Immuno-Enzymatic and Proteomic Approaches for Sexing the African Bonytongue (Heterotis niloticus Cuvier, 1829)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
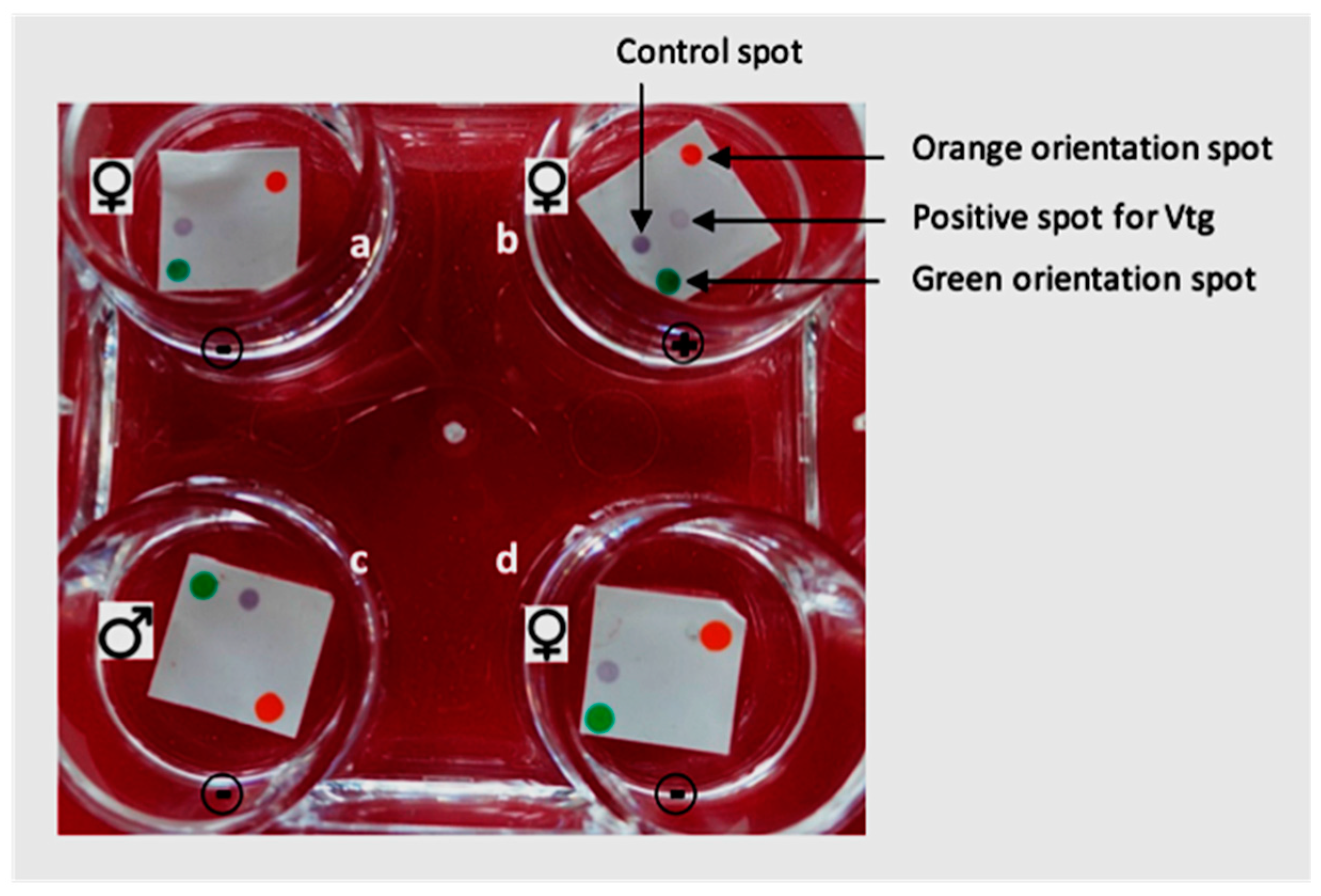
2.1. Testing of the Arapaima Sexing Kit
2.2. Induction of Heterotis Vtg by 17β-Estradiol Treatment in Immature Individuals and Purification
2.2.1. Vtg Induction in Immature Fish with 17β-Estradiol
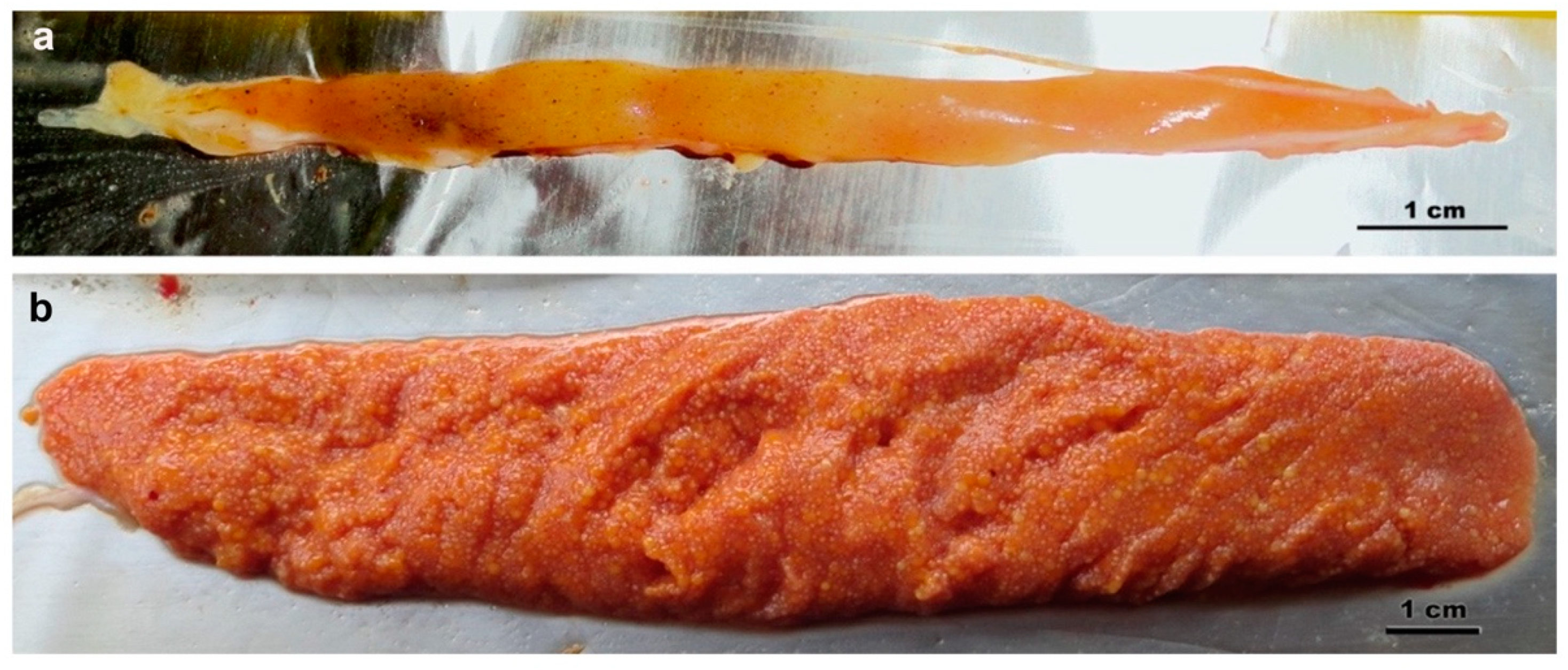
2.2.2. Vtg Purification
2.3. Development of a Heterotis Vtg Antibody
2.4. Arapaima, Osteoglossum, and Heterotis Vtg Antibody Tests
- Antigen coating: a series of 100 µL plasma dilutions (1:1000, 1:2000, 1:4000, 1:8000, 1:16,000, 1:32,000 and 1:64,000) in carbonate buffer (0.05 M; pH 9.6) were distributed in a 96-well plate and incubated at 4 °C overnight.
- Saturation: 100 μL of phosphate buffer saline with 1% Tween 20 (Sigma) and 2% normal pig serum (PBS-T-NPS) were added to each well, and the plate was incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. The contents of the wells were emptied, and each well was rinsed three times with 100 μL of PBS-T.
- First incubation of the Vtg antibody: 100 µL of 1:10,000 diluted Vtg antibody in PBS-T-NPS was added to each well. Then, the plate was incubated at 37 °C for 90 min or at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C) for 4 h, its contents were discarded, and each well was rinsed 3 times with 100 μL of PBS-T.
- Second incubation of the anti-rabbit IgG-peroxidase complex: 100 µL of anti-rabbit IgG labeled with peroxidase (Sigma) and diluted 1:3000 in PBS-T-NPS was added to each well, and the plate was incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. Then, each well was rinsed 3 times with 100 μL of PBS-T.
- Color development: peroxidase activity was revealed in the dark by adding 100 μL of a solution containing 20 mL of citrate buffer (0.2 M; pH 5.0) + 10 mg of o-phenylenediamine + 30 µL of 30% H2O2 (Sigma) to each well. The reaction was stopped after 30 min by adding 50 µL of 4 M H2SO4 to each well.
- The absorbance of each well was measured using a microplate reader at 490 nm. A blank well was added to aggregate the plate + reagents background; it contained all reagents except those of the coating step. The blank values were deduced from male plasma ODs to determine non-specific binding for a given antibody dilution.
