Abstract
Herein, we isolated the pathogenic strain ZZ051 from hemorrhagic channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Physiological and biochemical identification, 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, and MALDI-TOF-MS showed that the ZZ051 strain was Aeromonas veronii. After artificial infection, the diseased fish showed symptoms similar to the natural disease, and the characteristics of the bacteria reisolated from the tissues were the same as those of the original infection, indicating that the isolated strain ZZ051 was the pathogen responsible for the channel catfish disease. The ZZ051 isolate was highly sensitive to enrofloxacin but resistant to florfenicol. This study provided a theoretical basis for preventing and controlling hemorrhagic disease in channel catfish.
1. Introduction
Channel catfish [1] is a freshwater fish that was imported into China in 1984 from the USA [2]. This population of species has strong growth within the breeding areas, with a high yield after environmental adaptation [2]. It has been widely bred in over 30 provinces and cities in China, such as Henan, Jiangxi, Hubei, and Guangdong, and has become the primary breed to earn foreign exchange from China’s exports [3]. Pollution of the breeding environment can cause several diseases. Recently, the breeding industry of channel catfish has gradually increased due to the development of the domestic consumption market [4]. In 2020, the overall channel catfish yield was as high as 308,000 tons, increasing by 3.61% [5]. Among these, the breeding industry of channel catfish in Henan province is developing rapidly. According to statistics, the breeding output of channel catfish in the Henan province in 2020 was more than 30,800 tons, accounting for 10% of the total pond breeding in China.
As the channel catfish farming scale and production increases, the germplasm resources, degradation [6], poor quality of the breeding technology, the breeding density increase, aquaculture environmental degradation, and other issues are also increasingly prominent. These issues seriously limit the channel catfish industry’s further development and have resulted in various disease outbreaks that have gradually become dangerous to channel catfish [7]. A previous study reported that infectious diseases cause great harm to channel catfish breeding, including bacterial [8,9], parasitic, viral, and fungal diseases, especially bacterial and viral diseases [10]. The main bacterial pathogens infecting channel catfish are Aeromonas hydrophila, Yersinia ruckeri, Edwardsiella ictaluri, and Streptococcus iniae, which have caused severe harm and economic loss to the aquaculture industry [9,11].
A hemorrhagic disease outbreak occurred in cultured channel catfish in a pond in Henan Province, China, in 2020 and 2021. The clinical symptoms included hemorrhage in the skin fin bases, visceral enlargement, and hemorrhage accompanied by intussusception. The number of dead fish increased from 3–5 at the beginning to more than 300 within five days. The disease lasted more than two months, and the cumulative mortality rate was 50–70%. In the present study, we focused on identifying the pathogenic microorganisms from the channel catfish to lay the foundation to effectively control and prevent this disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish
Diseased channel catfish were collected from a channel catfish pond in Henan Province between March and May 2021. Healthy channel catfish (juveniles; mean body length was 6.05 cm and mean weight was 5.29 g, respectively) were obtained from another unaffected pond. The fish were maintained in aerated tanks under 28 °C for 7 d to guarantee that the fish were healthy before the pathogenicity test and bacterial challenge analysis.
2.2. Histopathology
The liver, spleen, and kidney tissues were collected from naturally infected fish and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 48 h. The slices were dehydrated until, dipped in wax, and embedded in paraffin. The thickness of the slices was 3 μm, and the tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. After neutral resin sealing, the sections were observed and photographed microscopically (Olympus CX21), and the pathological changes in the tissues were analyzed [12].
2.3. Etiological Examination
The gills, skin mucus, and viscera were microscopically examined for parasites. For bacterial isolation, liver, kidney, and ascites material from each moribund fish were inoculated in brain heart infusion (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) agar plates and incubated at 28 °C for 3 d. The dominant colonies with different morphological characteristics were collected and purified twice and then identified with the methods described in Section 2.4 [13].
