Abstract
Tetramethyl bisphenol A (TMBPA), a novel alternative to Bisphenol A, is widely used as an industrial flame retardant and a raw material for tetramethyl polycarbonate plastics. With the increasing use of TMBPA, its aquatic ecological risks remain unclear. Therefore, this study investigated the developmental toxicity of TMBPA using zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model, exposing embryos to 0.5, 5, 50, and 200 μg/L TMBPA for 120 h. The results showed that treatment with 5, 50, and 200 μg/L TMBPA decreased the hatching rate of zebrafish embryos at 48 h post-fertilization (hpf), while no significant difference was observed at 72 hpf. Meanwhile, TMBPA exposure at all concentrations showed no significant effect on the survival rate. Furthermore, a high concentration of TMBPA (200 μg/L) significantly reduced the total length and suppressed swimming ability in zebrafish larvae. In addition, gene expression analysis revealed impacts on antioxidant system (cat, gpx, mn-sod, keap1, ucp2, nrf2), hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid (HPT) axis (ttr, ugt1ab, trβ), cardiac developmental (tbx2b, myl7, bmp4, notch1b, amhc), and the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis (pomca and nr3c1). The results indicated that TMBPA exposure adversely disrupted embryo hatching and larval development of zebrafish, accompanied by altering the expression of functional genes in larvae. These results provide further evidence for the potential environmental hazard posed by TMBPA.
Key Contributions:
1. Effects of 120 h TMBPA exposure on zebrafish embryonic–larval development were evaluated. 2. TMBPA exposure affected embryo hatching and larval development. 3. TMBPA exposure inhibited the swimming behavior of larvae. 4. TMBPA exposure disrupted the function of the antioxidant system, the HPT and HPA axes, and heart development.
1. Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA), an industrially synthesized compound, serves as a critical raw material for global production of polycarbonate plastics (accounting for 65% of output) and epoxy resins (30% of output) [1,2,3]. Owing to its pivotal role in fundamental polymer manufacturing, BPA is extensively utilized in diverse daily necessities, including storage containers, food packaging, toys, adhesives, thermal papers, and electronic devices, thereby establishing its pervasive presence in everyday life [3,4]. Market analyses indicate that global BPA demand increased from 7.00 million metric tons (Mt) in 2013 to 9.62 Mt in 2020, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7%. Production volume is projected to reach 10.0 Mt by 2022 [5,6]. The extensive use of BPA has made its release into the environment inevitable [7]. Consequently, humans are inevitably exposed to BPA, raising substantial concerns about the potential health risks posed by its large-scale production and application. However, as an endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC), BPA can mimic or block endogenous hormones, particularly as an estrogen receptor (ER) agonist, thereby interfering with normal endocrine function [5]. Numerous studies have demonstrated the reproductive toxicity, neurotoxicity, immunotoxicity, and metabolic toxicity of BPA exposure on organisms, with particularly significant effects on embryonic development and reproductive function [8,9,10]. Due to its potential health hazards, many countries and regions have restricted BPA use (e.g., in baby bottles) and promoted research and application of BPA analogues such as bisphenol S (BPS), bisphenol F (BPF), and bisphenol AF (BPAF). Unfortunately, growing evidence indicates that these substitutes disrupt the endocrine system through mechanisms similar to those of BPA [11,12,13].
Among the newly introduced BPA analogues, tetramethyl bisphenol A (TMBPA) has gained attention due to its widespread use in high-performance membranes and printed circuit boards [14]. Despite its increasing industrial application, toxicological data on TMBPA remain limited. In vitro and molecular studies indicated that TMBPA exhibits endocrine-disrupting activity comparable to or even stronger than BPA in certain pathways. For instance, a comparative study of the endocrine-disrupting activity of BPA and its 19 analogues indicated that TMBPA not only exhibited estrogenic activity in the human breast cancer cell model MCF-7 with potency similar to BPA but also displayed the highest anti-androgenic activity of 5α-dihydrotestosterone in mouse fibroblast cell line NIH3T3 among all tested compounds [15]. Further supporting the findings, another study revealed that TMBPA acted as an agonist for human estrogen receptorα (ESR1) and as an antagonist for human androgen receptor (NR3C4), demonstrating comparable potency to BPA [16]. Notably, TMBPA has been reported to affect the proliferation and function of fetal Leydig cells through ESR1, thereby interfering with the development of the male reproductive system [17]. Moreover, TMBPA inhibited the activity of steroidogenic enzymes in rat Leydig cells and triggers their ferroptosis, ultimately inhibiting the testosterone synthesis of Leydig cells in late puberty [18]. Beyond reproductive effects, TMBPA also interacts with thyroid hormone receptors and thyroxine-binding globulin [19]. These findings highlight the urgent need to evaluate the ecological and health risks posed by TMBPA, particularly its systemic toxicity in organisms.
