Shifts in Eastern Mediterranean Fish Communities: Abundance Changes, Trait Overlap, and Possible Competition between Native and Non-Native Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
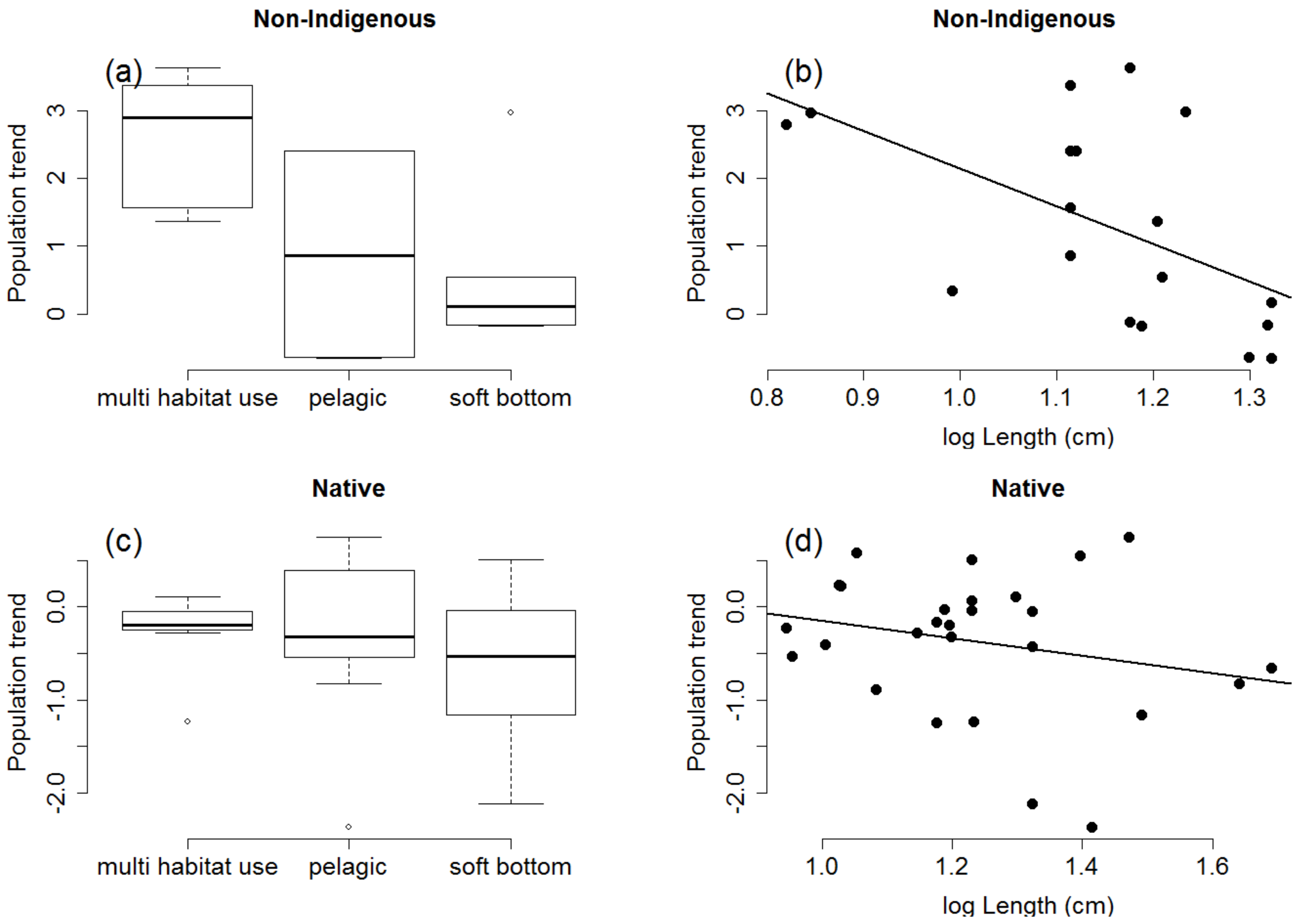
2.1. Species Traits Linked to Population Trends
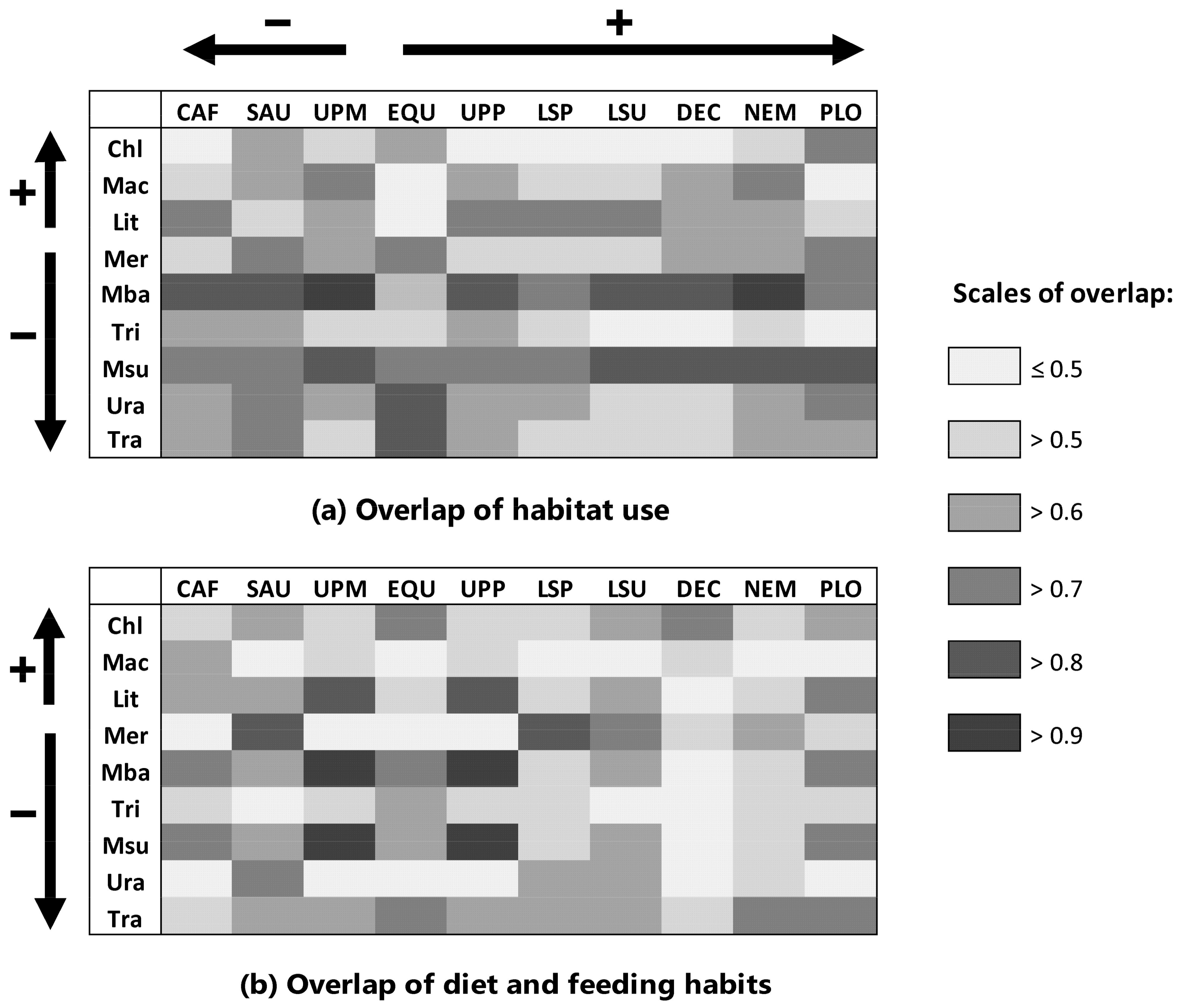
2.2. Estimation of Competition: Overlap in Habitat Use and Diet
3. Discussion
3.1. Competitive Displacement of Native Species by Non-Indigenous Fishes
3.2. Alternative Causes for Species Decline
3.3. Caveats
4. Materials and Methods
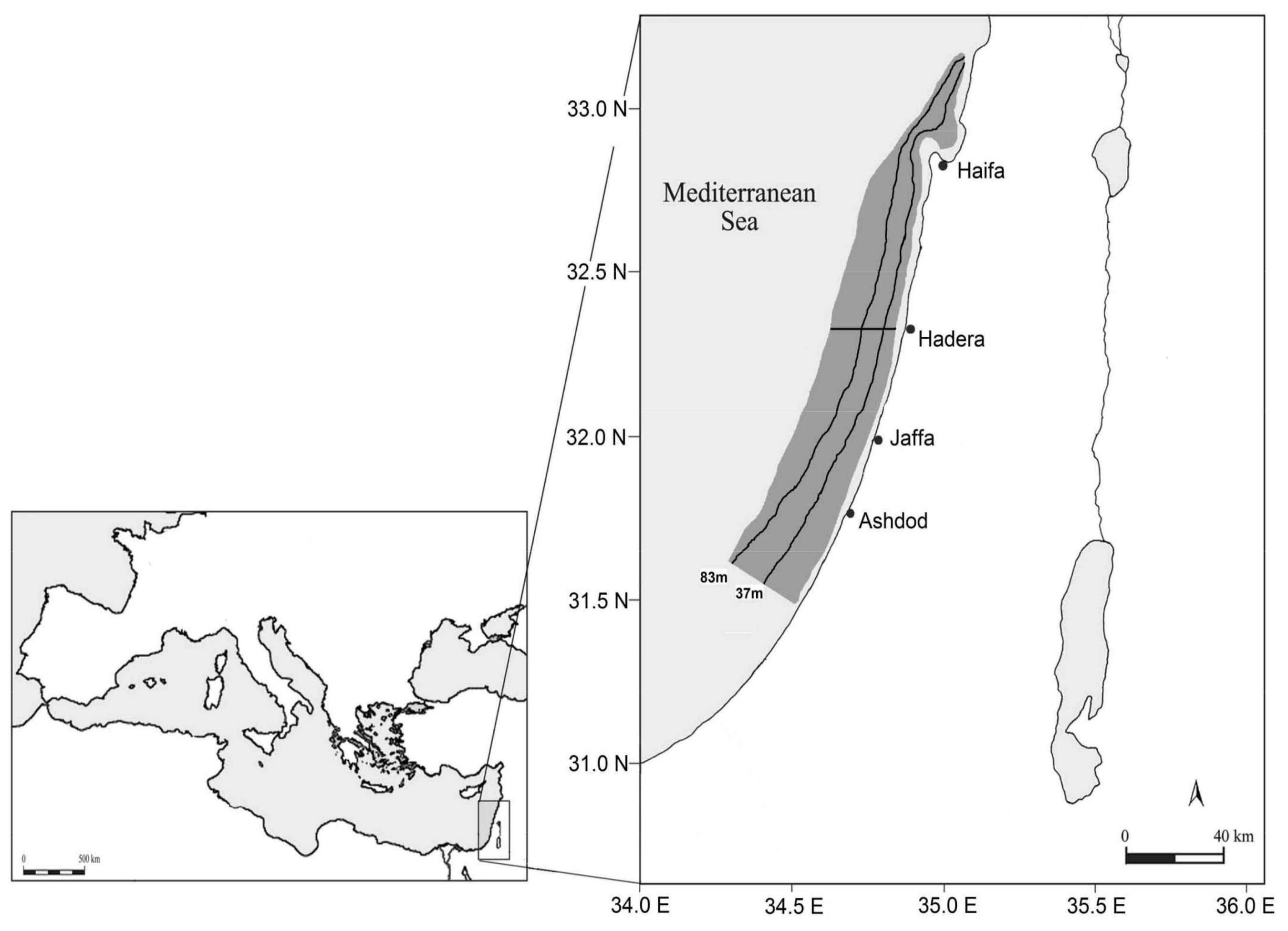
4.1. Study Area and Sampling Data
4.2. Statistical Analyses
4.2.1. Analyses of Traits Linked to Population Trends
4.2.2. Estimation of Competitive Displacement of Native Fishes
- Habitat-related traits:
- Diet-related traits:
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myers, R.A.; Worm, B. Rapid worldwide depletion of predatory fish communities. Nature 2003, 423, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, B.; Lotze, H.K.; Myers, R.A. Ecosystem effects of fishing and whaling in the North Pacific and Atlantic Ocean. In Whales, Whaling and Ocean Ecosystems; Estes, J.A., DeMaster, D.P., Doak, D.F., Williams, T.M., Brownell, R.L., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkley, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, J.K.; Worm, B. Cascading top-down effects of changing oceanic predator abundances. J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, V.; Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Buszowski, J.; Steenbeek, J.; Pauly, D. Fish biomass in the world ocean: A century of decline. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 512, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genner, M.J.; Sims, D.W.; Wearmouth, V.J.; Southall, E.J.; Southward, A.J.; Henderson, P.A.; Hawkins, S.J. Regional climate warming drives long-term community changes of British marine fish. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 2004, 271, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, P.L.; Jones, G.P.; Pratchett, M.S.; Williams, A.J. Climate change and the future for coral reef fishes. Fish Fish. 2008, 9, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.D.; Jennings, S.; Johnson, M.P.; Blanchard, J.L.; Schon, P.J.; Sims, D.W.; Genner, M.J. Continental shelf-wide response of a fish assemblage to rapid warming of the sea. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Dalsgaard, J.; Froese, R.; Torres, F., Jr. Fishing down the marine food web. Science 1998, 279, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenstreet, S.P.R.; Spence, F.E.; McMillan, J.A. Fishing effects in northeast Atlantic shelf seas: Patterns in fishing effort, diversity and community structure. V. Changes in structure of the North Sea groundfish species assemblage between 1925 and 1996. Fish. Res. 1999, 40, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Greenstreet, S.P.R.; Reynolds, J.D. Structural change in an exploited fish community: A consequence of differential fishing effects on species with contrasting life histories. J. Anim. Ecol. 1999, 68, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daan, N.; Gislason, H.; Pope, J.G.; Rice, J.C. Changes in the North Sea fish community: Evidence of indirect effects of fishing? ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.P.; McCormick, M.I.; Srinivasan, M.; Eagle, J.V. Coral decline threatens fish biodiversity in marine reserves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8251–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airoldi, L.; Balata, D.; Beck, M.W. The Gray Zone: Relationships between habitat loss and marine diversity and their applications in conservation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.K.; Fisher, R.; Pratchett, M.S.; Graham, N.A.J.; Dulvy, N.K.; Turner, R.A.; Cakacaka, A.; Polunin, N.V.C.; Rushton, S.P. Exploitation and habitat degradation as agents of change within coral reef fish communities. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 2796–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.J.; Thrush, S.F.; Hewitt, J.E.; Cummings, V.J.; Funnel, G. Fishing impacts and the degradation or loss of habitat structure. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 1999, 6, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchett, M.S.; Munday, P.L.; Wilson, S.K.; Graham, N.A.J.; Cinner, J.E.; Bellwood, D.R.; Jones, G.P.; Polunin, N.V.C.; McClanahan, T.R. Effects of climate-induced coral bleaching on coral-reef fishes: Ecological and economic consequences. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: Annual Review; Gibson, R.N., Atkinson, R.J.A., Gordon, J.D.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; Volume 46, pp. 251–296. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, G.E.; Crawley, N.; Lunde, I.G.; Munday, P.L. Elevated temperature reduces the respiratory scope of coral reef fishes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, M.; Galil, B.S. A review of changes in the fish assemblages of Levantine inland and marine ecosystems following the introduction of non-native fishes. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmelin-Vivien, M.L.; Bitar, G.; Harmelin, J.G.; Monestiez, P. The littoral fish community of the Lebanese rocky coast (eastern Mediterranean Sea) with emphasis on Red Sea immigrants. Biol. Invasions 2005, 7, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golani, D.; Appelbaum-Golani, B. (Eds.) Fish Invasions of the Mediterranean Sea: Change and Renewal; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Beaugrand, G.; Georgopoulos, D.; Zenetos, A.; Pancucci-Papadopoulou, A.M.; Theocharis, A.; Papathanassiou, E. Global climate change amplifies the entry of tropical species into the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Azzurro, E.; Bariche, M. The Ongoing Shift of Mediterranean Coastal Fish Assemblages and the Spread of Non-Indigenous Species. In Environmental Sciences—Biodiversity Enrichment in a Diverse World; Lameed, G.L., Ed.; InTech: New York, NY, USA; 2012; pp. 263–280. [Google Scholar]
