Facilitation and Interference Between Native Fishes Influence Invasion Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
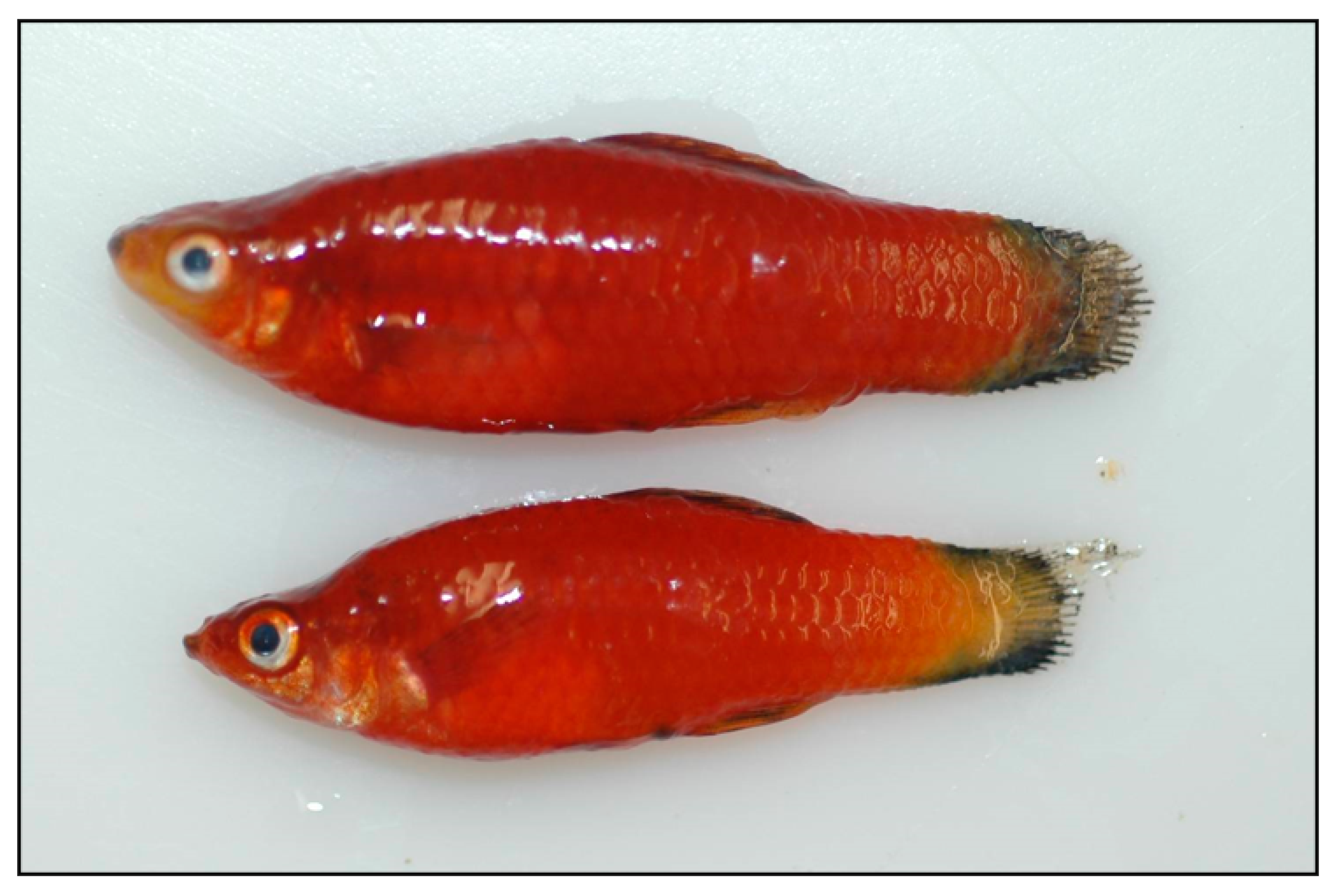
2.2. Study Species
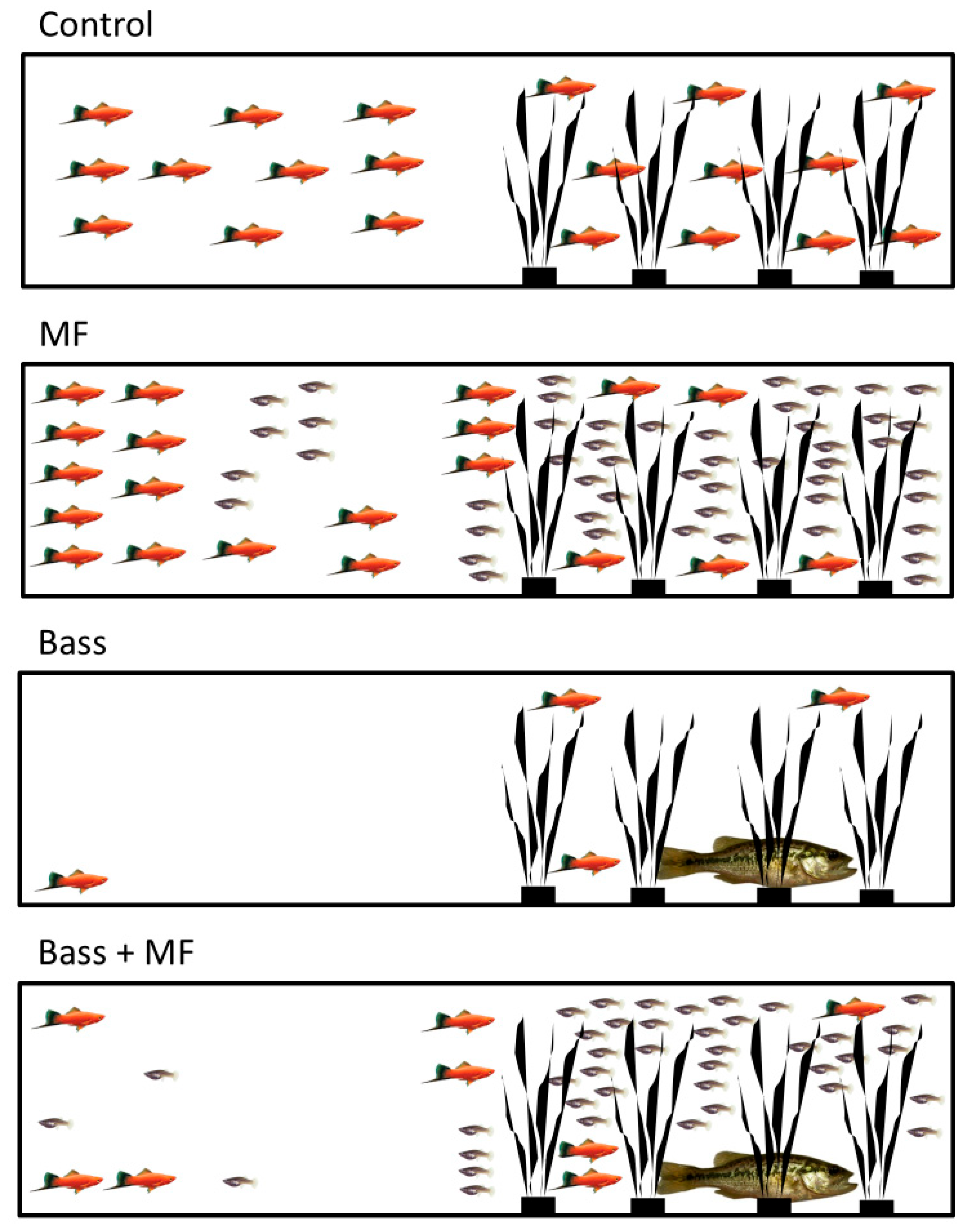
2.3. Experimental System and Design
2.4. Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
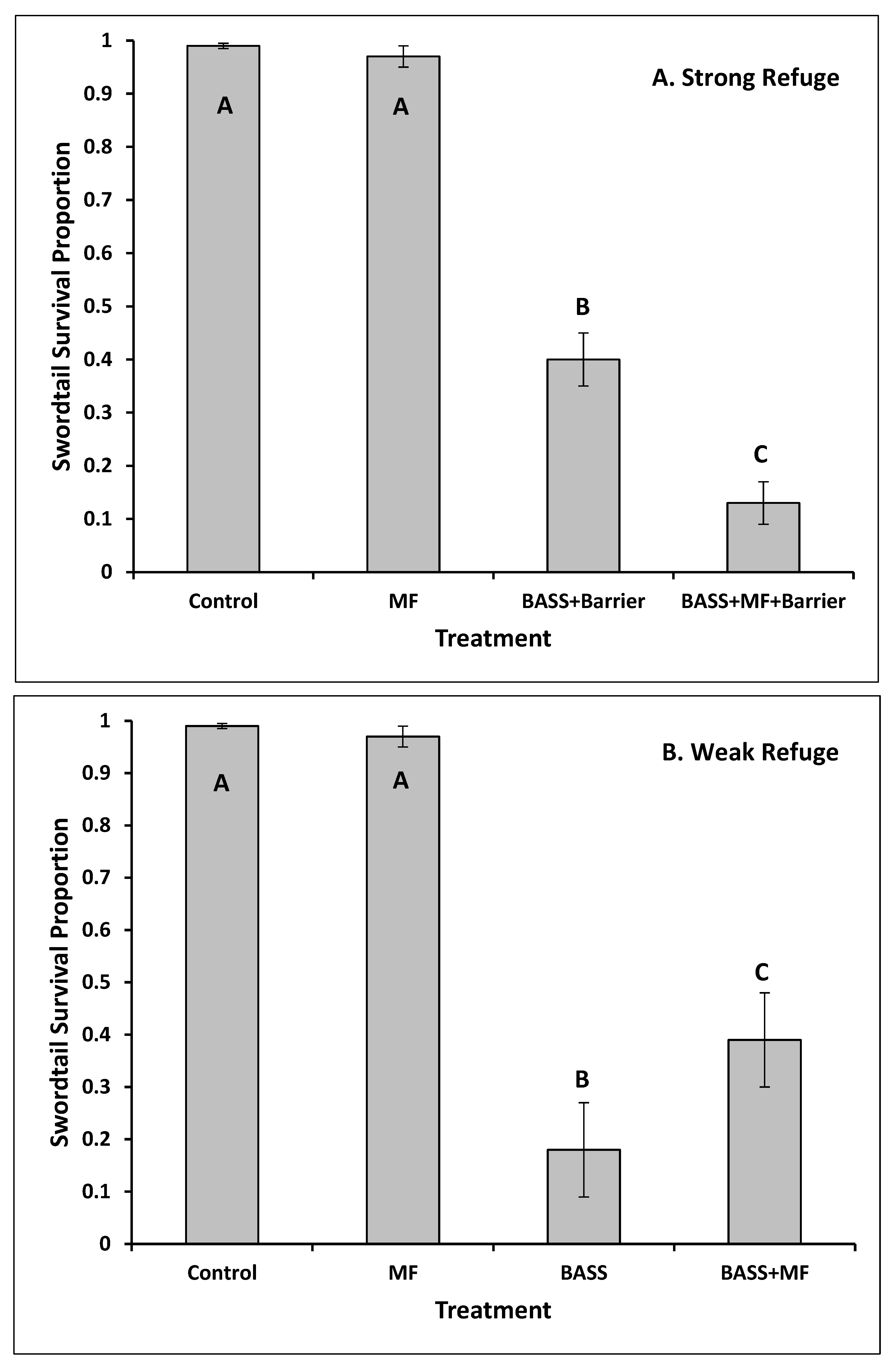
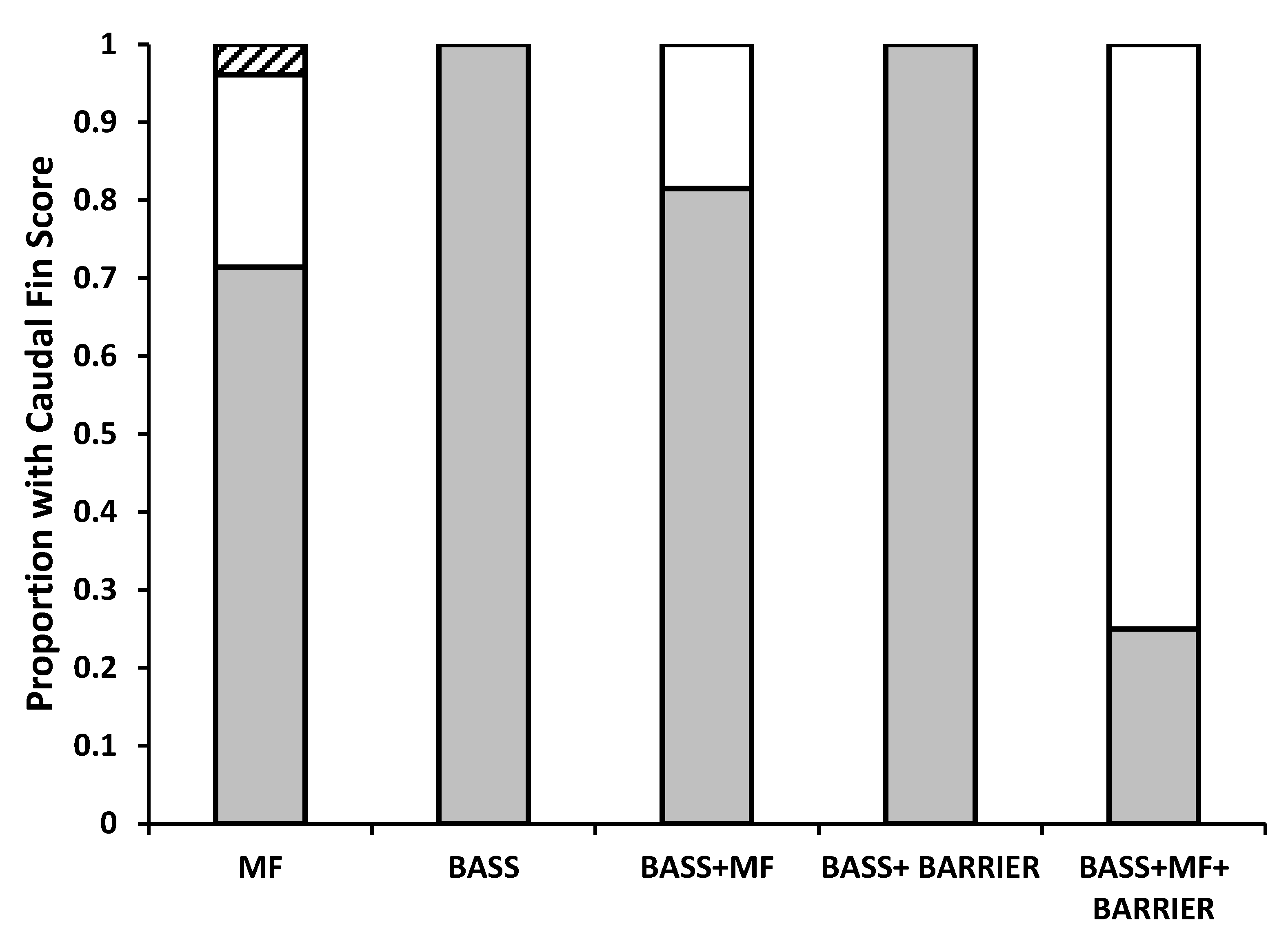
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Habitat influenced invasion resistance by altering the interaction of mosquitofish and bass.
- Facilitation of increasing predation effects was observed when mosquitofish aggression largely excluded swordtails from structurally complex habitat, increasing swordtail vulnerability to bass.
- Interference reducing predation effects was observed at lower levels of structural complexity when bass consumed mosquitofish and suppressed their aggression effects on swordtails.
- Despite interference, swordtails still encountered invasion resistance from bass.
- Small-bodied fish invaders must remain in structurally complex habitat while facing intense mosquitofish harassment, or leave this cover and expose themselves to bass.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beaury, E.M.; Finn, J.T.; Corbin, J.D.; Barr, V.; Bradley, B.A. Biotic resistance to invasion is ubiquitous across ecosystems of the United States. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernery, C.; Bellard, C.; Courchamp, F.; Brosse, S.; Gozlan, R.E.; Jarić, I.; Teletchea, F.; Leroy, B. Freshwater fish invasions: A comprehensive review. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 53, 427–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRivera, C.E.; Ruiz, G.M.; Hines, A.H.; Jivoff, P. Biotic resistance to invasion: Native predator limits abundance and distribution of an introduced crab. Ecology 2005, 86, 3364–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skein, L.; Alexander, M.E.; Robinson, T.B. Co-occurring predators increase biotic resistance against an invasive prey. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 157, 104929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajer, P.G.; Cross, T.K.; Lechelt, J.D.; Chizinski, C.J.; Weber, M.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Across-ecoregion analysis suggests a hierarchy of ecological filters that regulate recruitment of a globally invasive fish. Divers. Distrib. 