Abstract
Mussels have been used as animal models for studying ecotoxicology, biomineralization, and bio-adhesion for many years. Despite a wealth of studies on their shell matrix and byssus proteins, few studies have focused on the extracellular matrix molecules in mussel soft tissues. Extracellular matrix molecules may play important roles in biomineralization, immune reaction, and tissue homeostasis. In the present study, extracellular matrix and mineralization-related molecules in zebra mussel soft tissue were immunolocalized using well-characterized monoclonal antibodies. Our results demonstrate specific immunolocalization for collagen IV, fibronectin, and keratan sulfate in hemocytes; collagen IV in peripheral nerves; and aggrecan, link protein, and collagen XVIII in foot tissue. Laminin, decorin, and osteonectin were also broadly immunolocalized in mussel soft tissues. The distributions of these extracellular matrix molecules in mussel tissues are in line with the cell-mediated shell mineralization hypothesis, providing evidence for the molecules involved in the peripheral nervous system and byssus formation, and explaining the conservation of extracellular matrix molecules during evolution. These results further contribute to establishing zebra mussels as an attractive animal model in biomedical research.
1. Introduction
Mollusks are the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals on earth, occurring in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial habitats [1]. They comprise a diversity of marine and freshwater mussels and clams (also referred to as bivalves) which play an important role in ecosystem processes, e.g., by contributing to water purification [2,3,4] or acting as ecological engineers [5]. In addition, mussels have also become prominent targets of bionics and human-centered research. Biomineralization mechanisms of shells, bio-adhesive molecules in byssus, and bio-indicator usages for the detection of toxic chemicals [6,7] have all been of particular interest. However, apart from the shell and byssus, few studies have dealt with the extracellular matrix of the soft body tissues within bivalves [8].
The extracellular matrix is a cell-secreted and -maintained three-dimensional framework present in almost all tissues and organs. The emergence of the extracellular matrix promoted the evolution from unicellular organisms to multicellular organisms. The extracellular framework plays important roles in tissue organization, modulation of innate immune response, cell adhesion, and structural support [9], as well as in signal transduction and regulation of many cell functions during growth, differentiation, migration, regeneration, and degeneration [10]. The extracellular matrix contains collagen, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, many glycoproteins, and, in certain cases, enzymes [11]. During the evolution of Metazoa from the sponges to vertebrates (including the human species), a surprisingly large number of extracellular matrix components were conserved [12]. The investigation of extracellular matrix molecules in different species can help to better understand the evolutionary path of biological structures, functions, mechanisms in certain tissues, and the effects of pathogens or toxicants on these functions and mechanisms. This especially relates to mineralized tissues, because, despite the universal use of calcium as a prevailing mineral, mussels and vertebrates differ regarding the use of certain anions [13].
The present study was conducted using soft tissues of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) which is a well-explored animal model in environmental and toxicological studies [14,15]. Zebra mussels can be bred and maintained under controlled laboratory conditions, which allows systematic testing of external factors on this species. In an environmental context, they are already used as bioindicators, for example, to assess chemical contamination since they are sessile animals and represent the conditions from the site they were collected [16].
Shell mineralization in mussels has been regarded as a prototypical biomineralization model in nature. Consequently, we previously used zebra mussels for studying the stimulation of bio-mineralization after exposure to extracorporeal shock waves [17,18]. The motivation behind these studies was the fact that extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is one of the most promising approaches for treating fracture nonunions [19]; however, the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms of induced bio-mineralization following ESWT are only poorly understood and cannot be comprehensively investigated in a realistic context using cell culture models only. We also used zebra mussels for studying disturbed bio-mineralization after exposure to possible aetiological factors of molar–incisor hypomineralization (MIH) (including bisphenol-A), which may pave the way for better understanding of the pathogenesis of MIH, for which no treatment is currently available [20].
In comparison with human osteoblast- and osteoclast-mediated mineralization [21,22], the question arises whether the mineralization-related extracellular matrix molecules typically present in mammalian mineralized tissues are also present in certain mussel soft tissues. To address this question, a panel of well-characterized monoclonal antibodies that have previously been demonstrated in mammalian (especially human) extracellular matrix tissues were selected for immunohistochemical staining. The set of antigens investigated in this study comprises collagens, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and basal lamina-related antigens. Specifically, we hypothesized a high degree of conservation of certain extracellular matrix molecules during evolution. Therefore, we demonstrate that a set of antibodies, originally developed for use in mammalian tissues, are also recognizing epitopes in zebra mussel soft tissue.
2. Materials and Methods
All mussels (n = 7, 3 males and 4 females) investigated in this study originated from the river Ischler Achen (Upper Danube Drainage, Bavaria, Germany) and from the river Schinderbach (Bavaria, Germany) in July 2014 and February 2020. Mussels with a shell length of over 2 cm from anterior to posterior were selected and maintained in individual holding units at the Aquatic System Biology Unit, Technical University of Munich (Freising, Germany). The mussels were incubated in multi-well plates (VWR catalog number: 734–2323, VWR part of Avantor, Radnor, Pennsylvania, U.S.) which were fixed in a bucket. The bucket was filled with 10 L groundwater (dissolved oxygen 12.5 ± 2.1 mg/L, pH 7.98 ± 0.21, electric conductivity at 20 °C 1049 ± 55 mS/cm2) at a mean temperature of 12.5 °C and with 30% of the water changed daily. Mussels were fed by adding 0.2 mL/L Shellfish Diet 1800 (Reed Mariculture, Campbell, CA, USA) to the incubation water once per week before the immunohistochemical experiments were conducted [23,24].
All experiments were performed according to German animal protection regulations. No requirement of registration or approval of experiments was necessary for the investigation of zebra mussels, which are considered invasive invertebrates in Germany.
