Influence of Age on Stress Responses of White Seabream to Amyloodiniosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
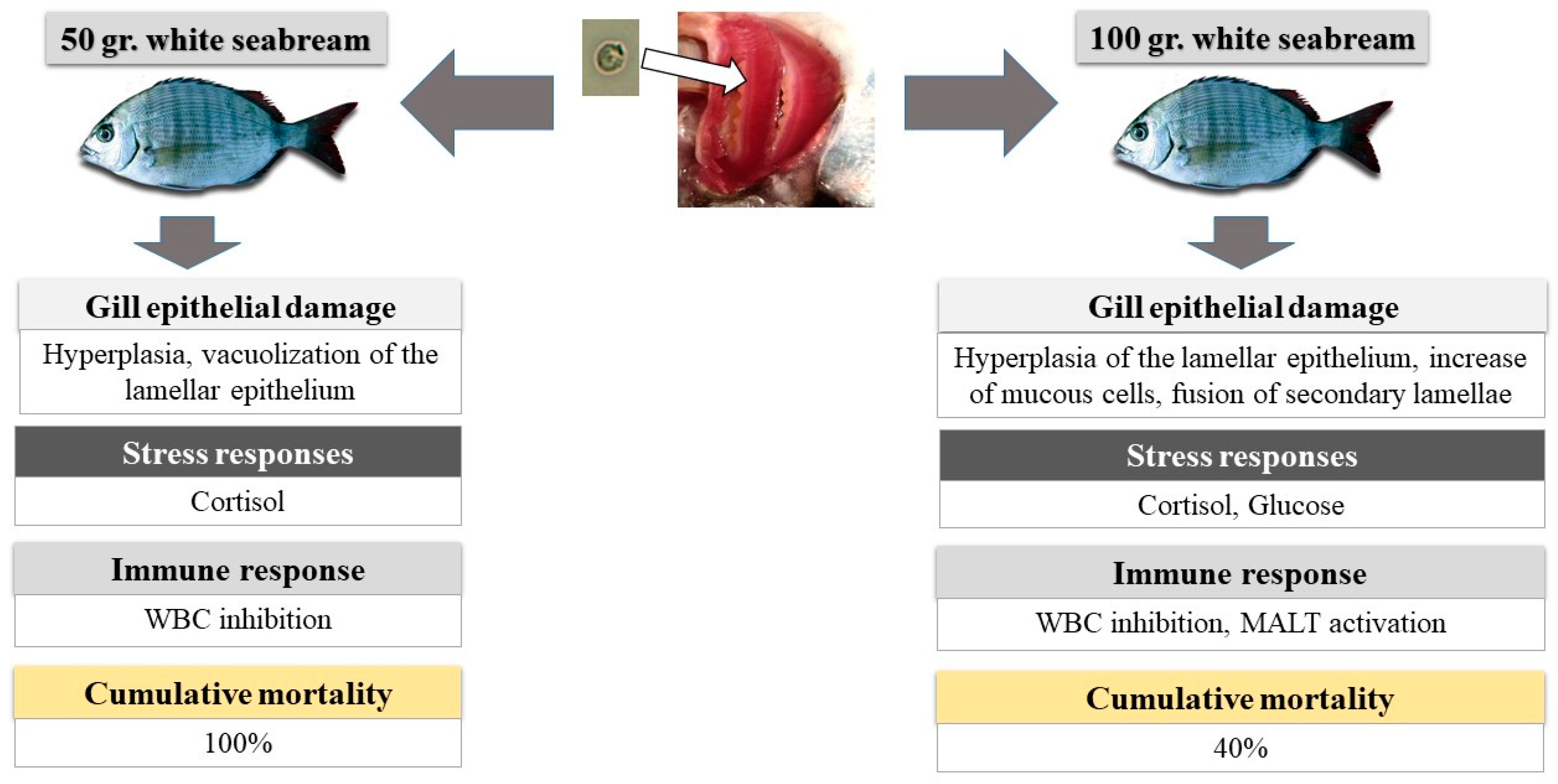
2.1. Gill Analysis
2.2. Mortality
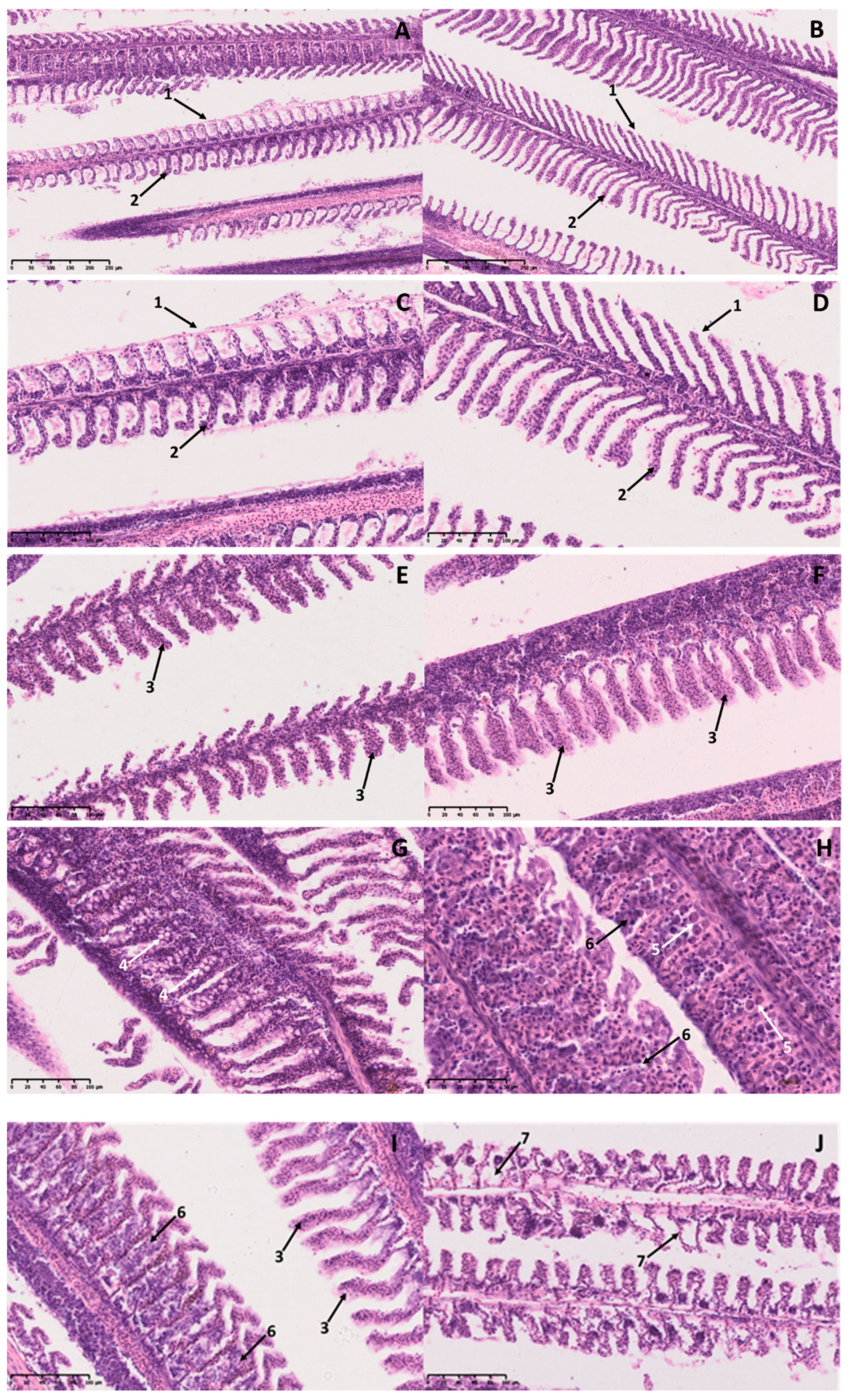
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
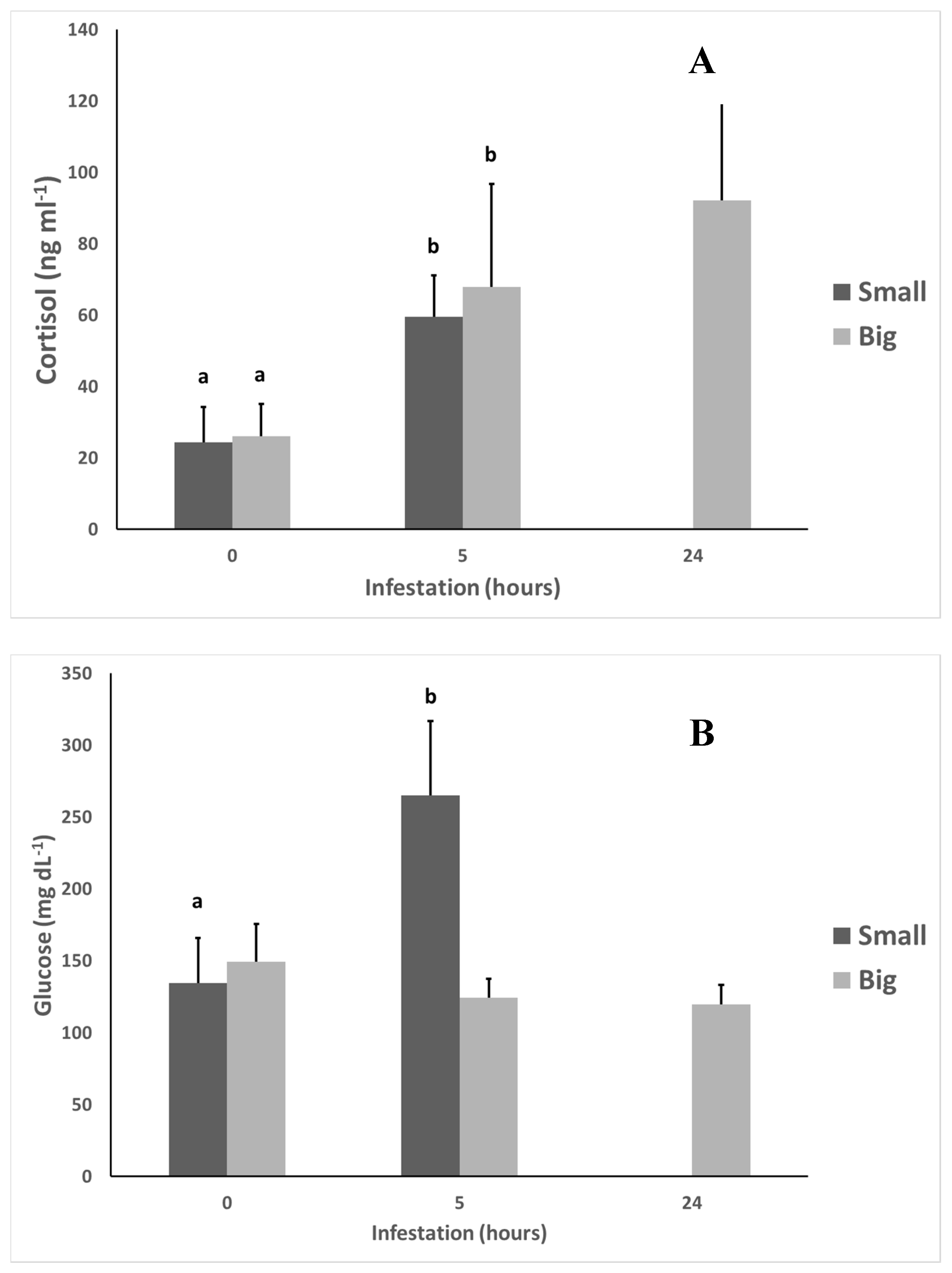
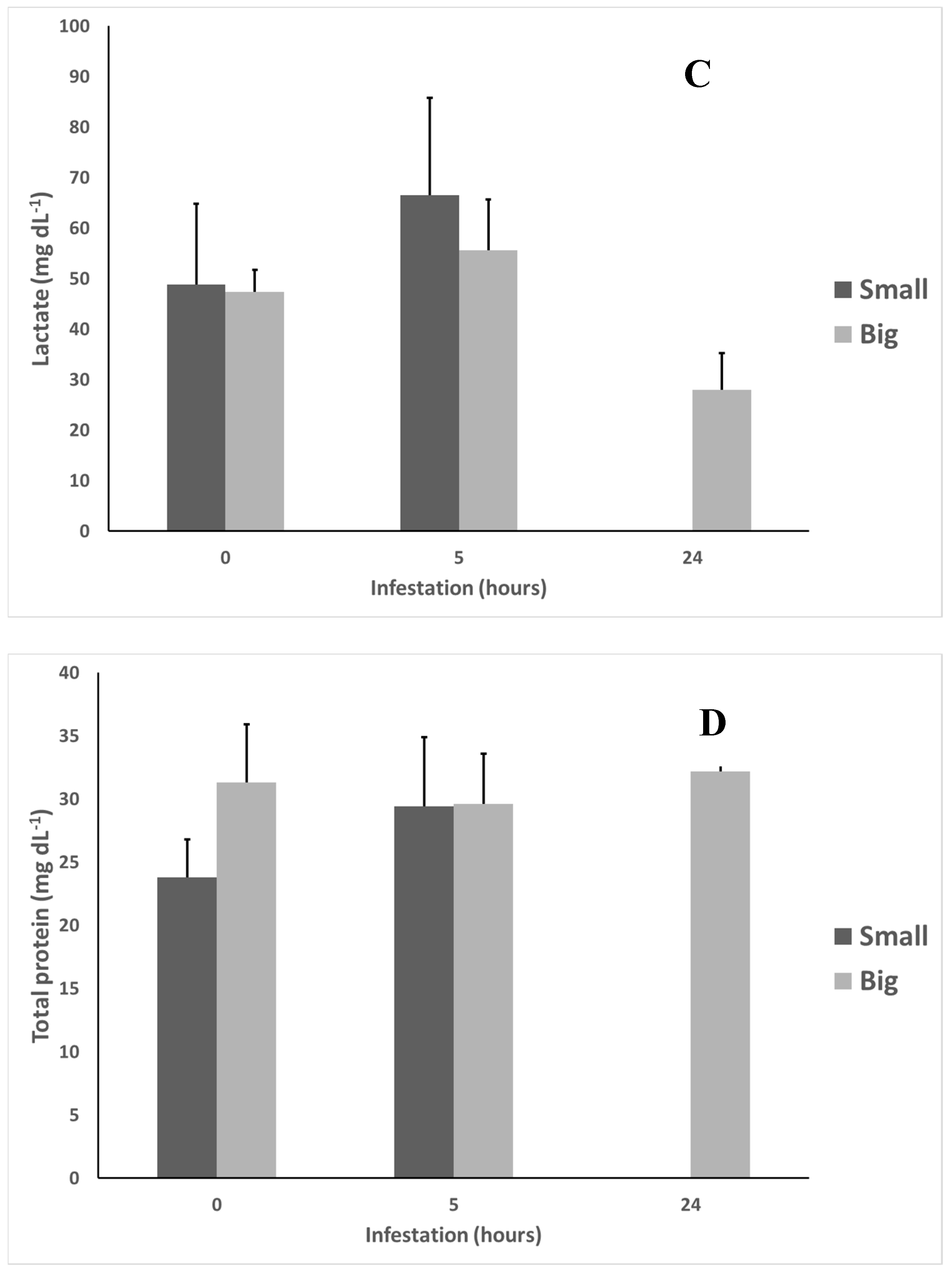
2.4. Stress Indicators
2.5. Hematological Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fish Culture Conditions
4.2. Preparation of A. Ocellatum Infection Tanks
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Sampling Protocol
4.5. Histopathological Analysis
4.6. Stress Indicator Analysis
4.7. Hematological Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soares, F.; Quental Ferreira, H.; Cunha, E.; Pousão-Ferreira, P. Occurrence of Amyloodinium ocellatum in aquaculture fish production: A serious problem in semi-intensive earthen ponds. Aquac. Eur. 2011, 36, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Paperna, I.; Ross, B.; Colorni, A.; Colorni, B. Diseases of Marine Fish Cultured in Eilat Mariculture Project Based at the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea; 92-5-000964-X; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1980; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg, J.H.; Steidinger, K.A.; Blakesley, B.A.; Zondervan, R.L. Scanning Electron-Microscope Study of Dinospores of Amyloodinium cf Ocellatum, a Pathogenic Dinoflagellate Parasite of Marine Fish, and Comments on Its Relationship to the Peridiniales. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1994, 20, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Lacierda, E.R.; Maeno, Y.; Pineda, A.J.T.; Matey, V.E. Mass mortality of hatchery-reared milkfish (Chanos chanos) and mangrove red snapper (Lutjanus argentimaculatus) caused by Amyloodinium ocellatum (Dinoflagellida). Aquaculture 2004, 236, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperman, B.I.; Matey, V.E. Massive infestation by Amyloodinium ocellatum (Dinoflagellida) of fish in a highly saline lake, Salton Sea, California, USA. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 39, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinn, A.P.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bron, J.E.; Paladini, G.; Brooker, E.E.; Brooker, A.J. Economic costs of protistan and metazoan parasites to global mariculture. Parasitology 2015, 142, 196–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L.; Blas, I.D.