Characterization of the NFAT Gene Family in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and Functional Analysis of NFAT1 During GCRV Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Cells, and Pathogens
2.2. Characterization of the NFAT Gene Family Members in Grass Carp
2.3. Physicochemical Characteristics and Subcellular Location Prediction of NFAT Genetic Family Members in Grass Carp
2.4. Protein Structure Analysis and Phylogenetic Tree Construction of Grass Carp NFAT Gene Family Members
2.5. Chromosomal Mapping and Collinearity Analysis of NFAT Gene Family Members in Grass Carp
2.6. GCRV Infection and Sample Collection
2.7. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of CiNFAT1
2.8. Construction and Transfection of CiNFAT1 Recombinant Vector
2.9. Subcellular Localization
2.10. Extracting Protein and Western Blot Analysis
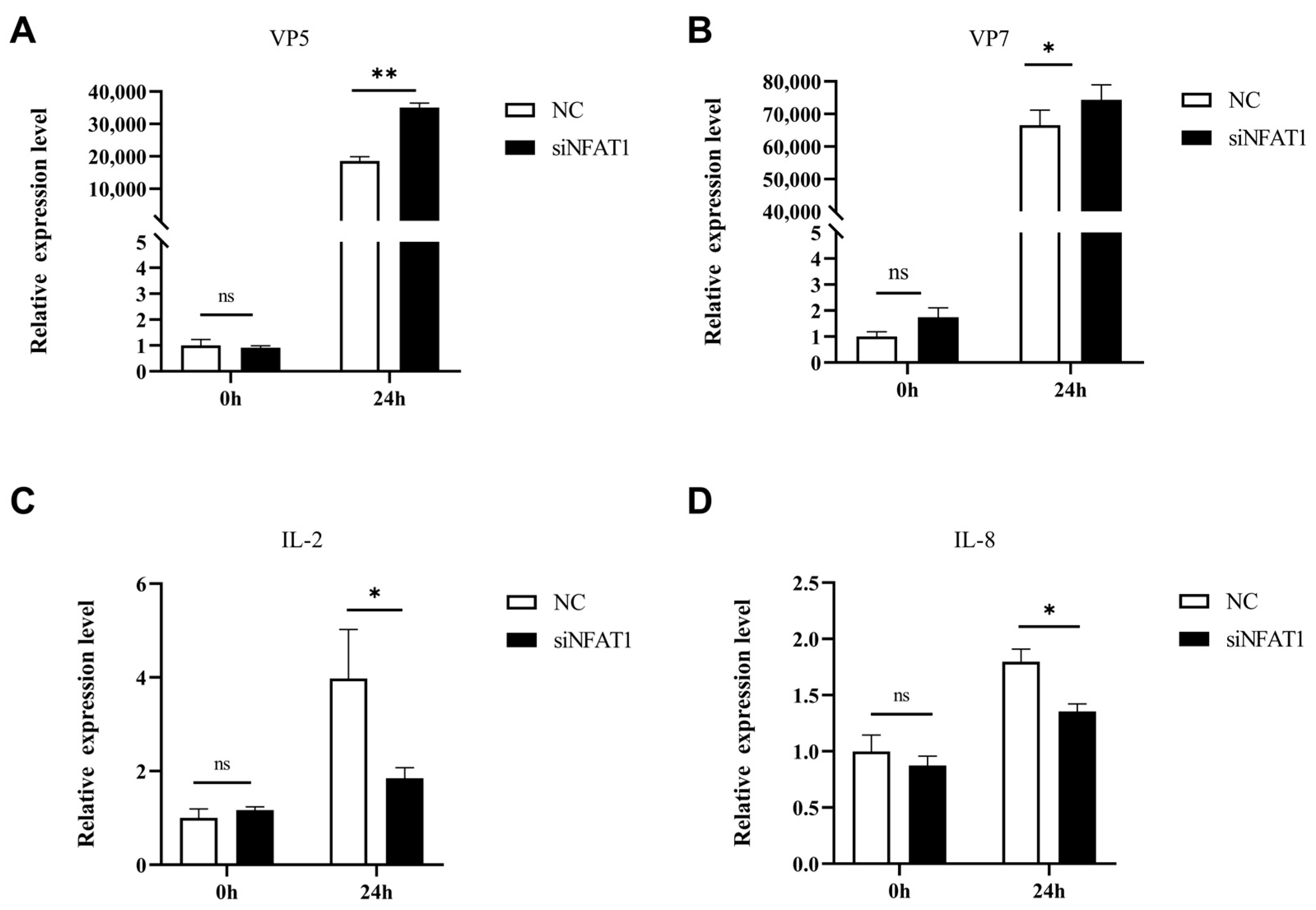
2.11. RNA Interference Assay
2.12. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
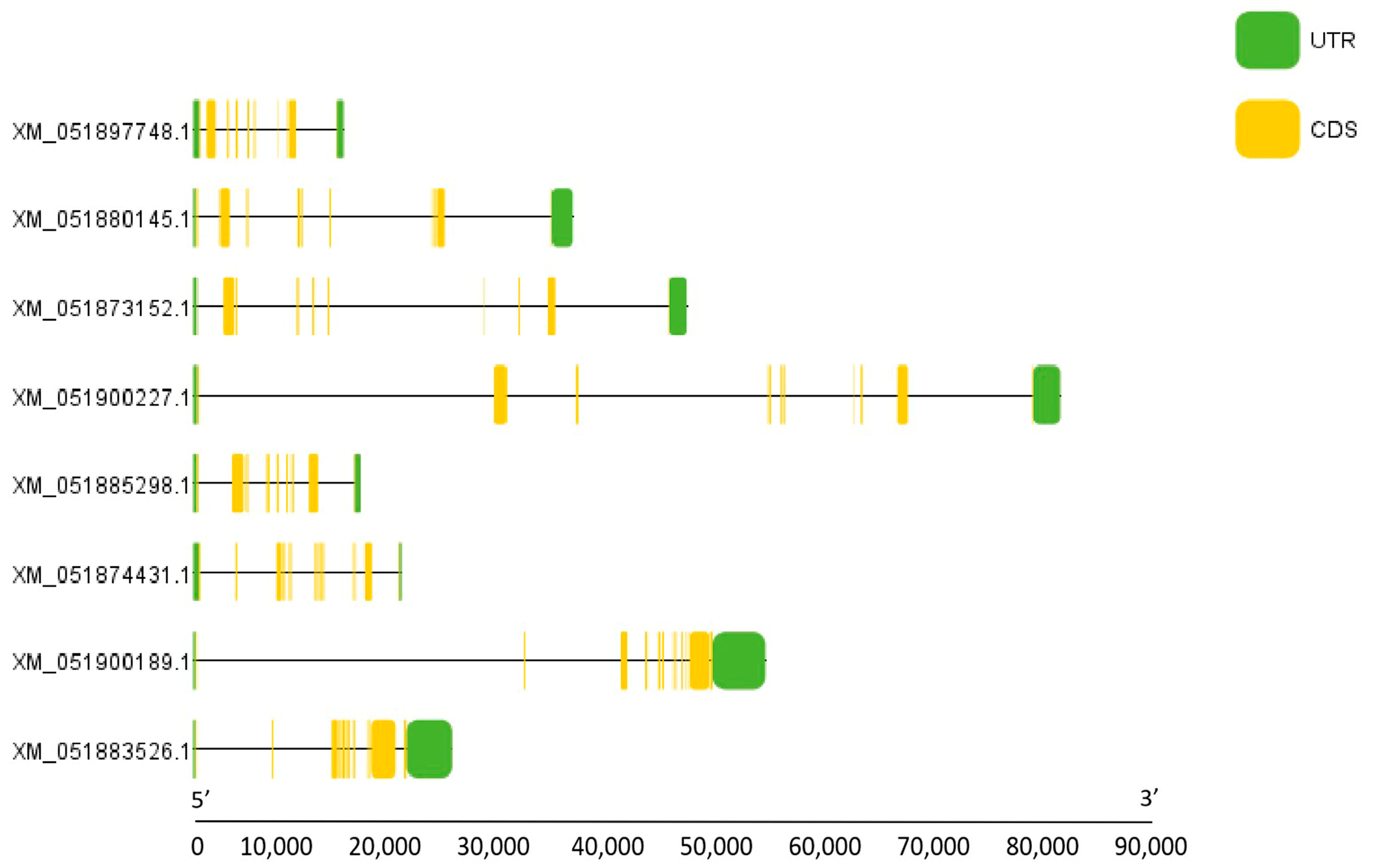
3.1. Identification and Feature Analysis of NFAT Genetic Family Members in Grass Carp
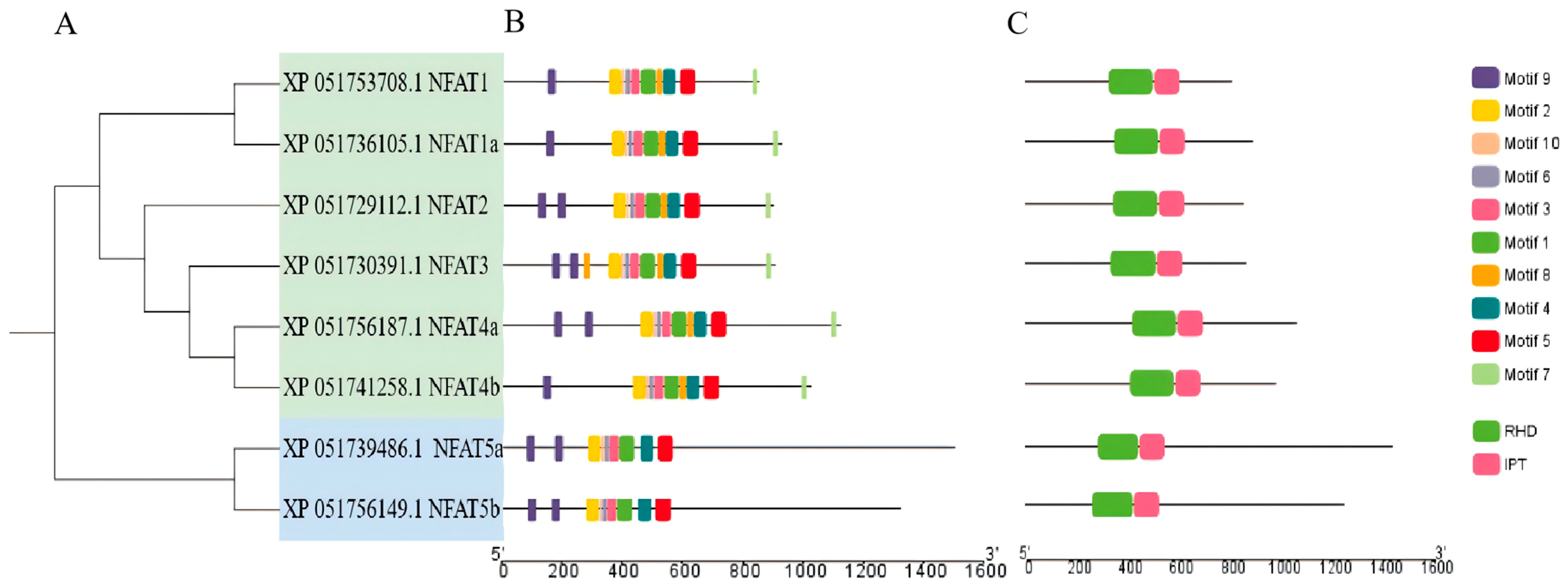
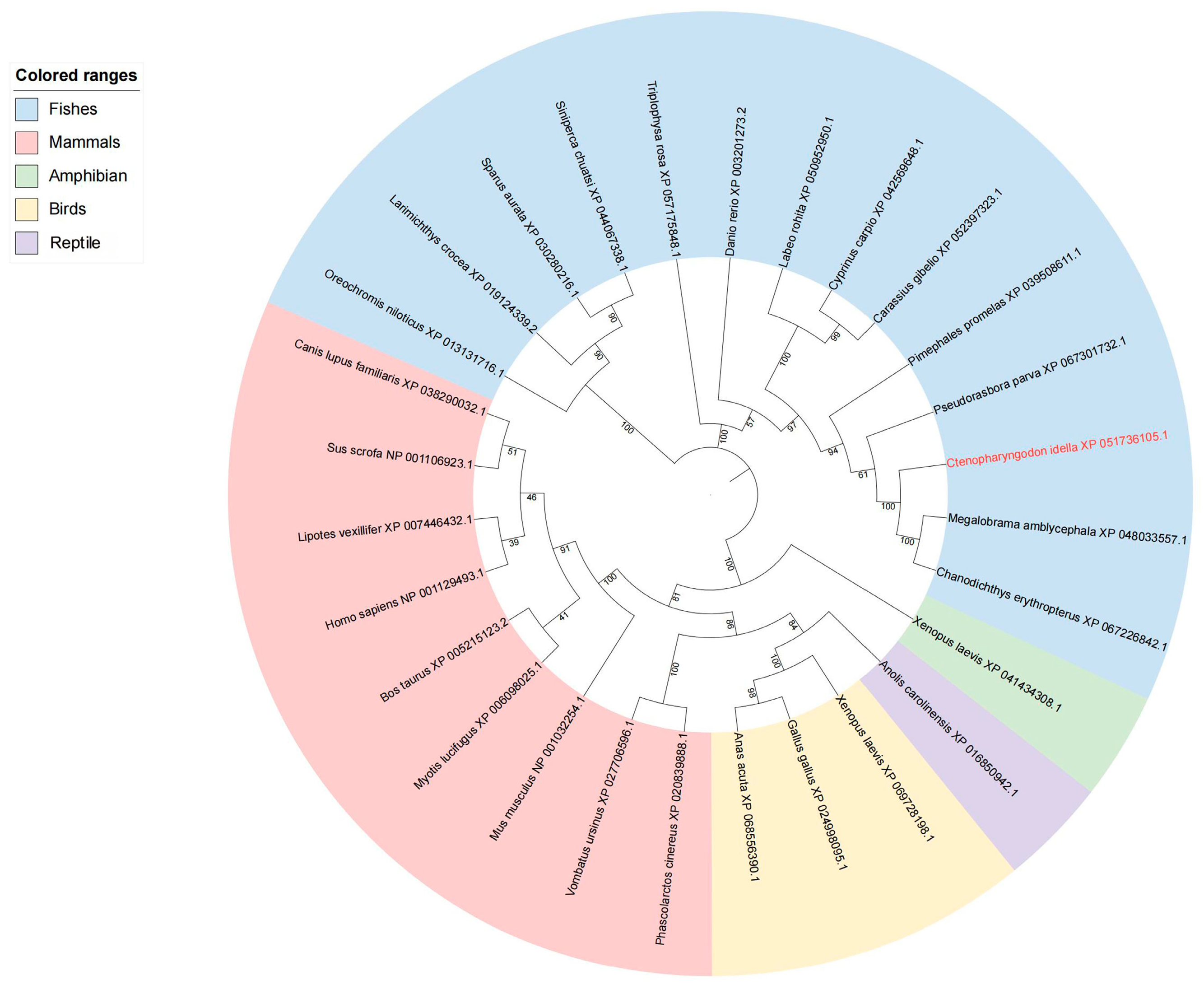
3.2. Structure and Phylogenetic Analysis of NFAT Gene Family Members in Grass Carp
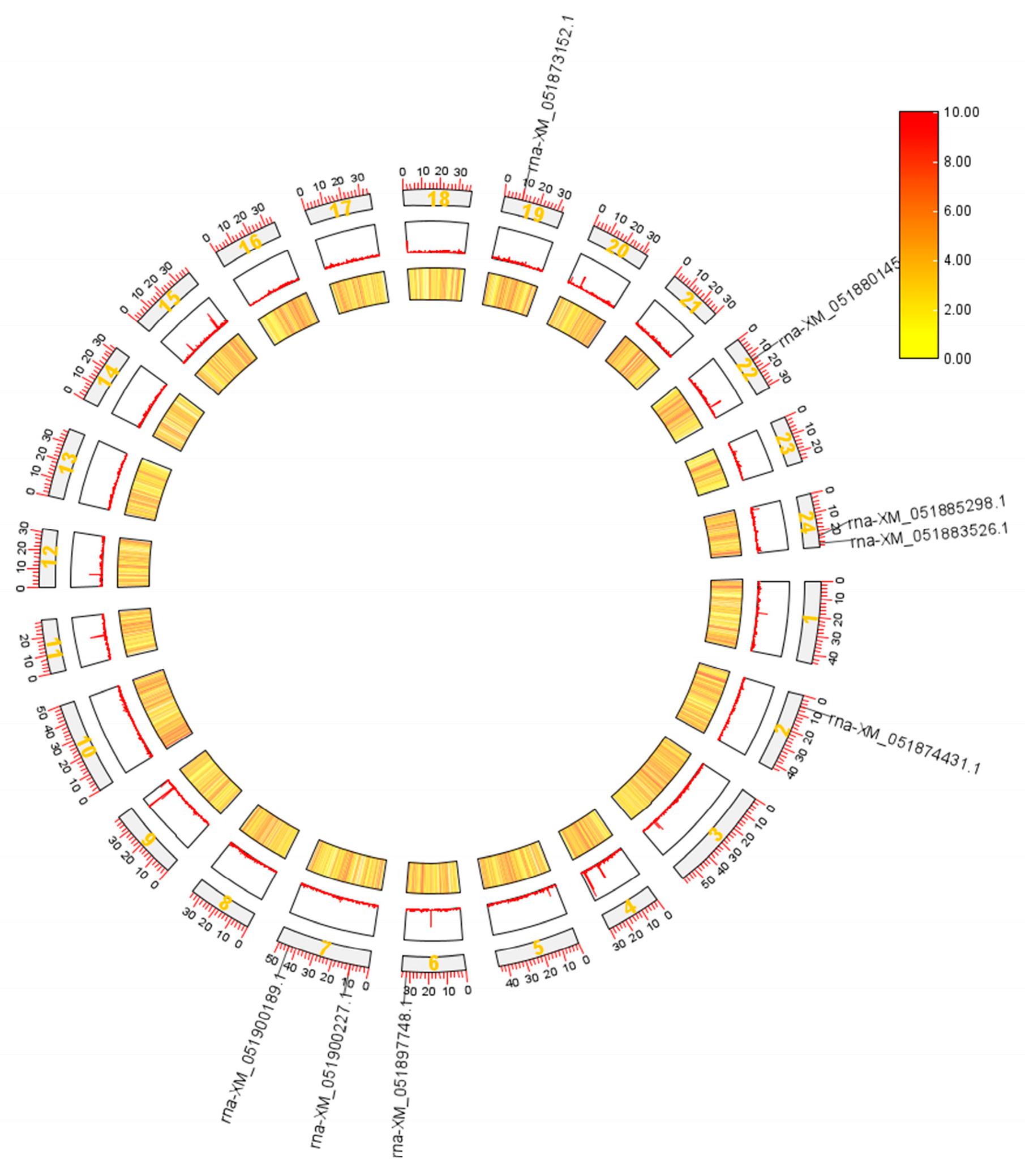
3.3. Chromosomal Localization of NFAT Gene Family Members in Grass Carp
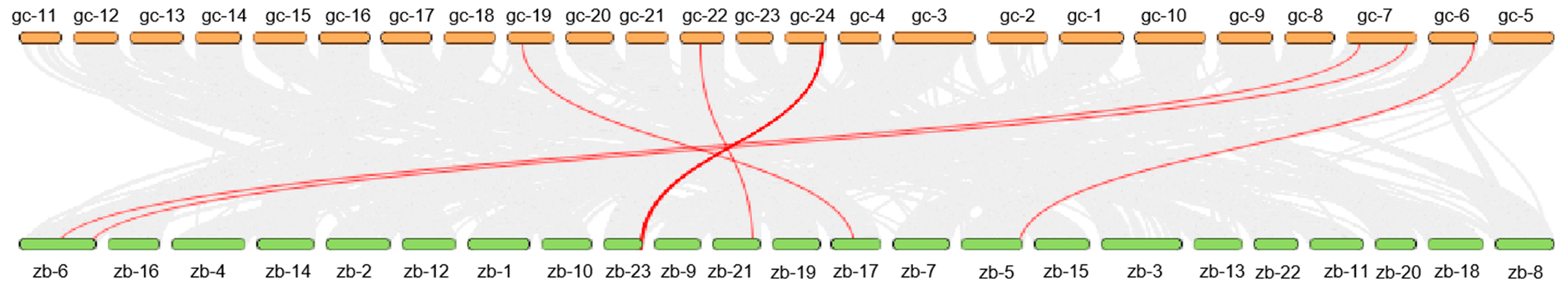
3.4. Gene Collinearity Between Grass Carp NFAT Gene Family and Zebrafish
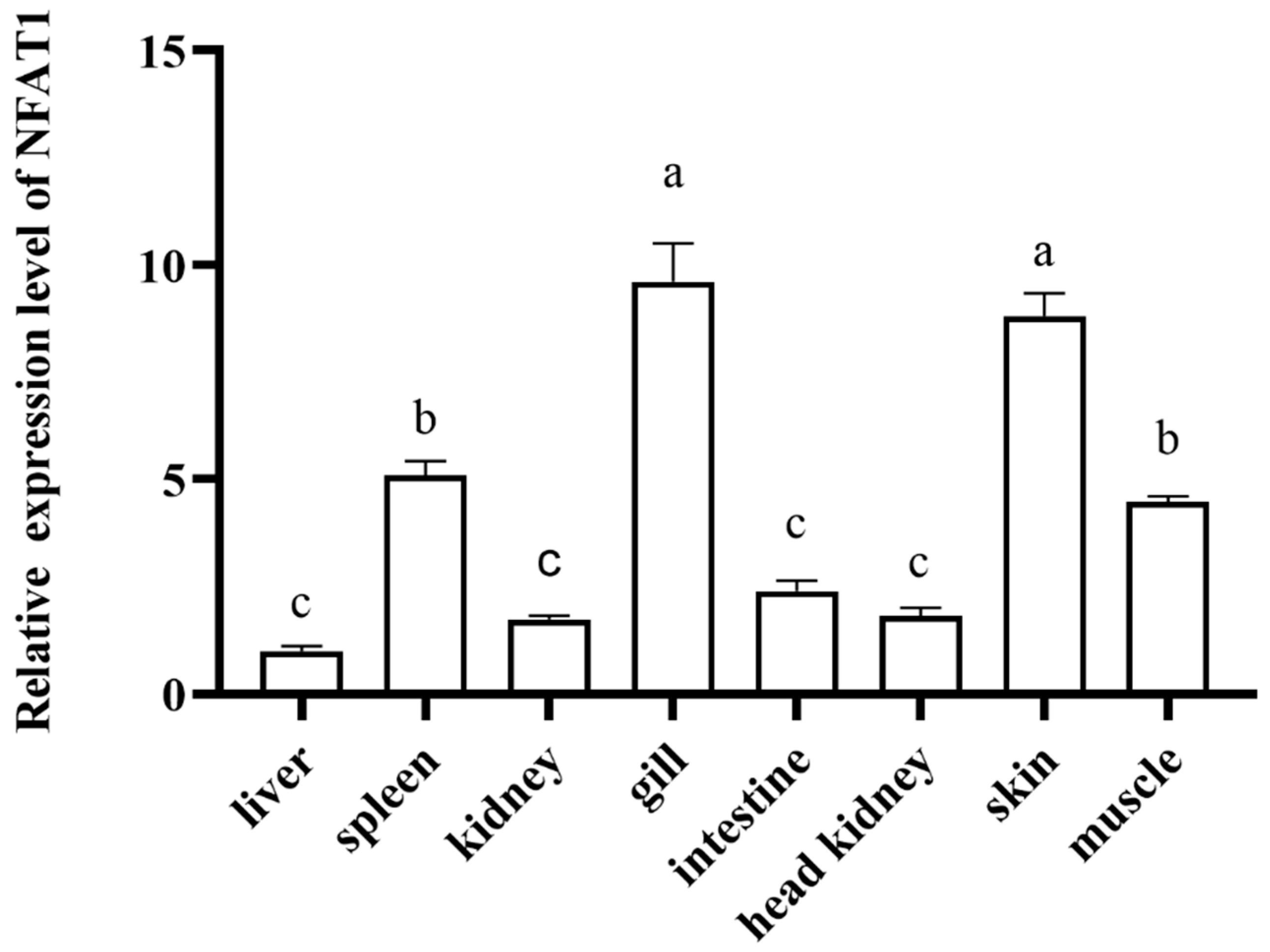
3.5. Sequence and Characteristics Analysis of CiNFAT1
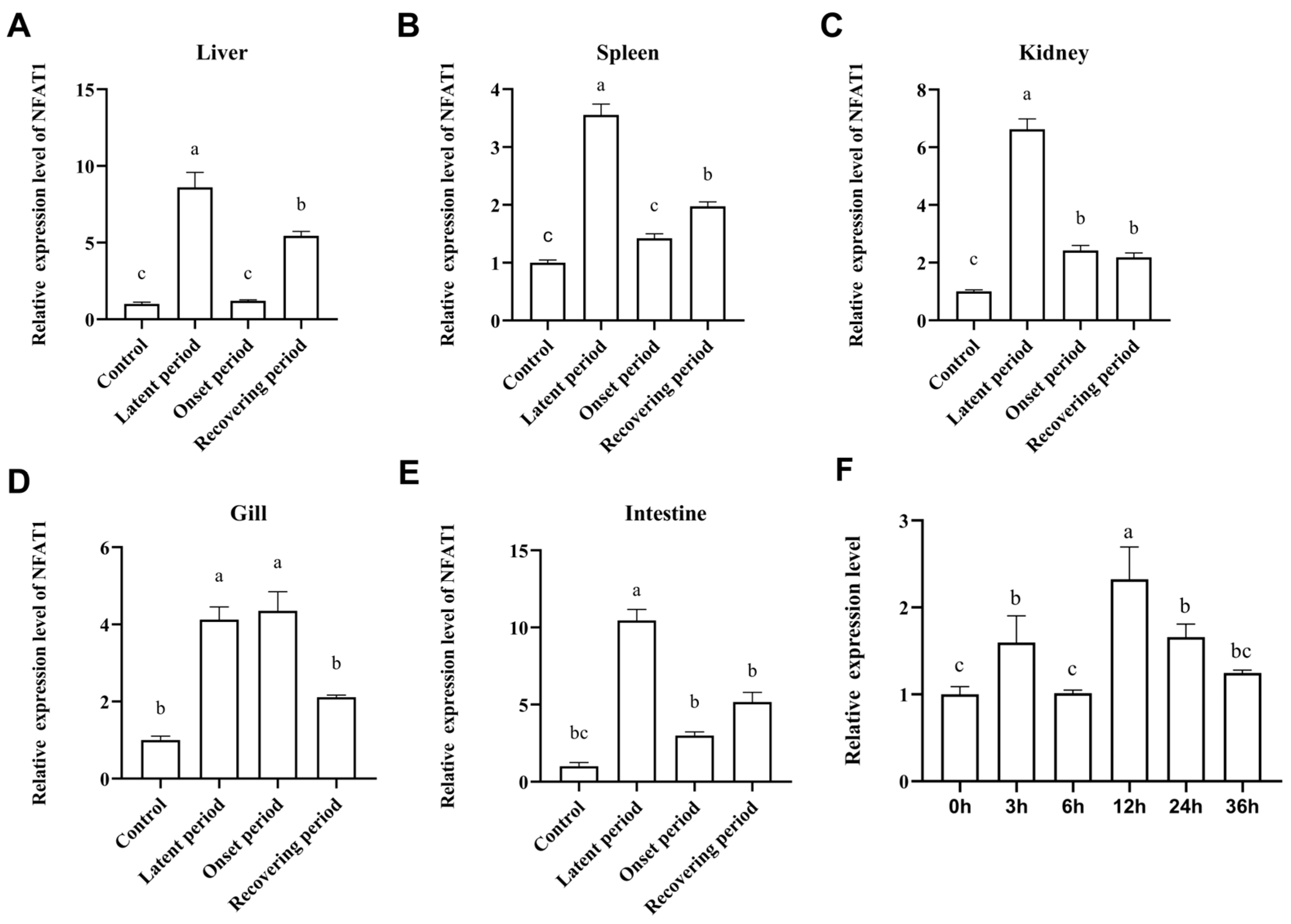
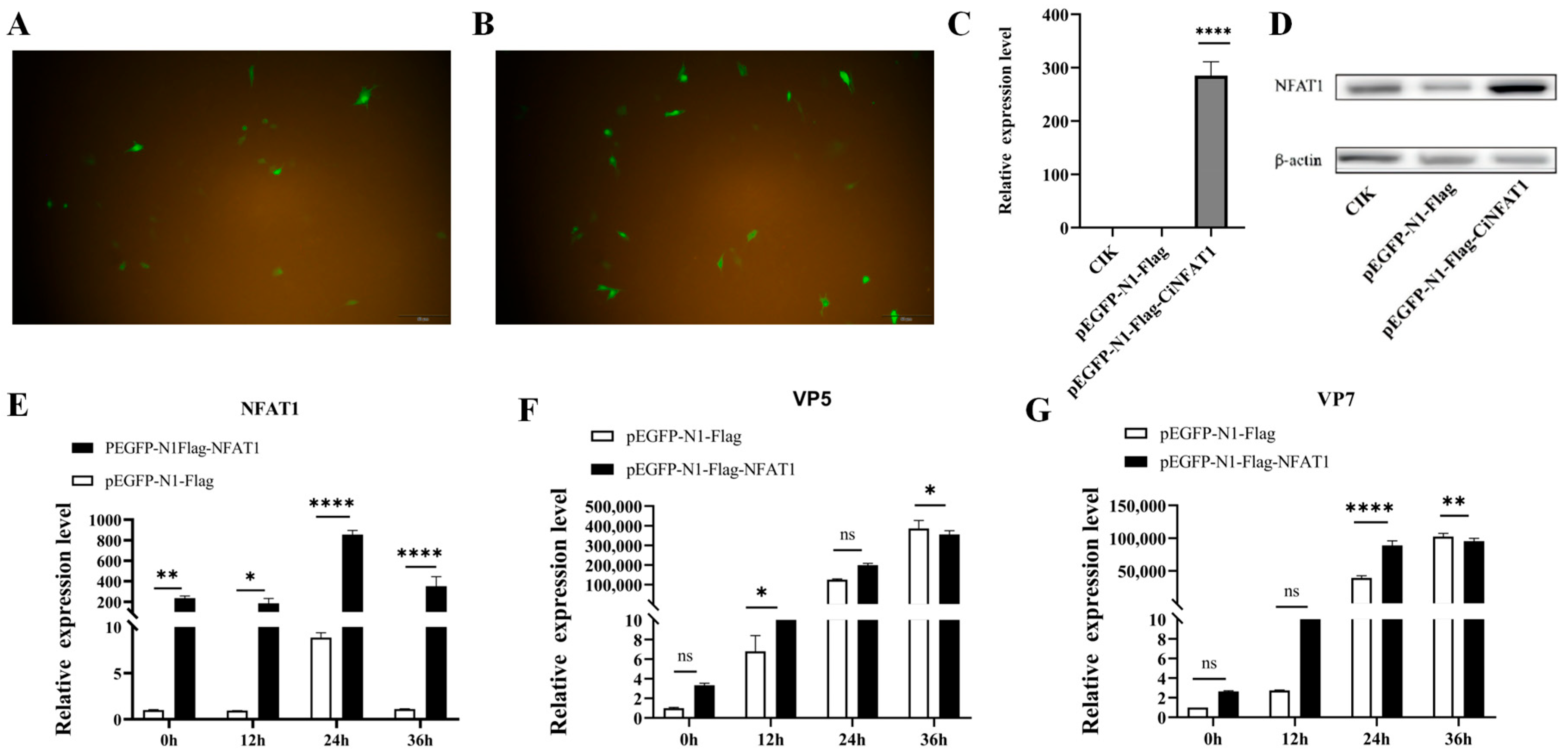
3.6. The mRNA Expression Levels of CiNFAT1 In Vivo and In Vitro After GCRV Infection
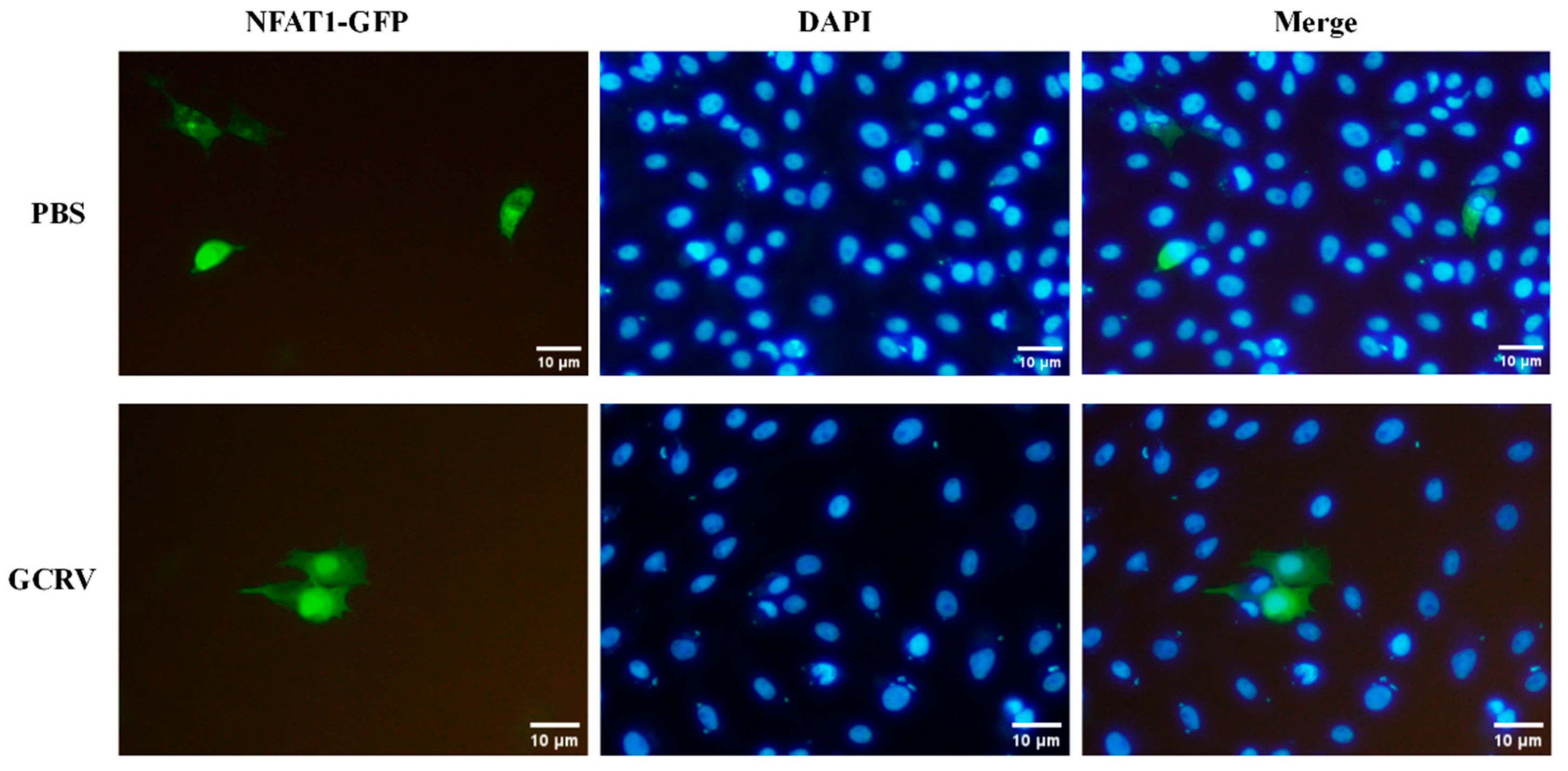
3.7. GCRV Infection Induces CiNFAT1 Transfer from Cytoplasm to Nucleus in CIK Cells
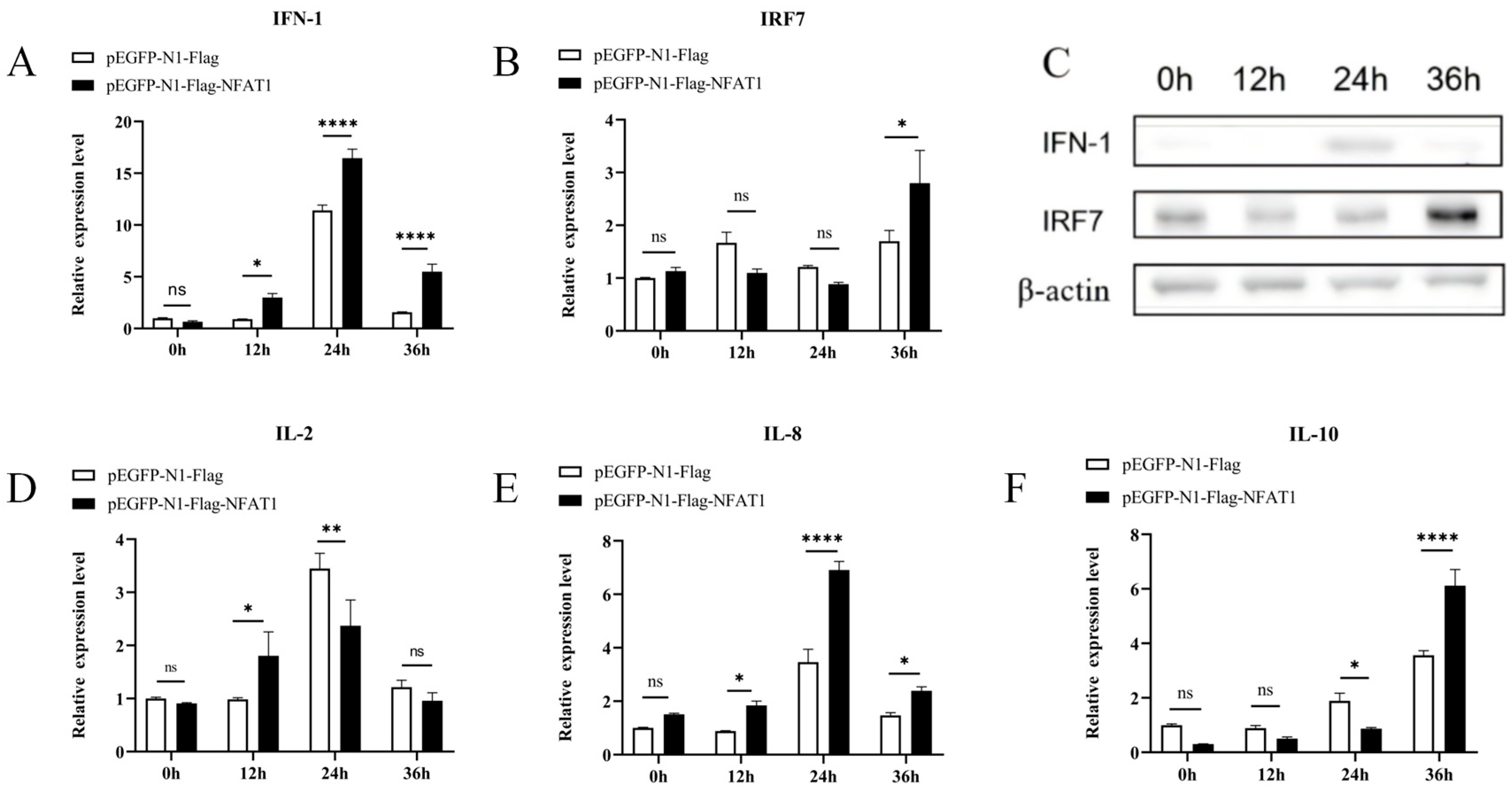
