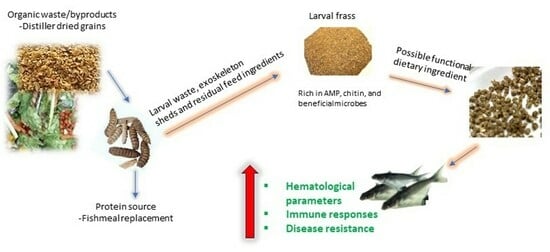
Frass from Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens, as a Possible Functional Dietary Ingredient in Channel Catfish Feed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish
2.2. Experimental Diets, Feeding and Sampling
2.3. Hematological Assay
2.4. Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.5. Nonspecific Immune Responses
2.6. Bacterial Challenge
2.7. Statistical Analysis
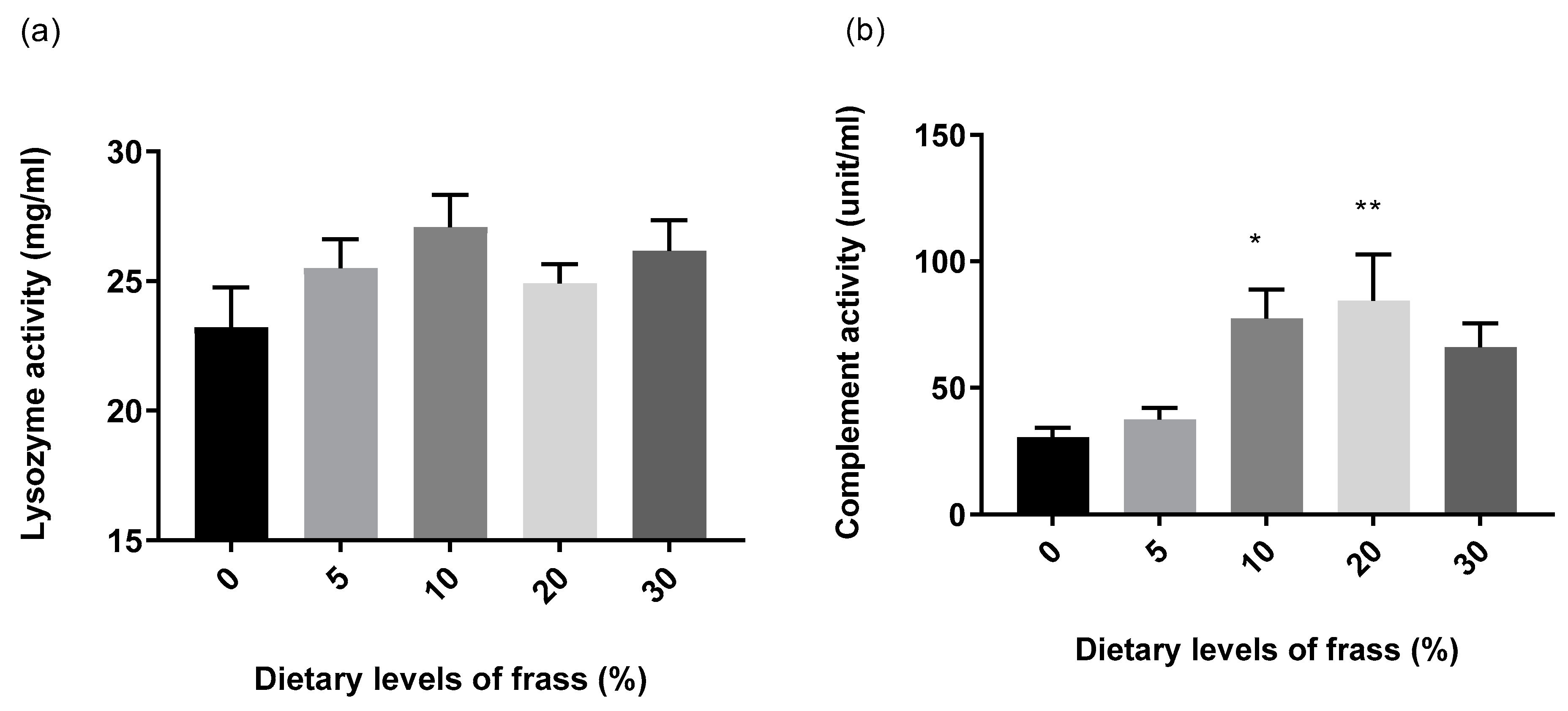
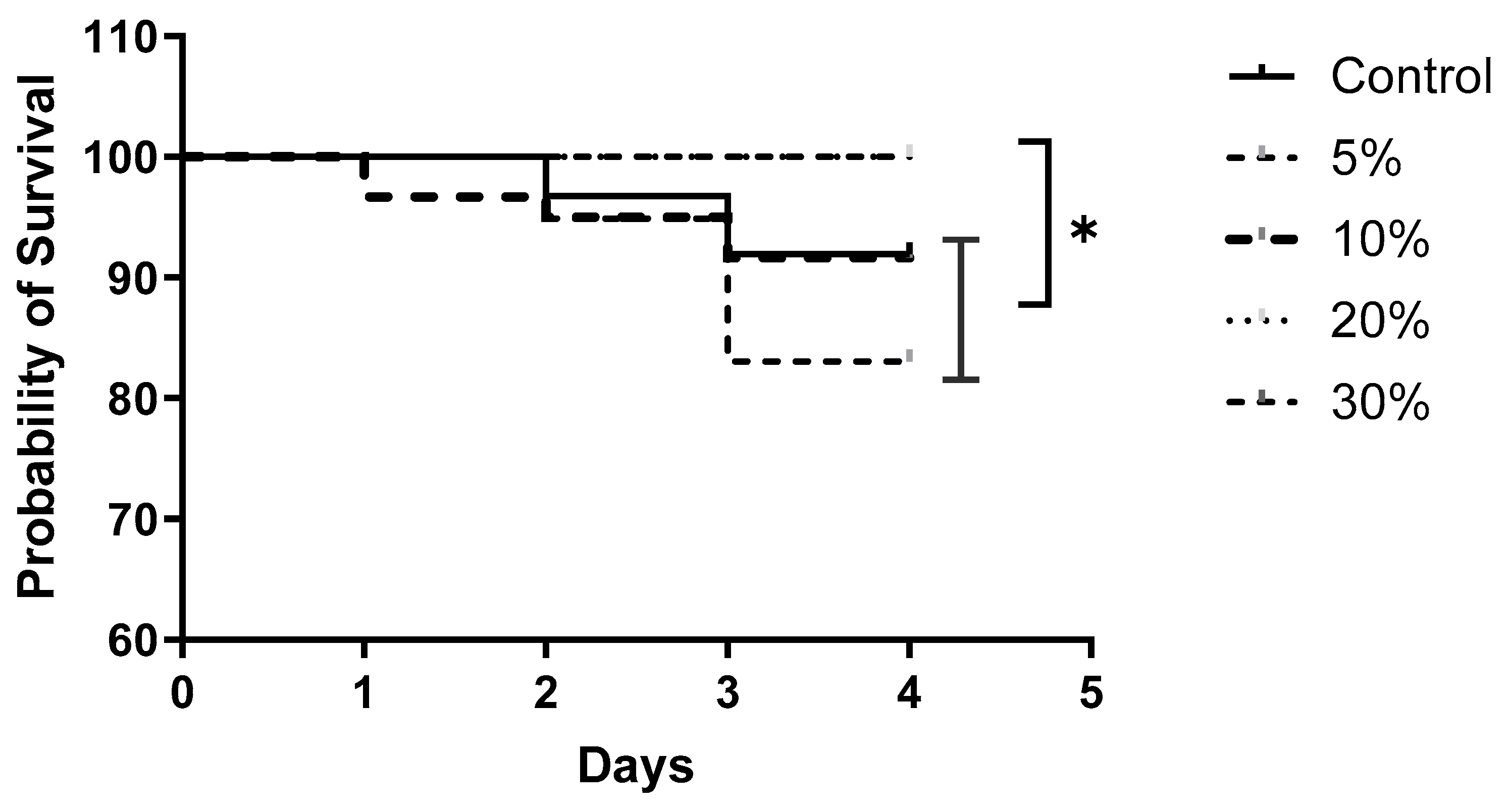
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hargreaves, J.A. Channel catfish farming in ponds: Lessons from a maturing industry. Rev. Fish Sci. 2002, 1, 499–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) Catfish Production; The USDA Economics, Statistics and Market Information System (ESMIS) February 10, 2023. Available online: https://usda.library.cornell.edu/concern/publications/bg257f046?locale=en (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Balcázar, J.L.; Blas, I.D.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Cunningham, D.; Vendrell, D.; Múzquiz, J.L. The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 114, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagum, N.; Monir, M.S.; Khan, M.H. Present status of fish diseases and economic losses due to incidence of disease in rural freshwater aquaculture of Bangladesh. J. Innov. Dev. Strategy 2013, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Elala, N.; Marzouk, M.; Moustafa, M. Use of different Saccharomyces cerevisiae biotic forms as immune-modulator and growth promoter for Oreochromis niloticus challenged with some fish pathogens. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2013, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the use of insects in the diet of farmed fish: Past and future. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Henry, M.; Piccolo, G.; Marono, S.; Gai, F.; Renna, M.; Lussiana, C.; Antonopoulou, F.; Mola, P.; Chatzifotis, S. Tenebrio molitor meal in diets for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) juveniles: Growth performance, whole body composition and in vivo apparent digestibility. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 220, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Shelomi, M. Review of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) as animal feed and human food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Cranfill, K.; Mcguire, M.; Mosley, E.; Tomberlin, J.; Newton, L.; Sealey, W.; Sheppard, C.; Irving, S. Fish offal recycling by the black soldier fly produces a foodstuff high in omega-3 fatty acids. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2007, 38, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Yong, H.I.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, Y.S. Edible Insects as a Protein Source: A Review of Public Perception, Processing Technology, and Research Trends. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2019, 39, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, D.; Swift, J.A.; Field, L.M. Opportunities and hurdles of edible insects for food and feed. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govorushko, S. Global status of insects as food and feed source: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, F.G.; de Haro, C.; Sanchez-Muros, M.J.; Venegas, E.; Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Perez-Ban, C. The potential of various insect species for use as food for fish. Aquaculture 2014, 422–423, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Muros, M.