Properties and Characteristics of Acid-Soluble Collagen from Salmon Skin Defatted with the Aid of Ultrasonication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
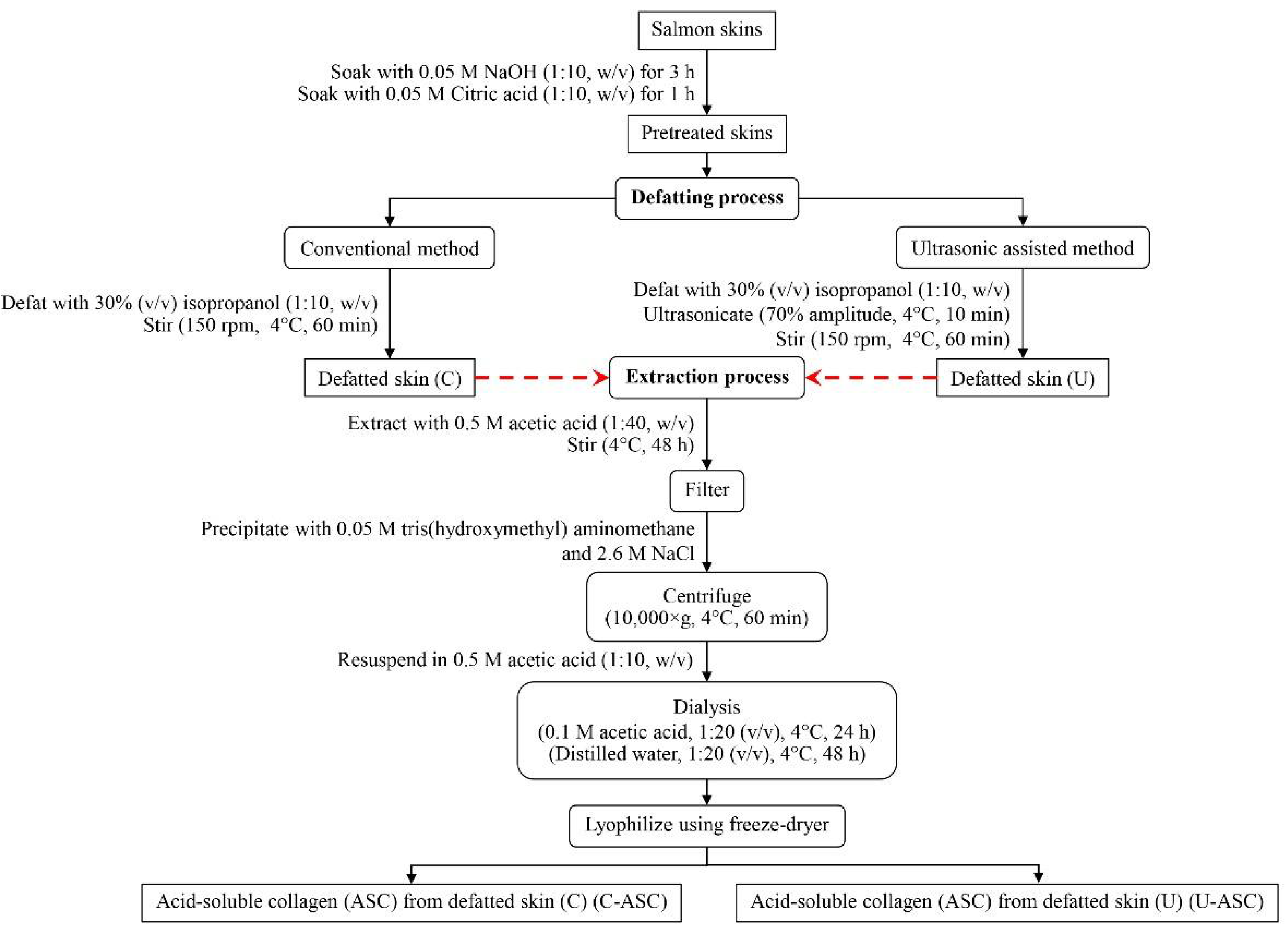
2.2. Preparation of Salmon Skin
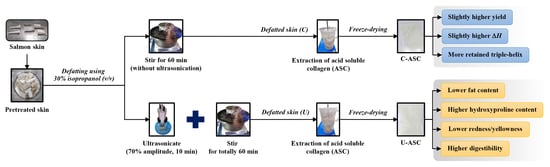
2.3. Effect of Defatting Process of Salmon Skin
2.3.1. Conventional Method
2.3.2. Ultrasonic-Assisted Method
2.4. Collagen Extraction from Defatted Salmon Skins
2.5. Analyses
2.5.1. Extraction Yield
2.5.2. Fat Content
2.5.3. Hydroxyproline Content
2.5.4. Color
2.5.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
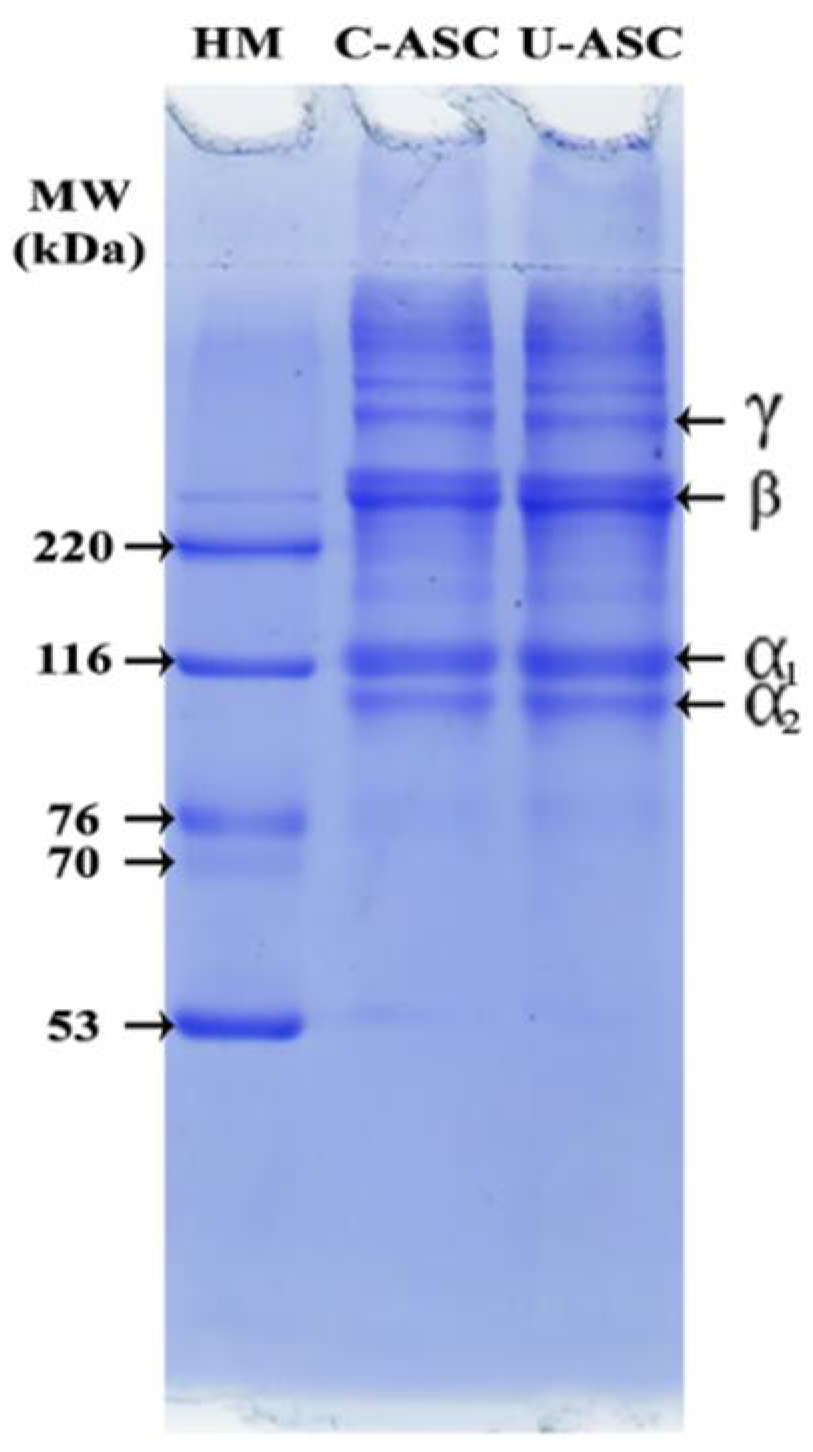
2.5.6. Protein Patterns
2.5.7. Zeta Potential
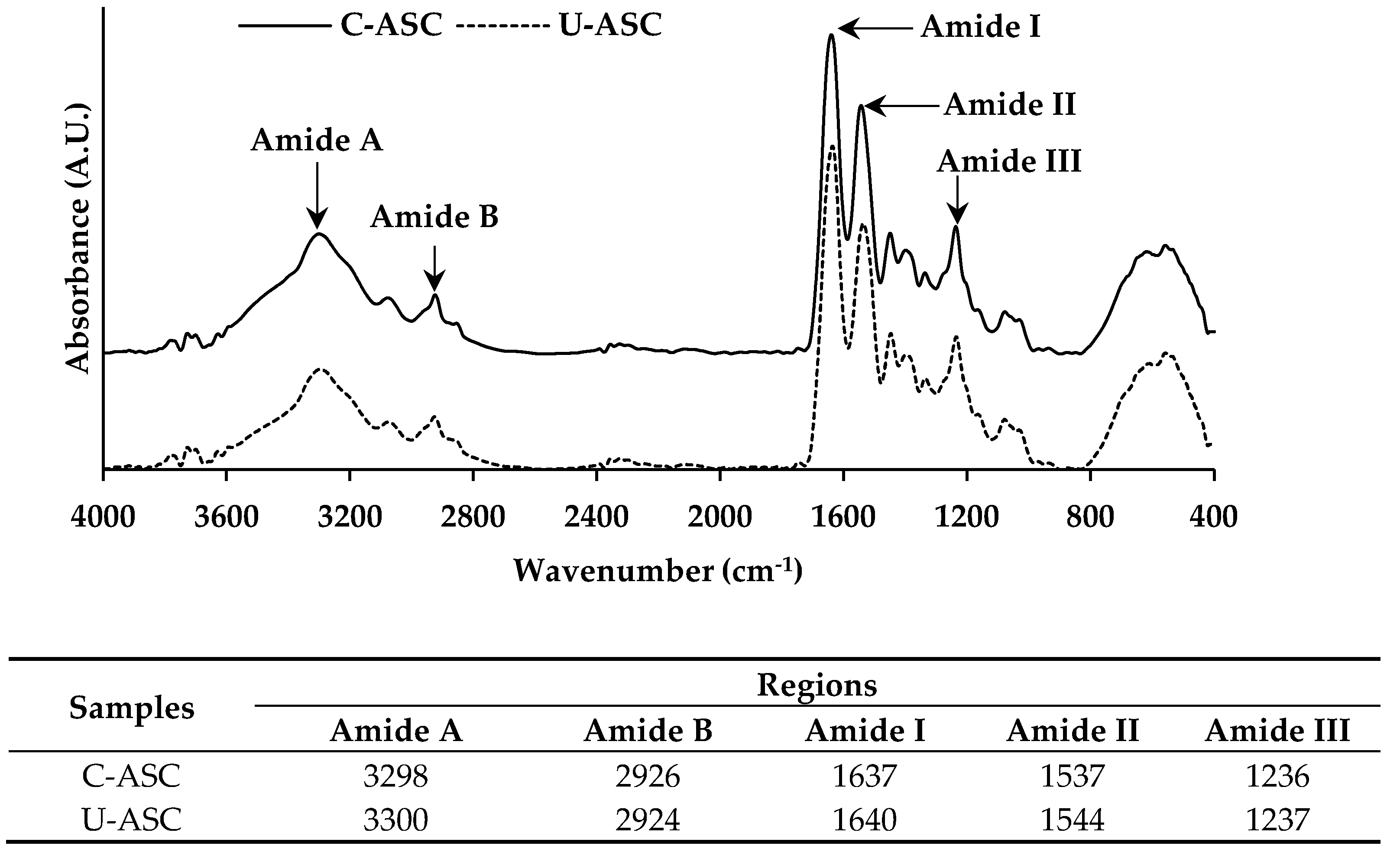
2.5.8. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.5.9. Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.5.10. Amino Acid Composition
2.5.11. Digestibility and Antioxidant Activities of ASC in Gastrointestinal Digestion Model System
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extraction Yield
3.2. Fat Content
3.3. Hydroxyproline Content
3.4. Color
3.5. DSC Thermogram
3.6. Protein Pattern
3.7. Zeta Potential
3.8. FTIR Spectra
3.9. CD Spectra
3.10. Amino Acid Composition
3.11. Digestibility and Antioxidant Activities of C-ASC and U-ASC in Gastrointestinal Digestion Model System
3.11.1. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
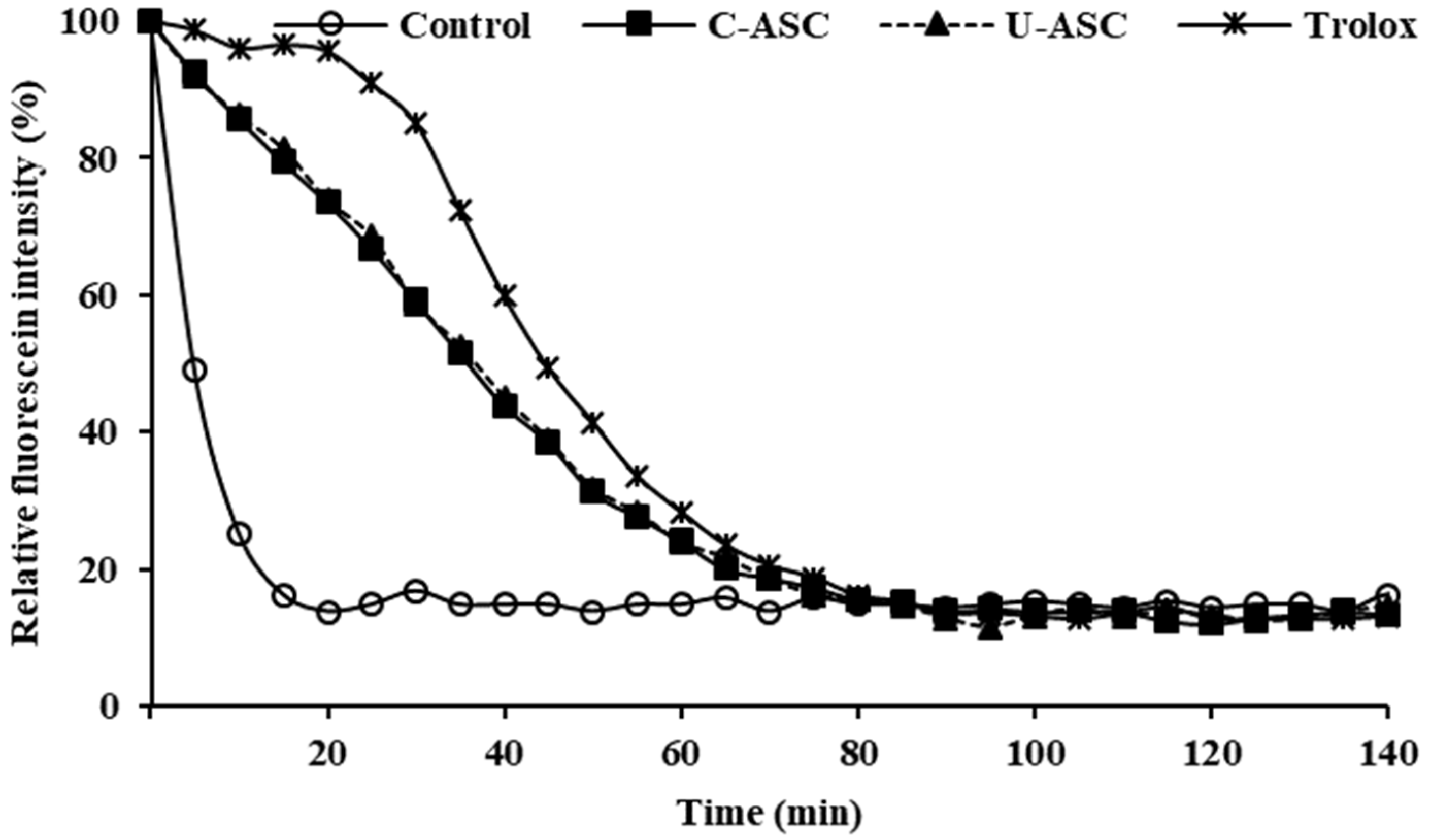
3.11.2. Antioxidant Activities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCormick, R.J. Collagen. In Applied Muscle Biology and Meat Science; Du, M., McCormick, R.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 130–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Structural, functional, rheological, and biological properties of the swim bladder collagen extracted from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, R. Identification and release kinetics of peptides from tilapia skin collagen during alcalase hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lau, C.