Abstract
The effects of temperature manipulation, addition of sperm solution, and exposure to alkalized pH and/or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as possible spawning inducers in laboratory-conditioned and unconditioned adults of the yellow clam (Amarilladesma mactroides) were evaluated. In three trials, clams were laboratory-conditioned for 14 days and exposed to thermal shocks (from 20 °C to 23–29 °C), while clams from three additional trials were not conditioned but acclimatized for 45 min before spawning induction. Although conditioning advanced gonad maturity and increased the condition factor, none of the thermal treatments triggered spawning in these first trials. Histological analysis indicated that the gonads of conditioned clams were not mature. Alternatively, unfertilized and fertilized eggs, and larvae were observed after unconditioned clams were induced to spawn. The gonads of unconditioned clams were in an advanced stage of maturity. Exposure to temperature shocks, alone or in combination with the addition of sperm solution and with H2O2, resulted in spawning. Clams exposed to H2O2 kept their valves closed and had a high mortality rate. Temperature manipulation is the most promising stimulus to induce spawning in A. mactroides. As the success of conditioning depends on the stage of gonadal development at the time of capture in the wild, a period longer than 14 days may be necessary.
1. Introduction
The yellow clam Amarilladesma mactroides is an ecologically and economically important bivalve found in the intertidal zones of sandy beaches from southern Brazil to northern Argentina (24–41° S) [1,2,3]. A. mactroides is generally the dominant species in these environments in terms of biomass [1,4,5].
Due to the abundance, it has been exploited as a food resource for over 4000 years [6,7] and, more recently, it has also been collected to be used as fishing bait [8]. Several populations have suffered from unregulated and unreported capture [1,4,8,9,10]. Drastic reductions in yellow clam populations have also occurred due to recurrent mass mortality events [11,12,13,14,15]. The increasing degradation of coastal environments, including contamination with heavy metals [16], chemicals [17], and microplastics [18], and the intense use of vehicles on beaches [19], have also negatively impacted natural populations of A. mactroides. Currently, the yellow clam is cited in the Red Book of Endangered Species of the Brazilian Institute of Biodiversity Conservation [20]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to adopt practices that ensure the species’ conservation. One way to guarantee the conservation of natural populations and, at the same time, meet market demands is the production of yellow clam juveniles (or “seeds”) in captivity. This would allow the development of studies considering both the restocking of natural environments and the production in integrated aquaculture systems [21,22].
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in closing the life cycle of A. mactroides in captivity [22,23,24,25,26]. One of the main constraints on the production of seeds of this species in captivity is the inability to control reproduction. Although the spawning of other clams of the family Mesodesmatidae has been achieved in laboratory conditions [27,28,29], the reproduction of A. mactroides in captivity has only been possible through gamete stripping [1,22], an invasive technique that involves the sacrifice of breeders [30] and can negatively affect larval survival and growth, and the duration of the larval period [31]. Therefore, this study evaluated the effects of different stimuli (temperature manipulation, addition of male gonad extracts, and exposure to hydrogen peroxide and/or pH) as possible non-invasive spawning inducers in laboratory-conditioned and unconditioned adults of Amarilladesma mactroides.
2. Materials and Methods
Wild clams visually longer than 50 mm were collected in the intertidal zone of the beaches of Cassino and Mar Grosso, municipalities of Rio Grande and São José do Norte, RS, southern Brazil, respectively (Table 1). Seawater temperature and salinity at the collection sites were measured with a portable thermometer and an optical refractometer (Atago, Tokyo, Japan), respectively. The clams were transported to the laboratory in coolers containing no water in less than 90 min.

Table 1.
Date, site, temperature, and salinity during field collection, and means (±SD) of initial and final wet weight (WWi and WWf, respectively), dry weight (DW), total length (L), height (H), condition factor (CF), and survival rates of yellow clam (Amarilladesma mactroides) collected at the beaches of Cassino and Mar Grosso, southern Brazil, for trials with a 14-day conditioning period (Trials I, II, and III) and no conditioning period (Trials IV, V, and VI). Superscripts indicate significant differences between initial and final parameters within the same trial. Parameters that were not measured are referred to as nd (=not determined).
A total of six trials were carried out (Table 1). In the first three (Trials I, II, and III), clams were conditioned, i.e., they were maintained in the laboratory for 14 days before exposure to different stimuli. For the subsequent trials (Trials IV, V, and VI), the clams were not conditioned, but exposed to possible spawning-inducing stimuli 45 min after their arrival in the laboratory. At the beginning of trials I, II, and III, and at the end of all trials, the clams were blotted dry and had their total length (L) and total height (H) measured with a manual caliper (Vonder, Curitiba, PR, Brazil). The wet weight (WW) and dry weight (DW) [32] were quantified with an electronic scale (Marte Científica, São Paulo, SP, Brazil). The condition factor (CF) was determined as CF = (L × WW3) × 100 [33].