-J.; Barroso, F.G.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Insect meal as renewable source of food for animal feeding: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A. Potential of insects as food and feed in assuring food security. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huis, A.; van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects. Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Eljack, R.; Beck, B.H. Nutritional value of frass from black 561 soldier fly larvae Hermetia illucens, in a channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, diet. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Datta, S.N.; Pande, G.S.J.; Sinha, A.K.; Yamamoto, F.Y.; Beck, B.H.; Webster, C.D. Dietary inclusions of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae frass enhanced production of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) juveniles, stevia (Stevia rebaudiana), and lavender (Lavaridula angustifolia) in an aquaponic system. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Eljack, R.; Schrimsher, C.; Beck, B.H. Use of dietary frass from black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens, in hybrid tilapia (Nile × Mozambique, Oreochromis niloticus x O. mozambique) diets improves growth and resistance to bacterial diseases. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banavar, A.; Amirkolaei, S.K.; Duscher, L.; Khairunisa, B.H.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Schwarz, M.; Urick, S.; Ovissipour, R. Nutritional Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly Frass as an Ingredient in Florida Pompano (Trachinotus carolinus L.) Diets. Animals 2022, 12, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.A.; Cuesta, A.; Ortuno, J.; Meseguer, J. Immunomodulatory effects of dietary intake of chitin on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) innate immune system. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2001, 11, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.; Rowley, A.F. The effect of dietary chitin supplementation on the survival and immune reactivity of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2007, 147, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildrim-Aksoy, M.; Eljack, R.; Beck, B.H.; Peatman, E. Nutritional evaluation of frass from black soldier fly larvae as potential feed ingredient for Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M. Current research status of fish immunostimulants. Aquaculture 1999, 172, 63–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Olsen, R.E.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Simon Wadsworth, S.; Song, S.K. Use of immunostimulants and nucleotides in aquaculture: A review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. Res. Dev. 2012, 2, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, R.; Srivastava, P.K.; Verma, N.; Sharma, J. Effect of seeds of Achyranthesaspera on the immune responses and expression of some immune-related genes in carp Catlacatla. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwicki, A.K.; Anderson, D.P.; Rumsey, G.L. Dietary intake of immunostimulants by rainbow trout affects non-specific immunity and protection against furunculosis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 41, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC (National Research Council). Nutrient Requirements of Fish; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, B.A. Routine hematology procedures. In Hematology: Principles and Procedures; Brown, B.A., Ed.; Leo and Febiger: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1988; pp. 7–122. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, H.N. Comparison of various methods of hemoglobin detection of channel catfish blood. Prog. Fish Cult. 1964, 26, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Lim, C.; Davis, D.A.; Shelby, R.; Klesius, P.H. Influence of dietary lipid sources on the growth performance, immune response and resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, to Streptococcus iniae challenge. J. Appl. Aquac. 2007, 19, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwack, G. Photometric determination of lysozyme activity. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1955, 89, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, K.; Gurnani, S. On the variation in the catalytic activity of lysozyme in fishes. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 1972, 9, 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Sunyer, J.O.; Tort, L. Natural hemolytic and bactericidal activities of sea bream Sparus aurata serum are affected by the alternative complement pathway. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995, 45, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufek, N.M.; Aspani, F.; Muin, H.; Raji, A.A.; Razak, S.A.; Alias, Z. The effect of dietary cricket meal (Gryllus bimaculatus) on growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activities, and haematological response of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Khan, R.; Khan, S.; Suhail, S.M.; Khan, K.; Ahmad, I.; Wahab, A.; Ayari-Akkari, A.; Othman, G. Effect of dietary inclusion of mealworm frass on growth, hematology, and serum biochemistry of sheep. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tippayadara, N.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Krutmuang, P.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Doan, H.V.; Paolucci, M. Replacement of Fish Meal by Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal: Effects on Growth, Haematology, and Skin Mucus Immunity of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Animals 2021, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyder, M.A.; Hasan, M.; Mohieldein, A.H. Comparative levels of ALT, AST, ALP and GGT in liver associated diseases. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 3, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikhzadeh, N.; Tayefi-Nasrabadi, H.; Oushani, A.K.; Enferadi, M.H.N. Effects of Haematococcus pluvialis supplementation on antioxidant system and metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. Effects of fishmeal replacement with soy protein hydrolysates on growth performance, blood biochemistry, gastrointestinal digestion and muscle composition of juvenile starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Aquaculture 2014, 426, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.N.; Liu, W.B.; Lu, K.L.; Xu, W.N.; Cai, D.S.; Zhang, C.N.; Qian, Y. Effects of dietary carbohydrate/lipid ratios on non-specific immune responses, oxidative status and liver histology of juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquaculture 2014, 426, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, V.; Zubair, M.; Minter, D.A. Liver Function Tests. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482489/ (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Coz-Rakovac, R.; Strunjak-Perovic, I.; Hacmanjek, M.; Topic Popovic, N.; Lipej, Z.; Sostaric, B. Blood Chemistry and Histological Properties of Wild and Cultured Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in the North Adriatic Sea. Vet. Res. Commun. 2005, 29, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpo, K.E.; Onigbinde, A.O.; Asia, I.O. Pharmaceutical potentials of the oils of some popular insects consumed in southern Nigeria. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 3, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, N. Effects of Substitution of Fish Meal with Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal, in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Diets. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2017, 69, 1382. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Chatzifotis, S.; Piccolo, G. Does dietary insect meal affect the fish immune system? The case of mealworm, Tenebrio molitor on European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 81, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heesterbeek, D.A.C.; Angelier, M.L.; Harrison, R.A.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M. Complement and Bacterial Infections: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Applications. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsos, E.; Modica, B.; Freel, T. Immunomodulatory potential of black soldier fly larvae: Applications beyond nutrition in animal feeding programs. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2022, 6, txac084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.J.; Kim, T.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Evaluation of supplementation of defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal in beagle dogs. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2019, 19, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Muller, A.; Heckel, D.G.; Gutzeit, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Nutritional immunology: Diversification and diet-dependent expression of antimicrobial peptides in the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.H.; Yun, J.H.; Chu, J.P.; Chu, K.B. Antibacterial effect of extracts of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae against gram-negative bacteria. Entomol. Res. 2012, 42, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, D.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Treilhou, M.; Tene, N.; Castillo, D.; Sauvain, M. Prospecting peptides isolated from black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) with antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori (Campylobacterales: Helicobacteraceae). J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlystiarini, R.M.; Wibawan, I.W.T.; Astuti, D.A. In vitro antibacterial activity of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larva extracts against gram-negative bacteria. ISSTAP Bull. Anim. Sci. 2019, 432, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Chang, B.S.; Yoe, S.M. Detection of antimicrobial substances from larvae of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Entomol. Res. 2014, 44, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.