Analysis of Edaphic Factors on the Role of Probiotics in the Development of Sustainable and Productive Aquaculture
Abstract
1. Introduction
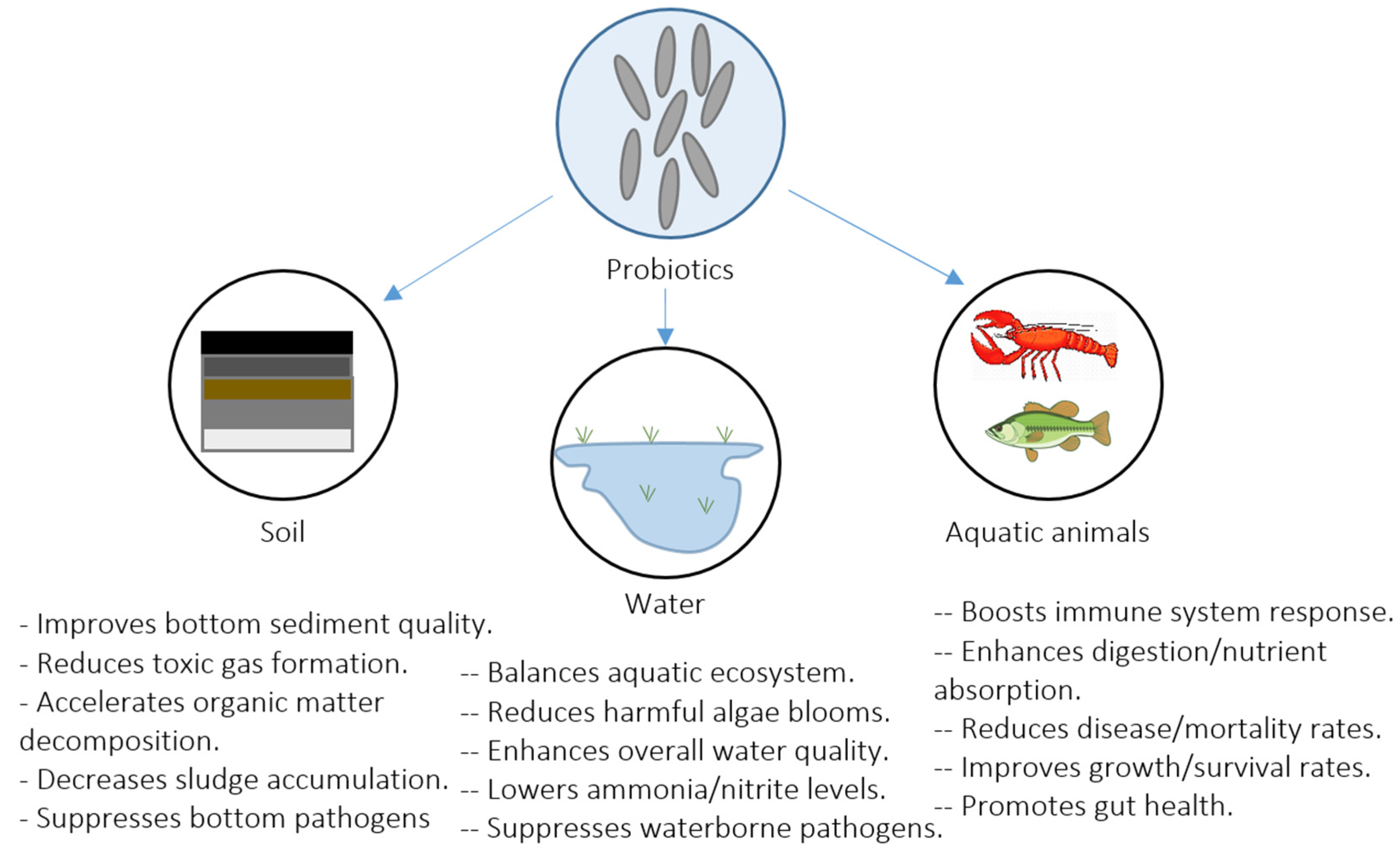
2. Effect of Probiotics on Aquaculture
2.1. Potential Applications of Probiotics
2.2. Soil in Aquaculture
2.3. Effects of Probiotics on Pond Soils
2.4. Effect of Probiotics on Physicochemical Soil Properties
Comprehensive Improvement of the Pond Ecosystem
2.5. Soil Investigation Methods in Aquaculture
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| A-Cu | available copper (Cu) |
| A-Fe | available ferrum (Fe) |
| AHN | hydrolyzable nitrogen (N) |
| AK | available potassium (K) |
| A-Mn | available manganese (Mn) |
| AN | available nitrogen (N) |
| AP | available phosphorus (P) |
| A-Zn | available zinc (Zn) |
| BD | bulk density |
| CEC | cation exchange capacity |
| DOC | dissolved organic carbon |
| SIN | soil inorganic carbon |
| SL | salinity |
| SOC | soil organic content |
| SON | soil organic nitrogen |
| STN | soil total nitrogen |
| SWC | soil water content |
| TK | total potassium |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| TP | total phosphorus |
| EC | electrical conductivity |
References
- Parker, R.B. Probiotics, the other half of the antibiotic story. Anim. Nutr. Health 1974, 29, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, R. Probiotics in man and animals. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1989, 66, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, L.; Rombaut, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W. Probiotic Bacteria as Biological Control Agents in Aquaculture. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, N.V. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics to control bacterial infections: Luminescent vibriosis in aquaculture as an example. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Cruz, P.; Ibáñez, A.L.; Monroy Hermosillo, O.A.; Ramírez Saad, H.C. Use of probiotics in aquaculture. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 916845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Probiotics: An overview of beneficial effects. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek 2002, 82, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamoura, C.; Kontogianni, A.; Katsipi, D.; Kandylis, P.; Varzakas, T. Probiotic fermented milks made of cow’s milk, goat’s milk and their mixture. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 185S, S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S. Natural products to drugs: Natural product-derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 475–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ward, L.R.; Burke, C. Screening of marine Streptomyces spp. for potential use as probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2010, 305, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, D.; Jacob, J.C.; Philip, R. Exclusion of Vibrio spp. by an antagonistic marine actinomycete Streptomyces rubrolavendulae M56. Aquac. Res. 2015, 47, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazado, C.C.; Lacsamana, J.I.; Caipang, C.M.A. Mechanisms of probiotic actions in shrimp: Implications to tropical aquaculture. In Biotechnological Advances in Shrimp Health Management in the Philippines; Caipang, C.M.A., Bacano-Maningas, M.B.I., Fagutao, F.F., Eds.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2015; pp. 89–114. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, S.H.; Han, I.K.; Won, T.H.; Choi, Y.J. Effect of antibiotics, enzyme, yeast culture and probiotics on the growth performance of Israeli carp. Korean J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 36, 480–486. [Google Scholar]
- Bogut, I.; Milakovi, A.; Bukvic, Z.; Zimmer, R. Influence of probiotic (Streptococcus faecium, M 74) on growth and content of intestinal microflora in carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 43, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Sreenivasulu, P.; Naga Jyothi, P.; Subhan Ali, M.D.; Praveenkumar, K. Effect of water probiotic in water quality maintenance and growth of Rohu (Labeo Rohita) Fingerlings. Eur. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, P.V.; Prabhavathi, K. Efficacy and suitability of earth worm Megascolex sps as supplementary feed for cat fish Pangasius hypophthalmus in response to different animal protein sources. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kozasa, M. Toyocerin (Bacillus toyoi) as growth promotor for animal feeding. Microbiol. Aliment. Nutr. 1986, 4, 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, P.C.; Sultana, S.; Kabiraj, M.; Hossain, S.S. Role of probiotics in aquaculture practice of Satkhira region of Bangladesh. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019, 7, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture Software World Aquaculture Performance Indicators (WAPI); FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Verdegem, M.; Buschmann, A.H.; Latt, U.W.; Dalsgaard, A.J.; Lovatelli, A. The contribution of aquaculture systems to global aquaculture production. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 54, 206–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Division. Global Aquaculture Production 1950–2021 (FishStatJ) [Data Set]. FAO. Retrieved 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/statistics/software/fishstatj (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Standen, B.T.; Rawling, M.D.; Davies, S.J.; Castex, M.; Foey, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O.; Merrifield, D. Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici modulates both localised intestinal- and peripheral-immunity in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Abdel-Rahman, A.M.; Ismael, N.E.M. Evaluation of commercial live bakers’ yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a growth and immunity promoter for fry Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) challenged in situ with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Olsen, R.E.; Jensen, I.; Romero, J.; Lauzon, H.L. Application of vaccines and dietary supplements in aquaculture: Possibilities and challenges. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2014, 24, 1005–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragnya, M.; Dinesh Kumar, S.; Solomon Raju, A.J.; Murthy, L.N. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in different organs of Labeo rohita, Pangasius hypophthalmus, and Katsuwonus pelamis from Visakhapatnam, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghe, R.; Curry, D.; McGladdery, S.; Bartley, D. Recent technological innovations in aquaculture. FAO Fish. Circ. 2003, 886, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, X.-H.; Boon, N.; Bossier, P. Probiotics in aquaculture of China—Current state, problems and prospect. Aquaculture 2009, 290, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazar, K.K.; Pemmineti, N.J.; Mohammad, S.A. Effect of soil probiotic on water quality and soil quality maintenance and growth of freshwater fish Pangasius hypophthalmus. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2021, 11, 3291–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzula, A.; Wambura, P.N.; Mdegela, R.H.; Shirima, G.M. Present status of aquaculture and the challenge of bacterial diseases in freshwater farmed fish in Tanzania; A call for sustainable strategies. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.N.; Banerjee, G. Recent studies on probiotics as beneficial mediator in aquaculture: A review. J. Basic. Appl. Zool. 2020, 81, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengpipat, S.; Rueangruklikhit, T.; Piyatiratitivorakul, S. Evaluations of lactic acid bacteria as probiotics for juvenile seabass Lates calcarifer. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Gross, A. Use of probiotics for improving soil and water quality in aquaculture ponds. In Advances in Shrimp Biotechnology; Flegel, T.W., Ed.; National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology: Bangkok, Thailand, 1998; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E.; Hollerman, W.D.; Plumb, J.A.; Saeed, M. Effect of treatment with a commercial bacterial suspension on water quality in channel catfish ponds. Prog. Fish-Cult. 1984, 46, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.S.; Lloyd, S.W. Evaluation of potassium ricinoleate as a selective blue-green algicide in channel catfish ponds. Aquaculture 1987, 65, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiayvareesajja, S.; Boyd, C.E. Effects of zeolite, formalin, bacterial augmentation, and aeration on total ammonia nitrogen concentrations. Aquaculture 1993, 116, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, J.F.; Boyd, C.E. Effects of a bacterial inoculum in channel catfish ponds. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1998, 29, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.G.; McCormick, J.H.; Stefan, H.G.; Hondzo, M. Extreme value analysis of a fish/temperature field database. Ecol. Eng. 1995, 4, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.M.S.; Clemente, J.J.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Cunha, A.E. Enhanced spore production of Bacillus subtilis grown in a chemically defined medium. Adv. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesarcodi-Watson, A.; Kaspar, H.; Lategan, M.J.; Gibson, L. Probiotics in aquaculture: The need, principles and mechanisms of action and screening processes. Aquaculture 2008, 274, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarasu, T.; Micheal Babu, M.; Raja Jeya Sekar, R.; Peter Marian, M. Developing Artemia enriched herbal diet for producing quality larvae in Penaeus monodon, Fabricius. Asian Fish. Sci. 2002, 15, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Z. Effect of probiotics on alkaline phosphatase activity and nutrient level in the sediment of shrimp, Penaeus vannamei, ponds. Aquaculture 2009, 287, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Roy, S.; Meena, D.K.; Sarkar, U.K. Application of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture: Importance, mechanisms of action, and methods of administration. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, V.; Ramesh, G.; Mohan, D.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Subbulakshmi, G.; Raffi, S.M. The efficiency of probiotics (Ecoforce) in the growth and survival of Penaeus monodon. Arthropods 2013, 2, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Swapna, B.; Venkatrayulu, C.; Swathi, A.V. Effect of probiotic bacteria Bacillus licheniformis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus on the growth of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 5, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Manam, D.V.K. Probiotics in Aquatic Ecosystem—A Review. J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 9, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.T.H.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H. Streptomyces bacteria as potential probiotics in aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tiu, L.; Wang, H.H. Characterization of antibiotic resistance in commensal bacteria from an aquaculture ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. An insight of traditional plasmid curing in Vibrio species. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, V.; Pusparajah, P.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Yin, W.-F.; Lee, L.-H.; Chan, K.-G. Occurrence and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from shellfish in Selangor, Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, V.; Yin, W.-F.; Lee, L.-H.; Chan, K.-G. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from retail shrimps in Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Buschmann, A.H.; Rioseco, M.L.; Kalsi, R.K.; Godfrey, H.P.; Cabello, F.C. Antimicrobial resistance genes in marine bacteria and human uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a region of intensive aquaculture. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zeng, Z. Antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and bacterial community composition in fresh water aquaculture environment in China. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.-R.; Liu, S.-S.; Zhou, G.-J.; Sun, K.-F.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.-G. Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: Occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.M.; Silva, L.J.; Meisel, L.M.; Pena, A. Fluoroquinolones and tetracycline antibiotics in a portuguese aquaculture system and aquatic surroundings: Occurrence and environmental impact. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2015, 78, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, D.K.; Chu, J.; Do, N.T.; Brose, F.; Degand, G.; Delahaut, P.; De Pauw, E.; Douny, C.; Van Nguyen, K.; Vu, T.D.; et al. Monitoring antibiotic use and residue in freshwater aquaculture for domestic use in Vietnam. EcoHealth 2015, 12, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Al-Harbi, A.H.; Austin, B. Review: Developments in the use of probiotics for disease control in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.K.; Mishra, S.S.; Pradhan, P.K.; Manna, S.K.; Abraham, T.J.; Solanki, H.G.; Patel, M.T.; Bally, S.; Behera, S.; Swain, P.; et al. Usage pattern of chemicals, biologicals and veterinary medicinal products in Indian aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 2038–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. (Ed.) Bottom Soils, Sediment, and Pond Aquaculture; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pantjara, B.; Mustafa, A. Preparation of acid sulphate soil ponds for cultivation of tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). In Monograph: The Breeding and Growth of Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon); Research Institute for Coastal Aquaculture: Maros, Indonesia, 2015; pp. 129–135. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, S.; Ahmed, W.; Mahmood, M.; Rizwan, M.S.; Asghar, R.M.A.; Alatalo, J.M.; Nawab, J.; Shaheen, S.M. Aquaculture sediments amended with biochar improved soil health and plant growth in a degraded soil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castex, M.; Lemaire, P.; Wabete, N.; Chim, L. Effect of probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici on antioxidant defences and oxidative stress of Litopenaeus stylirostris under Vibrio nigripulchritudo challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, W.H.; Haberer, P.; Snel, J.; Schillinger, U.; Huis in’t Veld, J.H.J. Overview of gut flora and probiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 41, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter-Cevera, J.; Karl, V.; Buckley, M. Marine Microbial Diversity: The Key to Earth’s Habitability; American Academy of Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; 28p. [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty, D.J.W.; Decamp, O. Microbial remediation of pollution in tropical coastal environment. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Lyla, P.S.; Ajmal Khan, S. Application of Streptomyces as a probiotic in the laboratory culture of Penaeus monodon (Fabricius). Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2006, 58, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, X. Characterization of a ras-related nuclear protein (Ran protein) up-regulated in shrimp antiviral immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazado, C.C.; Caipang, C.M.A. Atlantic cod in the dynamic probiotics research in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2014, 424–425, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantjara, B.; Kristanto, A.H. Pond bottom management and probiotic application in extensive Tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon) culture on acid sulfate soil. AACL Bioflux 2020, 13, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kamilya, D.; Devi, W.M. Bacillus probiotics and bioremediation: An aquaculture perspective. In Bacilli in Agrobiotechnology: Plant stress Tolerance, Bioremediation, and Bioprospecting; Islam, M.T., Rahman, M.M., Pandey, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghribi, D.; Elleuch, M.; Abdelkefi, L.; Ellouze-Chaabouni, S. Evaluation of Larvicidal Potency of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 Biosurfactant Against Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Larvae and Influence of Abiotic Factors on Its Insecticidal Activity. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2012, 48, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimrat, S.; Suksawat, S.; Maleeweach, P.; Vuthiphandchai, V. Effect of Different Shrimp Pond Bottom Soil Treatments on the Change of Physical Characteristics and Pathogenic Bacteria in Pond Bottom Soil. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninawe, A.S.; Selvin, J. Probiotics in shrimp aquaculture: Avenues and challenges. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, J.M.; Weller, D.M.; Thomashow, L.S. Frequency of antibiotic–producing Pseudomonas spp. in natural environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, B.T.; Kasan, N.A. Recent Advances in Shrimp Aquaculture Wastewater Management. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosazza, T.; Eigentler, L.; Earl, C.; Davidson, F.A.; Stanley-Wall, N.R. Bacillus subtilis Extracellular Protease Production Incurs a Context-Dependent Cost. Mol. Microbiol. 2023, 120, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeon, H.; Han, H.S.; Hur, J.W. Evaluation of Bacillus albus SMG-1 and B. safensis SMG-2 Isolated From Saemangeum Lake as Probiotics for Aquaculture of White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, H.; Veerasamy, G.; Mukkalil, R. Harnessing Bacillus Probiotics: An Approach for Vibrio Pathogen Control and Organic Sludge Management in Shrimp Aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2025, 2025, 2767593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Xu, Z.R.; Xia, M.S. The effectiveness of commercial probiotics in northern white shrimp Penaeus vannamei ponds. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Effect of probiotics on larvae shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) based on water quality, survival rate, and digestive enzyme activities. Aquaculture 2009, 287, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, H.M.; Owatari, M.S.; Martins, M.A.; Lopes, G.R.; Ferreira, M.B.; Jesus, G.F.A.; Mouriño, J.L.P. Probiotic BioPlus® PS modulate shrimp-tilapia polyculture pond soil microbiome and exhibit bioremediation potential. J. Appl. Aquac. 2024, 36, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buruiană, T.; Buruiana, C.T.; Georgiana, P.A.; Vizireanu, C. Effects of probiotic Bacillus species in aquaculture—An overview. AUDJG Food Technol. 2014, 38, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jasmin, M.Y.; Syukri, F.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Karim, M. Potential of Bioremediation in Treating Aquaculture Sludge: Review Article. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, K.K.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Castex, M.; Gram, L.; Bentzon-Tilia, M. The aquaculture microbiome at the centre of business creation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y.; Ritvo, G. Shrimp and fish pond soils: Processes and management. Aquaculture 2003, 220, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y. A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Ghosh, K.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Kumar, V.; Lymbery, A.J.; Roy, S.; Ringø, E. Genus Bacillus, promising probiotics in aquaculture: Aquatic animal origin, bio-active components, bioremediation and efficacy in fish and shellfish. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2019, 27, 331–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmin, G.; Kathiresan, K.; Purushothaman, A. Effect of probiotics on bacterial population and health status of shrimp in culture pond ecosystem. Indian. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 939–942. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Cheng, X.; Sample, D.J.; Yazdi, M.N. Effect of Intermittent Aeration Mode on Nitrogen Concentration in the Water Column and Sediment Pore Water of Aquaculture Ponds. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 90, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, H.B.; Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M.; Azhar, O. Effects of commercial microbial products on water quality in tropical shrimp culture ponds. Asian Fish. Sci. 2002, 15, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva-Maia, E.; Alves-Modesto, G.; Otavio-Brito, L.; Vasconcelos-Gesteira, T.C.; Olivera, A. Effect of a commercial probiotic on bacterial and phytoplankton concentration in intensive shrimp farming (Litopenaeus vannamei) recirculation systems. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 41, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.X.; Zhao, S.M.; Peng, N.; Xu, C.P.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.X. Effects of a probiotic (Bacillus subtilis FY99-01) on the bacterial community structure and composition of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei, Boone) culture water assessed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and high-throughput sequencing. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, L.; Deng, B.; Liang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, H.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Wenying, S.; et al. Bacillus subtilis SC02 supplementation causes alterations of the microbial diversity in grass carp water. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, R. The metagenomics of soil. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Athmann, M.; Kautz, T.; Köpke, U. Grouping and classification of wheat from organic and conventional production systems by combining three image forming methods. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2011, 27, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemonnier, H.; Bernard, E.; Boglio, E.; Goarant, C.; Cochard, J.C. Influence of sediment characteristics on shrimp physiology: pH as principal effect. Aquaculture 2004, 240, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.L.; Treseder, K.K. Microbial communities and their relevance for ecosystem models: Decomposition as a case study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, P.; Vadstein, O. Ecological theory as a foundation to control pathogenic invasion in aquaculture. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; He, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yen, L.; Cao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Lee, S.Y. Spatial variation of soil properties impacted by aquaculture effluent in a small-scale mangrove. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Boyd, C.E. Laboratory tests of bacterial amendments for accelerating oxidation rates of ammonia, nitrite and organic matter in aquaculture pond water. Aquaculture 2016, 460, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello Júnior, C.C.; Owatari, M.S.; Schleder, D.D.; Poli, M.A.; Gelsleichter, R.R.Y.; Postai, M.; Krüger, E.K.; De Carvalho, F.G.; Silva, B.P.P.; Teixeira, B.L.; et al. Identification and characterization of microorganisms potentially beneficial for intensive cultivation of Penaeus vannamei under biofloc conditions: Highlighting Exiguobacterium acetylicum. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3628–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Hlordzi, V.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y.; Mraz, J. Bacillus probiotics as the bioremediatory tools in aquaculture. In Bacillus Probiotics for Sustainable Aquaculture; Abarike, E.D., Mraz, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; pp. 128–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Romaire, R.P.; Johnston, E. Predicting Early Morning Dissolved Oxygen Concentrations in Channel Catfish Ponds. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1978, 107, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhia, N.; Cuq, J.L. Traditional methods of fish fermentation in Ghana. In Proceedings of the FAO Expert Consultation on Fish Technology in Africa, Accra, Ghana, 19–22 November 1991; pp. 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Farzanfar, A. The use of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 48, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhash, S.K.; Lipton, A.P.; Paulraj, R. Influence of probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus on the survival and growth of pearl oyster Pinctada fucata spat. Indian J. Fish. 2007, 54, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Mohideen, M.; Haniffa, M.A. Effect of Probiotic on Microbiological and Haematological Responsiveness of Cat fish (Heteropneustes fossilis) Challenged with Bacteria Aeromonas hydrophila and Fungi Aphanomyces invadans. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, V.; Patriche, N.; Iulia, G. The Effect On Biochemical Composition of Different Concentrations Probiotic Fed to Juvenile Carp (Cyprinus carpio, L. 1758) In A Recirculating Aquaculture System. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Ser. 2014, 63, unpaginated. [Google Scholar]
- Divya, K.R.; Isamma, A.; Arunjith, T.S.; Sureshkumar, S.; Krishnakumar, V. Effect of Enriched Artemia franciscana on Production, Survival, Growth and Biochemical Composition of the Freshwater Fish Catla catla (Hamilton, 1922). Int. J. Recent. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Janardana Reddy, S. Probiotics in Aquaculture: Importance, Influence and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Bioassays 2015, 4, 3710–3718. [Google Scholar]
- Abasali, H.; Mohmad, S. Effect of dietary probiotic level on the reproductive performance of female platy Xiphophorus maculatus. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivam, S.; Chandran, R.; Khan, S.A. Role of probiotics on the environment of shrimp pond. J. Environ. Biol. 2003, 24, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.S.; Chowdhury, M.Y.; Haque, A.K.M.A.; Haq, M.S. Limnological studies of four ponds. Bangladesh J. Fish. 1982, 5, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, S.; Wahab, M.A.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Rahman, M.H.; Sarkar, B.K. Food selection, electivity and dietary overlap among planktivorous Chinese and Indian major carp fry and fingerlings grown in extensively managed, rain-fed ponds in Bangladesh. Aquac. Fish. Manag. 1991, 22, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.A.; Aziz, M.E.; Haque, M.M.; Ahmed, Z.F. Effects of frequency of fertilization on water quality and fish yields. Prog. Agric. 1996, 7, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Demaine, H.; Muir, J.F. Freshwater prawn farming in Bangladesh: History, present status and future prospects. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.P. Geochemistry of Early Permian cold-water carbonates (Tasmania, Australia). Chem. Geol. 1983, 38, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhendra, T.; Handoko, J.; Octaviano, D.; Porubcan, R.S.; Douillet, P. Management with bacterial probiotics for Vibrio and virus control in an Indonesian prawn farm. In Proceedings of the IV Central American Aquaculture Symposium: Sustainable Culture of Shrimp and Tilapia, Tegucigalpa, Honduras, 22 April 1997; pp. 201–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.; Al Harbi, A.; Uddin, M.N. Bacterial diversity of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in brackish water in Saudi Arabia. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y.; Mozes, N.; Kochba, M. Rates of organic carbon and nitrogen degradation in intensive fish ponds. Aquaculture 1995, 134, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.K.; Swarnakumar, N.S.; Sivakumar, K.; Thangaradjou, T.; Kannan, L. Probiotics in aquaculture: Importance and future perspectives. Indian. J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantjara, B. Technology Utilization of Sustainable Aquaculture on the Tidal Swamp Land; Research and Development Agency of Marines and Fisheries: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014; 82p. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, K.; Gao, H.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Soil organic carbon as affected by land use in young and old reclaimed regions of a coastal estuary wetland, China. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, N.S.; Qu, J.F.; Li, G.