2.1. Trials with Laboratory-Conditioned Clams
The maintenance system, feeding, and management of clams in trials I, II, and III were previously described [26]. Each experimental unit (EU) was initially stocked with 6 to 8 clams (L ≥ 50 mm) and placed in a maintenance tank filled with 500 L of filtered (1 µm) and dechlorinated seawater. Temperature, salinity, pH, and the concentrations of dissolved oxygen, total ammonia, and nitrite were measured daily, while nitrate and alkalinity were checked weekly with standard analytical procedures [34,35,36]. Mean values were as follows: temperature, 17.7 to 20.2 °C; salinity, 23.7 to 30.7; dissolved oxygen, 7.0 mg.L−¹; pH, 7.49 to 7.80; total ammonia nitrogen, 0.04–0.06 mg.L−¹; and nitrite, 0.01–0.08 mg.L−¹. Levels of nitrate were always below 3.5 mg.L−¹, and alkalinity above 130 mg.L−¹. In trial I, clams were fed a mix of Isochrysis galbana and Chaetoceros muelleri (proportion of 70:30) at a concentration of 15 × 10⁴ cell.mL−1. For trials II and III, a monospecific diet of C. muelleri at a concentration of 10 × 10⁴ cell.mL−1 was offered.
On day 15, each EU was removed from the maintenance tank, allowed to drain for 15 min, and inserted into replicated plastic containers with 22 L of seawater at 23 °C, 26 °C, or 29 °C in trials I and II; and 23 °C, 25 °C, or 27 °C in trial III. The immersion time of the EU in the shock temperature lasted 60 min. The temperature of the water in the plastic containers and in the sediment of each EU during the thermal shock were monitored for 60 min at 5 min intervals. If necessary, chilled (20 °C) or heated (29 °C) water was added to the containers to keep the shock temperature stable. An airlift attached to each EU [26] remained running during the thermal shock and assisted in homogenizing temperature. During and after the thermal shocks, clams were observed for spawning. Gonadal tissues were then sampled for histological analysis.
When a possible spawning event was observed, three 1 mL aliquots from each container were sampled after homogenization to estimate the number of eggs and/or larvae. Counting was performed in a Sedgewick-Rafter chamber. After confirmation of spawning, the water was filtered and transferred to individual containers to allow for larvae to develop. Eggs and larvae were observed under a Nikon E3100 microscope and photographed with a Nikon D3200 camera (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) at 10× magnification.
2.2. Trials with Laboratory-Unconditioned Clams
In trials IV, V, and VI, clams that had just been collected from the wild were kept for 45 min in a maintenance tank filled with seawater at the same temperature and salinity at the time of collection. The clams were then exposed to different experimental treatments and, after 60 min, were transferred back to the maintenance tank where they were kept overnight. The next morning, the water was filtered through a 25 µm sieve, and three 1 mL aliquots were collected after homogenization to verify the occurrence of spawning and to estimate the number of eggs in a Sedgewick-Rafter chamber. When spawning occurred, the water was filtered and transferred to individual containers to allow for larvae to develop. Eggs and larvae were observed in a similar fashion as described earlier. Adult clams were then blotted dry and L, H, WW, and DW were measured as described above. As in the previous trials, gonadal tissues were sampled for histological analysis.
The temperature and salinity at the time of collection of clams in trial IV were 21.5 °C and 25, respectively (Table 1). Groups of 40 clams were exposed to higher temperatures (23 °C, 25 °C, or 27 °C) and to sperm solutions (range of 694,000 to 862,000 sperm.mL−1). Sperm from three males was diluted in 100 mL seawater at 23 °C, 25 °C, or 27 °C. Three 1 mL aliquots of each solution were fixed in Lugol solution and counted in 5 of 25 fields of a Neubauer chamber. The sperm concentration per mL (Cspz) was calculated as Cspz = (Ʃ Spz/2) × 100 × 0.5.106 [37], where ∑Spz = mean of the total number of sperms counted in 5 squares in each chamber, 100 = dilution factor (1:100), and 0.5 × 10⁶ = number of spermatozoa in 1 mL aliquots. After 60 min of exposure, the clams were transferred back to the maintenance tank, where they were kept separately at 21.5 °C with constant aeration until the next morning. The occurrence of spawning was verified immediately after exposure to thermal shocks and sperm solution, but also the following morning.
In trial V, the temperature and salinity at the time of collection were 22.5 °C and 28, respectively (Table 1). Four treatments were tested: (1) thermal shock (from 22.5 to 25.5 °C); (2) thermal shock (22.5 to 25.5 °C) and the addition of a sperm solution (concentration of 693,750 sperm.mL−1) at 30 min intervals; (3) thermal (22.5 to 25.5 °C) and salinity shock (from 28 to 35); and (4) thermal shock (22.5 to 25.5 °C) and the addition of 6% hydrogen peroxide solution in alkalinized medium (pH 8.72). Each treatment had 3 replicates with 6 clams per container (4 treatments × 3 replicates × 6 clams = 72 individuals). For each treatment, clams were placed into rectangular 100 L black tanks filled with 20 L of seawater. After 60 min of exposure, clams were transferred to and kept overnight in 20 L containers with constant aeration in a water bath in the maintenance tank at an average temperature of 25.5 °C.