- Çınar, M.E.; Bilecenoğlu, M.; Öztürk, B.; Katagan, T.; Yokeş, M.B.; Aysel, V.; Dağlı, E.; Açık, Ş.; Özcan, T.; Erdoğan, H. An updated review of alien species on the coasts of Turkey. Med. Mar. Sci. 2011, 12, 257–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelist, D.; Sonin, O.; Golani, D.; Rilov, G.; Spanier, E. Spatiotemporal patterns of catch and discards of the Israeli Mediterranean trawl fishery in the early 1990s: Ecological and conservation perspectives. Sci. Mar. 2011, 75, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillier, J.B. Le Canal de Suez et sa fauna ichthyologique. Mém. Soc. Zool. 1902, 15, 279–318. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, E.; Schembri, P.S. Common traits associated with establishment and spread of Lessepsian fishes in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelist, D.; Rilov, G.; Golani, D.; Carlton, J.T.; Spanier, E. Restructuring the Sea: profound shifts in the world’s most invaded marine ecosystem. Divers. Distrib. 2013, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givan, O.; Edelist, D.; Sonin, O.; Belmaker, J. Thermal affinity as the dominant factor changing Mediterranean fish abundances. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 24, E80–E89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golani, D. Colonization of the Mediterranean by Red Sea fishes via the Suez Canal—Lessepsian migration. In Fish Invasions of the Mediterranean Sea: Change and Renewal; Golani, D., Appelbaum-Golani, B., Eds.; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2010; pp. 145–188. [Google Scholar]
- Albins, M.; Hixon, M. Worst case scenario: Potential long-term effects of invasive predatory lionfish (Pterois volitans) on Atlantic and Caribbean coral-reef communities. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2011, 96, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albins, M. Effects of invasive Pacific red lionfish, Pterois volitans, versus a native predator on Bahamian coral-reef fish communities. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.J.; Akins, J.L.; Maljković, A.; Côté, I.M. Invasive Lionfish Drive Atlantic Coral Reef Fish Declines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Yami, M.; Glaser, T. The invasion of Saurida undosquamis (Richardson) into the Levant basin—An example of biological effect of interoceanic canals. Fish B-NOAA 1974, 72, 359–373. [Google Scholar]