2.5. Proteomic Approach
2.5.1. NanoLC-MS/MS
2.5.2. Peptide Sequencing and Protein Identification
3. Results
3.1. Sexing of H. niloticus with the A. gigas Sexing Kit
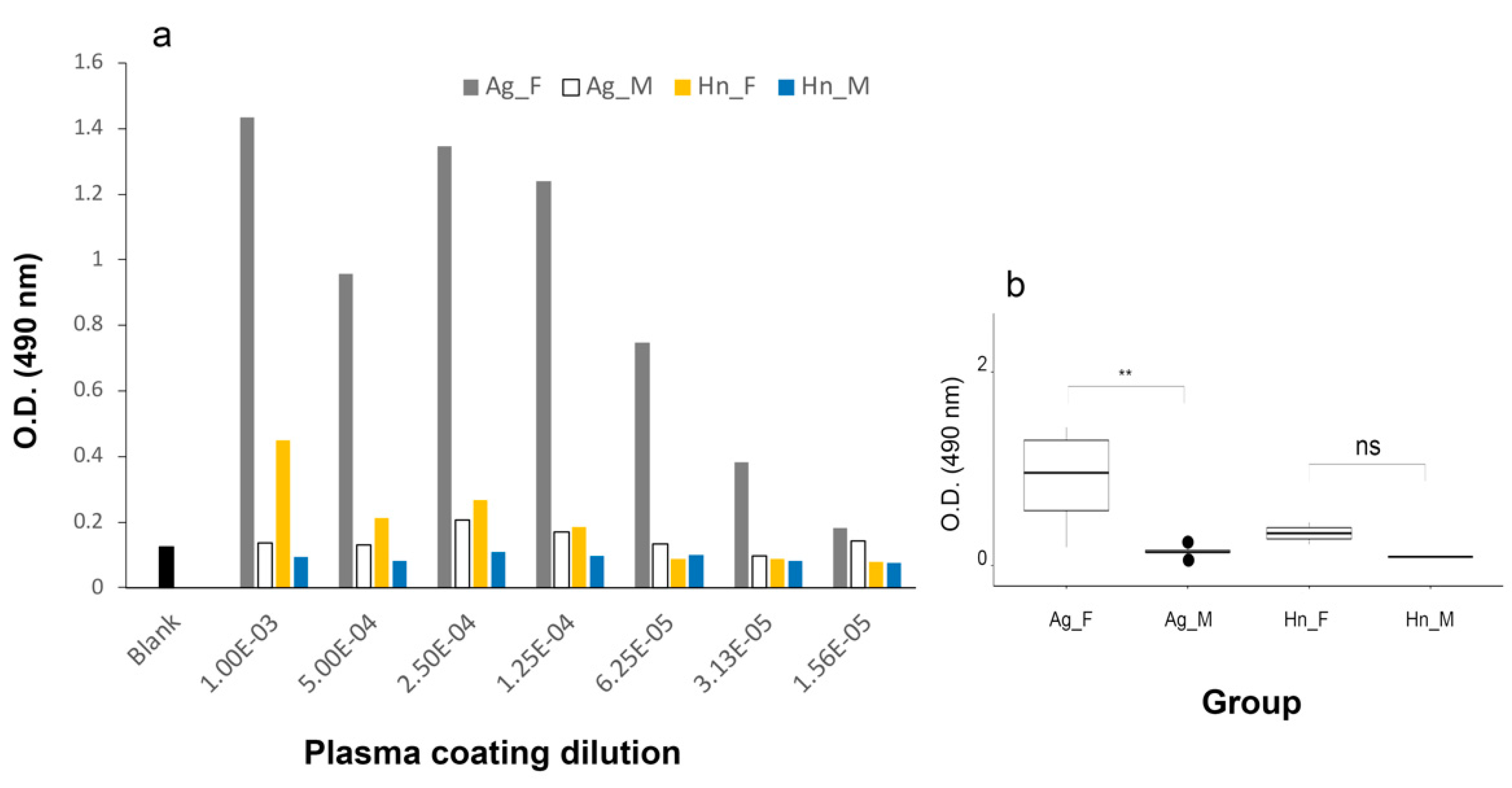
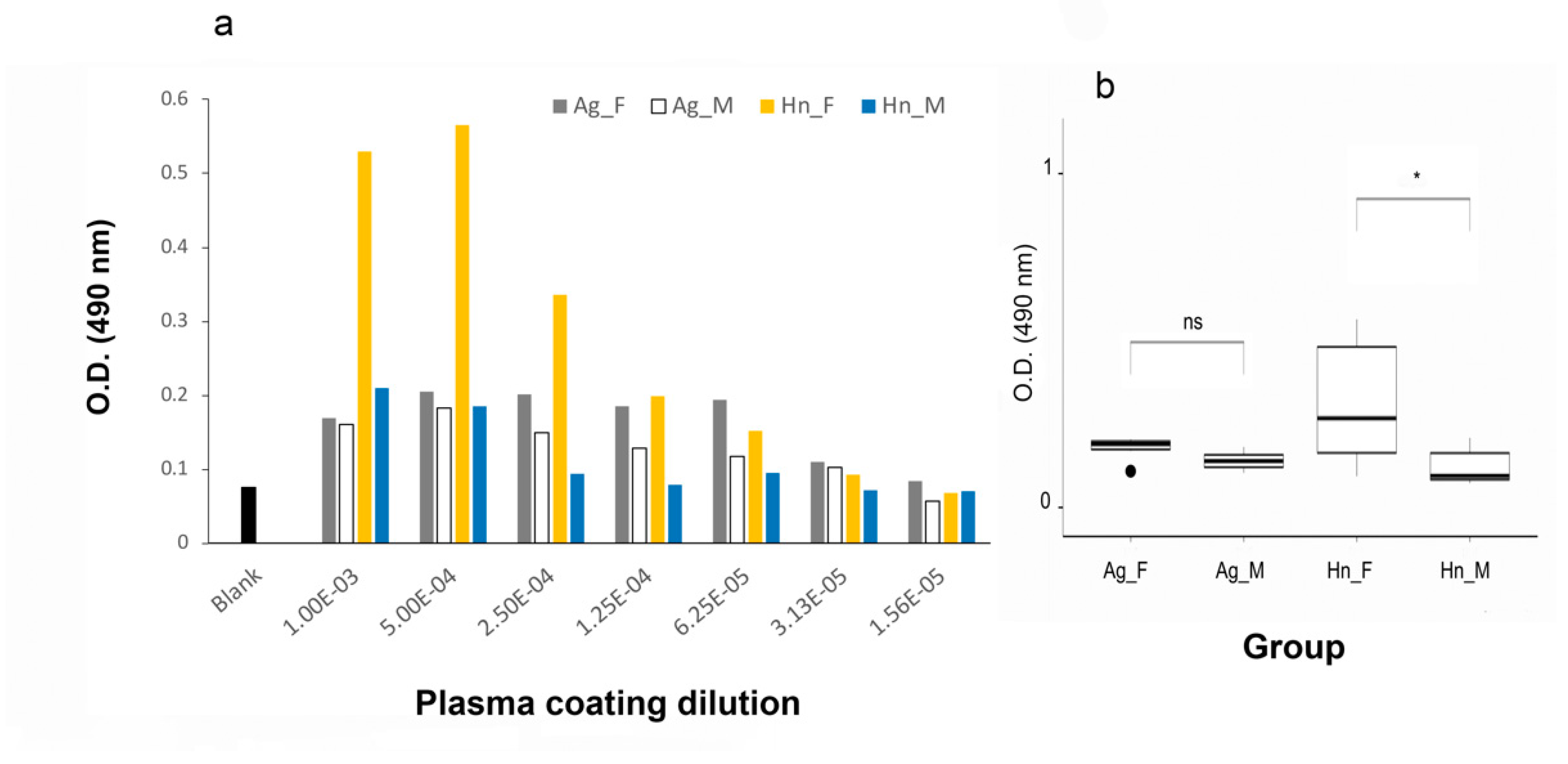
3.2. Sexing of H. niloticus with Heterologous Vtg Antibodies by Direct ELISA
3.2.1. A. gigas Vtg1 Antibodies
3.2.2. O. bicirrhosum Vtg Antibody
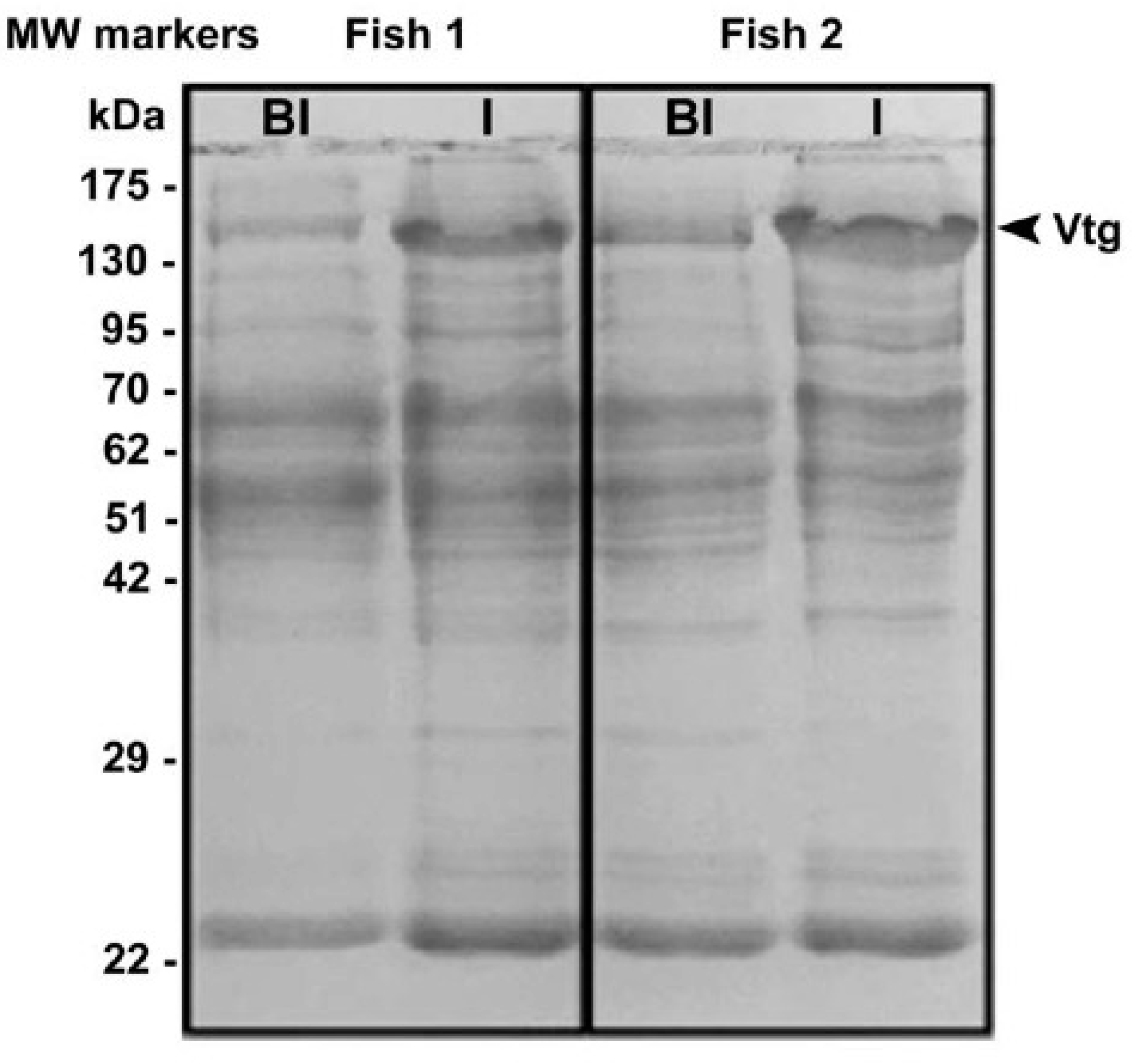
3.3. Purification of H. niloticus Vtg
3.4. Sexing of H. niloticus with the Developed H. niloticus Vtg Antibody
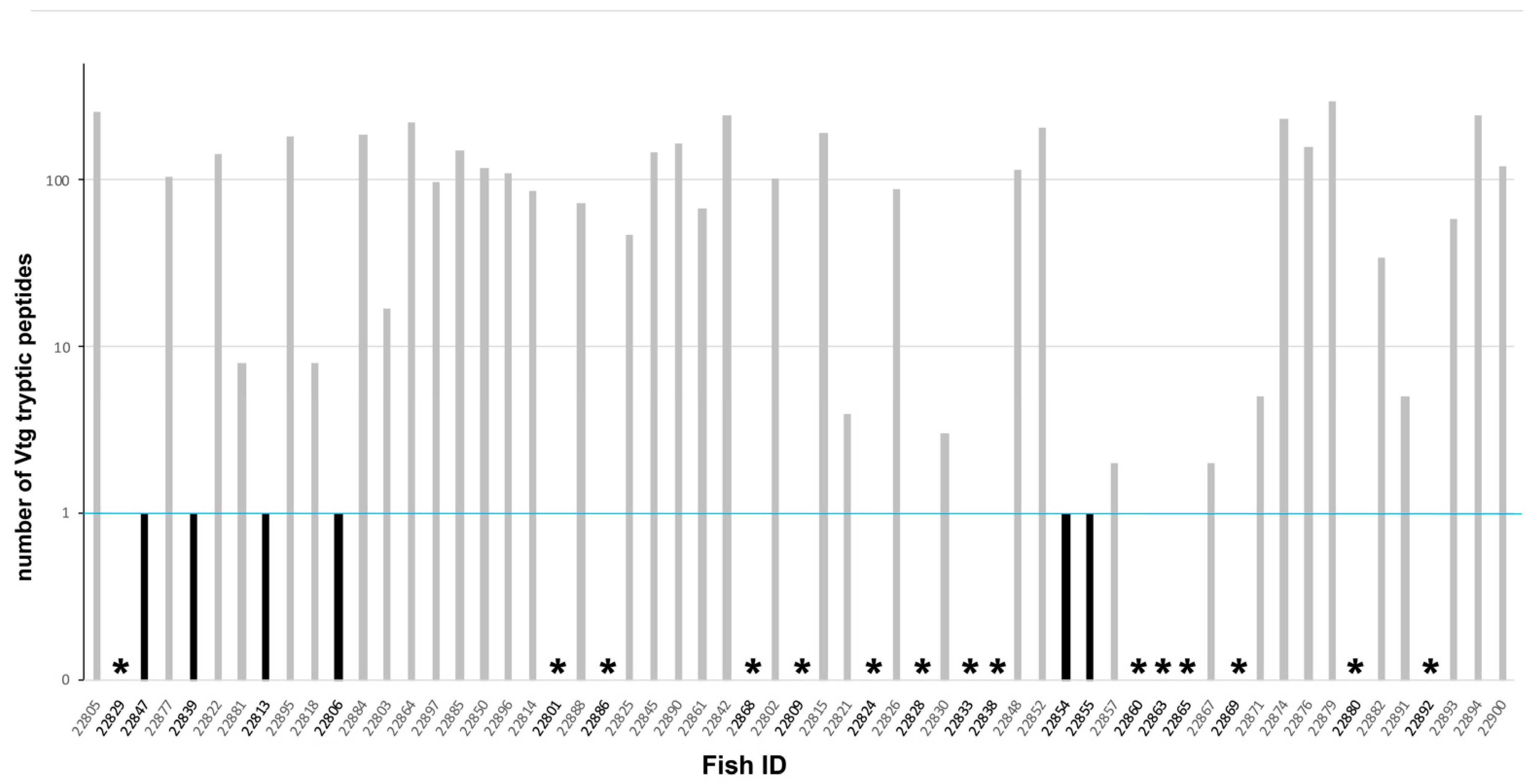
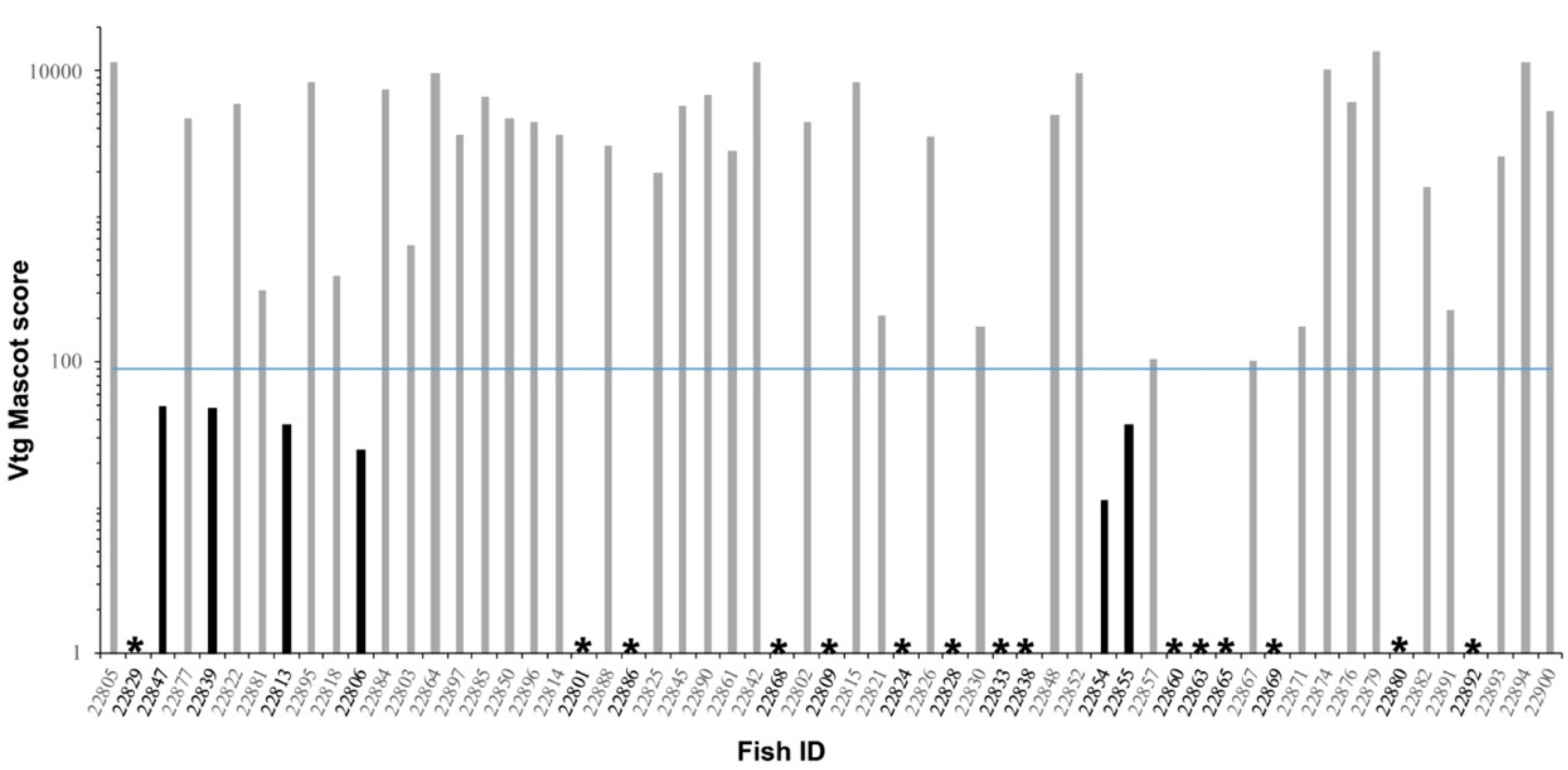
3.5. Mass Spectrometry Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ezekiel, E.N.; Abowei, J.F.N. Length-Weight Relationship and Condition Factor of Heterotis