Given its increasing use, environmental concentrations of TMBPA are anticipated to rise, following trends observed for BPA and its other analogues. Notably, aquatic environments represent the primary sink for bisphenol compounds (BPs), with reported concentrations reaching μg/L levels in natural waters. Investigations have revealed that BPA concentrations reach up to 7.5 μg/L in surface water and 17.2 mg/L in Japanese wastewater, whereas BPAF levels in surface water can attain 15.3 μg/L [20,21,22]. These environmentally relevant concentrations are particularly concerning given the established toxicity of BPs. A large number of studies have shown that BPs adversely affect embryonic–larval development and sexual development and function in teleosts [23,24,25]. However, while the hazards of conventional bisphenols are well-documented, until now the toxicological effects of TMBPA on fish remain poorly understood. Therefore, this study used zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model organism to study the toxic effects of TMBPA. Zebrafish embryos were exposed to various concentrations of TMBPA for 120 h, then changes in embryonic–larval phenotypes (hatchability, survival rate, total length, morphology, swimming behavior) and expression levels of genes related to the antioxidant system, hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid (HPT) axis, cardiac development, hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis were analyzed. The objectives of this study are to (1) characterize the developmental and behavioral toxicity of TMBPA in zebrafish, and (2) elucidate its mechanistic effects on endocrine and stress pathways. The results will improve understanding of the toxic effects of TMBPA on zebrafish and help assess the potential ecological risk of TMBPA in aquatic environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Embryo Collection and TMBPA Exposure
Adult zebrafish were obtained from the South China Sea Key Laboratory of Aquatic Economic Animal Breeding and Enhancement, Guangdong Ocean University. They were cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) with a water temperature of 26.0 ± 1.0 °C and light–dark cycle of 14 h:10 h. For breeding, females and males (at a female-to-male ratio of 2:3) were transferred to the same breeding tank but separated by a divider under complete darkness. The following morning, the divider was removed, and females and males initiated chasing, mating, and spawning under light stimulation. At 4 h post-fertilization (hpf), healthy blastula-stage embryos exhibiting translucent spherical morphology were selected for exposure experiments by excluding unfertilized (milky-white) and morphologically abnormal embryos under microscopic examination (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
TMBPA (CAS 5613-46-7) was purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). A stock solution (20 mg/mL) was prepared by dissolving TMBPA in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Ghtech, Guangzhou, China) and stored in darkness at 4 °C. For exposure experiments, TMBPA concentrations of 0 (control), 0.5, 5, 50, and 200 μg/L were prepared by serial dilution of the stock solution in water from RAS. Embryos were exposed to TMBPA at varying concentrations for 120 h in 90 mm Petri dishes (25 mL solution per dish), with 4 replicates per group (50 embryos per replicate) (N = 4, n = 50). To maintain exposure stability, the exposure solutions were completely renewed daily. All dishes were maintained in an illuminated incubator at 28 °C under a 14 h:10 h light–dark photoperiod. Survival rates were recorded at 24, 48, 72, 96, and 120 hpf, and hatching rates were recorded at 48 and 72 hpf.
2.2. Behavior Test
At the end of the exposure, larval fish from three randomly selected replicates per treatment were subjected to behavioral assays using the ZebraLab Video Tracking System (ViewPoint, Lyon, France). For each selected replicate, 10 larvae were systematically sampled (N = 3, n = 10). Before the test, larvae were placed in the test chamber for a 10 min acclimation. Then, a 15 min swimming behavior test was conducted under dark conditions. The swimming behavior of zebrafish larvae was classified into high-speed swimming (≥1.6 mm/s), medium-speed swimming (≥0.6 mm/s to <1.6 mm/s), and low-speed swimming or freezing (speed < 0.6 mm/s). The ZebraLab Video Tracking System collected data every 3 min, recording swimming time, trajectory, and distance of larvae.
2.3. Morphologic Observation and Full-Length Measurement
After the swimming behavior test, all larvae were anesthetized on ice. Subsequently, morphological characteristics (including body axis curvature, yolk sac cyst, mandibular hypoplasia, and delayed yolk sac absorption, etc.) of larvae were observed and photographed using a stereomicroscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). Total length was measured using ImageJ 1.54p (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
2.4. Total RNA Isolation and Transcriptional Expression Analysis
After 120 h of exposure, 20 larvae were pooled from each Petri dish for RNA extraction (N = 4, n = 20). Total RNA was extracted from zebrafish larvae using TRIzol™ reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA quality and quantity were assessed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and Nanodrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), respectively. cDNA was synthesized from 1 µg total RNA using the TransScript® All-in-One First-Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China).
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed on a LightCycler® 96 instrument (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) to assess the transcript levels of candidate genes [26,27,28] (Table 1). The PCR system (10 µL) contained 6 µL of 2 × TransStart® Green qPCR SuperMix (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China), 0.4 µL each of forward and reverse primers (10 µM), 1 µL cDNA template, and 4.2 µL nuclease-free ddH2O. The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: 95 °C for 30 s, 40 cycles for 5 s at 95 °C, 15 s at 60 °C, and 10 s at 72 °C. Melting curves were analyzed from 65 to 95 °C to ensure the specificity of the primers, showing a single peak. Each sample was amplified in triplicate, and each plate included two no-template controls (NTCs). Gene expression quantification was performed using the 2−ΔΔCt method with normalization to the geometric mean of two reference genes (β-actin and eef1a) [29,30].

Table 1.
Primer sequences used in the qPCR.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Experimental data were presented as the mean ± standard error (SEM). Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics (version 27.0.1). Data was tested for normality of distribution (Shapiro–Wilk test) and homogeneity of variance (Levene’s test) prior to analysis. When assumptions were met, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan multiple comparison test were used to analyze the significance of control and treatment groups. If the assumptions were violated, the Kruskal–Wallis test was used instead. Differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of TMBPA Exposure on Survival and Growth of Zebrafish Embryo-Larvae
Exposure to TMBPA at concentrations of 5, 50, and 200 μg/L significantly reduced the hatching rate of zebrafish embryos at 48 hpf, compared to the control (p < 0.05; Figure 1A). However, no statistically significant differences in cumulative hatching rate were observed between control and treatment groups at 72 hpf (p > 0.05; Figure 1A). Survival rates showed no significant differences among groups during the exposure period (p > 0.05), although a concentration-dependent decreasing trend was noted (Figure 1B). At 120 hpf, the total length of larvae was unaffected by exposure to TMBPA at 0.5, 5, or 50 μg/L, but significantly reduced by 200 μg/L TMBPA (p < 0.05; Figure 1C).
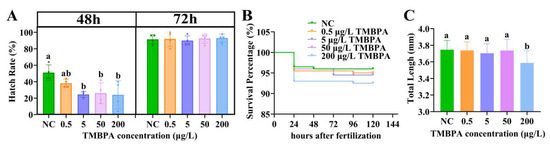
Figure 1.
Effects of TMBPA exposure on hatching rate (A), survival percentage (B), and total length (C) in zebrafish. NC denotes the control group. The data were shown as mean ± S.E. (n = 4). Different lowercase letters above bars indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatment groups.
