Abstract
The early host–pathogen interaction between European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Betanodavirus was examined by using juvenile fish infected intramuscularly with RGNNV (red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus). The time course selected for sampling (0–144 h post-infection (hpi)) covered the early stages of infection, with hematological, antioxidant and immunological responses examined. Early activation of the host’s immune system was seen in the first few hours post-infection (6 to 9 hpi), as evidenced by an increase in tnfα, cd28 and c3 expression in the head kidney of infected fish. Most hematological parameters that were examined showed significant differences between sampling times, including differences in the number of thrombocytes and various leukocyte populations. The plasma lysozyme concentration decreased significantly over the course of the trial, and most antioxidant parameters examined in the liver showed significant differences over the infection period. At 144 hpi, peak expression of tnfα and il-1β coincided with the appearance of disease symptoms, peak levels of virus in the brain and high levels of fish mortality. The results of the study show the importance of analyzing the early interactions between European seabass and Betanodavirus to establish early indicators of infection to prevent more severe outcomes of the infection from occurring.
1. Introduction
Intensification of marine fish production has resulted in high stocking densities and stressful culture conditions for fish, thus contributing to increased disease outbreaks within aquaculture farming systems. Viral diseases are an important obstacle for aquaculture development, due to the high economic impact associated with disease outbreaks [1]. One viral disease that has been a major problem for the aquaculture industry is viral encephalopathy and retinopathy (VER), also known as viral nervous necrosis (VNN), caused by nervous necrosis virus (NNV) [2]. NNV belongs to the family Nodaviridae, genus Betanodavirus [3]. It is a non-enveloped virus, with a diameter of 20–25 nm [4], constituting two single-stranded positive-sense RNA segments, with RNA1 encoding RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and RNA2 encoding the capsid protein [4,5]. Of the four NNV genotypes affecting fish, RGNNV (red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus) is widely distributed in Southern Europe, across the Asian coast and also in Australia [2,6,7]. The clinical signs observed depend on the fish species, the age and the developmental stage of the fish [2,8], but they usually include spiral swimming, looping behavior, exophthalmia and eye opacity [7]. Betanodavirus outbreaks mainly affect larval and juvenile stages, with mortality levels as high as 100% [7,9] in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) [10], seabream (Sparus aurata) [11] and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) [1,12].
Understanding virus pathogenicity is important for the development of therapeutic and prophylactic measures to mitigate against pathogen proliferation [13]. The first line of defense against the virus is produced by the host’s innate immune system [14], which produces a rapid and non-specific response, which is mediated by type I and II interferons (IFN), as reported to occur in NNV-infected European seabass [15]. The adaptive immune system, on the other hand, responds specifically to the pathogen, producing a highly specific and long-lasting immune response [16,17].
Early detection of the viral infection in fish is an important strategy to identify potential disease outbreaks before they occur, and it may be possible to identify biomarkers of early infection by assessing the host’s response to the developing viral infection. Although several studies have reported on the dynamics of NNV infection and associated virulence factors of the virus [7,13,15], few studies have examined early activation of the host’s response to the virus immediately after infection. The aim of this study was to evaluate the hematological, antioxidant and immunological and molecular responses in European seabass juveniles shortly after NNV infection in order to understand these responses and identify possible biomarkers that could help in an early diagnosis of the disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Time-Course Infection with RGNNV
The study was conducted in accordance with “The guidelines on animals protection used for scientific purposes from the European Directive 2010/63/EU” under project permission 0421/000/000/2019. A time-course study was performed at CETEMARES facilities (Polytechnic of Leiria, Peniche, Portugal), using 156 European seabass juveniles (31.2 ± 7.2 g). Fish were acclimated in a 2000 L tank at 25 °C and sampled to confirm that they were NNV-free. After two weeks, fish were randomly distributed into nine recirculating seawater systems, i.e., three systems per experimental condition (21 fish per tank), and three (10 fish per tank) for monitoring mortality. The animals received an intramuscular (IM) injection of either 100 µL phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.3 as the control group or 100 µL of RGNNV at 107 TCID50 mL−1 (strain ERV378/03) according to Reference [18]. The fish were maintained at 25 °C, with aeration, and were fed ad libitum with a commercial diet. Mortality, temperature, salinity and dissolved oxygen were monitored daily. Two animals per tank (n = 6 per treatment) were sampled at 0 (pre-challenge), 6, 9, 24, 48, 120 and 144 h post-infection (hpi). Fish were anesthetized with 2-phenoxyethanol (VWR Chemicals, Radnor, PA, USA) (0.5 mL L−1), blood sampled and euthanized with an overdose of anesthetic before liver, head-kidney and brain-tissue collection. Blood was sampled from the caudal vein with heparinized syringes and stored in microtubes containing 20 µL of heparin (3000 U). After hematological parameters analysis, the remaining blood was centrifuged (10,000× g at 4 °C for 10 min) for plasma collection and was stored at −80 °C until the analysis of innate humoral parameters (lysozyme concentration, peroxidase activity, antiproteases, proteases activity and production of nitric oxide). The liver, collected for determination of oxidative stress parameters (lipid peroxidation, catalase, superoxide dismutase, total glutathione and glutathione-S-transferase), was snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen after collection and stored at −80 °C until analyzed. Head kidney and brain (collected at 0 h pre-challenge, 48 and 144 hpi) were preserved in RNAlater (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 24 h at 4 °C; the RNAlater was decanted, and the samples stored at −80 °C until analysis for gene expression or virus quantification, respectively.