3.8. NFAT1 Regulates Interferon and Inflammatory Cytokines Levels Following GCRV Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China Fisheries Statistics Yearbook; Bureau of Fisheries and Fishery Administration; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2024; Volume 25.
- Zhu, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Deng, H.; Bai, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, X. Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) SIRT3 enhances MAVS-mediated antiviral innate immunity in response to GCRV infection. Aquaculture 2024, 587, 740871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yin, J.; Zhou, W.; Gao, T.; Li, Y.; Bergmann, S.M.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. An iTRAQ-based comparative proteomic analysis of grass carp infected with virulent and avirulent isolates of grass carp reovirus genotype II. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lv, Z.; Li, B.; Ying, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiao, T.; Xion, S. Characterization of multi-copy C3 genes and association analysis of C3.1 polymorphism with GCRV resistance traits in Ctenopharyngodon idella. Aquaculture 2024, 583, 740567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Wan, Q.; Shang, X.; Su, J. Large-scale SNP screenings identify markers linked with GCRV resistant traits through transcriptomes of individuals and cell lines in Ctenopharyngodon Idella. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.P.; Utz, P.J.; Durand, D.B.; Toole, J.J.; Emmel, E.A.; Crabtree, G.R. Identification of a putative regulator of early T cell activation genes. Science 1988, 241, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefjes, M.; Van Caam, A.P.M.; Van der Kraan, P.M. Transcription Factors in Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis. Biology 2020, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, J.; Jing, J.; Xie, J.; You, L.; Jing, Z.; Yao, J.; Han, W.; Pan, H. Nuclear