Feed Additives in Aquaculture: Benefits, Risks, and the Need for Robust Regulatory Frameworks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Natural Immunostimulants as Feed Additives in Fish and Shrimp Diets
Fish and Shrimp Immune Response to Natural Immunostimulants as a Feed Additive
3. Probiotics and Prebiotics as Feed Additives in Fish and Shrimp Diets
3.1. Immune Response of Fish to Probiotics and Prebiotics as Feed Additives
3.2. The Immune Response of Shrimps to Probiotics and Prebiotics as Feed Additives
3.3. Growth Response of Fish to Probiotics and Prebiotics as Feed Additives
4. Feed Additives in Fish and Shrimp Diets
5. Phytogenics as Feed Additives in Fish and Shrimp Diets
| Phytogenic Compounds | Benefit | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ginger, oregano, thyme, garlic | Growth promotion | Enhances feed intake and digestion, leading to improved growth performance | [170,171] |
| Carvacrol, thymol | Antimicrobial activity, growth promotion | Inhibits pathogenic bacteria and fungi in the gut | [172] |
| Echinacea, garlic, turmeric | Immune system enhancement | Stimulates innate immune responses and disease resistance | [173] |
| Curcumin, flavonoids, polyphenols | Antioxidant properties, disease resistance, reproductive, and growth performance | Reduces oxidative stress and improves cellular health, survival, and growth | [174] |
| Fennel and anise essential oils | Antibacterial, antioxidant, growth performance, lipid metabolism | Enhanced growth performance and well-being | [175,176] |
| Liquorice | Antioxidant properties, disease-resistant, immunostimulant | Enhances growth and survival, reduces oxidative stress | [177] |
| Herbal blends | immune responses, antioxidants, and disease resistance | Enhanced growth and survival | [178] |
5.1. Emerging and Next-Generation Feed Additives in Aquaculture
5.2. Mechanisms of Action and Measurable Biomarkers
6. Environmental Concerns About Aquatic Feed Additives
7. Regulatory Framework for the Use of Feed Additives in Fish and Shrimp Farming
7.1. International Regulatory Framework
7.2. Regional and National Regulatory Frameworks
8. Key Issues and Measurable Endpoints in the Application of Feed Additives
9. Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities
10. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, P.; Zhang, W.; Belton, B.; Little, D.C. Misunderstandings, myths and mantras in aquaculture: Its contribution to world food supplies has been systematically over reported. Mar. Policy 2019, 106, 103547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidane, D.G.; Brækkan, E.H. Global seafood demand growth differences across regions, income levels, and time. Mar. Resour. Econ. 2021, 36, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2024: Blue transformation in action. In The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Bateman, I.J.; Hinchliffe, S.J.; Bass, D.; Hartnell, R.; Santos, E.M.; Devlin, M.J.; Feist, S.W.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; et al. Sustainable aquaculture through the One Health lens. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.C.; Hamidoghli, A.; Bae, J. Feed additives: An overview. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 195–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G. Trends in global aquaculture and aquafeed production: 2000–2017. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; McNevin, A.A. Overview of aquaculture feeds: Global impacts of ingredient production, manufacturing, and use. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Marimuthu, V.; Shanmugam, S.; Sarawagi, A.D.; Kumar, A.; Kim, I.H.; Balasubramanian, B. A glimpse on influences of feed additives in aquaculture. eFood 2022, 3, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, P. Functional feed additives in aquaculture feeds. In Aquafeed Formulation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 217–237. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, J.X.H.; Tan, L.T.H.; Law, J.W.F.; Ser, H.L.; Khaw, K.Y.; Letchumanan, V.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H. Harnessing the potentialities of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, paraprobiotics, and postbiotics for shrimp farming. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1478–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Romo, J.P.; Cornejo-Granados, F.; Lopez-Zavala, A.A.; Viana, M.T.; Sánchez, F.; Gallardo-Becerra, L.; Luque-Villegas, M.; Valdez-López, Y.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Cota-Huízar, A.; et al. Agavin induces beneficial microbes in the shrimp microbiota under farming conditions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, U.D.; Lin, N.; Akhter, N.; Siddiqui, T.; Li, S.; Wu, B. Overview of the latest developments in the role of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in shrimp aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 114, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Yuan, M.; Xu, L.; Lio, E.; Zhang, F.; Mou, H.; Secundo, F. Application of enzymes as a feed additive in aquaculture. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busti, S.; Rossi, B.; Volpe, E.; Ciulli, S.; Piva, A.; D’Amico, F.; Soverini, M.; Candela, M.; Gatta, P.P.; Bonaldo, A.; et al. Effects of dietary organic acids and nature identical compounds on growth, immune parameters and gut microbiota of European sea bass. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (EFSA FEEDAP Panel); Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; Puente, S.L.; et al. Guidance on the assessment of the safety of feed additives for the environment. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05648. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Saxena, M.J. Feed additives in animal health. Nutraceuticals Vet. Med. 2019, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, N.; Stenson, I.; Pettersson, M.N.; Warshan, D.; Nguyen-Kim, H.; Tedengren, M.; Kautsky, N. Antibiotic use in Vietnamese fish and lobster sea cage farms; implications for coral reefs and human health. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.H.; Rossi, P.; Dinh, H.D.K.; Pham, N.T.A.; Tran, P.A.; Ho, T.T.K.M.; Dinh, Q.T.; De Alencastro, L.F. Analysis of antibiotic multi-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in the effluent of an intensive shrimp farm (Long An, Vietnam). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, A.V.; Navashin, S.M. Natural immunostimulants. Antibiotiki 1983, 28, 702–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zebeaman, M.; Tadesse, M.G.; Bachheti, R.K.; Bachheti, A.; Gebeyhu, R.; Chaubey, K.K. Plants and Plant-Derived Molecules as Natural Immunomodulators. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 7711297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooljun, C.; Jariyapong, P.; Wongtawan, T.; Hirono, I.; Wuthisuthimethavee, S. Effect of feeding different types of β-glucans derived from two marine diatoms (Chaetoceros muelleri and Thalassiosira weissflogii) on growth performance and immunity of banana shrimp (Penaeus merguiensis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 130, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Advances in research on immunoregulation of macrophages by plant polysaccharides. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servin Arce, K.; de Souza Valente, C.; do Vale Pereira, G.; Shapira, B.; Davies, S.J. Modulation of the gut microbiota of Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei Boone, 1931) by dietary inclusion of a functional yeast cell wall-based additive. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, G.; Hafezieh, M.; Karimi, A.A.; Azra, M.N.; Van Doan, H.; Tapingkae, W.; Abdelrahman, H.A.; Dawood, M.A. The synergistic effects of plant polysaccharide and Pediococcus acidilactici as a synbiotic additive on growth, antioxidant status, immune response, and resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, K.; Ravichandran, S.; Muralisankar, T.; Uthayakumar, V.; Chandirasekar, R.; Seedevi, P.; Rajan, D.K. Potential uses of fungal polysaccharides as immunostimulants in fish and shrimp aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. Enhancement of seaweed polysaccharides (fucoidan and laminarin) on the phagocytosis of macrophages via activation of intelectin in blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1124880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.B. Stimulatory effect of β-glucans on immune cells. Immune Netw. 2011, 11, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahasrabudhe, N.M.; Dokter-Fokkens, J.; de Vos, P. Particulate β-glucans synergistically activate TLR4 and Dectin-1 in human dendritic cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, M.J.; Webster, S.J.; Chee, R.; Williams, D.L.; Hill Gaston, J.S.; Goodall, J.C. β-Glucan size controls dectin-1-mediated immune responses in human dendritic cells by regulating IL-1β production. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadiuzzaman, M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Shahjahan, M.; Bai, S.C.; Min, T.; Hossain, Z. β-Glucan: Mode of Action and Its Uses in Fish Immunomodulation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 905986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie-Hanson, L.; Peterman, A.E. Trained immunity provides long-term protection against bacterial infections in channel catfish. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.J.; Grinstein, S.; Roth, Z. Diversity and versatility of phagocytosis: Roles in innate immunity, tissue remodeling, and homeostasis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, H.; Ebbeskotte, V.; Gruenwald, J. Immune-modulatory effects of dietary Yeast Beta-1, 3/1, 6-D-glucan. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Pan, Y.; Luo, L.; Luo, L. Effects of dietary β-1, 3-glucan, chitosan or raffinose on the growth, innate immunity and resistance of koi (Cyprinus carpio koi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, D.K.; Das, P.; Kumar, S.; Mandal, S.C.; Prusty, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; Akhtar, M.S.; Behera, B.K.; Kumar, K.; Pal, A.K.; et al. Beta-glucan: An ideal immunostimulant in aquaculture (a review). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 431–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Álvarez, N.A.; Casillas-Hernández, R.; Magallón-Barajas, F.J.; Ramirez-Orozco, J.M.; Carbajal-Millan, E. Protector effect of beta-glucans from shrimp pond-related yeasts in Penaeus vannamei rearing under white spot syndrome virus presence. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2021, 49, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrino, K.G.S.; Augusto, E.; Serrano, J.; Valeriano, L.; Corre, J. Effects of dietary nucleotides on the immune response and growth of juvenile Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Asian Fish. Sci. 2012, 25, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A. Modulation of the immune response mediated by dietary nucleotides. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Yi, L.; Xu, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Effects of dietary nucleotides on growth, non-specific immune response and disease resistance of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Yin, P.; Tian, L.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, J. Dietary supplementation of astaxanthin improved the growth performance, antioxidant ability and immune response of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) fed high-fat diet. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidoghli, A.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, S.; Choi, W.; Choi, Y.H.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of Yeast Hydrolysate in a Low-Fishmeal Diet for Whiteleg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Animals 2023, 13, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, P.; Kurian, A.; Lakshmi, S.; Faggio, C.; Esteban, M.A.; Ringø, E. Herbal immunomodulators in aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, E.; Kucukkosker, B.; Bilen, S.; Kenanoglu, O.N.; Corum, O.; Özbek, M.; Parug, S.S. A novel herbal immunostimulant for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) against Yersinia ruckeri. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 110, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar Ali, I.; Radhakrishnan, D.K.; Kumar, S. Immunostimulants and Their Uses in Aquaculture. In Aquaculture Science and Engineering; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 291–322. [Google Scholar]
- Muahiddah, N.; Diamahesa, W.A. Potential use of brown algae as an immunostimulant material in the aquaculture field to increase non-specific immunity and fight disease. J. Fish Health 2022, 2, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, H.; Qin, C. Comparison of dietary arginine or/and inulin supplementation on growth, digestive ability and ammonia tolerance of juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetvicka, V.; Vannucci, L.; Sima, P. The effects of β–glucan on fish immunity. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 5, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos-Vidal, E.; Reyes-López, F.; Teles, M.; MacKenzie, S. The response of fish to immunostimulant diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 34–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, A.K.; Singh, S.P.; Awasthi, A. Immunostimulants for shrimp aquaculture: Paving pathway towards shrimp sustainability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 25325–25343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.J.; Brown, J.H.; Hauton, C. Immunostimulation in crustaceans: Does it really protect against infection? Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2003, 15, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos, S.; Filho, L.G.A.; Diniz, F.M.; Pereira, A.M. Immunostimulants derived from plants and algae to increase resistance of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) against vibriosis. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2023, 77, 297–337. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Small, B.C.; Kumar, V.; Hardy, R. Utilisation of functional feed additives to produce cost-effective, ecofriendly aquafeeds high in plant-based ingredients. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 16, 121–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiataramgul, A.; Maneenin, S.; Purton, S.; Areechon, N.; Hirono, I.; Brocklehurst, T.W.; Unajak, S. An oral delivery system for controlling white spot syndrome virus infection in shrimp using transgenic microalgae. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikucka, A.; Deptuła, A.; Bogiel, T.; Chmielarczyk, A.; Nurczyńska, E.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Bacteraemia Caused by Probiotic Strains of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus—Case Studies Highlighting the Need for Careful Thought before Using Microbes for Health Benefits. Pathogens 2022, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kaur, P. Green tea (Camellia sinensis): It’s promising health benefits for the welfare of humans. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zaib, S.; Hayat, A.; Khan, I. Probiotics and their beneficial health effects. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 24, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel, S.; Martín, R.; Bridonneau, C.; Robert, V.; Sokol, H.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Thomas, M.; Langella, P. Ecology and metabolism of the beneficial intestinal commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Faas, M.M.; de Vos, P. Disease managing capacities and mechanisms of host effects of lactic acid bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 1365–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yvon, S.; Schwebel, L.; Belahcen, L.; Tormo, H.; Peter, M.; Haimoud-Lekhal, D.A.; Eutamène, H.; Jard, G. Effects of thermized donkey milk with lysozyme activity on altered gut barrier in mice exposed to water-avoidance stress. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7697–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, M.B. Antimicrobial Compounds Activities of d2. 2 Biocontrol Bacteria Against Bacterial Pathogens on Shrimp and Fish In Vitro Aktifitas Senyawa Antimikroba Dari Bakteri Biokontrol d2. 2 Terhadap Bakteri PatogenPada Udang Dan Ikan Secara In Vitro. 2014. Available online: https://digilib.unila.ac.id/3667/1/ABSTRACT.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Kurashima, Y.; Kiyono, H. Mucosal ecological network of epithelium and immune cells for gut homeostasis and tissue healing. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 119–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didierlaurent, A.M.; Collignon, C.; Bourguignon, P.; Wouters, S.; Fierens, K.; Fochesato, M.; Dendouga, N.; Langlet, C.; Malissen, B.; Lambrecht, B.N.; et al. Enhancement of adaptive immunity by the human vaccine adjuvant AS01 depends on activated dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.G.; Wu, T.X.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Pan, X.D. Effects of fish protein hydrolysate on growth performance and humoral immune response in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea R.). J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahe, M.C.; Murtaugh, M.P. Mechanisms of adaptive immunity to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Viruses 2017, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.C.; Secombes, C.J. Immunology of fish. eLS 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum promotes intestinal barrier function by strengthening the epithelium and modulating gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, M.J. The immune response in fish: A review. J. Fish Biol. 1975, 7, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zijderveld, S.M.; Fonken, B.; Dijkstra, J.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Perdok, H.B.; Fokkink, W.; Newbold, J.R. Effects of a combination of feed additives on methane production, diet digestibility, and animal performance in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küçükyılmaz, K.; Bozkurt, M.; Çatlı, A.U.; Çınar, M.; Bİntaș, E. The effect of dietary supplementation of yeast and humate on broiler performance and some slaughter characteristics. Ziraat Fakültesi Derg. Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi 2012, 7, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y. Low fish meal diet supplemented with probiotics ameliorates intestinal barrier and immunological function of Macrobrachium rosenbergii via the targeted modulation of gut microbes and derived secondary metabolites. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1074399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakostelska, Z.; Kverka, M.; Klimesova, K.; Rossmann, P.; Mrazek, J.; Kopecny, J.; Hornova, M.; Srutkova, D.; Hudcovic, T.; Ridl, J.; et al. Lysate of probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114 001 ameliorates colitis by strengthening the gut barrier function and changing the gut microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwandari, A.R. Sari DNRSystem of Leukocytes Respiratory Burst Activity (RBA) in Grouper (Epinephelus coioides). J. Biota 2022, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Lee, C.S.; Webster, C.D. (Eds.) Alternative Protein Sources in Aquaculture Diets; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.H.; Chiu, C.H.; Wang, S.W.; Cheng, W. Dietary administration of the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20, enhances the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarike, E.D.; Cai, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, L.; Jian, J.; Tang, J.; Jun, L.; Kuebutornye, F.K. Effects of a commercial probiotic BS containing Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth, immune response and disease resistance in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, T.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, J. Enhancement of growth, survival, immunity and disease resistance in Litopenaeus vannamei, by the probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum Ep-M17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 129, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Shekrabi, S.P.H.; Soltani, M.; Mehrgan, M.S. Effects of potential probiotic Enterococcus casseliflavus (EC-001) on growth performance, immunity, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila infection in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyar, Y.; Abedian Kenari, A.; Paknejad, H.; Gandomi, H. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 7469 on different parameters related to health status of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and the protection against Yersinia ruckeri. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1370–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Vidal, S.; Lobo, C.; Prieto-Álamo, M.J.; Jurado, J.; Cordero, H.; Cerezuela, R.; Banda, G.; Esteban, M.A.; Balebona, M.C.; et al. The treatment with the probiotic Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11 of specimens of Solea senegalensis exposed to high stocking densities to enhance their resistance to disease. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.; Faggio, C. Importance of prebiotics in aquaculture as immunostimulants. Effects on immune system of Sparus aurata and Dicentrarchus labrax. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 54, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, A.; Irshad, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Xiong, H. The functionality of prebiotics as immunostimulant: Evidences from trials on terrestrial and aquatic animals. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 76, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Zhou, Z.; Van Doan, H.; Davies, S.J.; Harikrishnan, R. Boosting immune function and disease bio-control through environment-friendly and sustainable approaches in finfish aquaculture: Herbal therapy scenarios. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirzadeh, A.; Marhamati, A.; Rabiee, R.; Faggio, C. Immunomodulation, antioxidant enhancement and immune genes up-regulation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed on seaweeds included diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillehaug, A.; Børnes, C.; Grave, K. A pharmaco-epidemiological study of antibacterial treatments and bacterial diseases in Norwegian aquaculture from 2011 to 2016. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 128, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaş, S.; Kubilay, A.; Basmaz, N. Effect of bacterial load in feeds on intestinal microflora of seabream (Sparus surata) larvae and juveniles. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2005, 57, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Mancilha, I.M. Non-digestible oligosaccharides: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, J.; Quach, A.; Wongkrasant, P.; Nazir, S.; Tariq, M.; Barrett, K.E.; Zaidi, A. Potentially probiotic Limosilactobacillus reuteri from human milk strengthens the gut barrier in T84 cells and a murine enteroid model. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahor, W.; Thongprajukaew, K.; Suanyuk, N. Effects of dietary supplementation of oligosaccharides on growth performance, gut health and immune response of hybrid catfish (Pangasianodon gigas × Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Aquaculture 2019, 507, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Feng, L. Mannan oligosaccharides supplementation enhanced head-kidney and spleen immune function in on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi-Katuli, K.; Mohammadi, Y.; Ranjbaran, M.; Ghanaatian, H.; Khazaali, A.; Paknejad, H.; Santander, J. Effects of mannan oligosaccharide and synbiotic supplementation on growth performance and immune response of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) before and after thermal stress. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qi, C.; Limbu, S.M.; Han, F.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Xin, J.G.; Chen, L. Dietary mannan oligosaccharide (MOS) improves growth performance, antioxidant capacity, non-specific immunity and intestinal histology of juvenile Chinese mitten crabs (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquaculture 2019, 510, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, S.; Makol, A.; Caballero, M.J.; Montero, D.; Robaina, L.; Real, F.; Sweetman, J.; Tort, L.; Izquierdo, M.S. Immune stimulation and improved infection resistance in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed mannan oligosaccharides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alak, G.; Atamanalp, M. Usage of probiotics and prebiotics in aquaculture. Yüzüncü Yil Üniversitesi J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 22, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Buentello, A.; Gatlin, D., III; Lightner, D.; Hume, M.; Lawrence, A. Effects of fructooligosaccharides (FOS) on growth, survival, gut microflora, stress, and immune response in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, cultured in a recirculating system. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2020, 41, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Murthy, S.; Gatlin, D.M., III; Castille, F.L.; Lawrence, A.L. Effect of dietary supplementation of brewer’s yeast and Grobiotic®-A on growth, immune responses, and low-salinity tolerance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei cultured in recirculating systems. J. Appl. Aquac. 2009, 21, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin, D.M., III; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Burr, G.S.; Castille, F.; Lawrence, A.L. Potential application of prebiotics in aquaculture. In Avances en Nutrición Acuicola; Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León: Monterrey, Mexico, 2006; ISBN 970-694-333-5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Chu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, M.; Wang, Y. Contrasting eutrophication risks and countermeasures in different water bodies: Assessments to support targeted watershed management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiin, M.K.; Lahay, A.F.; Putriani, R.B.; Reza, M.; Putri, S.M.E.; Sumon, M.A.A.; Jamal, M.T.; Santanumurti, M.B. The role of probiotics in vannamei shrimp aquaculture performance–A review. Vet. World 2023, 16, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javahery, S.; Noori, A.; Hoseinifar, S.H. Growth performance, immune response, and digestive enzyme activity in Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei Boone, 1931, fed dietary microbial lysozyme. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, R.; Thanigaivel, S. Analysis and Evaluation of Probiotic (Lactococcus) Based Feed Supplements to Improve the Growth and Immune Related Responses of Rohu Fishes. ECS Trans. 2022, 107, 14051. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, E.S.H.; Ahmed, R.A.; Abd Elghany, N.A.; Elfeky, A.; Saadony, S.; Ahmed, N.H.; Sakr, S.E.; Tolenada, C.P.; Atienza, A.A.; Mabrok, M.; et al. Potential Symbiotic Effects of β-1, 3 Glucan, and Fructooligosaccharides on the Growth Performance, Immune Response, Redox Status, and Resistance of Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei to Fusarium solani Infection. Fishes 2023, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolanchinathan, P.; Kumari, P.R.; Raja, K.; John, G.; Balasundaram, A. Analysis of feed composition and growth parameters of Penaeus monodon supplemented with two probiotic species and formulated diet. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Hatamleh, A.A.; Biji, G.D.; Rady, A.M. Host associated mixed probiotic bacteria induced digestive enzymes in the gut of tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.V.; Ferriols, V.M.E.N.; Traifalgar, R.F.M. Synergistic influence of hydrolyzed squid processing by-products and Bacillus probiotics as dietary supplements on growth performance, immunological responses, and gut health of juvenile black tiger shrimp fed fishmeal-free diets. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 4551–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NavinChandran, M.; Iyapparaj, P.; Moovendhan, S.; Ramasubburayan, R.; Prakash, S.; Immanuel, G.; Palavesam, A. Influence of probiotic bacterium Bacillus cereus isolated from the gut of wild shrimp Penaeus monodon in turn as a potent growth promoter and immune enhancer in P. monodon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, M.N.; Suganya, A.M.; Immanuel, G.; Palavesam, A. Immunomodulatory and growth-promoting potential of low-cost probiotic product in Penaeus monodon culture system. Croat. J. Fish. 2017, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Pattukumar, V.; Kanmani, P.; Satish Kumar, R.; Yuvaraj, N.; Paari, A.; Arul, V. Enhancement of innate immune system, survival and yield in Penaeus monodon reared in ponds using Streptococcus phocae PI 80. Aquac. Nutr. 2014, 20, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S. Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum on the growth, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant capacity, and resistance to nitrite stress of Penaeus monodon. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Packyam, M.; Kim, K. Growth enhancement of shrimp and reduction of shrimp infection by Vibrio parahaemolyticus and white spot syndrome virus with dietary administration of Bacillus sp. Mk22. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 44, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utiswannakul, P.; Sangchai, S.; Rengpipat, S. Enhanced growth of black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon by dietary supplementation with Bacillus (BP11) as a probiotic. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenyogbe, E.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Huang, B.; Li, H. The exploitation of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in aquaculture: Present study, limitations and future directions.: A review. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 1017–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Swelum, A.A.; Ghanima, M.M.A.; Shukry, M.; Omar, A.A.; Taha, A.E.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; El-Terabily, K.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E. Shrimp production, the most important diseases that threaten it, and the role of probiotics in confronting these diseases: A review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 144, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, C.M.; Vickram, A.S.; Sowndharya, B.B.; Saravanan, A.; Kamalesh, R.; Dinakarkumar, Y. A comprehensive review on the utilisation of probiotics in aquaculture towards sustainable shrimp farming. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 147, 109459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamilselvan, M.; Raja, S. Exploring the role and mechanism of potential probiotics in mitigating the shrimp pathogens. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 31, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, M.; Ahmadivand, S.; Ringø, E. Bacillus as Probiotics in Shellfish Culture. In Bacillus Probiotics for Sustainable Aquaculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 192–207. [Google Scholar]