3.2. TMBPA Exposure Causes Developmental Abnormalities in Zebrafish Larvae
TMBPA exposure caused abnormal development of zebrafish larvae. At 48 hpf, TMBPA-exposed larvae exhibited teratogenic effects, including manifesting as body axis curvature (Figure 2B,C; I), yolk sac cysts (Figure 2C; II), and pericardial edema (Figure 2D; IV). By 72 hpf, larvae under TMBPA exposure displayed cardiovascular hemorrhage (Figure 2F; V), pericardial edema (Figure 2F,H; IV), and tail curvature (Figure 2G; VI). At 96 hpf, novel malformations emerged, including mandibular defects (Figure 2J; III), delayed yolk sac absorption (Figure 2K,L; VII), and pigmentation deficiency (Figure 2K; VIII). Additionally, a subset of larvae showed significantly reduced body size (Figure 2L).
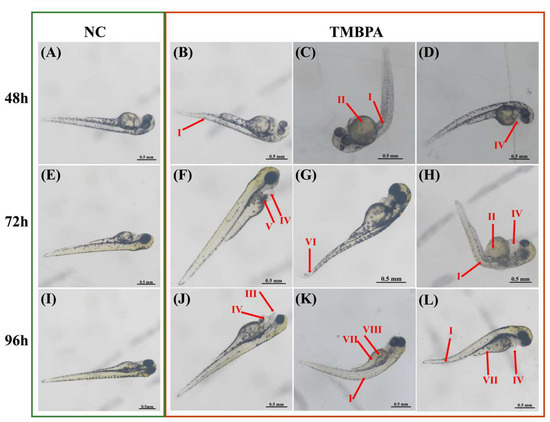
Figure 2.
Teratogenic effects of TMBPA exposure on zebrafish larval development. Normal larval development in control group (NC) at 48 hpf (A), 72 hpf (E), and 96 hpf (I). Representative malformations in TMBPA-exposed larvae at 48 hpf (B–D), 72 hpf (F–H), and 96 hpf (J–L). I: Body axis curvature; II: yolk sac cyst; III: mandibular hypoplasia; IV: pericardial edema; V: cardiovascular hemorrhage; VI: tail curvature; VII: delayed yolk sac absorption; VIII: pigmentation deficiency.
3.3. Effects of TMBPA Exposure on Larval Swimming Behavior
Compared to the control group, exposure to 200 μg/L TMBPA significantly increased the resting time and reduced large movement time in zebrafish larvae (p < 0.05; Figure 3A,C), while no significant difference was observed in small movement time (p > 0.05; Figure 3B). No significant differences were observed in resting time, short movement time, and large movement time among control groups and the 0.5, 5, and 50 μg/L TMBPA groups (p > 0.05). Larvae exposed to higher concentrations of TMBPA (50 μg/L and 200 μg/L) exhibited significantly reduced total movement distance compared to the control group (p < 0.05; Figure 3D). Furthermore, the behavior trajectory route maps demonstrated that TMBPA-exposed larvae showed depressed activity levels and shorter swimming distances than the controls (Figure 3E). A concentration-dependent suppression of both activity levels and total swimming distance was observed in the treatment groups.
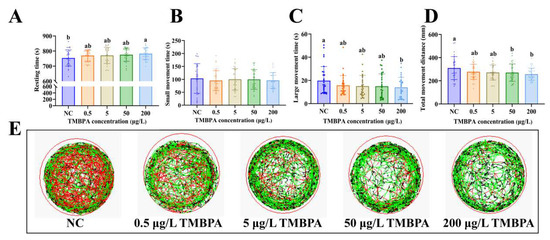
Figure 3.
Effects of TMBPA exposure on locomotor activity in zebrafish larvae. Resting states (A), short movement states (B), large movement states (C), total movement distance (D), and the behavior trajectory route maps (E). NC denotes the control group. The data were shown as mean ± S.E. (n = 30). Different lowercase letters above indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.4. Effects of TMBPA on Expression of Antioxidant System-Related Genes in Zebrafish Larvae
The expression levels of cat, mn-sod, gpx, keap1, ucp2, and nrf2 were significantly decreased in mRNA in all treatment groups compared to the control (p < 0.05; Figure 4A–E). Additionally, nrf2 expression exhibited a concentration-dependent decline, reaching its lowest level in the 200 μg/L group (p < 0.05; Figure 4F).
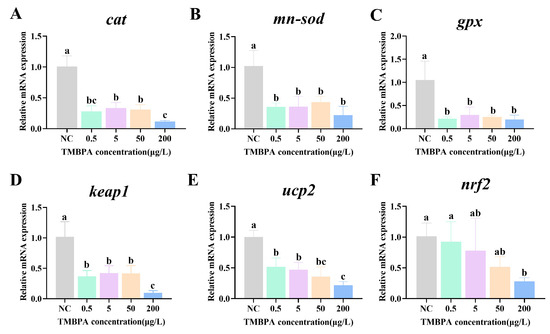
Figure 4.
Effects of TMBPA exposure on mRNA expression levels of cat (A), mn-sod (B), gpx (C), keap1 (D), ucp2 (E) and nrf2 (F) related to antioxidant system-related in zebrafish larvae. NC denotes the control group. The data were shown as mean ± S.E. (n = 4). Different lowercase letters above indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.5. Effects of TMBPA on Expression of HPT Axis-Related Genes in Zebrafish Larvae
Compared to the control, exposure to 0.5, 5, and 50 μg/L TMBPA had no significant effect on the expression of ugt1ab or trβ (p > 0.05), but 200 μg/L TMBPA significantly reduced the expression levels of the two genes (p < 0.05; Figure 5A,B). No significant difference was observed in dio1, crh, or tshβ expression levels when comparing the treatment and control groups (p > 0.05; Figure 5C–E). The ttr expression was significantly downregulated in all treatment groups compared to the control (p < 0.05), and no significant difference was observed among the treatment groups (p > 0.05, Figure 5F).

Figure 5.
