oceanic dispersal and survival of anguillid leptocephali. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Wouthuyzen, S.; Aoyama, J.; Sugeha, H.Y.; Watanabe, S.; Kuroki, M.; Syahailatua, A.; Suharti, S.; Hagihara, S.; Tantu, F.Y.; et al. Will the high biodiversity of eels in the Coral Triangle be affected by climate change? In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Jakarta Selatan, Indonesia, 20 November 2020; Volume 789, p. 12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G. Notacanthiform leptocephali in the Western North Atlantic. Copeia 1970, 1970, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, P.H.J.; Raju, N.S. Some rare leptocephali from the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific Oceans. Dana Rep. 1975, 85, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Kurogi, H.; Chow, S.; Yanagimoto, T.; Konishi, K.; Nakamichi, R.; Sakai, K.; Ohkawa, T.; Saruwatari, T.; Takahashi, M.; Ueno, Y.; et al. Adult form of a giant anguilliform leptocephalus Thalassenchelys coheni Castle and Raju 1975 is Congriscus megastomus (Günther 1877). Ichthyol. Res. 2016, 63, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G.; Miller, M.J. Cyematid larvae of the Leptocephalus holti group in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans (Pisces: Saccopharyngiformes). Breviora 1996, 503, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen, J.Y.; Miller, M.J.; Sado, T.; Hanel, R.; Tsukamoto, K.; Miya, M. Resolving deep-sea pelagic saccopharyngiform eel mysteries: Identification of Neocyema and Monognathidae leptocephali and indication of a new fish family “Neocyematidae” based on larvae, adults and mitogenomic gene orders. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.G. Dysommid eel larvae in the western North Atlantic. Copeia 1974, 1974, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Shima, Y.; Tamaru, O.; Takahashi, Y.; Ohmura, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Kamoshida, M.; Arimoto, M.; Yamano, K.; Yatabe, T. Japanese eel jaw and vertebra ossification occurring respectively during the larval stage and metamorphosis. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulet, W.C.; Robins, C.R. The evolutionary significance of the leptocephalus larva. In Fishes of the Western North Atlantic; Böhlke, E.B., Ed.; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 669–677, Part 9, Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.G. Congridae: Leptocephali. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic; Böhlke, E.B., Ed.; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 723–763, Leptocephali, Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Tabeta, O.; Mochioka, N. Leptocephali. In An Atlas of the Early Stages Fishes in Japan; Okiyama, M., Ed.; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1988; pp. 15–64. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Mochioka, N.; Tabeta, O. Leptocephali. In An Atlas of the Early Stage Fishes in Japan, 2nd ed.; Okiyama, M., Ed.; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 2–89. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K. Studies on eels and leptocephali in Southeast Asia: A new research frontier. Coastal Mar. Sci. 2006, 30, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Castle, P.H.J. Garden eel leptocephali: Characters, generic identification, distribution, and relationships. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 6–22. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.G. Larvae of the garden eel genus Gorgasia (Congridae, Heterocongrinae) from the western Caribbean Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 70, 831–836. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Moser, H.G. Stomiatoidea: Development. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Cohen, D.M., Fahay, M.P., Kendall, A.W., Jr., Richardson, S.L., Eds.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 169–181, Spec. Publ. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Charter, S.R. Ophichthidae: Snake eels and worm eels. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 93–99, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Charter, S.R. Nemichthyidae: Snipe Eels. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1966; pp. 122–129, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Charter, S.R. Nettastomatidae: Duckbill eels. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1966; pp. 135–139, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, T. Early life history of the gonostomatid fish, Pollichthys mauli, in the oceanic region off southern Japan. Japan. J. Ichthyol. 1976, 23, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, H.G. Chauliodontidae: Viperfishes. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 297–299, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Ruxton, G.D.; Sherratt, T.N.; Speed, M.P. Avoiding Attack: The Evolutionary Ecology of Crypsis, Mimicry and Aposematism; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, J.E. A review of mimicry in marine fishes. Zool. Stud. 2005, 44, 299–328. [Google Scholar]