- Abo-Al-Ela, H.G.; Mahdi, S.; Angthong, P.; Rungrassamee, W. Probiotic modulation of key immune macromolecules in shrimp. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 203, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hai, N.; Fotedar, R. A review of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture. J. Appl. Aquac. 2010, 22, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.T.; Abdulrahman, I.A.; Al Harbi, M.; Chithambaran, S. Probiotics as alternative control measures in shrimp aquaculture: A review. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Duan, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. The effect of Lactobacillus plantarum administration on the intestinal microbiota of whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruta, K.J.C.; Caipang, C.M.A. Local aquatic microflora as a potential source of probionts in biofloc technology for whiteleg shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. Environ. Exp. Biol. 2025, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, L.E.; Rivera, L.; Hardy, E.; Llumiquinga, E.M.; Garrido, F.; Chávez, J.A.; Abril, V.H.; País-Chanfrau, J.M. Estrategias Naturales para Mejorar el Crecimiento y la Salud en los Cultivos Masivas de Camarón en Ecuador. Rev. Bionatura 2017, 2, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.; Kazmi, S.S.U.H.; Saqib, H.S.A.; Fiaz, U.; Pastorino, P.; Barcelò, D.; Tayyab, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Yaseen, Z.M. Harnessing probiotics and prebiotics as eco-friendly solution for cleaner shrimp aquaculture production: A state of the art scientific consensus. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, Z.A.; Wee, W.; Hamid, N.K.A.; Dawood, M.A.; Zakaria, N.N.A.B.; Wei, L.S. The roles of polysaccharides in tilapia farming: A review. Aquac. Fish. 2024, 9, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Dharumadurai, D. Growth and immunomodulatory postbiotic effects in shrimp. In Postbiotics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.C.; Chang, H.T.; Lee, T.Y.; Lin, J.S.; Liu, C.H. SYNLAC prime probiotics enhances growth performance, and resistance of white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei to Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei and Vibrio alginollyticus: Insights into immune and metabolic pathway modulations. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 155, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization. Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. In Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, M.; Aysul, N.; Küçükyilmaz, K.; Aypak, S.; Ege, G.; Catli, A.U.; Akşit, H.; Çöven, F.; Seyrek, K.; Çınar, M. Efficacy of in-feed preparations of an anticoccidial, multienzyme, prebiotic, probiotic, and herbal essential oil mixture in healthy and Eimeria spp.-infected broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Z.; Ramzan, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M. Resistant starch-based edible coating composites for spray-dried microencapsulation of Lactobacillus acidophilus, comparative assessment of thermal protection, in vitro digestion and physicochemical characteristics. Coatings 2021, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov-Nikishin, A.; Nikiforov-Nikishin, D.; Kochetkov, N.; Smorodinskaya, S.; Klimov, V. The influence of probiotics of different microbiological composition on histology of the gastrointestinal tract of juvenile Oncorhynchus mykiss. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinrauch, A.M.; Hoogenboom, J.L.; Anderson, W.G. A review of reductionist methods in fish gastrointestinal tract physiology. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 254, 110571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparagon, W.J.; Gentry, E.C.; Minich, J.J.; Vollbrecht, L.; Laurens, L.M.; Allen, E.E.; Sims, N.A.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Kelly, L.W. Nelson, C.E. Fine scale transitions of the microbiota and metabolome along the gastrointestinal tract of herbivorous fishes. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, H.; Javadian, S.R.; Bahram, S. Evaluation of feed efficiency, growth and biochemical parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mikyss) juveniles fed with different levels of Alphamune prebiotic. Sustain. Aquac. Health Manag. J. 2021, 7, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maytorena-Verdugo, C.I.; Peña-Marín, E.S.; Alvarez-Villagómez, C.S.; Pérez-Jiménez, G.M.; Sepúlveda-Quiroz, C.A.; Alvarez-González, C.A. Inclusion of mannan-oligosaccharides in diets for tropical gar atractosteus tropicus larvae: Effects on growth, digestive enzymes, and expression of intestinal barrier genes. Fishes 2022, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Farsani, M.N.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Raeeszadeh, M. Dietary Lactobacillus helveticus and Gum Arabic improves growth indices, digestive enzyme activities, intestinal microbiota, innate immunological parameters, antioxidant capacity, and disease resistance in common carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 135, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Ringø, E.; Merrifield, D.L. The gut microbiota of fish. In Aquaculture Nutrition: Gut Health, Probiotics and Prebiotics; John Willie and the Suns: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 75–100. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, T.P.; Wynne, J.W.; Weyrich, L.S.; Oxley, A.P. Investigating both mucosal immunity and microbiota in response to gut enteritis in yellowtail kingfish. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, Q. Directional changes in the intestinal bacterial community in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Animals 2021, 11, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, J.C.; Zeltzer, L.K. Complementary and alternative medicine approaches for pediatric pain: A review of the state-of-the-science. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2005, 2, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Garg, R. Probiotics. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 27, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunkalu, O. Effects of feed additives in fish feed for improvement of aquaculture. Eurasian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 3, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Cuvin-Aralar, M.L.A.; Ricafort, C.H.; Salvacion, A. An Overview of Agricultural Follution in the Philippines: The Fisheries Sector; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Khosravi, S.; Chang, K.H.; Lee, S.M. Effects of dietary inclusion of astaxanthin on growth, muscle pigmentation and antioxidant capacity of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Guo, Y.C.; Huai, M.Y.; Li, L.; Man, C.; Pelletier, W.; Wei, H.L.; Yao, R.; Niu, J. Comparison of the Retention Rates of Synthetic and Natural Astaxanthin in Feeds and Their Effects on Pigmentation, Growth, and Health in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Liang, G.; Leng, X. Dietary astaxanthin improved the body pigmentation and antioxidant function, but not the growth of discus fish (Symphysodon spp.). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, S.P.; Kaushik, S.J. Nutrition and metabolism of minerals in fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Zhao, W.; Hu, W.S.; Zhu, B.; Xie, J.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Tian, L.X.; Niu, J. Lipid metabolism, growth performance, antioxidant ability and intestinal morphology of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under cage culture with flowing water were affected by dietary lipid levels. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, R.; Heqiu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Zuo, R. Effects of dietary lipid sources on the survival, growth, body composition, antioxidant capacity and expression of antioxidant and pro-inflammatory genes in juvenile Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) reared under three salinities. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 5307–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Ayivi, R.D.; Zimmerman, T.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Altemimi, A.B.; Fidan, H.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Bakhshayesh, R.V. Lactic acid bacteria as antimicrobial agents: Food safety and microbial food spoilage prevention. Foods 2021, 10, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, A.; Mokhtari, S.; Khomeiri, M.; Saris, P. EAntifungal preservation of food by lactic acid bacteria. Foods 2022, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.Z.; Sun, H.M.; Guo, J.W.; Luo, P.; Hu, C.Q.; Huang, W.; Shu, H. Molecular characterisation of a RNA polymerase (RNAP) II (DNA directed) polypeptide H (POLR2H) in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and its role in response to high-pH stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 96, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, K. The Effect of Sodium Bicarbonate Injection on the Physico-Chemical Quality of Post-Harvest Trout. Foods 2023, 12, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Wu, G. Nutrition and metabolism of glutamate and glutamine in fish. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmawati, D.; Nurhayati, D. Effect of dietary lysine on the growth performance of Pangasius hypophthalmus. Depik 2022, 11, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Duan, M.; Qiu, X.; Masagounder, K.; Davis, D.A. Characterisation of methionine uptake and clearance in the hemolymph of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmed, M.K.; Ahmmed, F.; Tian, H.; Carne, A.; Bekhit, A.E.D. Marine omega-3 (n-3) phospholipids: A comprehensive review of their properties, sources, bioavailability, and relation to brain health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 64–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, C.; Teodósio, R.; Colen, R.; Richard, N.; Rønnestad, I.; Dias, J.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Ribeiro, L. Taurine Supplementation to Plant-Based Diets Improves Lipid Metabolism in Senegalese Sole. Animals 2023, 13, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koven, W.; Bracha, C.; Nixon, O.; Israeli, D.; Tandler, A.; Meiri-Ashkenazi, I.; Rosenfeld, H. The effect of dietary taurine and its potential biosynthesis on juvenile grey mullet (Mugil cephalus) performance. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2023, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yin, P.; Tian, L.; Niu, J.; Liu, Y. Exposure to acute ammonia stress influences survival, immune response and antioxidant status of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) pretreated with diverse levels of inositol. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Azm, F.R.A.; Yuan, J.; Tan, Q. Effect of dietary vitamin C on the growth performance, non-specific immunity and antioxidant ability of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, G.B.; Varghese, T.; Mishal, P.; Sandeep, K.P.; Praveen, K.V. Food security in India: Is aquaculture a solution in the offing. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 4, 553–560. [Google Scholar]
