Molecular Cloning of Heat Shock Protein 60 (SpHSP60) from Schizothorax prenanti and the Gene Expressions of Four SpHSPs during Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Treatment
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Full-Length cDNA Cloning of the SpHSP60 Gene
2.4. Sequence Analysis
2.5. Tissue Distribution of SpHSP60 mRNA in Unstressed Conditions
2.6. Detection of the Expression Patterns Induced by LPS
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
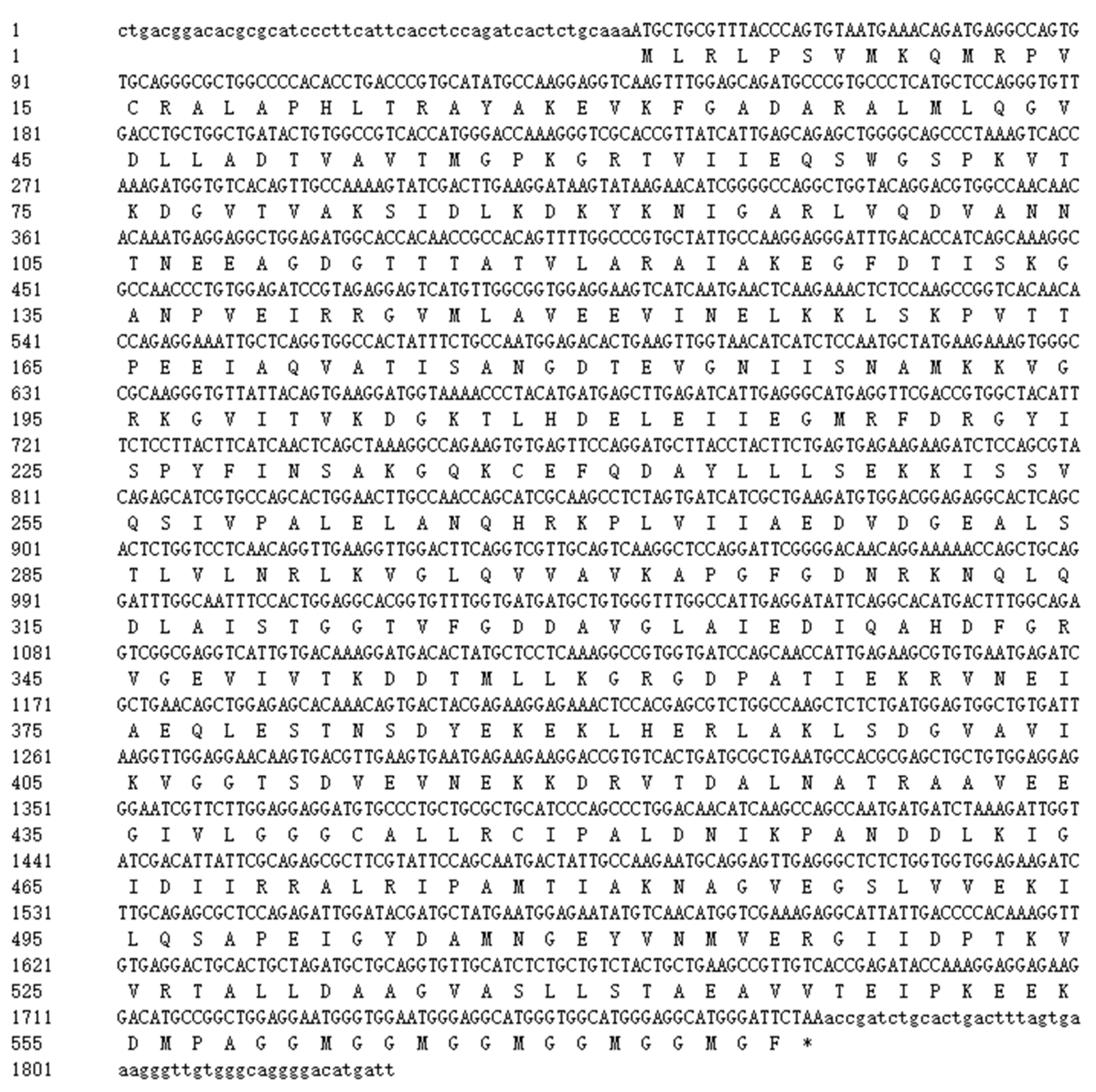
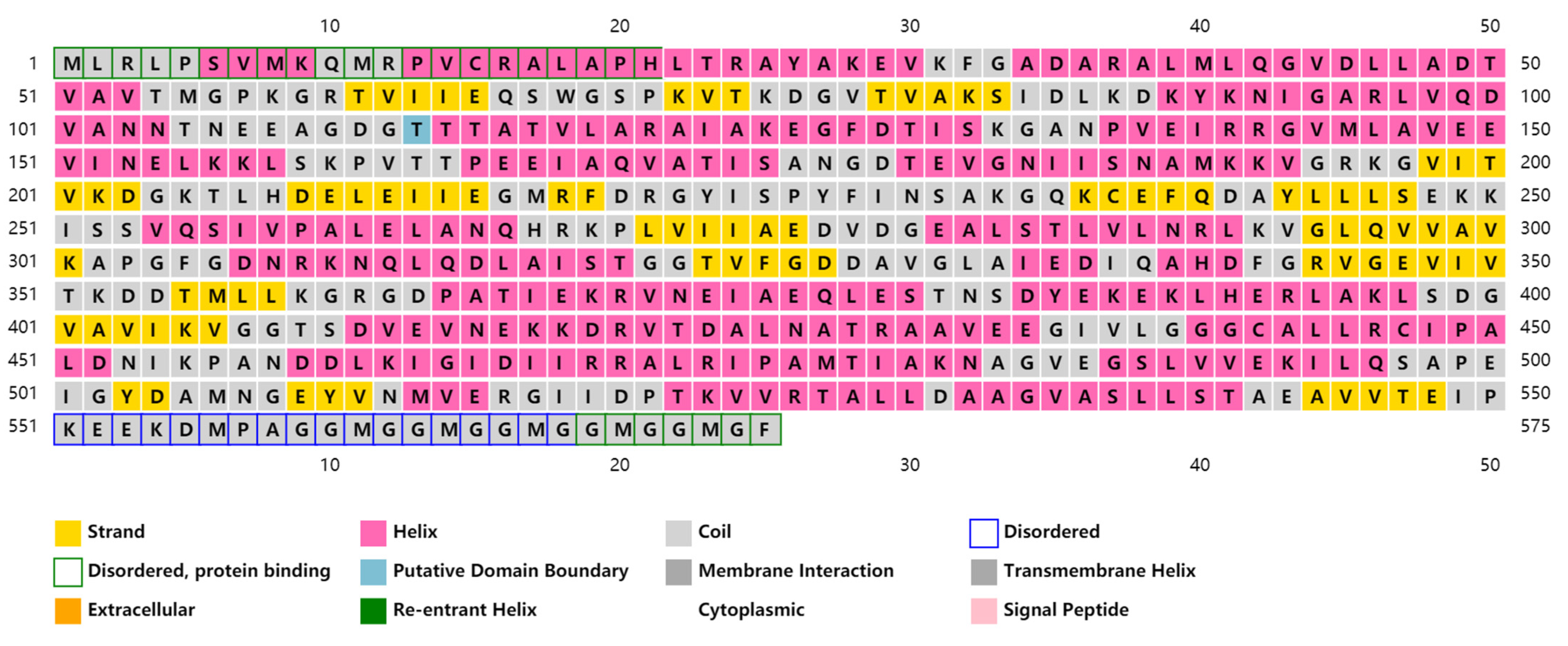
3.1. Characterization of the SpHSP60 Gene cDNA
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
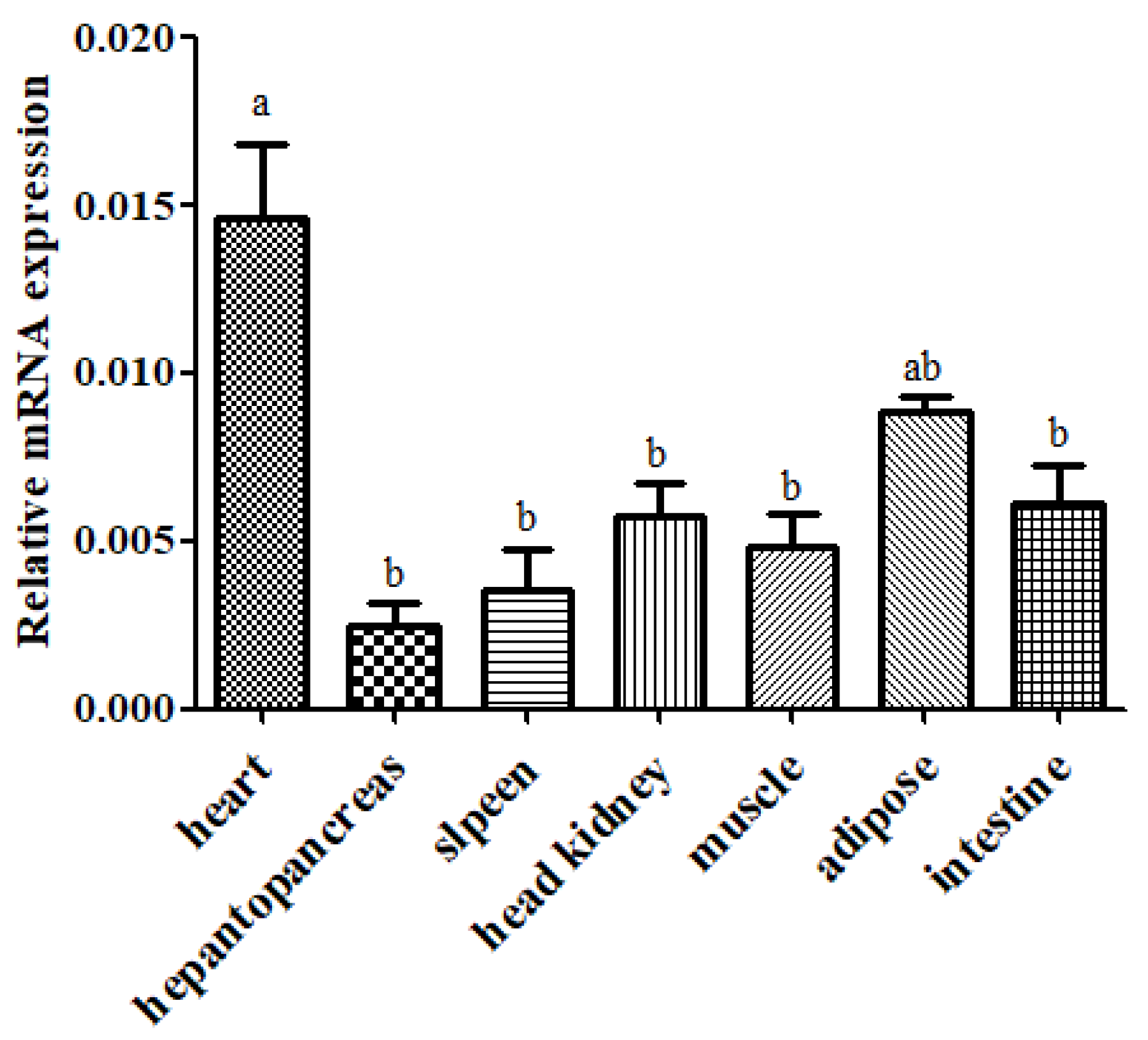
3.3. Tissue Distribution of SpHSP60 Expression in S. prenanti
3.4. Expression Pattern Analysis of SpHSPs following LPS Challenge
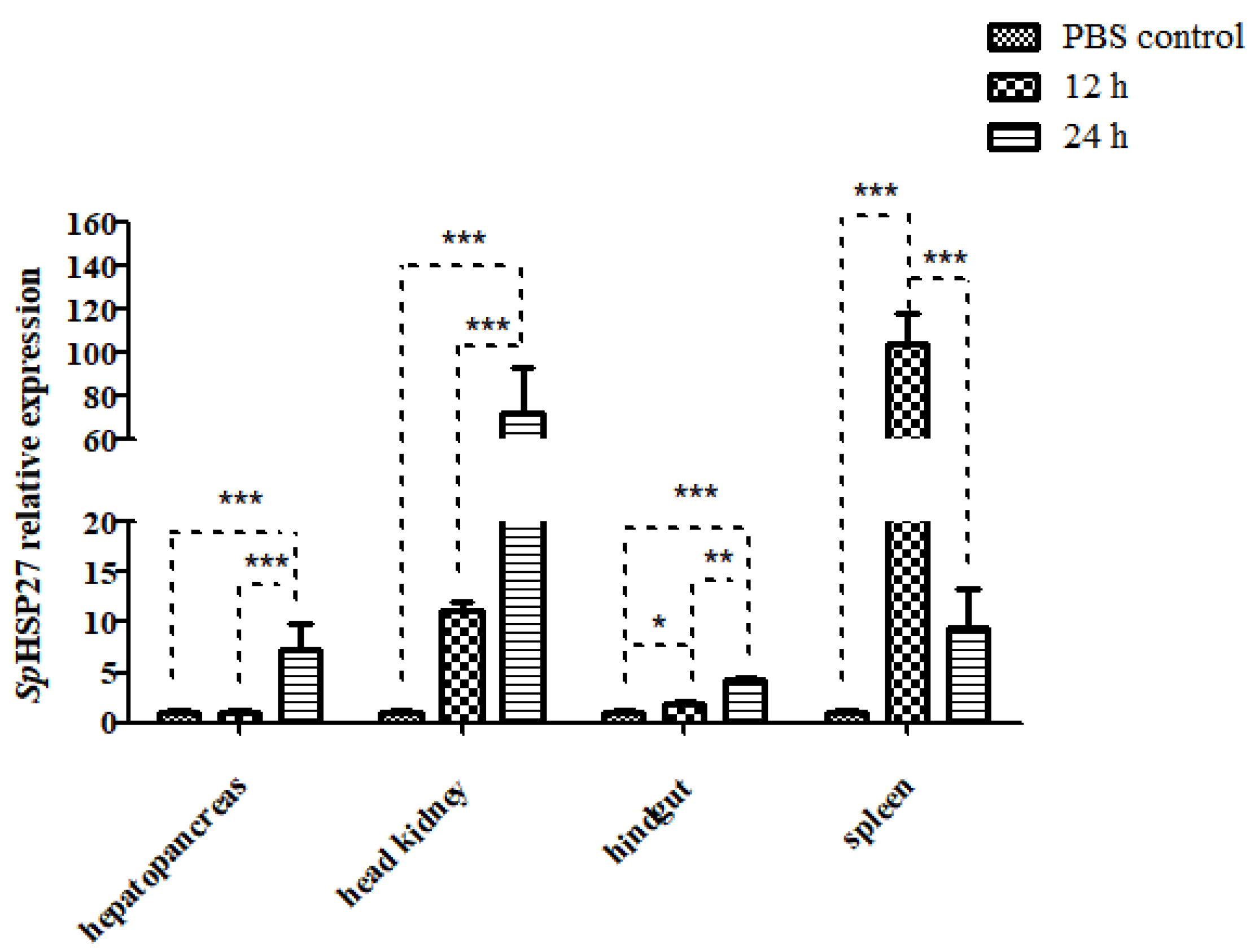
3.4.1. Expression of SpHSP27 after Challenge with LPS
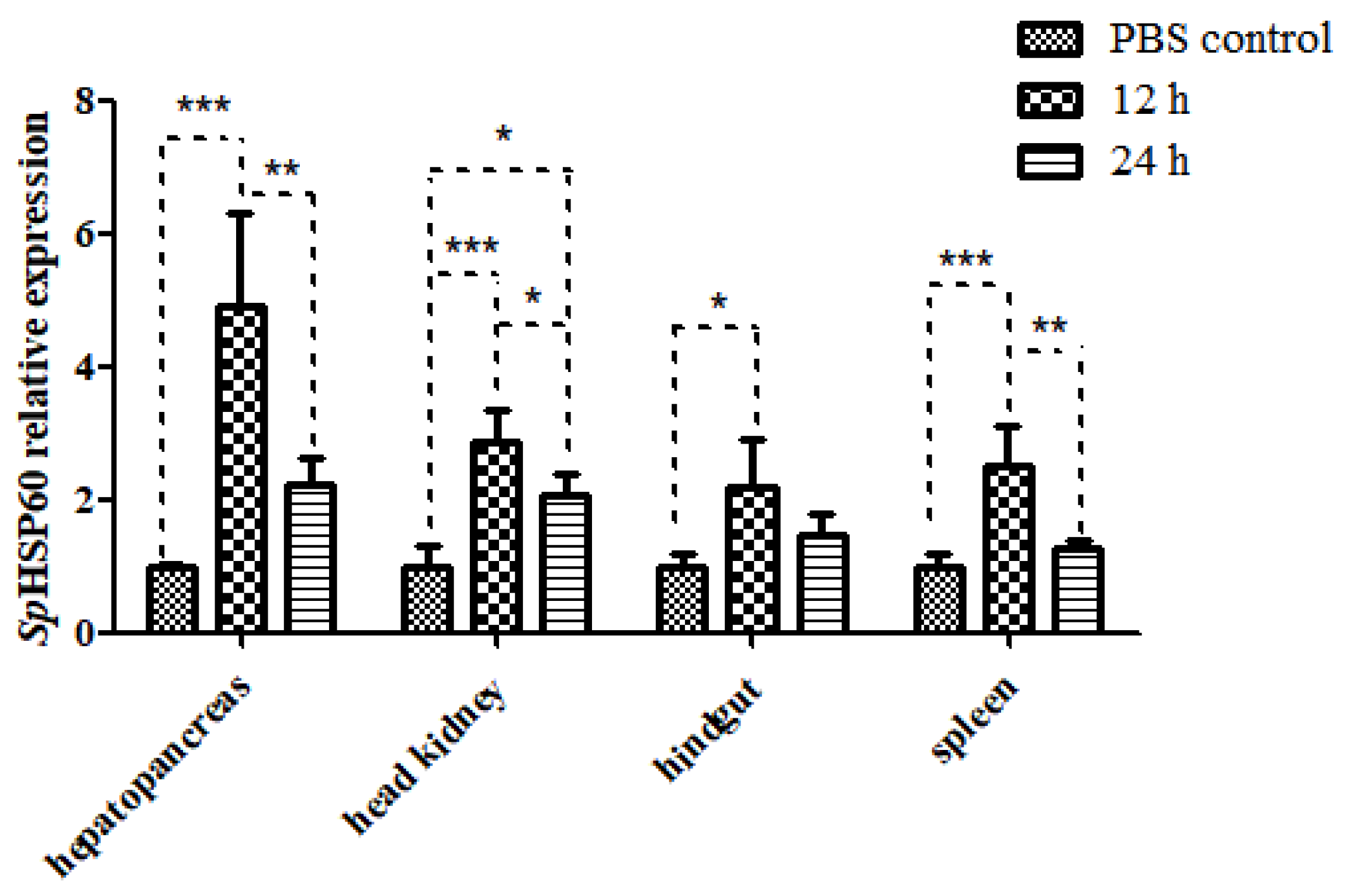
3.4.2. Expression of SpHSP60 after Challenge with LPS
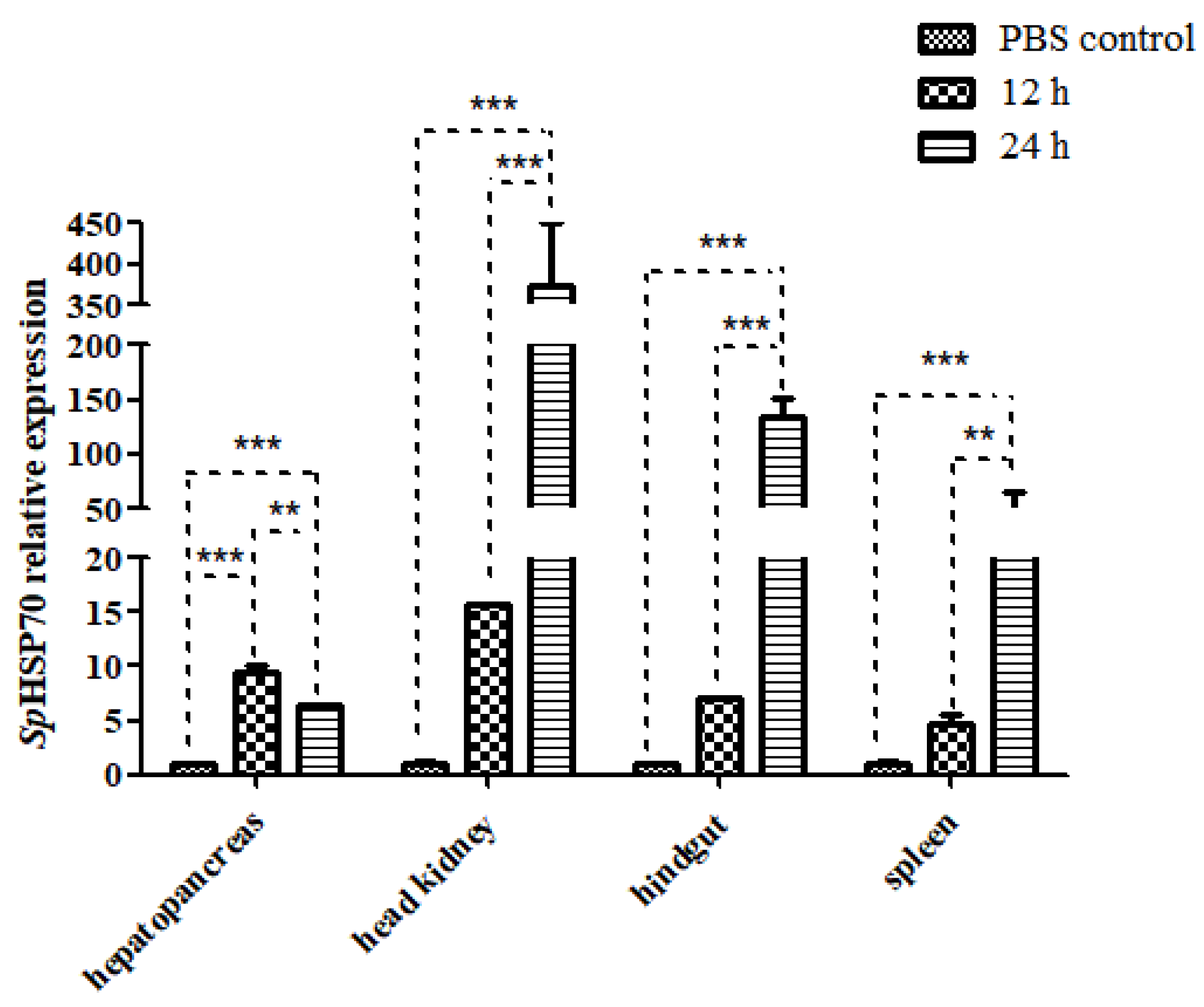
3.4.3. Expression of SpHSP70 after Challenge with LPS
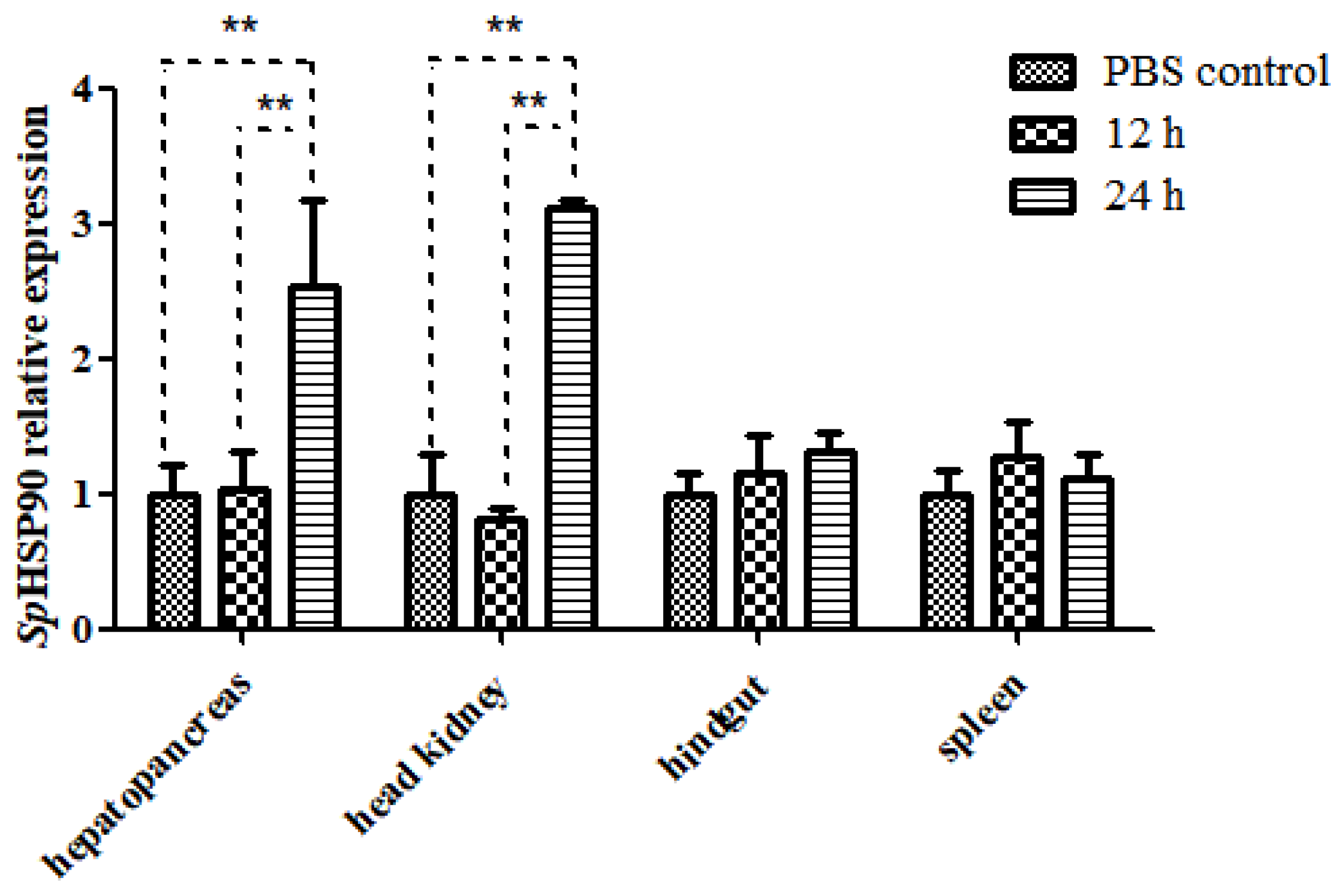
3.4.4. Expression of SpHSP90 after Challenge with LPS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sørensen, J.G.; Kristensen, T.N.; Loeschcke, V. The evolutionary and ecological role of heat shock proteins. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 6, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, R.B.; Candido, E.P.M.; Babich, S.L.; Iwama, G.K. Stress protein expression in coho salmon with bacterial kidney disease. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1997, 9, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cara, J.B.; Aluru, N.; Moyano, F.J.; Vijayan, M.M. Food-deprivation induces HSP70 and HSP90 protein expression in larval gilthead sea bream and rainbow trout. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2005, 142, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, P.A.; Iwama, G.K. Physiological and Cellular Stress Responses of Juvenile Rainbow Trout to Vibriosis. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2001, 13, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermesz, E.; Abrahám, M.; Nemcsók, J. Identification of two hsp90 genes in carp. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2001, 129, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Gao, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, T. A heat shock protein 90β isoform involved in immune response to bacteria challenge and heat shock from Miichthys miiuy. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Shen, Y.; Fu, J.; Liu, F.; Guo, S.; Yang, X.; Li, J. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression patterns of HSP60 in the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.X.; Zhao, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Ma, M.S.; Mao, H.L.; Hu, C.Y. Overexpression of Hsp90 from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) increases thermal protection against heat stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Yan, T.; Song, Z. Molecular cloning and expression of two heat-shock protein genes (HSC70/HSP70) from Prenant’s schizothoracin (Schizothorax prenanti). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Wu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of Hsp90 in Schizothorax prenanti. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2016, 21, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.D.; Yew, F.H.; Li, G.C. Thermal adaptation and heat shock response of tilapia ovary cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 1988, 134, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Song, Z.; Yue, B.; Zheng, W. Assessing genetic diversity of wild populations of Prenant’s schizothoracin, Schizothorax prenanti, using AFLP markers. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2006, 77, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Huang, X.L.; Chen, D.F.; Li, C.W.; Ren, S.Y.; Liao, Y.T.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, Q.F.; Du, Z.J.; et al. Streptococcus agalactiae, an emerging pathogen for cultured Ya-fish, Schizothorax prenanti, in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, Y.; Begum, N.A.; Kobayashi, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Toyoshima, K.; Seya, T. Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin and its cell wall complex induce a novel lysosomal membrane protein, SIMPLE, that bridges the missing link between lipopolysaccharide and p53-inducible gene, LITAF(PIG7), and estrogen-inducible gene, EET-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 23065–23076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform xtraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The Clustal_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids. Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Pellitero, P. Fish immunity and parasite infections: From innate immunity to immunoprophylactic prospects. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 126, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocchieri, L.; Karlin, S. Conservation among HSP60 sequences in relation to structure, function, and evolution. Protein Sci. 2010, 9, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hightower, L.E.; Norris, C.E.; Dilorio, P.J.; Fielding, E. Heat shock responses of closely related species of tropical and desert fish. Am. Zool. 1999, 39, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koll, H.; Guiard, B.; Rassow, J.; Ostermann, J.; Horwich, A.L.; Neupert, W.; Hartl, F.U. Antifolding activity of Hsp60 couples protein import into the mitochondrial matrix with export to the intermembrane space. Cell 1992, 68, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgopoulos, C.; Welch, W.J. Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1993, 9, 601–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeilstra-ryalls, J.; Fayet, O.; Georgopoulos, C. The universally conserved groE (Hsp60) chaperonins. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1991, 45, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Burns, T.F. Targeting Heat Shock Proteins in Cancer: A Promising Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenzi, C.; Palazzuoli, A.; Giordano, N.; Alegente, G.; Gonnelli, C.; Campagna, M.S.; Santucci, A.; Sozzi, M.; Papakostas, P.; Rollo, F.; et al. H pylori infection and systemic antibodies to CagA and heat shock protein 60 in patients with coronary heart disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7815–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, K.N.; Muth, A.; Arnold, J.; King, F.W.; Yeh, R.-F.; Fish, J.E.; Hsiao, E.C.; Schwartz, R.J.; Conklin, B.R.; Bernstein, H.S.; et al. MicroRNA regulation of cell lineages in mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gullo, C.A.; Teoh, G. Heat shock proteins: To present or not, that is the question. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelkebeck, K.W.; Odom, T.W. Laying hen responses to acute heat stress and carbon dioxide supplementation: I. Blood gas changes and plasma lactate accumulation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Comp. Physiol. 1994, 107, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luan, W.; Li, Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, S. Molecular cloning and characterization of a heat shock protein 70 gene in swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohaszka, Z.; Fust, G. Immunological aspects of heat-shock proteins-the optimum stress of life. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Kot, M.; Konturek, S.J.; Pawlik, W.W. Endotoxemia in the infant rats modulates HSP60 protein level in the pancreatic acinar cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, P. Roles of heat-shock proteins in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrao, S.; Campanella, C.; Anzalone, R.; Farina, F.; Zummo, G.; de Macario, E.C.; Macario, A.J.; Cappello, F.; La Rocca, G. Human Hsp10 and Early Pregnancy Factor (EPF) and their relationship and involvement in cancer and immunity: Current knowledge and perspectives. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Dong, S.; Liu, G.; Yu, X. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of Hsp60, Hsp70 and Hsp90 in the golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilou, K.; Triantafilou, M.; Dedrick, R.L. A CD14-independent LPS receptor cluster. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Young, D.W.; Golenbock, D.T.; Christ, W.J.; Gusovsky, F. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates lipopolysaccharide- induced signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10689–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komatsuda, A.; Wakui, H.; Oyama, Y.; Imai, H.; Miura, A.B.; Itoh, H.; Tashima, Y. Overexpression of the human 72 kDa heat shock protein in renal tubular cells confers resistance against oxidative injury and cisplatin toxicity. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, K.J.; Issels, R.D.; Slosman, D.O.; Guillet, J.G.; Soussi, T.; Polla, B.S. Cancer and the heat shock response. Eur. J. Cancer 1994, 30, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Shelden, E.A. Developmentally regulated gene expression of the small heat shock protein Hsp27 in zebrafish embryos. Gene Expr. Patterns 2006, 6, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Ning, X.; Chen, A.; Zhang, L.; Qin, S.