Environmental DNA Metabarcoding Reflects Fish DNA Dynamics in Lentic Ecosystems: A Case Study of Freshwater Ponds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
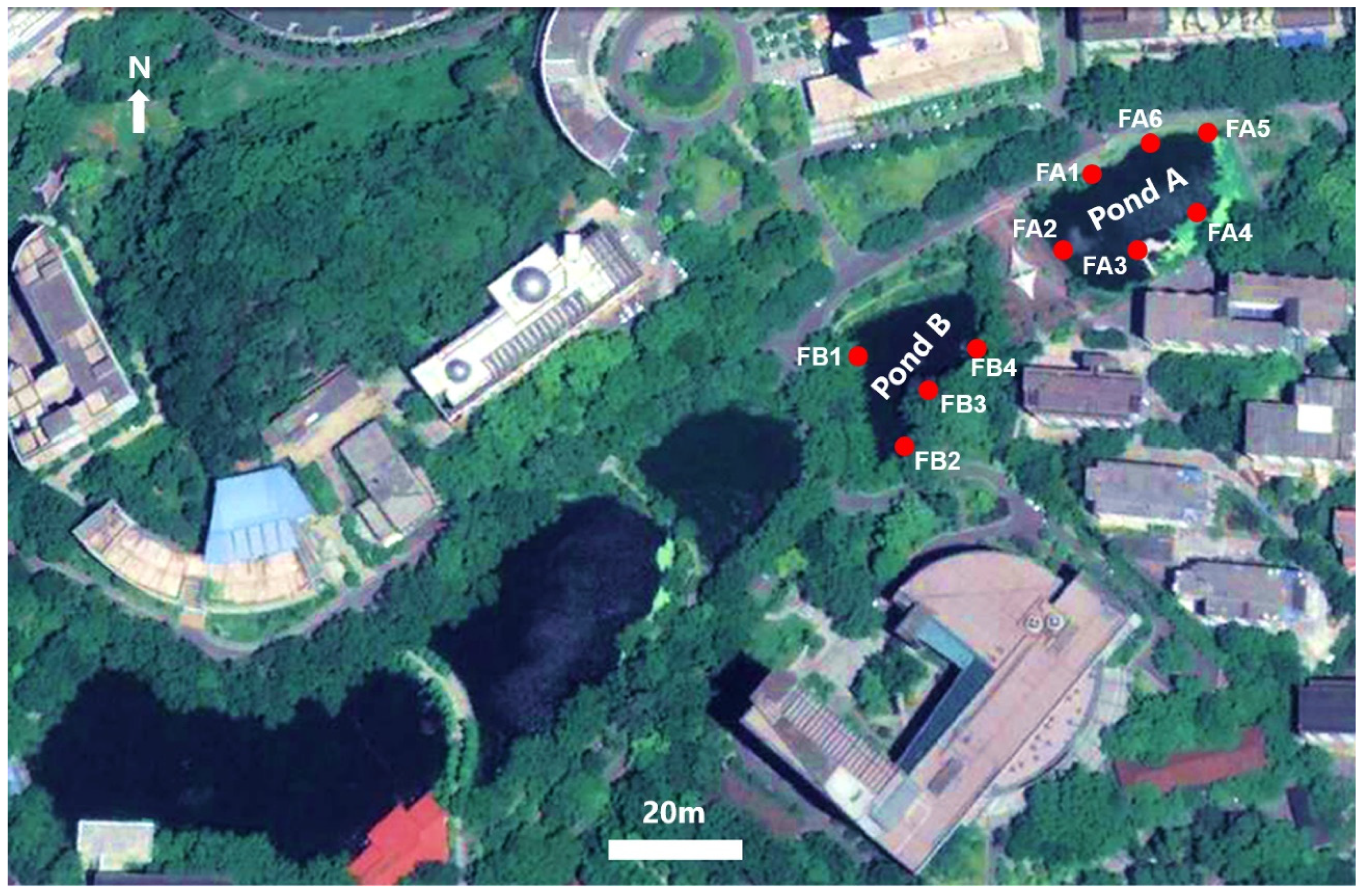
2.1. Study Sites and Field Sampling Protocol
2.2. eDNA Extraction, Amplification, and Illumina Sequencing
2.3. Metabarcoding Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fish Diversity
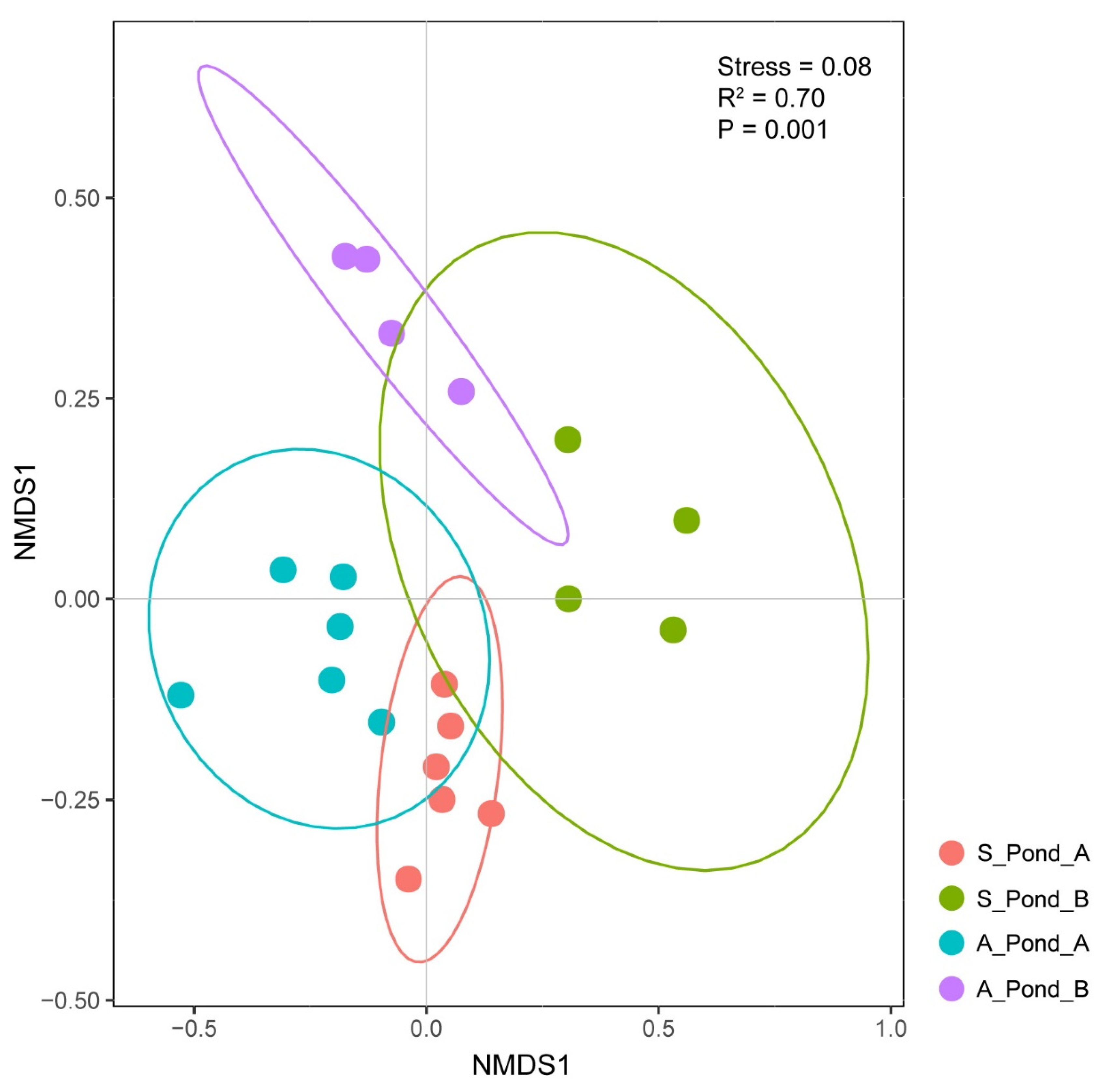
3.2. Differences in Spatial and Temporal Fish eDNA Detections

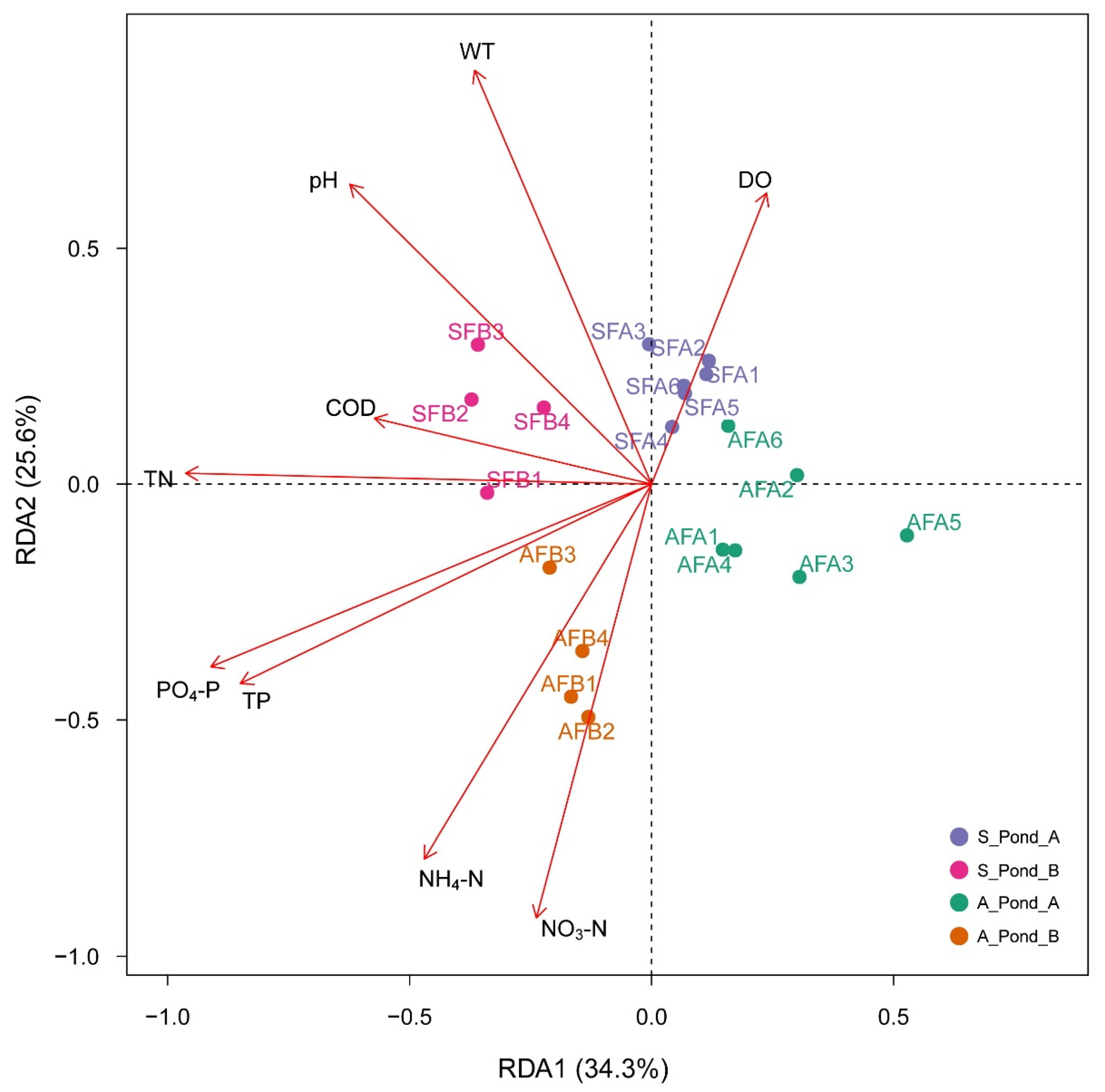
3.3. Correlations between Environmental Factors and Fish eDNA Distributions
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential of eDNA Metabarcoding and Limitations of the Primers
4.2. eDNA Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in Lentic Ecosystems
4.3. Effects of Water Temperature, pH, and Total Nitrogen on Fish eDNA Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coble, A.A.; Flinders, C.A.; Homyack, J.A.; Penaluna, B.E.; Cronn, R.; Weitemier, K. eDNA as a tool for identifying freshwater species in sustainable forestry: A critical review and potential future applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 649, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, S.; Takahara, T.; Doi, H.; Shibata, N.; Yamanaka, H. The detection of aquatic macroorganisms using environmental DNA analysis—A review of methods for collection, extraction, and detection. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, N.T.; Shirey, P.D.; Wieringa, J.G.; Mahon, A.R.; Lamberti, G.A. Comparative Cost and Effort of Fish Distribution Detection via Environmental DNA Analysis and Electrofishing. Fisheries 2017, 42, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt, A.D.; Sales, N.G.; Browett, S.S.; Sparnenn, A.O.; Mariani, S.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Coscia, I.; Benvenuto, C. Environmental DNA metabarcoding as an effective and rapid tool for fish monitoring in canals. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, K.M.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, S. Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Nielsen, I.B.; Carl, H.; Krag, M.A.; Knudsen, S.W.; Xing, Y.; Holm-Hansen, T.H.; Møller, P.R.; Thomsen, P.F. Seawater environmental DNA reflects seasonality of a coastal fish community. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckle, M.Y.; Soboleva, L.; Charlop-Powers, Z. Aquatic environmental DNA detects seasonal fish abundance and habitat preference in an urban estuary. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhau, T.; Valentini, A.; Poulet, N.; Roset, N.; Jean, P.; Gaboriaud, C.; Dejean, T. Seasonal dynamics of riverine fish communities using eDNA. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 98, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Xian, W. Seasonal Fish Assemblage Structure Using Environmental DNA in the Yangtze Estuary and Its Adjacent Waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Altermatt, F. Transport Distance of Invertebrate Environmental DNA in a Natural River. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antognazza, C.M.; Britton, J.R.; Potter, C.; Franklin, E.; Hardouin, E.A.; Roberts, C.G.; Aprahamian, M.; Andreou, D. Environmental DNA as a non-invasive sampling tool to detect the spawning distribution of European anadromous shads (Alosa spp.). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 29, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, F.S.A.; Rooney, S.M.; Kelly-Quinn, M.; King, J.J.; Carlsson, J. Identifying spawning sites and other critical habitat in lotic systems using eDNA “snapshots”: A case study using the sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus L. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Moreno, M.; Ivanova, N.V.; Elías-Gutiérrez, M.; Pedersen, S.L.; Bessonov, K.; Hebert, P.D.N. Using eDNA to biomonitor the fish community in a tropical oligotrophic lake. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. Assessment of fish communities using environmental DNA: Effect of spatial sampling design in lentic systems of different sizes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 20, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brys, R.; Haegeman, A.; Halfmaerten, D.; Neyrinck, S.; Staelens, A.; Auwerx, J.; Ruttink, T. Monitoring of spatiotemporal occupancy patterns of fish and amphibian species in a lentic aquatic system using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3097–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handley, L.L.; Read, D.S.; Winfield, I.J.; Kimbell, H.; Johnson, H.; Li, J.; Hahn, C.; Blackman, R.; Wilcox, R.; Donnelly, R.; et al. Temporal and spatial variation in distribution of fish environmental DNA in England’s largest lake. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Handley, L.J.L.; Harper, L.R.; Brys, R.; Watson, H.V.; Di Muri, C.; Zhang, X.; Hänfling, B. Limited dispersion and quick degradation of environmental DNA in fish ponds inferred by metabarcoding. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.S.; Hernandez, C.; Laporte, M.; Côté, G.; Paradis, Y.; Kameni, T.D.W.; Normandeau, E.; Bernatchez, L. Fine-Scale environmental heterogeneity shapes fluvial fish communities as revealed by eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, K.M.; Stat, M.; Harvey, E.S.; Skepper, C.L.; DiBattista, J.D.; Richards, Z.T.; Travers, M.J.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M. eDNA metabarcoding survey reveals fine-scale coral reef community variation across a remote, tropical island ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, L.; Ludwig, A.; Peng, Z. Standards for Methods Utilizing Environmental DNA for Detection of Fish Species. Genes 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babraham Bioinformatics-FastQC a Quality Control Tool for High throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hatton-Ellis, T.W.; Handley, L.J.L.; Kimbell, H.S.; Benucci, M.; Peirson, G.; Hänfling, B. Development of an environmental DNA method for monitoring fish communities: Ground truthing in diverse lakes with characterised fish faunas. bioRxiv 2018. bioRxiv: 394718. [Google Scholar]
- Team R, C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Møller, P.R.; Rasmussen, M.; Willerslev, E. Detection of a Diverse Marine Fish Fauna Using Environmental DNA from Seawater Samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, B.P.; Jerde, C.L.; Renshaw, M.A.; Li, Y.; Evans, N.T.; Turner, C.R.; Deiner, K.; Deiner, A.R.; Brueseke, M.A.; Shirey, P.D.; et al. Estimating species richness using environmental DNA. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 4214–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Sugatani, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Imamura, A. Environmental DNA analysis as a non-invasive quantitative tool for reproductive migration of a threatened endemic fish in rivers. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 11964–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.R.; Griffiths, N.P.; Handley, L.L.; Sayer, C.D.; Read, D.S.; Harper, K.J.; Blackman, R.C.; Li, J.; Hänfling, B. Development and application of environmental DNA surveillance for the threatened crucian carp (Carassius carassius). Freshw. Biol. 2018, 64, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, Y.; Kume, G.; Gotou, M.; Kono, T.; Fujii, T.; Inui, R.; Kurita, Y. Using environmental DNA analyses to assess the occurrence and abundance of the endangered amphidromous fish Plecoglossus altivelis ryukyuensis. Biodivers. Data J. 2020, 8, e39679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, A.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C.; Civade, R.; Herder, J.; Thomsen, P.F.; Bellemain, E.; Besnard, A.; Coissac, E.; Boyer, F.; et al. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushio, M.; Murakami, H.; Masuda, R.; Sado, T.; Miya, M.; Sakurai, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T.; Kondoh, M. Quantitative monitoring of multispecies fish environmental DNA using high-throughput sequencing. bioRxiv 2017. bioRxiv: 113472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.P.; Port, J.A.; Yamahara, K.M.; Crowder, L.B. Using Environmental DNA to Census Marine Fishes in a Large Mesocosm. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Møller, P.R.; Sigsgaard, E.E.; Knudsen, S.; Jorgensen, O.A.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA from Seawater Samples Correlate with Trawl Catches of Subarctic, Deepwater Fishes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Sato, Y.; Sado, T.; Araki, H.; Kondoh, M.; Minamoto, T.; Miya, M. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals local fish communities in a species-rich coastal sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.L.; Clarke, L.J.; Wedderburn, S.D.; Barnes, T.C.; Weyrich, L.S.; Cooper, A. Comparison of environmental DNA metabarcoding and conventional fish survey methods in a river system. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 197, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmiller, J.J.; Bajer, P.G.; Sorensen, P.W. The Relationship between the Distribution of Common Carp and Their Environmental DNA in a Small Lake. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, S.F.; Wilcox, T.M.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Schwartz, M.K.; Lowe, W.H.; Letcher, B.H.; Whiteley, A.R. Distance, flow and PCR inhibition: eDNA dynamics in two headwater streams. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Yoon, S.; Kasai, A.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakata, M.K.; Horiuchi, T.; Sawada, H.; Kondoh, M.; Yamashita, Y.; et al. Dispersion and degradation of environmental DNA from caged fish in a marine environment. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.R.; Uy, K.L.; Everhart, R.C. Fish environmental DNA is more concentrated in aquatic sediments than surface water. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.T.; Li, Y.; Renshaw, M.A.; Olds, B.P.; Deiner, K.; Turner, C.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Lodge, D.M.; Lamberti, G.A.; Pfrender, M.E. Fish community assessment with eDNA metabarcoding: Effects of sampling design and bioinformatic filtering. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Murakami, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Minamoto, T. Effect of water temperature and fish biomass on environmental DNA shedding, degradation, and size distribution. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, R.; Klymus, K.; Richter, C.; Guan, X.; Farrington, H.; Carr, M.; Thompson, N.; Chapman, D.; Baerwaldt, K. Experimental observations on the decay of environmental DNA from bighead and silver carps. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2017, 8, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.; Pilgrim, E.; Knapp, M.; Yoder, C.; Domingo, J.S.; Banerji, A. High-Throughput environmental DNA analysis informs a biological assessment of an urban stream. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Order | Family | Genus | Species | July 2019 | November 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cypriniformes | Cobitidae | + | |||
| Cyprinidae | Carassius | + | + | ||
| Ctenopharyngodon | C. idella | + | + | ||
| Cyprinus | C. carpio | + | |||
| Hypophthalmichthys | H. molitrix | + | + | ||
| H. nobilis | + | + | |||
| Mylopharyngodon | M. piceus | + | |||
| Pseudorasbora | P. parva | + | + | ||
| Rhodeus | R. ocellatus | + | + | ||
| Cyprinodontiformes | Poeciliidae | Gambusia | G. affinis | + | + |
| Perciformes | Cichlidae | Oreochromis | + | + | |
| Gobiidae | Rhinogobius | R. cliffordpopei | + | + | |
| R. giurinus | + | + | |||
| Synbranchiformes | Synbranchidae | Monopterus | M. albus | + | |
| Total a | 12 | 12 |
| Fish | July 2019 | November 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pond A | Pond B | Pond A | Pond B | |||||||||||||||||
| SFA 1 | SFA 2 | SFA 3 | SFA 4 | SFA 5 | SFA 6 | SFB 1 | SFB2 | SFB3 | SFB4 | AFA1 | AFA2 | AFA3 | AFA4 | AFA5 | AFA6 | AFB1 | AFB2 | AFB3 | AFB4 | |
