Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential of Fish and Marine Invertebrates: Cross-Generational Impact of Environmental Experiences
Abstract
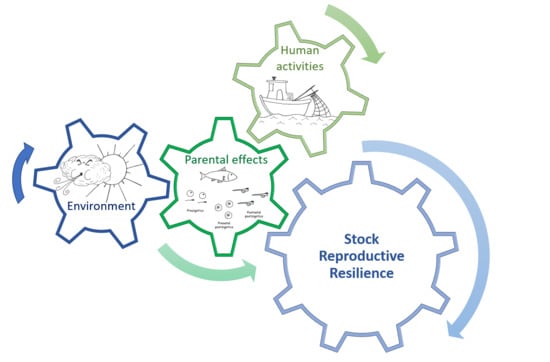
1. Introduction
2. Parental Effects and Population Dynamics
3. Influence of Life Strategies on Parental Effects
4. Temporal and Geographic Variability of Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential
5. Human-Induced Variability of Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential
6. Studies on Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential: Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Venturelli, P.A.; Shuter, B.J.; Murphy, C.A. Evidence for harvest-induced maternal influences on the reproductive rates of fish populations. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2008, 276, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trippel, E.A. Estimation of Stock Reproductive Potential: History and Challenges for Canadian Atlantic Gadoid Stock Assessments. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 1999, 25, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjesbu, O.S.; Murua, H.; Saborido-Rey, F.; Witthames, P.R. Method development and evaluation of stock reproductive potential of marine fish. Fish. Res. 2010, 104, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bernardo, J. Maternal Effects in Animal Ecology. Am. Zool. 1996, 36, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznick, D.; Callahan, H.; Llauredo, R. Maternal Effects on Offspring Quality in Poeciliid Fishes. Am. Zool. 1996, 36, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Siebenthal, B.A.; Jacob, A.; Wedekind, C. Tolerance of whitefish embryos to Pseudomonas fluorescens linked to genetic and maternal effects, and reduced by previous exposure. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shama, L.N.S.; Strobel, A.; Mark, F.C.; Wegner, K.M. Transgenerational plasticity in marine sticklebacks: Maternal effects mediate impacts of a warming ocean. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, G.J.; Dietrich, M.; Kowalski, R.; Dobosz, S.; Karol, H.; Demianowicz, W.; Glogowski, J. Exposure of rainbow trout milt to mercury and cadmium alters sperm motility parameters and reproductive success. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, A.M. Selective Fishing Pressure on Large Male Blue Crabs Negatively Affect Small Size, Sex Ratio, and Population Reproductive Potential in the Upper Chesapeake Bay. Master’s Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rideout, R.M.; Trippel, E.A.; Litvak, M.K. Paternal effects on haddock early life history traits. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.R.; Bell, A.M. Paternal programming in sticklebacks. Anim. Behav. 2014, 95, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beirão, J.; Soares, F.; Herráez, M.; Dinis, M.; Cabrita, E. Changes in Solea senegalensis sperm quality throughout the year. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 126, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, E.-L.; Kvarnemo, C.; Dekhla, I.; Schöld, S.; Andersson, M.H.; Svensson, O.; Amorim, M.C.P. Continuous but not intermittent noise has a negative impact on mating success in a marine fish with paternal care. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Galindo, L.; Galindo-Sánchez, C.; Olivares, A.; Avila-Poveda, O.H.; Díaz, F.; Juárez, O.E.; Lafarga, F.; Pantoja-Pérez, J.; Caamal-Monsreal, C.; Rosas, C. Reproductive performance of Octopus maya males conditioned by thermal stress. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 96, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macartney, E.L.; Crean, A.J.; Bonduriansky, R. Epigenetic paternal effects as costly, condition-dependent traits. Heredity 2018, 121, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Linhart, O.; Krejszeff, S.; Żarski, D.; Pitcher, T.E.; Politis, S.N.; Butts, I.A.E. Paternal identity impacts embryonic development for two species of freshwater fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 245, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lymbery, R.A.; Berson, J.D.; Evans, J.P. Indirect parental effects on offspring viability by egg-derived fluids in an external fertilizer. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2020, 287, 20202538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, J.L.; Foran, C.M. Direct evidence for embryonic uptake of paternally-derived nutrients in two pipefishes (Syngnathidae: Syngnathus spp.). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2008, 179, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, A.S.; Monro, K.; Marshall, D. Transgenerational plasticity and environmental stress: Do paternal effects act as a conduit or a buffer? Funct. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.; Adams, D. Maternal offloading of organochlorine contaminants in the yolk-sac placental scalloped hammerhead shark (Sphyrna lewini). Ecotoxicology 2014, 24, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G. Spawning-site choice by female Pseudolabrus celidotus (Pisces: Labridae) and its influence on the mating system. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1981, 8, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillotson, M.D.; Barnett, H.K.; Bhuthimethee, M.; Koehler, M.E.; Quinn, T.P. Artificial selection on reproductive timing in hatchery salmon drives a phenological shift and potential maladaptation to climate change. Evol. Appl. 2018, 12, 1344–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marteinsdottir, G.; Begg, G.A. Essential relationships incorporating the influence of age, size and condition on variables required for estimation of reproductive potential in Atlantic cod Gadus morhua. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 235, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, R.L.; Downing, P.A.; Griffin, A.S.; Green, J.P. The costs and benefits of paternal care in fish: A meta-analysis. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, F.M.; Clemmesen, C.; Wegner, K.M. Within- and transgenerational effects of ocean acidification on life history of marine three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasperse, L.; Levin, M.; Rogers, K.; Perkins, C.; Bosker, T.; Griffitt, R.J.; Sepúlveda, M.S.; De Guise, S. Transgenerational effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure on sheepshead minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus ). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 38, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Räsänen, K.; Kruuk, L.E.B. Maternal effects and evolution at ecological time-scales. Funct. Ecol. 2007, 21, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, W.R.; Tinghitella, R.M. Predator-induced maternal and paternal effects independently alter sexual selection. Evolution 2019, 74, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.; Allen, R.M.; Marshall, D.J. Adaptive maternal and paternal effects: Gamete plasticity in response to parental stress. Funct. Ecol. 2013, 28, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousseau, T. The adaptive significance of maternal effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curley, J.P.; Mashoodh, R.; Champagne, F.A. Epigenetics and the origins of paternal effects. Horm. Behav. 2011, 59, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, O.J. Daddy Issues: Paternal Effects on Phenotype. Cell 2012, 151, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crean, A.J.; Bonduriansky, R. What is a paternal effect? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, I.A.; Reglero, P.; Álvarez, I. Research on early life stages of fish: A lively field. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 650, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.C.; Trippel, E.A. Early Life History and Recruitment in Fish Populations; Chapman & Hall/CRC: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Green, B.S. Chapter 1: Maternal Effects in Fish Populations. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2008, 54, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, M.I. Mothers Matter: Crowding Leads to Stressed Mothers and Smaller Offspring in Marine Fish. Ecology 2006, 87, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggett, W.; Deblois, E. Recruitment in marine fishes: Is it regulated by starvation and predation in the egg and larval stages? Neth. J. Sea Res. 1994, 32, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andree, S.R.; Feiner, Z.S.; Bledsoe, J.W.; Cragun, A.M.; Höök, T.O. Ontogenetic variability of maternal effects in an iteroparous fish. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2014, 24, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, W. Size, Function, and Life History; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Valentinsson, D. Reproductive cycle and maternal effects on offspring size and number in the neogastropod Buccinum undatum (L.). Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlesinger, T.; Loya, Y. Depth-dependent parental effects create invisible barriers to coral dispersal. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, R.W. Effects of Female Age and Egg Size on Growth and Mortality in Rainbow Trout. Progress. Fish-Culturist 1979, 41, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, J.H.S.; Hempel, G. The Influence of Egg Size on Herring Larvae (Clupea harengus L.). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1963, 28, 211–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marteinsdottir, G.; Steinarsson, A. Maternal influence on the size and viability of Iceland cod Gadus morhua eggs and larvae. J. Fish Biol. 1998, 52, 1241–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, S.P.; Sponaugle, S. Selective Mortality during the Larval-Juvenile Transition in Two Coral Reef Fishes. Ecology 2001, 82, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjesbu, O.; Solemdal, P.; Bratland, P.; Fonn, M. Variation in annual egg production in individual captive Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Kjesbu, O.S.; Jørgensen, T. Effects of ration on the maturation and fecundity in captive Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjesbu, O.; Witthames, P.; Solemdal, P.; Walker, M.G. Temporal variations in the fecundity of Arcto-Norwegian cod (Gadus morhua) in response to natural changes in food and temperature. J. Sea Res. 1998, 40, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideout, R.M.; Rose, G.A.; Burton, M.P.M. Skipped spawning in female iteroparous fishes. Fish Fish. 2005, 6, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solemdal, P.; Kjesbu, O.S.; Fonn, M. Egg Mortality in Recruit- and Repeat-Spawning Cod—An Experimental Study. In ICES CM 1995/G35; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1995; 10p, Available online: https://imr.brage.unit.no/imr-xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/100329/G35_1995.pdf?sequence=4&isAllowed=y (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Wright, P.J.; Trippel, E.A. Fishery-induced demographic changes in the timing of spawning: Consequences for reproductive success. Fish Fish. 2009, 10, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowerre-Barbieri, S.K.; Ganias, K.; Saborido-Rey, F.; Murua, H.; Hunter, J.R. Reproductive Timing in Marine Fishes: Variability, Temporal Scales, and Methods. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2011, 3, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, G.; Myers, R.A. Match/mismatch predictions of spawning duration versus recruitment variability. Fish. Oceanogr. 1994, 3, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, P.; Richardson, A.; Wilson, G.; Ellison, T. River regulation and recruitment in a protracted-spawning riverine fish. Ecol. Appl. 2013, 23, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkevold, D. Male size composition affects male reproductive variance in Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. spawning aggregations. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trippel, E.; Kraus, G.; Köster, F. Maternal and paternal influences on early life history traits and processes of Baltic cod Gadus morhua. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 303, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.S.; McCormick, M. Maternal and paternal effects determine size, growth and performance in larvae of a tropical reef fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 289, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, S.; Mizuno, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Kurokura, H. Rearing Takifugu rubripes larvae in communal tanks: Paternal genetic contribution to survivability. Fish. Sci. 2014, 80, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crean, A.J.; Dwyer, J.M.; Marshall, D.J. Adaptive paternal effects? Experimental evidence that the paternal environment affects offspring performance. Ecology 2013, 94, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, H.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Gibson, M.C.; Tarrant, A.M. Plasticity in parental effects confers rapid larval thermal tolerance in the estuarine anemone Nematostella vectensis. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb236745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.; Lenz, T.; Milinski, M.; Eizaguirre, C. Experimental parasite infection reveals costs and benefits of paternal effects. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz-Ocaňa, S.; Schütz, D.; Pachler, G.; Taborsky, M. Paternal inheritance of growth in fish pursuing alternative reproductive tactics. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznick, D. Grandfather Effects: The Genetics of Interpopulation Differences in Offspring Size in the Mosquito Fish. Evolution 1981, 35, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, G.J.; Pájaro, M.; Madirolas, A. Can a change in the spawning pattern of Argentine hake (Merluccius hubbsi) affect its recruitment? Fish. Bull. 2005, 103, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Lowerre-Barbieri, S.K.; Henderson, N.; Llopiz, J.; Walters, S.; Bickford, J.; Muller, R. Defining a spawning population (spotted seatrout Cynoscion nebulosus) over temporal, spatial, and demographic scales. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 394, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchfield, P.J.; Ridgway, M.S. The relative influence of breeding competition and habitat quality on female reproductive success in lacustrine brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 2694–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Colombo, G.; Dato, C.; Macchi, G.; Palma, E.; Machinandiarena, L.; Christiansen, H.; Betti, P.; Derisio, C.; Martos, P.; Castro-Machado, F.; et al. Distribution and behavior of Argentine hake larvae: Evidence of a biophysical mechanism for self-recruitment in northern Patagonian shelf waters. Cienc. Mar. 2011, 37, 633–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marteinsdottir, G.; Gudmundsdottir, A.; Thorsteinsson, V.; Stefansson, G. Spatial variation in abundance, size composition and viable egg production of spawning cod (Gadus morhua L.) in Icelandic waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitgas, P.; Reid, D.; Planque, B.; Nogueira, E.; O’Hea, B.; Cotano, U. The Entrainment Hypothesis: An Explanation for the Persistence and Innovation in Spawning Migrations and Life Cycle Spatial Patterns. In ICES CM2006/B:07; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006; 9p, Available online: https://www.ices.dk/sites/pub/CM%20Doccuments/2006/B/B0706.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Lambert, T.C. The effect of population structure on recruitment in herring. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1990, 47, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.L.; Sass, G.G.; Vandehey, J.A. Maternal effects better predict walleye recruitment in Escanaba Lake, Wisconsin, 1957–2015: Implications for regulations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 75, 2320–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloor, I.S.; Attrill, M.J.; Jackson, E.L. A Review of the Factors Influencing Spawning, Early Life Stage Survival and Recruitment Variability in the Common Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). Adv. Mar. Biol. 2013, 65, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.J. Transgenerational plasticity in the sea: Context-dependent maternal effects across the life history. Ecology 2008, 89, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwindt, A.R.; Winkelman, D.L.; Keteles, K.; Murphy, M.; Vajda, A.M. An environmental oestrogen disrupts fish population dynamics through direct and transgenerational effects on survival and fecundity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Po, B.H.; Chiu, J.M. Transgenerational impairments of reproduction and development of the marine invertebrate Crepidula onyx resulted from long-term dietary exposure of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, A.J.; Vásquez, G.; Brumbach, B.H.; Schneider, S.M.; Sefcek, J.A.; Tal, I.R.; Hill, D.; Wenner, C.J.; Jacobs, W.J. Consilience and Life History Theory: From genes to brain to reproductive strategy. Dev. Rev. 2006, 26, 243–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianka, E.R. On r- and K-Selection. Am. Nat. 1970, 104, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, C.M.S.; Gordon, E.; Hale, R.E. Environmental effects on egg development and hatching success in Jordanella floridae, a species with parental care. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGhee, K.E.; Bell, A.M.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Dombeck, E.; Gerber, J.; Knuth, K.A.; Mueller, N.D.; Mueller, M.; Ziv, G.; Klein, A.-M. Paternal care in a fish: Epigenetics and fitness enhancing effects on offspring anxiety. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, R.S.; Somarakis, S.; Fitzhugh, G.R.; Albert, A.; Yaragina, N.A.; Wuenschel, M.J.; Alonso-Fernández, A.; Basilone, G. Energy acquisition and allocation to egg production in relation to fish reproductive strategies. Fish Fish. 2013, 16, 23–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, A.; Shackelford, T.K. Polygynandry. In Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior; Vonk, J., Shackelford, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cam, S.; Pechenik, J.A.; Cagnon, M.; Viard, F. Fast versus Slow Larval Growth in an Invasive Marine Mollusc: Does Paternity Matter? J. Hered. 2009, 100, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, L.; Marshall, D.J. Do Genetic Diversity Effects Drive the Benefits Associated with Multiple Mating? A Test in a Marine Invertebrate. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasker, R. The role of a stable ocean in larval fish survival and subsequent recruitment. In Marine Fish Larvae: Morphology, Ecology and Relation to Fisheries; Lasker, R., Ed.; Washington Sea Grant Program: Seattle, WA, USA, 1981; pp. 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cury, P.; Roy, C. Optimal Environmental Window and Pelagic Fish Recruitment Success in Upwelling Areas. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, G.; Wootton, R. Fish Reproduction: Strategies and Tactics, 3rd ed.; Academic Press Limited: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, R.J. Marine fish production trends off the Pacific coast of Canada and the United States. In Climate Change and Northern Fish Populations; Beamish, R.J., Ed.; Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences; NRC Research Press: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1995; Volume 121, pp. 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Dygert, P.H. Seasonal Changes in Energy Content and Proximate Composition Associated with Somatic Growth and Reproduction in a Representative Age-Class of Female English Sole. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1990, 119, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.; Magalhães, A.; Miller, E. Important prey species of marine vertebrate predators in the northwest Atlantic:proximate composition and energy density. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 164, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, B.; Kooijman, S.A.L.M. Dynamic Energy Budget Theory, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, Y.; Dutil, J.-D. Energetic consequences of reproduction in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) in relation to spawning level of somatic energy reserves. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J.; Shulman, G.; Love, R.M. Condition and Health Indicators of Exploited Marine Fishes; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Trippel, E.A. Estimation of male reproductive success of marine fishes. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 2003, 33, 81–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, G.M.; Tilseth, S. Growth, Development, and Feeding Success of Atlantic Cod Larvae Gadus morhua Related to Egg Size. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1985, 114, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Petit, R. Study of Reproductive Potencial of Merluccius Merluccius in the Galician Shelf. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Vigo, Vigo, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, C.G.; Domínguez-Petit, R.; Aldanondo, N.; Saborido-Rey, F. Seasonal variability of maternal effects in European hake Merluccius merluccius. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 650, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, J.; Hunter, J. The Biology of the Clupeoid Fishes. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1982, 20, 1–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.A.; Cowan, J.H.; Winemiller, K.; Myers, R.A.; Hilborn, R. Compensatory density dependence in fish populations: Importance, controversy, understanding and prognosis. Fish Fish. 2001, 2, 293–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samhouri, J.F. Food supply influences offspring provisioning but not density-dependent fecundity in a marine fish. Ecology 2009, 90, 3478–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, J.T. The ecology of fertilization of echinoid eggs: The consequences of sperm dilution, adult aggregation, and synchronous spawning. Biol. Bull. 1985, 169, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, D.R. Predicting Optimal and Unique Egg Sizes in Free-Spawning Marine Invertebrates. Am. Nat. 1996, 148, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marilú, B.C.; Julio, M.P.; Cecilia, P.T.; Pepe, E.; Larry, H.; Betsy, B.D.; Ángel, P.d.; Carlos, G.V.; Monique, M. Biología de la anchoveta peruana, Engraulis ringens Jenyns. Boletín del Inst. del Mar del Perú 2010, 25, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pájaro, M.; Leonarduzzi, E.; Hansen, J.; Macchi, G. Analysis of the reproductive potential of two stocks of Engraulis anchoita in the Argentine Sea. Cienc. Mar. 2011, 37, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Norbis, W.; Vizziano, D. Efectos de los cambios ambientales en la estrategia reproductiva de la lacha (Brevoortia aurea) en una laguna costera de Uruguay. In IV Simposio Iberoamericano de Ecología Reproductiva, Reclutamiento y Pesquerías; Iquique, Chile, 2018; p. 76. Available online: http://docplayer.es/122775306-Libro-de-resumenes-sibecorp-iv-iquique-chile.html (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Olney, J.E.; McBride, R.S. Intraspecific variation in batch fecundity of American shad: Revisiting the paradigm of reciprocal latitudinal trends in reproductive traits. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 2003, 2003, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, D. Temperature and Organism Size—A Biological Law for Ectotherms? Adv. Ecol. Res. 1994, 25, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, F.; Martínez, P.A.; Olalla-Tárraga, M. Shallow water ray-finned marine fishes follow Bergmann’s rule. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2018, 33, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokita, T. Latitudinal compensation in female reproductive rate of a geographically widespread reef fish. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 71, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billerbeck, J.M.; Schultz, E.T.; Conover, D.O. Adaptive variation in energy acquisition and allocation among latitudinal populations of the Atlantic silverside. Oecologia 2000, 122, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wear, R.G. Incubation in British Decapod Crustacea, and the Effects of Temperature on the Rate and Success of Embryonic Development. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 1974, 54, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H. Climate variations and the physiological basis of temperature dependent biogeography: Systemic to molecular hierarchy of thermal tolerance in animals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2002, 132, 739–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brante, A.; Fernández, M.; Eckerle, L.; Mark, F.; Pörtner, H.; Arntz, W. Reproductive investment in the crab Cancer setosus along a latitudinal cline: Egg production, embryo losses and embryo ventilation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 251, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rätz, H.-J.; Lloret, J. Variation in fish condition between Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) stocks, the effect on their productivity and management implications. Fish. Res. 2003, 60, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M.; Massutí, E.; Moranta, J.; Cartes, J.; Lloret, J.; Oliver, P.; Morales-Nin, B. Seasonal and short spatial patterns in European hake (Merluccius merluccius L.) recruitment process at the Balearic Islands (western Mediterranean): The role of environment on distribution and condition. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 71, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoatey, P.; Baawain, M.S. Effects of pollution on freshwater aquatic organisms. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1272–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mearns, A.J.; Reish, D.J.; Oshida, P.S.; Morrison, A.M.; Rempel-Hester, M.A.; Arthur, C.; Rutherford, N.; Pryor, R. Effects of Pollution on Marine Organisms. Water Environ. Res. 2016, 88, 1693–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arukwe, A. Cellular and Molecular Responses to Endocrine-Modulators and the Impact on Fish Reproduction. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, P. Endocrine disruption in marine fish. Pure Appl. Chem. 2003, 75, 2249–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, C.J.; Feiner, Z.S.; Malinich, T.D.; Höök, T.O. A meta-analysis of the effects of exposure to microplastics on fish and aquatic invertebrates. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 631–632, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimska, A.; Konieczka, P.; Skóra, K.; Namieśnik, J. Accumulation of Metals in Tissues and Organs of Marine Organisms The Effect of Metals on Marine Organisms. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.C.; Reynolds, J.D. Effects of pollution on reproductive behaviour of fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1997, 7, 463–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-H.; Liu, Y.; Zeb, R.; Chen, F.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wang, K.-J. The intergenerational toxic effects on offspring of medaka fish Oryzias melastigma from parental benzo[a]pyrene exposure via interference of the circadian rhythm. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, K.A.; Macchi, G.J.; Militelli, M.I. Comparative study of spawning pattern and reproductive potential of the Northern and Southern stocks of Argentine hake (Merluccius hubbsi). J. Sea Res. 2015, 102, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firpo, C.; Wyngaard, J.; Mango, C.M.V. Análisis Preliminar de la Temporada de Pesca de Centolla (Lithodes santolla), 2015–2016; Informe Técnico Oficial; Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo Pesquero: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2016; p. 12. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308173455_Analisis_preliminar_de_la_temporada_de_pesca_de_centolla_patagonica_Lithodes_santolla_2015-16 (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Militelli, M.I.; Firpo, C.; Rodrigues, K.A.; Macchi, G.J. Egg production and validation of clutch fullness indices scale of southern king crab, Lithodes santolla, in the Central Patagonian Sector, Argentina (44°–48° S). Fish. Res. 2018, 211, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Salvatore, P.; Gowland-Sainz, M.; Florentin, O.; Lovrich, G.A. Effects of fishery practices on fecundity of two lithodid crab species of commercial interest in Southern South America. Fish. Res. 2018, 211, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckmann, U.; Heino, M. Probabilistic maturation reaction norms: Their history, strengths, and limitations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 335, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, A.M.; Boukal, D.S.; Persson, L. Evolutionary regime shifts in age and size at maturation of exploited fish stocks. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2006, 273, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.; Colbourne, E. Variation in maturity-at-age and size in three populations of American plaice. ICES J. Mar. 1999, 56, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J.; Muñoz, M.; Casadevall, M. Threats posed by artisanal fisheries to the reproduction of coastal fish species in a Mediterranean marine protected area. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musick, J.A.; Burgess, G.; Cailliet, G.; Camhi, M.; Fordham, S. Management of Sharks and Their Relatives (Elasmobranchii); Management of Sharks and Their Relatives (Elasmobranchii). Fisheries. 2000, 25, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslow, J.A.; Boehlert, G.W.; Gordon, J.D.M.; Haedrich, R.L.; Lorance, P.; Parin, N. Continental slope and deep-sea fisheries: Implications for a fragile ecosystem. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, A.J.; Kyne, P.; Hammerschlag, N. Ecological risk assessment and its application to elasmobranch conservation and management. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 1727–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeler, E.J.; Murray, A.G. Disease interaction between farmed and wild fish populations. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindar, K.; Ryman, N.; Utter, F. Genetic Effects of Cultured Fish on Natural Fish Populations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 48, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servili, A.; Canario, A.; Mouchel, O.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A. Climate change impacts on fish reproduction are mediated at multiple levels of the brain-pituitary-gonad axis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 291, 113439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveiten, H. Temperature influence on reproductive development and gamete quality in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Cybium 2008, 32 (Suppl. 2), 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahnsteiner, F.; Kletzl, M. The effect of water temperature on gamete maturation and gamete quality in the European grayling (Thymalus thymallus) based on experimental data and on data from wild populations. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 38, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, C. Egg production in an Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus L.) brood stock: Effects of temperature on the timing of spawning and the quality of eggs. Aquat. Living Resour. 1991, 4, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, C.; Breton, B.; Mikolajczyk, T.; Bodinier, P.; Fostier, A. Disruption of the secretion and action of 17,20β-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one in response to a rise in temperature in the Arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus. Consequences on oocyte maturation and ovulation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveiten, H.; Johnsen, H.K. Thermal influences on temporal changes in plasma testosterone and oestradiol-17beta concentrations during gonadal recrudescence in female common wolffish. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Záhorská, E. Climate warming and invasive fish species: Will they replace native fish species in waters of temperate zones? Biologia 2016, 71, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.A.; Westerman, E.L.; Harris, L.G. Elevated seasonal temperatures eliminate thermal barriers of reproduction of a dominant invasive species: A community state change for northern communities? Divers. Distrib. 2017, 23, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiguen, Y.; Fostier, A.; Piferrer, F.; Chang, C.-F. Ovarian aromatase and estrogens: A pivotal role for gonadal sex differentiation and sex change in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, N.W.; Munday, P.L. Effects of climate change on fish reproduction and early life history stages. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, C.M.; Adasme, N.A.; Cubillos, L.; Cuevas, M.J.; Sánchez, N.E. Variaciones en rasgos reproductivos de pequeños pelágicos conducidos por variables ambientales: El caso de E. ringens en Chile. In Actas del IV Simposio Iberoamericano de Ecología Reproductiva, Reclutamiento y Pesquerías; Iquique, Chile, 2018; p. 76. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360702639_Actas_del_IV_Simposio_Iberoamericano_de_Ecologia_Reproductiva_Reclutamiento_y_Pesquerias (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Miranda, L.A.; Chalde, T.; Elisio, M.; Strüssmann, C.A. Effects of global warming on fish reproductive endocrine axis, with special emphasis in pejerrey Odontesthes bonariensis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, A.L.; Low, P.J.; Ellis, J.R.; Reynolds, J.D. Climate Change and Distribution Shifts in Marine Fishes. Science 2005, 308, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudron, A.R.; Brunel, T.; Blanchet, M.; Hidalgo, M.; Chust, G.; Brown, E.J.; Kleisner, K.M.; Millar, C.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Nikolioudakis, N.; et al. Changing fish distributions challenge the effective management of European fisheries. Ecography 2020, 43, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Last, P.R.; White, W.T.; Gledhill, D.C.; Hobday, A.J.; Brown, R.; Edgar, G.J.; Pecl, G. Long-term shifts in abundance and distribution of a temperate fish fauna: A response to climate change and fishing practices. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 20, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, N.; Thomson, J.; Reich, P.; Stein, J. Using species distribution models to infer potential climate change-induced range shifts of freshwater fish in south-eastern Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, L.; Grenouillet, G. Distribution shifts of freshwater fish under a variable climate: Comparing climatic, bioclimatic and biotic velocities. Divers. Distrib. 2015, 21, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingfield, J.C.; Sapolsky, R.M. Reproduction and Resistance to Stress: When and How. J. Neuroendocr. 2003, 15, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trippel, E.A.; Kjesbu, O.S.; Solemdal, P. Effects of Adult Age and Size Structure on Reproductive Output in Marine Fishes. In Early Life History and Recruitment in Fish Populations; Chambers, R.C., Trippel, E.A., Eds.; Chapman & Hall Fish and Fisheries Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; Volume 21, pp. 31–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresino, R.D.H.; Gonçalves, R.J.; Helbling, E.W. Direct and indirect acquisition of photoprotective compounds in crab larvae of coastal Patagonia (Argentina). J. Plankton Res. 2014, 36, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.A.; Leonarduzzi, E.; Macchi, G.J.; Militelli, M.I. Maternal condition, fecundity and oocyte quality of Argentine hake (Merluccius hubbsi) from the Northern stock. Fish. Res. 2018, 197, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Lau, K.; Lai, K.-P.; Zhang, J.; Tse, A.C.-K.; Li, J.-W.; Tong, Y.; Chan, T.; Wong, C.K.-C.; Chiu, J.M.-Y.; et al. Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowerre-Barbieri, S.; DeCelles, G.; Pepin, P.; Catalán, I.; Muhling, B.; Erisman, B.; Cadrin, S.X.; Alós, J.; Ospina-Alvarez, A.; Stachura, M.M.; et al. Reproductive resilience: A paradigm shift in understanding spawner-recruit systems in exploited marine fish. Fish Fish. 2016, 18, 285–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Foo, S.A.; Ross, P.M.; Putnam, H.M. Limitations of cross- and multigenerational plasticity for marine invertebrates faced with global climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 26, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domínguez-Petit, R.; García-Fernández, C.; Leonarduzzi, E.; Rodrigues, K.; Macchi, G.J. Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential of Fish and Marine Invertebrates: Cross-Generational Impact of Environmental Experiences. Fishes 2022, 7, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040188
Domínguez-Petit R, García-Fernández C, Leonarduzzi E, Rodrigues K, Macchi GJ. Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential of Fish and Marine Invertebrates: Cross-Generational Impact of Environmental Experiences. Fishes. 2022; 7(4):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040188
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomínguez-Petit, Rosario, Cristina García-Fernández, Ezequiel Leonarduzzi, Karina Rodrigues, and Gustavo Javier Macchi. 2022. "Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential of Fish and Marine Invertebrates: Cross-Generational Impact of Environmental Experiences" Fishes 7, no. 4: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040188
APA StyleDomínguez-Petit, R., García-Fernández, C., Leonarduzzi, E., Rodrigues, K., & Macchi, G. J. (2022). Parental Effects and Reproductive Potential of Fish and Marine Invertebrates: Cross-Generational Impact of Environmental Experiences. Fishes, 7(4), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040188