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J. Identification of two small heat shock proteins with different response profile to cadmium and pathogen stresses in Venerupis philippinarum. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2010, 15, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, Q.N.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liang, H.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Zheng, Z. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of heat shock protein 20 (Hsp20) from the pearl oyster Pinctada martensii. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Hong, C.; Dai, J. The identification of heat shock protein genes in goldfish (Carassius auratus) and their expression in a complex environment in Gaobeidian Lake, Beijing, China. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2007, 145, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Cui, Y.; Liu, B.; Xie, J.; Ge, X.; Xu, P.; Ren, M.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, Y. HSP60 and HSP90β from blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala: Molecular cloning, characterization, and comparative response to intermittent thermal stress and Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gething, M.; Sambrook, J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature 1992, 355, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzellitti, S.; Fabbri, E. Differential Hsp70 gene expression in the Mediterranean mussel exposed to various stressors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellura, C.; Toubiana, M.; Parrinello, N.; Roch, P. Hsp70 gene expression in Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocytes is triggered by moderate heat shock and Vibrio anguillarum, but not by V. splendidus or Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, E.E.; Woo, N. Evidence for disruption of Na+-K+-ATPase and Hsp70 during vibriosis of sea bream, Sparus (= Rhabdosargus) sarba Forsskl. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 28, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.C.; Moarefi, I.; Hartl, F.U.; Kleijmeer, M.; Ramm, G.; Schuurhuis, D.; Griffith, J.; Rescigno, M.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. Hsp90: A specialized but essential proteinfolding tool. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, A.S.; Kalmár, É.; Csermely, P.; Shen, Y.F. Hsp90 isoforms: Functions, expression and clinical importance. FEBS Lett. 2004, 562, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Song, L.; Qiu, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ni, D. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of heat shock protein 90 gene in the haemocytes of bay scallop Argopecten irradians. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. Cloning and expression of a heat shock protein (Hsp) 90 gene in the haemocytes of Crassostrea hongkongensis under osmotic stress and bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.K.; Kozak, C.; Robinson, E.A.; Ullrich, S.J.; Appella, E. Murine 86-and 84-kDa heat shock proteins, cDNA sequences, chromosome assignments, and evolutionary origins. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 5343–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Wu, C.; Liu, H. The cooperative expression of heat shock protein 70 KD and 90 KD gene in juvenile Larimichthys crocea under Vibrio alginolyticus stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 58, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primers for full-length PCR | |||
| HSP60-F | CTGACGGACACGCGCATCCCTTCA | 55 | 1826 |
| HSP60-R | AATCATGTCCCCTGCCCACAACCCTTC | ||
| Primers for quantitative real-time PCR analysis | |||
| HSP27-F | CTCGGGAATGTCTGAGATAAAG | 62 | 130 |
| HSP27-R | CTCATGTTTGCCGGTGAT | ||
| HSP60-F | GGAGAGCACAAACAGTGACTAC | 62 | 130 |
