Multispecies Fresh Water Algae Production for Fish Farming Using Rabbit Manure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Seeding, Identification and Counting of Phytoplankton
2.3. Monitoring of Physico-Chemical and Trophic Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
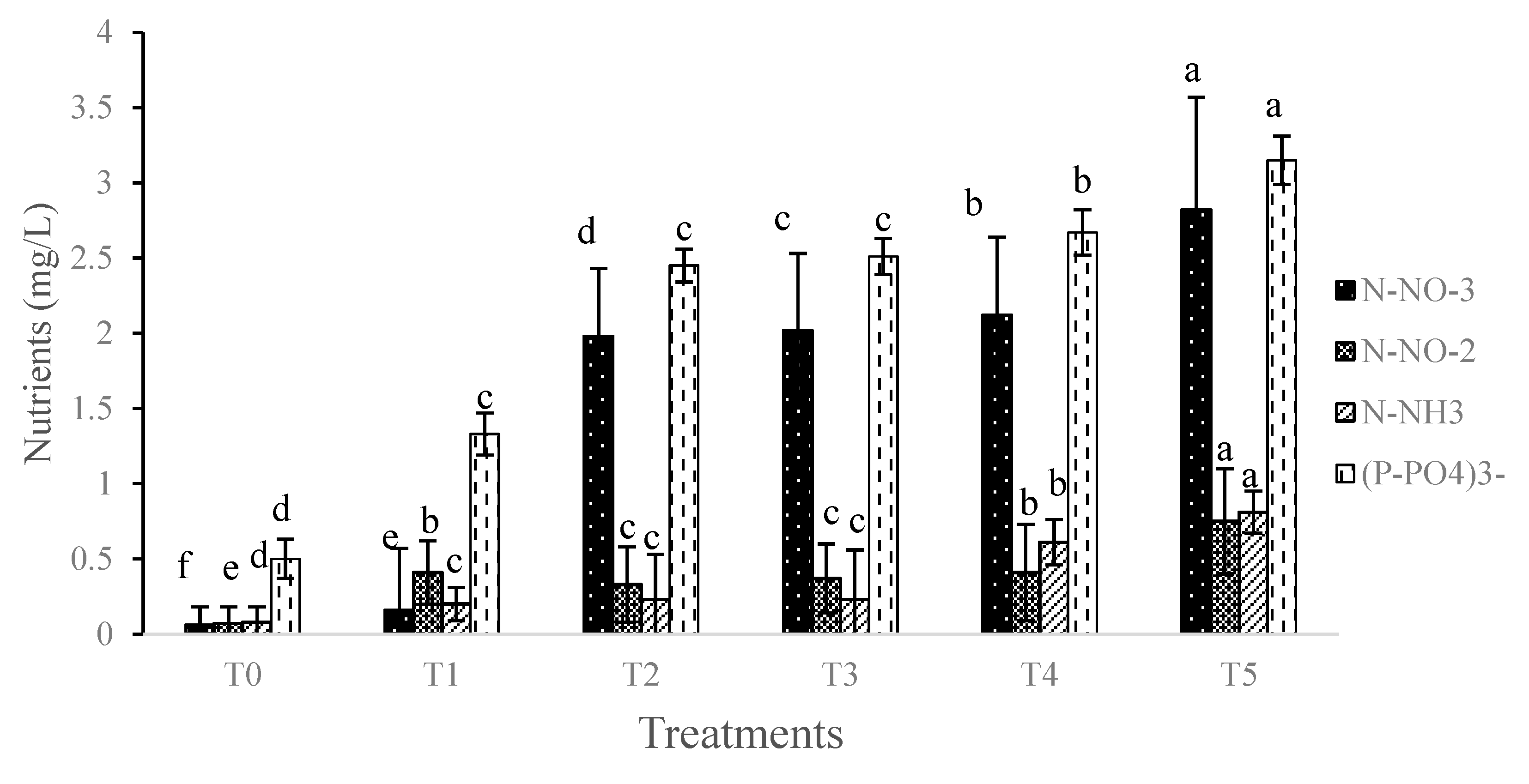
3.1. Abiotic Parameters
3.2. Biotic Parameters
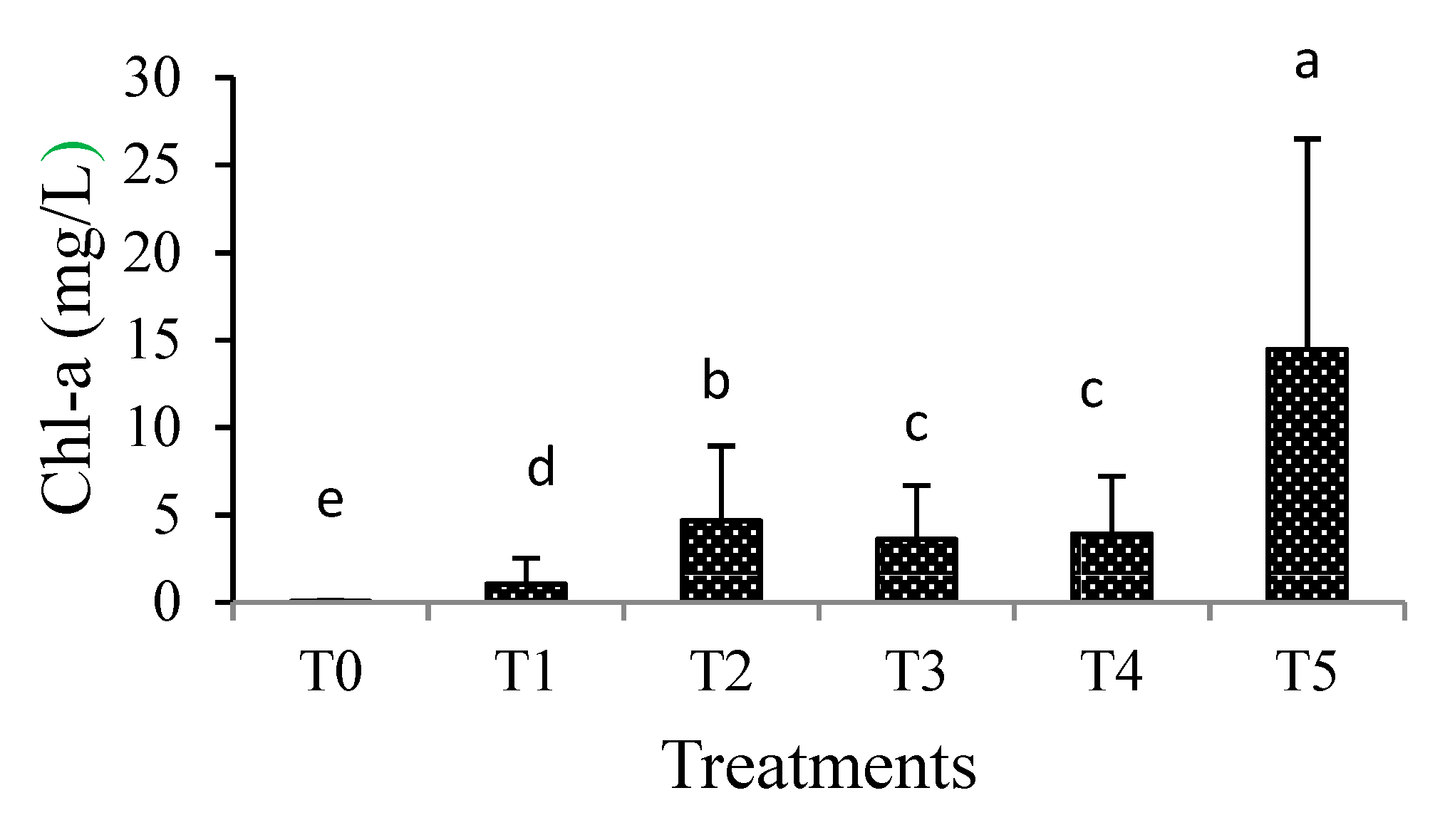
3.2.1. Chlorophyll-a Concentrations
3.2.2. Phytoplankton Diversity
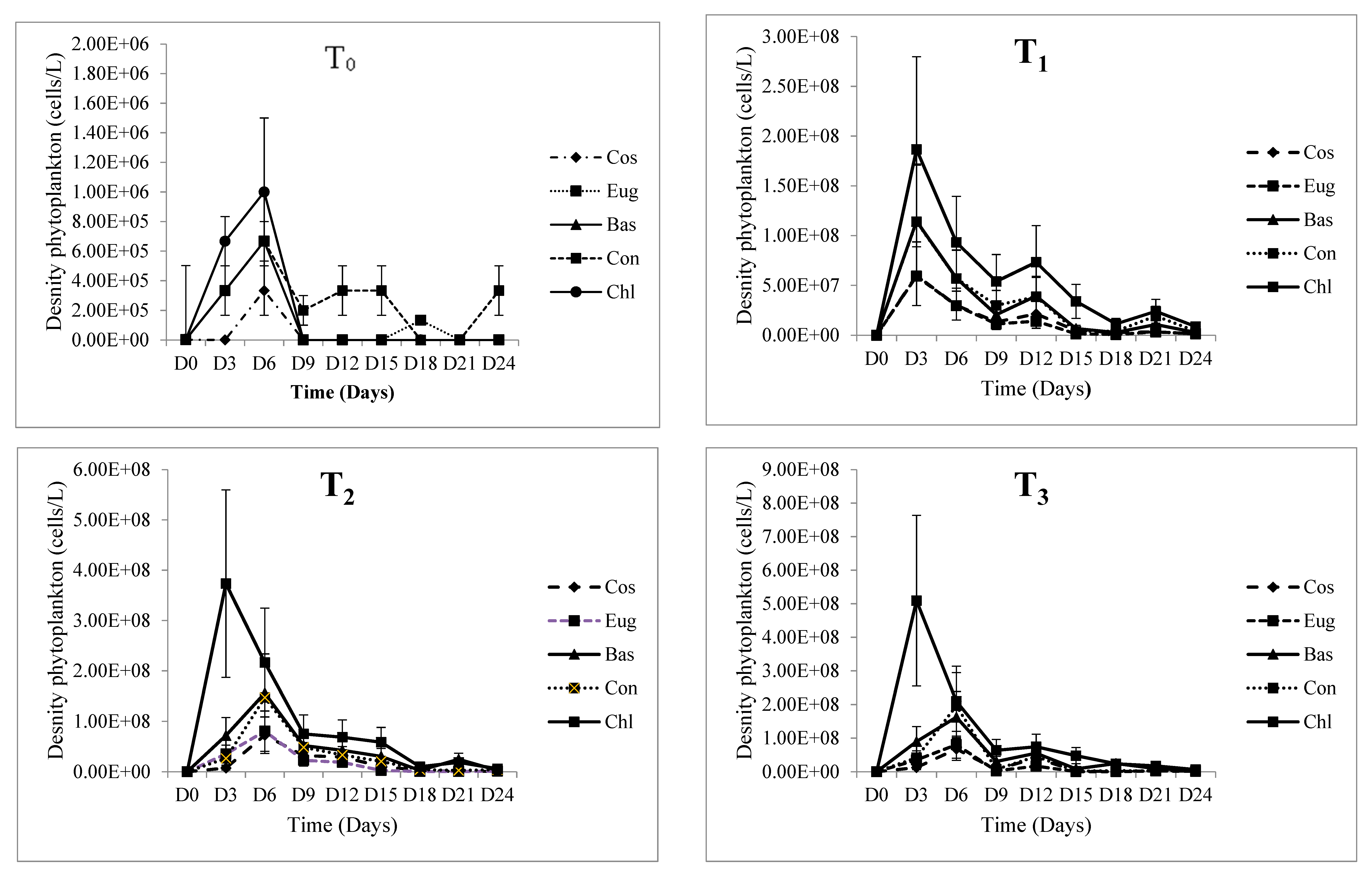
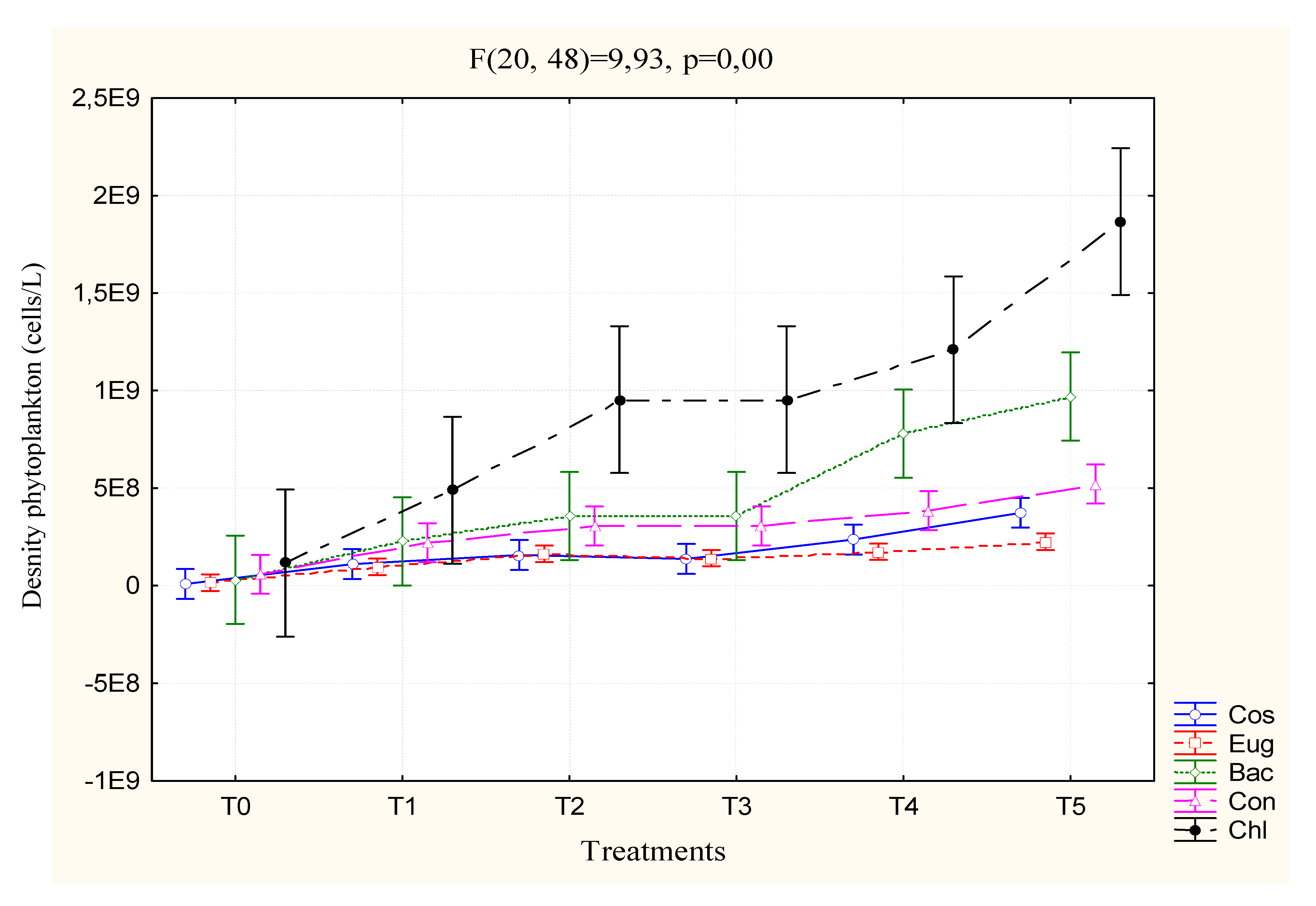
3.2.3. Phytoplankton Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sipaúba-Tavares, L.H.; Pereira, A.M.L. Large scale laboratory cultures of Ankistrodesmus gracilis (Reisch) Korsikov (Chlorophyta) and Diaphanosoma biergei Korinek, 1981 (Cladocera). Braz. J. Biol. 2008, 68, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, T. A review of on-farm feed management practices for North African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) in sub-Saharan Africa. In On-Farm Feeding and Feed Management in Aquaculture; Hasan, M.R., New, M.B., Eds.; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 583, pp. 463–479. [Google Scholar]