Mussels were acclimatized to experimental conditions for 2 weeks before sacrificing them by immersion into 70% (v/v) ethanol for 48 h. Shells were opened by severance of the adductor muscle. Soft bodies were carefully removed and post-fixed in 70% ethanol followed by standard gradient dehydration and subsequent embedding in paraffin (short protocol: 70%, 80%, 96%, 100%, 100% ethanol (dehydration), xylol-1, xylol-2 (clearing), paraffin-1, paraffin-2, paraffin-3 (embedding), 3 h for all steps mentioned). Alcohol fixation has proven useful in studying mammalian tissues, preserving the antigenicity of the extracellular matrix antigens that we aimed to investigate in this study. Routine paraffin embedding was processed using an automated tissue processor (Leica ASP 200S; Leica Microsystems, Nussloch, Germany). Using a LEICA SM2010R microtome (Leica Biosystems), paraffin blocks were serially sectioned into slides of 7 μm thickness along the standard ventral–dorsal plane, allowing all major organs and tissues (mantle, gill, digestive gland, gonad, foot, and byssus gland) to be incorporated into one single histological section [25]. A sketch drawing of mussel soft body sections in the cutting plane is shown in Figure 1 with anatomical structures marked [26]. For immunohistochemical labeling, a distinct magenta chromogen (EnVision FLEX HRP Magenta Substrate Chromogen System, GV925; Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark) was chosen because the mussels contained high quantities of dark brown endogenous pigment and the reddish color of the magenta chromogen was better discernable from it.
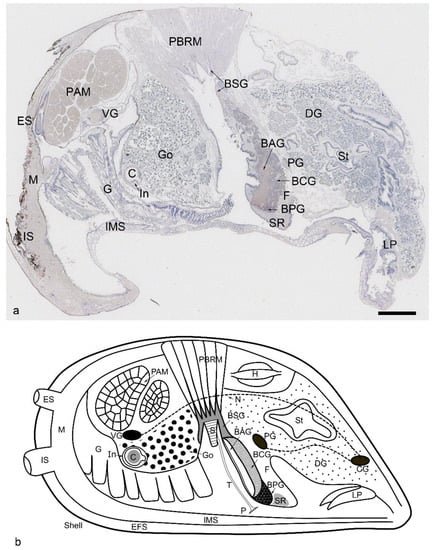
Figure 1.
Overview of a Dreissena polymorpha mussel soft body histology section stained with Mayer’s hematoxylin (a) and a sketch drawing of the soft body with the most important anatomical structures indicated (b). The scale bar in (a) represents 1 mm. Note that not all structures shown in the sketch drawing are visible in the histological section. The mussel’s body is surrounded by mineralized tissues (shells) which are represented by the outer thick black line. The soft tissue next to the shell is the mantle (M), which is involved in the cell-mediated mineralization process. The two shell valves are connected by the muscles (PAM, posterior adductor muscle), foot (F), and byssus apparatus (containing the byssal stem (S), byssus thread (T), byssus plaque (P), byssus stem gland (BSG), byssus accessory gland (BAG), byssus collagen gland (BCG), byssus phenol gland (BPG), and posterior byssal retractor muscle (PBRM)). The muscles are innervated by nerves and ganglia (PG: pedal ganglion, VG: visceral ganglion, CG: cerebral ganglion, N: peripheral nerves). The intestinal system has several parts (DG: digestive glands, St: stomach, C: crystalline style, LP: labial palp) and is in close connection to the gills (G) and gonads (Go). Additional abbreviations: IMR, inter mantle region; IS, inhalant siphon; ES, exhalant siphon; EFS, extrapallial fluid space; SR, the subepithelial region in the distal foot.
Sections were processed with immunohistochemistry using a panel of mouse monoclonal antibodies against collagens (type IV and XVIII), glycosaminoglycans (chondroitin 4 and 6 sulfates and keratan sulfates), proteoglycans (aggrecan, link protein, versican, decorin), and other matrix proteins (fibronectin, laminin, osteonectin). Reduction and alkylation were conducted according to a scheme described in Milz et al. [27] and were applied prior to the enzyme pretreatment. The activity of endogenous peroxidase was blocked with 3% (v/v) hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 30 min and the non-specific binding was reduced by incubating sections with 2.5% (v/v) normal horse serum (S-2012, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) for 60 min at room temperature. Antibody binding was detected with a sensitive Dako EnVision+ System- HRP Labeled Polymer (K4001; Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark) and visualized with an EnVision FLEX HRP Magenta Substrate Chromogen System (GV925; Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark), resulting in a strong, reddish signal. Counterstaining was performed using Mayer’s hematoxylin. For control sections, the primary antibody was replaced by phosphate-buffered saline. Primary antibody incubation was performed overnight at 4 degrees Celsius in a moist chamber. The secondary antibody detection system (Dako EnVision+ System-HRP Labeled Polymer, K4001; Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark) was used according to the manufacturers’ recommendation. An example protocol of the entire procedure is provided in Table 1; full details of the antibodies and specific pretreatments are provided in Table 2.

Table 1.
Immunohistochemistry protocol for detection with the DAKO Envision system. All steps were performed at room temperature if not otherwise stated.

Table 2.
List of monoclonal antibodies used in this study, together with their dilutions, pretreatments, and sources. All the antibodies are mouse monoclonals. Abbreviations: DSHB, developmental studies hybridoma bank; Ch ACII, chondroitinase ACII (Sigma); Ch ABC, chondroitinase ABC (Sigma); Hyal, hyaluronidase (Sigma). Antibodies 2B6, 3B3,1/20/5-D-4 were gifts from B. Caterson.