Effects of TMBPA exposure on mRNA expression levels of ugt1ab (A), trβ (B), dio1 (C), crh (D), tshβ (E) and ttr (F) related to HPT-related in zebrafish larvae. NC denotes the control group. The data were shown as mean ±S.E. (n = 4). Different lowercase letters above indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.6. Effects of TMBPA Exposure on Expression of Cardiac Development-Related Genes in Zebrafish Larvae
Exposure to 0.5, 5, and 50 μg/L TMBPA had no significant effect on the mRNA levels of tbx2b, amhc, or bmp4 (p > 0.05), whereas 200 μg/L TMBPA significantly decreased their mRNA levels (p < 0.05), compared to the control group (Figure 6A,B,D). The expression levels of myl7 were significantly lower in all treatment groups than those in the control group (p < 0.05; Figure 6C). Additionally, with increasing concentration, the expression levels of notch1b showed a gradual decrease, with the lowest levels in the 200 μg/L group (p < 0.05; Figure 6E).
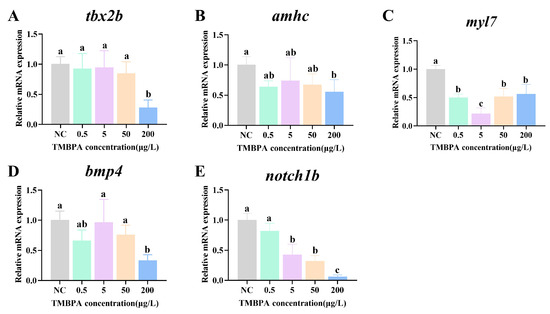
Figure 6.
Effects of TMBPA exposure on expression levels of tbx2b (A), amhc (B), myl7 (C), bmp4 (D) and ugt1ab (E) related to cardiac development-related in zebrafish larvae. NC denotes the control group. The data were shown as mean ± S.E. (n = 4). Different lowercase letters above indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.7. Effects of TMBPA Exposure on the HPA Axis-Related Genes in Zebrafish Larvae
Compared to the control, exposure to 50 μg/L and 200 μg/L TMBPA significantly downregulated pomca expression (p < 0.05; Figure 7A). Conversely, nr3c1 expression in all treatment groups was significantly upregulated compared to the control group (p < 0.05), and no significant difference was observed among the treatment groups (p > 0.05; Figure 7C). There was no significant difference in the expression levels of pomcb and crhb between the treatment group and the control group (p > 0.05; Figure 7B,D).
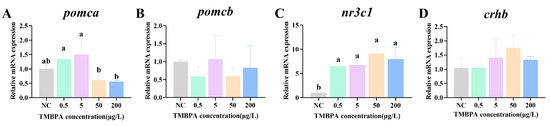
Figure 7.
Effects of TMBPA exposure on mRNA expression levels of pomca (A), pomcb (B), nr3c1 (C) and crhb (D) related to HPA axis-related in zebrafish larvae. NC denotes the control group. The data were shown as mean ±S.E. (n = 4). Different lowercase letters above indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. TMBPA Exposure Impacts the Hatching Rate, Survival Rate, Malformations, and Locomotor Activity in Zebrafish During Embryonic-to-Larval Developmental Stages
Hatching rate, malformation rate, and survival rate (mortality) serve as critical indicators for evaluating the developmental toxicity and safety assessment of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in fish. Extensive studies have demonstrated that BPA analogues (e.g., BPAF, BPF, BPS, and TBBPA), which are structurally similar to BPA, exhibit comparable endocrine-disrupting effects [31,32,33]. For instance, BPF exposure caused a concentration-dependent delay in the hatching rate of zebrafish embryos and induced various embryonic developmental defects [34]. Similarly, marine medaka embryos treated with a high concentration (5 mg/L) of BPAF showed significantly reduced survival and hatching rates, along with malformations such as spinal curvature [35]. In the present study, TMBPA exposure significantly decreased zebrafish embryo hatching rates at 48 hpf, but this effect was no longer statistically significant in the cumulative hatching rate at 72 hpf. Although survival rates from 0 to 120 hpf did not differ significantly across TMBPA treatment groups, a concentration-dependent downward trend was observed. These findings were similar to the study in which TMBPF exposure significantly suppressed zebrafish hatching rates at 48 hpf, with this inhibition persisting until 96 hpf before returning to control levels [36]. Moreover, TMBPA exposure adversely affected zebrafish larval development, significantly reducing body length at a concentration of 200 μg/L. It also induced severe malformations, such as spinal curvature, pericardial edema, yolk sac cysts, and cardiovascular hemorrhage. In summary, TMBPA may cause developmental toxicity during early life stages of fish, potentially posing ecotoxicological risks to aquatic ecosystems.
Swimming behavior, as a nervous system-mediated phenotype, serves as a well-established biomarker for assessing environmental neurotoxicants [37]. This behavioral metric reflects fundamental survival adaptation, enabling environmental exploration, efficient foraging, and predator avoidance strategies [38]. Extensive research confirms that bisphenol compounds (BPs) disrupt key behavioral responses in fish through neuroendocrine interference. For example, BPF exposure (5 mg/L and 10 mg/L) during early zebrafish embryonic development reduces locomotor activity by altering neurochemicals [34]. BPF also significantly reduced both the total distance traveled and the average swimming speed in zebrafish larvae [39]. Similarly, BPAF treatment significantly reduced macromotor state duration and total distance travelled in marine medaka [40]. Furthermore, prolonged exposure (75 days) to BPS was found to disrupt the neuroendocrine system in zebrafish, leading to impairments in social behavior in adult fish [41]. In the present study, TMBPA exposure suppressed swimming behavior in zebrafish larvae in a concentration-dependent manner. Similar results were observed in a study that direct exposure to TMBPF at 72 and 144 hpf affected the development of motor neuron axons, leading to the disruption of locomotor behavior in zebrafish larvae [36]. Collectively, these data indicated that TMBPA adversely affected locomotor behavior when exposed during early developmental stages in zebrafish.