2015, 21, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, A.; Yu, J.; Wardle, D.A.; Englund, G. Biotic resistance in freshwater fish communities: Species richness, saturation or species identity? Oikos 2015, 124, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.E.; Tuckett, Q.M. Abiotic and biotic contributions to invasion resistance for ornamental fish in west-central Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 2018, 817, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, A.E.; Fraser, D.F.; Farrell, A.D. Resistance from a resident heterospecific affects establishment success of a globally invasive freshwater fish. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 68, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, C. The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, T.A.; Naeem, S.; Howe, K.M.; Knops, J.M.H.; Tilman, D.; Reich, P. Biodiversity as a barrier to ecological invasion. Nature 2002, 417, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, J.H.; Carrasco, L.R.; Tan, H.H.; Yeo, D.C.J. Native richness and species level trophic traits predict establishment of alien freshwater fishes. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 3495–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Englund, G.; Wooster, D. Emergent impacts of multiple predators on prey. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, O.J. Predator diversity and trophic interactions. Ecology 2007, 88, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, T.J. Invasion resistance arises in strongly interacting species-rich model competition communities. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9610–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skein, L.; Alexander, M.E.; Robinson, T.B. Characteristics of native predators are more important than those of alien prey in determining the success of biotic resistance in marine systems. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, C.S.; Finke, D.L.; Snyder, W.E. Are the conservation of natural enemy biodiversity and biological control compatible goals? Biol. Control 2008, 45, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.C.; White, J.L.; Nakamoto, R.J. An emergent multiple predator effect may enhance biotic resistance in a stream fish assemblage. Ecology 2004, 85, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, J.E.; Stachowicz, J.J. The consequences of