A Novel Approach to Perivitelline Fluid Extraction from Live Water-Activated Eggs from Zebrafish, Danio rerio
Abstract
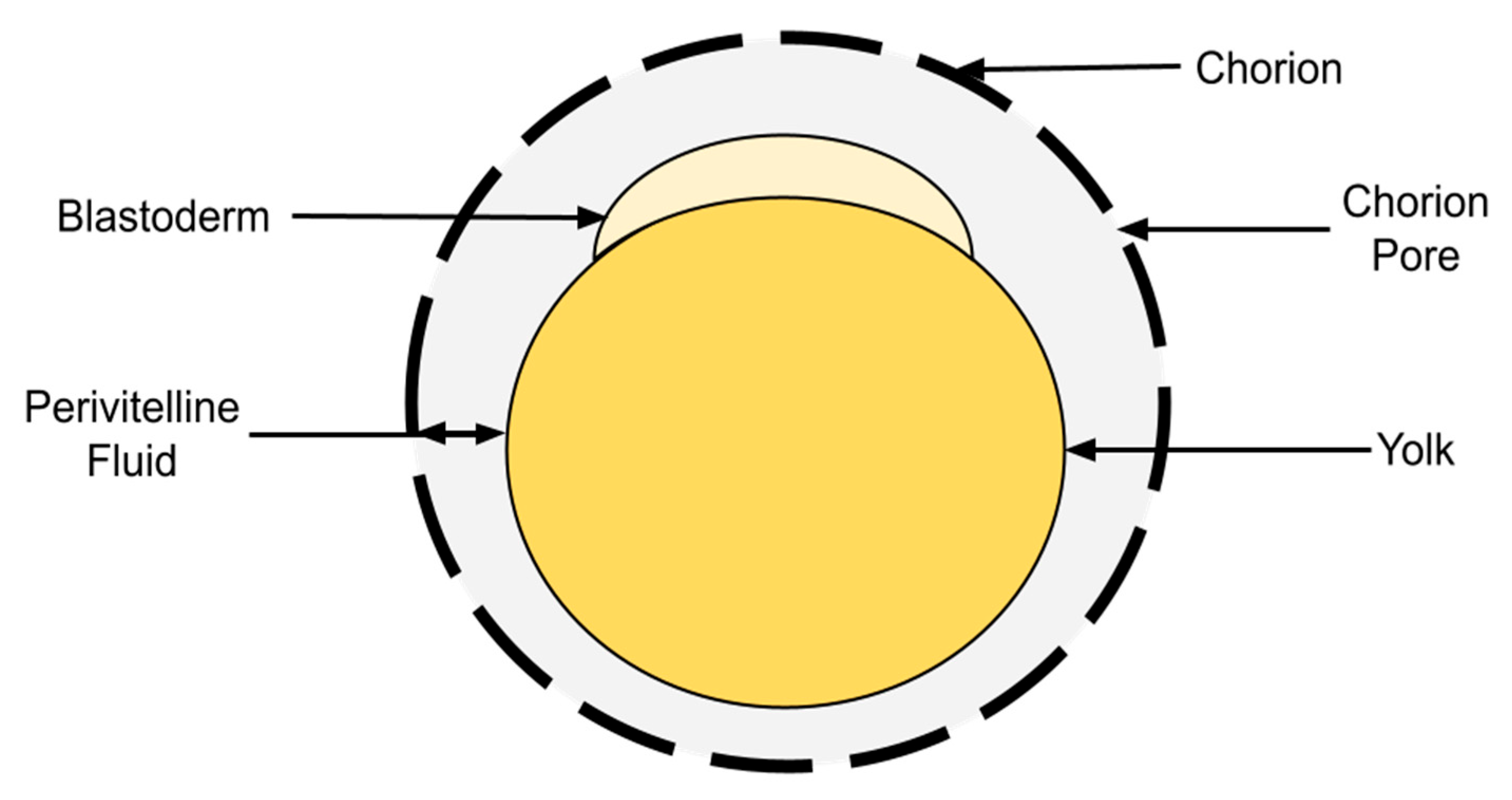
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Egg Collection
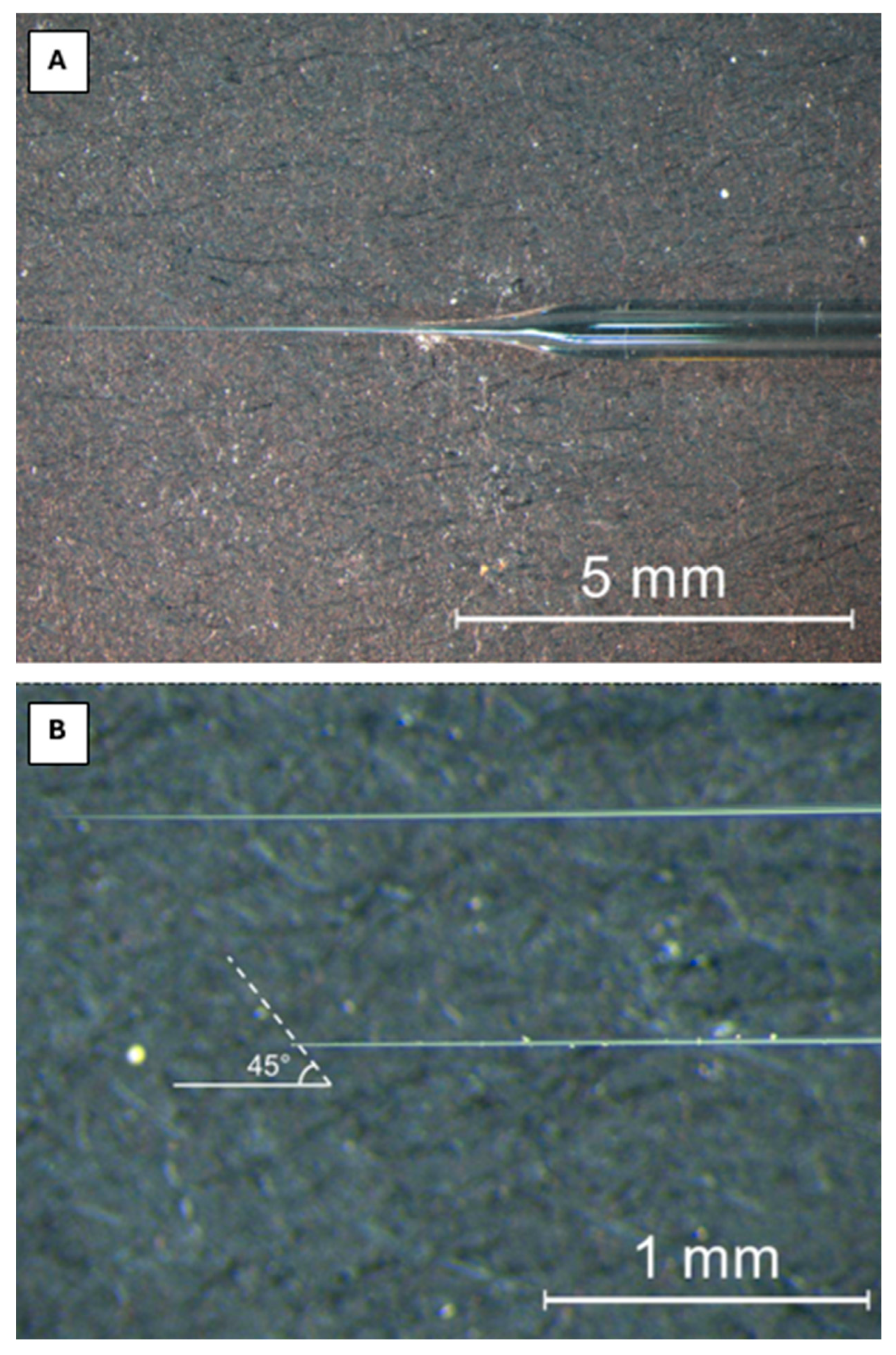
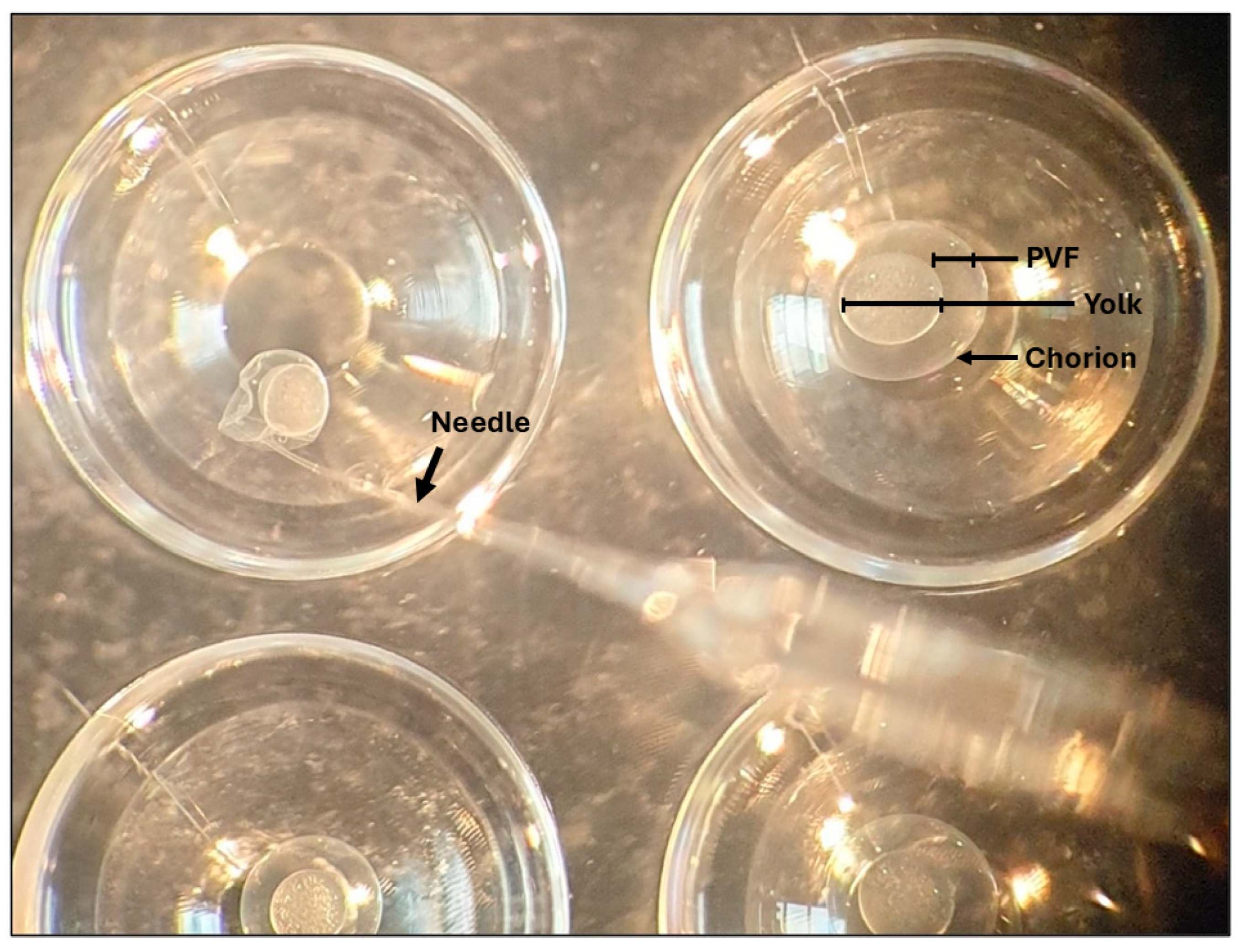
2.3. Extraction of Perivitelline Fluid
2.4. Histological Validation of Perivitelline Fluid Extraction
2.5. Visualisation of Sample Purity via SDS-PAGE
3. Results
3.1. Histological Validation of Perivitelline Fluid Extraction
3.2. Visualisation of Sample Purity via SDS-PAGE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | Cortical alveoli |
| PAS | Periodic acid–Schiff |
| PVF | Perivitelline fluid |
| PVS | Perivitelline space |
References
- Shephard, K.L. Ion-exchange phenomena regulate the environment of embryos in the eggs of freshwater fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1987, 88, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, K.L. Aluminium and calcium affect the perivitelline fluid in fish eggs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1988, 91, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Yazawa, S. Binding of antibiotics to glycoproteins of the vitelline and fertilization envelopes of cherry salmon eggs. Histochem. J. 1997, 29, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.S. Embryogenesis and oxygen consumption in benthic egg clutches of a tropical clownfish, Amphiprion melanopus (Pomacentridae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2004, 138, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.G.M.; Wuertz, S.; Mekkawy, I.A.; Exner, H.-J.; Kirschbaum, F. Lead induced malformations in embryos of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Environ. Toxicol. 2007, 22, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Smith, C.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Xia, W.; Xue, G.; Chen, J.; Xie, P. The evolution of alternative buoyancy mechanisms in freshwater fish eggs. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Smith, C.; Xue, G.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Alternative signal pathways underly fertilization and egg activation in a fish with contrasting modes of spawning. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Paz, J.F.; Anguita-Salinas, C.; Díaz-Celis, C.; Chávez, F.P.; Allende, M.L. The zebrafish perivitelline fluid provides maternally-inherited defensive immunity. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateno Hiroaki Ogawa, T.; Muramoto, K.; Kamiya, H.; Saneyoshi, M. Rhamnose-binding lectins from steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) eggs recognize bacterial lipopolysaccharides and lipoteichoic acid. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Tateno, H.; Nakamura-Tsuruta, S.; Kominami, J.; Hirabayashi, J.; Nakamura, O.; Watanabe, T.; Kamiya, H.; Naganuma, T.; Ogawa, T.; et al. The function of rhamnose-binding lectin in innate immunity by restricted binding to Gb3. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Yin, X.; Bai, H.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Qi, W.; Wang, B.; Ye, J. Expression and functional characterisation of an L-rhamnose-binding lectin from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in host defense against bacterial infection. Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.H.; Olafsen, J.A. Bacterial colonization of cod (Gadus morhua L.) and Halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) eggs in marine aquaculture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, A.; Nawata, A. Mode of the intra-ovum infection of Flavobacterium psychrophilum in salmonid eggs. Fish Pathol. 2010, 45, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumagai, A.; Yamaoka, S.; Takahashi, K.; Fukuda, H.; Wakabayashi, H. Waterborne transmission of Flavobacterium psychrophilum in coho salmon eggs. Fish Pathol. 2000, 35, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, M.; Kasai, H.; Yoshimizu, M. Intra-ovum infection in salmonid eggs artificially contaminated with fish pathogenic bacteria: Flavobacterium psychrophilum, Renibacterium salmoninarum and Aeromonas salmonicida. Fish Pathol. 2012, 47, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, K.L.; Jensen, J.O.T. The effects of temperature on external egg membranes in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and the occurrence of soft-shell disease. Can. J. Zool. 1994, 72, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, Ø.; Hansen, G.H.; Jelmert, A. Bacterial Diseases of Eggs and Yolk Sac Larvae of Halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.): Characterisation and Experimental Infection. ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; de Bruijn, I.; Jack, A.L.; Drynan, K.; van den Berg, A.H.; Thoen, E.; Sandoval-Sierra, V.; Skaar, I.; van West, P.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J.; et al. Deciphering microbial landscapes of fish eggs to mitigate emerging diseases. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2002–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Yazawa, S. Binding of bacterial toxins to glycoproteins in the envelopes of rainbow trout eggs. Histochem. J. 1995, 27, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.; Harishchandra, A.; Ranasinghe, P.; Giulio, R.; Jayasundara, N. The external microbiome communicates with the developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo through the protective chorion and influences developmental trajectory; bioRxiv: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Brox, S.; Ritter, A.P.; Küster, E.; Reemtsma, T. Influence of the perivitelline space on the quantification of internal concentrations of chemicals in eggs of zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 157, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.P.P.; Boyle, D.; Nogueira, A.; Handy, R.D. Differences in toxicity and accumulation of metal from copper oxide nanomaterials compared to copper sulphate in zebrafish embryos: Delayed hatching, the chorion barrier and physiological effects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegri, F. Maternal factors in zebrafish development. Dev. Dyn. 2003, 228, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żarski, D.; Le Cam, A.; Frohlich, T.; Kösters, M.; Klopp, C.; Nynca, J.; Ciesielski, S.; Sarosiek, B.; Dryl, K.; Montfort, J.; et al. Neurodevelopment vs. the immune system: Complementary contributions of maternally-inherited gene transcripts and proteins to successful embryonic development in fish. Genomics 2021, 113, 3811–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henn, K.; Braunbeck, T. Dechorionation as a tool to improve the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 153, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, J.; Neumann, D.; Dammer, E.; Duong, D.; Dunn, C.; Seyfried, N. Evaluating the effect of formalin fixation on mass spectrometry-based proteomic profiling (984.1). FASEB J. 2014, 28 (Suppl. 1), 984.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Wang, W.; Rudnick, P.A.; Song, T.; Li, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Weil, R.J.; DeVoe, D.L.; Lee, C.S.; Balgley, B.M. Proteome analysis of microdissected formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanca, A.; Pagnozzi, D.; Burrai, G.P.; Polinas, M.; Uzzau, S.; Antuofermo, E.; Addis, M.F. Comparability of differential proteomics data generated from paired archival fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed samples by GeLC–MS/MS and spectral counting. J. Proteom. 