| HSP60-R | GACACGGTCCTTCTTCTCATTC | ||
| HSP70-F | CTCTATGGTCCTGGTGAAGA | 60 | 106 |
| HSP70-R | CCTCTGGGAGTCATTGAAATAG | ||
| HSP90-F | AGGTCACGGTCATCACTAAAC | 62 | 182 |
| HSP90-R | GACCACTTCCTTCACTCTCTTC | ||
| β-actin-F | GACCACCTTCAACTCCATCAT | 62 | 126 |
| β-actin-R | GTGATCTCCTTCTGCATCCTATC | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Fang, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Kong, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q. Molecular Cloning of Heat Shock Protein 60 (SpHSP60) from Schizothorax prenanti and the Gene Expressions of Four SpHSPs during Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Infection. Fishes 2022, 7, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030139
Zhang J, Huang J, Fang C, Li W, Zhao H, Kong F, Zhang H, Zhang H, Wang Q. Molecular Cloning of Heat Shock Protein 60 (SpHSP60) from Schizothorax prenanti and the Gene Expressions of Four SpHSPs during Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Infection. Fishes. 2022; 7(3):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030139
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jianlu, Jiqin Huang, Cheng Fang, Wanchun Li, Hu Zhao, Fei Kong, Han Zhang, Hongxing Zhang, and Qijun Wang. 2022. "Molecular Cloning of Heat Shock Protein 60 (SpHSP60) from Schizothorax prenanti and the Gene Expressions of Four SpHSPs during Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Infection" Fishes 7, no. 3: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030139
APA StyleZhang, J., Huang, J., Fang, C., Li, W., Zhao, H., Kong, F., Zhang, H., Zhang, H., & Wang, Q. (2022). Molecular Cloning of Heat Shock Protein 60 (SpHSP60) from Schizothorax prenanti and the Gene Expressions of Four SpHSPs during Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Infection. Fishes, 7(3), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030139