-S.; Liang, K.; Wen, F.; Teoh, S.H. Marine collagen scaffolds in tissue engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, K.; Vashishtha, R.; Shaloo; Dan, S. Scientific advances and pharmacological applications of marine derived-collagen and chitosan. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 3540–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.M.; Kishimura, H.; Benjakul, S. Extraction efficiency and characteristics of acid and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin of golden carp (Probarbus Jullieni) as affected by ultrasonication. Process Biochem. 2018, 66, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, A.N.A.; Simpson, B.K.; Phillip, L.E.; Cue, R.I. Effect of temperature and time on the stability of salmon skin oil during storage. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 2012, 89, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylingo, R.; Mania, S.; Panek, A.; Piątek, R.; Pawłowicz, R. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagen from the skin of african catfish (Clarias gariepinus), salmon (Salmo salar) and baltic cod (Gadus morhua). J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Lista, A.; Siekapen, M.M.; Ghaffari-Bohlouli, P.; Nie, L.; Alimoradi, H.; Shavandi, A. Fish collagen: Extraction, characterization, and applications for biomaterials engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, A.N.A.; Simpson, B.K. Comparative studies on the yield and quality of solvent-extracted oil from salmon skin. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-leaw, T.; Benjakul, S.; O’Brien, N.M. Effect of pretreatments and defatting of seabass skins on properties and fishy odor of gelatin. J. Food Biochem. 2016, 40, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Benjakul, S.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Nalinanon, S. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of collagen from clown featherback (Chitala ornata) skin: Yield and molecular characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsuwan, K.; Chantakun, K.; Chotphruethipong, L.; Benjakul, S. Development of hydrolysis and defatting processes for production of lowered fishy odor hydrolyzed collagen from fatty skin of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Foods 2021, 10, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.M.