WSSV Infection in the Gut Microbiota of the Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
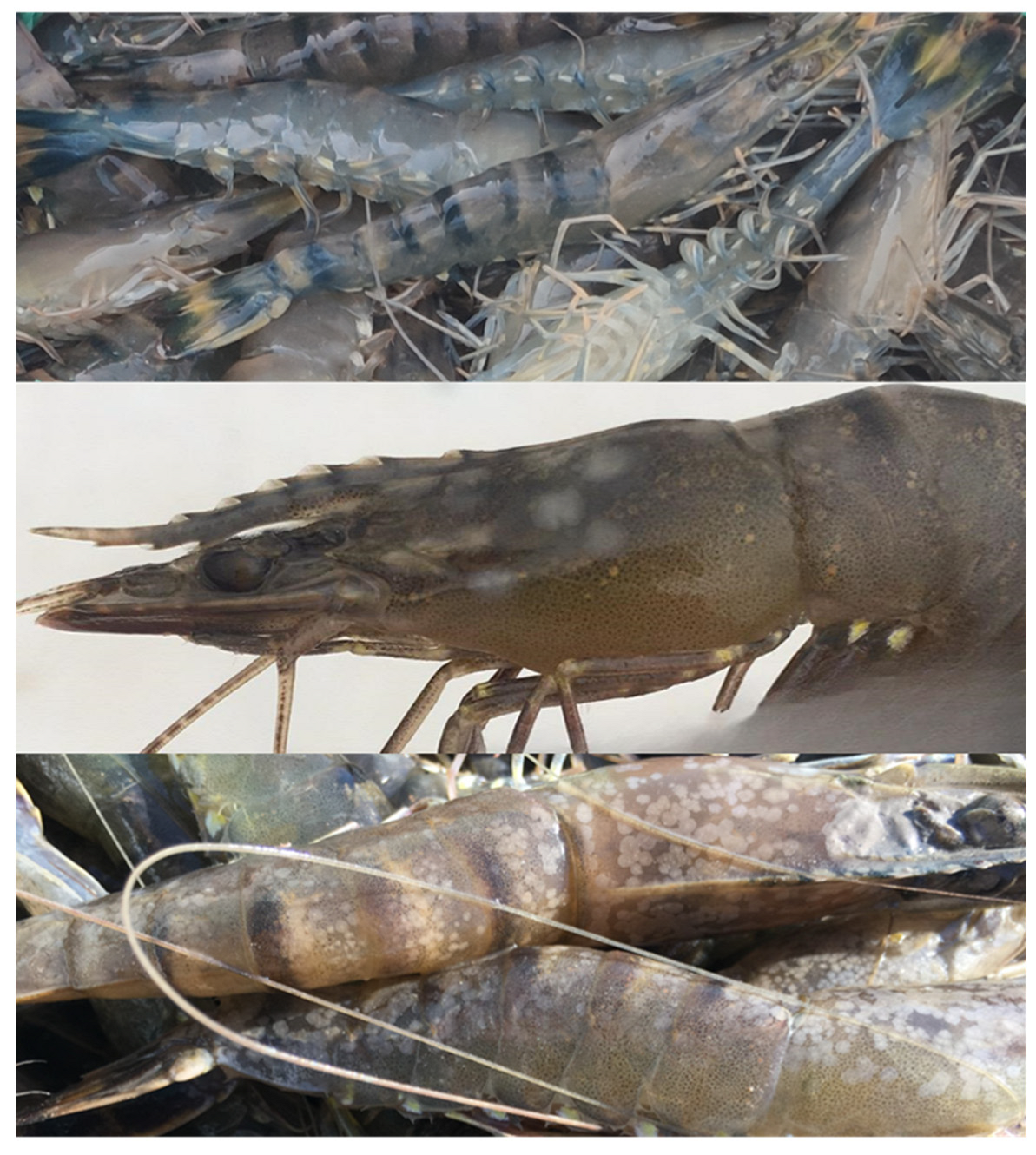
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
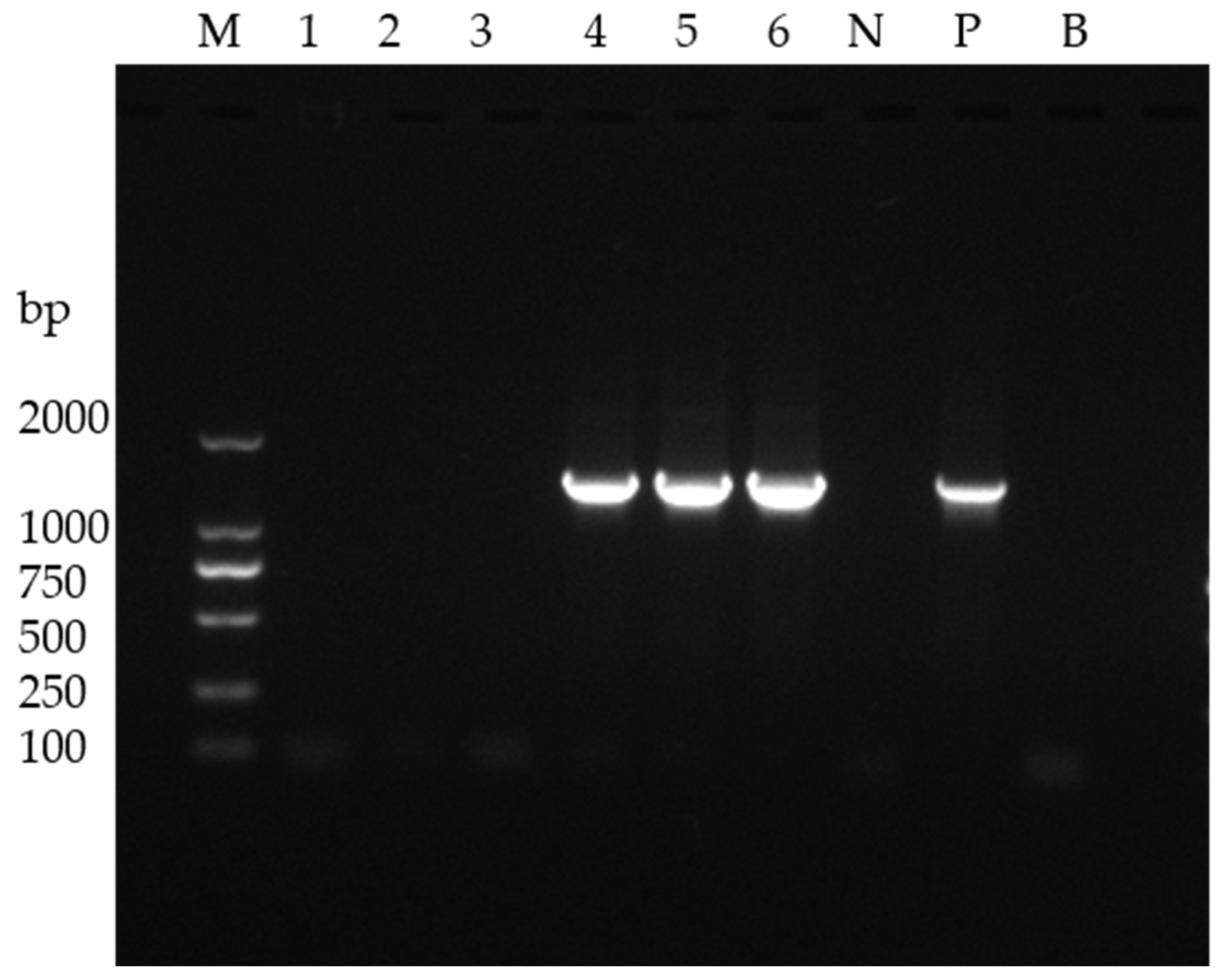
2.2. WSSV Detection
2.3. Intestinal DNA Extraction and 16S rDNA Amplification
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.4.1. Quality Control
2.4.2. OTU Cluster and Species Annotation
2.4.3. Alpha Diversity
2.4.4. Beta Diversity
3. Results
3.1. WSSV Detection of Diseased and Healthy Shrimp
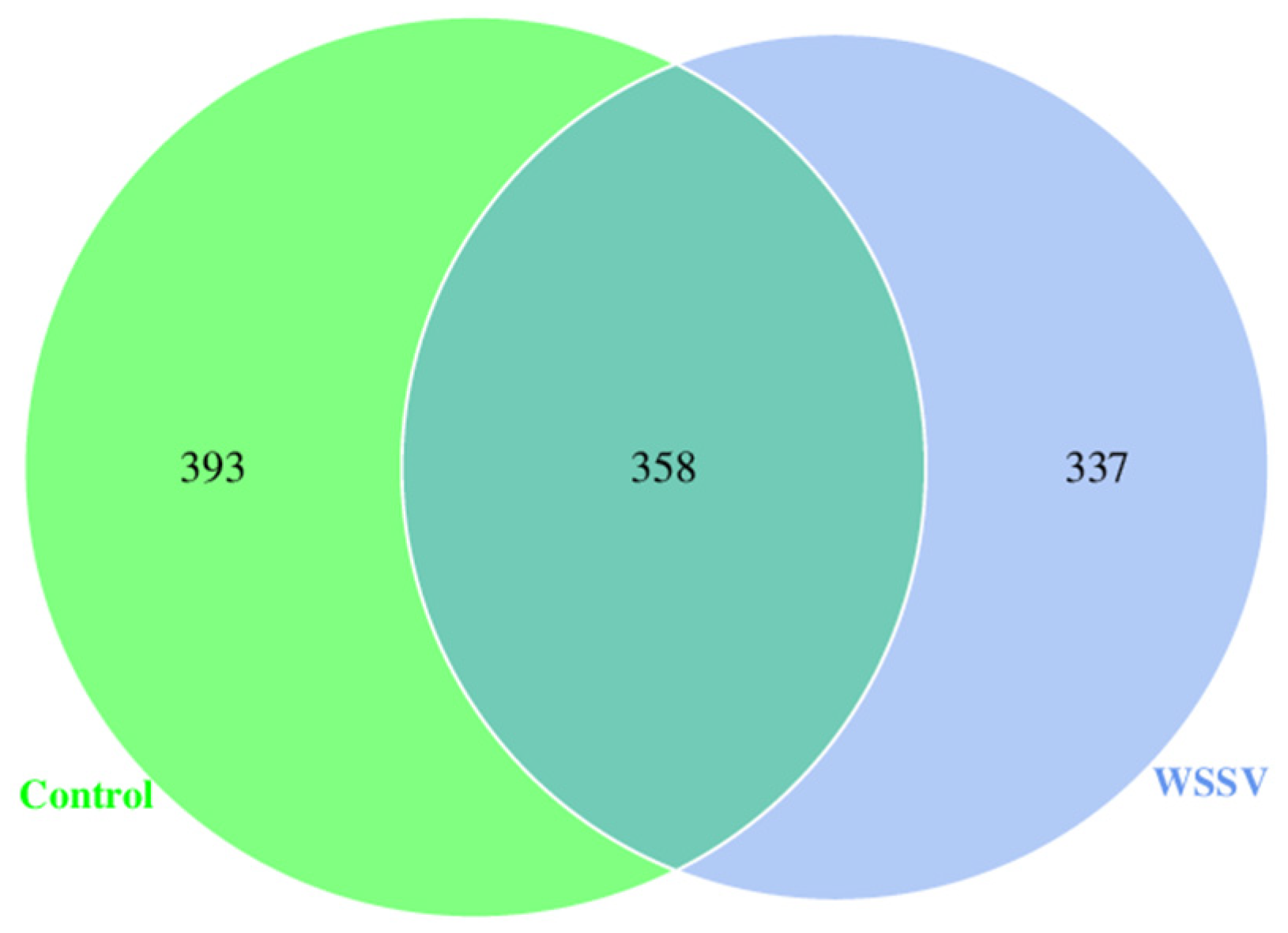
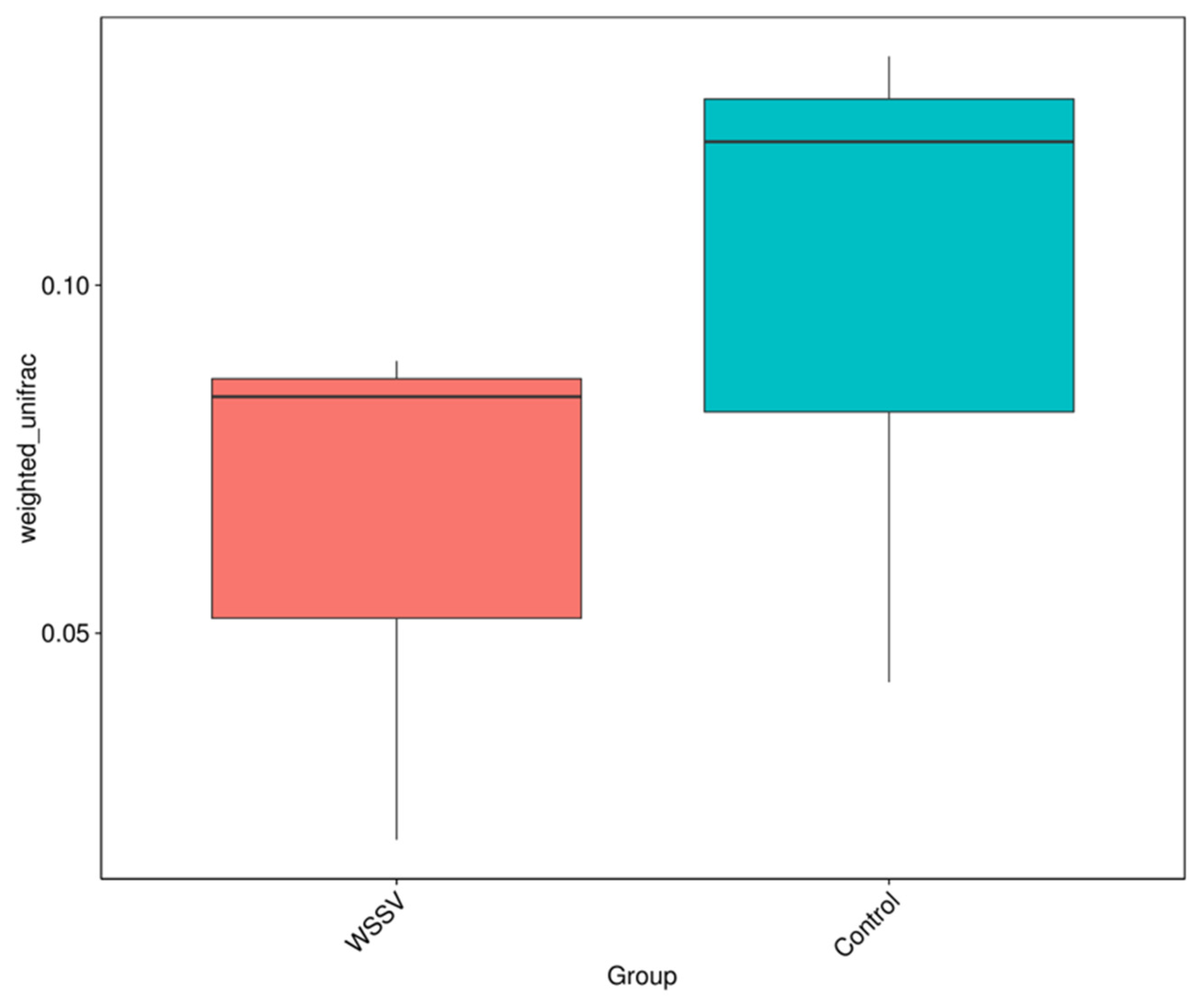
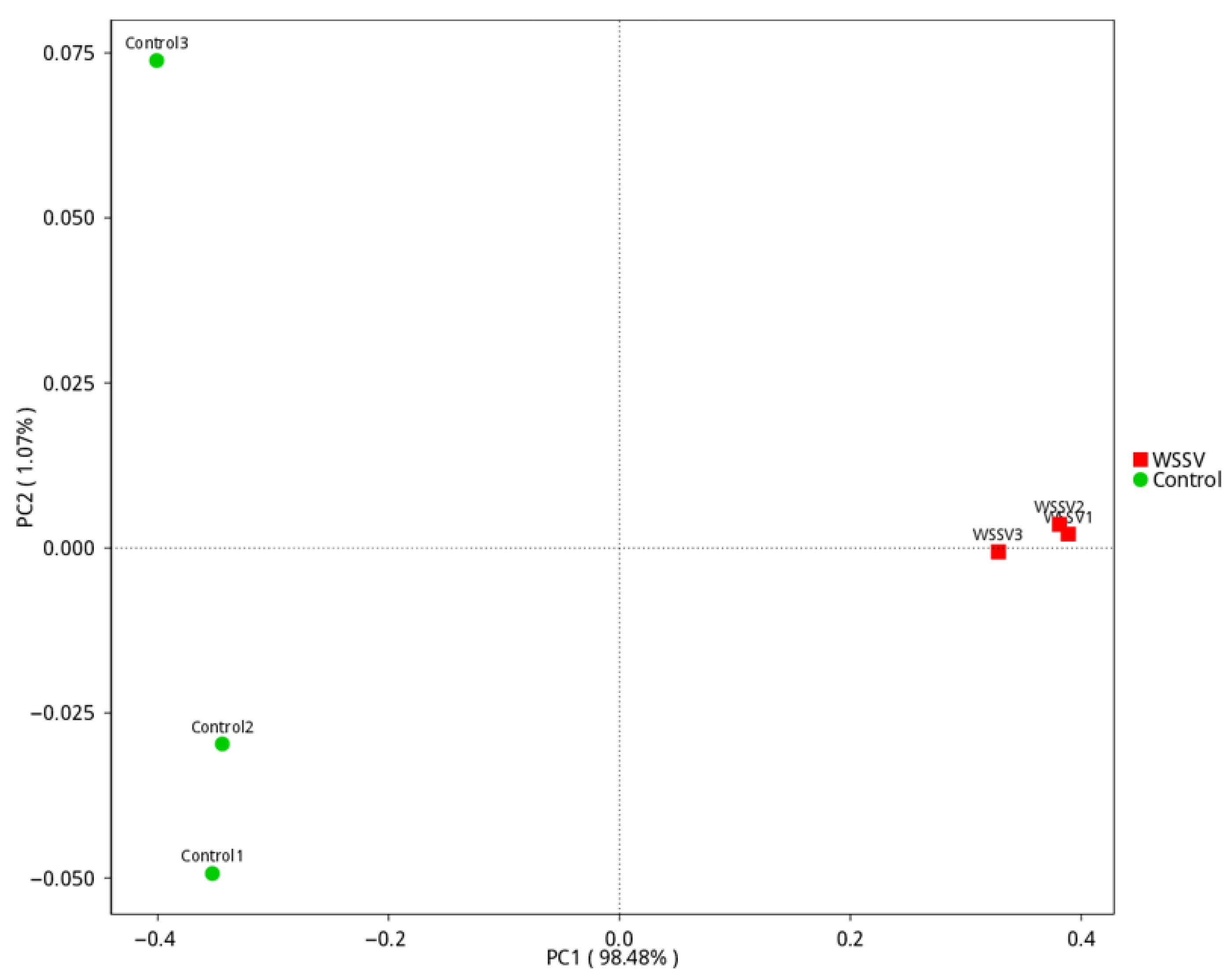
3.2. Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota Diversity
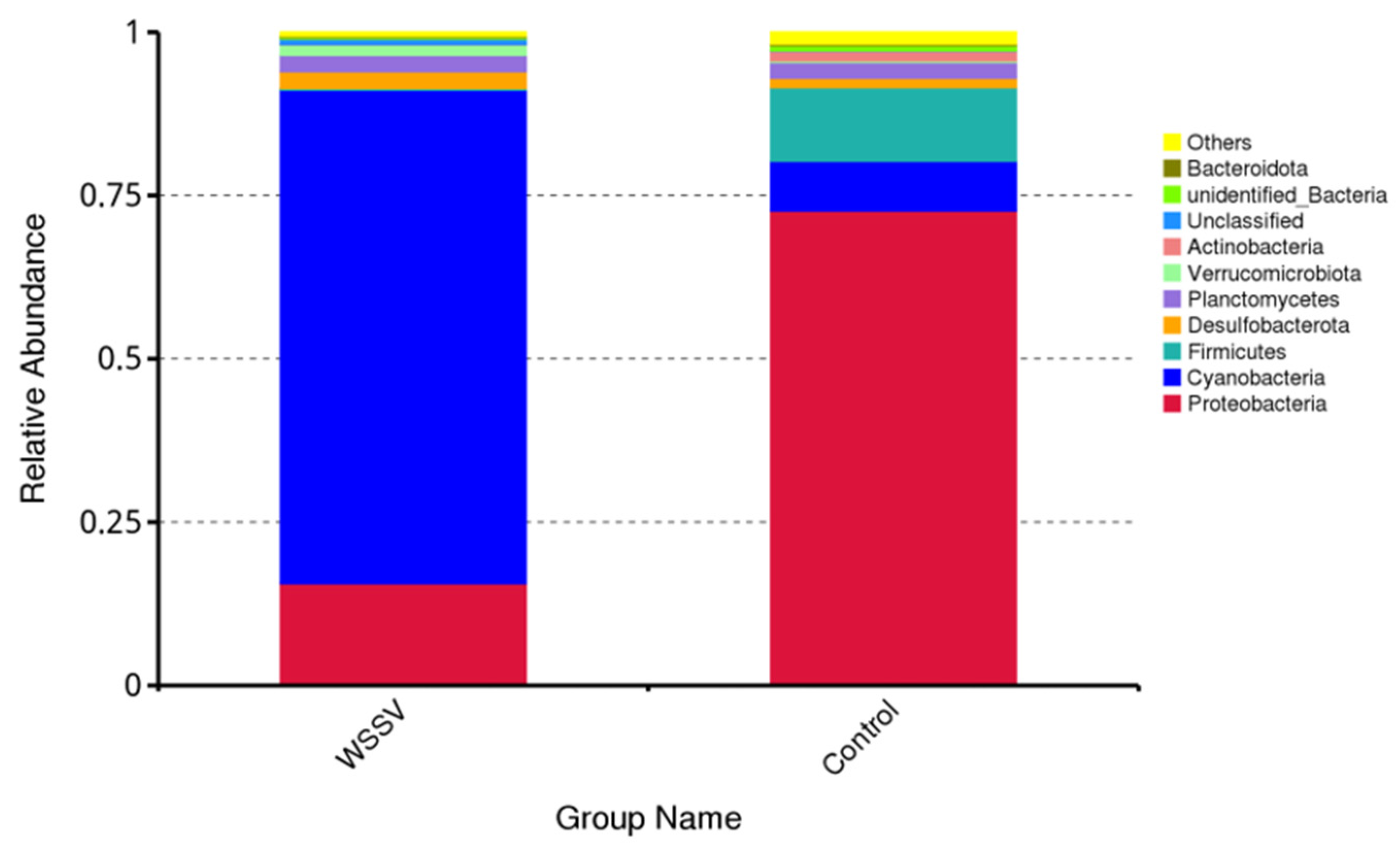
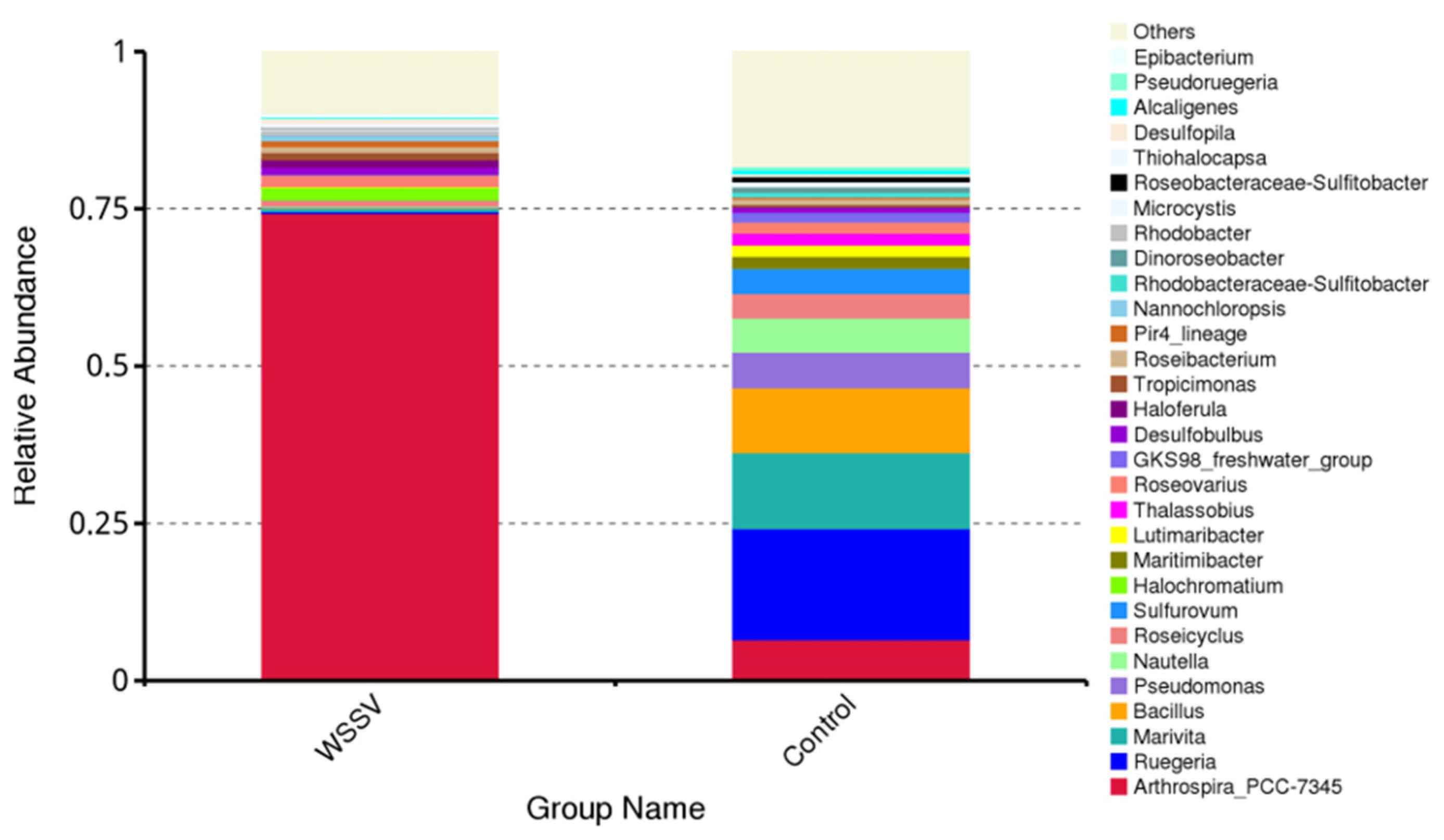
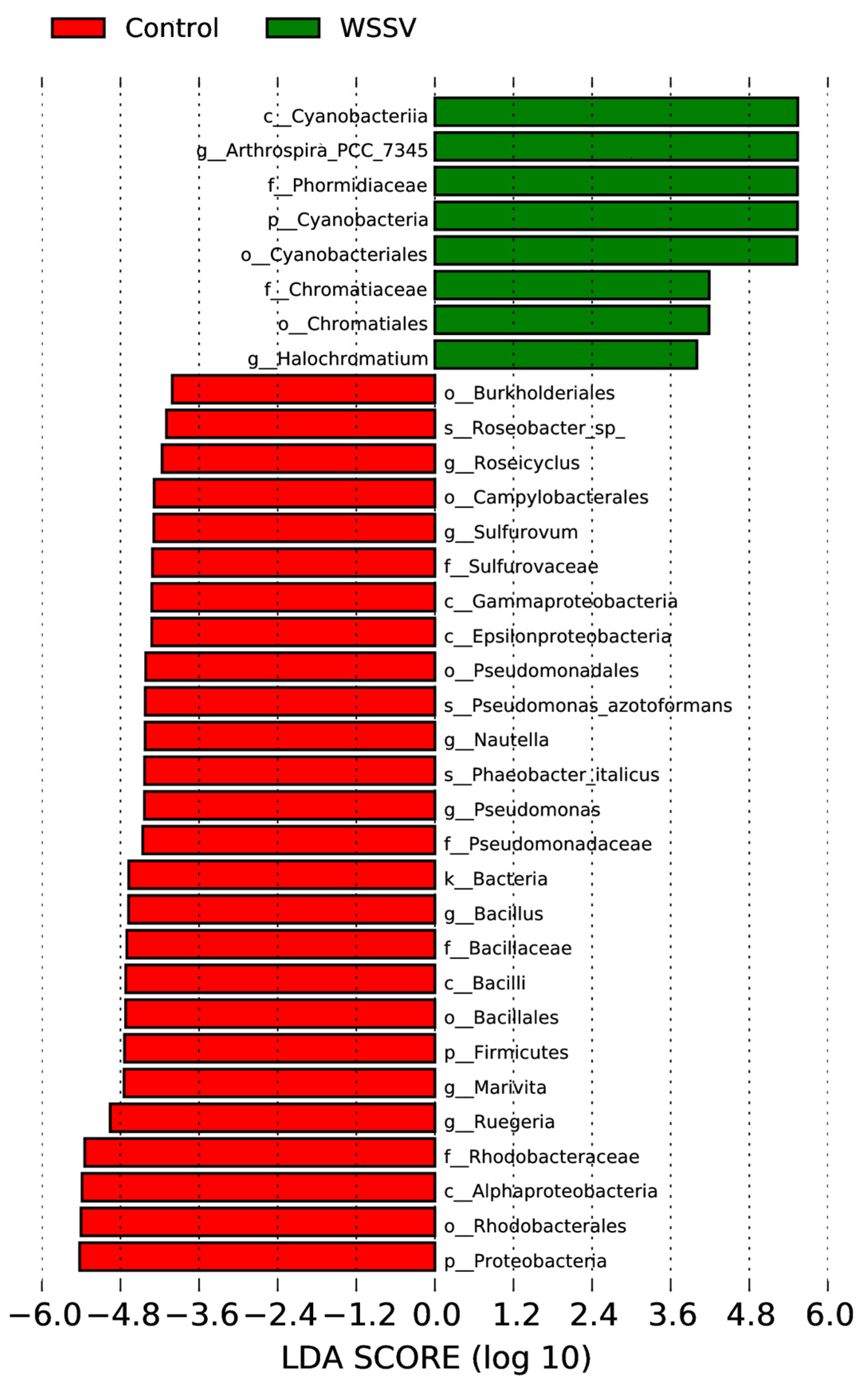
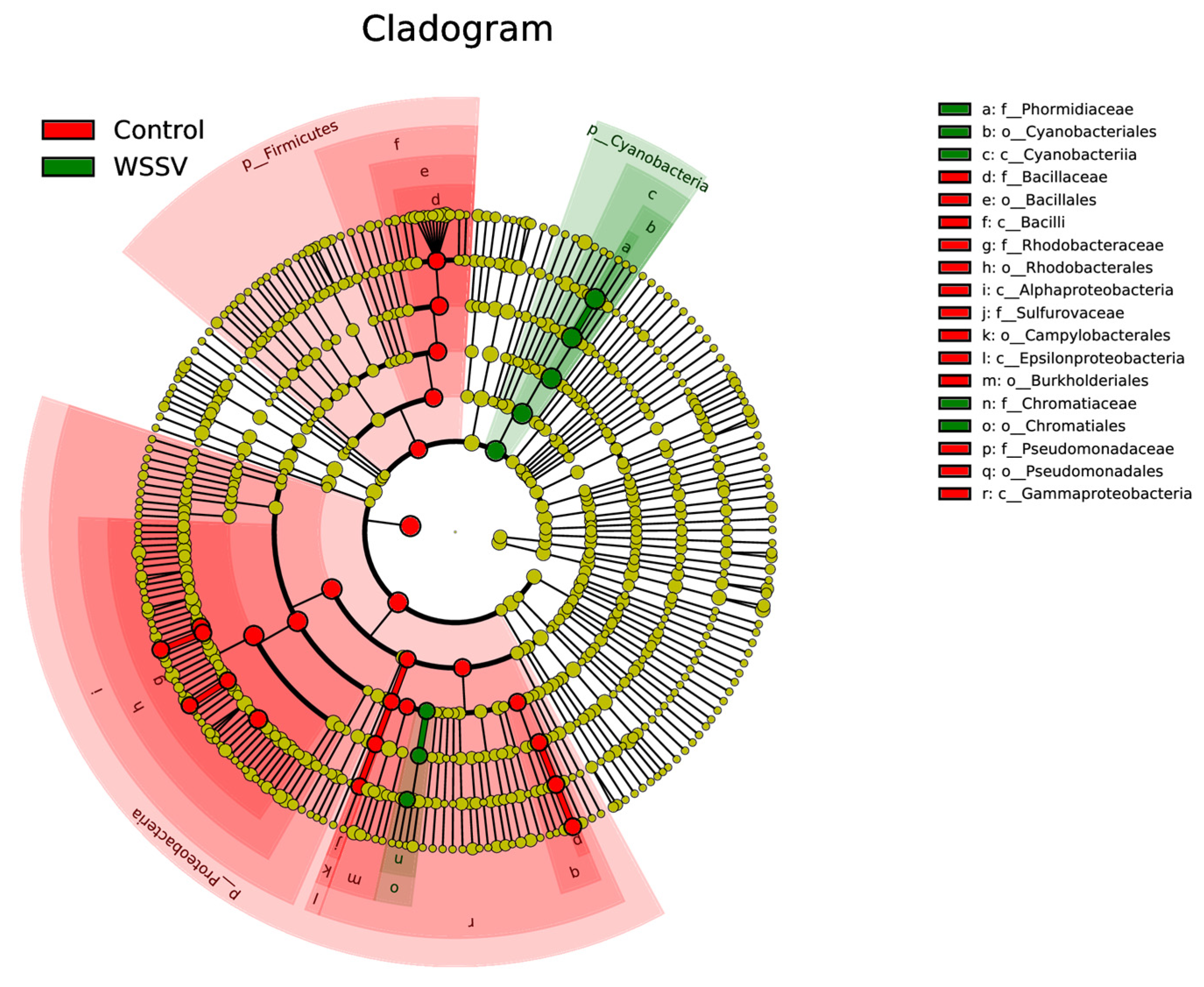
3.3. Composition and Differential Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota in P. monodon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.H.; Wang, X.L.; Yu, X.Q.; Xu, L.; Gai, C.L.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, H.J.; Diao, J. Effects of Chronic Nitrite Stress on Behavior, Digestive Enzyme Activities and Non-Specific Immunity of an African Population of Penaeus monodon. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2023, 53, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Qiu, Q.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, J. Contrasting Ecological Processes and Functional Compositions between Intestinal Bacterial Community in Healthy and Diseased Shrimp. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.L.Q.X. Characteristics of Intestinal Microbiota in the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Differing Growth Performances in the Marine Cultured Environment. Aquaculture 2019, 505, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesebeke, R.T. Balancing Microbial Ecosystems within Humans and Animals to Prevent Medical Conditions. J. Nutr. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Butto, L.F.; Haller, D. Dysbiosis in Intestinal Inflammation: Cause or Consequence. Int. J. Med. 2016, 306, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut Microbiota: Role in Pathogen Colonization, Immune Responses, and Inflammatory Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornejo-Granados, F.; Lopez-Zavala, A.A.; Gallardo-Becerra, L.; Mendoza-Vargas, A.; Sánchez, F.; Vichido, R.; Brieb, L.G.; Viana, M.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. Microbiome of Pacific White Leg Shrimp Reveals Differential Bacterial Community Composition between Wild, Aquacultured and AHPND/EMS Outbreak Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Zhou, S.H.; Balasubramanian, B.; Zeng, F.Y.; Sun, C.B.; Pang, H.Y. Dietary Seaweed (Enteromorpha) Polysaccharides Improves Growth Performance Involved in Regulation of Immune Responses, Intestinal Morphology and Microbial Community in Banana Shrimp Fenneropenaeus merguiensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xia, M.; Li, R.; Mu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Ye, Y.; Wang, C. Vibrio alginolyticus Infection Induces Coupled Changes of Bacterial Community and Metabolic Phenotype in the Gut of Swimming Crab. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanschagrin, S.; Yergeau, E. Next-generation sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA gene amplicons. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 90, e51709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, C.; Wei, K.; Li, X.; Mu, X.; Duan, M.; Zhu, C.; Jin, L.; He, X.; et al. MultiPrime: A Reliable and Efficient Tool for Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing. iMeta 2023, 2, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, K.D.; Wang, Q.; Nute, M.G.; Tyshaieva, A.; Reeves, E.; Soriano, S.; Wu, Q.; Graeber, E.; Finzer, P.; Mendling, W.; et al. Emu: Species-level microbial community profiling of full-length 16S rRNA Oxford Nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Fan, L.; Yan, M. White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) Infection Impacts Intestinal Microbiota Composition and Function in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuoc, L.H.; Corteel, M.; Nauwynck, H.J.; Pensaert, M.B.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Van den Broeck, W.