A potential obstacle relates to the fact that mussel hemocytes contain several enzymes [28], and the peroxidases, especially, might react with the magenta chromogen visualization system, which could result in false positives. In order to avoid this, the endogenous peroxidases were inactivated with 3% hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 30 min. Compared to other immunohistochemical protocols, usually applied in mammalian tissues, this is a long blocking step which we adopted after several pilot trials conducted for optimization of the labelling procedure. A further methodological precaution was to strictly limit the time for the magenta chromogen incubation to 5 min to avoid non-specific background staining.
The specimens were analyzed with a light microscope (Axiophot Photomicroscope, Carl Zeiss Microscopy, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with Plan-Neofluar objectives (20×/0.50, 40×/0.75 Carl Zeiss Microscopy, Oberkochen, Germany) and an Axiocam HRc (Carl Zeiss Microimaging, Goettingen, Germany) digital camera using Zeiss Axiovision software (version 4.9.1 SP2). Photographs were taken at the same magnification and exported as TIFF files, which were finally adjusted for brightness and contrast using Adobe Photoshop CS4 (version 11.0; Adobe Systems, CA, USA). Care was taken that the original appearance of the material remained unchanged.
3. Results
All mussel individuals presented consistent staining patterns in somatic and gonad tissues. The results of immunohistochemical labeling could be broadly categorized as follows: (i) Antibodies for collagen IV (M3F7), collagen XVIII (6C4), fibronectin (HFN7.1), keratan sulfate (MZ15), chondroitin-4 sulfate, and dermatan sulfate (2B6, with chondroitinase ABC/AC pretreatment), aggrecan (12/21/1-C-6), and link protein (9/30/8-A-4) labeled distinct anatomical structures in zebra mussel soft tissues. The results for all antibodies which labeled at least one region of the zebra mussel soft tissue are summarized in Table 3. (ii) Antibodies for laminin (2E8), decorin (CB-1, DS1), and osteonectin (AON-1) labeled many structures in zebra mussel soft tissues, without preference for a particular cell or tissue type. (iii) Positive labeling of keratan sulfate antibody MZ15 in hemocytes was not matched by another keratan sulfate antibody (1/20/5-D-4), which did not result in any labeling in zebra mussel soft tissues. (iv) Antibodies for chondroitin-6 sulfate (3B3, with chondroitinase ABC pretreatment) did not label any zebra mussel soft tissue. The immunohistochemical results of this study were not influenced by the sex of the mussels, except a higher number of hemocytes in testis than ovaries are cited.

Table 3.
Summary of the immunohistochemical labeling profile of specific regions of the soft body of Dreissena polymorpha found in this study. Results for antibody labeling per region. The numbers indicate the number of positive labeled regions (n = 7 specimens per group, 3 males and 4 females). (Abbreviations: Go: gonads, G: gill, M: mantle, IMS: inter-mantle space, PG: pedal ganglion, VG: visceral ganglion, CG: cerebral ganglion, PAM, posterior adductor muscle, PBRM: posterior byssal retractor muscle, BSG: byssus stem gland, BCG: byssus collagen gland, BAG: byssus accessory gland, SR: subepithelial region in the distal foot, St/In: stomach/intestine lamina propria, C: crystalline style, DSP: dermatan sulfate proteoglycan, C6s: chondroitin-6 sulfate, C4s: chondroitin-4 sulfate.)
3.1. Collagen IV, Fibronectin, and Keratan Sulfate (MZ15)
Collagen IV antibody was strongly labeled in the peripheral nerves and parts of the ganglions (including the visceral, pedal, and cerebral ganglions) of zebra mussels (Figure 2a–d). Within the intensively stained nerves, individual cell nuclei (of glia or supporting cells) could be recognized along with each axon (inset in Figure 2c). The labeled regions of ganglions were located mainly in the transition zone from the ganglion to the peripheral nerves and did not cover perikarya (Figure 2c). Along with the nerve and ganglion, some positively labeled hemocytes could be observed as well (Figure 2c). Besides collagen IV, fibronectin and keratan sulfate (MZ15) antibodies were both strongly positive in hemocytes, with distribution in the gonads, gills, muscle tissues, and central and edge regions of the mantle. Distribution of the positive hemocytes was mainly in the gonads (among germinal tissue of testis (Figure 2e,f) and side regions of ovaries), gills, inter-mantle spaces (central mantle region, shown in Figure 2i), mantle edge regions (Figure 2g,h), and among muscle fibers (Figure 2j,k). Although most hemocytes were labeled by the three antibodies, a small number of hemocytes remained unlabeled.
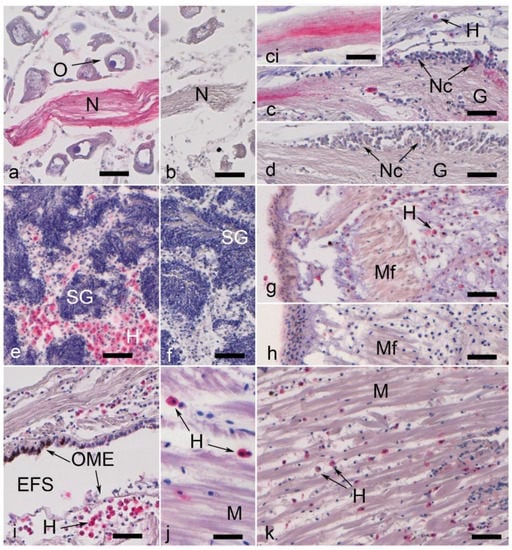
Figure 2.