2.4. Bacterial Identification
2.4.1. Identification of the Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Characteristics of the Pathogenic Bacteria
According to the Gram staining instructions, the morphological characteristics of the pathogenic bacteria were observed under a light microscope. To observe their ultra-structure, the purified bacteria were negatively stained with phosphotungstic acid (PTA), then observed with a transmission electron microscope at 80 kV (Hitachi-7650, Tokyo, Japan).
The physiological and biochemical indexes of the isolates were measured using biochemical identification tubes of the microbacteria, referring to Berger’s Manual of Bacterial Identification and Manual of Common Bacterial Systematic Identification.
2.4.2. Identification of Bacterial Species by MALDI-TOF-MS
The purified bacteria were inoculated in a nutrient agar plate for culture, and single colonies were selected and coated on the MALDI-TOF-MS target plate. One μL of 70% formic acid was added first, followed by 1 μL matrix solution. After the matrix was dried, the target plate was put back into the system to identify the strains.
2.4.3. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
Briefly, DNA was extracted using the bacterial genome DNA extraction kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China). The extracted DNA was used as a template to amplify the 16S rRNA of bacteria with the universal primer pair (27 F: 5′–AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG–3′; 1492 R: 5′–GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT–3′), leading to a 1506 bp product. The PCR amplification conditions were as follows: predenaturation for 4 min at 94 °C; denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 56.5 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, for a total of 35 cycles; extension at 72 °C for 6 min; and finally, 16 °C to end the reaction process. The PCR products were detected by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. After the gel was recovered, the purified PCR product was cloned into a T vector and sent to Sangong Bioengineering (Shanghai, China) Co., LTD (Shanghai, China) for sequencing. BLAST analysis was performed with the reference sequences published in GenBank. MEGA 7 was used for multiple sequence matching and cluster analysis. Neighbor-joining (NJ) was used to construct the phylogenetic tree.
2.5. Pathogenicity
An experimental infection study was performed to examine the pathogenicity of the bacterial isolate. The bacteria were cultured in liquid BHI medium at 28 °C for 20 h, harvested by centrifugation at 14,000× g and 4 °C for 10 min, and suspended in sterile saline (0.65% NaCl). The bacterial suspensions were diluted to 1 × 107, 1 × 106, 1 × 105, and 1 × 104 CFU/mL with sterile saline, respectively. Groups of 30 similarly sized channel catfish were intraperitoneally injected with 0.1 mL of each bacterial suspension, with challenge doses of 1 × 106, 1 × 105, 1 × 104, and 1 × 103 CFU/fish. The control group included 30 channel catfish injected with the same volume of sterile saline. All fish were raised in aerated tanks (100 L) at 25 ± 2 °C. The morbidity and mortality were observed and recorded every day for ten days. Necropsy examination, pathogen isolation, and identification were performed again on the moribund or fresh dead fish.
2.6. Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
We used the standard Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion approach to test the drug susceptibility of the pathogens. Briefly, the strain suspensions were evenly coated on a nutrient agar plate, and the sensitivity disk of different drugs was attached at equal distances. After 24 h of inverted culture in a constant temperature incubator at 28 °C, the diameter of the inhibition zone was observed and recorded. The diameter of the inhibition zone was used as a judgment indicator, and the susceptibility of the pathogenic strains to the drugs was determined by referring to the drug-sensitive paper instructions [13].
3. Results
3.1. Natural Features and Clinical Symptoms
The external symptoms of the diseased fish were severe hemorrhage on the head, lower jaw, and base of the pectoral fin and abdominal enlargement (Figure 1A). The necropsy showed a large amount of yellowish fluid in the abdominal cavity, severe black–purple hemorrhage in the spleen, pale and swollen liver with congestion, kidney enlargement, intestinal wall congestion and bleeding, no food in the intestinal tract, filled with a large amount of yellowish fluid (ascites), and typical symptoms of intussusception (Figure 1B).