2.2. Hematological Parameters
The hematological profile of the European seabass was carried out by determining total red blood cell (RBC) and white blood cell (WBC) counts, using a Neubauer chamber, hemoglobin concentration (hemoglobin, SPINREACT, Spain) and hematocrit values (Ht). Differential WBC counts were made from blood smears that had been air-dried and fixed with formaldehyde–ethanol solution (90% absolute ethanol with 3.7% formaldehyde) for 1 min [19]. Neutrophils were identified according to Reference [20], and 200 leucocytes were counted, from which the percentages of neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes and thrombocytes were determined. Blood indexes, including mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), were determined according to Reference [21].
2.3. Innate Immune Humoral and Antioxidant Parameters
Plasma lysozyme concentrations were determined by using a turbidimetric assay, as described by Costas et al. [22], and calculated from a standard curve. Plasma peroxidase activity was determined according to Quade and Roth [23], with one unit of peroxidase representing an absorbance change of 1.0 OD at 450 nm.
The activity of antiproteases was determined according to Machado et al. [21], by measuring trypsin inhibition in plasma. Thus 10 μL of plasma and 10 μL of trypsin in NaCO3 (5 mg mL−1) were added and incubated for 10 min at room temperature (RT). Then, 100 μL of PBS (13.9 mg mL−1, pH 7.0) and 125 μL of azocasein (20 mg mL−1 in NaHCO3, pH 8.3) were added and incubated for 1 h, at RT. The reaction was stopped with the addition of 250 μL of trichloroacetic acid (TCA) (100 mg mL−1) and subsequently incubated for 30 min at RT. The mixture was then centrifuged (10,000× g for 5 min), and the supernatant was collected and added to 100 µL of NaOH (40 mg mL−1). Finally, samples were read in duplicate at 450 nm. The activity of proteases was also quantified in plasma by measuring the level of uninhibited trypsin according to Reference [21]. For this analysis, 10 μL of plasma, 100 μL of PBS (13.9 mg mL−1, pH 7.0) and 125 μL of azocasein (20 mg mL−1 in NaHCO3, pH 8.3) were added and incubated for 24 h, at RT. The reaction was stopped with the addition of 250 μL of TCA (100 mg mL−1) and by following the same procedure as for the activity of anti-proteases, with the samples read at 450 nm.
The production of nitric oxide in plasma was measured according to Taffala et al. [24]. A total of 25 μL of plasma, 100 μL of 1% sulfanilamide solution in 2.5% phosphoric acid and 100 μL of N-naphthylethylenediamine solution in 2.5% phosphoric acid were mixed, and after a 10-min incubation at RT, the samples were read at 540 nm. The concentration of nitrite (μMol mL−1) in the samples was determined by using a standard curve with known concentrations of sodium nitrite.
Oxidative stress biomarkers were measured in the liver samples. Liver was homogenized with 10 volumes of ultrapure water, and then a 200 µL aliquot of the homogenate was placed in a microtube with 4 μL of 4% BHT (2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) in methanol. The tissue homogenate was mixed 1:1 (v/v) with potassium phosphate buffer (0.2 M, pH 7.4) and centrifuged at 10,000× g at 4 °C for 20 min. The supernatant was stored in a new microtube at −80 °C until analysis of the oxidative-stress biomarkers.
The total protein concentration of the liver homogenate was determined by using a commercial BCA Protein Assay Kit (Pierce™, Waltham, MA USA). Liver catalase (CAT) activity was measured according to the method described by Clairborne [25], adapted as a microplate assay [26], while liver lipid peroxidation (LPO) was determined according to Bird and Draper [27]. Liver glutathione-s-transferase (GST) activity was determined as reported by Habig et al. [28] and adapted as a microplate assay by [29]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) was determined as described by Almeida et al. [30]. Total glutathione (tGSH) was measured according to Baker et al. [31] and Rodrigues et al. [26]. Total albumin concentration in the plasma was analyzed with a BCG Albumin Assay Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), according to the manufacturer instructions.
Unless otherwise stated, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.4. Viral Quantification
Viral RNA from virus supernatant (with a known TCID50 mL−1) and brain were extracted by using the NucleoSpin RNA Mini kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The yield of RNA obtained was determined by using a NanoDrop 2000 (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and its quality and integrity were verified by electrophoresis (Wide Mini-Sub Cell GT, Bio-Rad, California, CA, USA) on 2% agarose gel.
NNV quantification was performed by using a SuperScript III Platinum One-Step qRT-PCR kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with a final volume of 10 µL. Primers used were Noda Taq1-FW (5′-CAACTGACARCGAHCACAC–3′) and Noda Taq1-RV (5′-CCCACCAYTTGGCVAC–3′) and a specific probe for Betanodavirus (5′-6FAM-CARGCRACTCGTGGTGCVG-BHQ1-3′) [10], at a final concentration of 10 µM. The samples and standard curve were prepared in triplicate. The standard curve was prepared with ten-fold serial dilutions [18]. The CFX ConnectTM Real-Time System (Bio-Rad, California, USA) was used with the following conditions: reverse transcriptase—10 min at 55 °C, 5 min at 95 °C; and 40 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C and 1 min at 60 °C. With the threshold cycle (Ct) obtained, the amount of virus in the fish brains was calculated by using the equation of the line [x = (yc)/m] determined with the standard curve Ct values plotted against TCID50.
2.5. Immune Gene Expression
RNA was extracted from the head kidney by using an NZY Total RNA isolation kit (NZYTech, Lisbon, Portugal), according to the supplier’s instructions. Extracted RNA was evaluated by spectrophotometry (NanoDrop 2000, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and the quality and integrity of RNA were verified as described above. Then cDNA synthesis was performed on a T100TM Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, California, CA, USA), following the instructions of the NZY First-Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (NZYTech, Lisbon, Portugal).