- Gaponov, N.V.; Gamko, L.N. Nutrient digestibility of fishmeal rations in primates. Vet. Sci. Today 2021, 10, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.D.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Baldisserotto, B.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Mancera, J.M. Essential oils as stress-reducing agents for fish aquaculture: A review. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Bossier, P. Toxicity assessment and anti-Vibrio activity of essential oils: Potential for application in shrimp aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1554–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbokane, E.M.; Moyo, N.A.G. Use of medicinal plants as feed additives in the diets of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and the African Sharptooth catfish (Clarias gariepinus) in Southern Africa. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1072369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefian, M.; Amiri, M.S. A review of the use of prebiotic in aquaculture for fish and shrimp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 7313–7318. [Google Scholar]
- Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Nutritional Interventions to Mitigate Parasitic Enteritis. Aquac. Eur. 2017, 17. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10261/191297 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Muthulakshmi, M.; Subramani, P.A.; Michael, R.D. Immunostimulatory effect of the aqueous leaf extract of Phyllanthus niruri on the specific and non-specific immune responses of Oreochromis mossambicus Peters. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 17, 200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.O.A.; Taştan, Y.; Bilen, S.; Terzi, E.; Sönmez, A.Y. Effects of white mustard (Sinapis alba) oil on growth performance, immune response, blood parameters, digestive and antioxidant enzyme activities in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 131, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immanuel, G.; Uma, R.P.; Iyapparaj, P.; Citarasu, T.; Punitha Peter, S.M.; Michael Babu, M.; Palavesam, A. Dietary medicinal plant extracts improve growth, immune activity and survival of tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanjoo, V.; Yahyavi, M.; Akrami, R.; Bahri, A.H. Influence of adding garlic (Allium sativum), Ginger (Zingiber officinale), thyme (Thymus vulgaris) and their combination on the growth performance, haematoimmunological parameters and disease resistance to Photobacterium damselae in sobaity sea bream (Sparidentex hasta) Fry. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2024, 18, 633–645. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.; Afzal, G.; Siddique, A.B.; Afzal, M.; Shahid, M.; Ramzan, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Ali, H.M.; Hira Ahsan, H.; Khan, M.S.; et al. Essential Oil-Based Functional Feeds for Promoting Growth in Aquaculture Species. Complement. Altern. Med. Essent. Oils 2024, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; El Basuini, M.F.; Yilmaz, S.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Alagawany, M.; Kari, Z.A.; Razab, M.K.; Hamid, N.K.; Moonmanee, T.; Van Doan, H. Exploring the roles of dietary herbal essential oils in aquaculture: A review. Animals 2022, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, E.; Awaad, A. Role of medicinal plants on growth performance and immune status in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Yousefi, M.; Karimi, M.; Fadaei Raieni, R.; Dadar, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Benefits of dietary polyphenols and polyphenol-rich additives to aquatic animal health: An overview. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 478–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, A.M.; Habiba, M.M.; El-Zayat, A.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Moonmanee, T.; Van Doan, H.; Shadrack, R.S.; Dawood, M.A. Dietary anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) enhances growth performance and serum immunity of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, A.M.; Habiba, M.M.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Younis, E.M.; Davies, S.J.; Elnakeeb, M.A.; Abdelghany, M.F.; El-Zayat, A.M.; El-Sebaey, A.M. Dietary effect of powdered herbal seeds on zootechnical performance, hemato-biochemical indices, immunological status, and intestinal microbiota of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquac. Rep. 2024, 36, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvan, P.; Malarvizhi, K.; Ranjan, A. Exploring phytobiotics in aquaculture: Sources, mode of action, effects, administration, and its bioavailability in fish. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 5737–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.B.; Hancz, C. Application of phytochemicals as immunostimulant, antipathogenic and antistress agents in finfish culture. Rev. Aquac. 2011, 3, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyi, C.O.; Atoyebi, M.O.; Obafunmiso, H.T.; Salaam, K.A. Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) in the nutrition of African catfish-A cholesterol reducer and fertility enhancer. Int. J. Aquac. Fish. Sci. 2020, 6, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparaku, N.F.; Ijem, N.; Nduka, J.C. Growth performance of Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) juveniles fed Zingiber officinale (Ginger) and Moringa oleifera bark supplemented diets. Acad. J. Med. Plants 2021, 9, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.S.; Kari, Z.A.; Kabir, M.A.; Khoo, M.I.; Azra, M.N.; Wee, W. Promoting growth and health of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus, through dietary novel supplement, ginger, zingiber officinale rosc, leaf powder. Aquac. Stud. 2023, 24, AQUAST1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanto, D. The effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) enrichment in artificial feed on the growth, survival, and profitability of giant gourami (Osphronemus goramy) cultivation. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2025, 18, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, N.N.; Wilhelm, M.R.; Habte-Tsion, H.M.; Chimwamurombe, P.; Omoregie, E.; Iipinge, L.N.; Shimooshili, K. Effect of dietary Aloe vera polysaccharides supplementation on growth performance, feed utilisation, hemato-biochemical parameters, and survival at low pH in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) fingerlings. Int. Aquat. Res. 2019, 11, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, N.; Musa, S.M.; Azfaralariff, A.; Mohamed, M.; Yusoff, A.H.; Lazim, A.M. Improving the efficiency of post-digestion method in extracting microplastics from gastrointestinal tract and gills of fish. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartila, S.S.Q.; Jusadi, D.; Setiawati, M.; Fauzi, I.A. Evaluation of dietary supplementation with cinnamon products on growth, blood composition, liver structure, and meat quality of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Tartor, Y.H. Carvacrol essential oil stimulates growth performance, immune response, and tolerance of Nile tilapia to Cryptococcus uniguttulatus infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2020, 141, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazempoor, R.; Alavinezhad, S.S.; Pargari, M.M.; Shakeri, Y.S.; Haghighi, M.M. A review on the application of phytogenics as feed additives for aquatic animals. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Environ. Stud. 2022, 2, 46–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onomu, A.J.; Okuthe, G.E. The role of functional feed additives in enhancing aquaculture sustainability. Fishes 2024, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tignani, M.V.; Santolini, E.; Secci, G.; Bovo, M.; Parisi, G.; Barbaresi, A. Assessing environmental sustainability of substitute feeding formulas for gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) using Life Cycle Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.P.; Erickson, M.C. Opportunities for mitigating pathogen contamination during on-farm food production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 152, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvanasundram, P.; Chong, C.M.; Sabri, S.; Yusoff, M.S.; Karim, M. Multi-strain probiotics: Functions, effectiveness and formulations for aquaculture applications. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, M.F.; Sîrbu, E.; Patriche, N.; Cristea, V.; Coadă, M.T.; Plăcintă, S. Effects of multi-strain probiotics on the growth and hematological profile in juvenile carp (Cyprinus carpio, Linnaeus 1758). Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 14, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y.; Hlordzi, V.; Sakyi, M.E.; Afriyie, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.X. Mechanisms and the role of probiotic Bacillus in mitigating fish pathogens in aquaculture. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 819–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midhun, S.J.; Arun, D.; Jyothis, M. Probiotic application of beneficial bacteria for improved health and disease control. In Recent Advances in Aquaculture Microbial Technology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- Calcagnile, M.; Tredici, S.M.; Alifano, P. A comprehensive review on probiotics and their use in aquaculture: Biological control, efficacy, and safety through the genomics and wet methods. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Ryu, S.; Song, S.H.; Chun, S.W.; Lee, N.; Lee, A.H. Characterization of novel bacteriophages for effective phage therapy against Vibrio infections in aquaculture. J. Microbiol. 2025, 63, e2502009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, N.M.; Hosny, N.S.; El-Desoky, N.; Soltan, Y.A.; Elolimy, A.A.; Sallam, S.M.; Abu-Tor, E.S.M. Alginate nanoencapsulated synbiotic composite of pomegranate peel phytogenics and multi-probiotic species as a potential feed additive: Physicochemical, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities. Animals 2023, 13, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MA, A.; Sarasan, M.; Kachiprath, B.; Sukumaran, V.; Singh, I.B.; Puthumana, J. Engineering the fish gut microbiome: Could it serve as future-proof strategy for sustainable aquaculture? Blue Biotechnol. 2025, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, N.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X. From probiotics to postbiotics: Concepts and applications. Anim. Res. One Health 2023, 1, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Abo-Al-Ela, H.G.; Hasan, M.T. Modulation of transcriptomic profile in aquatic animals: Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics scenarios. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla-Pineda, M.; Achou, C.G.; Díaz, J.; Gutiérrez-Falcon, A.; Bravo, M.; Herrera-Muñoz, J.I.; Peña-Navarro, N.; Alvarado, C.; Ibañez, F.C.; Marzo, F. In vitro evaluation of postbiotics produced from bacterial isolates obtained from rainbow trout and Nile tilapia against the pathogens Yersinia ruckeri and Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. Foods 2023, 12, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.T.; Lu, H.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.W.; Shan, X.F. The application and potential of postbiotics as sustainable feed additives in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2024, 592, 741237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasoni, L.F.; Gervasoni, K.; de Oliveira Silva, K.; Mendes, M.E.F.; Maddela, N.R.; Prasad, R.; Winkelstroter, L.K. Postbiotics in active food packaging: The contribution of cellulose nanocomposites. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 36, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, R.; Cecchini, B.; Zavagna, L.; Azimi, B.; Ricci, C.; Esin, S.; Milazzo, M.; Batoni, G.; Danti, S. Emerging Multiscale Biofabrication Approaches for Bacteriotherapy. Molecules 2024, 29, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Chen, G.; Ji, X.S.; Teng, J.; Yao, Z.L.; Hu, C.L.; Zhao, Y. Construction and evaluation of recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum expressing Micropterus salmoides hepcidin. Microb. Cell Factories 2025, 24, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Fu, Y.Z.; Zhang, N.F. Progress on mechanism and functional characteristics of next generation probiotics. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 34, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, K.Y.; Thong, J.Y.H.; Tan, L.T.H.; Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; Law, J.W.F. A Current Overview of Next-Generation Probiotics and Their Prospects in Health and Disease Management. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2024, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.C.; Machado, D.; Almeida, D.; Andrade, J.C.; Brandelli, A.; Gomes, A.M.; Freitas, A.C. Next-generation probiotics. In Probiotics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 483–502. [Google Scholar]
- Amphan, S.; Unajak, S.; Printrakoon, C.; Areechon, N. Feeding-regimen of β-glucan to enhance innate immunity and disease resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus Linn., against Aeromonas hydrophila and Flavobacterium columnare. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, P.; Wacyk, J.; Morales-Lange, B.; Rojas, V.; Guzmán, F.; Dixon, B.; Mercado, L. Immunomodulatory effect of cathelicidins in response to a β-glucan in intestinal epithelial cells from rainbow trout. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 51, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Gan, N.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X. Regulation of Il-10 gene expression by Il-6 via Stat3 in grass carp head kidney leucocytes. Gene 2020, 741, 144579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, J.; Guo, Z.P. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of IL-1β and two types of IL-1 receptor in barbel steed (Hemibarbus labeo). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 241, 110393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Ma, R.; Ma, J.; Han, D.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Dietary nucleotides improve the growth performance, antioxidative capacity and intestinal morphology of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magouz, F.I.; Abdel-Rahim, M.M.; Lotfy, A.M.; Mosbah, A.; Alkafafy, M.; Sewilam, H.; Dawood, M.A. Dietary nucleotides enhanced growth performance, carcass composition, blood biochemical, and histology features of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100738. [Google Scholar]
- Taklu, M.; Islami, H.R.; Mousavi, S.A.; Jourdehi, A.Y. Nucleotide supplementation in the diet of Sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus): Improved zootechnical performance, biochemical indices, and immune responses. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 288, 115322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doo, E.H.; Chassard, C.; Schwab, C.; Lacroix, C. Effect of dietary nucleosides and yeast extracts on composition and metabolic activity of infant gut microbiota in PolyFermS colonic fermentation models. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ramachandran, D.; Mansouri, A.; Dailey, M.J. Glucose stimulates intestinal epithelial crypt proliferation by modulating cellular energy metabolism. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 3465–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Van Doan, H.; Lee, S.H.; Soltani, M.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Harikrishnan, R.; Song, S.K. Probiotics, lactic acid bacteria and bacilli: Interesting supplementation for aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhulika Ngasotter, S.; Meitei, M.M.; Kara, T.; Meinam, M.; Sharma, S.; Rathod, S.K.; Singh, S.B.; Singh, S.K.; Bhat, R.A.H. Multifaceted Role of Probiotics in Enhancing Health and Growth of Aquatic Animals: Mechanisms, Benefits, and Applications in Sustainable Aquaculture—A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Aquac. Nutr. 2025, 1, 5746972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corr, S.C.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Understanding the mechanisms by which probiotics inhibit gastrointestinal pathogens. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Aleman, R.S.; Yadav, A. Systematic review of probiotics and their potential for developing functional nondairy foods. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 4, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsufyani, M.O.; Asiri, A.A.; Asiri, Y.M.; Alsughayyir, I.A.; Alzahrani, R.A.; Al Essa, T.A.; Lajhar, A.M.; Alshhrani, M.A.; Rabeh, M.A. Correlation between Probiotic and Prebiotic: A Systematic review. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 67, 2227–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.S. The role of prebiotics in modulating gut microbiota: Implications for human health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, T.; Bag, K.K.; Das, A.B.; Deka, S.C. Synergistic role of prebiotics and probiotics in gut microbiome health: Mechanisms and clinical applications. Food Bioeng. 2024, 3, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caipang, C.M.A.; Suharman, I.; Avillanosa, A.L.; Gonzales-Plasus, M.M. Influence of phytogenic feed additives on the health status in the gut and disease resistance of cultured fish. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 695, p. 012024. [Google Scholar]
- Firmino, J.P.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Gisbert, E. Phytogenic bioactive compounds shape fish mucosal immunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 695973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, M.A.; Alsenosy, A.A.; Manaa, E.A.; Abaza, S.; Elshenawi, M.A.; Aboelnour, A.; Alagawany, M. Phytobiotics and their application in poultry and aquaculture industry. In Organic Feed Additives for Livestock; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, M.A.; El Basuini, M.F.; Zaineldin, A.I.; Yilmaz, S.; Hasan, M.T.; Ahmadifar, E.; El Asely, A.M.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Alagawany, M.; Abu-Elala, N.M.; et al. Antiparasitic and antibacterial functionality of essential oils: An alternative approach for sustainable aquaculture. Pathogens 2021, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.; Shahin, S.E.; Alqahtani, L.S.; Hassan, Z.; Althobaiti, F.; Albogami, S.; Soliman, M.M.; El-Malt, R.M.S.; Al-Harthi, H.F.; Alqadri, N.; et al. Exploring the interactive effects of thymol and thymoquinone: Moving towards an enhanced performance, gross margin, immunity and Aeromonas sobria resistance of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals 2022, 12, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepehrfar, D.; Sudagar, M.; Paknejad, H.; Yousefi Siahkalroodi, S.; Norouzitallab, P. Role of phytochemicals in farmed fish reproductive performance: A review. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2023, 22, 1039–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.C.; Wu, J.W.; Jin, Z.H.; Ye, Z.F.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Fei, H. Exogenous enzymes as functional additives in finfish aquaculture. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalraaj, J.; Velayudhannair, K.; Arockiasamy, J.P.; Radhakrishnan, D.K. The effect of dietary supplementation of proteases on growth, digestive enzymes, oxidative stress, and intestinal morphology in fishes–A review. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 745–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Koh, C.B. The utilisation and mode of action of organic acids in the feeds of cultured aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, P.; Shamna, N.; Sahu, N.P. Acidifiers in aquafeed as an alternate growth promoter: A short review. Anim. Nutr. Feed Technol. 2020, 20, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flecker, A.S.; Shi, Q.; Almeida, R.M.; Angarita, H.; Gomes-Selman, J.M.; García-Villacorta, R.; Sethi, S.A.; Thomas, S.A.; Poff, N.L.; Forsberg, B.R.; et al. Reducing adverse impacts of Amazon hydropower expansion. Science 2022, 375, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, Y.; Peng, J.; Dai, Y.; Luo, S.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y. Effects of broad-spectrum antibiotic (florfenicol) on resistance genes and bacterial community structure of water and sediments in an aquatic microcosm model. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Peng, J.; Dai, Y.; Xie, X.; Luo, S.; Ding, Y.; Ma, Y. Effect of florfenicol on nirS-type denitrifying communities structure of water in an aquatic microcosm model. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1205394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, W.M.; El-Ashmawy, N.; Nofal, E.R. Analysing the evolution of environmental impacts due to fish farms expansion. Int. J. Eng. Tech. Res. 2020, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Parrao, C.; Shisler, S.; Moratti, M.; Yavuz, C.; Acharya, A.; Eyers, J.; Snilstveit, B. Aquaculture for improving productivity, income, nutrition and women’s empowerment in low-and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2021, 17, e1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J. Investigating Gasoline Contamination Effects on Daphnia’s Heartbeat in a Simulated Lake. J. Glob. Ecol. Environ. 2023, 17, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.V.T. The Production Cycle of Litopenaeus vannamei in Outdoor Ponds and Tank Culture of Trachinotus carolinus. Internship at Auburn University’s Fish and Shrimp Nutrition Lab, PQDT-Global. 