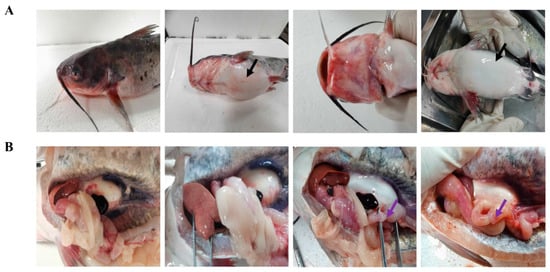
Figure 1.
Natural features of A. veronii infection in channel catfish. The black arrow represents abdominal enlargement (A), and the purple arrows represent intussusception (B) in channel catfish.
3.2. Histopathological Observation and Analysis
The following major histological changes were observed under the microscope (Figure 2): Liver (A): a small area of central vein and congestion in hepatic sinus (black arrow) can be seen at the edge of the liver tissue, and no other obvious abnormality was found. No apparent inflammatory cell infiltration was observed. Spleen (B): The parenchymal cells in the spleen tissue were reduced, the structure was necrotic (black arrows), and no other obvious abnormality was found. Kidney (C): there was a large amount of renal tubular necrosis, pyknosis, and fragmentation of the renal tubular epithelial cells, with disintegration and destruction of the original tissue structure (black arrow), and the yellow arrow points to hypertrophied glomeruli in renal tissue. No other evident abnormalities were found.
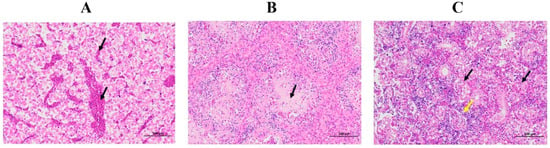
Figure 2.
Histopathological observation and analysis by HE. Liver (A): A small area of central vein and congestion in hepatic sinus (black arrows) can be seen at the edge of liver tissue. Spleen (B): the parenchymal cells in the spleen tissue are reduced, and the structure is necrotic (black arrow); kidney (C): there is a large amount of renal tubular necrosis, pyknosis, and fragmentation of the renal tubular epithelial cells, with disintegration and destruction of the original tissue structure (black arrows), and the yellow arrow points to hypertrophied glomeruli in the renal tissue.
3.3. Pathogen Isolation and Identification
No parasites were detected in the skin mucus, gills, or viscera. Bacterial colonies with the same morphological characteristics were isolated from the diseased fish’s liver, kidney, and ascites. The bacterial colonies were round, grayish white to light yellow, with smooth and moist surfaces and neat edges on BHI agar plates. The bacteria were Gram-negative, rod-shaped, blunt at both ends, arranged singly or in pairs, and without spores or pods. Electron microscopy also demonstrated that the bacterium was short rod-shaped and had a single polar flagellum (Figure 3).
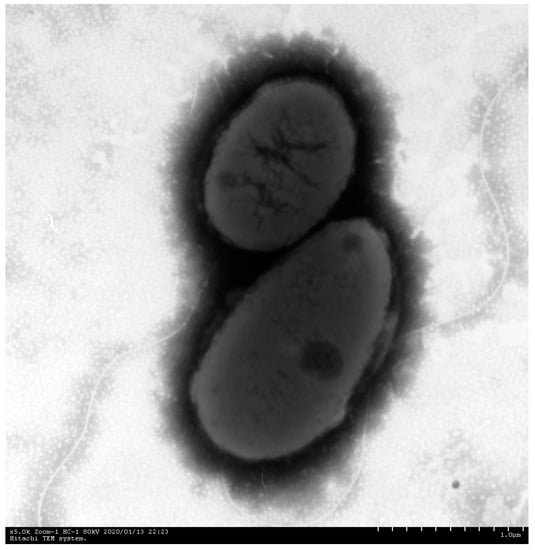
Figure 3.
Electron microscope images of the ZZ051 bacterium showed negative staining, a short rod shape, and only one polar flagellum. Scale bar = 1 μm.
Several randomly selected colonies isolated from the liver and kidney tissues were all identified as Aeromonas veronii by MALDI-TOF-MS, including isolate ZZ051 (Figure 4), and the MALDI-TOF score was 2.300. This isolate was selected for additional testing.
