Comparison of Behavioral Traits and Invasion Success Between Two Global Freshwater Fish Invaders—Gambusia holbrooki and Gambusia affinis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
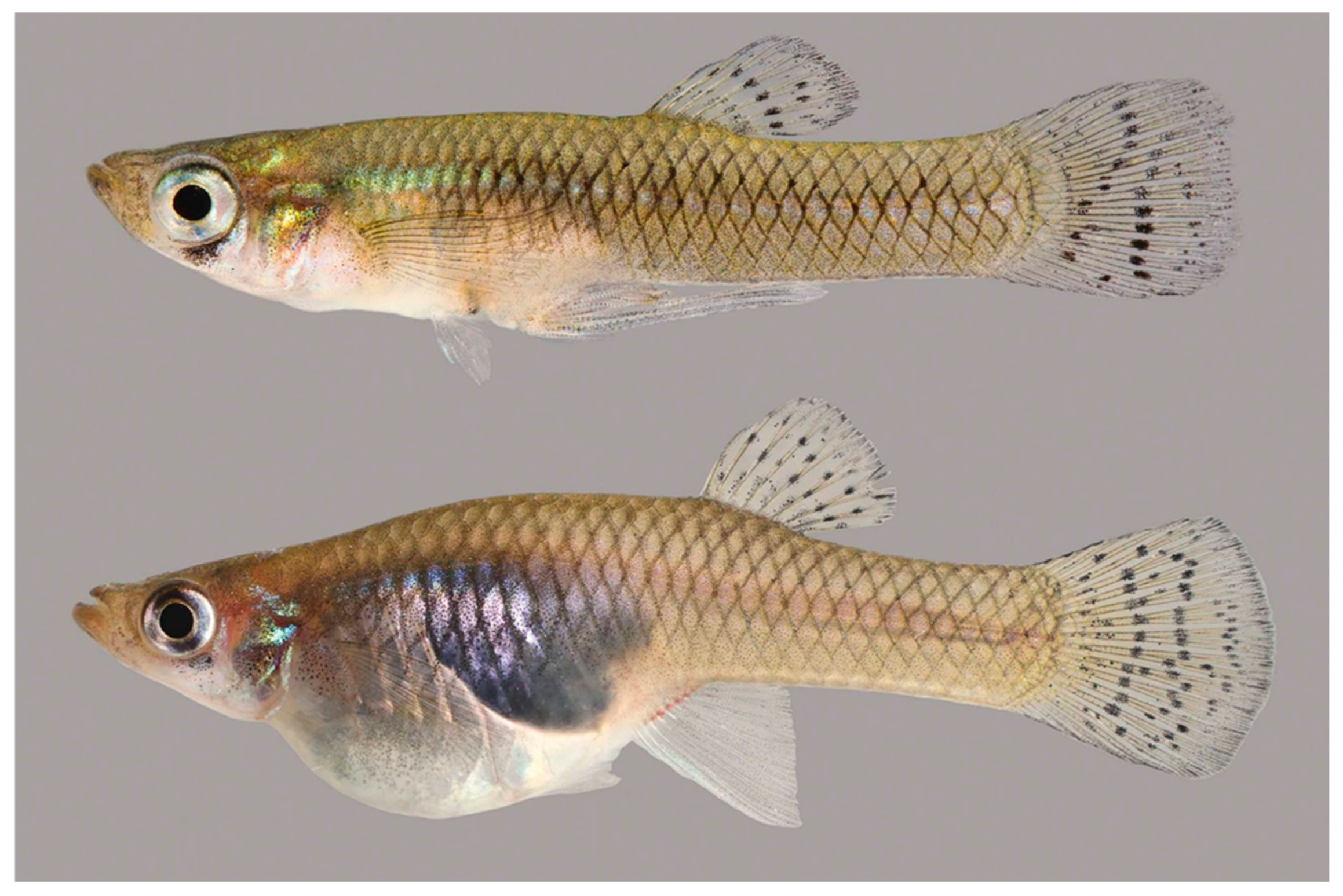
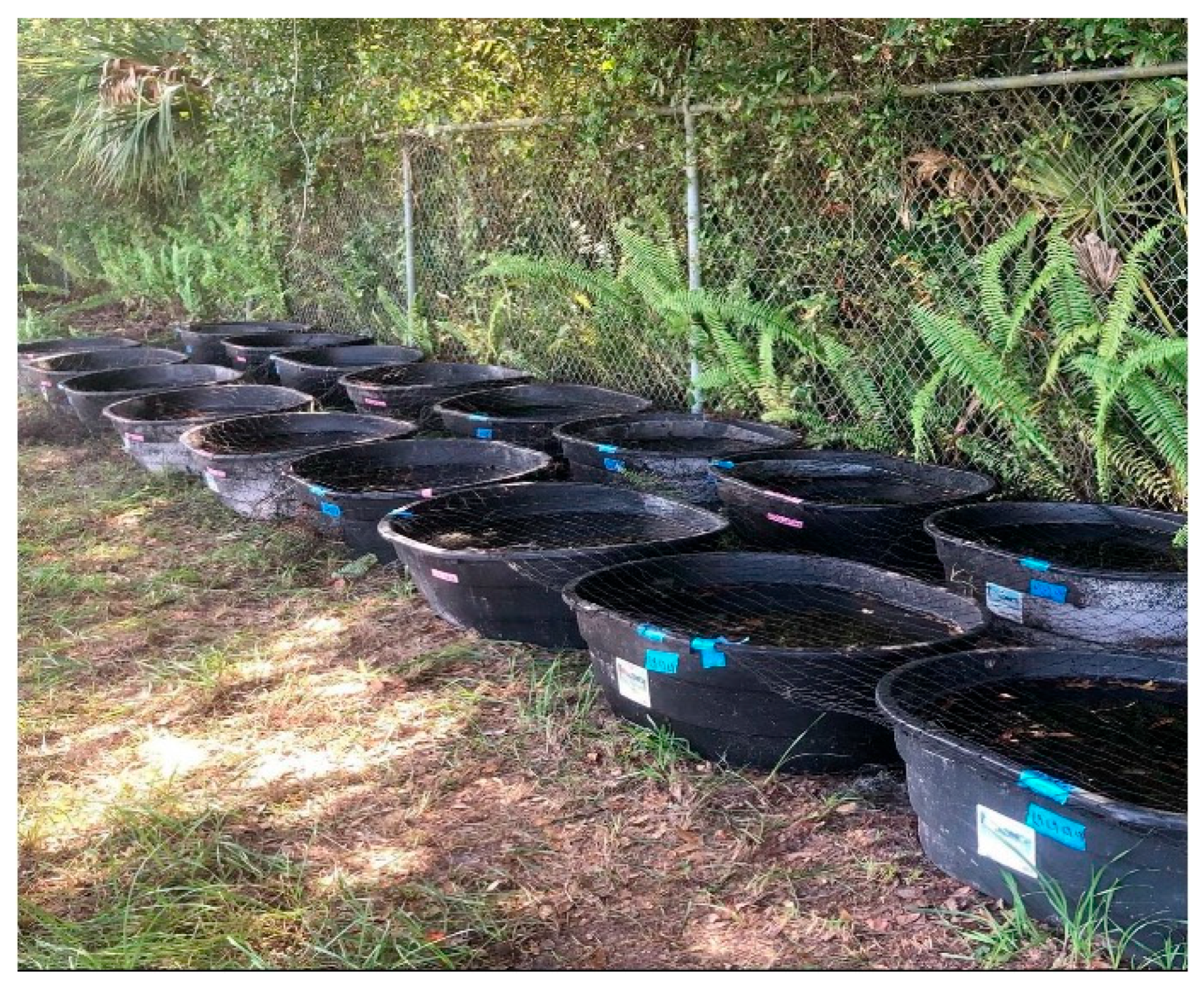
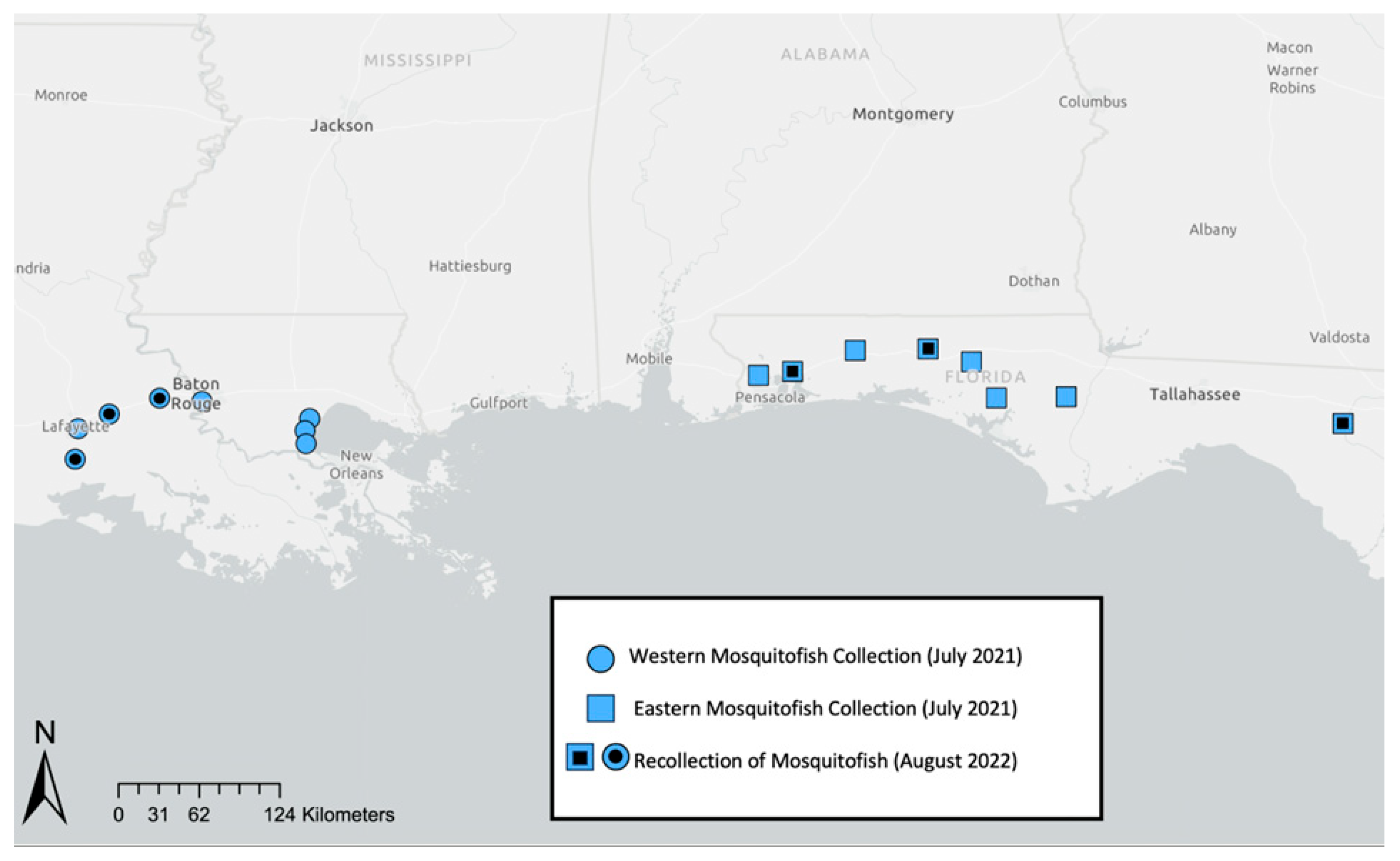
2.1. Fish Collection, Maintenance, and Experimental Design
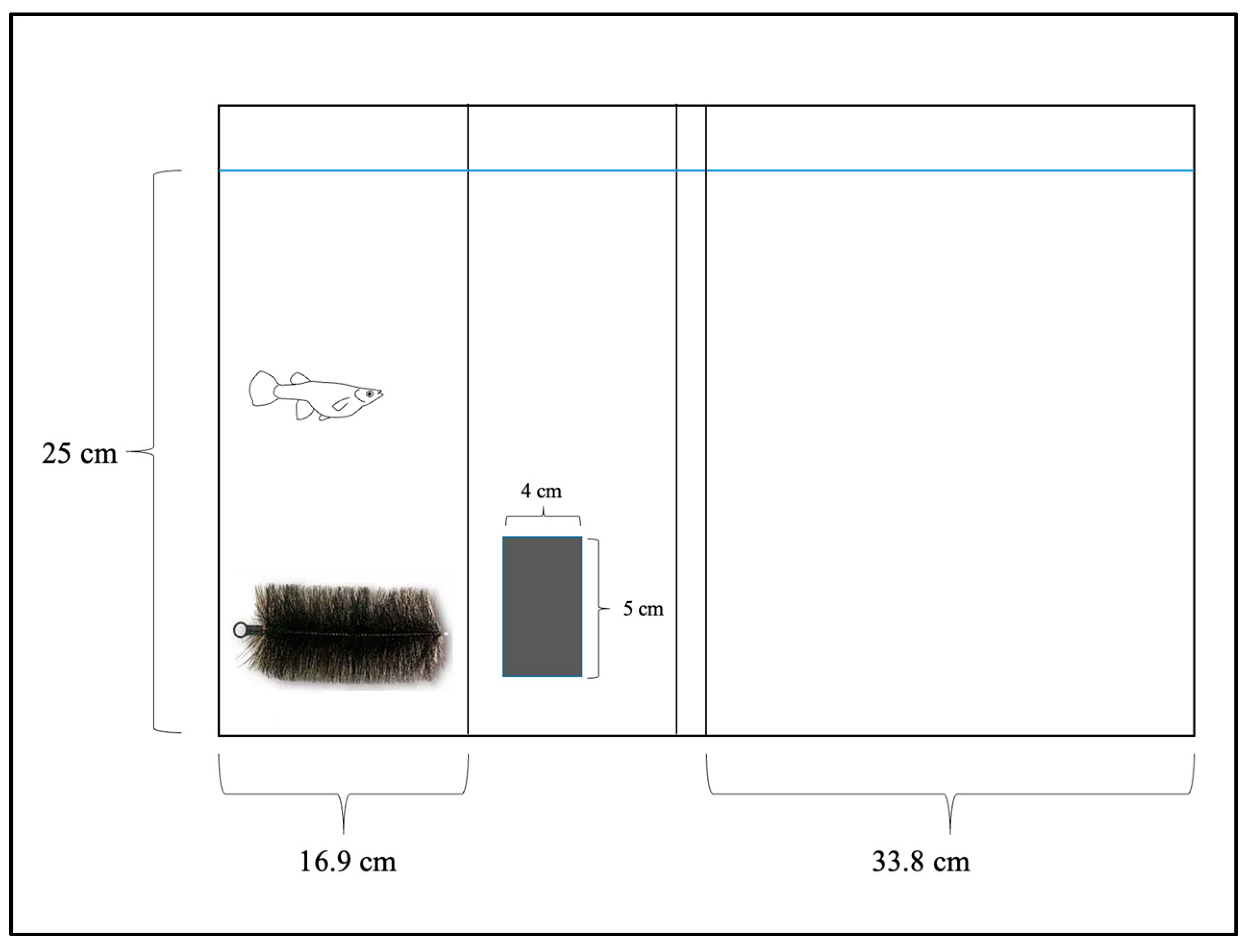
2.2. Aggression Trials
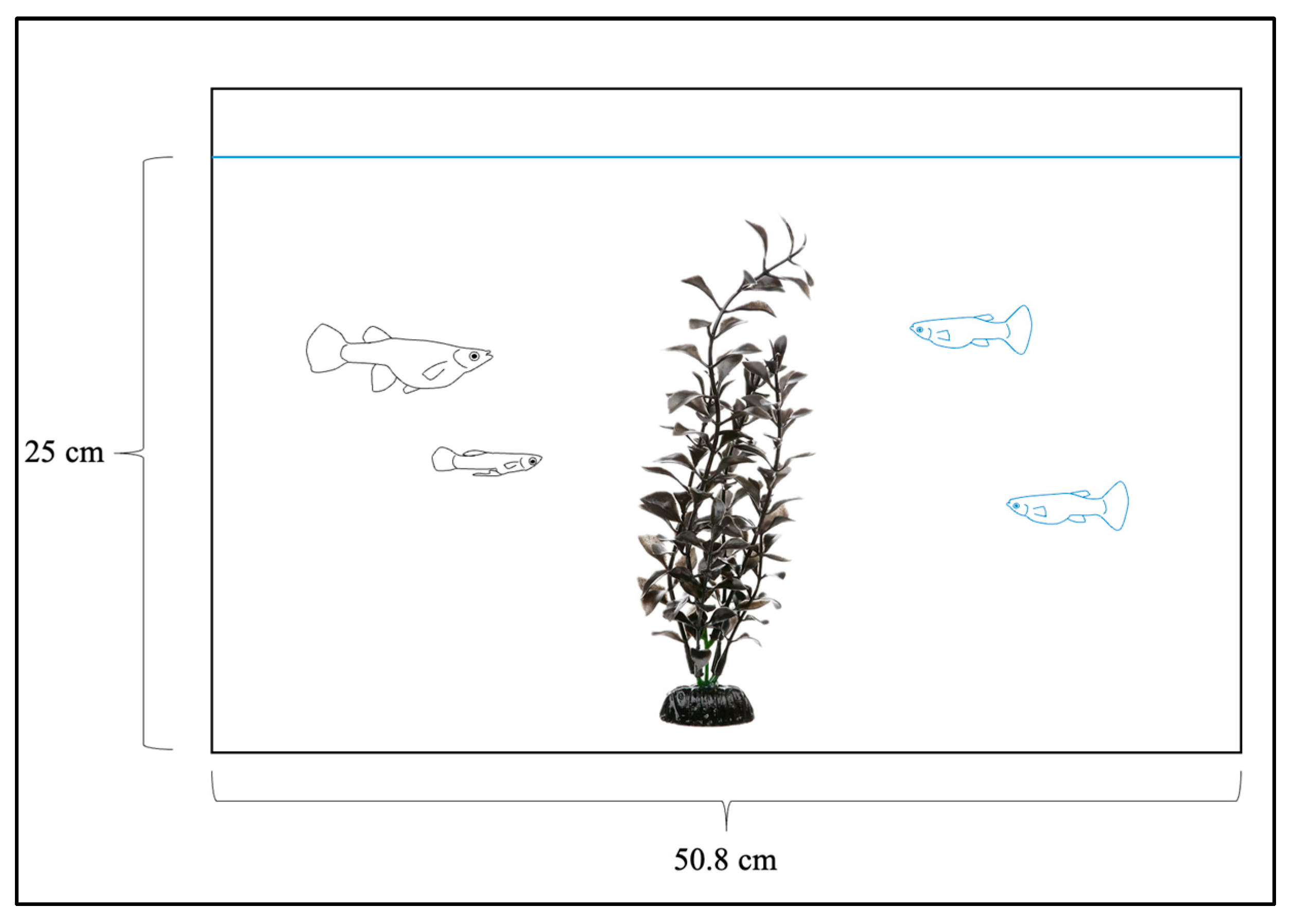
2.3. Boldness Trials
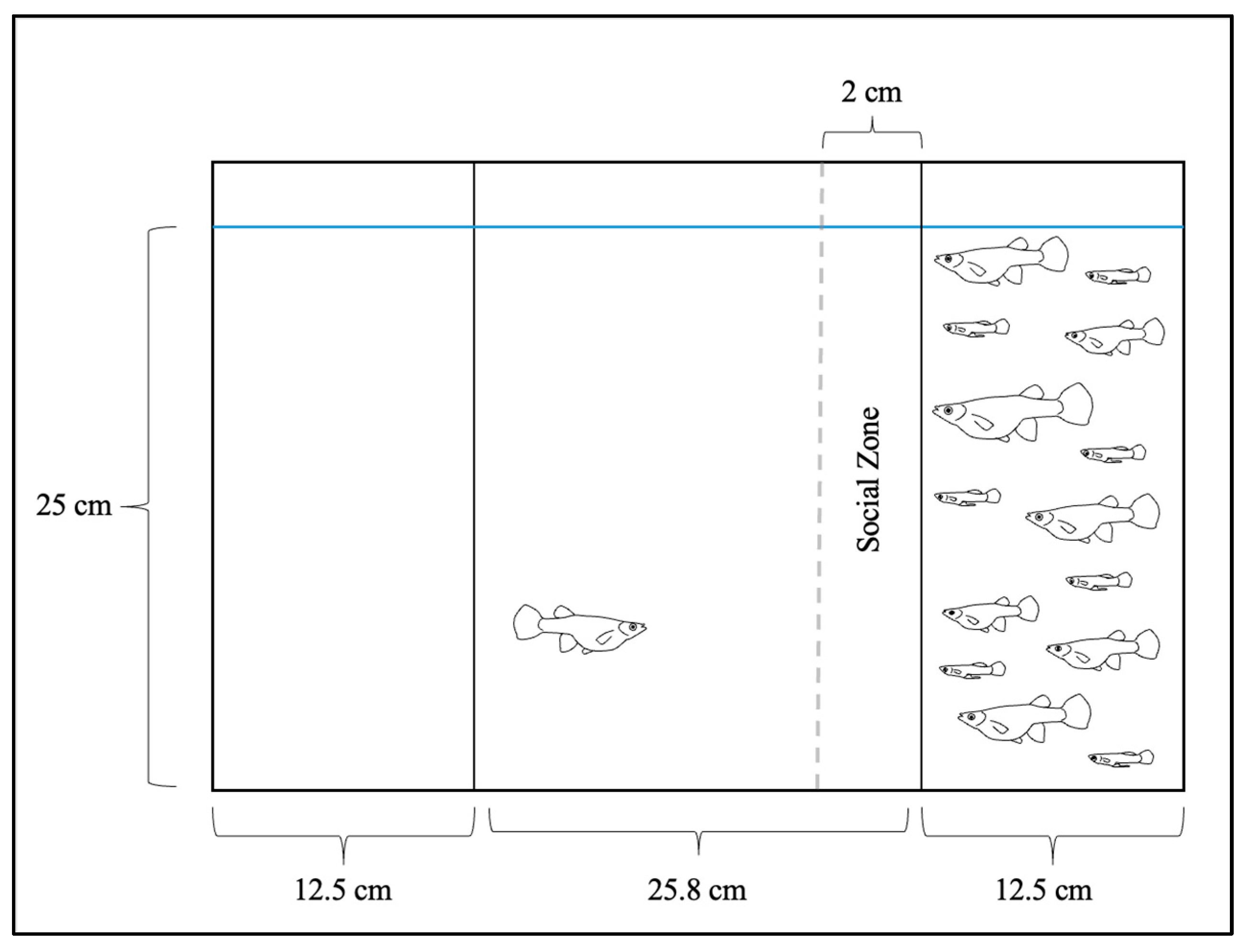
2.4. Sociability Trials
2.5. Mesocosms
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
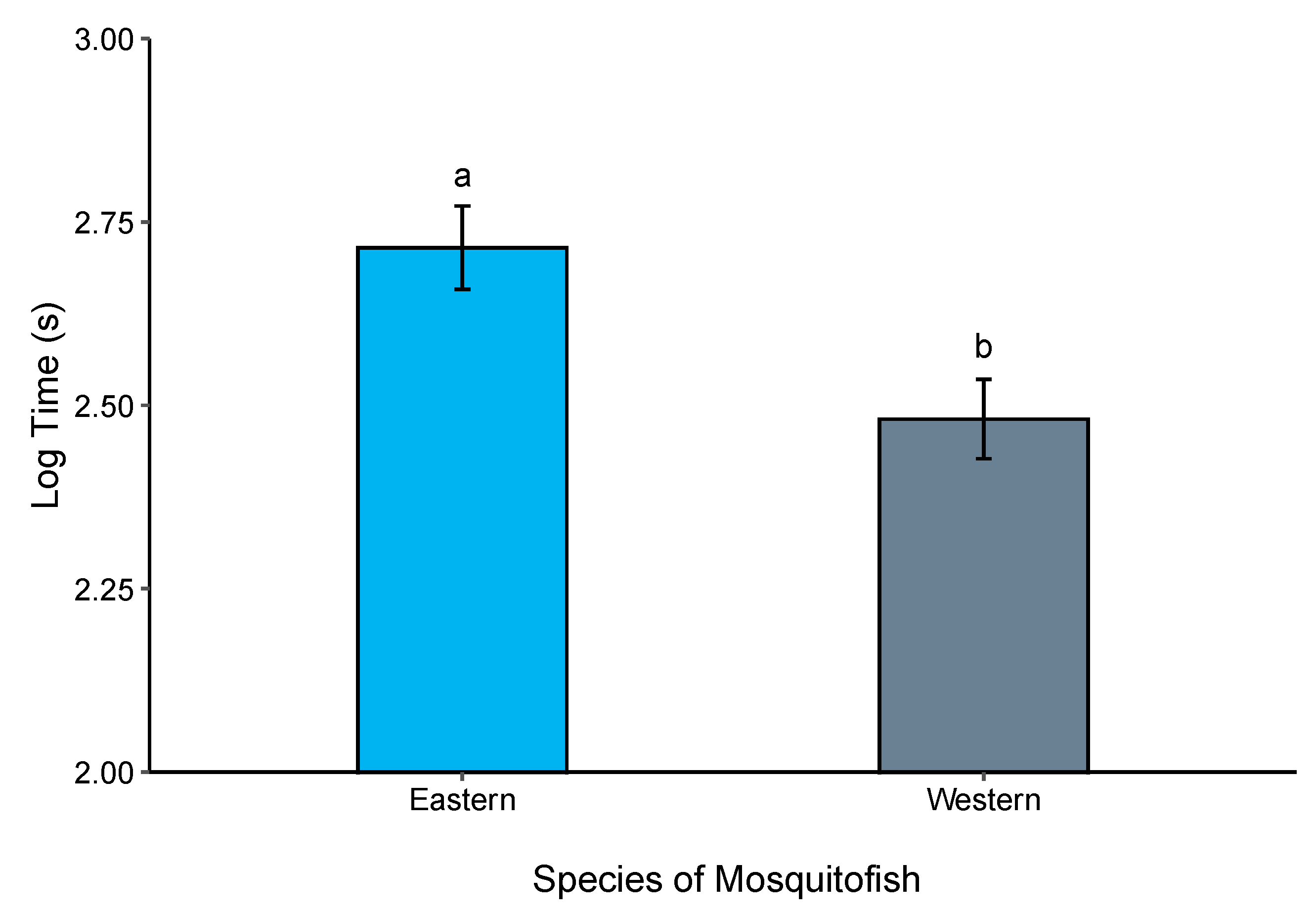
3.1. Aggression Trials
3.2. Boldness Trials
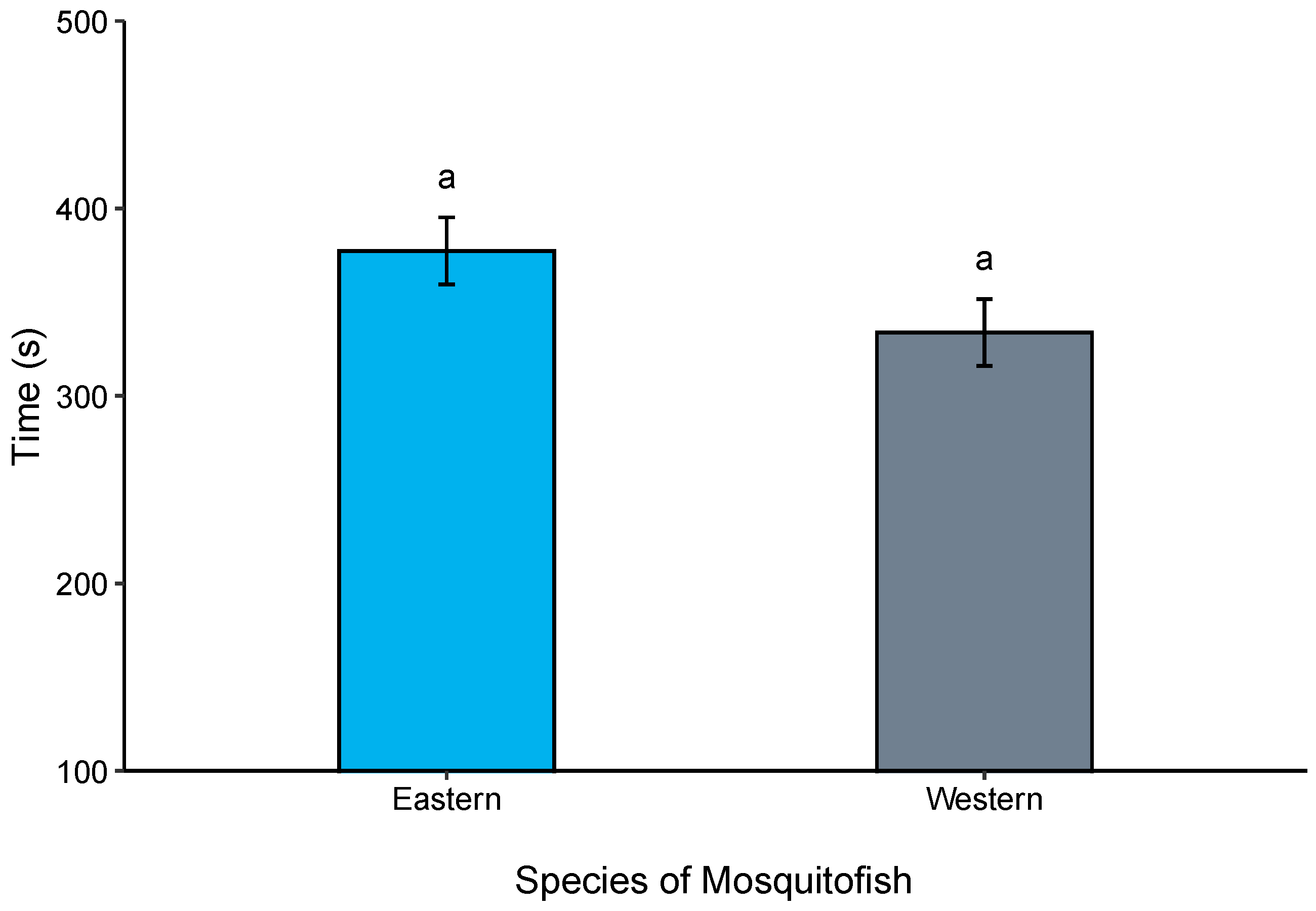
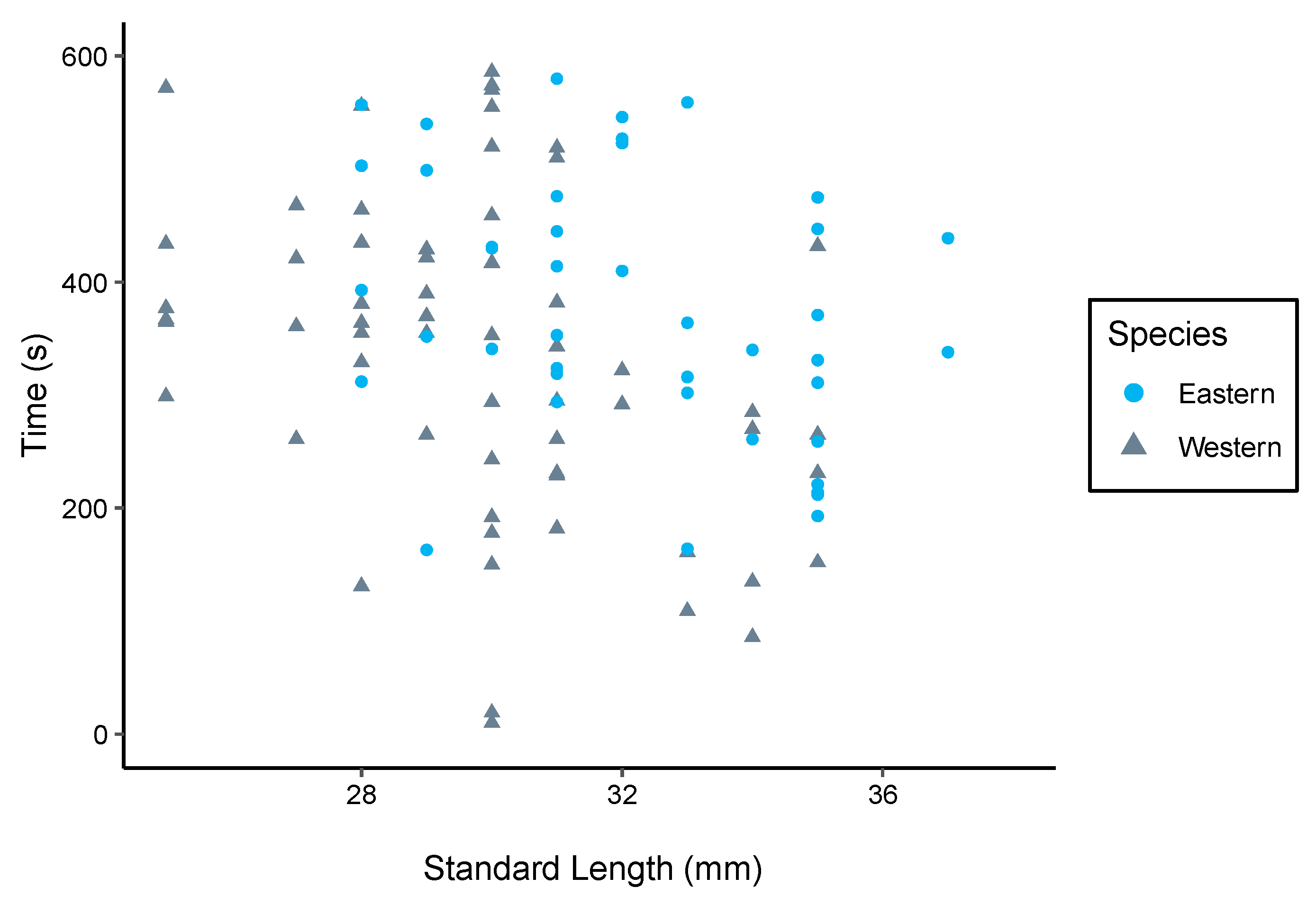
3.3. Sociability Trials
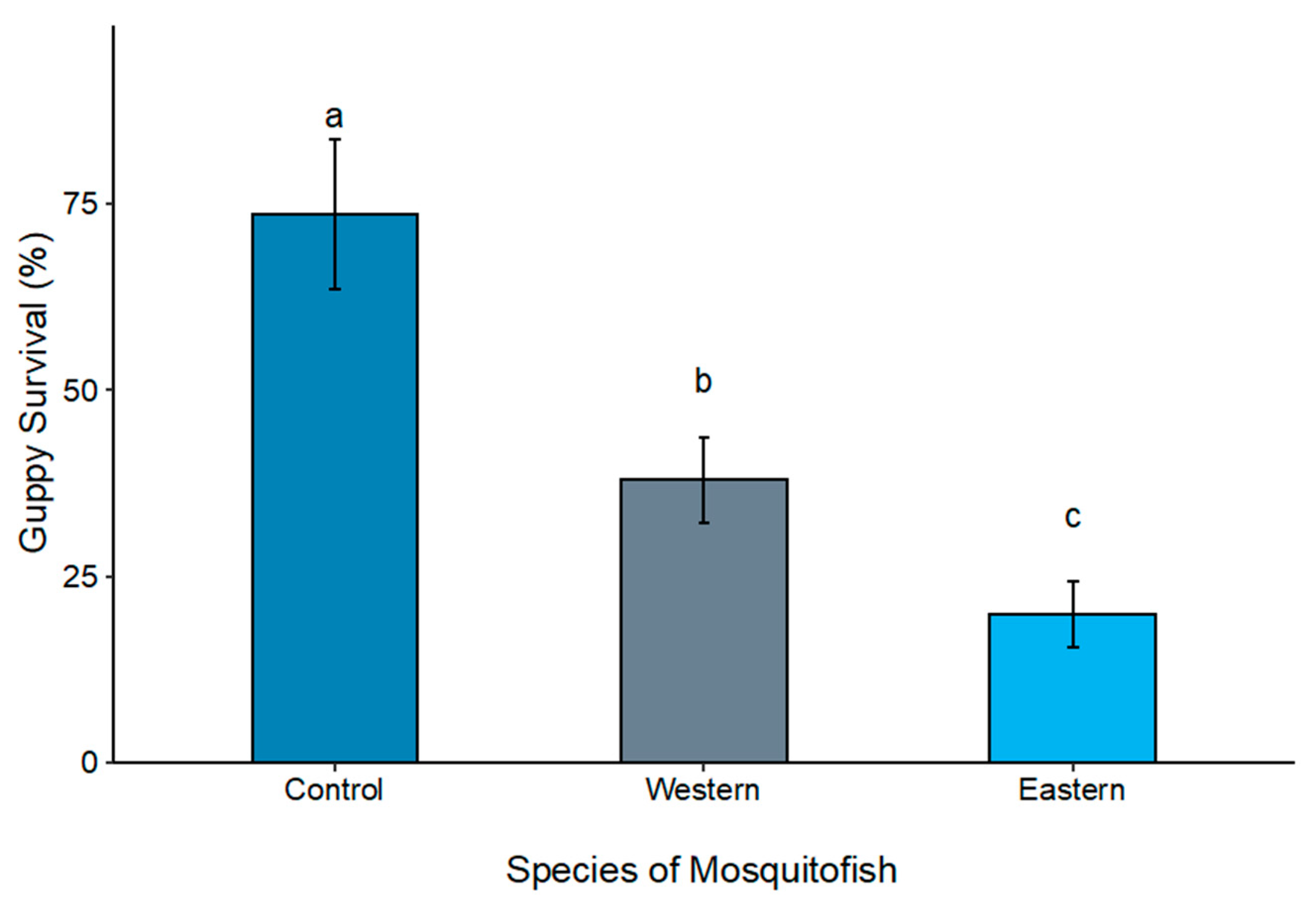
3.4. Mesocosms
4. Discussion
4.1. Aggression, Boldness, and Sociability
4.2. Invasion Success
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gentili, R.; Schaffner, U.; Martinoli, A.; Citteri, S. Invasive alien species and biodiversity: Impacts and management. Biodiversity 2021, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbelin, A.J.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Essl, F.; Haubrock, P.F.; Ricciardi, A.; Courchamp, F. Biological invasions are as costly as natural hazards. Perspect. Ecol. Cons. 2023, 21, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, D.G.; Simmonds, S.M.; Wong, B.B.M. Can behavioral and personality traits influence the success of unintentional species introductions? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juette, T.; Cucherousset, J.; Clobert, J. Animal personality and the ecological impacts of freshwater non-native species. Curr. Zool. 2014, 60, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, O.T.; O’Connell, M.J.; Schofield, P.J. Aggressive interactions between the invasive Rio Grande cichlid (Herichthys cyanoguttatus) and native bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus), with notes on redspotted sunfish (Lepomis miniatus). J. Ethol. 