Nerve and hemocyte labeling in Dreissena polymorpha tissue (the immunohistochemical signal is in magenta). All scale bars represent 50 µm, with the exception of the inset (*) in (c,j), which is 25 µm. (a) Collagen IV-labeled nerve fiber bundle surrounded by non-labeled oocytes (O). (b) Control to (a), showing a nerve fiber bundle (N). (c) Partially collagen IV-labeled ganglion (G). Note that most of the nerve cells (Nc) are not labeled, while the branching fibers show dye deposits. This is shown at higher magnification in the inset in (c). (d) Control to (c). (e) Collagen IV-positive hemocytes (H) in the germinal tissue of testis (T). Note that the tissue used for spermiogenesis (SG) is not labeled. (f) Control to (e). (g) Fibronectin labeling of hemocytes (H) in mantle edge region; muscular fibers (Mf) remain unstained. (h) Control to (g). (i) Distinct labeling for collagen IV exhibited by a number of hemocytes (H) in the central mantle. Note that not all hemocytes are labeled. Furthermore, the outer mantle epithelium (OME) in the mantle edge region exhibits a dark brown pigmentation. EFS: extrapallial fluid space. (j) Muscle tissue with collagen 4-positive labeled hemocytes. The muscle fibers are not labeled. (k) Keratan sulfate (antibody MZ15) labeling in a few hemocytes among muscle fibers (M).
The positive hemocytes were mainly large, round, hyalinocytes-like cells, with strong positive reactions in the cytoplasm (Figure 2e,i). No significant morphological difference was noticed within those positive hemocytes. A large number of immunopositive hyalinocyte-like cells could be observed in the gonads (Figure 2e,f), as described by Evariste et al. [29].
3.2. Aggrecan, Link Protein, Collagen XVIII, and Glycosaminoglycans
Immunolabeling for aggrecan and link protein was found in muscle fibers (Figure 3a–c), byssus stem gland cells (Figure 3a–c), and the lamina propria of the stomach and intestine (Figure 3e,f). Aggrecan immunolabeling was also found in the accessory and collagen glands (Figure 3d) in the foot. In the distal part of the foot, a specific subepithelial region was found to react positively with the collagen XVIII antibody (Figure 3g,h). This region was located at the ventral side of the distal foot, which was next to the plaque-forming gland.
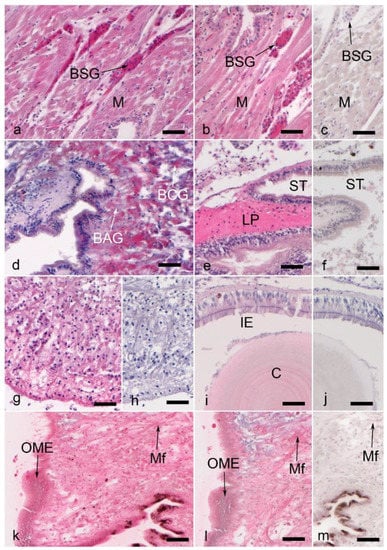
Figure 3.
Muscle, foot, byssus gland, and intestinal labeling with proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans in Dreissena polymorpha tissue (immunohistochemical signal is in magenta). All scale bars represent 50 µm. (a) Strong labeling for aggrecan and (b) link protein in byssus stem gland (BSG) cells within posterior byssal retractor muscles (M). (c) Muscle (M) and byssus stem gland (BSG) tissue, control to (a,b). (d) Aggrecan labeling in byssus collagen (BCG) and accessory gland (BAG) cells. (e) Link protein labeling in stomach (ST) lamina propria tissue (LP). (f) Control to (e). (g) Collagen XVIII labeling in the subepithelial region of the distal foot (SR in Figure 1). (h) Control to (g). (i) Chondroitin-4 sulfate labeling in the crystalline style (C) and some intestinal epithelial cells (IE). (j) Control to (i). (k) Mantle edge tissue labeled with an antibody against decorin (DS1), while (l) shows the decorin labeling with decorin antibody CB-1 in the same tissue. (m) Control to (k,l). Mf: muscular fibers; OME: outer mantle epithelium.
Moreover, the anti-chondroitin sulfate antibody 2B6 was used to identify and locate neoepitopes of chondroitin-4-sulfate (pre-digested with chondroitinase ABC) and dermatan sulfate GAG chains (pre-digested with chondroitinase ACII). Both pre-treatment methods showed immunopositive signals with particular concentrations in the crystalline style (Figure 3i,j) and the lamina propria of the stomach and intestine.
3.3. Laminin, Osteonectin, and Decorin
Laminin, osteonectin, and two types of decorin (DS1 and CB-1)-recognizing antibodies were broadly positive in almost all studied mussel soft tissues (mantle, muscular fibers, connective tissue (Figure 3k–m), nervous system, gill, digestive gland, gonads, and foot).
4. Discussion
As a notorious invasive species, the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha has been widely studied in genomics, proteomics, and ecotoxicology research, with few immunohistochemical studies made of the soft tissues [26,30]. The findings of our study provide novel insights into the characterization and localization of extracellular matrix components in the soft tissues of zebra mussels. In general, the high number of positive reactions of mammalian antibodies in zebra mussels support the hypothesis that many extracellular matrix components are structurally conserved during evolution [9,12]. Furthermore, some tissue-specific recognition may provide new points of interest for relevant studies. These findings also suggest that mussels may even be a good model organism in biomedical or ecotoxicology research, especially considering the 3Rs principle (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement) and the required reduction of vertebrate species in such research.
The expression of these extracellular matrix molecules in zebra mussel soft tissue is likely related to the specific function of tissues and organs. In the mussel soft body, the mantle epidermis secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin to form the shell. The gills are primarily used for respiration. In mussel soft bodies, the basal lamina key component collagen IV, adhesion-related fibronectin, and crystal formation-related keratan sulfate (MZ15) antibodies are labeled in hemocytes, which implies the involvement of hemocytes in growth, immune, and mineralization processes. The foot is used for moving short distances and assembly of byssus by various specialized byssus glands. In the byssus glands, aggrecan and link protein labeling is most likely related to the mechanical function of the tissue.