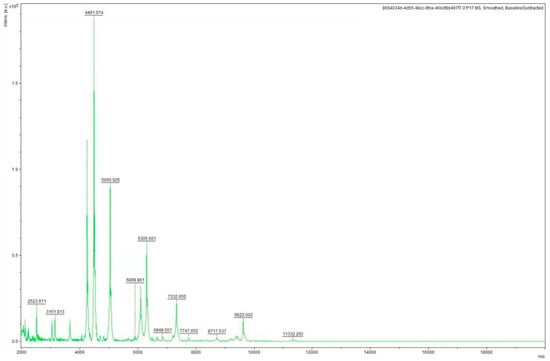
Figure 4.
The characteristic mass spectrum of A.veronii isolate ZZ051 by MALDI-TOF-MS.
The results of the 24 biochemical indexes of the pathogen ZZ051 are presented in Table 1. Ornithine decarboxylase was the primary reaction identified that differentiated A. veronii from other Aeromonas. According to the “Manual of Systematic Identification of Common Bacteria”, except for the arginine decarboxylase reaction that was different from the standard A. veronii strain, the other reactions were consistent with the standard strain, such as gelatin, ornithine decarboxylase, and lysine decarboxylase (all positive). Therefore, according to the physiological and biochemical characteristics, ZZ051 was classified as A. veronii (Table 1).

Table 1.
The biochemical characteristics of the pathogenic bacteria ZZ051.
The BLAST analysis results of the 16s rRNA sequence showed that ZZ051 had a 100% identity to other A. veronii strains. The phylogenetic analysis was based on the comparison of the 16S rRNA sequences between isolate ZZ051 and other Aeromonas, including A. veronii (ATCC 35624), A. jandaei (ATCC 49568), A. salmonicida (ATCC 33658), A. sobria (ATCC 43979), A. hydrophila (ATCC 7966), and A. caviae (ATCC 15467). As demonstrated by the phylogenetic tree, isolate ZZ051 was clustered into one group with the reference A. veronii strain (Figure 5). The BLAST and phylogenetic analysis results confirmed the identification of the ZZ051 isolate as A. veronii.
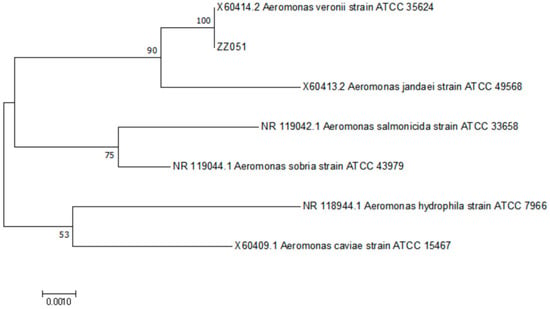
Figure 5.
The phylogenetic relationships based on 16S rRNA sequence comparisons between strain ZZ051 and other fish-pathogenic Aeromonas.
3.4. Pathogenicity
Healthy channel catfish were infected with strain ZZ051 suspensions at 1 × 106, 1 × 105, 1 × 104, 1 × 103 CFU/fish via intraperitoneal injection. For each infection dose, dead channel catfish were first observed at 2–3 days post-infection (dpi) (Figure 6). In the group infected with 1 × 106 CFU/fish, mortality first occurred at 2 dpi. Then, the cumulative mortality increased rapidly to 100% at 5 dpi. In the groups infected with 1 × 105 and 1 × 104 CFU/fish, mortality started at 2 dpi, and cumulative mortality reached 70 and 26.7%, respectively, at 8 dpi. The death of the group infected with a 1 × 103 CFU/fish started at 3 dpi, and the final cumulative mortality rate was only 10% at 8 dpi. No dead or sick channel catfish was observed in the negative control group. Bacteria were re-isolated from the kidney and liver of the dead fish and identified as A. veronii by 16S rRNA sequencing (data not shown).