2017. Source: Repositório Aberto da Universidade do Porto. Available online: https://share.google/NuKzLHbDz0ofNx6CH (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Gazi-Khan, L.; Haque, S.E. A review of the current status of water quality and eutrophication in Dhaka’s water bodies. Management 2022, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, M.; Persiano, M.; Gennaro, P.; Rubegni, F. Wind mitigating action on effects of eutrophication in coastal eutrophic water bodies. Int. J. Mar. Sci. Ocean Technol. 2016, 3, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S.; Schnoor, J.L. China’s ban on phenylarsonic feed additives, a major step toward reducing the human and ecosystem health risk from arsenic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12177–12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seidy, E.; Mohamed, K. General Tit-For-Tat Strategy in The Three Players Prisoner’s Dilemma Game. World Sci. Res. 2015, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Alayande, K.A.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Ateba, C.N. Probiotics in animal husbandry: Applicability and associated risk factors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Dubeux, J.C.; Franzluebbers, A.J. 2 Conducting and Communicating Environmental Impacts of Research: Forage Production, Soil Health, Sustainability. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100 (Suppl. S1), 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vutukuru, S.; Bodapati, A.K.; Bhimavarapu, V. Doxycycline induced alterations in the glycogen and protein content of the zebra fish, Danio rerio. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci 2022, 1, 271220031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Yun, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. A review on the ecotoxicological effect of sulphonamides on aquatic organisms. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, B. Revealing the response characteristics of periphyton biomass and community structure to sulfamethoxazole exposure in aquaculture water: The perspective of microbial network relationships. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 344, 123301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, M.; Rioboo, C.; Herrero, C.; Cid, Á. Toxicity induced by three antibiotics commonly used in aquaculture on the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica (Kylin) Butch. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 101, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, C.; Fan, L.; Qiu, L.; Wu, W.; Meng, S.; Hu, G.; Kamira, B.; Chen, J. Occurrence of antibiotics and their impacts to primary productivity in fishponds around Tai Lake, China. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gaya, B.; Cherta, L.; Nozal, L.; Rico, A. An optimised sample treatment method for the determination of antibiotics in seawater, marine sediments and biological samples using LC-TOF/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Diao, Z.H.; Sun, K.F.; Hao, Q.W.; Liu, S.S.; Ying, G.G. Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.X.; He, L.Y.; Gao, F.Z.; Wu, D.L.; Ye, P.; Cheng, Y.X.; Chen, Z.Y.; Hu, L.X.; Liu, Y.S.; Chen, J.; et al. Antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes and microbial community in grouper mariculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelland, H.V.; Føre, M.; Lader, P.; Kristiansen, D.; Holmen, I.M.; Fredheim, A.; Grøtli, E.I.; Fathi, D.E.; Oppedal, F.; Utne, I.B.; et al. Exposed aquaculture in Norway. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2015-MTS/IEEE Washington, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 October 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, H.M.; Bondouk, I.I.; Salama, E.; Mahmoud, H.H.; Omar, K.; Esawii, H.A. Asphaltene or polyvinylchloride waste blended with cement to produce a sustainable material used in nuclear safety. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.B.; Shimshack, J.P. The effectiveness of environmental monitoring and enforcement: A review of the empirical evidence. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2011, 5, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsletten, H. Optimisation Model Aimed for the Aquaculture Industry for Fleet Composition and Routing of Wellboats. Master’s Thesis, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Guidelines for the Simple Evaluation of Dietary Exposure to Food Additives (CAC/GL 3-1989) (Originally adopted in 1989, revised in 2014). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%3A%2F%2Fworkspace.fao.org%2Fsites%2Fcodex%2FStandards%2FCXG%2B3-1989%2FCXG_003e.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Forcella, S.; Tantawy, N.; Yilma, J. The development of a four-way linking framework in Egypt: An example of the FAO, OIE and WHO joint activities to facilitate national risk assessment. Vet. Ital. 2015, 51, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Aquilina, G.; Cubadda, F.; Marcon, F. Risk-benefit assessment of feed additives in the one health perspective. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 843124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguti, J.; Obiero, K.; Odame, H.; Kirimi, J.; Kyule, D.; Ani, J.; Liti, D. Key limitations of fish feeds, feed management practices, and opportunities in Kenya’s aquaculture enterprise. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2021, 21, 17415–17434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, M.L.; Otto, C.M.; Fine, A.H. The animal welfare science of working dogs: Current perspectives on recent advances and future directions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 666898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, A.; Gropp, J.; Mantovani, A.; Roncancio, C. Ten years of EFSA’s FEEDAP Panel and its main achievements. EFSA J. 2012, 10, s1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renshaw, D.W. Animal Feed Additives. Issues in Toxicology: Regulatory Toxicology in the European Union; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, T.; Wyss, U. Efficacy testing of silage additives—Methodology and existing schemes. Grass Forage Sci. 2019, 74, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G. Aquaculture in China. Species Syst. Sel. Sustain. Aquac. 2007, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Srivastava, A. The Use of Feed and Food Additives in United States. In Sustainable Use of Feed Additives in Livestock: Novel Ways for Animal Production; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 245–281. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, H.F.; Cowan, T. Genetically Engineered Salmon; US Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Xie, S.; Han, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S. Feed Developments in Freshwater Aquaculture. In Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends; John Willie and the Suns: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 431–450. [Google Scholar]
- Winger, R.J. Phosphorus Food Additive Use in the European Union. In Dietary Phosphorus; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 279–312. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP); Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.D.L.; Christensen, H.; Durjava, M.; Dusemund, B.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; Puente, S.L.; et al. Assessment of the safety of the feed additives acetic acid, calcium acetate and sodium diacetate for fish (FEFANA asbl). EFSA J. 2023, 21, e08176. [Google Scholar]
- Broughton, E.I.; Walker, D.G. Policies and practices for aquaculture food safety in China. Food Policy 2010, 35, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeuckelaere, W.; Berbejal, R.P.; Rosell, M.A.G. Food additives, enzymes, and flavourings legislation in the European Union. In Food Additives and Packaging; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- De Angelis, F.; Carreno, I. Achieving sustainability of the EU food chain with feed additives as a key tool: The European Commission intends to modernise the legal framework to foster innovation. Eur. J. Risk Regul. 2021, 12, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varchenko, O.; Artimonova, I. Formation of organisational and economic mechanism for regulation of agricultural market. Sci. J. Cahul State Univ. Bogdan Petriceicu Hasdeu Econ. Eng. Stud. 2018, 4, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Petković, G.; Užar, D. Marketing channels in value creation and delivery of cheese in the Republic of Serbia. Anal. Ekon. Fak. U Subotici 2020, 56, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.A.; Basiri, M.L.; McHenry, J.A.; Kosyk, O.; Otis, J.M.; Van Den Munkhof, H.E.; Bryois, J.; Hübel, C.; Breen, G.; Guo, W.; et al. Obesity remodels activity and transcriptional state of a lateral hypothalamic brake on feeding. Science 2019, 364, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, M.; Reinhard, A.; Beuerle, T. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) in honey and pollen-legal regulation of PA levels in food and animal feed required. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundmann, O.; Kumar, P.; Rogge, M. ACCPPublic Policy Committee Regulation of dietary supplements nutraceutical products in the United States: An argument for greater oversight uniform standards. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.S.; Kunamneni, A.; Kumar, V.; Habte-Tsion, H.M. Registration of food and feed additives (enzymes) in the United States, Canada, and China. In Enzymes in Human and Animal Nutrition; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 457–480. [Google Scholar]
- Lammersfeld, C.A.; Levin, M.D.; Reilly, P.; Coyne, J.W.; Birdsall, T.C.; Markman, M. Assuring quality of dietary supplements for cancer patients: An integrative formulary systems approach. Integr. Med. A Clin. J. 2017, 16, 38. [Google Scholar]
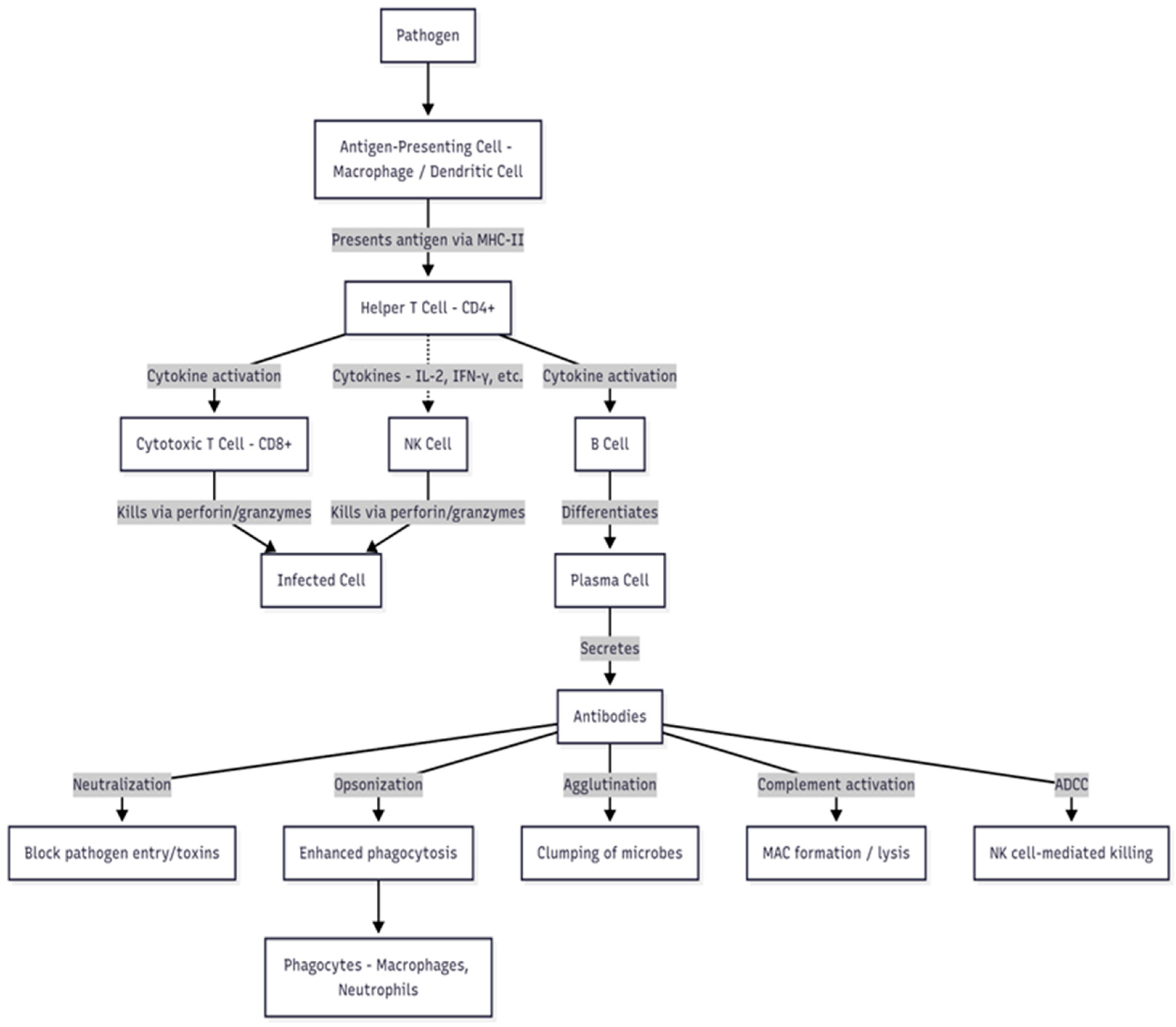
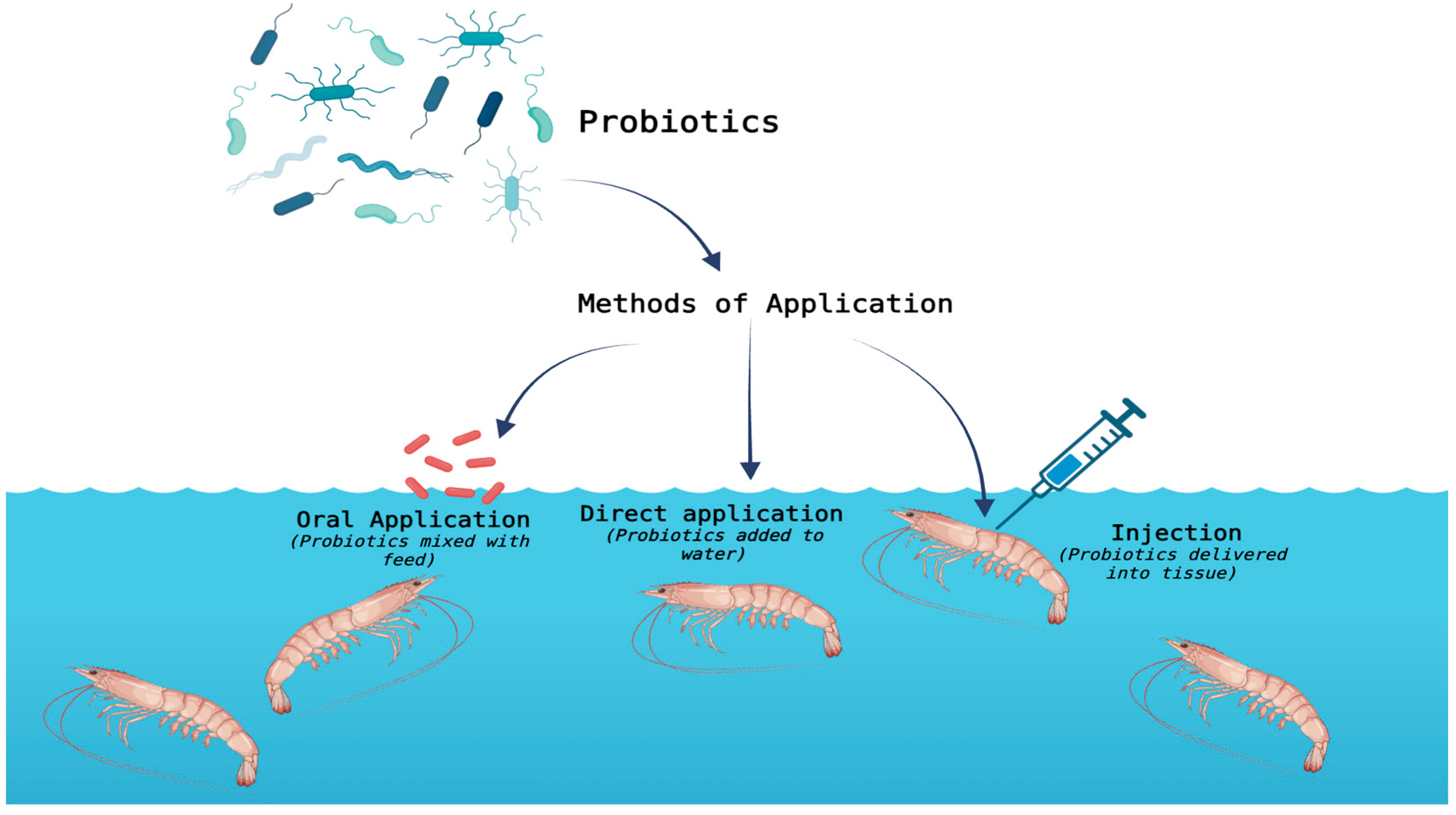
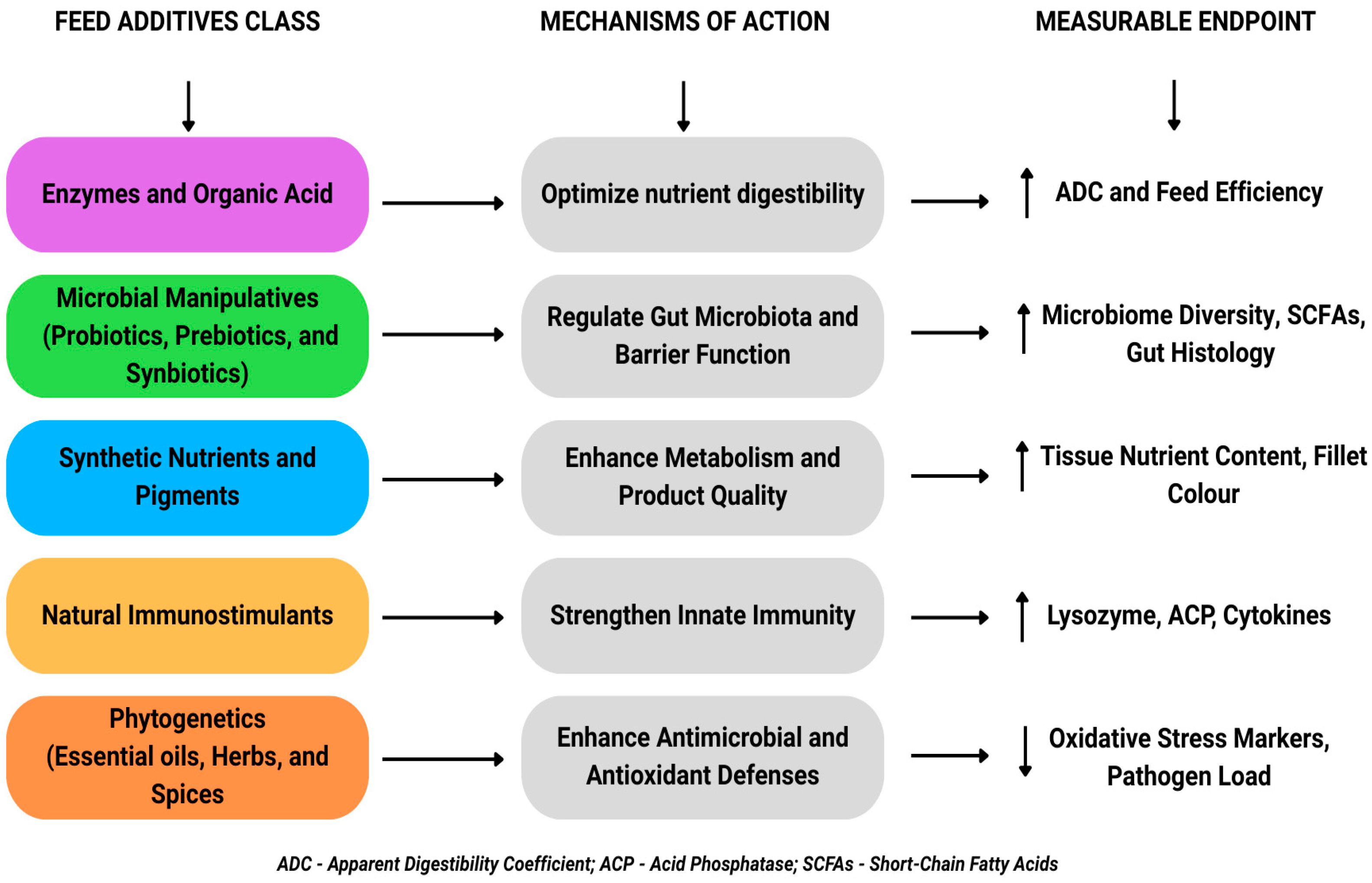
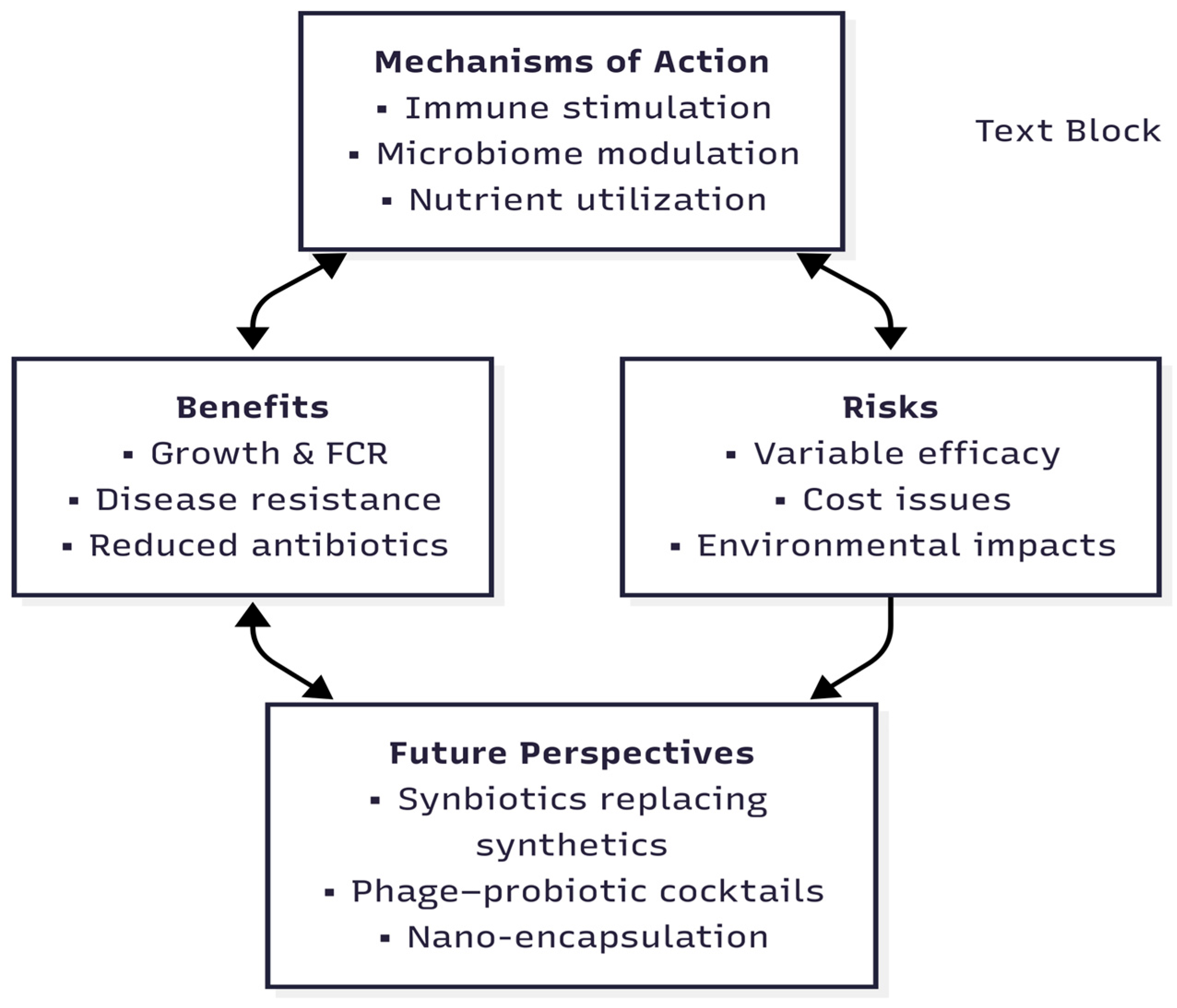
| Probiotic Strain (Fish Species) | Dosage | Observed Immune Effects | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis E20 (Epinephelus coioides) | 1 × 104–1 × 108 CFU g−1 feed | ↑ Lysozyme, phagocytosis, superoxide dismutase (SOD), serum ACP | [74] |
| B. subtilis + fructooligosaccharides—FOS (Trachinotus ovatus) | 1.05–5.62 × 107 CFU g−1 feed + 0.2% or 0.4% FOS | ↑ Specific growth rate (SGR), lysozyme, disease resistance, serum ACP | [7] |