In general, collagen IV, fibronectin, and keratan sulfate (detected by antibody MZ15) were all located in the cytoplasm of a subpopulation of hemocytes (the hyalinocytes-like cells, as reported in [29,31]). Our results revealed the functional heterogeneity of hemocytes with respect to the content of proteins or proteoglycans. As described in the literature, those hyalinocytes-like cells are fully capable of performing innate immune responses [29]. In previous studies, the immunolocalization of fibronectin in the subpopulations of hemocytes was reported in Pacific blue mussels (Mytilus trossulus) and Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) [32,33]. In addition, a fibronectin-like protein (with a fibronectin type III domain) was identified in zebra mussel hemolymph plasma by proteomic analysis and was observed to be upregulated during in vivo immune response [34]. Fibronectin is a high-molecular glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix which is related to cell adhesion and migration. In vertebrates, there are two types of fibronectins, the plasma-soluble fibronectin, and the insoluble cellular fibronectin. The fibronectin plays a key role in matrix assembly, wound healing, and tumor development in vivo [35]. Here our finding of fibronectin in zebra mussel hemocytes is consistent with previous studies and suggests that fibronectin may play an important role in the hemocyte-mediated immune reaction in zebra mussels.
An important function of mussel hemocytes, other than immunity, is their involvement in shell mineralization. The mechanism of shell formation has been studied for a long time and two concurrent principles have been proposed, one is the matrix-mediated hypothesis, another is the cell-mediated hypothesis [36,37]. The traditional matrix-mediated hypothesis was mainly supported by in vitro experiments, indicating that the matrix proteins have some mineralization-inducing effect. Still, the effect of matrix proteins in whole shell formation and mineralization has remained questionable. The cell-mediated hypothesis was supported by recent reports of crystal-carrying hemocytes observed in circulation and in the extrapallial space in mollusks, which indicated the potential involvement of hemocytes in shell biomineralization [38,39].
Other than the reports of crystal-carrying hemocytes, the gene expressions of shell matrix proteins in hemocytes were very low, which led to the need for additional evidence [39]. A previous study had identified a fibronectin type III domain and an alpha 1 type IV collagen in the acid-soluble matrix extract and acid-insoluble matrix of the zebra mussel shell matrix, respectively [40]. As we also immunolocalized collagen IV and fibronectin in zebra mussel hemocytes, the participation of hemocytes in shell mineralization in zebra mussels is likely. The distribution of positive hemocytes in the central and edge regions of mantle tissues also fit the hemocyte-mediated shell mineralization hypothesis.
Keratan sulfate has Ca2+ counterions and may act as a calcium reserve in eggshell production and bone mineralization in birds [41,42]. With the immunolocalization of keratan sulfate (with antibody MZ15) in zebra mussel hemocytes, we can suppose that the shell formation in mussels and avian eggs might be similar in the participation of keratan sulfate proteoglycans. In contrast, another keratan sulfate antibody 1/20/5-D-4 was negative in zebra mussel soft tissues. Since the two antibodies recognize different epitopes, we have to note that only the epitope recognized by antibody MZ15 is expressed in zebra mussel soft tissue. In this regard, it is of note that keratan sulfate-containing proteoglycans are widely distributed among species and show considerable complexity in structure, with numerous epitopes recognized by different antibodies [42]. Accordingly, keratan sulfate proteoglycans may be less conserved in evolution and thus prone to exhibit different epitopes in different species.
Apart from hemocytes, the collagen IV antibody is also specifically bound to peripheral nerves and parts of ganglions in the nervous system of zebra mussels [43]. In the previous immunohistochemical study of connective tissues in the bivalves Pecten jacobaeus and Mytilus galloprovincialis, the anti-human type IV collagen antibody recognized a subepidermal basement membrane structure [44]. This is consistent with our results in Dreissena polymorpha and it suggests that type IV collagen is conserved and widely distributed in multicellular organisms, even sponges [45].
Unlike most members of the collagen family, type IV collagen in vertebrates is found only in the basal lamina of tissues (epithelial, muscle fibers, blood vessels, and peripheral nerves). Basal laminae are believed to be an ancient evolutionary structure and essential in the development of metazoan species [46]. Functions of basal lamina include tissue organization, barrier and filter formation, control of material diffusion, cell adhesion, cell migration, and axon outgrowth. Here, our study provides immunohistochemical evidence for the existence of basal lamina major component collagen IV and laminin (broadly positive) in the peripheral nervous system of zebra mussels. In the peripheral nervous system of vertebrates (especially mammals), axons are wrapped by a myelin sheath which is formed by Schwann cells (i.e., peripheral glia) and surrounded by a basal lamina [47]. In the vertebrate, collagen IV is not only a major component of the Schwann cell basement membrane but is also connected with various functions in the regulation of Schwann cells, promoting peripheral axonal growth and myelination [48]. Our results suggest that certain cells, perhaps comparable to Schwann cells, in the zebra mussel peripheral nervous system express collagen IV. However, it is interesting that, unlike vertebrates, there would be no collagen IV-positive basal lamina surrounding the muscle fibers, although some positive hemocytes were also present in the muscle.
In the vertebrate extracellular matrix, aggrecan and link protein are usually associated with load-bearing structures, such as articular cartilage and specific parts of the intervertebral discs. The aggregates formed by proteoglycan (mainly aggrecan), hyaluronan, and link protein can form a hydrated gel structure, with the collagen framework restricting the movement of hydrated aggrecan complexes, allowing the tissues to resist compression [49]. Other than the compressive loading, the proteoglycans in tendons (mainly aggrecan and versican) and their aggregate with hyaluronan provide tendon tissue with the capacity to resist physical stress [50].