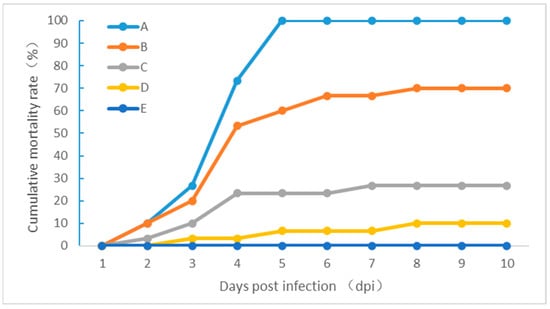
Figure 6.
The pathogenicity of the isolate ZZ051 in healthy channel catfish experimentally infected with (A) 1 × 106, (B) 1 × 105, (C) 1 × 104, and (D) 1 × 103 CFU/fish. (E) Negative control.
3.5. Drug Sensitivity Test
The drug-sensitivity test results of strain ZZ051 to 27 antibiotics are shown in Table 2. ZZ051 was highly sensitive to six antibacterial agents, including Cefotaxime, Azithromycin, Minocycline, Doxycycline, Ofloxacin, and Enrofloxacin, moderately sensitive to four antibacterial agents, including Furazolidone, Polymyxin B, Vancomycin, and Rifampicin, and resistant to 15 antibacterial agents, including Penicillin, Chlorophenicol, and Florfenicol, etc.

Table 2.
Drug sensitivity test.
4. Discussion
Channel catfish, native to North America, are the dominant freshwater species in the USA, comprising 60% of the fish farming in the country [14]. As a new type of freshwater economic aquaculture fish with fast growth, high disease resistance, no intramuscular spines, and high nutritional value, channel catfish has been widely promoted in China since it was introduced from the USA in 1984 [15,16]. Currently, Chinese channel catfish breeding is an important part of the world’s channel catfish industry. In recent years, diseases have become a more prominent problem with the continuous expansion of the channel catfish breeding industry in Henan province. Among the pathogens, A. veronii and A. hydrophila have caused severe health issues for the fish in this province.
After isolating and identifying the pathogen and the regression infection experiment, we found that the channel catfish’s hemorrhagic disease pathogen was A. veronii. This pathogen mainly infects freshwater fish, such as carp [17]. Infections with A. veronii can cause septicemia, bleeding, ulcer, ascites, and other symptoms, leading to high mortality and morbidity and bringing substantial economic losses to aquaculture. A. veronii can infect not only aquatic animals but also mammals, including humans. It is an opportunistic pathogen for humans and has some infectivity for people with normal immune competence. The general symptoms observed in this outbreak were similar to the samples of channel catfish disease collected by Huang et al. from Meishan, Sichuan province, with typical symptoms of abdominal enlargement, bloody ascites, anal redness and swelling, severe enteritis, fat spot bleeding, and diffuse bleeding of parenchymal organs [18]. Here, we characterized a similar A. veronii isolated from the liver, spleen, and kidney of the diseased channel catfish, showing that the infection was multisystemic. This also explains the severe disease with high death rates and the perseverance of the infection in the population. At scanning electron microscopy, short flagellated rods were observed. The histopathological observations of different degrees of hyperemia, hemorrhage, degeneration, and necrosis in parenchymal organs such as the liver, spleen, and kidney were similar to the pathological changes observed by previous reports on A. veronii-infected channel catfish [19].
Traditional physio-biochemical analysis and 16S rRNA sequencing has laid the foundation for bacterial identification [20]. Nonetheless, A. hydrophila and A. caviae are almost indistinguishable at the genotypic and phenotypic levels. In addition, routine physio-biochemical approaches cannot precisely distinguish them, resulting in a high species misidentification rate [21]. MALDI-TOF-MS is a novel soft ionization technology for analyzing and determining biological macromolecules (e.g., proteins and nucleic acids) [22]. Due to its rapid and efficient characteristics, it has been widely used to identify microorganisms automatically [23]. This technology mainly measures the molecular weight or characteristic protein spectrum changes in microbial cells for identification and other related detections [24]. At present, according to the research progress in China and abroad, MALDI-TOF MS has been used in clinical detection and basic research for microbial typing, bacterial drug resistance, epidemiological analysis, and recombinant protein expression in bacteria, not only improving the efficiency and accuracy of microbial detection but also being used to study microorganisms at the proteomics level. However, MALDI-TOF-MS also has some defects, which need to be combined with other means for bacterial identification [25,26,27]. In the present study, 16S rRNA sequence analysis, physiological and biochemical determination, and MALDI-TOF-MS technology were used to identify the pathogenic bacteria ZZ051 of channel catfish, increasing the accuracy of the results.