The immune genes selected for analysis included endogenous Mx protein (MXA), interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), complement component (C3), T-cell-specific surface glycoprotein (CD28), tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β). The housekeeping gene, β-actin (ACTB), was used for gene normalization. Published primers for the selected immune genes are shown in Supplementary Table S1. The efficiency of the primers was evaluated through linear regression, taking into account the slope and the average threshold cycle (Ct) obtained. CFX ConnectTM Real-Time System (Bio-Rad, California, CA, USA) was used for the immune-gene quantitative PCR (qPCR). The qPCR reaction was performed with 1 µL of cDNA (5-fold dilution factor), 0.3 µL of each primer (reverse and forward, at 10 µM each) and 5 µL of iTaqTM Universal SYBR® Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, California, CA, USA) at a final volume of 10 µL. Standard cycle conditions were 95 °C for initial denaturation for 3 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s for denaturation and annealing/extension for 20 s with temperature-specific conditions for each set of primers (Supplementary Table S1). All the samples were analyzed in triplicate. The samples were normalized by using the housekeeping gene, and gene expression was determined according to Pfaffl [32].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Hematological data, innate immune and antioxidant parameters, and gene expression are presented as the mean of six replicates ± standard deviation (SD). Data from each parameter were tested for significant statistical differences, using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), with sampling time as a factor, followed by multiple comparison’s tests—Tukey’s test, whenever assumptions of homogeneity and normality were met. For virus quantification, a t-test was performed. In cases where data did not meet homogeneity and normality assumptions, a Kruskal–Wallis test was performed. Statistical significance was tested at p < 0.05, and all statistical analysis was performed by using IBM’s SPSS software (version 27, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Mortality
The level of cumulative mortality obtained in the experimentally infected European seabass is presented in Figure 1. No mortality was observed in the control group. Typical clinical signs of VER, exophthalmia and fast looping were observed in the infected group with 33.3% mortality 5 days post-infection (dpi), and reaching maximum mortality of 86.7% by 9 dpi.
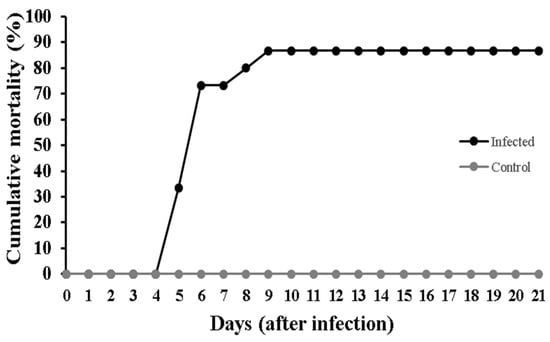
Figure 1.
Percentage of cumulative mortality recorded in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) control and RGNNV-infected fish, using triplicate tanks of ten fish per group.
3.2. Hematological Parameters
The hematological profile of European seabass infected with RGNNV is presented in Table 1. Most parameters showed significant differences between sampling times (p < 0.05), except for the total erythrocyte counts, hematocrit % and MCV. Leucocyte and thrombocytes counts decreased significantly at 9 hpi. Neutrophil numbers increased at almost every sampling point, except at 48 hpi, and monocytes displayed a similar trend, but they did not increase at 9 hpi. Lymphocytes decreased at 6 hpi and returned to basal values at 48 hpi, only to decrease again at 144 hpi. Hemoglobin concentration increased at 24 hpi, accompanied by the increase in MCH and MCHC values at the same sampling time point.

Table 1.
Hematological parameters of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) infected with RGNNV at different sampling times post-infection.
3.3. Innate Humoral Parameters and Biomarkers
The immune parameters evaluated in European seabass infected with RGNNV are presented in Figure 2. The plasma lysozyme concentration decreased significantly over the course of the trial, from pre-challenge to 144 hpi (p < 0.05), while plasma peroxidase, antiproteases and proteases activity did not show any significant differences related to the infection (p > 0.05). Nitric oxide, however, showed a significant increase at 24 and 144 hpi (p < 0.05).
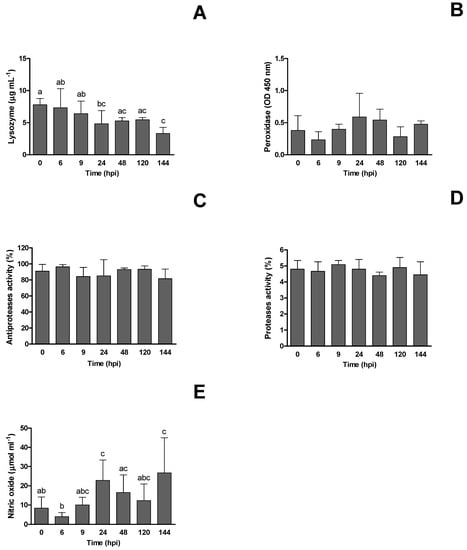
Figure 2.
Innate humoral parameters of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) infected with RGNNV at different hours post-infection (hpi): (A) lysozyme concentration, (B) peroxidase activity, (C) antiproteases activity, (D) proteases activity and (E) nitric oxide are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). One-way ANOVA was used to compare between different sampling times. Different letters show statistically significant differences between sampling times (p < 0.05).
The antioxidant activity in the liver and albumin in the blood of European seabass infected with RGNNV are presented in Figure 3. All parameters showed significant differences between sampling times (p < 0.05), except for SOD activity and plasma albumin concentration (p > 0.05). The CAT started to decrease after 9 hpi and remained lower until the final sampling time at 144 hpi. The GST activity was reduced at 144 hpi when compared to values at 9, 24 and 48 hpi. A similar trend was observed for tGSH, but values were also reduced at 120 h when compared to 9, 24, and 48 hpi. The LPO increased after 48 hpi until the end of the sampling period.