Byssus is a bundle of filaments secreted by mussels for anchoring, including the adhesive plaque, stiff distal thread, elastic proximal thread, and stem [51]. The formation of byssus is initiated by byssus-secreting glands (stem gland, collagen gland, accessory gland, and phenol gland), in which the byssus proteins are synthesized and reserved for secretion. The specific labeling of aggrecan and link protein antibodies in byssus gland cells (with the proximal stem gland most significant) of zebra mussels may be related to the physical properties of these structures.
There are two possibilities for the function of the aggrecan and link protein expressed in byssus glands. The first possibility is that they may participate in the assembling process of the byssus matrix, especially in the byssus stem and proximal part of the byssus. In previous ultrastructural studies of those byssus glands, numerous secretory granules were observed in gland cells [52,53]. A study of the secretory granules suggested that proteins or glycoproteins seem to be the major constituent. Additionally, a common constitution of byssus was revealed, with organized filaments embedded in an amorphous matrix. The pattern of filament organization and quantity of matrix differed in regions with a higher ratio of matrix proteins in the proximal byssus [54]. The distribution of the amorphous matrix component in byssus is consistent with our immunolocalization results for aggrecan and link protein, showing a significant positive staining in the proximal byssus stem glands and less positive staining in the distal glands. It is intriguing to note that this is very similar to the principle of vertebrate insertional fibrocartilage formation [55]. Here, we suppose that aggrecan and link protein may participate in the constitution of the byssus matrix. The second possibility is that the aggrecan and link protein in the stem gland act as a connection between the byssus stem and retractor muscle, providing load-bearing capacities to tissues, as in the tendon [50].
Other than the byssus gland, the extracellular matrix molecules (aggrecan, link protein, chondroitin-4-sulfate, and dermatan sulfate (2B6, pre-digested with chondroitinase ABC and AC)) were also located in the lamina propria of the stomach and intestine. This suggests that these stress-bearing molecules may be necessary for the physical strength of the stomach and intestine lamina propria. A specific subepithelial region with mainly fibrous cells in the distal foot was labeled with the collagen XVIII antibody. During mussel adhesion, the foot attaches to the object by this region with the plaque gland secreting adhesion proteins meanwhile. The presence of collagen XVIII in this region might be related to the structural supporting abilities of collagen XVIII, which so far has been described as a heparan sulfate proteoglycan expressed in the basement membranes of vertebrates [56].
Laminin plays an important role in the formation and maintenance of basement membrane structure and characteristics, as well as the regulation of several biological functions (cell adhesion, migration, differentiation, etc.) [57]. In a previous immunohistochemical study of connective tissues in the bivalves Pecten jacobaeus and Mytilus galloprovincialis, laminin 1 also was recognized within a subepidermal basement membrane structure [44]. Decorin, which is a dermatan sulfate containing proteoglycan, may play an antagonistic role in prohibiting biomineralization within zebra mussel soft tissues, for in the eggshell biomineralization model, a 200 kDa dermatan sulfate proteoglycan had been extracted from the eggshell and was verified with concentration-dependent crystal morphology-modulating abilities in vitro [58].
It is worth noting that the labeling for CB-1 (originally designed to recognize a chicken antigen) and DS1 (directed towards a bovine antigen) showed minor intensity variation in certain zebra mussel soft tissues. The initial publication of CB-1 stated that the CB-1 antibody could not react with mammalian samples and supposed a potential structural difference in the core proteins of avian and mammalian PG-II (decorin) [59]. In our study, both epitopes of avian and mammalian (bovine) decorin were recognized in zebra mussel soft tissues, indicating that mussels could be closer to the evolutionary origin of decorin in the early stages of development.
Osteonectin (SPARC) is a non-collagenous component in bone tissue regulating osteoblast and osteoclast activities. In the mineralization of zebra mussels, so far, no specific mineralization cells, such as osteoclasts or osteoblasts, have been reported, but the mantle cells seem to possess some of the capabilities of these vertebrate bone cells. The broadly expressed pattern of SPARC in zebra mussel soft tissues was also consistent with the report of gene expression of collagen IV and SPARC in oyster tissues [8]. SPARC expression in mussels might regulate the formation and growth of mineral crystals, cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions, and inhibition of cell migration [60], which is also important for immune responses.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, an immunohistochemical labeling strategy for extracellular matrix molecules in zebra mussel soft tissues was established. Furthermore, the presence of collagen IV, fibronectin, and keratan sulfate epitopes in hemocytes was reported, as well as the presence of collagen IV in peripheral nerves, aggrecan and link protein in byssus glands, collagen XVIII in distal foot, and a broader occurrence of laminin, osteonectin, and decorin in mussel soft tissues. The results support the cell-mediated shell formation hypothesis, hemocyte-mediated immune reaction, and provide evidence for some associated molecules in peripheral nerves and byssus formation in zebra mussels. Furthermore, the results confirm that certain extracellular matrix molecules seem to be well conserved during evolution. This means that the zebra mussel constitutes a promising model that can be used in biochemistry, molecular biology, ecotoxicology research, and research focusing on the stimulation and disturbance of bio-mineralization instead of conventional vertebrate models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S. and S.M.; methodology, C.S. and S.M.; software, S.M.; validation, W.W. and S.M.; formal analysis, W.W. and S.M.; investigation, W.W.; resources, C.S.; data curation, W.W.; writing—original draft preparation, W.W.; writing—review and editing, W.W., C.S., S.M., K.S., S.B. and J.G.; visualization, W.W.; supervision, C.S.; project administration, C.S. and S.M.; funding acquisition, C.S. and W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the China Scholarship Council (CSC), grant number no. 201808500132. The funding source had no involvement in the conduct of this study or submission for publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experiments in this study were performed according to German animal protection regulations which do not require registration or approval of experiments using zebra mussels.