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Cunningham, D.; Vendrell, D.; Múzquiz, J.L. The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 114, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladineo, I. Check list of the parasitofauna in Adriatic Sea cage-reared fish. Acta Vet. 2006, 56, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, A.R. Studies on Amyloodinium ocellatum (Dinoflagellata) in Mississippi Sound: Natural and Experimental Hosts. Gulf Res. Rep. 1980, 6, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paperna, I. Chemical control of Amyloodinium ocellatum (Brown 1931) (Dinoflagellida) infections: In vitro tests and treatment trials with infected fishes. Aquaculture 1984, 38, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajer-Avila, E.J.; Abdo-de la Parra, I.; Aguilar-Zarate, G.; Contreras-Arce, R.; Zaldivar-Ramirez, J.; Betancourt-Lozano, M. Toxicity of formalin to bullseye puffer fish (Sphoeroides annulatus Jenyns, 1843) and its effectiveness to control ectoparasites. Aquaculture 2003, 223, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata, Z. Parasites and Diseases of Fish Cultured in the Tropics; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Virgula, J.C.; Cruz-Lacierda, E.R.; Estante, E.G.; Corre, V.L., Jr. Copper sulfate as treatment for the ectoparasite Amyloodinium ocellatum (Dinoflagellida) on milkfish (Chanos chanos) fry. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2017, 10, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Bessat, M.; Fadel, A. Amyloodiniosis in cultured Dicentrarchus labrax: Parasitological and molecular diagnosis, and an improved treatment protocol. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 129, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery-Brock, D.; Sato, V.T.; Brock, J.A.; Tamaru, C.S. The application of hydrogen peroxide as a treatment for the ectoparasite Amyloodinium ocellatum (Brown 1931) on the Pacific threadfin Polydactylus sexfilis. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2001, 32, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoud, S.S.M.; Zaki, V.H.; Ahmed, G.E.; El-Khalek, N.K.A. Studies on Amyloodinium Infestation in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax.) Fishes with Special Reference for Treatment. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestmann, D.J.; Lewis, D.H.; Zettler, B.A. Communications: Clearance of Amyloodinium ocellatum Dinospores by Artemia salina. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1995, 7, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, S.; Ennaffah, B.; Belattmania, Z.; Reani, A.; Sabour, B. First Report on the Occurrence and Dynamics of the Ectoparasitic Dinoflagellate Amyloodinium ocellatum in the Moroccan Atlantic Coast. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 12, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, F.; Gast, R.J. Dinoflagellates Amyloodinium and Ichthyodinium (Dinophyceae), parasites of marine fishes in the South Atlantic Ocean. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 131, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo de Magalhães, C.S.F.; Cerqueira, M.A.C.; Schrama, D.; Moreira, M.J.V.; Boonanuntanasarn, S.; Rodrigues, P.M.L. A Proteomics and other Omics approach in the context of farmed fish welfare and biomarker discovery. Rev. Aquac. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, F.S. Stress and the welfare of cultured fish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2004, 86, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, M.; Angellotti, L.; Papandroulakis, N.; Divanach, P. Evaluation of transportation procedures on water quality and fry performance in red porgy (Pagrus pagrus) fry. Aquaculture 2003, 218, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Aragão, C.; Dias, J.; Costas, B.; Terova, G.; Martins, C.; Tort, L. Dietary nitrogen and fish welfare. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.N.; Cordeiro, O.; Silva, T.S.; Richard, N.; de Vareilles, M.; Marino, G.; Di Marco, P.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Conceição, L.E.C. Metabolic molecular indicators of chronic stress in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) using comparative proteomics. Aquaculture 2010, 299, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, O.; Silva, T.; Alves, R.; Costas, B.; Wulff, T.; Richard, N.; de Vareilles, M.; Conceição, L.C.; Rodrigues, P. Changes in Liver Proteome Expression of Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis) in Response to Repeated Handling Stress. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 714–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, L. The effects of stocking density on fish welfare. Plymouth Stud. Sci. 2011, 4, 372–383. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, P.J. Fish welfare: Current issues in aquaculture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, T. Disease and Medicines—The Welfare Implications. In Fish Welfare; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Einarsdóttir, I.E.; Nilssen, K.J.; Iversen, M. Effects of rearing stress on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) antibody response to a non-pathogenic antigen. Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paperna, I. Reproduction cycle and tolerance to temperature and salinity of Amyloodinium ocellatum (Brown, 1931) (Dinoflagellida). Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1984, 59, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J. Amyloodinium ocellatum. In Fish Parasites: Pathobiology and Protection; Woo, P.T.K., Buchmann, K., Eds.; CABI Publishers: Preston, UK, 2012; pp. 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kuperman, B.I.; Matey, V.E.; Hurlbert, S.H. Parasites of fish from the Salton Sea, California, USA. Hydrobiologia 2001, 466, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.C.; Abrantes, I.; Martins, I.; Barata, J.; Frias, P.; Pereira, I. Ecological and morphological features of Amyloodinium ocellatum occurrences in cultivated gilthead seabream Sparus aurata L.; A case study. Aquaculture 2011, 310, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J.; Fan, Z.; Silphaduang, U. Host site of activity and cytological effects of histone-like proteins on the parasitic dinoflagellate Amyloodinium ocellatum. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2002, 52, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorni, A.; Ullal, A.; Heinisch, G.; Noga, E.J. Activity of the antimicrobial polypeptide piscidin 2 against fish ectoparasites. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.T. Protective immunity in fish against protozoan diseases. Parassitologia 2007, 49, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Pellitero, P. Fish immunity and parasite infections: From innate immunity to immunoprophylactic prospects. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 126, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byadgi, O.; Beraldo, P.; Volpatti, D.; Massimo, M.; Bulfon, C.; Galeotti, M. Expression of infection-related immune response in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) during a natural outbreak from a unique dinoflagellate Amyloodinium ocellatum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozzi, V.; Strofaldi, S.; Piquer, I.F.; Di Crescenzo, D.