- Bullard, S.G.; Hay, M.E. Palatability of marine macro-holoplankton: Nematocysts, nutritional quality, and chemistry as defenses against consumers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiørboe, T. Zooplankton body composition. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, J.J.; Olney, J.E.; Markle, D.F.; Curtsinger, W.R. Observations on structure and evaluation of possible functions of the vexillum in larval Carapidae (Ophidiiformes). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1984, 34, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Olney, J.E.; Markle, D.F. Description and occurrence of vexillifer larvae of Echiodon (Pisces, Carapidae) in the western North-Atlantic and notes on other carapid vexillifers. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1979, 29, 365–379. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, G.O.; Pugh, P.R.; Purcell, J.E. Siphonophore biology. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1988, 24, 97–262. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, S.; Robinson, M.D.; Tintori, S.C.; Goetz, F.; Helm, R.R.; Smith, S.A.; Shaner, N.; Haddock, S.H.D.; Dunn, C.W. Differential gene expression in the siphonophore Nanomia bijuga (Cnidaria) assessed with multiple next generation sequencing workflows. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, C.; Siebert, S.; Zapata, F.; Howison, M.; Damian-Serrano, A.; Church, S.H.; Goetz, F.E.; Pugh, P.R.; Haddock, S.H.; Dunn, C.W. Improved phylogenetic resolution within Siphonophora (Cnidaria) with implications for trait evolution. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 127, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damian-Serrano, A.; Hetherington, E.D.; Choy, C.A.; Haddock, S.H.D.; Lapides, A.; Dunn, C.W. Characterizing the secret diets of siphonophores (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) using DNA metabarcoding. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershwin; Lewis, M.; Gowlett-Holmes, K.; Kloser, R. The Ctenophores. In Pelagic Invertebrates of South-Eastern Australia: A Field Reference Guide; Version 1.1.; CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research: Hobart, TAS, Australia, 2014; Available online: https://publications.csiro.au/rpr/download?pid=csiro:EP1312314&dsid=DS2 (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Gibbons, M.J.; Haddock, S.H.; Matsumoto, G.I.; Foster, C. Records of ctenophores from South Africa. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.Y.; Grassian, B.; Tang, D.; Irisson, J.-O.; Greer, A.T.; Guigand, C.M.; McClatchie, S.; Cowen, R.K. Environmental drivers of the fine-scale distribution of a gelatinous zooplankton community across a mesoscale front. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 510, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüskow, F.; Neitzel, P.; Miller, M.J.; Marohn, L.; Wysujack, K.; Freese, M.; Pohlmann, J.-D.; Hanel, R. Distribution and abundance of net-captured calycophoran siphonophores and other gelatinous zooplankton in the Sargasso Sea European eel spawning area. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2333–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.D.; Paxton, J.R.; Sutton, T.T.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Nishida, M.; Miya, M. Deep-sea mystery solved: Astonishing larval transformations and extreme sexual dimorphism unite three fish families. Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, T.H.; Smith, M.M. An exterilium larval fish from South Africa with comments on its classification. Copeia 1974, 1974, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahay, M.P.; Nielsen, J.G. Ontogenetic evidence supporting a relationship between Brotulotaenia and Lamprogrammus (Ophidiiformes: Ophidiidae) based on the morphology of exterilium and rubaniform larvae. Ichthyol. Res. 2003, 50, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, A.; Kuroda, H. Larvae of Lamprogrammus shcherbachevi (Ophidiiformes: Ophidiidae) from the western North Pacific Ocean. Ichthyol. Res. 2007, 54, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, S.H.D.; Dunn, C.W. Fluorescent proteins function as a prey attractant: Experimental evidence from the hydromedusa Olindias formosus and other marine organisms. Biol. Open 2015, 4, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.W., Jr.; Ahlstrom, E.H.; Moser, H.G. Early life history stages of fishes and their characters. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Cohen, D.M., Fahay, M.P., Kendall, A.W., Jr., Richardson, S.L., Eds.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 11–22, Spec. Publ. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Keene, M.J.; Tighe, K.A. Beryciformes: Development and relationships. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Cohen, D.M., Fahay, M.P., Kendall, A.W., Jr., Richardson, S.L., Eds.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 292–383, Spec. Publ. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mochioka, N.; Kakuda, S.; Tabeta, O. Congrid leptocephali in the western North and Middle Pacific I: Exterilium Ariosoma-type larvae. J. Fac. Appl. Biol. Sci. Hirosh. Univ. 1982, 21, 35–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mochioka, N.; Tabeta, O.; Kakuda, S.; Tsukahara, H. Congrid leptocephali in the western north and middle Pacific II. Non-exterilium Ariosoma type larvae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1991, 48, 606–622. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.J.; Yamaguchi, M.; Wouthuyzen, S.; Aoyama, J.; Suharti, S.; Ma, T.; Yoshinaga, T.; Minegishi, Y.; Kawakami, T.; Tsukamoto, K. Ariosoma-type Leptocephali (Congridae: Bathymyrinae) in the Mentawai Islands region off western Sumatra, Indonesia. Zool. Stud. 2013, 52, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.A.; Fenolio, D.B.; Cook, A.B.; Sutton, T.T. Hiding in plain sight: Elopomorph larvae are important contributors to fish biodiversity in a low-latitude oceanic ecosystem. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B. Changes in the behavior of the eel during transformation. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1912, 22, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiby, M.M. Family Ophichthidae: Leptocephali. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic; Böhlke, E.B., Ed.; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; pp. 764–897, Part 9, Vol. 2 Leptocephali, S Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Castle, P.H.J. Larvae of the ophichthid genus Neenchelys in the Indo-Pacific. Pac. Sci. 1980, 34, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Castonguay, M.; McCleave, J.D. Vertical distributions, diel and ontogenetic vertical migrations and net avoidance of leptocephali of Anguilla and other common species in the Sargasso Sea. J. Plankt. Res. 1987, 9, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J. Nighttime vertical distribution and regional species composition of eel larvae in the western Sargasso Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2015, 1, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, H.; Miller, M.J.; Takeshige, A.; Miyake, Y.; Kuroki, M.; Aoyama, J.; Kimura, S. Vertical distribution and assemblage structure of leptocephali in the North Equatorial Current region of the western Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 575, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrini, A.M.; McClain-Counts, J.; Artabane, S.J.; Roa-Varon, A.; McIver, T.C.; Rhode, M.; Ross, S.W. Assemblage structure, vertical distributions, and stable isotopic compositions of anguilliform leptocephali in the Gulf of Mexico. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 621–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K.; Leis, J.M. Shallow larval depth-distribution and life history characteristics of the tropical congrid eel Ariosoma scheelei in the Northwest Coral Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 42, 101610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, H.G.; Pommeranz, T. Vertical distribution of eggs and larvae of northern anchovy, Engraulis mordax, and of the larvae of associated fishes at two sites in the Southern California Bight. Fish. Bull. 1999, 97, 920–943. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.; Cabrero, A.; Gago, J.; Guevara-Fletcher, C.; Herrero, M.; de Rojas, A.H.; Garcia, A.; Laiz-Carrion, R.; Vergara, A.; Alvarez, P.; et al. Vertical distribution and migration of fish larvae in the NW Iberian upwelling system during the winter mixing period: Implications for cross-shelf distribution. Fish. Oceanogr. 2015, 24, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, S.D.; Bellwood, D.R. Light sensitivity in larval fishes: Implications for vertical zonation in the pelagic zone. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.M.; Loew, E.R.; Grace, M.S. A rod-dominated visual system in leptocephalus larvae of elopomorph fishes (Elopomorpha: Teleostei). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 92, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.M.; Loew, E.R.; Grace, M.S. Ontogenic retinal changes in three ecologically distinct elopomorph fishes (Elopomorpha:Teleostei) correlate with light environment and behavior. Vis. Neurosci. 2015, 32, E005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charter, S.R.; Moser, H.G. Trachipteridae: Ribbonfishes. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 669–677, CalCOFI Atlas 33. [Google Scholar]