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, R.J.; Fang, C.M. Reclamation of coastal salt marshes promoted carbon loss from previously-sequestered soil carbon pool. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Hughes, A.R.; Kimbro, D.L. Loss of ‘blue carbon’ from coastal salt marshes following habitat disturbance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Mou, X.; Liu, X. Effects of reclamation on soil carbon and nitrogen in coastal wetlands of Liaohe River Delta, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, C.; Zhong, C.; Li, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Responses of soil nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry to different human land uses in a subtropical tidal wetland. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Babka, B.; Giani, L. Changes in soil organic matter quality during sea-influenced marsh soil development at the North Sea coast. Catena 2013, 107, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Ge, Z.; Ji, Y.; Lai, D.Y.; Temmerman, S.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Tang, J. Land use and land cover changes in coastal and inland wetlands cause soil carbon and nitrogen loss. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2022, 31, 2541–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, C.; Zeng, F.; Song, Z.; Tariq, A.; Peñuelas, J. Losses and destabilization of soil organic carbon stocks in coastal wetlands converted into aquaculture ponds. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 32, e17480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, J.; Waheed, K.N.; Mirza, Z.S.; Zafarullah, M. A Method for Soil Samples Collection during Site Assessment for Aquaculture: Sampling method to assess soil for aquaculture. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. B Life Environ. Sci. 2021, 58, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Almutari, M.M.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Swadi, H.A.; Ahmad, J.; Al-Farraj, A.S.F. Impacts of aquaculture wastewater irrigation on soil health, nutrient availability, and date palm fruit quality. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Sardans, J.; Xue, K.; Zeng, F.; Tariq, A.; Peñuelas, J. Soil carbon pools and microbial network stability depletion associated with wetland conversion into aquaculture ponds in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, G.C.; Lu, H.L.; Zhu, H.; Ye, Y. Effects of shrimp pond effluents on stocks of organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in soils of Kandelia obovate forests along Jiulong River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lu, H.; Hong, H.; Qian, L.; Yuan, B.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. Potential and mechanism of glomalin-related soil protein on metal sequestration in mangrove wetlands affected by aquaculture effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yang, P.; Lin, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tong, C.; Hong, Y.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Tang, K.W. Latitudinal responses of wetland soil nitrogen pools to plant invasion and subsequent aquaculture reclamation along the southeastern coast of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 363, 108874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.L.; da Silveira Pereira, A.C.; Correia, A.M.; Giumbelli, L.D.; Brunetto, G.; Loss, A.; Arana, L.A.V. A new strategy to study pond soil chemistry in intensive and extensive cultures of Litopenaeus vannamei: A case study in Brazil. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1973; Volume 498. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. Estimation of soil organic carbon by the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analysis Methods of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry; Agriculture Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Benton, J.J. Agronomic Handbook: Management of Crops, Soils, and Their Fertility; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. (Eds.) Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A.P. Discovering Statistics using IBM SPSS Statistics, 4th ed.; Sage: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, B. A comprehensive system of leaf analyses and its use for diagnosing crop nutrient status. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1982, 13, 1035–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanpour, P.N.; Schwab, A.P. A new soil test for simultaneous extraction of macro-and micro-nutrients in alkaline soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1977, 8, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H.; Dickey, D.A. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 400–428. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.B.