Preliminary Monitoring of Praziquantel in Water and Sediments at a Japanese Amberjack (Seriola quinqueradiata) Aquaculture Site
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
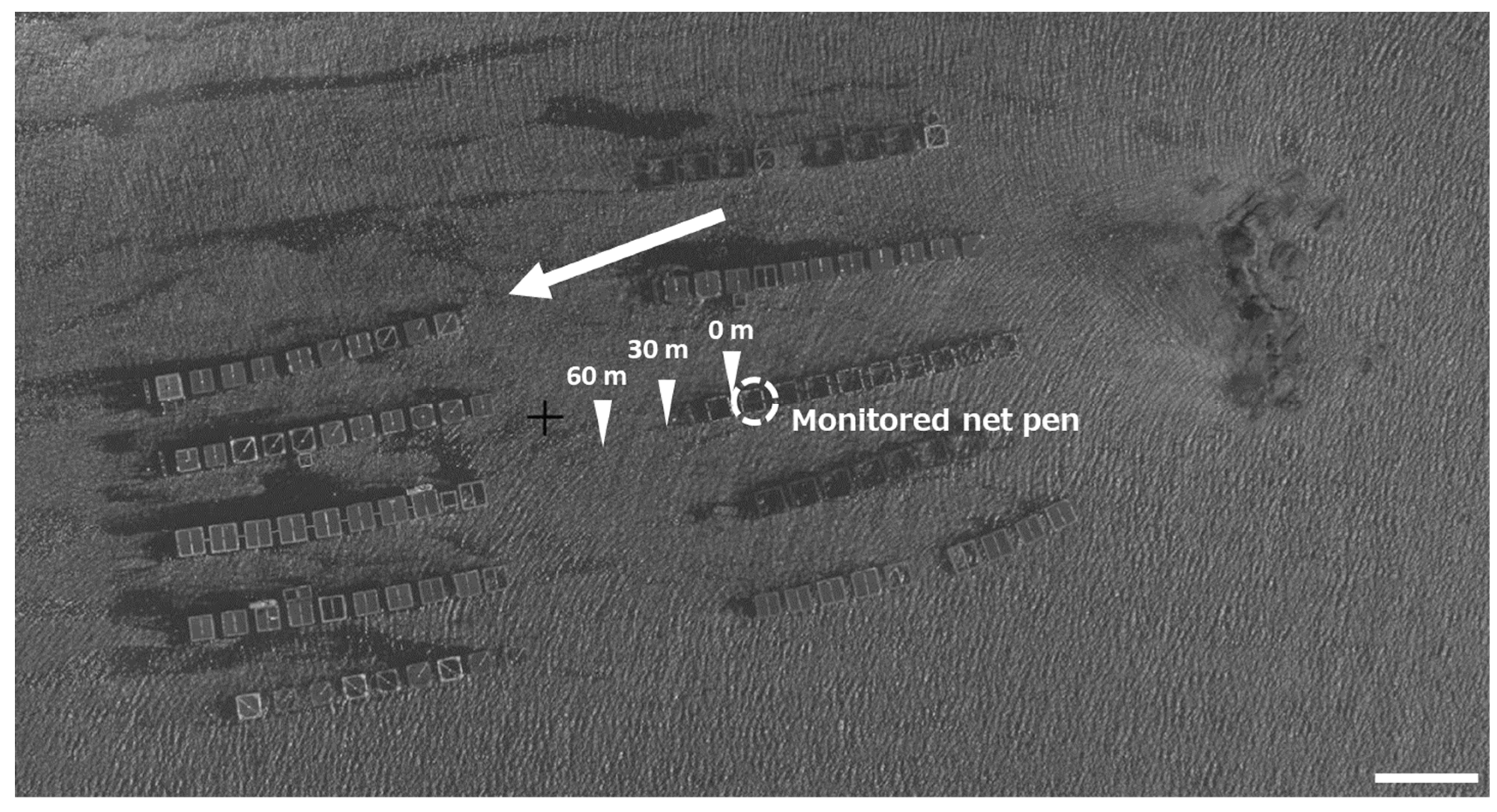
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. PZQ Detection
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doenhoff, M.J.; Cioli, D.; Utzinger, J. Praziquantel: mechanisms of action, resistance and new derivatives for schistosomiasis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J. Praziquantel Treatment in Trematode and Cestode Infections: An Update. Infect. Chemother. 2013, 45, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K. Diseases of cultured marine fishes caused by Platyhelminthes (Monogenea, Digenea, Cestoda). Parasitology 2015, 142, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.E.; Ernst, I.; Chambers, C.B.; Whittington, I.D. Efficacy of orally administered praziquantel against Zeuxapta seriolae and Benedenia seriolae (Monogenea) in yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2007, 77, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, G.J.; Burge, T.; Lymbery, A.J. A comparison of the palatability of racemic praziquantel and its two enantioseparated isomers in yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi (Valenciennes, 1833). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, C.; Starling, D.E.; Jones, D.E.; Brewer, M.T. Use of praziquantel to control platyhelminth parasites of fish. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, F.C. Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: A growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bártíková, H.; Podlipná, R.; Skálová, L. Veterinary drugs in the environment and their toxicity to plants. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2290–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Dawson, M.R.; Ellis, H.; Stamper, M.A. Praziquantel degradation in marine aquarium water. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telfer, T.C.; Baird, D.J.; McHenery, J.G.; Stone, J.; Sutherland, I.; Wislocki, P. Environmental effects of the anti-sea lice (Copepoda: Caligidae) therapeutant emamectin benzoate under commercial use conditions in the marine environment. Aquaculture 2006, 260, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DFO. Assessment of the Fate of Emamectin Benzoate, the Active Ingredient in SLICE®, near Aquaculture Facilities in British Columbia and its Effect on Spot Prawns (Pandalus platyceros). Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Science Advisory Report 2011/082. Available online: http://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/Library/346389.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2019).