The temperature and salinity when clams for trial VI were collected in the wild were 21.8 °C and 31, respectively (Table 1). Four treatments were tested: (1) thermal shock (from 22 to 26 °C); (2) thermal shock (22 to 26 °C) coupled with a pH rise to 9.15; (3) thermal shock (22 to 26 °C) and the addition of ~5.5 µm hydrogen peroxide; and (4) thermal shock (22 to 26 °C) and the addition of ~5.5 µm hydrogen peroxide in an alkaline medium (pH 8.83). Each treatment had three replicates containing 6 animals each. Twenty-liter containers supplied with constant aeration were used as EU. After exposure to the assigned treatment, the clams were removed from the containers, which were rinsed and refilled with seawater so that the clams could be transferred back to be kept overnight.
2.3. Histological Analysis
Samples of gonadal tissue from conditioned and unconditioned clams were submitted to standard analysis with hematoxylin and eosin (H-E). In trial I, five clams were sampled after the 14-day conditioning period, while in trials II and III, clams were sampled before (n = 5) and after (n = 5) the conditioning period. In trials IV, V, and VI, five clams of each trial were sampled after the exposure to the different experimental treatments. Tissues were fixed with 20% saline formaldehyde until further analysis. They were then cut, placed in labelled cassettes, and processed in a Leica TP1020 automatic processor (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Paraplast-embedded blocks were sectioned at 5 µm with a Leica RM 2245 microtome (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Slides stained with hematoxylin-eosin were examined on a Zeiss Primo Star optical microscope equipped with a camera and AxioVision 4.8.2 software (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The gonads were classified into eight sequential stages of development: sexual rest, early active, late active, early ripe, ripe, partially spawned, spent, and recovery [4,38]. Larger and smaller diameters of 15 oocytes with visible nuclei from each female (D and d, respectively) at the beginning and/or at the end of the trials were measured using the ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data from all trials were tested for normality, independence, and homoscedasticity using Levene and Shapiro–Wilk, or Levene and Kolgomorov–Smirnov tests prior to the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). When the assumptions were not met, the arcsine of the square root (×) or log(×) was performed. The occurrence of significant differences was initially verified through post-hoc Tukey HSD (initial parameters) or unequal Tukey (final parameters). Differences in survival between trials were assessed using the Chi-square test (χ2). Larger and smaller diameters of the oocytes (D and d) in the same trial were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. Spawning induction success was evaluated by the presence or absence of gametes. Spawning induction treatments on trials V and VI were tested through non-parametric ANOVA and Kruskal–Wallis test. Df and df were evaluated by one-way ANOVA. Differences in survival between treatments were evaluated by the Chi-square test (χ2). Regardless of trial, all analyses were performed at a p < 0.05 significance level.
3. Results
The mean survival of clams from trials I, II, and III ranged from 76.67 to 88.3% and were not significantly different (χ2 = 2.9211; p = 0.23). No significant differences in survival were observed either between the different shock temperatures that clams were exposed to (χ2 = 3.1625 and p = 0.53) as it varied from 66.7 to 77.8%. Most biometric parameters of clams from trials I, II, and III were different (Table 1). Overall, the clams from trial II were larger than individuals from trials I and III. The CF was significantly higher in clams at the end of trials II and III than at the beginning. Biometric features of clams from trials IV, V, and VI were slightly different, but within the same range as the previous clams (Table 1). In trial IV, survival of clams 18 h after spawning induction was not different between treatments (χ2 = 0.5437; p = 0.7620), with mean rates of 87.5%, 82.5%, and 87.5% in treatments in which the temperature was abruptly increased from 20 °C to 23 °C, 25 °C, or 27 °C, respectively. In trial V, there were also no significant differences in the survival 18 h after spawning induction (χ2 = 2.505; p = 0.1135), being 100% in the temperature treatment of 25.5 °C and ranging from 83.33 to 94.44% in the other treatments. In trial VI, survival was 100% in the thermal shock treatment and 94.4% in the alkaline pH treatment. However, in treatments with the addition of H2O2, survival rates ranged between 55.6 and 66.7% and were significantly lower (χ2 = 18.99; p = 0.0003). Clams exposed to H2O2 in trials V and VI remained with their valves closed most of the exposure time.
None of the thermal shock treatments in trials I, II, and III triggered the spawning of laboratory-conditioned clams. In trial IV, although no spawning was observed soon after the exposure of unconditioned clams to the experimental treatments, a whiteish foam was observed in the tank after the overnight period. The tank volume was then filtered, and fertilized and unfertilized eggs, and veliger larvae were observed. After 48 h, D-veliger larvae were detected. In trial V, again no spawning was initially observed, but approximately 18 h after the exposure to the combined stimuli of thermal shock and H2O2 at an alkaline pH, unfertilized and fertilized eggs were found. After 42 h, both trochophore and D-veliger larvae were observed. The presence of eggs was observed in all treatments of trial VI: one of the three replicates of the thermal shock treatment (3.3 egg.L−1); two replicates of the thermal shock treatment associated with increased pH (20.0 and 46.6 eggs. L−1); two replicates of the thermal shock associated with the addition of H2O2 (6.7 and 23.3 egg.L−1); and one replicate of the treatment combining thermal shock with the addition of H2O2 in alkalinized seawater (20.0 egg.L−1). Despite this, the only treatment in trial VI in which zygotes were observed was thermal shock combined with the addition of H2O2 (1.1 egg. L−1), but no larvae were found. No significant differences were detected between spawning-inducing treatments (p = 0.815) in trial VI. The density of eggs also did not differ significantly between treatments (p = 0.585).