- Djissou, A.S.M.; Tossavi, E.C.; Vodounnou, J.D.; Toguyeni, A.; Fiogbe, E.D. Valorization of agro-alimentary waste for aproduction of maggots like source of proteins in the animal feeds. Int. J. Agron. Agric. Res. 2015, 7, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Adandé, R.; Bokossa, H.K.J.; Liady, M.N.D.; Fiogbe, E.D. Valorization of various sources of rabbit manure in agro- piscicultural system in Benin (West Africa): Dynamics and effect of mineralization upon quality of fresh water. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Agric. Waste 2017, 6, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Jean, L.; Bonou, C.A.; Pagano, M. Développement et croissance en poids de Moina (cf) micrura et de Mesocyclops ogunnus dans un milieu saumâtre tropical: Les étangs de pisciculture de Layo (Côte d’Ivoire). Rev. Hydrobiol. Trop. 1994, 24, 287–303. [Google Scholar]
- Dalme, D.K.; Chari, M.S. Performance evaluation of different animal wastes on culture of Daphnia Sp. J. Fish. Aquat. Sc. 2011, 6, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Renaghan, M.J.; Buck, N.J. Impacts of nutrients and grazing mortality on the abundance of Aureococcus anophagefferens during a New York brown tide bloom. Limnol. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akodogbo, H.H.; Bonou, C.A.; Adande, R.; Sossou, D.S.; Fiogbe, E.D. Optimization of zooplankton production from pig dung optimal dose: Renewed medium. Agric. Adv. 2015, 4, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adandé, R.; Liady, M.N.D.; Bokossa, H.K.J.; Djidohokpin, G.; Zouhir, F.; Mensah, G.A.; Fiogbe, E.D. Utilisation rationnelle de fertilisants organiques pour la production de macroinvertébrés benthiques d’eau douce en pisciculture. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2018, 22, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Sander, K.; Murthy, G.S. Life cycle analysis of algae biodiesel. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess 2010, 15, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agadjihouèdé, H.; Bonou, A.C.; Montchowui, E.; Laleye, P. Recherche de la dose optimale de fiente de volaille pour la production spécifique de zooplancton à des fins piscicoles. Cah. Agric. 2011, 20, 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, K.M.; Padmavati, G.; Anandavelu, I. Biochemical composition and calorific value of zooplankton from the coastal waters of South Andaman. Proceed. Inter. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 278–287. [Google Scholar]
- Nandini, S.; Ortiz, A.R.N.; Sarma, S.S.S. Elaphoidella grandidieri (Harpacticoida: Copepoda): Demographic characteristics and possible use as live prey in aquaculture. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adandé, R.; Adjahouinou, D.C.; Liady, M.N.D.; FIOGBE, E.D. Alimentation des lapins (Oryctolagus cuniculus L.) à base de Azolla filiculoïdes, Elaeis guineensis, Ipomoea aquatica et Panicum maximum: Effet sur la croissance des lapins et potentiel nutritif des crottes pour l’aquaculture. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 11, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar]
- Santeiro, M.R.; Ricardo Motta, P.-C.; Sipaúba-Tavares, L.H.D. variation of zooplankton biochemical composition and biomass in plankton production tanks Acta Scientiarum. Biol. Sci. 2006, 28, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Agadjihouèdé, H.; Bonou, C.A.; Chikou, A.; Lalèyè, P. Production comparée de zooplancton en bassins fertilisés avec la fiente de volaille et la bouse de vache. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2010, 4, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjahouinou, D.C.; Liady, N.D.; Fiogbe, E.D. Diversité phytoplanctonique et niveau de pollution des eaux du collecteur de Dantokpa (Cotonou-Bénin). Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2012, 6, 1938–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrelly, P. Les Algues d’Eau Douce: Algues Jaunes et Brunes (Tome 2); Edition Boubée N et Cie: Paris, France, 1981; p. 521. [Google Scholar]
- Bourrelly, P. Les Algues d’Eau Douce: Algues Bleues et Rouges (Tome 3); Edition Boubée N. et Cie: Paris, France, 1985; p. 608. [Google Scholar]
- Bourrelly, P. Les Algues d’Eau Douce:Algues Vertes (Tome 1); Edition Boubée N. et Cie: Paris, France, 1990; p. 576. [Google Scholar]
- Compère, P. Algues de la région du lac Tchad. II- Cyanophycées. Cah. Orstom Série Hydrobiol. 1974, 8, 165–198. [Google Scholar]
- Compère, P. Algues de la région du lac Tchad. III- Rhodophycées, Euglénophycées, Cryptophycées, Dinophycées, Chrysophycées, Xanthophycées. Cah. Orstom. Série Hydrobiol. 1975, 9, 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- Compère, P. Algues de la région du lac Tchad. IV- Diatomophycées. Cah. Orstom. Série Hydrobiol. 1975, 9, 203–290. [Google Scholar]
- Compère, P. Algues de la région du lac Tchad. V- Chorophycophytes 1èrre partie. Cah. Orstom. Série Hydrobiol. 1976, 10, 77–118. [Google Scholar]
- Compère, P. Algues de la région du lac Tchad. VI- Chorophycophytes 2e partie: Ulotrichophycées, Zygnématacées. Cah. Orstom. Série Hydrobiol. 1976, 10, 135–164. [Google Scholar]
- Compère, P. Algues de la région du lac Tchad. VII- Chorophycophytes 3e partie: Desrnidiées. Cah. Orstom. Série Hydrobiol. 1977, 11, 77–177. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, J.R.; Lévêque, C. Flore et Faune Aquatiques de l’Afrique Sahélo- Soudanienne (Tome I); Durand, J.R., Lévêque, C., Eds.; Éditions ORSTOM, Collection Initiations Initiations-Documentations Techniques: Paris, France, 1980; Volume 44, pp. 9–61. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D. Algae Base. Worldwide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 25 June 2017).