- Fishelson, L. Marine animal assemblages along the littoral of the Israeli Mediterranean seashore: The Red-Med communities of species. Italian J. Zool. 2000, 67, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariche, M.; Letourneur, Y.; Harmelin-Vivien, M. Temporal fluctuations and settlement patterns of native and Lessepsian herbivorous fishes on the Lebanese coast (Eastern Mediterranean). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2004, 70, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumi, S. Distribution patterns of the invasive herbivore Siganus luridus (Rüppell, 1829) and its relation to native benthic communities in the central Aegean Sea, Northeastern Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. 2014, 35, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubs, D.O.L.; Corkum, L.D. Behavioral interactions between round gobies (Neogobius melanostomus) and mottled sculpins (Cottus bairdi). J. Great Lakes Res. 1996, 22, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabik, T.R.; Magnuson, J.J.; McLain, A.S. Predicting the effects of rainbow smelt on native fishes in small lakes: Evidence from long-term research on two lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, C.; Bisazza, A.; García-Berthou, E. Salinity mediates the competitive interactions between invasive mosquitofish and an endangered fish. Oecologia 2008, 155, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leunda, P.M. Impacts of non-native fishes on Iberian freshwater ichthyofauna: Current knowledge and gaps. Aquat. Invasions 2010, 5, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucherousset, J.; Olden, J.D. Ecological Impact of Non-native Freshwater Fishes. Fisheries 2011, 36, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, M.; Novotná, K.; Potužák, J.; Hůda, J.; Pechar, L. Impact of topmouth gudgeon (Pseudorasbora parva) on production of common carp (Cyprinus carpio)—Question of natural food structure. Biología 2014, 69, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, J.; Przybylski, M. Life-history traits of non-native freshwater fish invaders differentiate them from natives in the Central European bioregion. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, A.M.L.; Almqvist, G.; Skóra, K.E.; Appelberg, M. Indications of competition between non-indigenous round goby and native flounder in the Baltic Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järv, L.; Kotta, J.; Kotta, I.; Raid, T. Linking the structure of benthic invertebrate communities and the diet of native and invasive fish species in a brackish water ecosystem. Ann. Zool. Fennici 2011, 48, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakauskas, V.; Pūtys, Ž.; Dainys, J.; Lesutienė, J.; Ložys, L.; Arbačiauskas, K. Increasing population of the invader round goby, Neogobius melanostomus (Actinopterygii: Perciformes: Gobiidae), and its trophic role in the Curonian Lagoon, SE Baltic Sea. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2013, 43, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.; Lorenz, J.J.; Trexler, J.C. Per capita effects of non-native Mayan Cichlids (Cichlasoma urophthalmus Günther) on native fish in the estuarine southern Everglades. Copeia 2013, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, M.; Galil, B.S.; Diamant, A.; Stern, N.; Levitt-Barmats, Y. Invading up the food web? Invasive fish in the southeastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elleouet, J.; Albouy, C.