All five clams sampled at the end of trial I were male and in an immature reproductive stage (Figure 1A). In trial II, male clams sampled before the conditioning period were in the stage of sexual rest, while females were in the spent stage of development (Figure 1B). After conditioning, female gonads had peduncular-shaped immature oocytes (IO) attached to the follicle wall, mature oocytes (MO), and residual oocytes (RO) (Figure 1C). Many large and free rounded oocytes were observed in the lumen surrounded by connective tissue, as well as some mature, polygonal oocytes that would probably be reabsorbed (Figure 1C). All this indicates that the females from trial II were in the stage of partial spawning. Likewise, as spermatogonia and mature sperm cells were both present, the reproductive stage of the males may also be described as partially spawned. Females sampled before conditioning in trial III were in the early ripe stage, and presented mature, polygonal oocytes; some immature oocytes attached to the follicle wall, which was also thicker than in previous samples (Figure 1D). Likewise, male gonads had histological features typical of the early ripe stage: the spermatic duct had a light lilac color and was visible in the center of the follicle. Moreover, the follicular wall was surrounded by spermatocyte nests, and spermatids were concentrated within the follicle. After conditioning, the stage of sexual maturity of females in trial III had evolved to ripe, with a higher number of free polygonal oocytes in the lumen (Figure 1E). When compared to clams from trial II, those from trial III appeared to be at a more advanced stage of maturity.
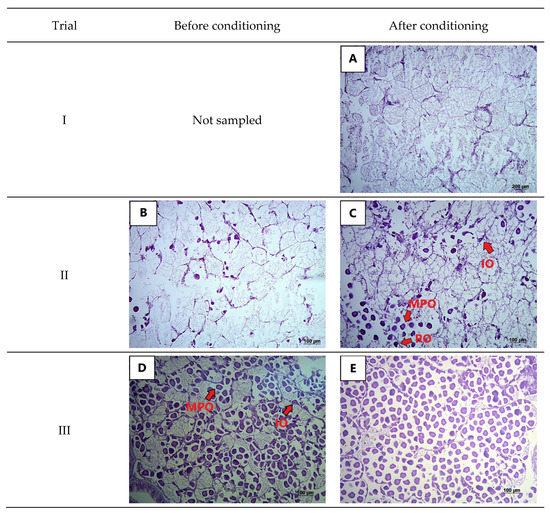
Figure 1.
Histological sections of yellow clam (Amarilladesma mactroides) before and after the laboratory-conditioning period: (A) male gonad of clam from trial I after 14 days of conditioning; (B) female gonad with residual (RO) and immature oocytes (IO) characteristic of the spent stage of development; (C) female gonad after the conditioning period in trial II showing peduncular-shaped immature oocytes (IO) adhered to the follicle wall; mature, polygonal oocytes (MPO); and residual oocytes (RO); (D) stage 3 gonad of female clam at the beginning of trial III where immature oocytes (IO) and mature, polygonal oocytes (MPO) are present; (E) female gonad at stage 4 after conditioning in trial III.
Histological analysis indicated that clams from trial IV were partially spawned (Figure 2A,B). There were mature, polygonal oocytes (MPO, Figure 2A) with empty spaces, deformed follicular walls with ruptures, as well as the presence of deteriorating oocytes (DO). No spermatic ducts were observed in the center of the follicle, the follicular walls present ruptures, and immature cells were also present in the walls (Figure 2B). In trial V, females were partially spawned, i.e., RO, MPO, and a few IO were present (Figure 2C). The males were also partially spawned, but the spermatozoa were not at the center, and the follicle center was quite empty in comparison to mature males (Figure 2D). Finally, gonads of females and males from trial VI were also in the partial spawning stage. The females had comparatively smaller follicles with a few polygonal oocytes, more rounded oocytes, and some oocytes undergoing deterioration (Figure 2E). The central region of the follicles of the males were partially empty with few spermatozoa (Figure 2F).
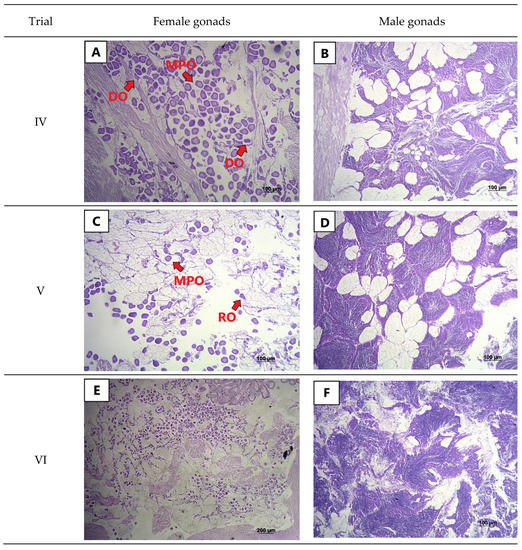
Figure 2.