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Singh, B.P.; Collins, D.; Armstrong, R.; Van Zwieten, L.; Tavakkoli, E. Nutrient stoichiometry and labile carbon content of organic amendments control microbial biomass and carbon-use efficiency in a poorly structured sodic-subsoil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Mei, J.; Tang, X.; Wang, T.; Long, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Assessing the suitability of three purple soils for aquaculture by physiological responses in freshwater bivalves (Hyriopsis cumingii). Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasibuan, S.; Syafriadiman, S.; Aryani, N.; Fadhli, M.; Hasibuan, M. The age and quality of pond bottom soil affect water quality and production of Pangasius hypophthalmus in the tropical environment. Aquac. Fish. 2023, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wan, S.; Wang, R. Assessment of soil enzyme activities of saline–sodic soil under drip irrigation in the Songnen plain. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 11, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, D.M.; Talley, T.S. Salinity. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Jørgensen, S.E., Fath, B.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 1–5, pp. 3127–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, P.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tong, C.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Lin, Y.; Tan, L.; Tian, Y.; et al. Soil organic nitrogen content and composition in different wetland habitat types along the south-east coast of China. Catena 2023, 232, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.P.; Wang, W.Q.; Song, Z.L.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Guo, L.D.; Van Zwieten, L.; Li, Q.; Hartley, I.P.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.D.; et al. Spartina alterniflora invasion controls organic carbon stocks in coastal marsh and mangrove soils across tropics and subtropics. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 1627–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.Z.; Liu, M.; Hou, L.J.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Wang, W.Q.; Li, X.F.; Yin, G.Y. Effects of shrimp-aquaculture reclamation on sediment nitrate dissimilatory reduction processes in a coastal wetland of southeastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.K. Chemistry Analysis Methods of Soil and Agriculture; Agricultural Science Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Processes Affected in Pond | References |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size and texture | erosion and sedimentation, embankment stability, seepage, suitability of bottom habitat | [69,72,85,99,130,131,132] |
| pH (acidity) | nutrient availability, microbial activity, benthic productivity, hydrogen ion toxicity | [42,69,85,96,100,132] |
| Organic matter | embankment stability, oxygen demand, nutrient supply, suitability of bottom habitat | [42,85,90,99,120,130,133] |
| Nitrogen concentration and C:N ratio | decomposition of organic matter, nutrient availability | [42,69,85,120,134,135,136] |
| Redox potential | toxin production, mineral solubility | [69,85,90,99,130,132,135] |
| Sediment depth | reduction in pond volume, suitability of bottom habitat | [69,72,85,99,130,132,133] |
| Nutrient concentration | nutrient availability and productivity | [69,85,90,99,115,132,136] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudoy, D.; Meskhi, B.; Olshevskaya, A.; Kozyrev, D.; Shevchenko, V.; Odabashyan, M.; Teplyakova, S.; Rybak, A. Analysis of Edaphic Factors on the Role of Probiotics in the Development of Sustainable and Productive Aquaculture. Fishes 2025, 10, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090457
Rudoy D, Meskhi B, Olshevskaya A, Kozyrev D, Shevchenko V, Odabashyan M, Teplyakova S, Rybak A. Analysis of Edaphic Factors on the Role of Probiotics in the Development of Sustainable and Productive Aquaculture. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090457
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudoy, Dmitry, Besarion Meskhi, Anastasiya Olshevskaya, Denis Kozyrev, Victoria Shevchenko, Mary Odabashyan, Svetlana Teplyakova, and Alexander Rybak. 2025. "Analysis of Edaphic Factors on the Role of Probiotics in the Development of Sustainable and Productive Aquaculture" Fishes 10, no. 9: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090457
APA StyleRudoy, D., Meskhi, B., Olshevskaya, A., Kozyrev, D., Shevchenko, V., Odabashyan, M., Teplyakova, S., & Rybak, A. (2025). Analysis of Edaphic Factors on the Role of Probiotics in the Development of Sustainable and Productive Aquaculture. Fishes, 10(9), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090457