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Amyloodinum ocellatum in Dicentrarchus labrax: Study of infection in salt water and freshwater aquaponics. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 57, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Santos, B.; Albinati, R.C.B.; Moreira, E.L.T.; Lima, F.W.M.; de Azevedo, T.M.P.; Costa, D.S.P.; de Medeiros, S.D.C.; Lira, A.D. Parameters hematological and histopathologic alterations in cobia (Rachycentron canadum Linnaeus, 1766) com amyloodiniose. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2012, 32, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.; Schrama, D.; Soares, F.; Wulff, T.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Rodrigues, P. Physiological responses of reared sea bream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758) to an Amyloodinium ocellatum outbreak. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1545–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, M.; Herrera, M.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Navas Triano, J.I.; Soares, F. Stress effects of amyloodiniosis in gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 127, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivanco-Aranda, M.; Del Río-Zaragoza, O.B.; Lechuga-Sandoval, C.E.; Viana, M.T.; Rombenso, A.N. Health response in yellowtail Seriola dorsalis exposed to an Amyloodinium ocellatum outbreak. Cienc. Mar. 2018, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Becerril, M.; Ascencio-Valle, F.; Alamillo, E.; Hirono, I.; Kondo, H.; Jirapongpairoj, W.; Angulo, C. Molecular cloning and comparative responses of Toll-like receptor 22 following ligands stimulation and parasitic infection in yellowtail (Seriola lalandi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.J.; Nigrelli, R.F.; Ruggieri, G.D. Oodinium ocellatum (Brown, 1931) (Dinoflagellata) in the kidney and other internal tissues of pork fish, Anisotremus virginicus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 1981, 4, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemmen, C.; Bahri, S. Seasonality of Amyloodinium ocellatum Brown 1931 (Dinophyceae) infesting the Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis from Bizerte lagoon, Tunisia. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.; Quental-Ferreira, H.; Moreira, M.; Cunha, E.; Ribeiro, L.; Pousao-Ferreira, P. First report of Amyloodinium ocellatum in farmed meagre (Argyrosomus regius). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2012, 32, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.R.; Nazar, A.K.A.; Jayakumar, R.; Tamilmani, G.; Sakthivel, M.; Kalidas, C.; Balamurugan, V.; Sirajudeen, S.; Thiagu, R.; Gopakumar, G. Amyloodinium ocellatum infestation in the broodstock of silver pompano Trachinotus blochii (Lacepede, 1801) and its therapeutic control. Indian J. Fish. 2015, 62, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ángeles Esteban, M. An Overview of the Immunological Defenses in Fish Skin. ISRN Immunol. 2012, 2012, 853470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Cuesta, A.; Abellán, E.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. Comparative analysis of the humoral immunity of skin mucus from several marine teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paperna, I. Amyloodinium-Ocellatum (Brown, 1931) (Dinoflagellida) Infestations in Cultured Marine Fish at Eilat, Red-Sea—Epizootiology and Pathology. J. Fish Dis. 1980, 3, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, Z.; Grutter, A.S.; Bshary, R.; Ros, A.F.H. Effects of short-term exposure to ectoparasites on fish cortisol and hematocrit levels. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotto, I.; Mosconi, G.; Maradonna, F.; Cardinali, M.; Carnevali, O. Diplodus sargus interrenal–pituitary response: Chemical communication in stressed fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 127, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.E.; Sundell, K.; Ringø, E.; Myklebust, R.; Hemre, G.-I.; Hansen, T.; Karlsen, Ø. The acute stress response in fed and food deprived Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, R.; Martins, N.; Martins, S.; Lopes, T.; Diáz-Rosales, P.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Peres, H. Is dietary taurine required for white seabream (Diplodus sargus) juveniles? Aquaculture 2019, 502, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enes, P.; Peres, H.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Sanchez-Gurmaches, J.; Navarro, I.; Gutiérrez, J.; Oliva-Teles, A. Glycemic and insulin responses in white sea bream Diplodus sargus, after intraperitoneal administration of glucose. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Gómez, M.P.; Marín Arribas, S.L.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Stress response of Salmo salar (Linnaeus 1758) facing low abundance infestation of Caligus rogercresseyi (Boxshall & Bravo 2000), an object in the tank, and handling. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, C.J.; Gerwick, L. The acute phase response and innate immunity of fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Pellitero, P.; Palenzuela, O.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Histopathology and cellular response in Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa) infections of Diplodus puntazzo (Teleostei). Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, T.; Okamura, B. Post-haemorrhagic anaemia in sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.), caused by blood feeding of Ceratothoa oestroides (Isopoda: Cymothoidae). J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portz, D.E.; Woodley, C.M.; Cech, J.J. Stress-associated impacts of short-term holding on fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2006, 16, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, F.J.; Khara, H.; Rohi, J.D.; Sayadborani, M. Hematological parameters associated with parasitism in pike, Esox lucius caught from Anzali wetland. J. Parasit. Dis. Off. Organ Indian Soc. Parasitol. 2015, 39, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Gonçalves, C.; Dores, E. Larval Rearing of Four Sparidae Species; Special Publication No. 36; European Aquaculture Society: Oostende, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barata, M.; Soares, F.; Aragão, C.; Almeida, A.C.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Ribeiro, L. Efficiency of 2-phenoxyethanol and Clove Oil for Reducing Handling Stress in Reared Meagre, Argyrosomus regius (Pisces: Sciaenidae). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 47, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martoja, R.; Martoja-Pierson, M. Initiation aux techniques de l’histologie animale; Masson: Paris, France, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, M.; Ruiz-Jarabo, I.; Vargas-Chacoff, L.; de la Roca, E.; Mancera, J.M. Metabolic enzyme activities in relation to crowding stress in the wedge sole (Dicologoglossa cuneata). Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 2808–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.; Leitão, A.; Moreira, M.; de Sousa, J.T.; Almeida, A.C.; Barata, M.; Feist, S.W.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Ribeiro, L. Sarcoma in the thymus of juvenile meagre Argyrosomus regius reared in an intensive system. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2012, 102, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, A.C.; Ribeiro, L.; Araujo, R.L.; Pousão-Ferreira, P. Preliminary studies on haematological and plasmatic parameters in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) held under day/night temperature variations. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, D.; Oprea, L.; Bucur, C.; Costache, M.; Oprea, D. Characteristics of haematological parameters for carp culture and Koi (Cyprinus carpio Linneaus, 1758) reared in an intensive system. Bull. Uasvm Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 66, 336–342. [Google Scholar]

| Hematological Indicators | Small | Big | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 24 | 0 | 5 | 24 | |
| Hct (% ± SD) | 29.7 ± 5.90 | 34.5 ± 6.47 | NA | 31.2 ± 3.74 | 32.5 ± 3.80 | 30.4 ± 4.80 |
| Hemoglobin (g dL−1 ± SD) | 5.24 ± 0.85 | 5.38 ± 1.21 | NA | 6.39 ± 0.74 | 6.93 ± 0.82 | 6.42 ± 0.78 |
| RBC (% ± SD) | 99.9 ± 1.38 | 99.9 ± 0.54 | NA | 99.3 ± 1.30 | 99.6 ± 1.57 | 99.6 ± 1.52 |
| WBC (% ± SD) | 0.081 ± 0.030 a | 0.034 ± 0.014 b | NA | 0.703 ± 0.151 a | 0.422 ± 0.082 b | 0.430 ± 0.141 b |
| MCV (fl ± SD) | 73.6 ± 1.46 | 75.1 ± 1.41 | NA | 71.4 ± 1.47 a | 80.0 ± 1.87 b | 82.5 ± 1.79 b |
| MCH (pg ± SD) | 13.0 ± 2.11 | 11.7 ± 2.64 | NA | 14.6 ± 1.48 | 17.0 ± 2.01 | 17.3 ± 2.11 |
| MCHC (gHb 100mL−1 ± SD) | 1.76 ± 0.29 | 1.56 ± 0.35 | NA | 2.05 ± 0.21 | 2.13 ± 0.25 | 2.10 ± 0.26 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, M.; Cordeiro-Silva, A.; Barata, M.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Soares, F. Influence of Age on Stress Responses of White Seabream to Amyloodiniosis. Fishes 2019, 4, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020026
Moreira M, Cordeiro-Silva A, Barata M, Pousão-Ferreira P, Soares F. Influence of Age on Stress Responses of White Seabream to Amyloodiniosis. Fishes. 2019; 4(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Márcio, Anaísa Cordeiro-Silva, Marisa Barata, Pedro Pousão-Ferreira, and Florbela Soares. 2019. "Influence of Age on Stress Responses of White Seabream to Amyloodiniosis" Fishes 4, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020026
APA StyleMoreira, M., Cordeiro-Silva, A., Barata, M., Pousão-Ferreira, P., & Soares, F. (2019). Influence of Age on Stress Responses of White Seabream to Amyloodiniosis. Fishes, 4(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020026