Histological analysis of the gonadal tissues of laboratory-unconditioned yellow clam (Amarilladesma mactroides) exposed to different spawning-inducing treatments in trials IV, V, and VI: (A) Partial spawning stage (Stage 5) of a female clam presenting free mature, polygonal oocytes (MPO) and deteriorating oocytes (DO); (B) Partial spawning stage of male clam from trial IV; (C) Partial spawning stage (Stage 5) of a female with mature, polygonal oocytes (MPO) and rounded residual oocytes (RO); (D) Male yellow clam in the partial spawning stage (stage 5); (E) Female clam in the partial spawning stage (stage 5) displaying free mature, polygonal oocytes and a large number of rounded oocytes; (F) Male clam in the partial spawning stage (stage 5).
Both D and d of clams from trial II were significantly larger after the conditioning period (Table 2). In trial III, d was also significantly larger after the conditioning period, but, although a trend towards an increase in D was observed, this difference was only numerical. Although the experimental design allows no comparisons between trials, there were obvious differences in D and d from clams from the various trials (Table 2). Mean D varied from 32.26 to 44.17 µm (Table 2).

Table 2.
Mean (± SD) size (µm) of larger (D) and smaller diameters (d) of oocytes from yellow clam (Amarilladesma mactroides) at the beginning and the end of the 14-day conditioning period in trials II and III, and at the end of trials IV, V, and VI. Superscripts indicate significant differences between D or d within the same trial.
4. Discussion
The maintenance of clams in the laboratory for 14 days (i.e., the conditioning period in trials I, II, and III) resulted in high survival (from 71.8 to 88.3%) and, despite the relatively short period, significant increases in size and condition factor were detected. In addition, larger oocytes and more advanced stages of gonadal development were observed at the end of trials II and III. All this confirms previous results that the experimental system and management practices used here were minimally adequate for the maintenance of adult A. mactroides in captivity [26]. On the other hand, as no spawning was observed for conditioned clams, a longer conditioning period may be required. The laboratory-conditioning period of bivalves from temperate areas is recommended to last from 4 to 8 weeks to reach spawning readiness [32], but its duration may vary according to the stage of gametogenesis at the time of capture in the wild. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that the closer to the natural breeding season the clams are captured and transferred to the hatchery, the larger the oocytes will be and, hence, the shorter the conditioning period.
Our results also indicate that, at the end of the conditioning period, the mean largest oocyte diameter (44.17 µm) was smaller than that of a mature oocyte, which is usually between 50 and 55 µm [1]. This size range is somewhat in agreement with previous studies that reported spawning females with oocytes ranging from 43 to 58 μm [4] and newly fertilized oocytes with a mean (±SD) diameter of 51.2 μm (±6.6) [22]. A reproductive scale based on oocyte diameter has been proposed as a methodology to assess the gametogenic development of bivalves [39]. Using this approach, it is possible to estimate that the minimum oocyte diameter for ready-to-spawn A. mactroides would likely be larger than 50 μm. Further work is required to confirm this hypothesis.
One factor that may have prevented the conditioned clams from spawning is the quantity and quality of the microalgal diet, which is a key issue in the reproduction of bivalves [32,40,41]. From a nutritional point of view, the provision of a monospecific diet of C. muelleri in trials II and III may be considered minimally adequate, as clams survived, grew, and their gonads continued to develop. However, providing a diet containing a mixture of two or more algal species, usually a combination of at least a diatom and a flagellate, would probably increase the chances that the oocytes reach full maturation and are released. Mixed algal diets provide a more nutritionally balanced diet, particularly in terms of essential fatty acids, cholesterol and pigments [42,43], and may also be more morphologically compatible and digestible [43]. In this regard, a strong relationship between the reproductive cycle of wild A. mactroides and phytoplankton biomass and species composition was pointed out [4]. For its congener Mesodesma donacium, a mixed diet also had a positive effect on gonadal development [29].
Regardless of the experimental treatment, the release of gametes and the occurrence of larvae in trials IV, V, and VI indicate that the freshly collected clams were ready to spawn, which was confirmed by histological analysis. As these clams were collected in November–December, this concurs with an earlier study in Argentina [4]. For A. mactroides collected at the southern limit of its distribution range, spawning occurred mainly from October to November–December. Although this is in line with our findings, an assessment of the reproductive cycle of natural populations in Brazil would further confirm this, especially in view of the different environmental conditions (temperature, salinity, and availability/quality of food) between locations.
The induction of spawning is a process in which mature individuals, in response to one or more stimuli, release gametes into the water. There are a variety of spawning induction methods applied to bivalves, and these include physical, biological, and chemical stimuli, or a combination of them [32,41,44,45]. Temperature manipulation is the most used stimulus due to its low cost and ease of application. It usually consists of exposing bivalves to cycles of cold and warm water temperatures, in a method called “thermal cycling” [32,44]. To increase the chances of spawning, temperature manipulation can be associated with the addition of microalgae, mature gametes, or extract from mature gonads [30,46,47]. In this study, spawning occurred when unconditioned clams from trial IV were exposed to increased temperatures in conjunction with the addition of sperm solution. In trial VI, the sole increase of temperature also resulted in the release of gametes, but no larvae were observed. It is worth highlighting that the presence of embryos and larvae were detected only after the overnight period, which might be considered as a good strategy to be used at hatchery level and in future studies.