-C.; Lee, Y.-H.; Ong, J.-H.; Manan, F.A.; Sabri, M.Z.; Chai, T.-T. Exploring the Potential of Black Soldier Fly Larval Proteins as Bioactive Peptide Sources through in Silico Gastrointestinal Proteolysis: A Cheminformatic Investigation. Catalysts 2023, 13, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, S.E.; Heinrich, T.K.; Hales, B.J.; Hazell, L.A.; Holt, D.C.; Fischer, K.; Thomas, W.R. The Chitinase Allergens Der p 15 and Der p 18 from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakannan, A.; Arul, V. Immunomodulatory effects of dietary intake of chitin, chitosan and levamisole on the immune system of Cyprinus carpio and control of Aeromonas hydrophila infection in ponds. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, N.; Mastoraki, M.; Lazarina, M.; Chatzifotis, S.; Mente, E.; Kormas, K.A.; Antonopoulou, E. Configuration of Gut Microbiota Structure and Potential Functionality in Two Teleosts under the Influence of Dietary Insect Meals. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, L.; Pastorelli, R.; Viti, C.; Gasco, L.; Parisi, G. Characterization of the intestinal microbial communities of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed with Hermetia illucens (black soldier fly) partially defatted larva meal as partial dietary protein source. Aquaculture 2018, 487, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyben, D.; Vidaković, A.; Werner Hallgren, S.; Langeland, M. High-Throughput Sequencing of Gut Microbiota in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fed Larval and Pre-Pupae Stages of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). Aquaculture 2019, 500, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimoldi, S.; Gini, E.; Iannini, F.; Gasco, L.; Terova, G. The Effects of Dietary Insect Meal from Hermetia illucens Prepupae on Autochthonous Gut Microbiota of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Animals 2019, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terova, G.; Rimoldi, S.; Ascione, C.; Gini, E.; Ceccotti, C.; Gasco, L. Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gut microbiota is modulated by insect meal from Hermetia illucens prepupae in the diet. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, C.L.R.; Scarborough, P.; Rayner, M.; Nonaka, K. Are edible insects more or less ‘healthy’ than commonly consumed meats? A comparison using two nutrient profiling models developed to combat over- and undernutrition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranghers, T.; Ottoboni, M.; Klootwijk, C.; Ovyn, A.; Deboosere, S.; DeMeulenaer, B.; De Smet, S. Nutritional composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) prepupae reared on different organic waste substrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Experimental Diets (%) 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Menhaden fish meal | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Soybean meal | 45 | 44 | 43 | 41 | 39 |
| Frass | -- | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Wheat short | 24 | 20.4 | 16.9 | 9.8 | 2.5 |
| Corn meal | 14 | 13.8 | 13.5 | 13.0 | 12.8 |