- Bouali, M.; Zrafi, I.; Mouna, F.A. Bakhrouf, Pilot study of constructed wetlands for tertiary wastewater treatment using duckweed and immobilized microalgae. Africa. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 31, 6066–6074. [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, J.B.L.; Merlet, N. Coll. Analyse de l’eau; Paris, France, 2012; p. 20225. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Chao, T.M. Effects of temperature and growth phase on lipid and biochemical composition of Isochrysis galbana TK1. J. Appl. Phycol. 1997, 9, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.; Leslie, K.; Vacek, P.; Socinski, M.; Weaver, D. Estrogen-receptor-related protein p29 in primary nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: Pathologic and prognostic correlations. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 1998, 82, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liady, M.N.D.; Kpèhouénou, O.B.; Adandé, R.; Noumavo, A.D.P.; Kouadio, L.A.; Aïna, M.P.; Fiogbe, E.D. Valorisation of the supernatant of brewery effluent in plankton production for fish farming: An alternative for environment protection in southern countries. Biotec. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2020, 24, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Tahiri, M.; Benider, A.; Belkoura, M.; Dauta, A. Caractérisation biochimiques de l’algue verte Scenedesmus abundans: Influence des conditions de culture. In Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology; EDP Sciences: Ulis, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Oswald, W.J. Micro-algae and wastewater treatment. In Micro-algal Biotech; Bor-owitzka, M.A., Borowitzka, L.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988; pp. 305–328. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, R.; Guieysse, B. Algal-bacterial processes for the treatment of hazardous contaminants: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2799–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y. Nitrogen removal pathways in shallow-water duckweed-based wastewater treatment systems. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2006, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hodaifa, G.M.; Martínez, E.; Sánchez, S. Influence of pH on the Culture of Scenedesmus obliquus in Olive-mill Wastewater. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmo, O.R.; Van, D.N.P.; Gijzen, H.J. Nitrogen mass balance across pilot-scale algae and duckweed-based wastewater stabilisation ponds. Water Res. 2004, 38, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaidi, M.S.; Hamaidi, F.; Zoubiri, A.; Benouaklil, F.; Dhan, Y. Etude de la dynamique des populations phytoplanctoniques et résultats préliminaires sur les blooms toxiques a cyanobacteries dans le barrage de Ghrib (Ain Defla-Algérie). Europ. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 32, 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Toyub, M.A.; Miah, M.I.; Habib, M.A.B.; Rahman, M.M. Growth performance and nutritional value of Scenedesmus obliquus cultured in different concentrations of sweetmeat factory waste media Bang. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 37, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality Management for Pond Fish Culture; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; p. 318. [Google Scholar]
- Schlumberger, O.; Bouretz, N. Réseaux trophiques et production piscicole en étangs fertilisés (Dordogne, France). J. Water Sci. 2002, 15, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barbe, J.; Schlumberger, O.; Bouretz, N. Evaluation de la production piscicole potentielle des étangs. IRSTEA 2000, 49–62, hal-00464073. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.S. The ecology of freshwater phytoplancton. In Cambridge Studies in Ecology; Beck, E., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, M.; Baccar, L.; Ben, K.R. La lagune de Ghar El Melh: Diagnostic écologique et perspectives d’aménagement hydraulique. J. Water Sci. 2005, 18, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Benzha, F.; Taoufik, M.; Dafir, J.E.; Kemmou, S.; Loukili, L. Qualité physico-chimique des eaux du réservoir Daourat; impact de la vidange sur son fonctionnement. J. Water Sci. 2005, 18, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Canovas, S.; Casellas, C.; Picot, B.; Pena, G.; Bontoux, J. Evolution annuelle du peuplement zooplanctonique dans un lagunage à haut rendement et incidence du temps de séjour. J. Water Sci. 1991, 4, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gonzalez, C.; Marciniak, J.; Villaverde, S.; Garcia-Encina, P.A.; Munoz, R. Microalgal-based processes for the degradation of pre-treated piggery wastewaters. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 2008, 80, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacio, G.; Virginia, A.V.; Saul, B.; Maria, C.; Roberto, S.; Pedro, A.; Eloy, B.; Raul, M.A. Comparative evaluation of microalgae for the degradation of piggery wastewater under photosynthetic oxygenation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5150–5158. [Google Scholar]
- Pourriot, R.; Meybeck, M. Limnologie Générale; Masson: Paris, France, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, I.; Ranjith, K.R.; Mutanda, T.; Bux, F. Dual role of microalgae: Phycoremediation of domestic wastewater and biomass for sustainable biofuels production. Appl. Energ. 2011, 88, 3411–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, B.; Sahu, A.K. Microalgae growth for nutrient recovery from sludge liquor and production of renewable bioenergy. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T°C | 33.74 ± 1.70 | 34.02 ± 1.81 | 34.30 ± 1.70 | 34.34 ± 1.87 | 34.48 ± 1.86 | 34.51 ± 1.78 | F(5, 12) =12.63 |
| Cond (µs/cm) | 37.66 ± 23.17 c | 597.82 ± 34.10 b | 604.50 ± 23.17 b | 607.19 ± 22.12 b | 625.58 ± 36.08 ab | 664.45 ± 50.63 a | F(5,12) = 41.86 |
| pH | 6.87 ± 0.94 b | 7.29 ± 0.79 a | 7.33 ± 0.94 a | 7.12 ± 0.92 a | 7.09 ± 1.05 a | 7.16 ± 1.05 a | F(5,12) = 5.53 |
| DO (mg/L) | 3.81 ± 0.72 d | 7.48 ± 1.95 c | 9.42 ± 0.72 a | 8.58 ± 2.40 a | 8.99 ± 2.95 a | 9.66 ± 3.33 a | F(5, 12) = 59.40 |
| Sal (mg/L) | 0.08 ± 0.01 c | 0.31 ± 0.02 b | 0.32 ± 0.01 b | 0.32 ± 0.01 b | 0.33 ± 0.01 ab | 0.36 ± 0.03 a | F(5, 12) = 9.33 |
| TDS | 64.60 ± 8.77 c | 296.92 ± 17.07 b | 302.56 ± 8.77 b | 303.43 ± 7.47 b | 318.76 ± 16.81 ab | 338.61 ± 27.11 a | F(5, 12) = 7.88 |
| Transp (cm) | 27.91 ± 0.37 a | 22.50 ± 1.13 b | 16.85 ± 1.51 ce | 17.63 ± 1.41 de | 14.43 ± 1.38 fh | 12.98 ± 1.50 gh | F(5, 12) = 17.69 |
| Phylum | Classes | Families | Genuses and Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillariophytes | Coscinodiscophyceae | Melosiraceae | Melosira italica |
| Melosira sp | |||
| Bacillariophyceae | Pinnulariaceae | Pinnularia viridis | |
| Pinnularia sp | |||
| Naviculaceae | Navicula sp | ||
| Charophytes | Conjugatophyceae | Closteriaceae | Closterium sp |
| Desmidiaceae | Staurastrum margaritaceum | ||
| Staurastrum pinnatum | |||
| Chlorophyceae | Scenedesmaceae | Coelastrum sp | |
| Scenedesmus javanensis | |||
| Scenedesmus apiculatus | |||
| Scenedesmus quadricauda | |||
| Palmellopsidaceae | Asterococcus sp | ||
| Euglenophytes | Euglenophyceae | Euglenaceae | Euglena ehrenbergii |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Richard, A.; Nourou Dine, L.M.; Gildas, D.; Dogbè Clément, A.; Tobias Césaire, A.M.; Jean-Claude, M.; Didier Emile, F. Multispecies Fresh Water Algae Production for Fish Farming Using Rabbit Manure. Fishes 2020, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes5040035
Richard A, Nourou Dine LM, Gildas D, Dogbè Clément A, Tobias Césaire AM, Jean-Claude M, Didier Emile F. Multispecies Fresh Water Algae Production for Fish Farming Using Rabbit Manure. Fishes. 2020; 5(4):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes5040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleRichard, Adandé, Liady Mouhamadou Nourou Dine, Djidohokpin Gildas, Adjahouinou Dogbè Clément, Azon Mahuan Tobias Césaire, Micha Jean-Claude, and Fiogbe Didier Emile. 2020. "Multispecies Fresh Water Algae Production for Fish Farming Using Rabbit Manure" Fishes 5, no. 4: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes5040035
APA StyleRichard, A., Nourou Dine, L. M., Gildas, D., Dogbè Clément, A., Tobias Césaire, A. M., Jean-Claude, M., & Didier Emile, F. (2020). Multispecies Fresh Water Algae Production for Fish Farming Using Rabbit Manure. Fishes, 5(4), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes5040035