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The monoclonal antibodies M3F7 developed by H. Furthmayr, 6C4 by W.M. Halfter, MZ15 by F.M. Watt, DS1 by A.R. Poole, CB-1 by D.A. Carrino, HFN 7.1 by R.J. Klebe, 12/21/1-C-6, 9/30/8-A-4 by B. Caterson, and AON-1 by J.D. Termine, were obtained from the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, created by the NICHD of the NIH and maintained at the University of Iowa, Department of Biology, Iowa City, IA 52242. Antibodies 2B6, 3B3,1/20/5-D-4 were gifts from B. Caterson. The authors thank Andrea Haderer, Claudia Harbauer, Beate Aschauer, Barbara Mosler, and Astrid Baltruschat for expert technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rosenberg, G. A New Critical Estimate of Named Species-Level Diversity of the Recent Mollusca. Am. Malacol. Bull. 2014, 32, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lummer, E.-M.; Auerswald, K.; Geist, J. Fine sediment as environmental stressor affecting freshwater mussel behavior and ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, C.C. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 2018, 810, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.T.; Beggel, S.; Auerswald, K.; Stoeckle, B.C.; Geist, J. Establishing mussel behavior as a biomarker in ecotoxicology. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeker, C.; Lueders, T.; Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. Alteration of physico-chemical and microbial properties in freshwater substrates by burrowing invertebrates. Limnologica 2016, 59, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuykov, M.; Pelletier, E.; Harper, D.A.T. Bivalve mollusks in metal pollution studies: From bioaccumulation to biomonitoring. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lusher, A.L.; Rotchell, J.M.; Deudero, S.; Turra, A.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Sun, C.; Shahadat Hossain, M.; Li, Q.; Kolandhasamy, P.; et al. Using mussel as a global bioindicator of coastal microplastic pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyachuk, V. Extracellular matrix components in bivalvia: Shell and ECM components in developmental and adult tissues. Fish Aquac. J. 2018, 9, 1000248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.H. Extracellular matrix in development: Insights from mechanisms conserved between invertebrates and vertebrates. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.D.; Skandalis, S.S.; Gialeli, C.; Karamanos, N.K. Extracellular matrix structure. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzer, M.L. Current concepts of extracellular matrix. J. Orthop. Sci. 2006, 11, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbek, S.; Balasubramanian, P.G.; Chiquet-Ehrismann, R.; Tucker, R.P.; Adams, J.C. The evolution of extracellular matrix. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 4300–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushiro, A.; Miyashita, T. Evolution of hard-tissue mineralization: Comparison of the inner skeletal system and the outer shell system. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2004, 22, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzocchi, U.; Bonaglia, S.; Zaiko, A.; Quero, G.M.; Vybernaite-Lubiene, I.; Politi, T.; Samuiloviene, A.; Zilius, M.; Bartoli, M.; Cardini, U. Zebra Mussel Holobionts Fix and Recycle Nitrogen in Lagoon Sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 610269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prud’homme, S.M.; Hani, Y.M.I.; Cox, N.; Lippens, G.; Nuzillard, J.-M.; Geffard, A. The zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a model organism for ecotoxicological studies: A prior 1H NMR Spectrum Interpretation of a Whole Body Extract for Metabolism Monitoring. Metabolites 2020, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarengo, A.; Canesi, L. Mussels as biological indicators of pollution. Aquaculture 1991, 94, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternecker, K.; Geist, J.; Beggel, S.; Dietz-Laursonn, K.; de La Fuente, M.; Frank, H.-G.; Furia, J.P.; Milz, S.; Schmitz, C. Exposure of zebra mussels to extracorporeal shock waves demonstrates formation of new mineralized tissue inside and outside the focus zone. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio033258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Maffulli, N.; Furia, J.P.; Meindlhumer, L.; Sternecker, K.; Milz, S.; Schmitz, C. Exposure of zebra mussels to radial extracorporeal shock waves: Implications for treatment of fracture nonunions. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertzman, P.; Császár, N.B.M.; Furia, J.P.; Schmitz, C. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is efficient and safe in the treatment of fracture nonunions of superficial bones: A retrospective case series. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2017, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Reichl, F.-X.; Milz, S.; Wölfle, U.C.; Kühnisch, J.; Schmitz, C.; Geist, J.; Hickel, R.; Högg, C.; Sternecker, K. Disrupted biomineralization in zebra mussels after exposure to bisphenol-A: Potential implications for molar-incisor hypomineralization. Dent. Mater. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titorencu, I.; Pruna, V.; Jinga, V.V.; Simionescu, M. Osteoblast ontogeny and implications for bone pathology: An overview. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 355, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kylmaoja, E.; Nakamura, M.; Tuukkanen, J. Osteoclasts and remodeling based bone formation. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 11, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Society of Testing and Materials (ASTM). Standard Guide for Conducting Laboratory Toxicity Tests with Freshwater Mussels. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Sicuro, B. Freshwater bivalves rearing: A brief overview. Int. Aquat. Res. 2015, 7, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignell, J.P.; Stentiford, G.D.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Lyons, B.P. Histopathology of mussels (Mytilus sp.) from the Tamar estuary, UK. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 72, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, B. Chapter 12 The Anatomy of Dreissena polymorpha and the Evolution and Success of the Heteromyarian Form in the Dreissenoidea. In Zebra Mussels: Biology, Impacts, and Control, 1st ed.; Nalepa, T.F., Schloesser, D.W., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 185–215. [Google Scholar]