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Increased Susceptibility of White Spot Syndrome Virus-Infected Litopenaeus vannamei to Vibrio campbellii. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Liao, X.; Long, X.; Zhao, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Sun, C. Host-Microbiota Interactions and Responses of Metapenaeus ensis Infected with Decapod Iridescent Virus 1. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1097931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, D. Gastrointestinal Microbiota Imbalance is Triggered by the Enrichment of Vibrio in Subadult Litopenaeus vannamei with Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.F.; He, P.M.; Jia, R. iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in the Hepatopancreas of Litopenaeus vannamei after WSSV Infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2021, 145, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, X.; Luan, S.; Kong, J.; Cao, B.; Luo, K.; Tan, J.; Cao, J.; Cao, J.; Chen, B.; et al. Evaluation of Genetic Parameters for Growth and Survival Traits of Penaeus vannamei During White Spot Syndrome Virus Infection. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2024, 45, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.F.; Hsu, H.C.; Tsai, M.F.; Ch, H.; Peng, S.; Kou, G. Specific Genomic DNA Fragment Analysis of Different Geographical Clinical Samples of Shrimp White Spot Syndrome Virus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 35, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Yuan, J. Effects of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) Infection on Intestinal Flora Composition of Procambarus clarkii. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2020, 30, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Wei, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Y. Clinical signs of naturally white spot syndrome virus (WSSV)-infected kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicas, based on their physiological and behavioural states. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 28630.2-2012; Diagnostic Protocols for White Spot Disease—Part 2: Nested PCR Method. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Sha, H.