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Kishimura, H. Extraction and characterisation of collagen from the skin of golden carp (Probarbus jullieni), a processing by-product. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Method of Analysis; Association of Official Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, I.; Loxley, R. Two improved and simplified methods for the spectrophotometric determination of hydroxyproline. Anal. Chem. 1963, 35, 1961–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Visessanguan, W. Production and characterization of odorless antioxidative hydrolyzed collagen from seabass (Lates calcarifer) skin without descaling. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, D.A.; Failla, M.L.; Sarama, R.J. Development of an in vitro digestion method to assess carotenoid bioavailability from meals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4301–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjakul, S.; Morrissey, M.T. Protein hydrolysates from Pacific whiting solid wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kijroongrojana, K.; Prodpran, T.; Kishimura, H. Protein hydrolysates from Pacific white shrimp cephalothorax manufactured with different processes: Compositions, characteristics and antioxidative activity. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo-Rios, D.E.; Rios, L.A.; Zapata-Montoya, J.E. Kinetic modeling of the alkaline deproteinization of Nile-tilapia skin for the production of collagen. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Gu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, S. A quantitative comparable study on multi-hierarchy conformation of acid and pepsin-solubilized collagens from the skin of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiansilakul, Y.; Benjakul, S.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative activity of protein hydrolysate from round scad muscle using alcalase and flavourzyme. J. Food Biochem. 2007, 31, 266–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Nalinanon, S.; Shahidi, F. Fish Collagen. Food Biochem. Food Processing 2012, 20, 365–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, R.R.; Phang, S.-M.; Ravi, S.; Aswathanarayana, R.G. Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications—A review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, B.; Song, W.; Si, L.; Hou, H. Characterization of Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) skin collagen and fabrication of collagen sponge as a good biocompatible biomedical material. Process Biochem. 2017, 63, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongnuanchan, P.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Pisuchpen, S.; Osako, K. Mechanical, thermal and heat sealing properties of fish skin gelatin film containing palm oil and basil essential oil with different surfactants. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.M.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Molecular characteristics of acid and pepsin soluble collagens from the scales of golden carp (Probarbus jullieni). Emir. J. Food Agric. 2017, 29, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, R.; Haq, M.; Chun, B.-S. Characterization of marine derived collagen extracted from the by-products of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Xue, C.; Liu, Z.; Mao, X. Characterization of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) skin and the extracted acid-soluble collagen. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2019, 18, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, N.H. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on collagen extraction from skins of the sea bass Lateolabrax japonicus. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Sriket, C.; Kishimura, H.; Benjakul, S. Characteristics of acid and pepsin solubilized collagens from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) scale. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2019, 31, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Thiansilakul, Y.; Visessanguan, W.; Roytrakul, S.; Kishimura, H.; Prodpran, T.; Meesane, J. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagens from the skin of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus and Priacanthus macracanthus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plepis, A.M.D.; Goissis, G.; Das-Gupta, D.K. Dielectric and pyroelectric characterization of anionic and native collagen. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, H.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Cortes-Santiago, Y.; López, L.M. Comparison of collagen characteristic from the skin and swim bladder of Gulf corvina (Cynoscion othonopterus). Tissue Cell 2021, 72, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foegeding, E.A. Characteristics of edible muscle tissues. In Food Chemistry; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Deng, C. Characterization and comparison of collagen extracted from the skin of the Nile tilapia by fermentation and chemical pretreatment. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Fujikawa, K.; Yahara, K.; Nakamura, T. Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autoxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | C-ASC | U-ASC |
|---|---|---|
| Yield (%, dry weight basis) | 25.95 ± 0.88 a | 23.18 ± 1.07 b |
| Fat content (%, dry weight basis) | 2.10 ± 0.07 a | 1.86 ± 0.12 b |
| Hydroxyproline content (mg/g dry sample) | 48.28 ± 0.11 b | 49.15 ± 0.42 a |
| L* | 85.53 ± 0.53 a | 85.37 ± 0.24 a |
| a* | −0.04 ± 0.01 a | −0.12 ± 0.01 b |
| b* | 4.20 ± 0.06 a | 1.72 ± 0.07 b |
| ΔE* | 8.20 ± 0.56 a | 7.62 ± 0.25 a |
| Tonset (°C) | 6.84 | 5.93 |
| Tmax (°C) | 11.3 | 11.6 |
| Tendset (°C) | 16.58 | 15.65 |
| ΔH (J/g) | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| Amino Acids | Content (Residues per 1000 Residues) | |
|---|---|---|
| C-ASC | U-ASC | |
| Alanine | 109 | 107 |
| Arginine | 59 | 55 |
| Aspartic acid/Asparagine | 57 | 56 |
| Cystine | 1 | 0 |
| Glutamic acid/Glutamine | 68 | 69 |