- Stone, J.; Sutherland, I.H.; Sommerville, C.; Richards, R.H.; Endris, R.G. The duration of efficacy following oral treatment with emamectin benzoate against infestations of sea lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Kroyer), in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 2000, 23, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, L.; Ellis, S.; Robinson, T.; Marenghi, F.; Endris, R. Efficacy of emamectin benzoate against sea lice infestations of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L.: evaluation in the absence of an untreated contemporary control. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubbs, L.; Tingle, M. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of a praziquantel bolus in kingfish Seriola lalandi. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2006, 69, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubbs, L.A.; Tingle, M.D. Effect of dose escalation on multiple dose pharmacokinetics of orally administered praziquantel in kingfish Seriola lalandi. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, K.; Mine, R.; Shirakashi, S.; Kaneko, E.; Kubono, K.; Okada, T.; Sawada, Y.; Ogawa, K. Praziquantel treatment against Cardicola blood flukes: Determination of the minimal effective dose and pharmacokinetics in juvenile Pacific bluefin tuna. Aquaculture 2013, 402–403, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Safety Commission of Japan. Risk Assessment Report on an Oral Administering Agent for Veterinary Use into Hoses, Containing Ivermectin and Praziquantel as Active Ingredients. Available online: http://www.fsc.go.jp/fsciis/evaluationDocument/show/kya20071024027 (accessed on 22 February 2019).
- Tubbs, L.; Mathieson, T.; Tingle, M. Metabolism of praziquantel in kingfish Seriola lalandi. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 78, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Yokoyama, H. Parasitic Diseases of Cultured Marine Fish in Japan. Fish Pathol. 1998, 33, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.-S. Susceptibility or resistance of praziquantel in human schistosomiasis: A review. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Status | Sampling Date | Distance from Pen | n | PZQ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | 22 June 2018 | 0 m | 3 | <0.0001 |
| During the treatment | 26 July 2018 | 0 m | 3 | 0.00343 ± 0.00021 |
| 30 m | 3 | 0.00013 ± 0.00006 | ||
| 60 m | 2 | <0.0001 | ||
| 3 days post-treatment | 30 July 2018 | 0 m | 3 | 0.00008 ± 0.00003 |
| 30 m | 3 | <0.0001 | ||
| 60 m | 3 | <0.0001 |
| Status | Sampling Date | Distance from Pen | n | PZQ (mg/kg Dry Weight) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | 22 June 2018 | 0 m | 3 | <0.01 |
| 30 m | 3 | <0.01 | ||
| 60 m | 3 | <0.01 | ||
| Outside | 1 | <0.01 | ||
| 1 week post-treatment | 3 August 2018 | 0 m | 3 | <0.01 |
| 30 m | 3 | <0.01 | ||
| 60 m | 3 | <0.01 | ||
| 4 weeks post-treatment | 24 August 2018 | 0 m | 3 | <0.01 |
| 30 m | 3 | <0.01 | ||
| 60 m | 3 | <0.01 |
| Sampling Point | Latitude/Longitude | Water Depth |
|---|---|---|
| 0 m | 34°04′38.8″ N/136°13′12.4″ E | 29.1 m |
| 30 m | 34°04′38.46″ N/136°13′11.03″ E | 29.4 m |
| 60 m | 34°04′38.41″ N/136°13′10.01″ E | 29.6 m |
| Outside of the site | 34°04′16.70″ N/136°13′28.62″ E | 34.5 m |
| Number of Fish | Body Weight | Biomass | Oral Administration of PZQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9811 | 200 g/fish | 1962.2 kg | 50 mg/kg/day |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ido, A.; Kanemaru, M.; Tanioka, Y. Preliminary Monitoring of Praziquantel in Water and Sediments at a Japanese Amberjack (Seriola quinqueradiata) Aquaculture Site. Fishes 2019, 4, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020024
Ido A, Kanemaru M, Tanioka Y. Preliminary Monitoring of Praziquantel in Water and Sediments at a Japanese Amberjack (Seriola quinqueradiata) Aquaculture Site. Fishes. 2019; 4(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdo, Atsushi, Motohisa Kanemaru, and Yoshiharu Tanioka. 2019. "Preliminary Monitoring of Praziquantel in Water and Sediments at a Japanese Amberjack (Seriola quinqueradiata) Aquaculture Site" Fishes 4, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020024
APA StyleIdo, A., Kanemaru, M., & Tanioka, Y. (2019). Preliminary Monitoring of Praziquantel in Water and Sediments at a Japanese Amberjack (Seriola quinqueradiata) Aquaculture Site. Fishes, 4(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4020024