2011, 29, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, M.; Sopinka, N.; Marentette, J.R.; Reddon, A.R.; Brownscombe, J.W.; Fox, M.D.; Marsh-Rollo, S.E.; Balshine, S. Is there a role for aggression in round goby invasion fronts? Behaviour 2012, 149, 685–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenden, T.; Rooke, A.C.; Fox, M.G. Boldness and dispersal tendency of native and invasive Pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus): Is spatial sorting creating superior invaders? Aquat. Invasions 2017, 12, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, J.; Zięba, G.; Przybylski, M.; Smith, C. The role of intraspecific competition in the dispersal of an invasive fish. Freshwater Biol. 2019, 64, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, F. Variation in Behavior and the Success of an Invasive Species: Comparison of Sociability and Activity Between Four Populations of the Round Goby (Neogobius melanostomus) in the Baltic Sea. Bachelor’s Thesis, Department of Ecology and Environmental Science (EMG), Umeå, Sweden, 2012. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:572097/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Thorlacius, M.; Hellström, G.; Brodin, T. Behavioral dependent dispersal in the invasive round goby Neogobius melanostomus depends on population age. Curr. Zool. 2015, 61, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, G.H. A review of the biology of Gambusia affinis and G. holbrooki. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fisher 2005, 15, 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.; Willis, K.J. Impacts of mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis on black mudfish, Neochanna diversus. N. Z. J. Mar. Fresh 2005, 39, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magellan, K.; García-Berthou, E. Influences of size and sex on invasive species aggression and native species vulnerability: A case for modern regression techniques. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fisher 2015, 25, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, S.; Lear, K.O.; Allen, M.G.; Lymbery, A.J.; Tweedley, J.R.; Morgan, D.J. What factors influence fin-nipping damage by the invasive Gambusia holbrooki (Poeciliidae) on native fishes in riverine systems? Freshwater Biol. 2021, 67, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komak, S.; Crossland, M.D. An assessment of the introduced mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis holbrooki) as a predator of eggs, hatchlings and tadpoles of native and non-native anurans. Wildlife Res. 2000, 27, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karraker, N.E.; Arrigoni, J.; Dudgeon, D. Effects of increased salinity and an introduced predator on lowland amphibians in Southern China: Species identity matters. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, A.; Bruni, G.; Ricciardi, G.; Platania, L.; Mori, E.; Tricarico, E. Gambusia holbrooki, the ‘tadpolefish’: The impact of its predatory behaviour on four protected species of European amphibians. Aquat. Conserv. 2018, 28, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryxell, D.C.; Moffett, E.R.; Kinnison, M.T.; Simon, K.S.; Palkovacs, E.P. From southern swamps to cosmopolitan model: Humanity’s unfinished history with mosquitofish. Fish. Fish. 2021, 23, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database (Volume 12); Nvasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, D.; Freeman, B.J. Distribution of Gambusia (Poeciliidae) in a southeastern river system and the use of fin ray counts for species determination. Copeia 2000, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottler, V.A.; Feron, R.; Nanda, I.; Klopp, C.; Du, K.; Kneitz, S.; Helmprobst, F.; Lamatsch, D.K.; Lopez-Roques, C.; Lluch, J.; et al. Independent origin of XY and ZW sex determination mechanisms in mosquitofish sister species. Genetics 2000, 214, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, L.N.; Tomasov, J.F. Taxonomic status of the mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis (Poeciliidae), in Australia. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1985, 36, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.L.; Weinersmith, K.L.; Brodin, T.; Saltz, J.B.; Sih, A. Behavioural syndromes in fishes: A review with implications for ecology and fisheries management. J. Fish. Biol. 2011, 78, 395–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehage, J.S.; Sih, A. Dispersal behavior, boldness, and the link to invasiveness: A comparison of four Gambusia species. Biol. Invasions 2002, 6, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, H.A.; Kinnison, M.T. Predator-induced phenotypic plasticity