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Mouillot, D.; Leprieur, F. A trait-based approach for assessing and mapping niche overlap between native and exotic species: The Mediterranean coastal fish fauna as a case study. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Yildirim, D.; Ballesteros, E. Alien Marine Fishes Deplete Algal Biomass in the Eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergés, A.; Tomas, F.; Cebrian, E.; Ballesteros, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Spiegel, D.; Sala, E. Tropical rabbitfish and the deforestation of a warming temperate sea. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelist, D.; Golani, D.; Rilov, G.; Spanier, E. The invasive venomous striped eel catfish Plotosus lineatus in the Levant: Possible mechanisms facilitating its rapid invasional success. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelist, D. (National Institute of Oceanography, Tel-Shikmona, Haifa, Israel). Personal communication, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gücü, A.C.; Bingal, F. Trawlable species assemblages on the continental shelf of the Northeastern Levant Sea (Mediterranean) with an emphasis on Lessepsian migration. Acta Adriat. 1994, 35, 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Golani, D.; Ben-Tuvia, A. Lessepsian migration and the Mediterranean fisheries of Israel. In Condition of the World’s Aquatic Habitats, Proceedings of the World Fisheries Congress 1992, Theme 1; Athens, Greece; Armantrout, N.B., Wolotira, R.J., Jr., Eds.; Oxford & IBH Publishing Company: Delhi, India, 1995; pp. 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Carpentieri, P.; Lelli, S.; Colloca, F.; Mohanna, C.; Bartolino, V.; Moubayed, S.; Ardizzone, G.D. Incidence of lessepsian migrants on landings of the artisanal fishery of south Lebanon. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2009, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Tuset, V.M.; Lombarte, A.; Maynou, F.; Simberloff, D.; Rodríguez-Pérez, A.; Solé, R.V. External morphology explains the success of biological invasions. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givan, O.; Parravicini, V.; Kulbicki, M.; Belmaker, J. Trait structure reveals the processes underlying fish establishment in the Mediterranean. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G.; Gislason, H.; Graham, K.; Hill, L.; Jin, X.; Koranteng, K.; Manickchand-Heileman, S.; Payá, I.; Sainsbury, K.; Sanchez, F.; et al. Impact of fishing on size composition and diversity of demersal fish communities. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Kaiser, M.J.; Reynolds, J.D. Marine Fisheries Ecology; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.D.; Dulvy, N.K.; Goodwin, N.B.; Hutchings, J.A. Biology of extinction risk in marine fishes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittensor, D.P.; Myers, R.A.; Worm, B. Macroecology of exploited marine systems. In Marine Macroecology; Witman, J., Roy, K., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009; pp. 310–340. [Google Scholar]