4.2. TMBPA Exposure Affects the Antioxidant Capacity in Zebrafish Larvae
Maintaining redox homeostasis is crucial for various aspects of cellular survival, development, and growth. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), the byproducts of cellular metabolism, have been shown to play an essential role in maintaining cell homeostasis [42]. As second messengers, ROS primarily participate in cellular signal transduction through redox reactions. When ROS levels exceed the physiological range, they disrupt redox reactions catalyzed by antioxidant enzymes, thereby inducing systemic oxidative stress [43,44]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), Glutathione peroxidase (GPX), and catalase (CAT) are key enzymes responsible for the regulation of oxidative stress in the antioxidant defense system of organisms. These enzymes synergistically reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in the organism [45,46]. In this study, TMBPA exposure significantly downregulated the expression of mn-sod, cat, and gpx in zebrafish larvae, which may induce an increase in ROS levels. Gu et al. found that BPAF inhibited the activity of both SOD and CAT enzymes and cat mRNA expression in both zebrafish and HCM cells, leading to a significant increase in ROS [37]. Additionally, chronic exposure to low concentrations of BPS and E2 decreased the transcriptional levels of gpx1a, cat, and Cu/Zn-sod in the brains of zebrafish [47,48]. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that TMBPA exposure induced elevated ROS levels, suppressed antioxidant enzyme activities, and consequently triggered oxidative stress in zebrafish larvae.
The Nrf2-Keap1 pathway is an important signaling pathway that mediates resistance to oxidative stress by regulating the expression of sod, cat, and gpx [49]. Ucp2 encodes a mitochondrial uncoupling protein that counteracts oxidative stress through a “mild uncoupling” process, thereby reducing ROS production [50,51]. When external oxidative insults surpass the body’s adaptive capacity, Nrf2 dissociates from Keap1, translocates into the nucleus, and initiates transcription of antioxidant genes (e.g., Sod, Cat, Gpx) [52]. In this study, TMBPA exposure significantly downregulated the expression of nrf2, keap1, and ucp2 in zebrafish larvae. The decreased mRNA levels of these antioxidant-related genes observed in this study indicated that TMBPA adversely affects the antioxidant-related activity in zebrafish larvae, potentially leading to the accumulation of ROS. TMBPA induced intestinal oxidative stress in zebrafish larvae by disrupting the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway.
4.3. TMBPA Exposure Affects Thyroid Function in Zebrafish Larvae
In teleosts, thyroid hormones (THs) play a critical role in the regulation of reproduction, development, growth, metabolism, and energy balance [53,54]. The homeostasis of thyroid hormones is controlled by the HPT axis [55,56]. In this study, TMBPA (>5 μg/L) exposure significantly decreased the mRNA levels of ttr, ugt1ab, and trβ in zebrafish larvae. Similarly, exposure to BPA, BPF, or BPS significantly changed the expression of ttr and ugt1ab, as well as hhex and tg related to thyroid development in zebrafish larvae [32]. In addition, BPAF exposure altered whole-body thyroid hormone concentrations, accompanied by upregulating the expression of tshβ and tg while downregulating the expression of trα and trβ in zebrafish larvae [57]. Ttr encodes a key carrier protein for THs [58], and ugt1ab encodes a phase II excretion enzyme to catalyze the glucuronidation of triiodothyronine (T4) [59]. TH receptors (TRs), such as TRα and TRβ, act as inducible ligand-activated transcription factors and play important roles in embryonic and larval development [60]. The downregulation of ttr, ugt1ab, and trβ in this study indicated the disrupting effects of TMBPA on TH transport, TH metabolism, and TR signaling systems during larval development in zebrafish.
4.4. TMBPA Exposure Affects Cardiac Development in Zebrafish Larvae
The heart is the first organ to form and function during embryonic development in zebrafish [61]. Its development is a highly sensitive process that can be disrupted by exposure to an environmentally toxic molecule during cardiogenesis. EDCs, such as BPs and acrylamide, have been reported to induce cardiotoxicity in zebrafish by interfering with the expression of genes critical for cardiac development [37,62]. In this study, five cardiac marker genes (notch1b, bmp4, tbx2b, amhc, myl7) were selected to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of TMBPA in zebrafish. Notch1b is essential for the specification of central cardiac conduction tissue [63]. Bmp4 involves the development of atrioventricular canal (AVC), arteries, and outflow tract (OFT) septation, and its deficiency resulted in a lack of cardiac crescent and primitive ventricle, as well as AVC defect and OFT septation [64]. Tbx2b, a member of the T-box family of transcription factors, is involved in heart cushion formation and cardiac chamber differentiation [65,66]. Amhc, the zebrafish ortholog of mammalian mhy6, is critical for cardiac chamber differentiation, morphogenesis, and functional maintenance [67,68]. Mutation of amhc caused ventricular wall thickening and a narrowed ventricular lumen in the embryos of zebrafish [68]. Myl7 is involved in cardiac contraction control and cardiomyocyte proliferation [69]. In mice, myl7 inactivation resulted in embryonic lethality and abnormal cardiac morphogenesis [70]. Acrylamide exposure reduced the expression of myl7, bmp4, tbx2b, and notch1b, leading to impaired ventricle and atrium development and failed AVC differentiation in zebrafish [71]. In this study, high concentrations of TMBPA significantly downregulated the expression of all five genes, indicating its adverse effects on the cardiac morphogenesis and function of zebrafish.