consumer diversity loss: Different answers from different experimental designs. Ecology 2009, 90, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance-Chalcraft, H.D.; Rosenheim, J.A.; Vonesh, J.R.; Osenberg, C.W.; Sih, A. The influence of intraguild predation on prey suppression and prey release: A meta-analysis. Ecology 2007, 88, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, R.J.; Alexander, M.E.; Dalu, T.; Ellender, B.R.; Kaiser, H.; Weyl, O.L. Using functional responses to quantify interaction effects among predators. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 1988–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Nonindigenous Aquatic Species Database: Gainesville, FL, USA. Available online: https://nas.er.usgs.gov (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Thompson, K.A.; Hill, J.E.; Nico, L.G. Eastern mosquitofish resists invasion by nonindigenous poeciliids through agonistic behaviors. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, I.C.; Rixon, C.A.; MacIsaac, H.J. Popularity and propagule pressure: Determinants of introduction and establishment of aquarium fish. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, P.J.; Loftus, W.F. non-native fishes in Florida freshwaters: A literature review and synthesis. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 117–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckett, Q.M.; Ritch, J.L.; Lawson, K.M.; Hill, J.E. Implementation and enforcement of best management practices for Florida ornamental aquaculture with an emphasis on nonnative species. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2016, 78, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckett, Q.M.; Ritch, J.L.; Lawson, K.M.; Hill, J.E. Landscape-scale survey of non-native fishes near ornamental aquaculture facilities in Florida, USA. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Ho, C.F.; Tapia, E.J. Hillsborough County, Florida’s stormwater GIS. In Proceedings of the ESRI International User Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Copp, G.H.; Wesley, K.J.; Vilizzi, L. Pathways of ornamental and aquarium fish introductions into urban ponds of Epping Forest (London, England): The human vector. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copp, G.H.; Vilizzi, L.; Gozlan, R.E. The demography of introduction pathways, propagule pressure and occurrences of non-native freshwater fish in England. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, M.V.; Canfield, D.E. Handbook of Common Freshwater Fish in Florida Lakes; Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Robins, R.H.; Page, L.M.; Williams, J.D.; Randall, Z.S.; Sheehy, G.E. Fishes in the Freshwaters of Florida: An Identification Guide and Atlas; University of Florida Press: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Meffe, G.K. Predation and species replacement in American southwestern fishes: A case study. Southwest. Nat. 1985, 30, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambright, K.D. Experimental analysis of prey selection by largemouth bass: Role of predator mouth width and prey body depth. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 1991, 120, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chick, J.H.; McIvor, C.C. Habitat selection by three littoral zone fishes: Effects of predation pressure, plant density and macrophyte type. Ecol. Fresh. Fish 1997, 6, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.R. Freshwater Fishes of Mexico; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nico, L.; Fuller, P.; Neilson, M. Xiphophorus hellerii Heckel, 1848: U.S. Geological Survey, Nonindigenous Aquatic Species Database, Gainesville, FL, USA. Revision Date: 14 November 2012. Available online: https://nas.er.usgs.gov/queries/FactSheet.aspx?SpeciesID=869 (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- CABI. Invasive Species Compendium; Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International: Wallingford, UK; Available online: http://www.cabi.org/isc (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Savino, J.F.; Stein, R.A. Predator-prey interaction between largemouth bass and bluegills as influenced by simulated, submersed vegetation. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1982, 111, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, S. The impact of submerged macrophytes on largemouth bass and bluegills. Lake Reserv. Manage. 1987, 3, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soluk, D.A.; Collins, N.C. Balancing risks? Responses and nonresponses of mayfly larvae to fish and stonefly predators. Oecologia 1988, 77, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swisher, B.J.; Soluk, D.A.; Wahl, D.H. Non-additive predation in littoral habitats: Influences of habitat complexity. Oikos 1998, 81, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettolli, P.W.; Maceina, M.J.; Noble, R.L.; Betsill, R.K. Piscivory in largemouth bass as a function of vegetation abundance. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1992, 12, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.E.; Gilliam, J.F.; Hall, D.J.; Mittelbach, G.G. An experimental test of the effects of predation risk on habitat use in fish. Ecology 1983, 64, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayse, J.W.; Wissing, T.E. Effects of stem density of artificial vegetation on abundance and growth of age-0 bluegills and predation by largemouth bass. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1996, 125, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukup, P.R.; Näslund, J.; Höjesjö, J.; Boukal, D.S. From individuals to communities: Habitat complexity affects all levels of organization in aquatic environments. WIREs Water 2022, 9, e1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.E.; Hall, D.J. Ontogenetic habitat shifts in bluegill: The foraging rate-predation risk trade-off. Ecology 1988, 69, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.C.; Trexler, J.C.; Loftus, W.F. Separating the effects of intra and interspecific age-structured interactions in an experimental fish assemblage. Oecologia 2001, 127, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuckett, Q.M.; Ressel, K.N.; Ritch, J.L.; Lawson, K.M.; Hill, J.E. Domestication and feralization influence the distribution and phenotypes of escaped ornamental fish. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.A. Ecological effects of Micropterus introductions: The dark side of black bass. In Black Bass: Ecology, Conservation, and Management; Phillip, D.P., Ridgway, M.S., Eds.; American Fisheries Society Symposium 31: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002; pp. 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura, R.; Kita, M.; Yuma, M. Species diversity in native fish community in Japan: Comparison between non-invaded and invaded ponds by exotic fish. Ichthyol. Res. 2004, 51, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, J.M.; Day, J.A.; Griffiths, C.L. Influence of largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides, on abundance and habitat selection of Cape galaxias, Galaxias zebratus, in a mountain stream in the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 33, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, E.; Howe, C.; Lim, R.; Burchett, M. Impact of the introduced poeciliid Gambusia holbrooki (Girard, 1859) on the growth and reproduction of Pseudomugil signifier (Kner, 1865) in Australia. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1997, 48, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, J.R.; Rader, R.B.; Belk, M.C.; Schaalje, G.B. Ground-truthing the impact of invasive species: Spatio-temporal overlap between native least chub and introduced western mosquitofish. Biol. Invasions 2007, 9, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, D.A.; Hoback, W.W.; Koupal, K.D. Complex interactions between native and invasive species: Investigating the differential displacement of two topminnows native to Nebraska. Aquat. Invasions 2015, 10, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, B.L.; Guadalupe, K.D.; Goodchild, S.C.; Stockwell, C.A. The Combined Effects of Multiple Invasive Species on Persistence of Imperiled Pahrump Poolfish. Fishes 2025, 10, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Hottola, J.; Sittonen, J. Modeling species co-occurrence by multivariate logistic regression generates new hypotheses on fungal interactions. Ecology 2010, 91, 2514–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custer, C.A.; Fischer, D.P.; Smith, G.; Henning, A.; Kepler Schall, M.; Shank, M.K.; Wertz, T.A.; Wagner, T. Quantifying the relative importance of biotic and abiotic factors in landscape-based models of stream fish distributions. Community Ecol. 2024, 25, 145–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hill, J.E.; Floyd, T.P. Facilitation and Interference Between Native Fishes Influence Invasion Resistance. Fishes 2025, 10, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080398
Hill JE, Floyd TP. Facilitation and Interference Between Native Fishes Influence Invasion Resistance. Fishes. 2025; 10(8):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080398
Chicago/Turabian StyleHill, Jeffrey E., and Theresa P. Floyd. 2025. "Facilitation and Interference Between Native Fishes Influence Invasion Resistance" Fishes 10, no. 8: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080398
APA StyleHill, J. E., & Floyd, T. P. (2025). Facilitation and Interference Between Native Fishes Influence Invasion Resistance. Fishes, 10(8), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080398