- Pinnegar, J.K.; Polunin, N.V.C.; Badalamenti, F. Long-term changes in the trophic level of western Mediterranean fishery and aquaculture landings. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Shannon, L.J.; Moloney, C.L.; Palomera, I.; Tudela, S. Comparing trophic flows and fishing impacts of a NW Mediterranean ecosystem with coastal upwelling systems by means of standardized models and indicators. Ecol. Model. 2006, 198, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E. The advance of thermophilic fishes in the Mediterranean Sea: Overview and methodological questions. In Climate Warming and Related Changes in Mediterranean Marine Biota; Briand, F., Ed.; Workshop Monographs No. 35; CIESM: Villa Girasole, Monaco, 2008; pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Despalatović, M.; Grubelić, I.; Nikolić, V.; Dragičević, B.; Dulčić, J.; Žuljević, A.; Cvitković, I.; Antoli, B. Climate Warming and Related Changes in Mediterranean Marine Biota; Briand, F., Ed.; Workshop Monographs No. 35; CIESM: Villa Girasole, Monaco, 2008; pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Albouy, C.; Guilhaumon, F.; Araujo, M.B.; Mouillot, D.; Leprieur, F. Combining projected changes in species richness and composition reveals climate change impacts on coastal Mediterranean fish assemblages. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 2995–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albouy, C.; Guilhaumon, F.; Leprieur, F.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Somot, S.; Aznar, R.; Velez, L.; Le Loc’h, F.; Mouillot, D. Projected climate change and the changing biogeography of coastal Mediterranean fishes. J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tuvia, A.; Golani, D. Temperature as the main factor influencing Lessepsian migration. In The Mediterranean Sea in the 21th Century: Who for? Mediterranean: Climatic Variability, Environment and Biodiversity; Benhamida, S., Le Goff, F., Eds.; Maison de l’environnement: Montpellier, France, 1996; pp. 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Mouillot, D. Increasing southern invasion enhances congruence between endemic and exotic Mediterranean fish fauna. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmaker, J.; Parravicini, V.; Kulbicki, M. Ecological traits and environmental affinity explain Red Sea fish introduction into the Mediterranean. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parravicini, V.; Azzurro, E.; Kulbicki, M.; Belmaker, J. Niche shift can impair the ability to predict invasion risk in the marine realm: An illustration using Mediterranean fish invaders. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. (Eds.) FishBase. Available online: http://www.fishbase.org (accessed on 23 September 2017).