Salinity is another physical factor that has a role in the regulation of the reproduction cycle and spawning induction in estuarine and marine bivalves [41]. Indeed, A. mactroides is sensitive to salinity fluctuations, and low salinity levels have been pointed out as a mortality cause [9]. An investigation on the salinity tolerance range of this species found that 100% of juveniles and adults survived in salinities over 15 [48]. Our results indicated that the combined increase of temperature and salinity had no apparent effect in the induction of spawning. One possible explanation for the lack of response is that the abrupt shock of salinity (from 28 to 35) might have stressed clams and disturbed them physiologically, diverting energy for osmoregulation instead of successfully responding to the induction technique. Even though no physiological parameters were evaluated here, it has been demonstrated that yellow clam adults exposed to a hyperosmotic shock (salinity of 35) had significant differences on mantle tissue hydration, such as increased Na+ concentration on mantle, gills, and adductor muscle as well as amino acid concentration on adductor muscle when compared to salinities 21 and 28 [49].
Chemical stimuli can also be applied to induce spawning in mollusks by injecting hormones or neurotransmitters into the gonad or mantle cavity [45], or by inoculating chemicals into the medium. The addition of H2O2 is reported to be efficient in inducing spawning, and its effectiveness depends on both the concentration of the compound and the alkalinity of the water [50,51,52]. Although exposure to H2O2 had a positive effect on inducing spawning in A. mactroides, higher mortality was observed compared to the other treatments. The clams also responded to H2O2 by keeping their valves closed, which could be taken as a sign that they were under a stressful condition.
In general, the survival after spawning induction of unconditioned clams (Trials IV, V, and VI) was high (80%), except for clams exposed to H2O2. Along with the high mortality, visual observation indicated that clams exposed to H2O2 quickly retracted their siphons and foot, and kept their valves closed. In the blood ark (Anadara tuberculosa) and limpets (Patella caerulea), no mortality was observed after exposure to H2O2 at concentrations of 5–10 mM and 6–10%, respectively [51,52]. On the other hand, the exposure of Acropora cerviconis corals to hydrogen peroxide (2 mM) resulted in the release of gametes, but 100% mortality was observed [53]. Exposing the mussel Mytilus edulis to H2O2 concentrations as low as 1.0 mg.L−1 negatively affected oxygen consumption, foot activity, and byssus production [54]. These authors concluded that M. edulis exposed to H2O2 respond by closing their valves and relying on anaerobic respiration and reserve nutrients until these resources are depleted or metabolic wastes reach toxic levels. The mortality of clams in the present study may be related to the harmful effects observed in M. edulis [54].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the spawning of A. mactroides in captivity. Although the consistent spawning of clams was not achieved here, the present results provide us with a better understanding of the environmental requirements and management practices that will eventually allow the captive reproduction of this species. Our results indicate that temperature manipulation and the addition of sperm solution show promise as spawning induction agents that will not result in excessive mortality of the yellow clam. Additional testing would be beneficial, especially if using wild-caught clams conditioned for periods longer than two weeks. Consideration should also be given to providing a microalgae diet consisting of two or more species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.B.G. and R.O.C.; methodology, N.B.G., F.R., L.A.R. and R.O.C.; software, N.B.G.; validation, N.B.G., F.S.G., V.F.P. and R.O.C.; formal analysis, N.B.G. and V.F.P.; investigation, N.B.G., F.S.G., L.A.R., F.R., V.F.P. and R.O.C.; writing—original draft preparation, N.B.G. and R.O.C.; writing—review and editing, N.B.G., L.A.R., F.R., V.F.P. and R.O.C.; supervision, L.A.R. and R.O.C.; project administration, R.O.C.; funding acquisition, R.O.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by FAPERGS—Foundation for the Support of Research in the State of Rio Grande do Sul (21/2551-0002250-7). The Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) provided study grants to N.B. Gauthier and F.S. Goes. V.F. Pedrosa and F. Roselet are postdoctoral fellows (PNPD) of the Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES). L.A. Romano and R.O. Cavalli are research fellows of CNPq.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, as Brazilian legislation does not require these procedures for studies involving invertebrates.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Coscarón, S. La almeja amarilla (Mesodesma mactroides, Deshayes) de la costa de la Provincia de Buenos Aires. Agro. Publ. Tec. 1959, 1, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, E.C. Seashells of Brazil, 1st ed.; Fundação Universidade do Rio Grande: Rio Grande, Brazil, 1994; 368p. [Google Scholar]
- Fiori, S.M.; Morsán, E.M. Age and individual growth of Mesodesma mactroides (Bivalvia) in the southernmost range of its distribution. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 61, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.; Alfaya, J.E.F.; Lepore, M.L.; Penchaszadeh, P.E.; Laudien, J. Reproductive cycle and gonad development of the northern Argentinean Mesodesma mactroides (Bivalvia: Mesodesmatidae). Helgol. Mar. Res. 2009, 63, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, A. Fisheries. In The Ecology of Sandy Shores, 3rd ed.; McLachlan, A., Defeo, O., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 331–372. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, A.O. A importância dos mariscos na subsistência de antigos grupos indígenas no litoral central Sítios RS-LC-81, 86, 87, 90, 92 e 96. Pesq. Antropol. 2006, 63, 259–288. [Google Scholar]