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Rationally Designed Probiotics Prevent Shrimp White Feces Syndrome via the Probiotics Gut Microbiome Immunity Axis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, H.; Song, T.; Zhan, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Sarafloxacin Hydrochloride Exposure Disrupts Gut Microbiota and Increases Shrimp Susceptibility to Vibrio anguillarum Infection. Aquaculture 2024, 586, 740810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, X. Core Gut Microbiota of Shrimp Function as a Regulator to Maintain Immune Homeostasis in Response to WSSV Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0246521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.B.; Sha, H.N.; Chen, J. Updated Roles of the Gut Microbiota in Exploring Shrimp Etiology, Polymicrobial Pathogens, and Disease Incidence. Zool. Res. 2024, 45, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.C.; Bass, D.; Stentiford, G.D.; van der Giezen, M. Understanding the Role of the Shrimp Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Bi, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Gai, C.; Xu, L.; Ye, H.; Li, L.; Diao, J.; et al. Distribution Characteristics of Microorganisms in Hepatopancreas and Intestine of Penaeus monodon under Industrial and High-Pond Culture Modes. Fish. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2024, 51, 362–372. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.N.; Lu, J.Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Consistent Features of the Gut Microbiota in Response to Diverse Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Fish Fish. 2023, 24, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.N.; Lu, J.Q.; Chen, J. A Meta-Analysis Study of the Robustness and Universality of Gut Microbiota–Shrimp Diseases Relationship. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 3924–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Microecological Koch’s Postulates Reveal that Intestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis Contributes to Shrimp White Feces Syndrome. Microbiome 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guri, M.; Durand, L.; Cueff-Gauchard, V.; Zbinden, M.; Crassous, P.; Shillito, B.; Cambon-Bonavita, M.A. Acquisition of Epibiotic Bacteria along the Life Cycle of the Hydrothermal Shrimp Rimicaris exoculata. ISME J. 2012, 6, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, L.; Dong, P.