- Milz, S.; Regner, F.; Putz, R.; Benjamin, M. Expression of a wide range of extracellular matrix molecules in the tendon and trochlea of the human superior oblique muscle. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Carballal, M.J.; López, C.; Azevedo, C.; Villalba, A. Enzymes involved in defense functions of hemocytes of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1997, 70, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evariste, L.; Auffret, M.; Audonnet, S.; Geffard, A.; David, E.; Brousseau, P.; Fournier, M.; Betoulle, S. Functional features of hemocyte subpopulations of the invasive mollusk species Dreissena polymorpha. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggel, S.; Cerwenka, A.; Brandner, J.; Geist, J. Shell morphological versus genetic identification of quagga mussel (Dreissena bugensis) and zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Aquat. Invas. 2015, 10, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggel, S.; Hinzmann, M.; Machado, J.; Geist, J. Combined impact of acute exposure to ammonia and temperature stress on the freshwater mussel Unio pictorum. Water 2017, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panara, F.; Di Rosa, I.; Fagotti, A.; Simoncelli, F.; Mangiabene, C.; Pipe, R.K.; Pascolini, R. Characterization and immunocytochemical localization of actin and fibronectin in haemocytes of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Histochem. J. 1996, 28, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyachuk, V.A.; Maiorova, M.A.; Odintsova, N.A. Identification of β integrin-like- and fibronectin-like proteins in the bivalve mollusk Mytilus trossulus. Dev. Growth Differ. 2015, 57, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leprêtre, M.; Almunia, C.; Armengaud, J.; Le Guernic, A.; Salvador, A.; Geffard, A.; Palos-Ladeiro, M. Identification of immune-related proteins of Dreissena polymorpha hemocytes and plasma involved in host-microbe interactions by differential proteomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, J.; Wang, K. Fibronectin in development and wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 170, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Recent advances of shell matrix proteins and cellular orchestration in marine molluscan shell biomineralization. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addadi, L.; Joester, D.; Nudelman, F.; Weiner, S. Mollusk shell formation: A source of new concepts for understanding biomineralization processes. Chemistry 2006, 12, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, A.S.; Wheeler, A.P.; Paradkar, R.P.; Snider, D. Hemocyte-mediated shell mineralization in the eastern oyster. Science 2004, 304, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xie, L.; Zhang, R. Hemocytes in the extrapallial space of Pinctada fucata are involved in immunity and biomineralization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immel, F.; Broussard, C.; Catherinet, B.; Plasseraud, L.; Alcaraz, G.; Bundeleva, I.; Marin, F. The shell of the invasive bivalve species Dreissena polymorpha: Biochemical, elemental and textural investigations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.W.; Son, M.J.; Yun, K.S.; Kim, Y.S. Relationship between eggshell strength and keratan sulfate of eggshell membranes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterson, B.; Melrose, J. Keratan sulfate, a complex glycosaminoglycan with unique functional capability. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 182–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, O.V.; Savelieva, A.V.; Kolotuchina, N.K.; Voronezhskaya, E.E.; Dyachuk, V.A. Peripheral sensory neurons govern development of the nervous system in bivalve larvae. Evodevo 2019, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbetta, S.; Bairati, A.; Vitellaro Zuccarello, L. Immunohistochemical study of subepidermal connective of molluscan integument. Eur. J. Histochem. 2002, 46, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boute, N.; Exposito, J.-Y.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Noro, N.; Miyazaki, K.; Yoshizato, K.; Garrone, R. Type IV collagen in sponges, the missing link in basement membrane ubiquity. Biol. Cell 1996, 88, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfter, W.; Oertle, P.; Monnier, C.A.; Camenzind, L.; Reyes-Lua, M.; Hu, H.; Candiello, J.; Labilloy, A.; Balasubramani, M.; Henrich, P.B.; et al. New concepts in basement membrane biology. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 4466–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernousov, M.A.; Yu, W.-M.; Chen, Z.-L.; Carey, D.J.; Strickland, S. Regulation of Schwann cell function by the extracellular matrix. Glia 2008, 56, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cescon, M.; Bonaldo, P. The Role of Collagens in Peripheral Nerve Myelination and Function. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, C.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.J.; Yee, A.J.; Yang, B.B. Structure and function of aggrecan. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Halper, J. Tendon proteoglycans: Biochemistry and function. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2005, 5, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Coyne, K.J.; Qin, X.X.; Waite, J.H. Extensible collagen in mussel byssus: A natural block copolymer. Science 1997, 277, 1830–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamarin, A. An ultrastructural study of byssus stem formation in Mytilus californianus. J. Morphol. 1975, 145, 151–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarello, L.V. The collagen gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis: An ultrastructural and cytochemical study on secretory granules. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1980, 73, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golser, A.; Scheibel, T. Routes towards Novel Collagen-Like Biomaterials. Fibers 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatuparisute, P.; Shinohara, Y.; Kirchhoff, C.; Fischer, F.; Milz, S. Immunohistochemical composition of the human lunotriquetral interosseous ligament. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2012, 20, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppinen, L.; Pihlajaniemi, T. The multiple functions of collagen XVIII in development and disease. Matrix Biol. 2011, 30, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, D.; Amaral, I.F.; Pêgo, A.P. Laminin-inspired cell-instructive microenvironments for neural stem cells. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrino, D.A.; Dennis, J.E.; Wu, T.M.; Arias, J.L.; Fernandez, M.S.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Fink, D.J.; Heuer, A.H.; Caplan, A.I. The avian eggshell extracellular matrix as a model for biomineralization. Connect. Tissue Res. 1996, 35, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, D.P.; Carrino, D.A.; Baber, M.A.; Caplan, A.I. Generation of a monoclonal antibody against avian small dermatan sulfate proteoglycan: Immunolocalization and tissue distribution of PG-II (Decorin) in embryonic tissues. Matrix 1991, 11, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, E.M.; Bradshaw, A.D. SPARC/osteonectin in mineralized tissue. Matrix Biol. 2016, 52–54, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).