4.5. TMBPA Affects the Function of Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis in Zebrafish Larvae
The hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (interrenal in fish) (HPA/I) axis is the major neuroendocrine system responsible for the regulation of stress responses, as well as the adaptation and/or acclimation of animals to dynamic environments [72,73]. Previous studies have suggested that exposure to BPA and its analogues could cause adverse effects on the function of the HPA axis in humans and rats [10,74]. In zebrafish, HPI axis-related genes are expressed at approximately 2.5 dpf, and the HPI axis starts responding to exogenous stressors by 3 to 4 dpf [75,76,77,78]. Long-term exposure from embryos to adults to BPS at environmentally relevant concentrations (1 and 10 μg/L) caused abnormal expressions of HPI axis genes [79]. The present study analyzed the effects of TMBPA on the expression of HPI axis-related genes in zebrafish at 5 dpf and found that the TMBPA exposure significantly promoted nr3c1 expression (≥0.5 μg/L) but significantly suppressed pomca expression (≥50 μg/L). Nr3c1 encodes the glucocorticoid receptor, which mediates glucocorticoid signaling to regulate stress responses and negative feedback in the HPI axis [78]. Pomca is one of the two pomc genes encoding pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) in zebrafish [80]. The POMC peptides are the pituitary precursors of circulating adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), melanocyte-stimulating hormones (MSHs), and β-endorphin [81]. The knockdown of pomca in zebrafish led to markedly decreased immunoreactivity of ACTH and attenuated melanosome dispersal at 5 dpf [82]. The upregulated expression of nr3c1 and downregulated mRNA levels of pomca in this study indicated that TMBPA exposure might affect the function of the HPI axis by altering glucocorticoid signaling and POMC signaling in zebrafish larvae.
5. Conclusions
The toxic effects of TMBPA exposure on zebrafish embryo-larvae were evaluated in this study. The results showed that the toxicity of TMBPA to zebrafish embryo-larvae increased with increasing TMBPA concentration, similar to other BPs. Specifically, TMBPA exposure at 5, 50, and 200 μg/L significantly decreased the hatching rate of zebrafish embryos and resulted in developmental abnormalities, including pericardial edema, cardiovascular hemorrhage, tail curvature, and delayed yolk sac absorption, among others. Furthermore, exposure to 200 μg/L TMBPA significantly reduced the total length of larvae and suppressed their swimming behavior. At the molecular level, TMBPA exposure altered the expression of genes related to the antioxidant system, HPT axis, cardiac development, and the HPA axis. These results enrich our understanding of the aquatic ecotoxicology of TMBPA. With the increasing use of TMBPA, its inevitable release into aquatic environments exerts toxic effects on fish, with the potential risk of damaging aquatic ecosystems.
Author Contributions
E.Y.: Conceptualization, data curation, software, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and validation. M.Z.: Data curation, validation, and writing—original draft. H.Y.: Data curation, validation, and writing—original draft. J.G.: Data curation, validation, and writing—original draft. Z.C.: Data curation, validation, and writing—original draft. N.Z.: Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, supervision, and validation. Y.G.: Writing—original draft, supervision, software, and methodology. Z.W.: Supervision, validation, and funding acquisition. Z.D.: Methodology, validation, writing—original draft, supervision, software, funding acquisition, and conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41806195), the Undergraduate Innovation Team of Guangdong Ocean University (CXTD2023004), and the Guangdong Provincial Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training for College Students (S202410566009, S202410566010).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research in this manuscript has been conducted under the guidance of the international ethical standards of Guangdong Ocean University (approval code: 20240112 and date: 6 March 2024).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xing, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hou, J. A critical review of presence, removal and potential impacts of endocrine disruptors bisphenol A. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 254, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Iacovidou, E.; Gerassimidou, S. An overview of the occurrence, fate, and human risks of the bisphenol-A present in plastic materials, components, and products. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, F.; Moreno-Harridan, C.; Barbaro, P. Biomass-derived chemical substitutes for bisphenol A: Recent advancements in catalytic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6329–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustieles, V.; D’Cruz, S.C.; Couderq, S.; Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; Fini, J.B.; Hofer, T.; Steffensen, I.L.; Dirven, H.; Barouki, R.; Olea, N.; et al. Bisphenol A and its analogues: A comprehensive review to identify and prioritize effect biomarkers for human biomonitoring. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.D.P.G.; Lora-Benítez, A.J.; Molina-López, A.M.; Mora-Medina, R.; Ayala-Soldado, N.; Moyano-Salvago, M.D.R. Evaluation of the toxicity of Bisphenol A in reproduction and its effect on fertility and embryonic development in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsmann, R.D.; Will, C.; Carasek, E. Determination of bisphenol A: Old problem, recent creative solutions based on novel materials. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1148–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, J.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Jia, Y.W.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Chen, C.E.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.T.; Ying, G.G. Occurrence, mass loads and risks of bisphenol analogues in the Pearl River Delta region, South China: Urban rainfall runoff as a potential source for receiving rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, I.; Fiory, F.; Perruolo, G.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; Oriente, F. Potential mechanisms of bisphenol A (BPA) contributing to human disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, F.; Ye, L.; Qiao, X.; Li, J.; Tian, L.; Su, M.; Lin, L.; Ge, R.; Wang, Y. Tetramethyl bisphenol A stimulates proliferation but inhibits fetal Leydig cell function in male rats by targeting estrogen receptor α after in utero exposure. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 2743–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Marwa, P.W.; Petlulu, P.; Chen, X.; et al. The adverse health effects of bisphenol A and related toxicity mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaderakhshan, R.; Kemp, P.; Breul, L.; Steinbichl, P.; Hartmann, C.; Fürhacker, M. Bisphenol A and its alternatives in Austrian thermal paper receipts, and the migration from reusable plastic drinking bottles into water and artificial saliva using UHPLC-MS/MS. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenza, C.J.; Farooq, A.; Shubear, N.S.; Donkor, K.K. A targeted review on fate, occurrence, risk and health implications of bisphenol analogues. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Qin, G.; Qian, N.; Zeng, X.; Li, R.; Lai, K.P. Bisphenol A and its replacement chemicals as endocrine disruptors and obesogens. Environ. Chem. Ecotox. 