- Frontini, R.; Bayón, C. Archaeomalacological remains from the Puente de Fierro site (Buenos Aires province, Argentina). Arqueologia 2017, 23, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Defeo, O.; Gianelli, I.; Ortega, L.; Pittman, J. Responses of a small-scale shellfishery to climate change: Foundations for adaptive management. In Adaptive Management of Fisheries in Response to Climate Change. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 667; Bahri, T., Vasconcellos, M., Welch, D.J., Johnson, J., Perry, R.I., Ma, X., Sharma, R., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; pp. 147–160. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, S.R.; Capezzani, D.A.A.; Carreto, J.I.; Christiansen, H.E.; Aizpun de Moreno, J.E.; Penchaszadeh, P.E. Estructura de la Comunidad, Dinámica de la Población y Biología de la Almeja Amarilla (Mesodesma mactroides Desh. 1854) en Mar Azul (Pdo. de Gral Madariaga, Bs. As., Argentina); Instituto de Biología Marina: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 1971; 90p. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, M.; Alfaya, J.E.F.; Lepore, M.L.; Penchaszadeh, P.E.; Arntz, W. Population structure, growth and production of the yellow clam Mesodesma mactroides (Bivalvia: Mesodesmatidae) from a high-energy, temperate beach in northern Argentina. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2011, 65, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odebrecht, C.; Rörig, L.R.; Garcia, V.M.T.; Abreu, P.C. Shellfish mortality and a red tide event in southern Brazil. In Harmful Marine Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Erard, E., Gentien, P., Marcaillou, C., Eds.; Lavoisier Science: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Fiori, S.M.; Cazzaniga, N.J. Mass mortality of the yellow clam, Mesodesma mactroides (Bivalvia: Mactracea) in Monte Hermoso beach, Argentina. Biol. Conserv. 1999, 89, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, Y.B.M.; Poersch, L.H.; Romano, L.A. Rickettsia-associated mortality of the yellow clam Mesodesma mactroides (Bivalvia: Mesodesmatidae) in southern Brazil. Malacologia 2013, 56, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonte, F.; Figueras, A. Parasites as possible cause of mass mortalities of the critically endangered clam Mesodesma mactroides on the Atlantic coast of Argentina. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2004, 24, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez, N.; Fiori, S.; Arzul, I.; Carcedo, C.; Cremonte, F. Mass mortalities affecting populations of the yellow clam Amarilladesma mactroides along its geographic range. J. Shellfish Res. 2016, 35, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Bock, M. Mortandad masiva de Mesodesma mactroides (Bivalvia: Mactracea) en el partido de la Costa, Buenos Aires, Argentina, en septiembre 2004. Atlântica 2007, 29, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, F.C.; Castro, M.R.; Barbosa, S.C.; Primel, E.G.; Martins, C.M.G. Effect of the UV filter, Benzophenone-3, on biomarkers of the yellow clam (Amarilladesma mactroides) under different pH conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchet, D.M.; Forero Lopez, A.D.; Ardusso, M.G.; Rimondino, G.N.; Buzzi, N.S.; Malanca, F.E.; Spetter, C.V.; Fernández Severini, M.D. Microplastics in bivalves, water and sediments from a touristic sandy beach of Argentina. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bom, F.C.; Colling, L.A. Impact of vehicles on benthic macrofauna on a subtropical sand beach. Mar. Ecol. 2020, 41, e12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICMBio—Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade. Livro Vermelho da Fauna Brasileira Ameaçada de Extinção—Invertebrados; ICMBio: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; 492p. [Google Scholar]
- Cledón, M.; Nuñez, J.D. Siphon nipping facilitates lethal predation in the clam Mesodesma mactroides (Reeve, 1854) (Mollusca: Bivalva). Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.J.S.; Bernardes, J.P.; Ramírez, J.R.B.; Gomes, C.H.A.M.; Romano, L.A. Embryo and larval development of the yellow clam Mesodesma mactroides (Reeve, 1854) (Mesodesmatidae) in laboratory. An. Acad. Bras. Cien. 2020, 92, e20190053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proverbio, C.; Carnevia, D.; Jorge-Romero, G.; Lercari, D. Tools for handling the yellow clam Mesodesma mactroides under experimental captivity conditions. INNOTEC 2019, 18, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.J.S.; Bernardes, J.P.; Ramírez, J.R.B.; Gomes, C.H.A.M.; Romano, L.A. Effect of salinity on embryo-larval development of yellow clam Mesodesma mactroides (Reeve, 1854) in laboratory. An Acad. Bras. Cien. 2020, 92, e20190169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.J.S.; Bernardes, J.P.; Ramírez, J.R.B.; Melo, C.M.R.; Romano, L.A.; Gomes, C.H.A.M. Effect of temperature on embryo-larval development of Amarilladesma mactroides (Reeve, 1854). Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3090–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, N.B.; Goes, F.S.; Quaresma, L.; Pedrosa, V.F.; Roselet, F.; Romano, L.A.; Cavalli, R.O. Design and optimization of an experimental maintenance system for yellow clam broodstock Amarilladesma mactroides (Reeve, 1854). Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 82, e243168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerbe, R.; Zevallos, S.; Castañeda, V.; Lope, F.; Bendita, H.; Sanz, Y. Manual: Cultivo de Macha Mesodesma Donacium (Lamarck, 1818) en la Región Moquegua; Instituto del Mar del Perú: El Callao, Peru, 2018; Volume 45, pp. 242–262. [Google Scholar]