| B. subtilis + B. licheniformis (Oreochromis niloticus) | 0–10 g kg−1 feed | ↑ Lysozyme, SGR protease, anti-protease, SOD, and immunoglobulin | [75] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum (Ep-M1) (Litopenaeus vannamei) | 5 × 108 CFU g−1 feed | ↑ SGR, SOD, immunometabolism, survival | [76] |
| Enterococcus casseliflavus (EC-001) (Cyprinus carpio) | 1 × 107–1 × 109 CFU g−1 feed | ↑ SGR, lysozyme, disease resistance, serum Acid Phosphatase (ACP) | [77] |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | 1 × 106 CFU g−1 feed | ↑ Weight gain, SOD, immunometabolism, lysozyme, disease resistance | [78] |
| Shewanella putrefaciens (Pdp11) (Solea senegalensis) | 1 × 107 CFU g−1 feed | ↑ Stress tolerance, disease resistance, and gut microbiota modulation | [79] |
| Potentials | Constraints | References |
|---|---|---|
| PROBIOTICS | ||
| Improve gut health and nutrient uptake. | Challenges in strain selection and dosage optimisation. | [112,113,114] |
| Enhance disease resistance, immune response, and the secretion of antibacterial compounds and antitoxins. | Environmental conditions impacting efficacy. | [112,113,114,115,116] |
| Maintain a balanced microbial community in ponds. | An overdose can cause immunosuppression. | [112,113,117] |
| Reduce pathogen levels and enhance water quality. | There is limited understanding of mechanisms in aquaculture systems. | [112,113,114,115,117] |
| Enhance feed efficiency, stimulate digestive enzyme activity, and promote growth and reproduction. | Storage and maintenance of live cultures. | [118,119] |
| Regulate the immune system and manage allergic responses. | Potential environmental incompatibility with aquatic hosts. | [112,116,120] |
| PREBIOTICS | ||
| Improve water quality and decrease pollution. | Limited research on specific prebiotic effects in shrimp. | [121,122] |
| Enhance growth and survival rates, increase stress resistance and health status, and modulate enteric microbiota and immune responses. | There is a need for further studies to understand the molecular impacts. | [121,122] |
| SYMBIOTICS | ||
| Combine the benefits of probiotics and prebiotics. | Complexity in formulation and application. | [123,124] |
| Improve metabolic pathways and energy metabolism, boost growth performance and immune function, and decrease the severity of infections, thereby raising survival rates. | There is a need for more research on specific symbiotic combinations. | [123,124,125] |
| Feed Additives | Function | Fish Species | Dosage Recommendation | Environmental Risk | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Growth and feed efficiency, reduced disease occurrence | Various fish species, shrimp | Varies with antibiotic type | High risk | [141] |
| Astaxanthin | Pigmentation, growth, and antioxidant | Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), Discus fish (Symphysodon spp.). | 50–100 mg kg−1 of feed | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [142,143] |
| Beta-carotene | Pigmentation, growth, and antioxidant | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), African catfish (Clarias gariepinus), shrimp | 50–100 mg kg−1 of feed | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [142] |
| Betaine | Osmoregulation, nutrient utilisation, and stress resistance | Barramundi (Lates calcarifer), prawn | 500–1000 mg kg−1 of feed | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [144] |
| Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) | Preservative | Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus), lobster (Homarus gammarus) | 50–100 mg kg−1 of feed | Potential risk due to low biodegradability | [143] |
| Choline Chloride | Growth promoter | Various fish species, shrimp | 500–1000 mg kg−1 of feed | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [5] |
| Enzymes (e.g., Phytase) | Digestive enhancer | Various fish species, shrimp | As per the enzyme activity levels | Generally considered safe | [5,145] |
| Ethoxyquin | Antioxidant | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), crab (Brachyura spp.) | 100–200 mg kg−1 of feed | Potential risk due to low biodegradability | [146,147] |
| Mould Inhibitors (e.g., Propionic Acid) | Antifungal agent | Various species | 2–4 g kg−1 of feed | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [148,149] |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | pH regulator | Carp (Cyprinus carpio), shrimp | 1–2 g kg−1 of feed | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [150,151] |
| Synthetic Arginine | Amino acid supplement | Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), African catfish (Clarias gariepinus), shrimp | Varies with species | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [46,152] |
| Synthetic Lysine | Amino acid supplement | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), African catfish (Clarias gariepinus), shrimp | Varies with species | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [153] |
| Synthetic Methionine | Amino acid supplement | Various fish species, shrimp | 2–4 g kg−1 of feed | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [154] |
| Synthetic Phospholipids | Emulsifiers, chemoattraction | Various fish species, shrimp | - | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [155] |
| Synthetic Taurine | Cellular and physiological processes | Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), African catfish (Clarias gariepinus), | - | Limited information, but likely biodegradable | [156,157] |
| Vitamin C | Immune booster, antioxidant, and stress resistance | Various fish species, shrimp | 100–300 mg kg−1 of feed | Generally considered safe | [158,159] |
| Additive | Main Action | Advantages | Limitations and Risks | Cost-Effectiveness | Environmental Impact | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional probiotics | Microbiome modulation, competitive exclusion | Widely available, several validated strains | Strain survival, variable effects | Moderate | Low–moderate | [195] |
| Bacteriophage–probiotic | Targeted pathogen lysis | Antibiotic alternative; specificity | Host range, regulatory, and environmental concerns | Moderate–high | Low–moderate | [196] |
| Nano-encapsulated phytogenics | Protected delivery, controlled release | Lower dose, improved bioavailability | Cost and potential nano-ecotoxicity | Moderate–high | Potential accumulation risk | [197] |
| Engineered/CRISPR probiotics | Precision metabolic modulation | High specificity potential | Genetically modified organism regulation; public acceptance | Currently high | Unknown | [198] |
| Postbiotics | Bioactive metabolites, immune modulation | Storage stability, no live microbes | Need to identify active compounds | High | Low | [199] |
| Synbiotics/microencapsulated probiotics | Enhanced survival + prebiotic support | Improved stability and colonisation | Cost, formulation complexity | High | Moderate | [197,200] |
| Antibiotic | Environmental Impact | References |
|---|---|---|
| Doxycycline |
| [248] |
| Sulfonamides |
| [249,250] |
| Florfenicol |
| [251,252] |
| Oxytetracycline |
| [251,253] |
| Chloramphenicol |
| [251] |
| Enrofloxacin; Ciprofloxacin |
| [254,255] |
| Erythromycin |
| [252,255] |
| Aspect | European Union (EU) | United States (US) | China | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Body |
|
| Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (MARA) | [265,266,267] |
| Approval Process |
|
|
| [265,266,267,268,269,270,271] |
| Safety Thresholds |
|
|
| [265,266,269,271,272,273] |
| Legislation |
|
|
| [265,268,270,274,275,276] |
| Focus Areas |
|
|
| [265,269,270,271,274] |
| Challenges |
|
|
| [270,274] |
| Parameters | Why | Assays | When |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth and performance | Primary production metric | WG, SGR, FCR, PER | Weekly or biweekly during trials (typical 4–12 week trials) |
| Survival and disease resistance | Real-world production viability | Cumulative survival, post-challenge survival curves; challenge tests with common pathogens | End of trial + challenge follow-up |
| Innate immunity | Mechanism and prophylactic value | Serum lysozyme activity, alternative complement (ACP), phagocytic activity, respiratory burst, SOD, and CAT | Baseline, mid-trial, end-trial, and post-challenge |
| Adaptive immunity | Longer-term protection | Specific antibody titres, lymphocyte proliferation, and cytokine gene expression | Later timepoints (weeks) and post-vaccination/challenge |
| Gut health and microbiome | Central to nutrient uptake and immunity | Intestinal histology, digestive enzyme activities, 16S rRNA gene sequencing (alpha/beta diversity), SCFA quantification | Mid and end trial |
| Digestibility and nutrient retention | Feed efficiency and waste output | Apparent digestibility coefficients (ADC), nutrient retention indices, and faecal nutrient analysis | Final phase ± periodic sampling |
| Oxidative stress and tissue health | Phytogenic and antioxidant effects | SOD, MDA, CAT in liver/muscle; histopathology | End trial |
| Residues and environmental fate | Public health and environmental risk (esp. antibiotics, antioxidants) | Antibiotic residues in tissue/water/sediment; ARGs (qPCR); chemical residuals (LC-MS) | During and after the feeding period, sediment sampling for benthic accumulation |
| Product quality and composition | Market value | Fillet colour, lipid profile, proximate composition | Harvest |
| Environmental metrics | eutrophication/ecosystem impact | Dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus, chlorophyll a, BOD, and benthic oxygen demand | Regular pond/pen/effluent monitoring |
| Economics/LCA | Adoption decisions | Cost per kg gain, feed cost ratio, basic LCA endpoints if available | End of trial and scenario modelling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okon, E.; Iyobhebhe, M.; Olatunji, P.; Adeleke, M.; Matekwe, N.; Okocha, R. Feed Additives in Aquaculture: Benefits, Risks, and the Need for Robust Regulatory Frameworks. Fishes 2025, 10, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090471
Okon E, Iyobhebhe M, Olatunji P, Adeleke M, Matekwe N, Okocha R. Feed Additives in Aquaculture: Benefits, Risks, and the Need for Robust Regulatory Frameworks. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090471
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkon, Ekemini, Matthew Iyobhebhe, Paul Olatunji, Mary Adeleke, Nelson Matekwe, and Reuben Okocha. 2025. "Feed Additives in Aquaculture: Benefits, Risks, and the Need for Robust Regulatory Frameworks" Fishes 10, no. 9: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090471
APA StyleOkon, E., Iyobhebhe, M., Olatunji, P., Adeleke, M., Matekwe, N., & Okocha, R. (2025). Feed Additives in Aquaculture: Benefits, Risks, and the Need for Robust Regulatory Frameworks. Fishes, 10(9), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090471