2025, 7, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.K.; Lv, H.; Qiao, W.H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Shen, J.Z.; Cao, G.P. Catalytic performance and mechanism of dual-functional mesoporous catalyst in the synthesis of tetramethyl bisphenol A. J. Mater. Sci. 2025, 60, 9529–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Suzuki, T.; Sanoh, S.; Kohta, R.; Jinno, N.; Sugihara, K.; Yoshihara, S.; Fujimoto, N.; Watanabe, H.; Ohta, S. Comparative study of the endocrine-disrupting activity of bisphenol A and 19 related compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 84, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.E.; Li, Y.; Perera, L.; Thayer, K.A.; Korach, K.S. Characterization of estrogenic and androgenic activities for bisphenol A-like chemicals (BPs): In vitro estrogen and androgen receptors transcriptional activation, gene regulation, and binding profiles. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 172, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Z. Long-term exposure to bisphenol A and its analogues alters the behavior of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) and causes hepatic injury. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Tian, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ge, R.S.; Wang, Y. Tetramethyl bisphenol a inhibits leydig cell function in late puberty by inducing ferroptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.A.; Sheikh, I.A. Endocrine disruption: Molecular interactions of environmental bisphenol contaminants with thyroid hormone receptor and thyroxine-binding globulin. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2020, 36, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yin, D.; Zhao, J. The occurrence and research progress of bisphenol analogues in aquatic environment. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Yan, S.; Meng, Z.; Huang, S.; Sun, W.; Jia, M.; Teng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. New insights into bisphenols induced obesity in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Activation of cannabinoid receptor CB1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Ruan, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, R.; Jing, G. Distribution and Preliminary Exposure Assessment of Bisphenol AF (BPAF) in Various Environmental Matrices around a Manufacturing Plant in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13136–13143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faheem, M.; Bhandari, R.K. Detrimental effects of bisphenol compounds on physiology and reproduction in fish: A literature review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 81, 103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, S.; Markle, T.; Thompson, S.; Wallace, E. Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: A wildlife perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreman, J.; Lee, O.; Trznadel, M.; David, A.; Kudoh, T.; Tyler, C.R. Acute toxicity, teratogenic, and estrogenic effects of bisphenol A and its alternative replacements bisphenol S, bisphenol F, and bisphenol AF in zebrafish embryo-larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Li, Y.; Ru, H.; Wu, L.; Xiao, Z.; Ni, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhong, L. Thyroid disruption and developmental toxicity caused by triphenyltin (TPT) in zebrafish embryos/larvae. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 394, 114957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Lv, L.; Wu, S.; An, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X. Developmental toxicity of kresoxim-methyl during zebrafish (Danio rerio) larval development. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Luan, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Sun, M.; Feng, X. Cardiotoxicity of zebrafish induced by 6-benzylaminopurine exposure and its mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, Q.; Lai, Z.; Cui, H.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Systematic selection of suitable reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization studies of gene expression in Lutjanus erythropterus. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, M.S.; Pang, M.G. Bisphenols threaten male reproductive Health via testicular cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Shin, H.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K. Comparison of thyroid hormone disruption potentials by bisphenols A, S, F, and Z in embryo-larval zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, J.S.; Yin, L.; Measel, E.; Liang, S.; Yu, X. Effects of bisphenol A and its analogs on reproductive health: A mini review. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 79, 96–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.S.; Park, B.H.; Hwang, K.S.; Bae, M.A.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.; Park, H.C. Mechanism of bisphenol F affecting motor system and motor activity in zebrafish. Toxics 2023, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Huan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Dong, Z. Toxic effects of bisphenol AF on the embryonic development of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Deng, J.; Gu, J.; Yang, J.; Ge, F.; Huang, C.; Wu, W. TMBPF-induced neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in zebrafish larvae: Impacts on central nervous system development and dopamine neurons. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Fan, D.; Shi, L.; Ji, G.; Gu, A. Oxidative stress in bisphenol AF-induced cardiotoxicity in zebrafish and the protective role of N-acetyl N-cysteine. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, E.M.; Björnfors, E.R.; Pallucchi, I.; Picton, L.D.; El Manira, A. Principles governing locomotion in vertebrates: Lessons from zebrafish. Front. Neural Circuit. 2018, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, D.; Shi, L.; Wang, J.; Ji, G. Bisphenol F exposure impairs neurodevelopment in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, T.; Chen, X.; Huan, Z.; Huang, J.; Lu, S.; Zeng, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Z. Toxic effects of chronic exposure to BPAF and perturbation of gut microbiota homeostasis in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahinejad, A.; Naderi, M.; Attaran, A.; Meuthen, D.; Niyogi, S.; Chivers, D.P. Effects of chronic exposure to bisphenol-S on social behaviors in adult zebrafish: Disruption of the neuropeptide signaling pathways in the brain. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 113992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D Autréaux, B.; Toledano, M.B. ROS as signalling molecules: Mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, G.A.; Ghaffar, A.; Hussain, R.; Jamal, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Mohamed, B.B.; Aljohani, A.S. Nuclear and morphological alterations in erythrocytes, antioxidant enzymes, and genetic disparities induced by brackish water in mrigal carp (Cirrhinus mrigala). Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 4972622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyre, E.O.; Valencia, A.T.; Guzmán, D.D.; Maldonado, I.C.; Ledezma, L.E.B.; Carrillo, M.F.; Escorza, M.A.Q. Oxidative stress as a molecular mechanism of exposure to organophosphorus pesticides: A review. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2021, 22, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Lv, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, C. Exploring the mechanism of intestinal injury induced by Bisphenol S in freshwater crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): Molecular and biochemical approaches. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 274, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Andresen, A.M.S.; Gjøen, T. Short-term effect of bisphenol-a on oxidative stress responses in Atlantic salmon kidney cell line: A transcriptional study. Toxicol. Mech. Method. 2016, 26, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahinejad, A.; Attaran, A.; Naderi, M.; Meuthen, D.; Niyogi, S.; Chivers, D.P. Chronic exposure to bisphenol S induces oxidative stress, abnormal anxiety, and fear responses in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahinejad, A. Neurobehavioural Toxicity of Bisphenol S in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatchewan, SK, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Xing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Meng, R.; Jia, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Lead exposure activates the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway, aggravates oxidative stress, and induces reproductive damage in female mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesci, S.; Rubattu, S. UCP2, a member of the mitochondrial uncoupling proteins: An overview from physiological to pathological roles. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Hussain, R.; Ghaffar, A.; Afzal, G.; Saad, A.Q.; Ahmad, N.; Nazir, U.; Ahmad, H.I.; Hussain, T.; Khan, A. Clinicohematological, mutagenic, and oxidative stress induced bypendimethalin infreshwater fishbighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2093822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Zhao, X.; Ji, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Thecombined toxic effects of polyvinyl chloride microplastics anddi(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate onthejuvenile zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugan, M.L.; Levi, Y.; Blondeau, J.P. Endocrine disruptors and thyroid hormone physiology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.; Kho, Y.; Kim, P.G.; Ji, K. Thyroid endocrine disruption in male zebrafish following exposure to binary mixture of bisphenol AF and sulfamethoxazole. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanton, M.L.; Specker, J.L. The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis in fish and its role in fish development and reproduction. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deal, C.K.; Volkoff, H. The role of the thyroid axis in fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 596585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, F.; Diao, X. Thyroid disruption in zebrafish larvae by short-term exposure to bisphenol AF. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13069–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, D.M.; Elias, N.P.; Richardson, S.J.; Mendes, J.; Soares, C.M.; Santos, C.R.A. Evolution of the thyroid hormone-binding protein, transthyretin. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2000, 119, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jung, J.; Lee, I.; Jung, D.; Youn, H.; Choi, K. Thyroid disruption by triphenyl phosphate, an organophosphate flame retardant, in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos/larvae, and in GH3 and FRTL-5 cell lines. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 160, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Lo, L.J.; Chan, W.K. Temporal expression and T3 induction of thyroid hormone receptors α1 and β1 during early embryonic and larval development in zebrafish, Danio rerio. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2000, 159, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glickman, N.S.; Yelon, D. Cardiac development in zebrafish: Coordination of form and function. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.R.; Green, J.M.; Moreman, J.; Gunnarsson, L.M.; Mourabit, S.; Ball, J.; Winter, M.J.; Trznadel, M.; Correia, A.; Hacker, C.; et al. Cardiovascular effects and molecular mechanisms of bisphenol A and its metabolite MBP in zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milan, D.J.; Giokas, A.C.; Serluca, F.C.; Peterson, R.T.; MacRae, C.A. Notch1b and neuregulin are required for specification of central cardiac conduction tissue. Development 2006, 133, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, J.; Deng, S.; Liu, B.; Jing, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; She, Q. The molecular mechanisms of cardiac development and related diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aanhaanen, W.T.; Brons, J.F.; Domínguez, J.N.; Rana, M.S.; Norden, J.; Airik, R.; Wakker, V.; Vries, C.G.; Brown, N.A.; Kispert, A.; et al. The Tbx2+ primary myocardium of the atrioventricular canal forms the atrioventricular node and the base of the left ventricle. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Hoogaars, W.M.; Barnett, P.; Grieskamp, T.; Rana, M.S.; Buermans, H.; Farin, H.F.; Petry, M.; Heallen, T.; Martin, J.F.; et al. Tbx2 and Tbx3 induce atrioventricular myocardial development and endocardial cushion formation. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 2012, 69, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfinson, M.; Fitts, R.H.; Lough, J.W.; James, J.M.; Simpson, P.M.; Handler, S.S.; Mitchell, M.E.; Tomita-Mitchell, A. Significance of α-Myosin Heavy Chain (MYH6) variants in hypoplastic left heart syndrome and related cardiovascular diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdougo, E.; Coleman, H.; Lee, D.H.; Stainier, D.Y.; Yelon, D. Mutation of weak atrium/atrial myosin heavy chain disrupts atrial function and influences ventricular morphogenesis in zebrafish. Development 2003, 130, 6121–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Guo, X.; Yu, P.; Liang, J.; Mo, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, L.; Huang, X.; Hu, B.; Liu, J.; et al. Vasorin deficiency leads to cardiac hypertrophy by targeting MYL7 in young mice. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucitti, J.L.; Jones, E.A.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Fraser, S.E.; Dickinson, M.E. Vascular remodeling of the mouse yolk sac requires hemodynamic force. Development 2007, 134, 3317–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jiao, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, Y. Exposure to acrylamide induces cardiac developmental toxicity in zebrafish during cardiogenesis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, C.; Jin, X.; He, J.; Yin, Z. Domestication of farmed fish via the attenuation of stress responses mediated by the hypothalamus–pituitary–inter-renal endocrine axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 923475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalafouta, A.; Papandroulakis, N.; Gorissen, M.; Katharios, P.; Flik, G.; Pavlidis, M. Ontogenesis of the HPI axis and molecular regulation of the cortisol stress response during early development in Dicentrarchus labrax. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Robaire, B. Effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on adrenal function. Endocrinology 2025, 166, bqaf045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderman, S.L.; Bernier, N.J. Ontogeny of the corticotropin-releasing factor system in zebrafish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 164, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsop, D.; Vijayan, M.M. Development of the corticosteroid stress axis and receptor expression in zebrafish. Am. J. Physiol Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R711–R719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesan, D.; Vijayan, M.M. Role of glucocorticoid in developmental programming: Evidence from zebrafish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 181, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, M.J.M.; Chatzopoulou, A.; Spaink, H.P. The zebrafish as a model system for glucocorticoid receptor research. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 153, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, X.; Ru, X. Long-term exposure of zebrafish to bisphenol S impairs stress function of hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal axis and causes anxiety-like behavioral responses to novelty. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, I.A.; To, T.T.; Wortmann, S.; Burmester, T.; Winkler, C.; Meyer, S.R.; Neuner, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Allolio, B. The pro-opiomelanocortin gene of the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 303, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesan, D.; Vijayan, M.M. Maternal cortisol mediates hypothalamus-pituitary-interrenal axis development in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, M.; Mathur, P.; Guo, S. Corticotropin-releasing factor critical for zebrafish camouflage behavior is regulated by light and sensitive to ethanol. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).