- Gadomski, K.; Moller, H.; Beentjes, M.; Lamare, M. Embryonic and larval development of the New Zealand bivalve Paphies ventricosa Gray, 1843, (Veneroida: Mesodesmatidae) at a range of temperatures. J. Mollus. Stud. 2014, 81, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevallos, S.; Toledo, P. Use of microalgae for broodstock conditioning of Mesodesma donacium (Mesodesmatidae). Biologist 2017, 15, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, F.; Aranda-Burgos, J.A.; Cerviño-Otero, A.; Fernández-Pardo, A.; Louzán, A.; Nóvoa, S.; Ojea, J.; Martínez-Patiño, D. Clam Reproduction. In Clam Fisheries and Aquaculture; González, F.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Chapter 3, pp. 45–71. [Google Scholar]
- Taynaros, S.; Tarangkoon, W. Variability in larval period, post-setting growth and survival of the oyster Crassostrea belcheri produced by gamete stripping method. Agric. Nat. Res. 2016, 50, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, M.; Bourne, N.; Lovatelli, A. Hatchery Culture of Bivalves—A Practical Manual, 1st ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004; 203p. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R. Cube law, condition factor and weight–length relationships: History, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO—United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Chemical Methods for Use in Marine Environmental Monitoring; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission: Paris, France, 1983; 53p. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC—Association of Official AnalyticaL Chemist. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; 90p. [Google Scholar]
- APHA—American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; 1258p. [Google Scholar]
- CBRA—Colégio Brasileiro de Reprodução Animal. Manual Para Exames Andrológicos e Avaliação de Sêmen Animal, 2nd ed.; CBRA: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 1998; 49p. [Google Scholar]
- Masello, A. Consideraciones Sobre Crecimiento y Biologia Reproductiva de la Almeja Amarilla Mesodesma mactroides (Deshayes, 1854). Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad de la Republica, Montevideo, Uruguay, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Lango-Reynoso, F.; Chavez-Villalba, J.; Cochard, J.C.; Le Pennec, M. Oocyte size, a means to evaluate the gametogenic development of the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Aquaculture 2000, 190, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utting, S.D. Techniques for the hatchery conditioning of bivalve broodstocks and the subsequent effect on egg quality and larval viability. Aquaculture 1997, 155, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E. Marine Bivalve Molluscs, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 157–202. [Google Scholar]
- Rico-Villa, B.; Le Coz, J.R.; Mingant, C.; Robert, R. Influence of phytoplankton diet mixtures on microalgae consumption, larval development and settlement of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Aquaculture 2006, 256, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Zhou, C.; Chu, R.; Chang, T.; Xu, J.; Ruan, R.; Chen, P.; Yan, X. Effect of microalgae diet and culture system on the rearing of bivalve mollusks: Nutritional properties and potential cost improvements. Algal Res. 2020, 51, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüello-Guevara, W.; Loor, A.; Sonnenholzner, S. Broodstock conditioning, spawning induction, and early larval development of the tropical rock oyster Striostrea prismatica (Gray 1825). J. Shellfish Res. 2013, 32, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowland, S.J.; O’Connor, W.A.; Elizur, A.; Southgate, P.C. Evaluating spawning induction methods for the tropical black-lip rock oyster, Saccostrea echinata. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslinga, G.; Watson, T.; Isamu, T. Giant Clam Farming; Pacific Fisheries Development Foundation (NMFS/NOAA): Honolulu, HI, USA, 1990; 179p.
- Trigos, S.; Vicente, N.; Prado, P.; Espinós, F.J. Adult spawning and early larval development of the endangered bivalve Pinna nobilis. Aquaculture 2018, 483, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, Y.B.M.; Romano, L.A.; Poersch, L.H.S. Effect of low salinity on the yellow clam Mesodesma mactroides. Braz. J. Biol. 2015, 75, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, I.; Faria, S.C.; Souza, M.M. Osmoionic homeostasis in bivalve mollusks from different osmotic niches: Physiological patterns and evolutionary perspectives. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2020, 240, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, D.E.; Duncan, H.; Hooker, N.; Morse, A. Hydrogen peroxide induces spawning in mollusks, with activation of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase. Science 1977, 196, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, M.P.; Monteggia, D.; Asnaghi, V.; Chiantore, M. Artificial reproduction protocol, from spawning to metamorphosis, through noninvasive methods in Patella caerulea Linnaeus, 1758. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3386–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.N.; Murillo, D.L.; Tabares, P.A.; Paredes, F.J.; Chapman, F.A. Induced spawning of the blood ark Anadara tuberculosa, using hydrogen peroxide. AACL Bioflux 2018, 11, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, M.; Than, J.T. Potential spawn induction and suppression agents in Caribbean Acropora cervicornis corals of the Florida Keys. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.N.; Kwon, S.H. Physiological effects of biocide on marine bivalve blue mussels in context prevent macrofouling. J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).