- Kolar, C.S.; Lodge, D.M. Ecological predictions and risk assessment for alien fishes in North America. Science 2002, 298, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, M.P.; Moyle, P.B.; Levine, R. Invasive species profiling? Exploring the characteristics of non-native fishes across invasion stages in California. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfman, G.S.; Collette, B.B.; Facey, D.E.; Bowen, B.W. The Diversity of Fishes, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. Factor-Analysis and Aic. Psychometrika 1987, 52, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Schmidt, T.S.B.; Rodrigues, J.F.M.; von Mering, C.A. Family of Interaction-Adjusted Indices of Community Similarity. ISME J. 2017, 11, 791–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyer, I.; Wesche, K. Multivariate Statistik in der Ökologie; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zaret, T.; Rand, S. Competition in tropical stream fishes: Support for the competitive exclusion principle. Ecology 1971, 52, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labropoulou, M.; Eleftheriou, A. The foraging ecology of two pairs of congeneric demersal fish species: Importance of morphological characteristics in prey selection. J. Fish Biol. 1997, 50, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogianni, E.; Giakoumi, S.; Andriopoulou, A.; Chatzinikolaou, Y. Prey utilisation and trophic overlap between the non native mosquitofish and a native fish in two Mediterranean rivers. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Helfman, G.S. Fish behaviour by day, night, and twilight. In Behaviour of Teleost Fishes, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1993; pp. 479–512. ISBN 0-412-42930-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hixon, M.A. Competition. In The Ecology of Marine Fishes: California and Adjacent Waters; Allen, L.G., Pondella, D.J., II., Horn, M.H., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 449–465. ISBN 0-520-24653-5. [Google Scholar]
- Colmenero, A.I.; Aguzzi, J.; Lombarte, A.; Bozzano, A. Sensory constraints in temporal segregation in two species of anglerfish, Lophius budegassa and L. piscatorius. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 416, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, K.I.; Karpouzi, V.S. Feeding habits and trophic levels of Mediterranean fish. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2002, 11, 217–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in California waters. Fish. Bull. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Cerino, D.; Overton, A.S.; Rice, J.A.; Morris, J.A. Bioenergetics and trophic impacts of the invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2013, 142, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkwitt, C.E. Non-linear effects of invasive lionfish density on native coral-reef fish communities. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Proportion 1990–1994 | Proportion 2008–2011 | Log-Ratio of Proportional Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plotosus lineatus (Thunberg, 1787) | <0.0001 | 0.0900 | 3.6302 |
| Nemipterus randalli Russell, 1986 | <0.0001 | 0.0493 | 3.3685 |
| Decapterus russelli (Rüppell, 1830) | <0.0001 | 0.0203 | 2.9839 |
| Jaydia smithi Kotthaus, 1970 | <0.0001 | 0.0196 | 2.9680 |
| Ostorhinchus fasciatus (White, 1790) | <0.0001 | 0.0133 | 2.8007 |
| * Etrumeus golanii Dibattista et al., 2012 | <0.0001 | 0.0107 | 2.4060 |
| * Trachurus indicus Nekrasov, 1966 | <0.0001 | 0.0053 | 2.4034 |
| Lagocephalus suezensis Clark & Gohar, 1953 | <0.0007 | 0.0238 | 1.5610 |
| Lagocephalus spadiceus (Richardson, 1845) | <0.0002 | 0.0044 | 1.3681 |
| * Dussumieria elopsoides Bleeker, 1849 | <0.0008 | 0.0055 | 0.8622 |
| * Scomber colias Gmelin, 1789 | 0.0033 | 0.0184 | 0.7480 |
| * Spicara maena (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0100 | 0.0382 | 0.5835 |
| * Trachurus trachurus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0056 | 0.0199 | 0.5511 |
| Upeneus pori Ben-Tuvia & Golani, 1989 | 0.0038 | 0.0133 | 0.5454 |
| Chlorophthalmus agassizi Bonaparte, 1840 | 0.0012 | 0.0038 | 0.5046 |
| Equulites klunzingeri (Steindachner, 1898) | 0.0595 | 0.1293 | 0.3371 |
| Macroramphosus scolopax (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0089 | 0.0154 | 0.2367 |