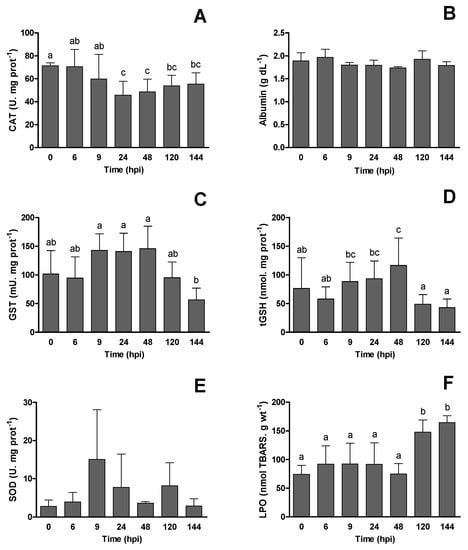
Figure 3.
Antioxidant activity in the liver and albumin plasma concentration in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) infected with RGNNV at different sampling times post-infection (hpi): (A) catalase activity (CAT), (B) albumin, (C) glutathione-s-transferase activity (GST), (D) total glutathione (tGSH), (E) superoxide dismutase (SOD) and (F) lipid peroxidation (LPO). Values are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). One-way ANOVA was used to compare between different sampling times. Different letters show statistically significant differences between sampling times (p < 0.05).
3.4. Viral Quantification
A standard curve was prepared by using serial dilutions of viral RNA to establish a linear regression between mean Ct values and dilutions, with a starting concentration of NNV at TCID50 = 107 mL−1 (Supplementary Figure S1). The quantification of the virus in unknown samples was determined from the following equation: y = −3.5422x + 36.407, with R2 = 0.9945.
The quantification of NNV in brain tissue was determined at 48 and 144 hpi. Virus was not detected at 0 hpi prior to infection. There was a significant increase (p < 0.05) in the amount of virus detected at 48 (8.24 × 105 TCID50 mL−1) and 144 hpi (1.18 × 107 TCID50 mL−1). No virus was detected in the control fish.
3.5. Immune Genes Expression
The expression of immune genes in the head kidney of European seabass was evaluated after infecting the fish with NNV. At 48 hpi, a significant increase in mxA gene expression was observed, and then it decreased until the end of the sampling period at 144 hpi (Figure 4A). irf3 expression peaked at 6 hpi and then decreased from that point until 24 hpi, with the expression between 6 and 24 hpi being significantly lower. Maximum expression was observed at 48 hpi (Figure 4B). Expression in c3 decreased during the first 9 hpi from its basal levels (0 hpi) to almost being undetectable, whereas it increased significantly thereafter, remaining almost constant until the last sampling point, when maximum expression was seen (Figure 4C). cd28 expression significantly increased up to 9 hpi, returned to baseline at 48 hpi, and then remained constant until the end of sampling (Figure 4D). tnfα expression significantly decreased at 48 hpi when compared to baseline values, and then it increased again significantly at 144 hpi (Figure 4E). Regulation of the il-1β gene increases significantly at 6 hpi, stabilizing its gene expression until 24 hpi, then decreasing at 48 hpi, and increasing again at 144 hpi, when the maximum expression of il-1β was observed (Figure 4F).
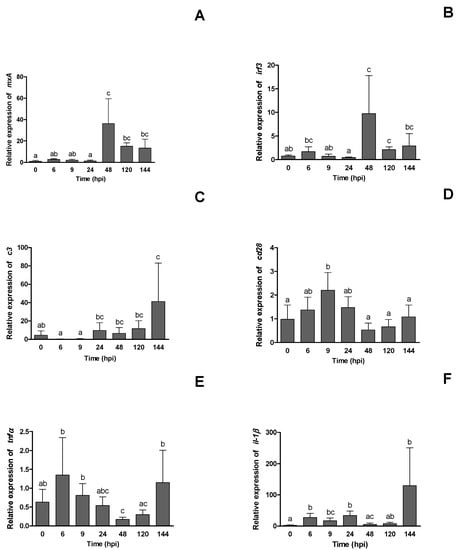
Figure 4.
Relative expression of selected immune genes: (A) endogenous Mx protein, mxA; (B) interferon regulatory factor 3, irf3; (C) complement component, c3; (D) T-cell-specific surface glycoprotein, cd28; (E) tumor necrosis factor alpha, tnfα; and (F) interleukin 1 beta, il-1β, in the head-kidney samples at 0 h (pre-challenge), 6, 9, 24, 48, 120 and 144 h post-infection (hpi) with NNV of European seabass. Values are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). One-way ANOVA was executed to compare between different sampling times. Different letters show statistically significant differences between sampling times (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
We examined the early host–pathogen interaction between European seabass juveniles and RGNNV in order to understand when distinct host defense mechanisms are activated against the virus. Infection-related mortalities started from 5 dpi, with peak mortalities occurring by 9 dpi. The time for the first mortalities to be observed was in line with other studies [33,34]. The duration of experimental infection was extended beyond the sampling period; however, it was based on the challenge model we used [35]. In accordance with the literature [36], seven band grouper (Hyporthodus sptemfasciatus) infected IM with 102.5 TCID50 100 µL−1 fish−1 recorded a peak mortality of 6 dpi (144 hpi). In this study, mortality started at 5 dpi, and at sampling period (6 dpi–144 hpi), the number of viral particles present in the brain (1.18 × 107 TCID50 mL−1) was statistically higher when compared to 48 hpi (8.24 × 105 TCID50 mL−1), indicating a significant increase in the viral load and consequent infection in the host.