niloticus from Amassoma flood plain, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Appl. Sci. Rep. 2013, 4, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Odo, G.E.; Nwamba, H.O.; Eyo, J.E. Aspects of the biology of Heterotis niloticus, Cuvier 1829 (Osteoglossiformes: Osteoglossidae) in the Anambra flood river system, Nigeria. Anim. Res. Int. 2009, 6, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adite, A.; Winemiller, K.O.; Fiogbé, E.D. Population structure and reproduction of the African bonytongue Heterotis niloticus in the Sô River-floodplain system (West Africa): Implications for management. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2006, 15, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, J. Les poissons de la famille des Osteoglossidae et la pisciculture. Bois For. Trop. 1973, 147, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lemasson, L. Chronique piscicole. Bois For. Trop. 1957, 54, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Reizer, C. Comportement et reproduction d’Heterotis niloticus en petits étangs. Bois For. Trop. 1964, 95, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, J.; Moreau, I. Etude du cycle annuel de la gamétogenèse chez Heterotis niloticus au lac Ivakoina (zone des Pangalanes) Madagascar. Rev. Hydrobiol. Trop. 1982, 15, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Bauchot, R.; Ridet, J.-M.; Diagne, M. The epibranchial organ, its innervations and its probable functioning in Heterotis niloticus (Pisces, Teleostei, Osteoglosssidae). Environ. Biol. Fishes 1993, 37, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, G.A.; Obi, A.; Oladosu, O.O. Sex determination in Heterotis niloticus (Cuvier 1829) Based on morphometric features. ASSET Ser. B 2007, 6, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kimou, N.B.; Koumi, R.A.; Koffi, M.K.; Atsé, C.B.; Ouattara, I.N.; Kouamé, P.L. Utilisation des sous-produits agroalimentaires dans l’alimentation des poissons d’élevage en Côte d’Ivoire. Cah. Agric. 2016, 25, 25006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.H.; Koumi, A.R.; Atse, B.C.; Kouamelan, E.P. Etat de connaissance sur la pisciculture en Côte d’Ivoire. Agron. Afr. 2017, 29, 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. FishStatJ. 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/software/fishstatj/en (accessed on 17 March 2021).