| * Engraulis encrasicolus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0300 | 0.0505 | 0.2269 |
| Stephanolepis diaspros Fraser-Brunner, 1940 | 0.0034 | 0.0050 | 0.1631 |
| Lithognathus mormyrus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0026 | 0.0034 | 0.1083 |
| Pagellus acarne (Risso, 1827) | 0.0425 | 0.0489 | 0.0613 |
| * Sardinella aurita Valenciennes, 1847 | 0.0063 | 0.0059 | −0.0292 |
| Bothus podas (Delaroche, 1809) | 0.0050 | 0.0046 | −0.0353 |
| Citharus linguatula (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0146 | 0.0130 | −0.0508 |
| Upeneus moluccensis (Bleeker, 1855) | 0.1267 | 0.0951 | −0.1246 |
| Dentex macrophthalmus (Bloch, 1791) | 0.0369 | 0.0252 | −0.1651 |
| Saurida lessepsianus Russell et al., 2015 | 0.0327 | 0.0223 | −0.1661 |
| Callionymus filamentosus Valenciennes, 1837 | 0.0238 | 0.0159 | −0.1748 |
| Pagellus erythrinus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.1065 | 0.0678 | −0.1958 |
| Serranus hepatus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0122 | 0.0072 | −0.2298 |
| Boops boops (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0899 | 0.0476 | −0.2762 |
| * Sardina pilchardus (Walbaum, 1792) | 0.0153 | 0.0074 | −0.3173 |
| * Spicara smaris (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0473 | 0.0187 | −0.4033 |
| * Trachurus mediterraneus (Steindachner, 1868) | 0.0328 | 0.0123 | −0.4238 |
| Lepidotrigla cavillone (Lacépède, 1801) | 0.0332 | 0.0097 | −0.5351 |
| * Alepes djedaba (Forsskål, 1775) | 0.0060 | 0.0014 | −0.6349 |
| * Sphyraena pinguis Günther, 1874 | 0.0093 | 0.0021 | −0.6542 |
| * Sphyraena sphyraena (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0052 | 0.0011 | −0.6596 |
| Merluccius merluccius (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0189 | 0.0028 | −0.8221 |
| Mullus barbatus Linnaeus, 1758 | 0.0872 | 0.0113 | −0.8878 |
| Trigla lyra Linnaeus, 1758 | 0.0027 | 0.0002 | −1.1608 |
| Mullus surmuletus Linnaeus, 1758 | 0.0704 | 0.0041 | −1.2345 |
| Uranoscopus scaber (Linnaeus, 1758) | 0.0027 | 0.0002 | −1.2475 |
| Trachinus draco Linnaeus, 1758 | 0.0066 | 0.0001 | −2.1136 |
| * Trachurus picturatus (Bowdich, 1825) | 0.0030 | <0.0001 | −2.3690 |
| Category | NIS | Growth rate | Habitat | Length log (cm) | Max. Depth log (m) | Min. Depth log (m) | Trophic Level | AICc | ∆AICc | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All species | 2.17 | + | −2.14 | 1.33 | 131.46 | 0.00 | 0.27 | |||
| 2.19 | + | −2.01 | 1.31 | 0.22 | 133.54 | 2.08 | 0.09 | |||
| 1.96 | 0.87 | + | −1.79 | 1.29 | 133.60 | 2.14 | 0.09 | |||
| 2.12 | + | −2.40 | 1.30 | 0.26 | 134.10 | 2.63 | 0.07 | |||
| 1.89 | 1.63 | + | 1.22 | 134.78 | 3.32 | 0.05 | ||||
| NIS | + | −5.62 | 1.80 | 64.05 | 0.00 | 0.29 | ||||
| −5.54 | 65.38 | 1.32 | 0.15 | |||||||
| + | −4.96 | 65.68 | 1.63 | 0.13 | ||||||
| −5.67 | 1.17 | 67.11 | 3.06 | 0.06 | ||||||
| 1.18 | −4.96 | 68.21 | 4.16 | 0.04 | ||||||
| Natives | 65.45 | 0.00 | 0.15 | |||||||
| 1.48 | 65.88 | 0.43 | 0.12 | |||||||
| −0.93 | 66.46 | 1.01 | 0.09 | |||||||
| 0.31 | 67.55 | 2.10 | 0.05 | |||||||
| −0.09 | 67.92 | 2.47 | 0.04 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arndt, E.; Givan, O.; Edelist, D.; Sonin, O.; Belmaker, J. Shifts in Eastern Mediterranean Fish Communities: Abundance Changes, Trait Overlap, and Possible Competition between Native and Non-Native Species. Fishes 2018, 3, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3020019
Arndt E, Givan O, Edelist D, Sonin O, Belmaker J. Shifts in Eastern Mediterranean Fish Communities: Abundance Changes, Trait Overlap, and Possible Competition between Native and Non-Native Species. Fishes. 2018; 3(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleArndt, Erik, Or Givan, Dor Edelist, Oren Sonin, and Jonathan Belmaker. 2018. "Shifts in Eastern Mediterranean Fish Communities: Abundance Changes, Trait Overlap, and Possible Competition between Native and Non-Native Species" Fishes 3, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3020019
APA StyleArndt, E., Givan, O., Edelist, D., Sonin, O., & Belmaker, J. (2018). Shifts in Eastern Mediterranean Fish Communities: Abundance Changes, Trait Overlap, and Possible Competition between Native and Non-Native Species. Fishes, 3(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3020019