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Lu, Z.; Hou, D.; Zhang, D. Fine-Scale Succession Patterns and Assembly Mechanisms of Bacterial Community of Litopenaeus vannamei Larvae across the Developmental Cycle. Microbiome 2020, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsman, A.; St-Pierre, B.; Rosales-Leija, M.; Brown, M.; Gibbons, W. Impact of Aquaculture Practices on Intestinal Bacterial Profiles of Pacific Whiteleg Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Khoruamkid, S.; Kongpakdee, W.; Wei, D.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Deng, Z.; Weng, S.; Huang, Z.; He, J.; et al. Dissimilarity of Microbial Diversity of Pond Water, Shrimp Intestine and Sediment in Aquamimicry System. AMB Express 2020, 1, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cui, X.; Cai, Z.; Huang, Y. Analysis of Changes in the Waterflora and Intestinal Microflora of Penaeus monodon in Different Cultural Models. J. Xichang Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 37, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.E. Succession of Intestinal Microbiota of Litopenaeus vannamei Larvae and the Impacts of Several Probiotics on Larviculture. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Yu, E.L.; Liu, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Yan, M.; Dong, P.; Zhang, D. Screening of Carbon Sources for Enrichment and Directional Isolation of Rhodobacteraceae from the Gut of Litopenaeus vannamei. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2022, 65, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Seabkongseng, T.; Limkul, S.; Sriphuttha, C.; Phiwthong, T.; Aunkam, P.; Suwannathit, R.; Jaree, P.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Tittabutr, P.; Teaumroong, N. Supplementation of Bacillus velezensis S141 in feed as a probiotic enhances growth performance, pathogenic tolerances, and immune system in shrimp. Aquaculture 2025, 604, 742448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, P.C.; Song, X.L.; Chen, G.F.; Xu, H.; Huang, J. Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus PC465 isolated from the gut of Fenneropenaeus chinensis improves the health status and resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei against white spot syndrome virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, L.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Hou, F.; Ye, H.; Liu, H.; Yue, X. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on Growth, Immunity, Digestase Activities and Gut Microbiota Composition of Sebastes schlegelii. J. Guangdong Ocean. Univ. 2024, 44, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, H.; Gatesoupe, F.J.; She, R.; Lin, Q.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Li, X. Bacterial Signatures of “Red-Operculum” Disease in the Gut of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus). Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Xu, C.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L. Physiological Change and Nutritional Requirement of Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei at Low Salinity. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A Core Gut Microbiome in Obese and Lean Twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of Human Gut Microbiome Correlates with Metabolic Markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, D.; Stentiford, G.D.; Wang, H.C.; Koskella, B.; Tyler, C.R. The Pathobiome in Animal and Plant Diseases. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Qiuqian, L.; Yang, K.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, D. Changes in Intestinal Bacterial Communities are Closely Associated with Shrimp Disease Severity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6911–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Dong, C.; Qiu, Q.; Li, C. Integrating Gut Microbiota Immaturity and Disease-Discriminatory Taxa to Diagnose the Initiation and Severity of Shrimp Disease. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Hu, J.; Shen, Y.; Deng, G.; Gao, W.; Mou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, H. Effect of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei Infection on the Intestinal Microflora of Exopalaemon carinicauda. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2022, 43, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.T.; Ko, H.T.; Wu, P.L.; Kumar, R.; Wang, H.C.; Lu, H.P. Gut Microbiota of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Exhibits Distinct Responses to Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0118023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, R.; Powrie, F. Microbiota, Disease, and Back to Health: A Metastable Journey. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 52, 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, M.G.; Marrero, R.M.; Campa-Córdova, Á.I.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.M. Probiotic Effect of Streptomyces Strains Alone or in Combination with Bacillus and Lactobacillus in Juveniles of the White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazón-Suástegui, J.M.; Salas-Leiva, J.S.; Medina-Marrero, R.; Medina-García, R.; García-Bernal, M. Effect of Streptomyces Probiotics on the Gut Microbiota of Litopenaeus vannamei Challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol. Open 2019, 9, e967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, D.; Jacob, J.C.; Philip, R. Exclusion of Vibrio spp. by an Antagonistic Marine Actinomycete Streptomyces rubrolavendulae M56. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2951–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Observed Otus | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE | Goods Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 480 | 5.357 | 0.939 | 507.516 | 506.698 | 0.999 |
| WSSV | 451 | 2.523 | 0.445 | 485.552 | 490.027 | 0.998 |
| Indices | WSSV-Infected–Control (p-Value) |
|---|---|
| Observed_otus | 0.4984 |
| Shannon | 0.007528 |
| Simpson | 0.00724 |
| Chao1 | 0.4661 |
| ACE | 0.6297 |
| Goods_coverage | 0.5185 |
| Indices | Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test (V) a | Shapiro–Wilk Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stats | df | P | Stats | df | P | |
| Observed_otus | 0.184 | 6 | 0.200 * | 0.913 | 6 | 0.0454 |
| Shannon | 0.313 | 6 | 0.067 | 0.756 | 6 | 0.230 |
| Simpson | 0.312 | 6 | 0.070 | 0.756 | 6 | 0.230 |