| Glycine | 297 | 308 |
| Histidine | 17 | 15 |
| Hydroxylysine | 7 | 6 |
| Hydroxyproline (Hyp) | 56 | 57 |
| Isoleucine | 11 | 10 |
| Leucine | 25 | 24 |
| Lysine | 37 | 30 |
| Methionine | 12 | 13 |
| Phenylalanine | 15 | 15 |
| Proline (Pro) | 135 | 136 |
| Serine | 52 | 57 |
| Threonine | 22 | 24 |
| Tyrosine | 3 | 3 |
| Valine | 17 | 16 |
| Total | 1000 | 1000 |
| Imino acids (Hyp + Pro) | 191 | 193 |
| Degree of Hydrolysis/Activities | C-ASC | U-ASC |
|---|---|---|
| Degree of hydrolysis (%) | 22.31 ± 0.29 b | 23.19 ± 0.70 a |
| ABTS radical-scavenging activity (µmol Trolox equivalent/g sample) | 442.64 ± 57.46 a | 475.81 ± 22.66 a |
| DPPH radical-scavenging activity (µmol Trolox equivalent/g sample) | 0.27 ± 0.04 a | 0.32 ± 0.03 a |
| Ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) (µmol Trolox equivalent/g sample) | 13.41 ± 0.79 a | 14.61 ± 1.89 a |
| Oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) (µmol Trolox equivalent/g sample) | 203.95 ± 32.15 a | 204.33 ± 10.83 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nilsuwan, K.; Fusang, K.; Pripatnanont, P.; Benjakul, S. Properties and Characteristics of Acid-Soluble Collagen from Salmon Skin Defatted with the Aid of Ultrasonication. Fishes 2022, 7, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010051
Nilsuwan K, Fusang K, Pripatnanont P, Benjakul S. Properties and Characteristics of Acid-Soluble Collagen from Salmon Skin Defatted with the Aid of Ultrasonication. Fishes. 2022; 7(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleNilsuwan, Krisana, Krittaphat Fusang, Prisana Pripatnanont, and Soottawat Benjakul. 2022. "Properties and Characteristics of Acid-Soluble Collagen from Salmon Skin Defatted with the Aid of Ultrasonication" Fishes 7, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010051
APA StyleNilsuwan, K., Fusang, K., Pripatnanont, P., & Benjakul, S. (2022). Properties and Characteristics of Acid-Soluble Collagen from Salmon Skin Defatted with the Aid of Ultrasonication. Fishes, 7(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010051