2012, 77, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, C.; Ducret, A.; Tille, J.-C.; Thomas, M.; McKee, T.A.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.A.; Scherl, A.; Lescuyer, P.; Cutler, P. Applications of mass spectrometry for quantitative protein analysis in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Proteomics 2014, 14, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, H. Isolation of proteins by heat-induced extraction from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue and preparation of tryptic peptides for mass spectrometric analysis. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, T.; Tsuruyama, T.; Hiratsuka, T.; Tsuruyama, T. Mass spectrometry analysis using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded pathological samples. In Electron Microscopes, Spectroscopy and Their Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, J.; Noels, H.; Theelen, W.; Lellig, M.; Orth-Alampour, S.; Boor, P.; Jankowski, V.; Jankowski, J. Sample preparation of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections for MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwosu, A.J.; Misal, S.A.; Truong, T.; Carson, R.H.; Webber, K.G.I.; Axtell, N.B.; Liang, Y.; Johnston, S.M.; Virgin, K.L.; Smith, E.G.; et al. In-depth mass spectrometry-based proteomics of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues with a spatial resolution of 50-200 μm. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.; Ahn, J.; Kim, A.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, K.M.; Yi, E.C. Proteomics analysis of an individual formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue section using isobaric-tag amplification. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedorn, M.; Carter, V.L. Zebrafish reproduction: Revisiting in vitro fertilization to increase sperm cryopreservation success. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.L.; Villarroel, M.; Rosengrave, P.; Carne, A.; Kleffmann, T.; Lokman, P.M.; Gemmell, N.J. Proteomic analysis of chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) ovarian fluid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.; Chagas, J.; Bashiyo-Silva, C.; Costa, R.; Veríssimo-Silveira, R.; Ninhaus-Silveira, A. Oocyte viability and cortical activation under different salt solutions in Prochilodus lineatus (Teleostei: Prochilodontidae). Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, S.G.; Samarin, A.M.; Franěk, R.; Pšenička, M.; Policar, T.; Linhart, O.; Samarin, A.M. Oocyte ageing in zebrafish Danio rerio (Hamilton, 1822) and its consequence on the viability and ploidy anomalies in the progeny. Animals 2021, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corley-Smith, G.E.; Lim, C.J.; Brandhorst, B.P. Production of androgenetic zebrafish (Danio rerio). Genetics 1996, 142, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahabadi, M.N.; Shoae, A.; Lokman, P.M. Effects of storage time, sex steroids and media composition on egg viability of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2011, 315, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueho, A.; Żarski, D.; Rime, H.; Guével, B.; Com, E.; Lavigne, R.; Nguyen, T.; Montfort, J.; Pineau, C.; Bobe, J. Evolutionarily conserved ovarian fluid proteins are responsible for extending egg viability in salmonid fish. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A. 4-Fixation of tissues. In Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 7th ed.; Suvarna, S.K., Layton, C., Bancroft, J.D., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Wu, D.; Yasumasu, S.; Hane, M.; Sato, C.; Kitajima, K. Critical role of the cortical alveolus protease alveolin in chorion hardening in vivo at medaka fertilization. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.; Patinote, A.; Nguyen, T.V.; Com, E.; Lavigne, R.; Pineau, C.; Sullivan, C.V.; Bobe, J. Scrambled eggs: Proteomic portraits and novel biomarkers of egg quality in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewis, B.A.; Lokman, P.M.; Beck, C.W. A Novel Approach to Perivitelline Fluid Extraction from Live Water-Activated Eggs from Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Fishes 2025, 10, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080369
Lewis BA, Lokman PM, Beck CW. A Novel Approach to Perivitelline Fluid Extraction from Live Water-Activated Eggs from Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Fishes. 2025; 10(8):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080369
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewis, Blake A., P. Mark Lokman, and Caroline W. Beck. 2025. "A Novel Approach to Perivitelline Fluid Extraction from Live Water-Activated Eggs from Zebrafish, Danio rerio" Fishes 10, no. 8: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080369
APA StyleLewis, B. A., Lokman, P. M., & Beck, C. W. (2025). A Novel Approach to Perivitelline Fluid Extraction from Live Water-Activated Eggs from Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Fishes, 10(8), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080369