- Umeton, D.; Read, J.C.A.; Rowe, C. Unravelling the illusion of flicker fusion. Biol. Lett. 2017, 13, 20160831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G. Nemichthyidae: Leptocephali. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic; Böhlke, E.B., Ed.; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 925–932, Part 9, Leptocephali, Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.G. Synaphobranchide: Leptocephali. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic; Böhlke, E.B., Ed.; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 682–698, Part 9, Leptocephali, Sears Found. Mar. Res. [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum, S. Studies on food organisms of pelagic fishes as revealed by the 1979 North Atlantic Eel Expedition. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1982, 35, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.R.; Knudsen, S.W.; Munk, P.; Thomsen, P.F.; Møller, P.R. Tracing European eel in the diet of mesopelagic fishes from the Sargasso Sea using DNA from fish stomachs. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasker, R. The role of a stable ocean in larval fish survival and subsequent recruitment. In Marine Fish Larvae: Morphology, Ecology, and Relation to Fisheries; Lasker, R., Ed.; Washington Sea Grant Program: Seattle, WA, USA, 1981; pp. 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Hjort, J. Fluctuations in the great fisheries of Northern Europe. Rapp. Internat. Conseil Pour L’Explor. Mer. 1914, 20, 1–228. [Google Scholar]
- Browman, H.I. Commemorating 100 years since Hjort’s 1914 treatise on fluctuations in the great fisheries of northern Europe: Where we have been, where we are, and where we are going. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Dubosc, J.; Vourey, E.; Tsukamoto, K.; Allain, V. Low occurrence rates of ubiquitously present leptocephalus larvae in the stomach contents of predatory fish. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Feunteun, E.; Tsukamoto, K. Did a “perfect storm” of oceanic changes and continental anthropogenic impacts cause Northern Hemisphere anguillid recruitment reductions? ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-L.K.; Miller, M.J. Possible influence of typhoons, volcanic ash, and ocean productivity on early larval survival and Japanese eel annual cohort recruitment. Deep Sea Res. Part I: Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2022, 192, 103940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, H.M.; Murphy, H.M.; Jenkins, G.P.; Fortier, L. Poor taxonomical knowledge of larval fish prey preference is impeding our ability to assess the existence of a “critical period” driving year-class strength. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 2042–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. Influence of siphonophore behavior upon their natural diets: Evidence for aggressive mimicry. Science 1980, 209, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, B.P.; Robison, B.H.; Sherlock, R.E. Behaviour and mimicry in the juvenile and subadult life stages of the mesopelagic squid Chiroteuthis calyx. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2014, 95, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, F.; Madin, L.P. Siphonophores eat fish larger than their stomachs. Deep Sea Res. II 2010, 57, 2248–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, D.J.; Munk, P.; Lundgreen, R.B.C.; Traving, S.J.; Jaspers, C.; Jørgensen, T.S.; Hansen, L.H.; Riemann, L. Gelatinous plankton is important in the diet of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) larvae in the Sargasso Sea. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, S.; Inaba, N.; Nagai, S.; Kurogi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Yanagimoto, T.; Tanaka, H.; Hasegawa, D.; Asakura, T.; Kikuchi, J.; et al. Molecular diet analysis of Anguilliformes leptocephalus larvae collected in the western North Pacific. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Nagai, S.; Kawakami, Y.; Asakura, T.; Kikuchi, J.; Inaba, N.; Taniuchi, Y.; Kurogi, H.; Chow, S.; Tomoda, T.; et al. 18Sr RNA gene sequences of leptocephalus gut contents, particulate organic matter, and biological oceanographic conditions in the western North Pacific. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.; Widder, E.A. Transparency and visibility of gelatinous zooplankton from the Northwestern Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico. Biol. Bull. 1998, 195, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, S. Hidden in plain sight: The ecology and physiology of organismal transparency. Biol. Bull. 2001, 201, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S. Lifting the cloak of invisibility: The effects of changing optical conditions on pelagic crypsis. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2003, 43, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S. Hide and seek in the open sea: Pelagic camouflage and visual countermeasures. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.; Torres, J.J.; Crabtree, R.E. Proximate composition and nucleic acid content of premetamorphic leptocephalus larvae of the congrid eel Ariosoma balearicum. Mar. Biol. 1995, 123, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, I.; Takai, T.; Kataoka, A. Leptocephalae of the eel Anguilla obscura found in the stomachs of skipjack tuna Katsuwonus pelamis caught near New Guinea. J. Shimonoseki Univ. Fish. 1970, 19, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D.E.; Vanwye, J.D.; Exum, A.M.; Cowen, R.K.; Crawford, D.L. High-throughput species identification: From DNA isolation to bioinformatics. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, N.; Delrieu-Trottin, E.; Irisson, J.-O.; Meyer, C.; Planes, S. Identifying coral reef fish larvae through DNA barcoding: A test case with the families Acanthuridae and Holocentridae. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2010, 55, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, N.; Espiau, B.; Meyer, C.; Planes, S. Identifying the ichthyoplankton of a coral reef using DNA barcodes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 15, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Miller, M.J.; Aoyama, J.; Tsukamoto, K. Genetic identification of Conger myriaster leptocephali in the East China Sea region. Fish. Sci. 2007, 73, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Miller, M.J.; Aoyama, J.; Minagawa, G.; Inoue, J.G.; Watanabe, S.; Tsukamoto, K. Genetic identification of two species of Ariosoma leptocephali. Coastal Mar. Sci. 2008, 32, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Aoyama, J.; Miller, M.J.; Minegishi, Y.; Inoue, J.G.; Tsukamoto, K. Genetic differentiation in the genus Uroconger in the Indo-Pacific region. Aquat. Biol. 2008, 2, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M. Ontogeny of behaviour in larvae of marine demersal fishes. Ichthyol. Res. 2010, 57, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syahailatua, A.; Taufik, M.; Wagiyo, K.; Sugeha, H.Y.; Simanjuntak, C.P.H.; Wouthuyzen, S.; Miller, M.J.; Aoyama, J. A century of ichthyoplankton research in Indonesian waters: Lessons from the past, challenges for the future. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 57, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenkämper, D.; Simon-Lledó, E.; Hosking, B.; Jones, D.O.B.; Nattkemper, T.W. On the impact of Citizen Science-derived data quality on deep learning based classification in marine images. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomer, K.; Tracy, B.M.; Chang, A.L.; Ruiz, G.M. Evaluating performance of photographs for marine citizen science applications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, e0218086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüskow, F.; Johnson, S.; Johnson, J.; Pakhomov, E.A. Gelatinous zooplankton of the Marshall Islands, Central Tropical Pacific: An inventory. Mar. Biodivers. 2021, 51, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milisen, J.W.; Matye, S.A.; Kobayashi, D.R. Nocturnal visual census of pelagic fauna using scuba near Kona, Hawai‘i. Pac. Sci. 2018, 72, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, M.J. 43 Years after H.G. Moser’s Seminal “Morphological and Functional Aspects of Marine Fish Larvae”: The Commonalities of Leptocephali and Larvae of Other Marine Teleosts. Fishes 2023, 8, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110548
Miller MJ. 43 Years after H.G. Moser’s Seminal “Morphological and Functional Aspects of Marine Fish Larvae”: The Commonalities of Leptocephali and Larvae of Other Marine Teleosts. Fishes. 2023; 8(11):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110548
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Michael J. 2023. "43 Years after H.G. Moser’s Seminal “Morphological and Functional Aspects of Marine Fish Larvae”: The Commonalities of Leptocephali and Larvae of Other Marine Teleosts" Fishes 8, no. 11: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110548
APA StyleMiller, M. J. (2023). 43 Years after H.G. Moser’s Seminal “Morphological and Functional Aspects of Marine Fish Larvae”: The Commonalities of Leptocephali and Larvae of Other Marine Teleosts. Fishes, 8(11), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110548