| Chao1 | 0.211 | 6 | 0.200 * | 0.945 | 6 | 0.697 |
| ACE | 0.234 | 6 | 0.200 * | 0.858 | 6 | 0.183 |
| Goods_coverage | 0.319 | 6 | 0.056 | 0.683 | 6 | 0.040 |
| Phylum | Abundance | |
|---|---|---|
| WSSV | Control | |
| Proteobacteria | 15.63% | 72.68% |
| Cyanobacteria | 75.51% | 7.59% |
| Firmicutes | 0.28% | 11.27% |
| Desulfobacterota | 2.59% | 1.47% |
| Planctomycetes | 2.48% | 2.39% |
| Verrucomicrobiota | 1.61% | 0.24% |
| Actinobacteria | 0.07% | 1.47% |
| Unclassified | 0.84% | 0.08% |
| unidentified_Bacteria | 0.24% | 0.80% |
| Bacteroidota | 0.19% | 0.24% |
| Others | 0.56% | 1.77% |
| Genus | Abundance | |
|---|---|---|
| WSSV | Control | |
| Arthrospira_PCC-7345 | 74.32% | 6.57% |
| Ruegeria | 0.30% | 17.67% |
| Marivita | 0.55% | 12.08% |
| Bacillus | 0.09% | 10.30% |
| Pseudomonas | 0.13% | 5.67% |
| Nautella | 0.15% | 5.41% |
| Roseicyclus | 0.92% | 3.90% |
| Sulfurovum | 0.00% | 4.01% |
| Halochromatium | 1.98% | 0.01% |
| Maritimibacter | 0.04% | 1.89% |
| Others | 21.51% | 32.48% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gai, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Fu, R.; Diao, J.; et al. WSSV Infection in the Gut Microbiota of the Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fishes 2025, 10, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090440
Wang Y, Wang X, Gai C, Li Y, Xu L, Wang S, Li L, Yu X, Fu R, Diao J, et al. WSSV Infection in the Gut Microbiota of the Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090440
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Youhong, Xiaolu Wang, Chunlei Gai, Yuanyuan Li, La Xu, Shuxian Wang, Li Li, Xiaoqing Yu, Ranghui Fu, Jing Diao, and et al. 2025. "WSSV Infection in the Gut Microbiota of the Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon" Fishes 10, no. 9: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090440
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, X., Gai, C., Li, Y., Xu, L., Wang, S., Li, L., Yu, X., Fu, R., Diao, J., Ye, H., Fan, Y., & Cao, H. (2025). WSSV Infection in the Gut Microbiota of the Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fishes, 10(9), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090440