| Carassius | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Cobitidae | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| Ctenopharyngodon idella | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| Cyprinus carpio | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| Gambusia affinis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Monopterus albus | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mylopharyngodon piceus | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| Oreochromis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| Pseudorasbora parva | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Rhinogobius cliffordpopei | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| Rhinogobius giurinus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| Rhodeus ocellatus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| Factor | RDA1 | RDA2 | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | −0.3657 | 0.8777 | 0.2025 | 0.001 |
| pH | −0.6234 | 0.6359 | 0.1997 | 0.001 |
| DO | 0.2375 | 0.6172 | 0.0959 | 0.018 |
| TN | −0.9626 | 0.0230 | 0.2850 | 0.001 |
| NO3−N | −0.2380 | −0.9185 | 0.1967 | 0.546 |
| TP | −0.8497 | −0.4226 | 0.2548 | 0.784 |
| NH4−N | −0.4696 | −0.7937 | 0.2022 | 0.496 |
| COD | −0.5728 | 0.1397 | 0.0792 | 0.764 |
| PO4−P | −0.9107 | −0.3872 | 0.2860 | 0.644 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, L.; Chen, S.; Li, P.; Peng, Z. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding Reflects Fish DNA Dynamics in Lentic Ecosystems: A Case Study of Freshwater Ponds. Fishes 2022, 7, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050257
Shu L, Chen S, Li P, Peng Z. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding Reflects Fish DNA Dynamics in Lentic Ecosystems: A Case Study of Freshwater Ponds. Fishes. 2022; 7(5):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050257
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Lu, Shijing Chen, Ping Li, and Zuogang Peng. 2022. "Environmental DNA Metabarcoding Reflects Fish DNA Dynamics in Lentic Ecosystems: A Case Study of Freshwater Ponds" Fishes 7, no. 5: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050257
APA StyleShu, L., Chen, S., Li, P., & Peng, Z. (2022). Environmental DNA Metabarcoding Reflects Fish DNA Dynamics in Lentic Ecosystems: A Case Study of Freshwater Ponds. Fishes, 7(5), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050257