of shape and behavior: Parallel and unique patterns across sexes and species. Curr. Zool. 2017, 63, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckett, Q.M.; Deacon, A.E.; Fraser, D.D.; Lyons, T.J.; Lawson, K.M.; Hill, J.E. Unstable intraguild predation causes establishment failure of a globally invasive species. Ecology 2021, 102, e03411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurui-Sato, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Deki, O.; Suzuki, T.; Tatsuta, H.; Tsuji, K. Reproductive interference in live-bearing fish: The male guppy is a potential biological agent for eradicating invasive mosquitofish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.; Fogarty, S.; Weinersmith, K.; Brodin, T.; Sih, A. Personality traits and dispersal tendency in the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.; Fogarty, S.; Brodin, T.; Weinersmith, K.; Sih, A. Personality-dependent dispersal in the invasive mosquitofish: Group composition matters. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culumber, Z.W. Variation in behavioral traits across a broad latitudinal gradient in a livebearing fish. Evol. Ecol. 2022, 36, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, R.J.; Horth, L. A genetically distinct hybrid zone occurs for two globally invasive mosquito fish species with striking phenotypic resemblance. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 8375–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzzante, D.E. Domestication effects on aggressive and schooling behavior in fish. Aquaculture 1994, 120, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntingford, F.A. Implications of domestication and rearing conditions for the behaviour of cultivated fishes. J. Fish. Biol. 2004, 65, 122–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, A.E.; Ramnarine, I.W.; Magurran, A.E. How reproductive ecology contributes to the spread of a globally invasive fish. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelangeli, M.; Clobert, J.; Chapple, D.J.; Sih, A.; Brodin, T.; Fogarty, S.; Bertram, M.G.; Eades, J.; Wong, B.B.M. Sex-dependent personality in two invasive species of mosquitofish. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E.; Garcia, C.M. Sex differences in behaviour as an indirect consequence of mating system. J. Fish. Biol. 2000, 57, 839–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, D.K.; Smith, J.G.; Baker, C.S. Agonistic interactions between Gambusia affinis and Galaxias maculatus: Implications for whitebait fisheries in New Zealand rivers. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2007, 23, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.E.; Kapuscinski, A.R.; Pavlowich, T. Fluorescent transgenic zebra danio more vulnerable to predators than wild-type fish. Am. Fish. Soc. 2011, 149, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.G.; Hill, J.; Nico, L.G. Eastern mosquitofish resists invasion by nonindigenous poeciliids through agonistic behaviors. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.; Godin, J.G.J.; Ward, A.J. Boldness and reproductive fitness correlates in the eastern mosquitofish, Gambusia holbrooki. Ethology 2010, 115, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Zhou, L.; Gomes-Silva, G.; Sommer-Trembo, C.; Plath, M. Personality differentially affects individual mate choice decisions in female and male western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.N.; Travis, J. The contribution of man-made ditches to the regional stream biodiversity of the new river watershed in the Florida panhandle. Hydrobiologia 2010, 661, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.; Venables, B.; Bates, D.M.; Hornik, K.; Gebhardt, A.; Firth, D.; Ripley, M.B. Package ‘mass’. Cran R 2013, 538, 822. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MASS (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Regression-based tests for overdispersion in the Poisson model. J. Econometr. 1990, 46, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.H.B. Regression Models for Ordinal Data. R Package Ordinal Version. 2022, pp. 11–16. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ordinal (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Bates, D.M.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royston, P. Remark AS R94: A Remark on Algorithm AS 181: The W-test for Normality. Appl. Stat-J. R. ST C 1995, 44, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, W.J.; Johnson, M.E.; Johnson, M.M. A comparative study of tests for homogeneity of variances, with applications to the outer continental shelf bidding data. Technometrics 1981, 23, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, G.H. Plague minnow or mosquito fish? A review of the biology and impacts of introduced Gambusia species. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, T.M.; Zeiber, R.; Fisher, B.E. Agonistic behavioral interactions between introduced western mosquitofish and native topminnows. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2012, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ward, A.J.W. Social facilitation of exploration in mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2011, 66, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E.; Oulton, W.J.; Pitcher, T.J. Vigilant behaviour and shoal size in minnows. Z. Tierpsychol. 1985, 67, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihs, D. Hydromechanics of fish schooling. Nature 1973, 241, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E.; Pitcher, T.J. Foraging, timidity and shoal size in minnows and goldfish. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1983, 12, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, D.J.; Krause, J.; Peuhkuri, N.; Godin, J.G.J. Body size and shoaling in fish. J. Fish. Biol. 2000, 57, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, S.; Clobert, J.; Sih, A. Social Personality Polymorphism and the Spread of Invasive Species: A Model. Am. Natt. 2011, 177, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, J.L.; Cashner, R.C. Life history and population dynamics of the western mosquitofish: A comparison of natural and introduced populations. J. Fish. Biol. 1995, 46, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, J.M.; Spadafore, S.; Olesen, D. Effects of predator cues on boldness and exploration of Eastern Mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) in temporary wetlands of the Everglades. Fla. Sci. 2022, 85, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Des Roches, S.; Robinson, R.R.; Kinnison, M.T.; Palkovacs, E.P. The legacy of predator threat shapes prey foraging behaviour. Oecologia 2022, 198, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft, G.; Baatrup, E.; Guillette, L.J., Jr. Altered social behavior and sexual characteristics in mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) living downstream of a paper mill. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 70, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryxell, D.C.; Wood, Z.T.; Robinson, R.; Kinnison, M.T.; Palkovacs, E.P. Eco-evolutionary feedbacks link prey adaptation to predator performance. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 20190626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culumber, Z.W. Behavioural response to simulated avian predation varies with latitude and predation intensity of natural populations. Evol. Ecol. 2020, 34, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, E.; Howe, C.J.; Lim, R.P.; Burchett, M.D. Impact of the introduced poeciliid Gambusia holbrooki (Girard, 1859) on the growth and reproduction of Pseudomugil signifer (Kner, 1865) in Australia. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1997, 48, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Brown, C.M. Behavioural interactions between the introduced plague minnow Gambusia holbrooki and the vulnerable native Australian ornate rainbowfish Rhadinocentrus ornatus, under experimental conditions. J. Fish. Biol. 2008, 73, 1714–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, S.; Haynes, T.B.; Fensham, R.; Kerezsy, A. Quantifying the impact of Gambusia holbrooki on the extinction risk of the critically endangered, red-finned blue-eye. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, L.K.; Buttemer, W.A. Predation by the non-native fish Gambusia holbrooki on small Litoria aurea and L. dentata tadpoles. Aust. Zool. 1996, 30, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klop-Toker, K.; Valdez, J.W.; Stockwell, M.P.; Fardell, L.; Clulow, S.; Clulow, J.; Mahony, M. We made your bed, why won’t you lie in it? Food availability and disease may affect reproductive output of reintroduced frogs. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, P.A.; Correas, A.M.; Morcillo, F.M.; Risueño, P.; Lobón-Cerviá, J. Interaction between the introduced eastern mosquitofish and two autochthonous Spanish toothcarps. J. Fish. Biol. 2002, 61, 1560–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiola, N.; Sostoa, A. Possible reasons for the decline of two native toothcarps in the Iberian Peninsula: Evidence of competition with the introduced eastern mosquitofish. J. App. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Guzmán, E.; Díaz-Paniagua, C.; Gomez-Mestre, I. Competitive and predatory interactions between invasive mosquitofish and native larval newts. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrier, R.F.G.; Hicks, B.J. Behavioral interactions between black mudfish (Neochanna diversus Stokell, 1949: Galaxiidae) and mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis Baird & Girard, 1854). Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 1994, 3, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Wei, L.; Ding, G. Effects of predation by invasive western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) on survival of eggs, embryos and tadpoles of Pelophylax nigromaculatus and Duttaphrynus melanostictus in South China. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2016, 7, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, N. Gambusia in New Zealand: Really bad or just misunderstood? N. Z. J. Mar. Fresh 2004, 38, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walsh, E.S.; Hill, J.E.; Tuckett, Q.M. Comparison of Behavioral Traits and Invasion Success Between Two Global Freshwater Fish Invaders—Gambusia holbrooki and Gambusia affinis. Fishes 2025, 10, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080421
Walsh ES, Hill JE, Tuckett QM. Comparison of Behavioral Traits and Invasion Success Between Two Global Freshwater Fish Invaders—Gambusia holbrooki and Gambusia affinis. Fishes. 2025; 10(8):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080421
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalsh, Elizabeth S., Jeffrey E. Hill, and Quenton M. Tuckett. 2025. "Comparison of Behavioral Traits and Invasion Success Between Two Global Freshwater Fish Invaders—Gambusia holbrooki and Gambusia affinis" Fishes 10, no. 8: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080421
APA StyleWalsh, E. S., Hill, J. E., & Tuckett, Q. M. (2025). Comparison of Behavioral Traits and Invasion Success Between Two Global Freshwater Fish Invaders—Gambusia holbrooki and Gambusia affinis. Fishes, 10(8), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080421