At 9 hpi, leukocytes and thrombocyte numbers were at their lowest level. This early decrease might indicate migration of the cells into the affected tissues at the infected site [37]. Both neutrophil and monocyte numbers displayed a similar trend, with numbers of cells increasing in the blood from 6 hpi and for most of the time thereafter. This rapid response by these cells is expected as part of the development of the inflammation process, since neutrophils are the first cells to move to a site of infection, followed by monocytes [38], explaining the higher number of these cells circulating as they move to the inflamed tissues. In the acute stage of an infection, a decrease in the number of lymphocytes is often seen, resulting in lymphopenia and being a sign of immune exhaustion [39]. Such a decrease in the lymphocytes population was observed on day 5 (120 hpi), when the first mortalities were observed, and a further drop was seen on day 6 (144 hpi), when mortality levels reached 73.3%. Hemoglobin and the associated indexes (MCH and MCHC) were augmented at 24 hpi, indicating that, at this time, oxygen was more efficiently transported in the blood, and with the infection undergoing, the capacity of the red blood cells to transport oxygen decreased.
Lysozyme, an innate humoral component, plays an important role in the primary line of defense against pathogens [40]. As the NNV infection progressed, lysozyme concentrations gradually reduced from 24 hpi onwards. This result is in line with immune depression previously noted by Reference [41], who described a similar relationship between lysozyme and lymphocytes levels being suppressed simultaneously. The fact that peroxidase activity was unchanged remains to be clarified, as it does not reflect the changes in neutrophil numbers observed. Nitric oxide has an active role in inhibiting virus replication, helping viral clearance and host recovery [42,43]. Its production can occur in neutrophils and monocytes [21,44], and it is critical for fish survival [45]. The production of nitric oxide in cells [45] may function as a response to pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), parasites [46] and viral infections [47]. Infection of Scophthalmus maximus renal macrophages with viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) in vitro [46] resulted in the production of nitric oxide induced by the viral infection. As seen in the present study, there was a significant increase in nitric oxide production at 24 and 144 hpi, suggesting that this increase may be involved in inhibiting viral replication [48]. These results indicate that, in the first hours after viral infection, nitric oxide is produced by neutrophils and monocytes, with peak production at 144 hpi.
Antioxidant enzyme activity is a defense mechanism against oxidative stress and is considered to be part of the innate immune response. In the case of CAT, this activity was reduced from 9 hpi onwards, showing a decreased capacity to deal with oxidative imbalance, which can have a detrimental effect on other cellular processes [49]. GST levels increased and then decreased over the course of the infection, with the lowest levels observed at 144 hpi, reflecting the activity of tGSH, which disrupts glutathione-based antioxidant systems and further increases oxidative stress [50]. The inhibition of both enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant systems is reflected by lipid peroxidation (LPO). Lipid peroxidation was significantly higher at 120 and 144 hpi, indicating the time when cells started to become damaged by an oxidative imbalance, and which corresponded with the mortality starting at 120–144 hpi.
After infection with Betanodavirus, viral particles enter the host cell’s cytoplasm and initiate transcription and translation through the release of their viral genome [1]. This results in a “signaling cascade” of intercellular molecules [17] that activates an antiviral response by the host. Endogenous Mx protein (Mx) interacts with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) right after its translation in an attempt to degrade the viral protein through the process of autophagy [51,52]. Mx plays an important role in the control of NNV infection, as reported in grouper (Epinephelus coioides) [53]. In the present study, a significant increase in mxA gene expression was noted after 48 hpi, suggesting that the host’s defenses had detected the presence of the virus and were trying to inhibit viral replication through the production of Mx. The expression of mxA was previously observed from 24 hpi in the brain and head kidney of European seabass and Gilthead seabream, using the same viral dose as we used in our study (106 TCID50 of NNV) [54]; however, mxA expression was still at basal levels at this time post-infection in our study. We also saw further upregulation of this gene at 120 and 144 hpi, in accordance with other study [14] whose authors observed a significant upregulation of mx expression in the head kidney of European seabass infected with NNV up to 168 hpi. On the other hand, the onset of mx expression in fish infection with RGNNV [55,56] appears to be related to their life stage, the viral isolates and method of infection, ranging from 6 to 72 hpi.
Interleukins (IL), interferon (IFN), tumor necrosis factor (TNF) [57], antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), T-cell markers and immunoglobulins are induced in a cascade as an immune response [1]. IRF3 is a key regulator of type I IFN gene expression in response to viral infection [1]. In the present study, irf3 expression was also upregulated at 48 hpi, again indicating the host’s attempt to control and eliminate the virus by inhibiting viral replication. The expression of mx and ifn genes in the brain of sea bream and seabass infected with NNV has been observed previously [14,58].
AMPs recruit effector cells to the site of infection [59,60]. They act against a wide range of pathogens, including non-enveloped viruses, such as NNV [61]. The C3 gene, which is an AMP, is part of the complement system and is directly involved in the host cell defense [62,63]. The expression of this gene increased significantly from 24 hpi, maintaining its expression until 144 hpi, suggesting that this gene is expressed early after the infection occurs and functions as an activator of the immune system [1]. Upregulation of c3 in the gonad and brain of European seabass and Gilthead sea bream was observed in response to infection with NNV [59].
Adaptive immunity is dependent on the activation of T cells [64], which are activated by a costimulatory signal from antigen-presenting cells (APCs) [65]. This signal arises from the binding of CD80 and CD86 to CD28 [66,67]. cd28 is expressed on the surface of most T cells, with higher values seen in activated cells [65]. Activation of CD28 promotes T-cell proliferation, which produces cytokines, such as interleukins, and aids cell survival [68]. The expression of this gene in the head kidney and brain of fish after infection with NNV has showed maximum expression at 24 hpi (first sampling time) and decreases thereafter [64]. We observed the expression of cd28 to achieve its maximum at 9 hpi, reducing its values until 48 hpi; thereafter, cd28 expression increased slightly until the end of the trial. Higher and lower cd28 expression suggests that, as the NNV infection progresses, cd28 expression tended to a stimulation of T cells and modulation of the metabolic processes that regulate the pro-inflammatory T-cell response [64].