Antibiotics are still the main drugs used to control bacterial diseases in domestic aquaculture production. However, the abuse of antibiotics and the emergence of drug-resistant strains often lead to disease control failure. Herein, we determined the susceptibility of the isolated strain ZZ051 to 27 drugs. ZZ051 was highly sensitive to six antibacterial drugs, including Cefotaxime, Azithromycin, Minocycline, Doxycycline, Ofloxacin, and Enrofloxacin, moderately sensitive to four, including Furazolidone, Polymyxin B, Vancomycin and Rifampicin, and resistant to 15, including Penicillin, Chlorophenicol, and Florfenicol. Among them, ZZ051 was resistant to florfenicol, commonly used in aquaculture. This suggests that we should scientifically screen sensitive drugs and use targeted and precise drugs to control pathogenic infection in fish to avoid the emergence of drug-resistant strains due to lack of knowledge and abuse. At the same time, we should strengthen the development of fish immune system enhancers, especially traditional Chinese medicine immune system enhancers, to improve the fish’s immunity, prevent these diseases, and reduce the use of antibiotics.
In conclusion, we found that A. veronii ZZ051 was the causal agent of Hemorrhagic Septicemia in channel catfish and highly sensitive to enrofloxacin but resistant to florfenicol. This study provided a theoretical basis for preventing and controlling hemorrhagic disease in channel catfish.
Author Contributions
G.Q.: Methodology, Software, Validation, Investigation, Data curation, Writing-original draft. J.X.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing—original draft. X.A.: Investigation. Y.Y.: Writing—review & editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration, and Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (NO. YFI202209), Yancheng Fishery High Quality Development Project (No. YCSCYJ2021026), the Special Fund for Henan Agriculture Research System (No. HARS-22-16-Z1), and Henan science and technology research project (No. 222102110401).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were approved and conducted in compliance with all experimental practices and standards developed by the Animal Welfare and Research Ethics Committee of Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute (YFI2021YYB0013).
Data Availability Statement
All the data generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to the anonymous reviewers who provided detailed comments that helped to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of the work described in this manuscript.
References
- Zhang, X.; Hao, K.; Li, S.; Meng, L.; Chen, H.; Wei, F.; Yu, F.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Z. Channel catfish virus ORF25 and ORF63 genes are essential for viral replication in vitro. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abass, N.Y.; Ye, Z.; Alsaqufi, A.; Dunham, R.A. Comparison of growth performance among channel-blue hybrid catfish, ccGH transgenic channel catfish, and channel catfish in a tank culture system. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Dong, L.; Gan, J.; Mao, T.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; He, L. Effects of moderate exercise on hepatic amino acid and fatty acid composition, liver transcriptome, and intestinal microbiota in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crider, J.; Quiniou, S.M.A.; Felch, K.L.; Showmaker, K.; Bengtén, E.; Wilson, M. A Comprehensive Annotation of the Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) T Cell Receptor Alpha/Delta, Beta, and Gamma Loci. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 786402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubytska, L.P.; Thune, R.L. Early Intracellular Trafficking and Subsequent Activity of Programmed Cell Death in Channel Catfish Macrophages Infected with Edwardsiella ictaluri. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, S.; Yoshimura, A.; Kawakami, Y.; Nakamura, O. Molecular evolution of kalliklectin in teleost and identification of the novel type with eight apple domains in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4305–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.A.; Shamkhalichenar, H.; Browning, V.E.; Byrd, V.J.; Liu, Y.; Gutierrez-Wing, M.T.; Novelo, N.; Choi, J.W.; Tierschc, T.R. A practical evaluation of machine learning for classification of ultrasound images of ovarian development in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2022, 552, 738039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, M.; Fu, L.; Zhong, L.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Bian, W. Liver transcriptome analysis and cortisol immune-response modulation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 101, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Ai, X. Dual RNA-Seq of Trunk Kidneys Extracted From Channel Catfish Infected With Yersinia ruckeri Reveals Novel Insights Into Host-Pathogen Interactions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 775708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simora, R.M.C.; Xing, D.; Bangs, M.R.