| Corn oil | 4 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 3.2 | 2.8 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CMC | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Vitamin premix 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Mineral premix 3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Nutritive Value (%) | |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 7.2 |
| Protein | 21.6 |
| Fat | 6.3 |
| Ash | 9.3 |
| Fiber | 7.0 |
| Starch | 35.0 |
| Fatty acid profile (% of crude fat) | |
| C12:0 Lauric acid | 0.2 |
| C14:0 Myristic acid | 0.1 |
| C16:1 Palmitic acid | 13.7 |
| C17:0 Margaric acid | 0.1 |
| C18:0 Stearic acid | 2.5 |
| C18:1 Oleic acid | 28.3 |
| C18:2 Linoleic acid | 50.5 |
| C18:3 Alpha Linoleic acid | 1.3 |
| C20:0 Arachidic acid | 0.5 |
| C20:1 Eicosenoic acid | 0.7 |
| C20:2 Eicosnoic acid | 0.3 |
| C20:3 Eurcostrienoic acid | 0.2 |
| C20:5 Eicosapentaenoic acid | 0.2 |
| C24:0 Lignoceric acid | 0.3 |
| C22:6 Docosahexaenoic acid | 0.2 |
| Dietary Levels | RBC | WBC | Hb | Ht | MCV 2 | MCH 2 | MCHC 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| of Frass (%) | ×106/μL | ×105/μL | (g/dL) | (%) | (fl) | (pg) | (%) |
| 0 | 2.28 | 1.81 | 7.22 | 30.50 | 138.50 | 32.70 | 23.80 |
| 5 | 2.75 | 2.56 | 7.34 | 32.00 | 117.17 | 26.96 | 23.10 |
| 10 | 3.10 ** | 2.63 | 7.70 | 32.75 | 111.32 * | 25.35 ** | 23.58 |
| 20 | 3.10 ** | 2.38 | 7.91 | 34.67 | 113.28 * | 25.75 * | 22.85 |
| 30 | 3.28 *** | 2.73 | 7.83 * | 36.17 * | 111.23 * | 24.03 ** | 21.66 |
| Pooled SEM | 0.399 | 0.363 | 0.369 | 2.229 | 11.277 | 3.191 | 0.798 |
| Dietary Levels of Frass | ALB | ALP | ALT | AMY | CA | PHOS | GL | K | Cholesterol | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | g/dL | u/L | u/L | u/L | mg/dL | mg/dL | mg/dL | mm/L | mg/dL | ug/dL |
| 0 | 2.27 | 56.83 | 7.42 | 18.83 | 13.14 | 11.33 | 98.45 | 4.93 | 185.50 | 0.30 |
| 5 | 2.29 | 51.42 | 6.25 | 18.83 | 12.96 | 10.97 | 81.91 ** | 5.03 | 213.38 | 0.23 |
| 10 | 2.27 | 52.83 | 6.42 | 18.33 | 13.02 | 10.40 | 79.67 ** | 5.13 | 213.13 | 0.28 |
| 20 | 2.26 | 54.08 | 5.92 | 21.42 | 13.13 | 10.72 | 82.91 * | 5.32 | 201.25 | 0.20 |
| 30 | 2.26 | 49.33 | 7.33 | 20.00 | 13.24 | 11.09 | 78.42 ** | 5.18 | 218.25 * | 0.38 |
| Pooled SEM | 0.014 | 2.934 | 0.672 | 1.240 | 0.112 | 0.348 | 7.851 | 0.143 | 10.782 | 0.050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yıldırım-Aksoy, M.; Eljack, R.; Aksoy, J.; Beck, B.H. Frass from Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens, as a Possible Functional Dietary Ingredient in Channel Catfish Feed. Fishes 2023, 8, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110542
Yıldırım-Aksoy M, Eljack R, Aksoy J, Beck BH. Frass from Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens, as a Possible Functional Dietary Ingredient in Channel Catfish Feed. Fishes. 2023; 8(11):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110542
Chicago/Turabian StyleYıldırım-Aksoy, Mediha, Rashida Eljack, Janset Aksoy, and Benjamin H. Beck. 2023. "Frass from Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens, as a Possible Functional Dietary Ingredient in Channel Catfish Feed" Fishes 8, no. 11: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110542
APA StyleYıldırım-Aksoy, M., Eljack, R., Aksoy, J., & Beck, B. H. (2023). Frass from Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens, as a Possible Functional Dietary Ingredient in Channel Catfish Feed. Fishes, 8(11), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110542