NNV infection in European seabass triggers the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNFα and IL-1β. TNFα is an important mediator in resistance against bacterial and viral infections, regulating inflammation and apoptosis of target cells [56]. It is produced mainly by macrophages [69] and triggers the expression of numerous genes, such as IL-1β, a chemoattractant pro-inflammatory cytokine for leukocytes in fish [70,71]. It regulates immune responses and is an indicator of inflammation and neurodegeneration of the central nervous system [72]. These two pro-inflammatory cytokines can be rapidly secreted in response to a stimulus caused by an infectious agent [73]. In the present study, an increase in tnfα expression was recorded in the first few hours ( 6, 9 and 24) post-infection and at 144 hpi, coinciding with the increase in nitric oxide also at this time, thus corroborating their relationship. This is explained by the fact that this gene regulates inflammation at the beginning of the infection, as it increases the phagocytic activity of leukocytes in fish [70]. The expression of il-1β may have been triggered by tnfα, which was also seen to be expressed in the first few hours post-infection. However, this interleukin showed a high level of expression at 144 hpi relative to basal levels seen at 0 hpi, when high numbers of neutrophils and monocytes were present in the blood. The presence of such blood cells suggests the presence of high levels of viral particles, and these blood cells migrate to the site of infection, due to the stimulation of leukocytes by the infection [70]. Typical brain-tissue damage caused by NNV infection may be related to the overexpression of these cytokines [14] that is associated with the high level of mortality recorded in the present study.
5. Conclusions
Early detection of responses against Betanodavirus infections could help the industry deal with disease problems more effectively, and that was evident in European seabass juveniles in this trial. The early reduction of WBCs is a common response to infection and seemed to also occur during NNV infection, while the increased neutrophils at 144 hpi were accompanied by an increase in nitric oxide concentration produced by these cells. Furthermore, the antioxidant defenses started to decrease by 120 hpi, resulting in lipidic damage. Interaction between NNV and the immune responses could be seen within a few hours after infection, as verified by the expression of c3 and cd28, and control of viral replication through the expression of mxA and irf3. The dynamics of the interaction between the virus and the host response could be seen over the time course of 144 hpi, coinciding with increased expression of tnfα and il-1β, which ultimately results in high levels of mortality. Acute infection was obtained with the virus dose used; however, a less severe infection in which fish can survive may help us to understand how the host’s immune response can overcome the virus.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes7020063/s1. Figure S1: Standard curve of the mean Ct value of each of the samples in real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), according to the 10 in 10 dilutions of known NNV TCID50 concentrations.. Table S1: Genes related to the immune system of NNV-infected European seabass analyzed in real-time PCR [74,75,76,77].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P., J.Z.C., K.D.T. and T.B.; methodology, M.V. and T.B.; software, M.V. and R.P.; validation, A.P., J.Z.C., K.D.T. and T.B.; formal analysis, M.V., M.S. and R.P.; investigation, M.V., D.P., P.P., P.S., B.d.C., R.P. and T.B.; resources, A.P. and T.B.; data curation, M.V., D.P., P.P., P.S., B.d.C. and R.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.V.; writing—review and editing, D.P., M.S., P.S., B.d.C., R.P., J.Z.C., K.D.T. and T.B.; visualization, M.V.; supervision, A.P. and T.B.; project administration, A.P. and T.B.; funding acquisition, A.P. and T.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) through the strategic projects UIDB /04292/2020 and UIDP/04292/2020 granted to MARE and the project MAR-02.05.01-FEAMP-0013.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with “The guidelines on animals protection used for scientific purposes from the European Directive 2010/63/EU” under project permission 0421/000/000/2019.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data regarding the results presented in this article will be made available upon reasonable request to the author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Yang, Z.; Yue, G.H.; Wong, S.-M. VNN disease and status of breeding for resistance to NNV in aquaculture. Aquac. Fish. 2022, 7, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandín, I.; Souto, S. Betanodavirus and VER Disease: A 30-year Research Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fauquet, C.M.; Mayo, M.A. The 7th ICTV Report. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.-I.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K.; Arimoto, M.; Mushiake, K.; Furusawas, I. Properties of a New Virus Belonging to Nodaviridae Found in Larval Striped Jack (Pseudocaranx dentex) with Nervous Necrosis. Virology 1992, 187, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delsert, C.; Morin, N.; Comps, M.A. Fish encephalitis virus that differs from other nodaviruses by its capsid protein processing. Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Furuhashi, M.; Nagai, T.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K. Genomic classification of fish nodaviruses by molecular phylogenetic analysis of the coat protein gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1633–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zorriehzahra, M.J. Chapter 30—Viral Nervous Necrosis Disease. Emerg. Reemerging Viral Pathog. 2020, 1, 673–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, B.L.; Kwang, J.; Moody, N. Betanodavirus infections of teleost fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, R.; Amundsen, M.; Dannevig, B.H.; Sommer, A.I. Acute and persistent experimental nodaviruses infection in spotted wolfish Anarhichas minor. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 57, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarin, V.; Patarnello, P.; Mori, A.; Rampazzo, E.; Cappellozza, E.; Bovo, G.; Cattoli, G. Development and validation of a real-time TaqMan PCR assay for the detection of betanodavirus in clinical specimens. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitchava, K.; Chassalevris, T.; Lampou, E.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Economou, V.; Dovas, C.I. Occurrence and molecular characterization of betanodaviruses in fish and invertebrates of the Greek territorial waters. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ødegård, J.; Sommer, A.-I.; Præbel, A.K. Heritability of resistance to viral nervous necrosis in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquaculture 2010, 300, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.; Souto, S.; Leiva-Rebollo, R.; Borrego, J.J.; Bandín, I.; Alonso, M.C. Capsid amino acids at positions 247 and 270 are involved in the virulence of betanodaviruses to European sea bass. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisa-Beiro, L.; Dios, S.; Montes, A.; Aranguren, R.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Nodavirus increases the expression of Mx and inflammatory cytokines in fish brain. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scapigliati, G.; Bounocore, F.; Randelli, E.; Casani, D.; Meloni, S.; Zarletti, G.; Tiberi, M.; Pietretti, D.; Boschi, I.; Manchado, M.; et al. Cellular and molecular immune responses of the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) experimentally infected with betanodavirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, S.K. The innate immune response of finfish—A review of current knowledge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnoy, A.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Srisapoome, P. Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Specific to the IgM Heavy Chain of Bighead Catfish (Clarias macrocephalus): A Biomolecular Tool for the Detection and Quantification of IgM Molecules and IgM+ Cells in Clarias Catfish. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, I.A.; Costa, J.Z.; Macchia, V.; Thompson, K.D. Detection of Betanodavirus in experimentally infected European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax, Linnaeus 1758) using non-lethal sampling methods. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplow, L.S.; Ladd, C. Brief report: Simplified myeloperoxidase stain using benzidine dihychloride. Blood 1965, 26, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afonso, A.; Lousada, S.; Silva, J.; Ellis, A.E.; Silva, M.T. Neutrophil and macrophage responses to inflammation in the peritoneal cavity of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. A light and electron microscopic cytochemical study. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1998, 34, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, M.; Azeredo, R.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; Afonso, A.; Peres, H.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Costas, B. Dietary tryptophan and methionine as modulators of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) immune status and inflammatory response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costas, B.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A.; Afonso, A. Dietary arginine and repeated handling increase disease resistance and modulate innate immune mechanisms of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quade, M.J.; Roth, J.A. A rapid, direct assay to measure degranulation of bovine neutrophil primary granules. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 58, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffala, C.; Gómez-León, J.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. Nitric oxide production by carpet shell clam (Ruditapes decussatus) hemocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairborne, A. Catalase activity. In Handbook of Methods of Oxygen Radical Research; Grenwald, R.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Gravato, C.; Quintaneiro, C.; Bordalo, M.D.; Barata, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pestana, J.L.T. Energetic costs and biochemical biomarkers associated with esfenvalerate exposure in Sericostoma vittatum. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, R.P.; Draper, A.H. Comparative studies on different methods of malondihaldehyde determination. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 90, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione-S-transferases: The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasco, M.F.; Guilhermino, L. Effects of dimethoate and betaphthoflavone on selected biomarkers of Poecilia reticulate. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 26, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Oliveira, C.; Gravato, C.; Guilhermino, L. Linking behavioural alterations with biomarkers responses in the European seabass Dicentrarchus labrax L. exposed to the organophosphate pesticide fenitrothion. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.A.; Ceniglia, G.J.; Zaman, A. Microtiter plate assay for the measurement of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in large numbers of biological samples. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 190, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skliris, G.P.; Richards, R.H. Induction of nodavirus disease in seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax, using different infection models. Virus Res. 1999, 63, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jimena, B.; Alonso, M.C.; Thompson, K.D.; Adams, A.; Infante, C.; Castro, D.; Borrego, J.J.; Garcia-Rosado, E. Tissue distribution of Red Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) genome in experimentally infected juvenile European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 154, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Mabrok, M.; Machado, M.; Azeredo, R.; Afonso, A.; Esteban, M.A.; Costas, B. Mucosal and systemic immune responses in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup) bath challenged with Tenacibaculum maritimum: A time-course study. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-O.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, J.-O.; Kim, W.-S.; Oh, M.-J. Distribution of nervous necrosis virus (NNV) in infected sevenband grouper, Hyporthodus septemfasciatus by intramuscular injection or immersion challenge. Aquaculture 2018, 489, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosik, M.; Tokarz-Deptula, B.; Deptula, W. Characterisation of thrombocytes in Osteichthyes. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campos-Sánchez, J.C.; Esteban, M.Á. Review of inflammation in fish and value of the zebrafish model. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, L.N.F.; Favero, G.C.; Zanuzzo, F.S.; Urbinati, E.C. Distinct β-glucan molecules modulates differently the circulating cortisol levels and innate immune responses in matrinxã (Brycon amazonicus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Cuesta, A.; Abellán, E.; Mesenguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. Comparative analysis of the humoral immunity of skin mucus from several marine teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, R.; Correia, A.P.; Pires, D.; Pires, P.; Ferreira, I.; Simões, M.; do Carmo, B.; Santos, P.; Pombo, A.; Afonso, C.; et al. Potential use of macroalgae Gracilaria gracilis in diets for European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax): Health benefits from a sustainable source. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 119, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, C.S.; Komatsu, T. Does nitric oxide play a critical role in viral infections? J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4547–4551. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/epdf/10.1128/JVI.72.6.4547-4551.1998 (accessed on 4 January 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eddy, F.B. Role of nitric oxide in larval and juvenile fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 142, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costas, B.; Rêgo, P.C.N.P.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Afonso, A. Dietary arginine supplementation decreases plasma cortisol levels and modulates immune mechanisms in chronically stressed turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquac. Nutr. 2013, 19, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Yang, D.; Jiang, M.; Zheng, J.; Peng, B. l-aspartic acid promotes fish survival against Vibrio alginolyticus infection through nitric oxide-induced phagocytosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taffala, C.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Role of nitric oxide on the replication of viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV), a fish rhabdovirus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 72, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Guerrero, J.A.; Carrasco, L. Effect of nitric oxide on poliovirus infection of two human cell lines. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2538–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lisi, F.; Zelikin, A.N.; Chandrawati, R. Nitric oxide to fight viral infections. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G.; Harikrishnan, R.; Paray, B.A.; Al-Sadoon, M.K.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Balasundaram, C. Effect of symbiotic supplemented diet on innate-adaptive immune response, cytokine gene regulation and antioxidant property in Labeo rohita against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Yousefi, S.; Doan, H.V.; Ashouri, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense in Fish: The Implications of Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Synbiotics. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Lu, Y.-F.; Chi, S.-C. Anti-viral mechanism of barramundi Mx against betanodavirus involves the inhibition of viral RNA synthesis through the interference of RdRp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Tsai, P.-Y.; Chan, J.-C.; Chi, S.-C. Endogenous grouper and barramundi Mx proteins facilitated the clearance of betanodavirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 59, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Su, Y.-L.; Shie, P.-S.; Huang, S.-L.; Yang, H.-L.; Chen, T.-Y. Grouper Mx confers resistance to nodavirus and interacts with coat protein. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Guardiola, F.A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A.; Cuesta, A. Nodavirus infection induces a great innate cell-mediated cytotoxic activity in resistant, gilthead seabream, and susceptible, European sea bass, teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, C.; Garcia-Rosado, E.; Borrego, J.J.; Alonso, M.C. SJNNV down-regulates RGNNV replication in European sea bass by the induction of the type I interferon system. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, P.; Lopez-Jimena, B.; Randelli, E.; Scapigliati, G.; Buonocore, F.; Garcia-Rosado, E.; Borrego, J.J.; Alonso, M.C. Immuno-related gene transcription and antibody response in nodavirus (RGNNV and SJNNV)-infected European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 78, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.Z.; Thompson, K.D. Understanding the interaction between Betanodavirus and its host for the development of prophylactic measures for viral encephalopathy and retinopathy. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 53, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Muñoz, A.; Sepulcre, M.P.; García-Moreno, D.; Fuentes, I.; Béjar, J.; Manchado, M.; Álvarez, M.C.; Mesenguer, J.; Mulero, V. Viral nervous necrosis virus persistently replicates in the central nervous system of asymptomatic gilthead seabream and promotes a transient inflammatory response followed by the infiltration of IgM+ B lymphocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 37, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, Y.; García-Alcázar, A.; Esteban, M.Á.; Cuesta, A.; Chaves-Pozo, E. Antimicrobial response is increased in the testis of European sea bass, but not in gilthead seabream, upon nodavirus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, Y.; Arizcun, M.; Cortés, J.; Ramírez-Cepeda, F.; Guzmán, F.; Mercado, L.; Esteban, M.Á.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. NK-lysin, dicentracin and hepcidin antimicrobial peptides in European sea bass. Ontogenetic development and modulation in juveniles by nodavirus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 103, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, A.; Ortega-Villaizan, M.; Chico, V.; Brocal, I.; Perez, L.; Coll, J.M.; Estepa, A. Antimicrobial Peptides as Model Molecules for the Development of Novel Antiviral Agents in Aquaculture. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshra, H.; Li, J.; Sunyer, J.O. Recent advances on the complement system of teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Lui, A.; Giari, L.; Castaldelli, G.; Mulero, V.; Noga, E.J. Infiltration and activation of acidophilic granulocytes in skin lesions of gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata, naturally infected with lymphocystis disease virus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, C.; Esteban, M.A.; Cuesta, A. Molecular characterization of the T cell costimulatory receptors CD28 and CTLA4 in the European sea bass. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 109, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeswin, J.; Jeong, S.-M.; Jeong, J.-M.; Bae, J.-S.; Kim, M.-C.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, C.-I. Molecular characterization of a T cell co-stimulatory receptor, CD28 of rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus): Transcriptional expression during bacterial and viral stimulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreno, B.M.; Collins, M. The B7 family of ligands and its receptors: New Pathways for Costimulation and Inhibition of Immune Responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Takizawa, F.; Furihata, M.; Soto-Lampe, V.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Fischer, U. Teleost cytotoxic T cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 95, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-h.; Sun, B.-g.; Deng, T.; Sun, L. Molecular characterization of Cynoglossus semilaevis CD28. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Tan, C.S.; Wang, T.-Y.; Hwong, C.-L.; Chen, T.-Y. Characterization of betanodavirus quasispecies influences on the subcellular localization and expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 103, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Chen, B.; Mao, M.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Cui, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the interleukin 1b gene in Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 88, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chi, S.-C. Interleukin-1β secreted from betanodavirus-infected microglia caused the death of neurons in giant grouper brains. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 70, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.O.; Chang, S.H.; Nurieva, R.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.; Hood, L.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, Q.; et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 6, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byadgi, O.; Beraldo, P.; Volpatti, D.; Massimo, M.; Bulfon, C.; Galeotti, M. Expression of infection-related immune response in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) during a natural outbreak from a unique dinoflagellate Amyloodinium ocellatum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, P.; Gemez-Mata, J.; Garcia-Rosado, E.; Bejar, J.; Labella, A.M.; Souto, S.; Alonso, M.C. Differential immunogene expression profile of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) in response to highly and low virulent NNV. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, Y.; Morcillo, P.; Meseguer, J.; Bounocore, F.; Esteban, M.Á.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. Characterization of the IFN pathway in the teleost fish gonad against vertically transmitted viral nervous necrosis virus. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 96, 2176–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.; Azeredo, R.; Fontinha, F.; Fernández-Boo, S.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Costas, B. Dietary Methionine Improves the European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Immune Status, Inflammatory Response, and Disease Resistance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).