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Su, B.; Khan, M.G.Q.; Qin, Z.; Lu, C.; Alston, V.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knock-in of alligator cathelicidin gene in a non-coding region of channel catfish genome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, J.; Nandi, S.; Mohanty, S.; Terhune, J.; Liu, Z.; Peatman, E. RNA-seq analysis of mucosal immune responses reveals signatures of intestinal barrier disruption and pathogen entry following Edw. Ictaluri infection in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2012, 32, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Luo, L.; Zuo, F.; Geng, Y.; Ou, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, S.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Immunosuppression and apoptosis activation mediated by p53-Bcl2/Bax signaling pathway—The potential mechanism of goldfish (Carassius auratus Linnaeus) gill disease caused by Myxobolus ampullicapsulatus. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 998975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Ai, X. Vibrio cholerae was found in cultured bullfrog. Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Xia, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Ran, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Partially replacing dietary fish meal by Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture improve growth performance, immunity, disease resistance, composition and function of intestinal microbiota in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 125, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detrich, H.W., 3rd; Prasad, V.; Ludueña, R.F. Cold-stable microtubules from Antarctic fishes contain unique alpha tubulins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 8360–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, N.; Fu, G.; Ai, X. RNA-Seq and 16S rRNA Analysis Revealed the Effect of Deltamethrin on Channel Catfish in the Early Stage of Acute Exposure. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 916100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, T.; Song, G.; Yue, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Q. Whole-genome sequencing and antimicrobial resistance analysis of multidrug-resistant Aeromonas veronii strain JC529 from a common carp. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 27, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, K.; Geng, Y.; Zhao, Q. Pathohistological observation of Ictalurus punctatus infected with Aeromonas veronii. Chin. Vet. Sci. 2010, 40, 738–742. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, R.; Rahman, A.; Paul, S.I.; Ador, M.A.A.; Haque, M.S.; Akter, T.; Rahman, M.M. Aeromonas veronii isolated from climbing perch (Anabas testudineus) suffering from epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS)—ScienceDirect. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 8, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shao-Wu, L.I.; Liu, H.B.; Yin, J.S.; Lu, T. Comparison Study on 16S rDNA of Nine Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Northeast Provinces. Chin. J. Fish. 2010, 23, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.C. Cloning, expression in Escherichia coli, and enzymatic properties of laccase from Aeromonas hydrophila WL-11. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonetani, S.; Ohnishi, H.; Ohkusu, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Watanabe, T. Direct identification of microorganisms from positive blood cultures by MALDI-TOF MS using an in-house saponin method. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2016, 52, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittar, F.; Ouchenane, Z.; Smati, F.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.M. MALDI-TOF-MS for rapid detection of staphylococcal Panton-Valentine leukocidin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Graphene as a novel matrix for the analysis of small molecules by MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6208–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Sancho, M.; Cerdá, I.; Fernández-Bravo, A.; Domínguez, L.; Figueras, M.J.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F.; Vela, A.I. Limited performance of MALDI-TOF for identification of fish Aeromonas isolates at species level. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.B.; Yoon, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, K. Comparison of MALDI-TOF MS, housekeeping gene sequencing, and 16S rRNA gene sequencing for identification of Aeromonas clinical isolates. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Abe, N.; Ui, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamashita, T.; Sakaguchi, A.; Suzuki, S.; Masuo, K.; Nakano, A.; et al. Comparison of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and rpoB gene sequencing for the identification of clinical isolates of Aeromonas spp. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).