- Monentcham, S.-E.E.; Kouam, J.; Pouomogne, V.; Kestemont, P. Biology and prospect for aquaculture of African bonytongue, Heterotis niloticus (Cuvier, 1829): A review. Aquaculture 2009, 289, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, J. Exposé synoptique des données biologiques sur Heterotis niloticus (Cuvier, 1829). FAO Synop. Pêches 1982, 131, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Torati, L.S.; Varges, A.P.S.; Galvão, J.A.S.; Mesquita, P.E.C.; Migaud, H. Endoscopy application in broodstock management of Arapaima gigas (Schinz, 1822). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2016, 32, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, H.P.; Santos, J.E.; Formagio, P.S.; Guimaraes-Cruz, R.J. Gonadal morphology and reproductive traits of the Amazonian fish Arapaima gigas (Schinz, 1822). Acta Zool. 2005, 86, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu-Koo, F.; Dugué, R.; Alván Aguilar, M.; Casanova Daza, A.; Alcántara Bocanegra, F.; Chávez Veintemilla, C.; Duponchelle, F.; Renno, J.F.; Tello, S.; Nuñez, J. Gender determination in the Paiche or Pirarucu (Arapaima gigas) using plasma vitellogenin, 17β-estradiol, and 11-ketotestosterone levels. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreiro, C.R.P.; Furtado-Neto, M.A.d.A.; Mesquita, P.E.C.; Bezerra, T.A. Sex determination in the Giant fish of Amazon Basin, Arapaima gigas (Osteoglossiformes, Arapaimatidae), using laparoscopy. Acta Amaz. 2011, 41, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau du Colombier, S.; Jacobs, L.; Gesset, C.; Elie, P.; Lambert, P. Ultrasonography as a non-invasive tool for sex determination and maturation monitoring in silver eels. Fish. Res. 2015, 164, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharczyk, D.; Malinovskyi, O.; Nowosad, J.; Kowalska, A.; Cejko, B.I. Comparison of responses to artificial spawning of ruffe (Gymnocephalus cernua) specimens captured from their natural habitat to those produced in cultured conditions. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 225, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa, R.; Nowosad, J.; Biegaj, M.; Cejko, B.I.; Kucharczyk, D. Use of ultrasonography to determine sex in sexually immature European river lamprey Lampetra fluviatilis (L.). Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 204, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, V.F.R.; Melo, N.; Di Chiacchio, I.M.; de Lima Assis, I.; Machado, G.J.; Paiva, I.M.; de Carvalho, A.F.S.; Pereira, R.N.; Solis Murgas, L.D. Sex identification of the ornamental amazon fish Astronotus ocellatus by videoceloscopy and gonadal biopsy. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 230, 106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghim, M.; Vajhi, A.; Veshkini, A.; Masoudifard, M. Determination of sex and maturity in Acipenser stellatus by using ultrasonography. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Betancur, R.R.; Wiley, E.O.; Arratia, G.; Acero, A.; Bailly, N.; Miya, M.; Lecointre, G.; Ortí, G. Phylogenetic classification of bony fishes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo-Qing, L.; Wilson, M.V.H. The discovery of Heterotidinae (Teleostei: Osteoglossidae) from the Paleocene Paskapoo Formation of Alberta, Canada. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 1996, 16, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, E.J. Tongue Bite Apparatus of Osteoglossomorph Fishes: Variation of a Character Complex. Copeia 2001, 2001, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koua, N.Z.D.; Núñez-Rodriguez, J.; Orjuela, J.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C.; Dubos, M.-P.; Bernay, B.; Pontin, J.; Corre, E.; Henry, J. Identification and structural characterization of the factors involved in vitellogenesis and its regulation in the African Osteoglossiforme of aquacultural interest Heterotis niloticus (Cuvier, 1829). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 296, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoué, S. Was Gondwanan breakup the cause of the intercontinental distribution of Osteoglossiformes? A time-calibrated phylogenetic test combining molecular, morphological, and paleontological evidence. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 99, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoué, S.; Sullivan, J.P. Simultaneous analysis of five molecular markers provides a well-supported phylogenetic hypothesis for the living bony-tongue fishes (Osteoglossomorpha: Teleostei). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 33, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.J. Gill arches of teleostean fishes of the division Osteoglossomorpha. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. Zool. 1968, 47, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.J. Infraorbital bones and their bearing on the phylogeny and geography of Osteoglossomorph fishes. Am. Mus. Novit. 1969, 2394, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Dugué, R.; Atta Shikema, R.K.; Corcuy Arana, N.; Legendre, M.; Duponchelle, F.; Renno, J.F.; Nuñez, J. Seasonality of reproduction in Piaractus brachypomus in South Bolivia. Cybium 2009, 32 (Suppl. 2), 241. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, R.A.; Hoch, K.L.; Carnevali, O. Placement of small lipovitellin subunits within the vitellogenin precursor in Xenopus laevis. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 213, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, Y.; Cui, P. Vitellogenin is an immunocompetent molecule for mother and offspring in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndiaye, P.; Forgue, J.; Lamothe, V.; Cauty, C.; Tacon, P.; Lafon, P.; Davail, B.; Fostier, A.; Le Menn, F.; Núñez, J. Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) vitellogenins: Development of homologous and heterologous ELISAs and analysis of vitellogenin pathway through the ovarian follicle. J. Exp. Zool. A 2006, 305A, 576–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.J.; Kim, J.L.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, H.K.; An, C.M. Characterization, expression profile, and promoter analysis of the Rhodeus uyekii vitellogenin Ao1 gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18804–18818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, J.T.T.; Emelyanov, A.; Korzh, V.; Gong, Z. Hepatic and extrahepatic expression of vitellogenin genes in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Gene 2005, 356, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z.; He, J.; Zhang, W.; Ma, G. Cloning, expression, and induction by 17-β estradiol (E2) of a vitellogenin gene in the white cloud mountain minnow Tanichthys albonubes. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arukwe, A.; Røe, K. Molecular and cellular detection of expression of vitellogenin and zona radiata protein in liver and skin of juvenile salmon (Salmo salar) exposed to nonylphenol. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 331, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Regueira, M.; Da Cuña, R.H.; Ferreira, M.F.; Varela, M.L.; Lo Nostro, F.L. Nonmonotonic response of vitellogenin and estrogen receptor α gene expression after octylphenol exposure of Cichlasoma dimerus (Perciformes, Cichlidae). Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 156, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.R.; Owen, T.G.; Ternan, T.A.; Hildebrand, L.D. Measurement of a sex-specific protein in skin mucus of premature coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquaculture 1984, 43, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meucci, V.; Arukwe, A. Detection of vitellogenin and zona radiata protein expressions in surface mucus of immature juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) exposed to waterborne nonylphenol. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncaut, N.; Nostro, F.L.; Maggese, M.C. Vitellogenin detection in surface mucus of the South American cichlid fish Cichlasoma dimerus (Heckel, 1840) induced by estradiol-17beta. Effects on liver and gonads. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 63, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Yuan, L.; Rao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liao, T.; Xu, Y.; Dai, H. Distribution of vitellogenin in zebrafish (Danio rerio) tissues for biomarker analysis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 149, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.D.; Wang, X.J.; Song, H.M.; Yang, Y.X.; Luo, D.; Gu, D.E.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Luo, J.R.; Hu, Y.c. Mitochondrial DNA as effective molecular markers for the genetic variation and phylogeny of the family Osteoglossidae. Gene 2012, 511, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.W.; McKinley, S.R.; Colavecchia, M. The use of clove oil as an anesthetic for Rainbow trout and its effects on swimming performance. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1997, 17, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugué, R.; Chu-Koo, F.; Alcantara, F.; Duponchelle, F.; Renno, J.-F.; Nuñez, J. Purification and assay of Arapaima gigas vitellogenin: Potential use for sex determination. Cybium 2008, 32 (Suppl. 2), 111. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, Z.; Tejero, E.; Schmidt, R.; Tucker, R.; Pedro, A. Identification of potential blood-derived extracellular vesicles biomarkers to diagnose and predict distant metastases in ER+ breast cancer patients. bioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Menze, B.H.; Kirchner, M.; Monigatti, F.; Parker, K.C.; Patterson, T.; Steen, J.J.; Hamprecht, F.A.; Steen, H. Robust prediction of the MASCOT score for an improved quality assessment in mass spectrometric proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3708–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.N.; Pappin, D.J.C.; Creasy, D.M.; Cottrell, J.S. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceapa, C.; Williot, P.; Le Menn, F.; Davail-Cuisset, B. Plasma sex steroids and vitellogenin levels in stellate sturgeon (Acipenser stellatus Pallas) during spawning migration in the Danube River. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, A.; Oka, M. Immunochemical sexing of living yellowfin tuna, Thunnus albacares (Bonnaterre), using a vitellogenin- like protein. Aquac. Res. 1998, 29, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottinger, T.G.; Pulman, K.G.T.; Carrick, T.R.; Scott, A.P. Evaluation of biochemical methods for the non-destructive identification of sex in upstream migrating salmon and sea trout. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 67, 1514–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.L.; Wildhaber, M.L.; Papoulias, D.M.; Delonay, A.J.; Tillitt, D.E.; Annis, M.L. Estimation of gonad volume, fecundity, and reproductive stage of shovelnose sturgeon using sonography and endoscopy with application to the endangered pallid sturgeon. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2007, 23, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kynard, B.; Kieffer, M. Use of a borescope to determine the sex and egg maturity stage of sturgeons and the effect of borescope use on reproductive structures. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, E.A.; Rosenberger, A.E.; Howell, P.J. Validation of endoscopy for determination of maturity in small salmonids and sex of mature individuals. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2007, 136, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, J.; Imbiriba, E.P. Piscicultura do pirarucu, Arapaima gigas. Ser. Doc. Circ. Téc. 1986, 52, 17. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, E.A.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Rab, P.; Ezaz, T.; Yano, C.F.; Hatanaka, T.; Jegede, O.I.; Tanomtong, A.; Liehr, T.; Sember, A.; et al. Cytogenetics, genomics and biodiversity of the South American and African Arapaimidae fish family (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214225. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, E.J. Comparative osteology and phylogenetic systematics of fossil and living bony-tongue fishes (Actinopterygii, Teleostei, Osteoglossomorpha). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 137, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez Rodriguez, J.; Dugué, R.; Otemé, Z.J.; Hem, S.; Le Menn, F. Vitellogenin plasma levels in two cultured African catfish species, Chrysichthys nigrodigitatus (Claroteidae) and Heterobranchus longifilis (Clariidae). Aquat. Living Resour. 1997, 10, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, M.; Pankhurst, N.W.; Pryce, A.; Sun, B. Vitellogenin isolation, purification and antigenic cross-reactivity in three teleost species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 134, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.L.; Marina, A.; Álvarez, G.; Vázquez, J. Application of proteomics for fast identification of species-specific peptides from marine species. Proteomics 2002, 2, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Pankhurst, N.W.; Watts, M. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for vitellogenin measurement in greenback flounder Rhombosolea tapirina. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 29, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Om, A.D.; Jasmani, S.; Ismail, N.; Yeong, S.Y.; Abol-Munafi, A.B. Application MALDI TOF on protein identification of vitellogenin in giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.M.; Banoub, J.H. Detection of Biological Agents for the Prevention of Bioterrorism; Banoub, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 301–318. [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez-Rodriguez, J.; Kah, O.; Geffard, M.; Le Menn, F. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for sole (Solea vulgaris) vitellogenin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1989, 92, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koua, N.D.; Henry, J.; Corre, E.; Pontin, J.; Bernay, B.; Nunez, J. Immuno-Enzymatic and Proteomic Approaches for Sexing the African Bonytongue (Heterotis niloticus Cuvier, 1829). Fishes 2022, 7, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030106
Koua ND, Henry J, Corre E, Pontin J, Bernay B, Nunez J. Immuno-Enzymatic and Proteomic Approaches for Sexing the African Bonytongue (Heterotis niloticus Cuvier, 1829). Fishes. 2022; 7(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoua, N’Zi Daniel, Joël Henry, Erwan Corre, Julien Pontin, Benoît Bernay, and Jésus Nunez. 2022. "Immuno-Enzymatic and Proteomic Approaches for Sexing the African Bonytongue (Heterotis niloticus Cuvier, 1829)" Fishes 7, no. 3: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030106
APA StyleKoua, N. D., Henry, J., Corre, E., Pontin, J., Bernay, B., & Nunez, J. (2022). Immuno-Enzymatic and Proteomic Approaches for Sexing the African Bonytongue (Heterotis niloticus Cuvier, 1829). Fishes, 7(3), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7030106