factor of activated T cells in cancer development and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2015, 361, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mognol, G.P.; Carneiro, F.R.G.; Robbs, B.K.; Faget, D.V.; Viola, J.P.D.B. Cell cycle and apoptosis regulation by NFAT transcription factors: New roles for an old player. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Tong, J.; Hao, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, K.; Xu, H.; Wang, A. Bile acid coordinates microbiota homeostasis and systemic immunometabolism in cardiometabolic diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2129–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Nag, S.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. NFAT as cancer target: Mission possible? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1846, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Burgeon, E.; Carew, J.A.; McCaffrey, P.G.; Badalian, T.M.; Lane, W.S.; Hogan, P.G.; Rao, A. Recombinant NFAT1 (NFATp) is regulated by calcineurin in T cells and mediates transcription of several cytokine genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 1, 3955–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Aramburu, J.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Viola, J.P.; Raghavan, A.; Tahiliani, M.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Hogan, P.G.; Rao, A. Concerted dephosphorylation of the transcription factor NFAT1 induces a conformational switch that regulates transcriptional activity. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trama, J.; Go, W.Y.; Ho, S.N. The osmoprotective function of the NFAT5 transcription factor in T cell development and activation. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5477–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.R.; Rao, A. NFAT, immunity and cancer: A transcription factor comes of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macian, F. NFAT proteins: Key regulators of T-cell development and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.D.; Wei, G.; Zhang, H.; He, M.X. Nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) in pearl oyster Pinctada fucata: Molecular cloning and functional characterization. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Liu, W.; Tang, X.; Sheng, X.; Chi, H.; Zhan, W. The Expression of CD28 and Its Synergism on the Immune Response of Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) to Thymus-Dependent Antigen. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 765036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Lv, M.; Liu, A.; Pang, Y.; Li, Q.; Su, P.; Gou, M. Identification and evolution of transcription factors RHR gene family (NFAT and RBPJ) involving lamprey (Lethenteron reissneri) innate immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 138, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Xiong, L.; Xiao, T.; Liu, Q. Identification of the C1qDC gene family in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and the response of C1qA, C1qB, and C1qC to GCRV infection in vivo and in vitro. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 148, 109477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Ma, Z.Y.; Zheng, G.D.; Zou, S.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, Y.A. Chromosome-level genome assembly of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) provides insights into its genome evolution. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Yamashita, R.A.; Marchler-Bauer, A. NCBI’s Conserved Domain Database and Tools for Protein Domain Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chu, P.; Huang, R.; Chen, K.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Ou, M. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1 in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and Its Expression Profile following Grass Carp Reovirus Challenge. Fishes 2024, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzi, H.; Rajabpour, A.; Roldan, E.; Hassanali, A. Learning the Hydrophobic, Hydrophilic, and Aromatic Character of Amino Acids from Thermal Relaxation and Interfacial Thermal Conductance. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Auger-Messier, M.; Molkentin, J.D. Interaction between NFκB and NFAT coordinates cardiac hypertrophy and pathological remodeling. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakur Ahammad, A.K.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Ceyhun, S.B.; Ceylan, H.; Asakawa, S.; Watabe, S.; Kinoshita, S. Multiple transcription factors mediating the expressional regulation of myosin heavy chain gene involved in the indeterminate muscle growth of fish. Gene 2019, 687, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; English, S.G.; Storey, K.B. Regulation of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and downstream myogenic proteins during dehydration in the African clawed frog. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, J.C.; Kalaitzidis, D.; Gilmore, T.D.; Finnerty, J.R. Rel homology domain-containing transcription factors in the cnidarian Nematostella vectensis. Dev. Genes Evol. 2007, 217, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Kim, D.; Kim, W. Role of NFAT5 in the Immune System and Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Van de Peer, Y. From 2R to 3R: Evidence for a fish-specific genome duplication (FSGD). Bioessays 2005, 27, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegg, S.; Meyer, A. Hox clusters as models for vertebrate genome evolution. Trends Genet. 2005, 21, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothova, J.; Blaauw, B.; Pallafacchina, G.; Rudolf, R.; Argentini, C.; Reggiani, C.; Schiaffino, S. NFATc1 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling is controlled by nerve activity in skeletal muscle. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminuma, O.; Kitamura, N.; Nishito, Y.; Nemoto, S.; Tatsumi, H.; Mori, A.; Hiroi, T. Downregulation of NFAT3 Due to Lack of T-Box Transcription Factor TBX5 Is Crucial for Cytokine Expression in T Cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zeng, W.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Mo, X.; Shi, C.; Bergmann, S.M.; Wang, Q. Comparative transcriptional analysis between virulent isolate HN1307 and avirulent isolate GD1108 of grass carp reovirus genotype II. Immunology 2023, 147, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthoudakis, S.; Viola, J.P.; Shaw, K.T.; Luo, C.; Wallace, J.D.; Bozza, P.T.; Luk, D.C.; Curran, T.; Rao, A. An enhanced immune response in mice lacking the transcription factor NFAT1. Science 1996, 272, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, M.R.; Ranger, A.M.; Charles De La Brousse, F.; Hoey, T.; Grusby, M.J.; Glimcher, L.H. Hyperproliferation and dysregulation of IL-4 expression in NF-ATp-deficient mice. Immunity 1996, 4, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.K.; Carrossini, N.; Secca, C.; Kroll, J.E.; DaCunha, D.C.; Faget, D.V.; Carvalho, L.D.S.; Viola, J.P. NFAT1 transcription factor regulates cell cycle progression and cyclin E expression in B lymphocytes. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 2346–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, P.; Mirams, G.R.; Christian, H.C.; Parekh, A.B. Control of NFAT Isoform Activation and NFAT-Dependent Gene Expression through Two Coincident and Spatially Segregated Intracellular Ca2+ Signals. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Yoo, S.A.; Kim, M.; Kim, W.U. The Role of Calcium-Calcineurin-NFAT Signaling Pathway in Health and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, A.C.; Clark, P.A.; Ferreira, A.C.; Heycock, M.; Griffiths, E.L.; Jou, E.; Mannion, J.; Luan, S.L. Mef2d potentiates type-2 immune responses and allergic lung inflammation. Science 2024, 384, l370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, G.L.; Volpert, O.V.; Iniguez, M.A.; Lorenzo, E.; Martinez-Martinez, S.; Grau, R.; Fresno, M.; Redondo, J.M. Selective inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis by cyclosporin A: Roles of the nuclear factor of activated T cells and cyclooxygenase 2. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Keller, A.; Martinez, G.J. NFAT1 and NFAT2 differentially regulate CTL differentiation upon acute viral infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Rao, A.; Harrison, S.C. Signal integration by transcription-factor assemblies: Interactions of NF-AT1 and AP-1 on the IL-2 promoter. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1999, 64, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, D.J.; Naya, I.; Bundick, R.V.; Smith, G.M.; Schmidt, J.A. Comparison of the effects of FK-506, cyclosporin A and rapamycin on IL-2 production. Immunology 1991, 73, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Ladd, A.V.; Biswal, M.R.; Valapala, M. Role of Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells (NFAT) Pathway in Regulating Autophagy and Inflammation in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Jang, S.; Fanzo, J.C.; Pernis, A.B. Modulation of T cell cytokine production by interferon regulatory factor-4. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49238–49246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, E.L.; Skerka, C.; Zipfel, P.F. The early growth response protein (EGR-1) regulates interleukin-2 transcription by synergistic interaction with the nuclear factor of activated T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26923–26930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, E.L.; Nehmann, N.; Kampen, E.; Kampen, E.; Eibel, H.; Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C. Early growth response proteins (EGR) and nuclear factors of activated T cells (NFAT) form heterodimers and regulate proinflammatory cytokine gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M. Therapeutic potential of RNA interference. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1772–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Fang, F.; Zeng, X.; Medler, T.R.; Fiorillo, A.A.; Clevenger, C.V. Negative cross talk between NFAT1 and Stat5 signaling in breast cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Hu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, T.; Xu, B.; Liu, Q. Characterization of the NFAT Gene Family in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and Functional Analysis of NFAT1 During GCRV Infection. Fishes 2025, 10, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090422
Shen Y, Zhang Y, Chen C, Hu S, Liu J, Zhang Y, Xiao T, Xu B, Liu Q. Characterization of the NFAT Gene Family in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and Functional Analysis of NFAT1 During GCRV Infection. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090422
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yao, Yitong Zhang, Chen Chen, Shitao Hu, Jia Liu, Yiling Zhang, Tiaoyi Xiao, Baohong Xu, and Qiaolin Liu. 2025. "Characterization of the NFAT Gene Family in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and Functional Analysis of NFAT1 During GCRV Infection" Fishes 10, no. 9: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090422
APA StyleShen, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, C., Hu, S., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Xiao, T., Xu, B., & Liu, Q. (2025). Characterization of the NFAT Gene Family in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and Functional Analysis of NFAT1 During GCRV Infection. Fishes, 10(9), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090422




